Introduction
Have you ever wondered why some companies seem to always be ahead of the curve, effortlessly navigating the challenges of today's fast-paced business world? I remember back in my early career days, working for a small manufacturing firm. We were constantly struggling to keep up with competitors, unsure of where we were falling short. It wasn't until our leadership team sat down to truly define our core competencies that we began to see a shift. Understanding what we did best—and focusing on it—was a game-changer.
Introduction
Defining Core Competencies
Research and Development
Insourcing vs. Outsourcing
Conclusion
In this article, we'll delve into the strategic importance of core competencies in business, explore how research and development drive competitive advantage, and weigh the advantages and disadvantages of outsourcing in supply chain management. By the end, you'll have a clearer picture of how these concepts intertwine and how they can propel a company forward.
Defining Core Competencies
At its heart, a core competency is that special something a company does exceptionally well—better than anyone else. It's the unique combination of skills, resources, and processes that set a business apart. Think of companies like Apple with its sleek design and user-friendly technology, or Toyota's reputation for manufacturing efficiency.
So, how do you identify your company's core competencies? Here are some steps to consider:
1- Assess Your Strengths: Look internally to determine what your company excels at. This could be superior customer service, innovative product design, or a robust distribution network.
2- Understand Your Market: Identify what your customers truly value and how your competencies meet those needs.
3- Analyze Competitors: Figure out what sets you apart from others in your industry.
Once you've pinpointed these competencies, it's crucial to nurture them. Investing in your strengths ensures that you maintain your competitive edge.
I recall a time when our firm mistakenly tried to be a jack-of-all-trades, dabbling in areas far outside our expertise. It wasn't until we refocused on our core competencies that we began to thrive. We honed in on our product design and development capabilities, which our customers valued most, and it made all the difference.
Introducing the SCOR Model: Unlocking Supply Chain Management
Improving Supply Chain with Six Sigma: Quality & Consistency
Maximizing Inventory Cost Savings In Supply Chain Management
Research and Development: Fueling Innovation
Research and development (R&D) is the lifeblood of innovation. It's through R&D that companies can develop new products and services, improve existing ones, and stay ahead of the competition. As Peter F. Drucker aptly puts it in Innovation and Entrepreneurship, "Innovation is the specific instrument of entrepreneurship... the act that endows resources with a new capacity to create wealth."
The key to successful supply chains lies in deciding between insourcing, outsourcing, and offshoring.
Investing in R&D offers several benefits:
Staying Competitive: Regularly updating and improving products keeps customers engaged and loyal.
New Market Opportunities: Innovation can open doors to new markets or customer segments.
Enhanced Reputation: Companies known for innovation often enjoy a positive brand image.
However, R&D isn't without its challenges. It requires significant investment, both in terms of time and resources. There's also no guarantee of success. But the potential rewards often outweigh the risks.
For instance, consider how pharmaceutical companies invest heavily in R&D to develop new medications. While not every project results in a breakthrough drug, the ones that do can save lives and generate substantial profits.
Insourcing vs. Outsourcing: Making the Right Choice
When it comes to tasks outside your core competencies, companies often face a choice between insourcing and outsourcing.
Insourcing
Insourcing involves bringing work back in-house. This strategy can provide:
Greater Control: Direct oversight of processes and quality.
Enhanced Coordination: Easier communication within the same organization.
Protection of Intellectual Property: Reduced risk of proprietary information leaks.
However, insourcing can also lead to:
Higher Costs: Infrastructure and training investments can be substantial.
Resource Strain: Diverting focus from core activities.
Outsourcing
On the flip side, outsourcing entails hiring external organizations to handle specific tasks. Benefits include:
Cost Savings: Leveraging the expertise of specialists can be more economical.
Focus on Core Competencies: Freeing up internal resources to concentrate on what you do best.
Access to Expertise: Gaining specialized skills or technology not available internally.
But outsourcing also has downsides:
Less Control: Reliance on third parties can lead to quality or timeline issues.
*Communication Challenges*: Potential language or cultural barriers.
Security Risks: Sharing sensitive information with external entities.
In my previous role, we faced a critical decision: should we outsource our customer service operations or keep them in-house? We weighed the pros and cons carefully. Ultimately, we chose to keep it in-house because excellent customer service was a core competency we didn't want to relinquish. This decision reinforced our brand's reputation and strengthened customer relationships.
Making Informed Sourcing Decisions
When deciding between insourcing and outsourcing, consider the following:
1- Is the task a core competency? If yes, it might be best to keep it internal.
2- What are the cost implications? Evaluate both short-term and long-term expenses.
3- Do you have the necessary expertise? If not, can you develop it, or is outsourcing more practical?
4- What are the risks? Consider potential security, quality, and operational risks.
It's also essential to communicate changes effectively within your organization. When people are reassigned or their roles shift due to insourcing or outsourcing decisions, providing reassignment request letter tips and information can help ensure a smooth transition.
For example, offering clear guidance on how employees can request reassignment, what information they need to include, and tips on navigating the process can alleviate anxiety and promote a positive work environment.
Lessons from the Field
Let's look at some real-world examples:
Nike: While Nike focuses on design and marketing (its core competencies), it outsources manufacturing to third-party suppliers. This allows Nike to leverage specialized manufacturing capabilities without the overhead.
Amazon: Amazon continues to invest heavily in its logistics and distribution networks—areas it considers core competencies. By insourcing these functions, Amazon maintains control over the customer experience and delivery times.
These companies illustrate how understanding and focusing on core competencies, coupled with strategic insourcing or outsourcing, can lead to success.
The Role of Customer Service in Core Competencies
An often-overlooked core competency is customer service. In an age where consumers have endless options, exceptional customer service can be a significant differentiator.
Underlining the importance of customer service, consider these points:
Building Loyalty: Customers are more likely to return if they have positive experiences.
Brand Reputation: Word-of-mouth and online reviews can make or break a company's image.
Competitive Advantage: Superior customer service sets you apart from competitors.
Investing in training and empowering your customer service team can pay dividends in the long run.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of global business, companies must continually adapt to remain competitive. By defining and honing your core competencies, investing in research and development, and making informed decisions about insourcing and outsourcing, you can position your company for enduring success.
Remember, it's not about doing everything—it's about doing the right things exceptionally well. As we've explored, focusing on what sets your company apart can lead to a sustainable competitive advantage in the supply chain.
So, take a moment to reflect:
What are your company's core competencies?
How can you leverage them to stay ahead?
The answers to these questions could be the key to unlocking your company's full potential.
References
Drucker, P. F. (1985). Innovation and Entrepreneurship. Harper & Row.
Prahalad, C. K., & Hamel, G. (1990). "The Core Competence of the Corporation." Harvard Business Review, 68(3), 79-91.
Barney, J. B. (1991). "Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage." Journal of Management, 17(1), 99-120.
Porter, M. E. (1985). Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. Free Press.
Frequently Asked Questions
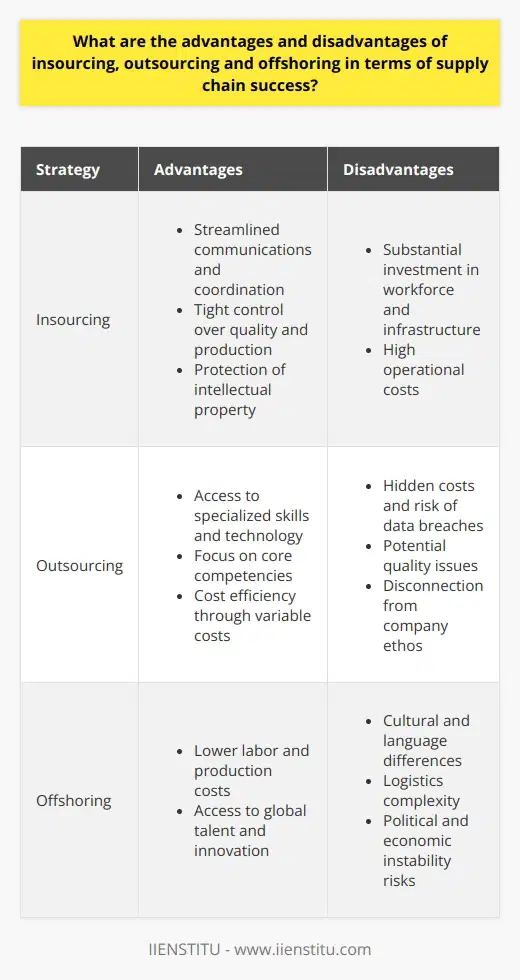
What are the advantages and disadvantages of insourcing, outsourcing and offshoring in terms of supply chain success?
In recent years, many businesses have turned to insourcing, outsourcing, and offshoring as part of their supply chain management strategies. However, each method has its advantages and disadvantages regarding supply chain success, and companies should be aware of these factors when choosing the right approach for their business.
Insourcing involves the use of internal resources to produce goods and services. This approach can be beneficial in terms of the quality and control of production. It also allows for better integration of the internal processes and systems with the supply chain, making it easier to manage. On the other hand, insourcing can be expensive, requiring the company to invest in personnel and infrastructure.
Outsourcing involves the use of external resources to produce goods and services. This method allows for flexibility and improved cost efficiency, reducing the need for in-house resources. However, it can lead to reduced quality control and a lack of integration between the internal processes and the supply chain.
Offshoring involves the use of external resources located in different countries. This approach can be beneficial in terms of cost savings and increased production capacity. However, it can lead to cultural and language barriers, difficulties tracking and managing the supply chain, and increased risks due to political and economic instability.
In conclusion, insourcing, outsourcing, and offshoring can all be beneficial in terms of supply chain success, depending on the business's individual needs. However, companies should carefully consider each approach's advantages and disadvantages before deciding.
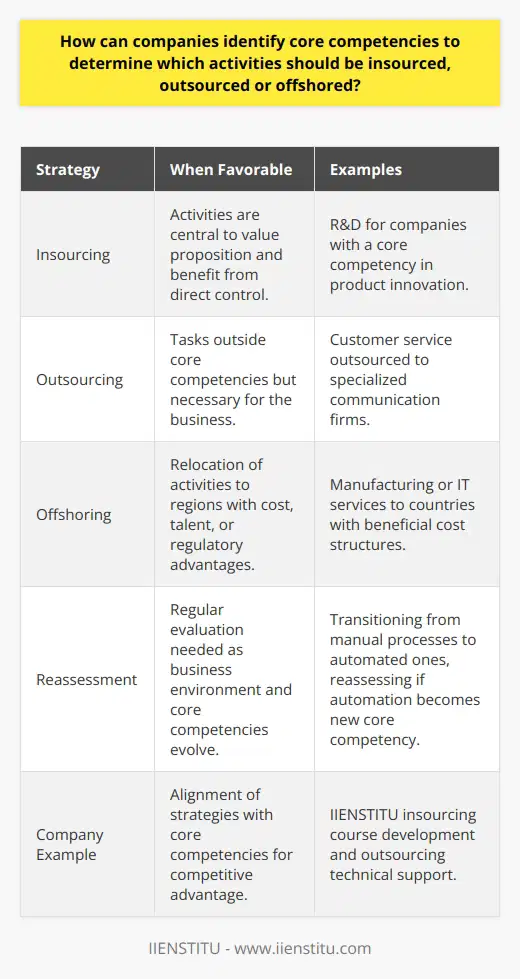
How can companies identify core competencies to determine which activities should be insourced, outsourced or offshored?
Companies must identify their core competencies to determine which activities should be insourced, outsourced, or offshored. This is an essential step in creating a successful business strategy. Core competencies are the set of capabilities that enable a company to differentiate itself from its competitors and create a sustainable competitive advantage. As such, understanding core competencies is essential to building a successful business.
The identification of core competencies begins with an analysis of the company's current capabilities and resources. This analysis should include reviewing the company's existing products, services, processes, and financial and human resources. From this analysis, the company should be able to identify the core competencies that are the source of its competitive advantage.
Once core competencies have been identified, the company must determine which activities should be insourced, outsourced, or offshored. Each of these strategies has its advantages and disadvantages. Insourcing activities refer to the process of bringing certain activities in-house, while outsourcing refers to the process of using external providers for specific actions. Finally, offshoring is the process of relocating certain activities to a different location.
When selecting activities to insource, companies should consider the activity's cost, complexity, and importance in general; activities that are costly, complex, and important to the company should be insourced. Conversely, activities that are less costly, less complex, and less important to the company should be outsourced or offshored.
When selecting outsourcing activities, companies should consider external service providers' cost, complexity, and availability. Generally, activities that are costly, complex, and difficult to source externally should be retained in-house. Conversely, activities that are less costly, less complex, and easy to source externally should be outsourced.
Finally, when selecting activities to go offshore, companies should consider the cost and complexity of the activity, as well as the availability of resources in the target location. Generally, costly, complex activities that can be easily sourced in the target location should be offshored. Conversely, activities that are less costly, less complex, and difficult to source in the target location should be retained in-house.
In summary, identifying core competencies is essential for companies to create a successful business strategy. Once core competencies have been identified, companies should then determine which activities should be insourced, outsourced, or offshored based on the activity's cost, complexity, and importance. By following this process, companies can ensure that they make the best business decisions.
What are the key considerations for companies when deciding whether to insource, outsource or offshore their supply chain activities?
Businesses must consider various factors when deciding whether to keep their supply chain activities in-house, outsource, or offshore. For example, it is essential to consider the cost of the activities, the availability of resources, the need for flexibility, and the impact on customer service.
Cost is often a significant consideration when managing a company's supply chain activities. For example, businesses must factor in hiring, training, and caring for staff costs when insourcing activities. On the other hand, outsourcing activities can reduce overhead costs, as the responsibility and cost of operating the activities are passed on to the external provider. Offshoring, meanwhile, can reduce costs by taking advantage of lower wages and other costs in other countries.
The availability of resources is also a critical factor in the decision-making process. Insourcing activities require the company to have the resources available to manage the activities. On the other hand, outsourcing activities to an external provider allows the company to access resources that it may not have in-house. Offshoring activities may also enable businesses to access resources unavailable in their home country.
Flexibility is also an essential factor to consider. Outsourcing and offshoring can provide businesses with greater flexibility, allowing them to scale up or down their activities as needed quickly. Insourcing, however, may limit the company's flexibility, as it can be difficult and expensive to scale up or down the activities as required.
Finally, businesses need to consider the impact on customer service when deciding whether to insource, outsource, or offshore their supply chain activities. Outsourcing and offshoring can potentially reduce customer service levels, as it may be challenging to establish and maintain a direct relationship with the external provider. Insourcing, however, can provide greater control over the customer service process, enabling businesses to ensure that customers are receiving the highest quality of service.
In conclusion, businesses must consider various factors when deciding whether to keep their supply chain activities in-house, outsource, or offshore. Cost, availability of resources, flexibility, and customer service levels must all be considered to make an informed decision.
What is the importance of insourcing and outsourcing in supply chain management?
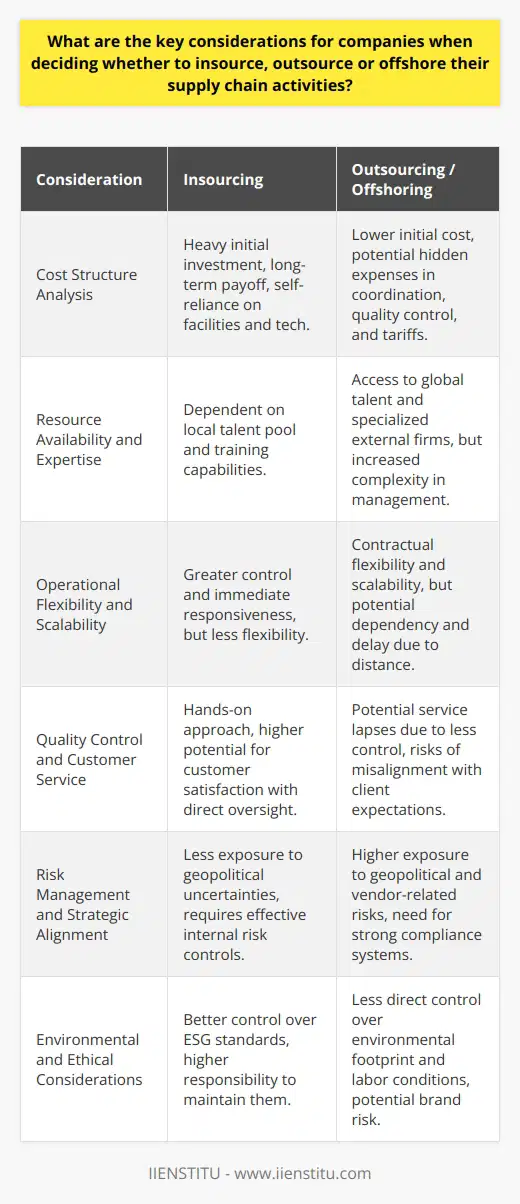
The Significance of Insourcing and Outsourcing
Effective supply chain management plays a crucial role in the success of businesses. Insourcing and outsourcing are two strategies used by companies to manage and optimize their supply chains. Understanding the importance of these strategies can help businesses make informed decisions and gain competitive advantages by leveraging the benefits of each approach.
Insourcing Benefits
Insourcing refers to the practice of performing business functions internally, utilizing a company's own resources and workforce. This strategy often leads to increased control over the supply chain, as companies can manage every aspect of the process. Companies can also tailor the supply chain to meet their specific needs, offering a greater degree of customization and flexibility. Furthermore, insourcing can contribute to better communication, coordination, and collaboration among various departments within the company, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Outsourcing Advantages
On the other hand, outsourcing involves contracting with third-party providers for various supply chain functions. This strategy can lead to cost savings and improved efficiency, as businesses can capitalize on the specialized expertise of outsourcing providers. Moreover, outsourcing enables companies to access resources and capabilities that might be difficult to develop in-house. By allowing external partners to focus on their core competencies, businesses can concentrate on their primary functions, streamlining operations and fostering innovation. Another advantage of outsourcing is the opportunity to expand the supply chain network, connecting a company to new markets and fostering collaboration with other players in the industry.
Strategic Balance
Ultimately, successful supply chain management requires a nuanced understanding of the benefits and drawbacks of both insourcing and outsourcing. Businesses must carefully weigh their unique needs, resources, and goals when deciding whether to insource or outsource supply chain functions. Striking the right balance between these two strategies can lead to effective cooperation among internal departments and external partners, minimizing risks while maximizing the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
In conclusion, insourcing and outsourcing in supply chain management are essential strategies that allow companies to optimize their operations and remain competitive in today's dynamic business landscape. The significance of these approaches lies in their ability to offer businesses varying levels of control, flexibility, and efficiency, driving overall supply chain success. By considering the advantages of each strategy, organizations can make informed decisions and develop supply chain management processes that best fit their unique circumstances and objectives.
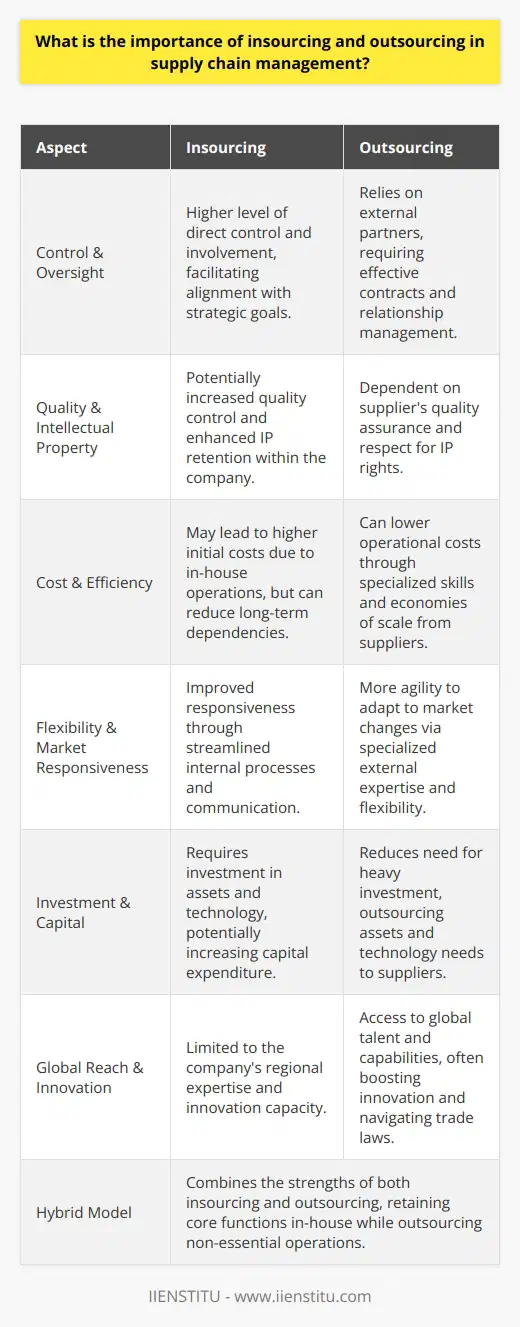
Is outsourcing a good strategy for a supply chain?
Benefits of Outsourcing in Supply Chain
Outsourcing in a supply chain is a good strategy because it can result in cost savings and competitive advantages. Companies often look to third parties for manufacturing or logistics services, allowing them to focus on core competencies. This specialization can lead to better quality goods and services at a lower cost.
Reducing Overhead and Labor Costs
When businesses outsource parts of their supply chain, they can reduce overhead and labor costs. Third-party providers often have more efficient processes and lower-priced resources, which can be passed on in the form of cost savings. In addition, companies can avoid the expense of maintaining facilities, equipment, and staff required for specific supply chain activities.
Access to Advanced Technologies and Expertise
Outsourcing also provides access to advanced technologies and expertise that might be too expensive or time-consuming for companies to develop in-house. External partners usually have more knowledge and experience in specific areas, which can lead to better results and increased efficiency. This access can ultimately lead to a more effective supply chain, ensuring a company stays competitive in the market.
Increased Flexibility and Scalability
By outsourcing, companies can increase their flexibility and scalability. The ability to quickly adapt to market changes or accommodate periods of increased demand is crucial for success. Outsourcing enables supply chain-related activities to be scaled up or down as needed with greater ease, allowing businesses to remain nimble and adapt to shifts in business conditions.
Risk Management and Mitigation
Another advantage of outsourcing is risk management and mitigation. When relying on in-house supply chain activities, disruptions and delays can adversely affect the entire operation. However, working with third-party providers can help minimize the impact of such events, as external partners often have more resources and greater resilience. Additionally, outsourcing can diversify a company's supply chain, reducing the reliance on a single source for any given resource or service.
Conclusion
In conclusion, outsourcing can be a highly effective strategy for a supply chain, offering cost savings, increased efficiency, flexibility, and risk management. Companies that embrace this approach can remain competitive in the market and better adapt to changing business conditions. Therefore, outsourcing should be carefully considered as an essential part of a company's supply chain strategy.
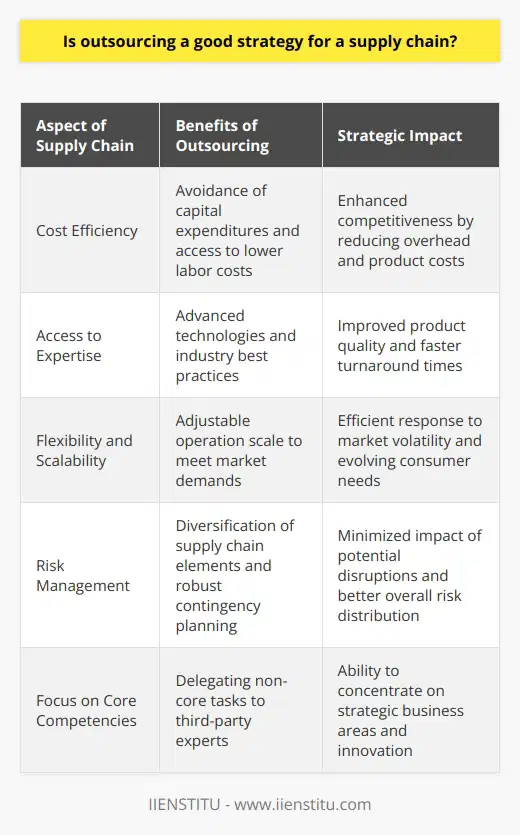
What is outsourcing and offshoring in supply chain?
Understanding Outsourcing in Supply Chain
Outsourcing refers to the strategic practice of delegating selected business operations to external organizations. These specialized organizations possess advanced capabilities and expertise for those specific tasks, resulting in enhanced efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Consequently, companies can focus on core business functions, driving competitive advantage and increased overall performance.
The Role of Offshoring in Supply Chain
Offshoring, on the other hand, is the relocation of business processes or services to another country, often to reduce costs or capitalize on labor arbitrage opportunities. This strategic approach also seeks to diversify the company's global sourcing, enhancing supply chain resilience.
Key Benefits
When implemented effectively, both outsourcing and offshoring can bring impactful benefits to organizations within the supply chain. Enhanced flexibility and scalability allow for quicker responses to fluctuations in market demand, while extended global reach can accommodate a more diverse range of suppliers and customers.
Risk Factors
Despite the potential benefits, outsourcing and offshoring involve certain risks. Loss of control over critical business processes may reduce overall performance, while inadequate communication can lead to misaligned goals or objectives. Moreover, increased dependency on external entities can weaken the organization's overall control, leaving the firm vulnerable to external disruptions or negative reputational consequences.
Effect on Supply Chain Performance
Combining outsourcing and offshoring can provide organizations with a highly optimized and efficient supply chain. However, striking a careful balance between internal and external operations is pivotal to avoiding the pitfalls that accompany excessive dependency on other parties. Regularly monitoring collaborations and maintaining transparent communication with external partners can ensure mutual understanding and alignment of goals, promoting success across the supply chain.
In conclusion, outsourcing and offshoring are strategic practices that can significantly improve the supply chain's efficiency, resilience, and competitiveness. While there are risks to mitigating, the potential benefits derived from a well-executed strategy often outweigh the challenges, leading to long-term success and value creation for the organization.
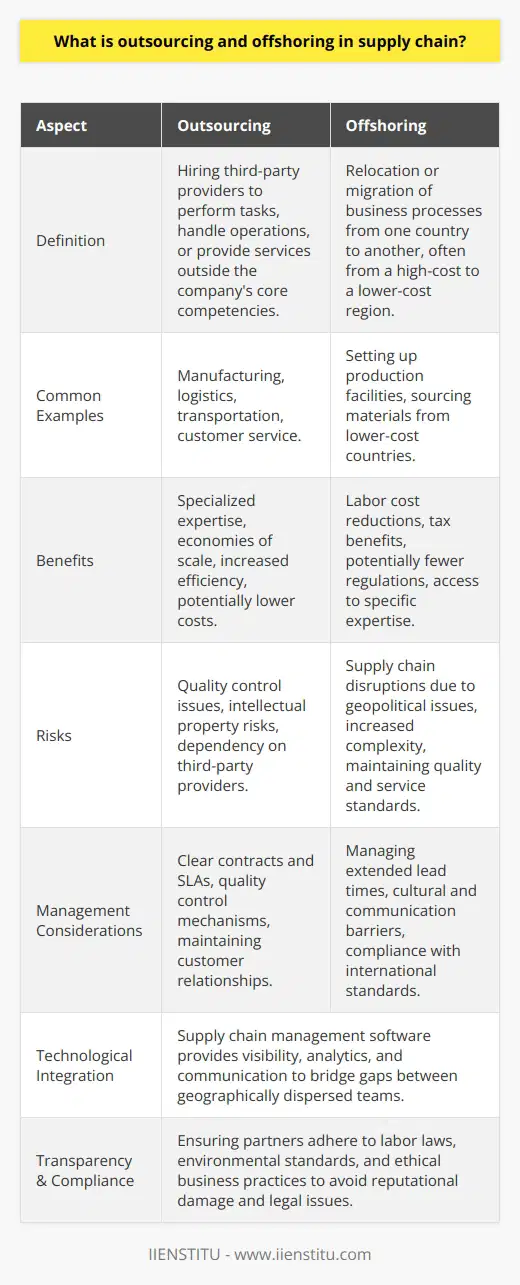
What factors should companies consider when evaluating the potential benefits and risks of insourcing vs outsourcing in supply chain management?
Factors to Consider
When evaluating the potential benefits and risks of insourcing vs outsourcing in supply chain management, companies must consider a variety of factors. These factors offer different advantages and disadvantages and can determine the overall success of a supply chain strategy.
Costs and Financial Risks
A primary consideration is cost, as both insourcing and outsourcing have varying direct and indirect financial implications. Companies must account for expenses such as labor, transportation, and equipment, as well as potential risks like fluctuating market prices and currency fluctuations.
Quality Control and Flexibility
Quality control is another significant factor to consider. While insourcing may offer better control over process and product quality, outsourcing can ensure access to specialized services and knowledge. Additionally, a company must weigh which option offers superior flexibility in responding to market demands and fluctuations.
Intellectual Property and Confidentiality
Companies should also assess the risks related to intellectual property and confidentiality. Insourcing may provide better protection for proprietary information, but outsourcing partners can be bound by stringent legal agreements to maintain data security and intellectual property protection.
Speed to Market
In an increasingly competitive market, speed is vital. Outsourcing may allow for faster scalability and growth, while insourcing may provide more control over the production process, ultimately affecting the ability to bring products to market rapidly.
Operational Resources
The availability of operational resources, such as skilled labor, adequate infrastructure, and access to raw materials, is crucial in determining whether insourcing or outsourcing is the suitable choice. Companies must evaluate if they have the capacity and capability to insource or if an outsourcing partner can meet their requirements.
Relationships and Communication
Lastly, the ability to establish and maintain strong relationships with partners is essential in supply chain management. Companies must weigh the benefits and potential drawbacks of managing third-party partnerships vs. internal communication and collaboration when deciding between insourcing and outsourcing.
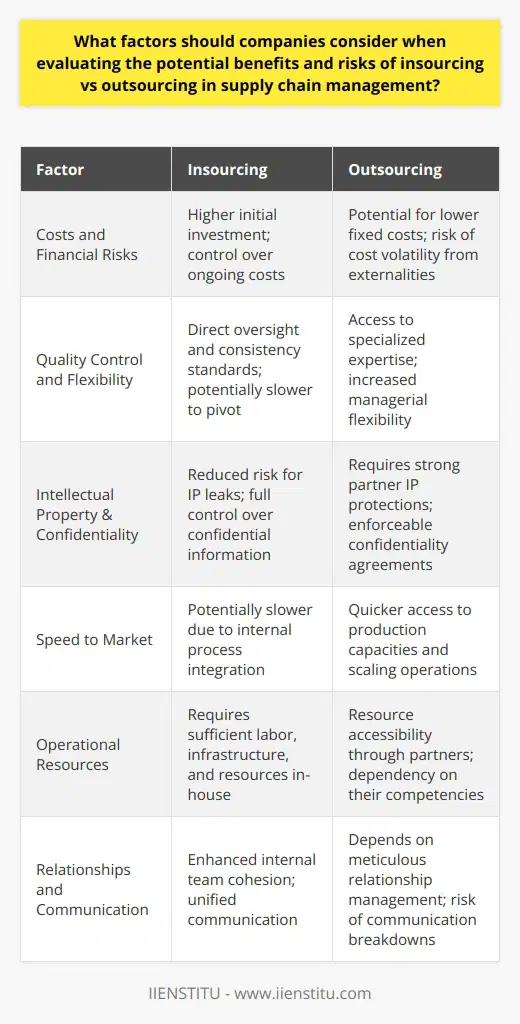
How can insourcing and outsourcing strategies create competitive advantages within a company's supply chain?
Innovation through insourcing and outsourcing
Insourcing and outsourcing strategies play a vital role in enhancing a company's competitiveness within its supply chain. By adopting insourcing, companies can bring critical processes in-house to maintain greater control, retain expertise, and improve efficiencies. This strategy enables organizations to invest in R&D, technology, and employee expertise, resulting in higher quality products and services.
Agility with the outsourcing model
Outsourcing, on the other hand, allows companies to delegate non-core processes to specialized third-party providers. This strategy results in cost savings, increased operational flexibility, and access to a skilled workforce. Companies that outsource can allocate resources and focus more on their core competencies, leading to improved productivity, innovation, and faster response to market changes.
Coordination and integration of insourcing and outsourcing
The optimal application of insourcing and outsourcing strategies creates a symbiotic relationship among different entities within the supply chain. Effective coordination and integration of both approaches result in improved risk management, end-to-end visibility, and a more agile supply chain. Companies can leverage this flexibility to adapt to volatile market conditions, customer preferences, and legal or regulatory changes.
Achieving cost optimization
Cost optimization is a critical factor in gaining a competitive advantage within a company's supply chain. By carefully selecting which processes to insource or outsource, organizations can achieve the optimal balance of cost and benefit. Insourcing can reduce dependency on external providers, minimize risks, and decrease costs related to external labor and overheads. Meanwhile, outsourcing enables companies to benefit from economies of scale and access to specialized resources at reduced costs.
Enhancing customer value
By strategically leveraging insourcing and outsourcing, businesses can create customer value within their supply chain. The ability to develop high-quality products, services, and unique partnerships enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty. In addition, a company can better cater to its customers' evolving needs and preferences by leveraging the expertise and capabilities of its partners.
In conclusion, insourcing and outsourcing strategies provide companies with a competitive advantage within their supply chain by driving innovation, agility, coordination, cost optimization, and customer value enhancement. The right mix of insource and outsource strategies allows organizations to manage risks, optimize resources, and respond effectively to market demands.
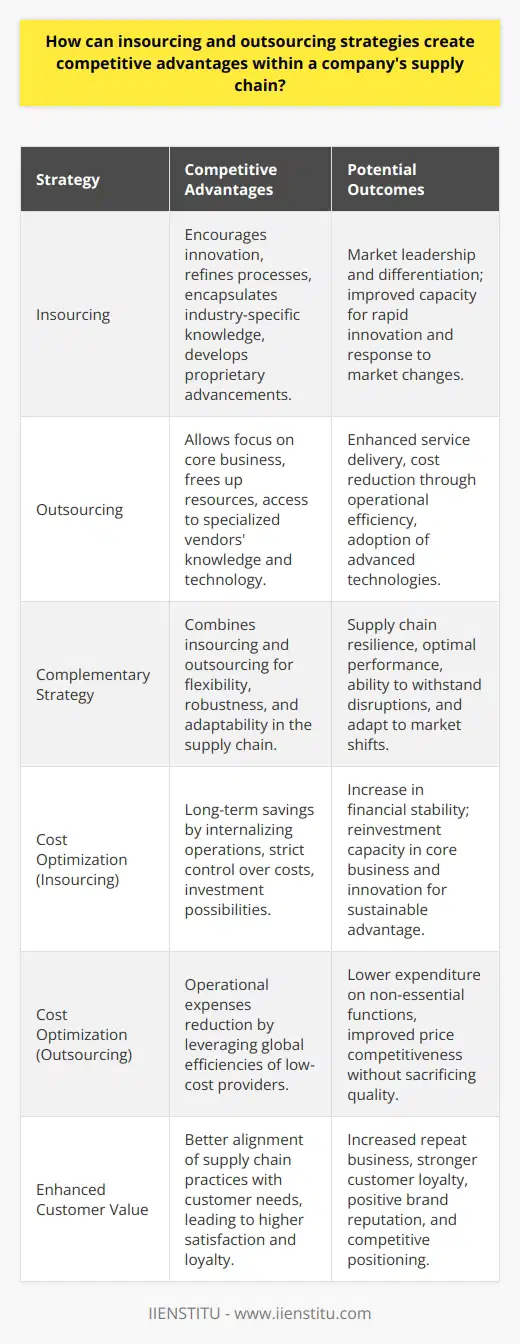
What are the main challenges and opportunities associated with implementing an insourcing or outsourcing initiative in supply chain management?
Challenges of Insourcing and Outsourcing Initiatives
Operational Control Limitations
One of the main challenges with insourcing and outsourcing initiatives in supply chain management is the potential loss of operational control. Companies that outsource various functions may find it more difficult to maintain efficiency, quality, and responsiveness in their supply chain operations.
Knowledge and Skill Gaps
Another challenge arises when a company insources or outsources activities, potentially creating knowledge and skill gaps. In-house teams may lack the necessary resources or expertise to successfully manage new functions in the supply chain, while outsourced providers may have limited knowledge of the company's specific needs and requirements.
Communication and Coordination Misalignments
Implementing insourcing or outsourcing initiatives can lead to communication and coordination misalignments between supply chain stakeholders. This may result in ineffective overall management, increased lead times, and a disruption in seamless operations.
Opportunities for Insourcing and Outsourcing Initiatives
Cost Savings
Despite the aforementioned challenges, there are several opportunities associated with insourcing and outsourcing supply chain activities. One such opportunity is cost savings. Companies can leverage the efficiencies of outsourcing providers to reduce their overhead costs, or deploy insourcing strategies to increase control over resources, resulting in cost benefits.
Scalable and Flexible Supply Chain Operations
Another opportunity lies in the scalability and flexibility of supply chain operations. Companies can opt for insourcing or outsourcing based on their current requirements, capabilities, and available resources, allowing for greater adaptability and resilience in the face of changing market conditions.
Access to Specialized Expertise
Moreover, insourcing and outsourcing initiatives enable companies to access specialized expertise and resources. By collaborating with third-party providers, firms can benefit from the knowledge and best practices of industry experts, while insourcing enables capitalization on internal strengths for enhanced supply chain performance.
In conclusion, while insourcing and outsourcing initiatives in supply chain management present several challenges, such as limited operational control and potential communication misalignments, they also offer numerous opportunities for cost savings, scalability, and access to specialized expertise. By understanding and addressing these challenges, organizations can unlock the potential benefits of these initiatives and drive improvements in their supply chain operations.
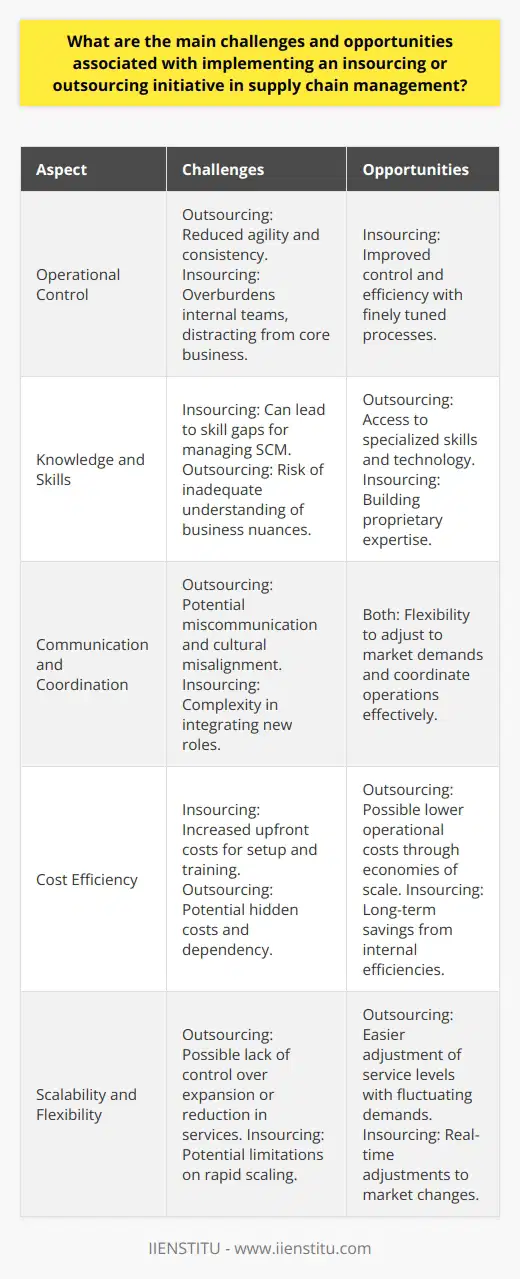
What role does organizational culture play in the success of insourcing and outsourcing supply chain strategies?
Organizational Culture and Supply Chain Strategies
The Role of Shared Values and Goals
Organizational culture plays a crucial role in the success of insourcing and outsourcing supply chain strategies, as it reflects the shared values and goals within a company. These cultural elements determine how employees, departments, and even business partners perceive and approach tasks and change initiatives, which are inherent in these strategies.
Support for Innovative Approaches
A strong organizational culture encourages the adoption of innovative supply chain management practices, such as insourcing and outsourcing. Cultures that promote creativity and adaptability to changing market needs are more likely to successfully implement new supply chain approaches, ensuring the organization remains competitive.
Balancing Risk and Opportunism
In both insourcing and outsourcing strategies, organizational culture affects the willingness to balance risk and opportunism. Cultures that foster trust and transparency may be more comfortable with the risks associated with outsourcing, while insular, risk-averse cultures may be more likely to focus on insourcing strategies that keep supply chain responsibilities within the organization.
Collaboration and Communication
Successful insourcing and outsourcing initiatives require strong collaboration and communication among all stakeholders, which is fostered by a robust organizational culture. Cultures that promote collaboration and open communication enable better alignment of objectives, resource allocation, and timely execution of supply chain strategies. Additionally, strong communication is vital when working with external supply chain partners during outsourcing efforts.
Handling Challenges and Conflicts
Finally, organizational culture governs how companies handle challenges and conflicts that may arise during the implementation of insourcing and outsourcing strategies. Cultures that emphasize problem-solving and continuous improvement will be more adept at identifying and resolving issues, thus contributing to the overall success of these supply chain strategies.
In conclusion, organizational culture plays a central role in determining the success of insourcing and outsourcing supply chain strategies. A strong, adaptable culture that supports innovation, collaboration, and effective risk management will be more likely to achieve desired results and ensure the organization remains competitive in today's ever-changing market landscape.
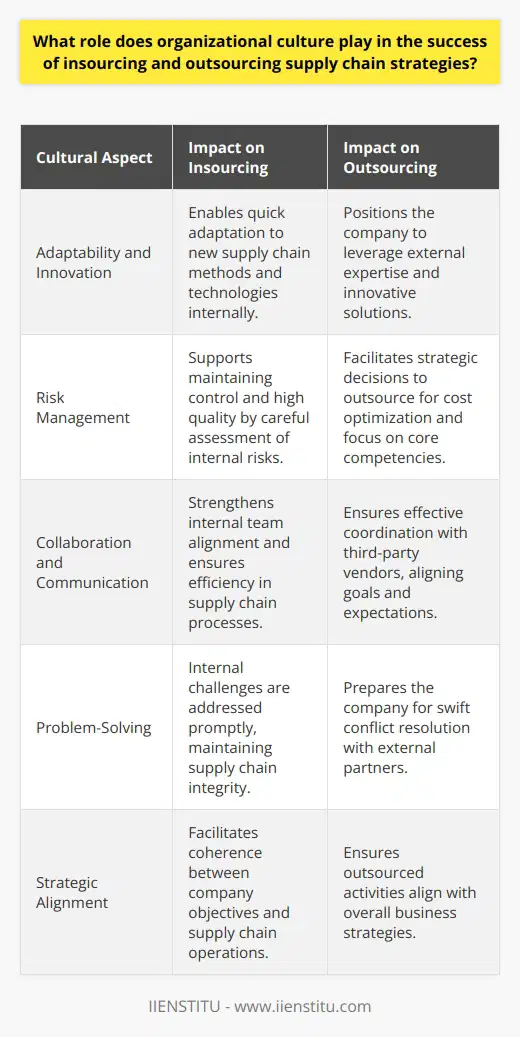
Can insourcing and outsourcing strategies coexist within a company's supply chain, and if so, how can this be effectively managed?
Balancing Insourcing and Outsourcing Strategies
Yes, insourcing and outsourcing strategies can coexist within a company's supply chain. To effectively manage this approach, organizations need to adopt a strategic mindset and prioritize critical business functions, while ensuring seamless integration of services.
Assessment of Core Competencies
The first step in managing a hybrid insourcing-outsourcing model is to analyze the company's core competencies. Firms must identify the key areas that contribute to their competitive advantage and decide whether to insource functions crucial to their unique value proposition or outsource non-core operations, preserving resources to focus on core areas.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
An essential element of managing insourcing and outsourcing strategies is conducting a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis. Firms need to determine the financial impact of each decision, such as the expenses associated with hiring or training employees for insourced functions and the cost savings from outsourcing non-core tasks. This evaluation enables companies to make informed decisions, aligning their supply chain strategy with overall business goals.
Building Strong Partnerships
To guarantee the success of a coexistent insourcing and outsourcing strategy, collaborations with reliable vendors and suppliers are crucial. Establishing strategic partnerships is essential, as they contribute to maintaining compliance with industry standards, ensuring timely deliveries, and accessing specialized resources.
Monitoring Performance and Quality
Despite opting for a hybrid model, companies must not compromise on quality and performance. To assure optimum outcomes, organizations need to continually monitor the effectiveness of both insourced and outsourced operations. Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) can help track and measure the efficiency of these strategies, thus enabling necessary adjustments and improvements over time.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Lastly, it is vital for companies to develop risk management and contingency plans in anticipation of potential challenges. The integration of insourcing and outsourcing strategies adds complexity to the supply chain, making it essential to proactively identify potential risks and devise appropriate mitigation measures. By being well-prepared, companies can adapt to unforeseen circumstances while safeguarding their operations.
In conclusion, insourcing and outsourcing strategies can coexist within a company's supply chain if effectively managed through a strategic mindset, proper analysis, strong partnerships, performance monitoring, and risk management. A balanced approach allows firms to leverage the benefits of both strategies, enhancing overall operational efficiency and supporting business growth.
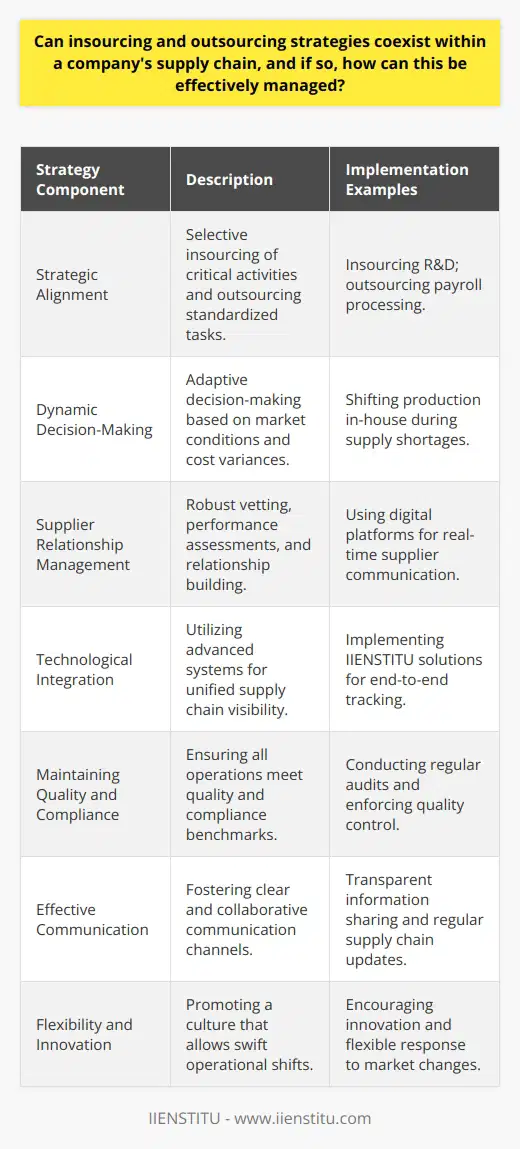
How do advancements in technology impact the decision-making process when determining whether to insource, outsource, or offshore in supply chain management?
The Role of Technology in Decision-Making
Advancements in technology play a crucial role in impacting the decision-making process related to insourcing, outsourcing, or offshoring in supply chain management. Specifically, such technological advancements enable organizations to streamline processes, access useful data, and make more informed decisions.
Data-Driven Decision Making
A critical aspect of technology in supply chain decision-making is the ability to collect, process, and analyze data. By utilizing advanced analytics software and tools, companies can examine their current supply chain operations and generate insights that inform their insourcing, outsourcing, or offshoring decisions. This data-driven approach reduces the risk of poor decision-making and ensures companies align their decisions with their strategic objectives.
Digital Communication & Collaboration
With the advent of digital communication tools such as video conferencing and cloud-based collaboration platforms, companies can easily communicate and collaborate with suppliers and partners across the globe. This enhanced connectivity simplifies the negotiation process by facilitating real-time communication and information sharing, leading to faster and more efficient decision-making.
Automation & AI in Supply Chain Management
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) have also become integral to supply chain management by improving efficiency and reducing manual work. For example, automated warehouse systems can streamline product handling and distribution, while AI-powered forecasting tools can optimize inventory management. Such advancements have significant implications for insourcing, outsourcing, and offshoring decisions, as organizations may seek to leverage technologically advanced providers to achieve higher efficiency and cost savings.
Monitoring & Evaluation
Technology has also improved the processes for monitoring and evaluating the performance of suppliers and service providers. Advanced track-and-trace solutions enable organizations to closely monitor their supply chain operations and make data-driven decisions about insourcing, outsourcing, or offshoring. This increased visibility helps organizations ensure they are partnering with the right suppliers and provides a solid foundation for decision-making.
In conclusion, advancements in technology have fundamentally transformed the decision-making process regarding insourcing, outsourcing, and offshoring in supply chain management. By leveraging data-driven insights, digital communication tools, automation and AI, and advanced monitoring solutions, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, cost savings, and successful decision-making.
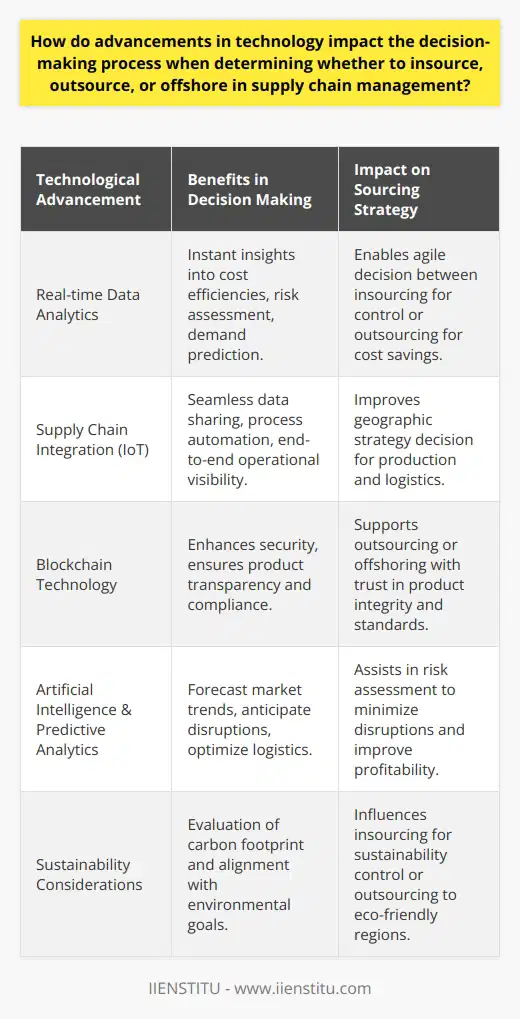
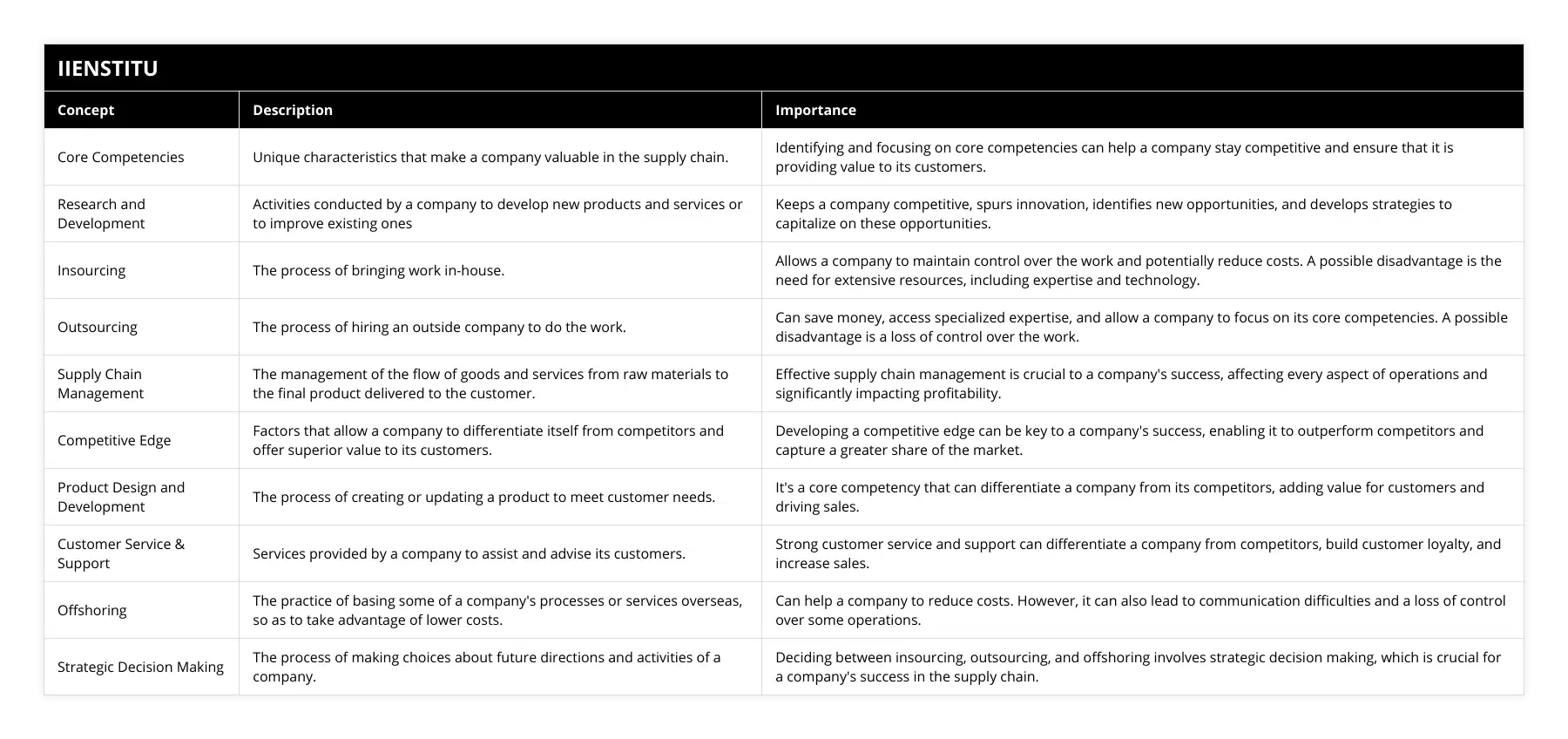
What are the critical success factors for companies implementing insourcing and outsourcing in their supply chain?
Critical Success Factors for Insourcing and Outsourcing
Strategic Alignment
Companies must ensure that their insourcing and outsourcing strategies are in line with their overall business objectives. This requires a thorough analysis of the benefits and risks associated with each approach and aligning them with the organization's long-term goals.
Partner Selection
Selecting the right partners for insourcing and outsourcing is critical in achieving success. Companies must carefully assess potential partners based on factors such as expertise, reputation, and financial stability to guarantee a high level of service and reduce potential risks.
Effective Communication
Clear and open communication between parties is essential for successful insourcing and outsourcing relationships. Companies must establish efficient communication channels to facilitate information sharing, problem-solving, and overall project management.
Risk Management
Both insourcing and outsourcing approaches can present various risks. Companies must develop comprehensive risk management plans to identify, address, and mitigate potential issues that may arise during project implementation.
Performance Measurement
Measuring the performance of insourcing and outsourcing initiatives is crucial in determining their success. Regular monitoring and evaluation of key performance indicators (KPIs) can help companies track their progress, identify potential issues, and make well-informed decisions on resource allocation.
Continuous Improvement
An ongoing commitment to continuous improvement is vital for companies engaged in insourcing and outsourcing projects. This involves ongoing assessment of processes and practices, as well as innovation and adaptation to evolving business environments.
In conclusion, critical success factors for companies implementing insourcing and outsourcing in their supply chain include strategic alignment, partner selection, effective communication, risk management, performance measurement, and continuous improvement. By carefully considering these factors, companies can maximize the benefits of insourcing and outsourcing, while minimizing potential risks and challenges.
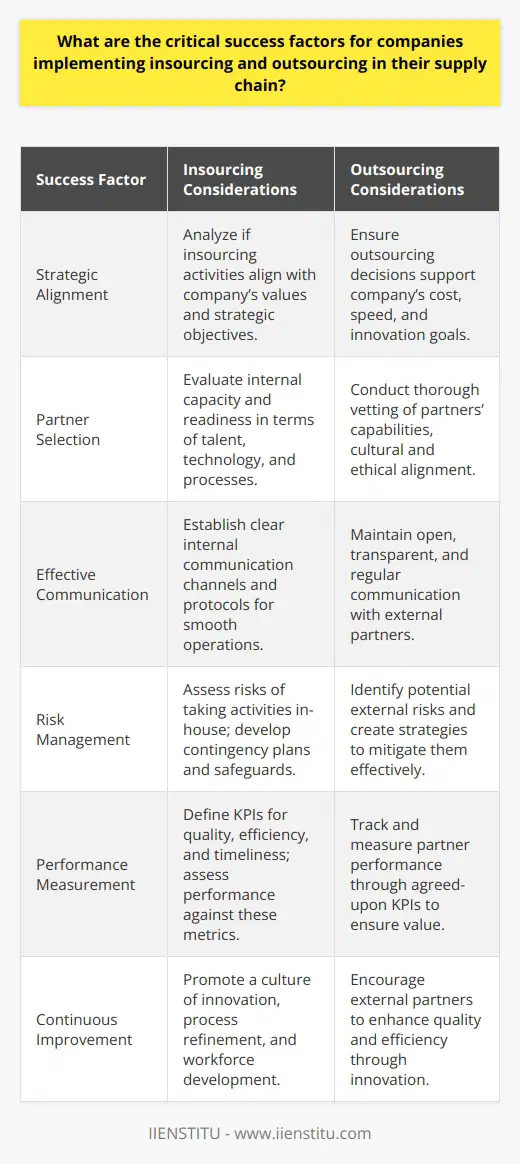
How do geopolitical factors and global economic trends influence the decision to insource or outsource supply chain operations?
Geopolitical Factors and Outsourcing Decisions
Geopolitical factors play a crucial role in determining the insourcing or outsourcing of supply chain operations. Countries with political stability, favorable trade agreements, and conducive business environments attract companies to outsource their operations for cost reduction, enhanced production capacity, and increased market access. Furthermore, stable currencies and strong legal frameworks for intellectual property protection make such countries viable options for businesses to mitigate geopolitical risks.
Global Economic Trends Influence Insourcing/Outsourcing
Global economic trends also significantly impact insourcing and outsourcing decisions. For instance, companies often consider global economies of scale, reduction of operational costs, and increased profits when evaluating outsourcing options. Additionally, fluctuating currency exchange rates and worldwide economic recessions may drive companies to reshape their supply chain operations by either insourcing or outsourcing activities to minimize the negative impact on their financial performance.
Labor Cost and Skill Availability
The availability of skilled labor at a competitive cost is another factor that influences the decision to insource or outsource. Companies may opt to outsource their supply chain operations to countries with low labor costs, thereby reducing their overall production expenses. Conversely, insourcing may become a viable option if the company identifies an opportunity for innovation within their home country, enabling them to strategically invest in the development of local talent and resources.
Infrastructure and Logistics
The quality of a country's infrastructure – including transportation, communication, and logistics – significantly affects the decision to insource or outsource supply chain operations. Effective infrastructure can decrease lead times, enhance distribution networks, and improve operational efficiencies. As such, businesses may favor outsourcing to countries with advanced infrastructure and logistics systems to capitalize on these assets.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Finally, corporate social responsibility (CSR) considerations also influence insourcing and outsourcing decisions. Companies today are increasingly conscious of ethical sourcing and strive to maintain a positive brand image. Actions such as using local suppliers, investing in green technologies, and giving back to the community can position a company as socially responsible. Therefore, when determining whether to insource or outsource, businesses must weigh the potential CSR implications of each option.
In conclusion, geopolitical factors and global economic trends are vital determinants in the insourcing/outsourcing decision-making process. Companies must carefully evaluate the political climate, economic trends, labor costs and skills availability, infrastructure, and corporate social responsibility implications before deciding on the most suitable supply chain strategy to maximize effectiveness and optimize costs.
In what ways can insourcing and outsourcing decisions impact a company's sustainability and corporate social responsibility initiatives in the supply chain?
Impact of Insourcing on Sustainability and CSR Initiatives
Insourcing refers to the practice of hiring internal staff to perform tasks that could be outsourced. Companies often choose this approach to maintain control over operations and ensure consistent quality standards. Insourcing can positively impact a company's sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives in the supply chain. By employing a local workforce, the company can maintain greater oversight of labor practices, reducing the risk of unfair wages, and poor working conditions. Additionally, insourcing can reduce the environmental impact associated with lengthy supply chains, as products and materials can be manufactured and transported within a more localized area. In sum, insourcing can significantly contribute to a company's sustainability and CSR efforts through enhanced control over ecological and labor conditions.
Effects of Outsourcing on Sustainability and CSR Initiatives
Outsourcing, on the other hand, involves the delegation of specific tasks or processes to external organizations, often due to cost or expertise reasons. While this approach can generate cost savings and enable access to skilled workforce, it may present challenges in upholding sustainability and CSR initiatives. A company may face difficulties in ensuring their suppliers abide by ethical labor practices and environmental standards. In addition, excessive outsourcing can lead to complex, highly concentrated supply chains, which can increase vulnerability to disruptions and result in higher carbon emissions. However, working with trusted suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to CSR and sustainability can mitigate these risks. By engaging in responsible outsourcing and selecting suppliers with aligned values, companies can maintain their CSR goals and minimize negative impacts on sustainability.
Balancing Insourcing and Outsourcing for Improved Sustainability and CSR Efforts
To navigate the trade-offs between insourcing and outsourcing, companies need to carefully assess the potential impacts on their sustainability and CSR objectives. By striking a balance between these strategies, a company can optimize control over its supply chain operations while tapping into external expertise and resources. Implementing appropriate monitoring and evaluation mechanisms, such as supplier audits and certifications, can help ensure suppliers adhere to ethical and environmental standards. Ultimately, a thoughtful combination of insourcing and outsourcing decisions can secure long-term success in achieving corporate sustainability and social responsibility.
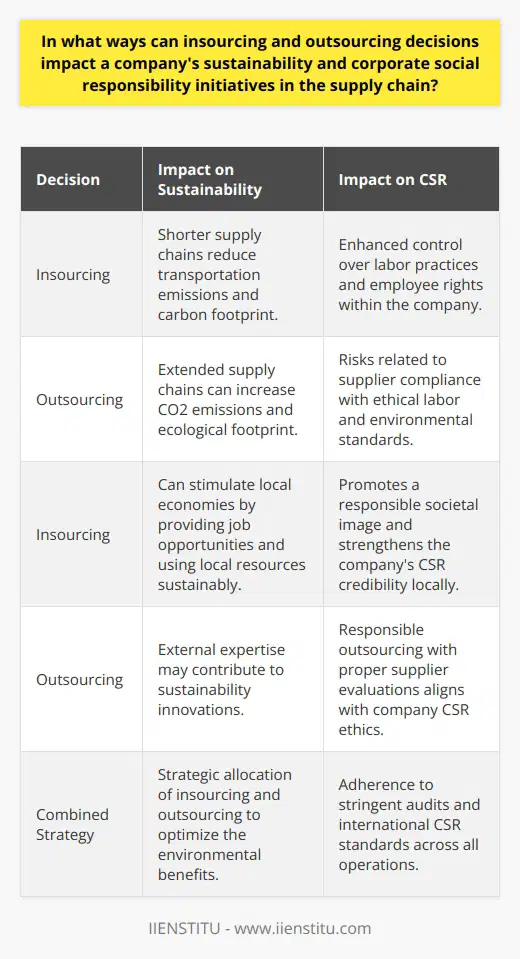
What are the best practices for managing risks and ensuring supply chain continuity when shifting between insourcing and outsourcing strategies?
Assessing Risks and Opportunities
A critical practice in managing risks and ensuring supply chain continuity includes the thorough assessment of risks and opportunities. By evaluating the potential impact of shifting between insourcing and outsourcing strategies, organizations can better anticipate disruptions and adopt countermeasures to mitigate those risks.
Establishing Flexible Contracts
Creating strategic supplier relationships and establishing flexible contracts enable organizations to swiftly adapt to changing circumstances. This flexibility, incorporated into agreements with suppliers, serves as a vital measure in managing uncertainties and guaranteeing supply chain robustness.
Maintaining Supplier Diversity
Another best practice involves maintaining a diverse supplier base. This approach limits dependence on a single outsourced service provider, reducing vulnerability to disruptions and allowing for a smoother transition between insourcing and outsourcing strategies.
Implementing Robust Monitoring Systems
Integrating real-time monitoring systems helps organizations track supplier performance and promptly identify potential risks. By employing data-driven performance indicators, companies can make informed decisions based on predictive analytics, improving their ability to manage supply chain disruptions and ensure continuity.
Developing a Contingency Plan
In order to minimize the adverse effect of disruptions during the transition, organizations should invest in developing comprehensive contingency plans. These plans outline alternative sourcing strategies and identify crucial resources that need to be in place to safeguard against unforeseen challenges and disruptions.
Fostering Collaboration and Communication
Effective communication and collaboration with internal and external stakeholders is paramount when adapting an organization's insourcing and outsourcing strategies. Transparent communication among all parties is essential for maintaining trust and shared understanding of the end-to-end supply chain processes, reducing uncertainties, and addressing potential challenges proactively.
Implementing Change Management Procedures
Lastly, a systematic change management plan facilitates successful transitions between insourcing and outsourcing. Leaders should consider and address any employee concerns, evaluate alternate strategies, and emphasize the importance of sustaining the supply chain flow throughout the transition process.
In conclusion, implementing best practices in risk management and supply chain continuity, such as risk assessment, flexible contracts, supplier diversity, robust monitoring systems, contingency plans, collaboration, communication, and change management, can significantly facilitate organizations' ability to adapt between insourcing and outsourcing strategies. By following these practices, organizations are better equipped to manage potential disruptions and maintain an agile and resilient supply chain ecosystem.
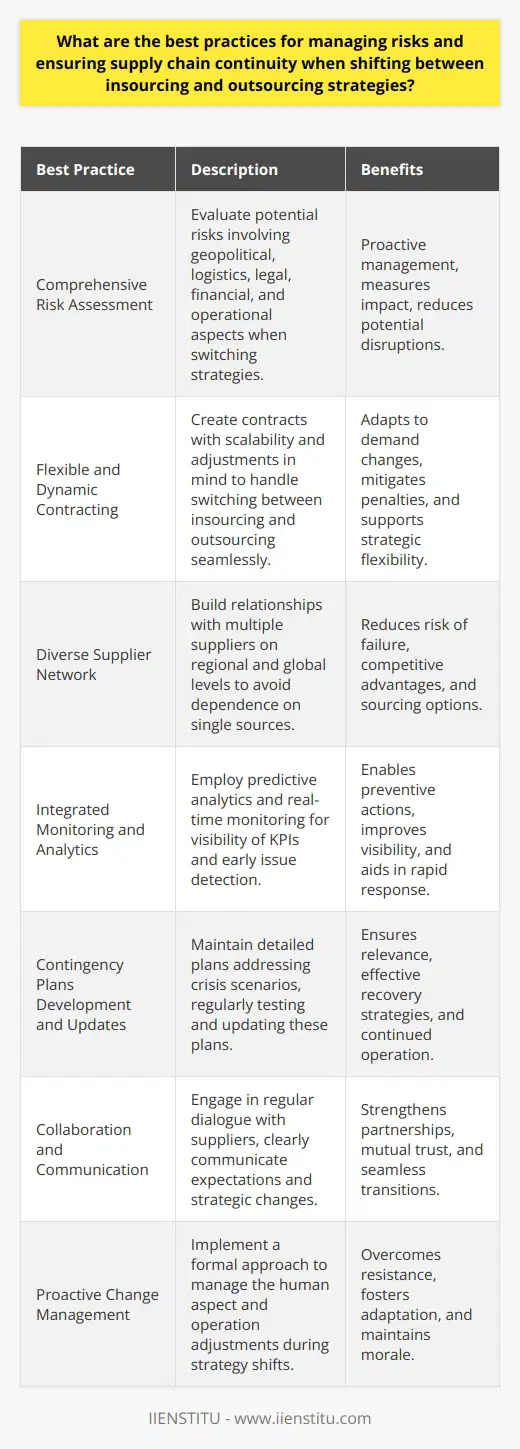
How do various industry sectors approach the decision to insource or outsource supply chain operations, and what can be learned from these examples?
Analyzing Industry Sectors' Strategies
The decision to insource or outsource supply chain operations varies among different industry sectors due to their unique needs, strengths, and goals. It is essential to understand how diverse industries approach such decisions and learn from their experiences to optimize supply chain management.
Automotive and Electronics Industries
The automotive and electronics industries provide clear examples of the benefits of outsourcing supply chain operations. These sectors often maintain a vast network of suppliers, service providers, and subcontractors across numerous countries. Outsourcing helps them to access specialized services, lower costs, and stay flexible in response to market demand fluctuations. For instance, companies like Apple and Ford primarily focus on design, marketing, and sales, while outsourcing major portions of their manufacturing and logistical functions.
Fashion and Textile Industry
The fashion and textile industries also widely adopt outsourcing practices due to similar reasons, such as cost minimization, flexibility, and access to global resources. In fact, many high-end fashion brands source products from a variety of countries to maintain competitive pricing without compromising on quality. However, the downside in this sector could be the lack of control over suppliers and production facilities, which may lead to issues like labor exploitation or environmental concerns.
Pharmaceutical Industry
However, the pharmaceutical industry often opts for insourcing to maintain strict control over quality, regulatory compliance, and intellectual property protection. Drug manufacturers research, develop, and produce their products within their own facilities or in joint ventures with strategic partners, largely due to the critical nature of their product quality and the required regulatory standards. Despite a higher initial cost, insourcing may prove more beneficial in the long run by ensuring trust and product consistency.
Food and Beverage Industry
Similarly, the food and beverage industry prefers insourcing for supply chain operations, given that food safety and quality are paramount concerns. Companies like Nestlé and Coca-Cola extensively invest in their in-house supply chain infrastructure to ensure consistent product quality and monitoring from farm to store shelf. Insourcing allows these companies to control their processes, uphold national brand standards, and implement sustainable practices throughout their value chain.
Key Takeaways and Learnings
From the examples discussed, the decision to insource or outsource supply chain operations largely depends on factors such as the company's core competencies, competitive advantages, quality control requirements, and industry-specific characteristics. The automotive, electronics, fashion, and textile industries benefit from outsourcing for cost reduction, efficiency, and flexibility. In contrast, industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and beverages benefit from insourcing due to the need for control, stringent quality assurance, and regulatory compliance. Ultimately, striking the right balance between insourcing and outsourcing can maximize efficiency and effectiveness in managing supply chain operations while aligning with the company's strategic goals.
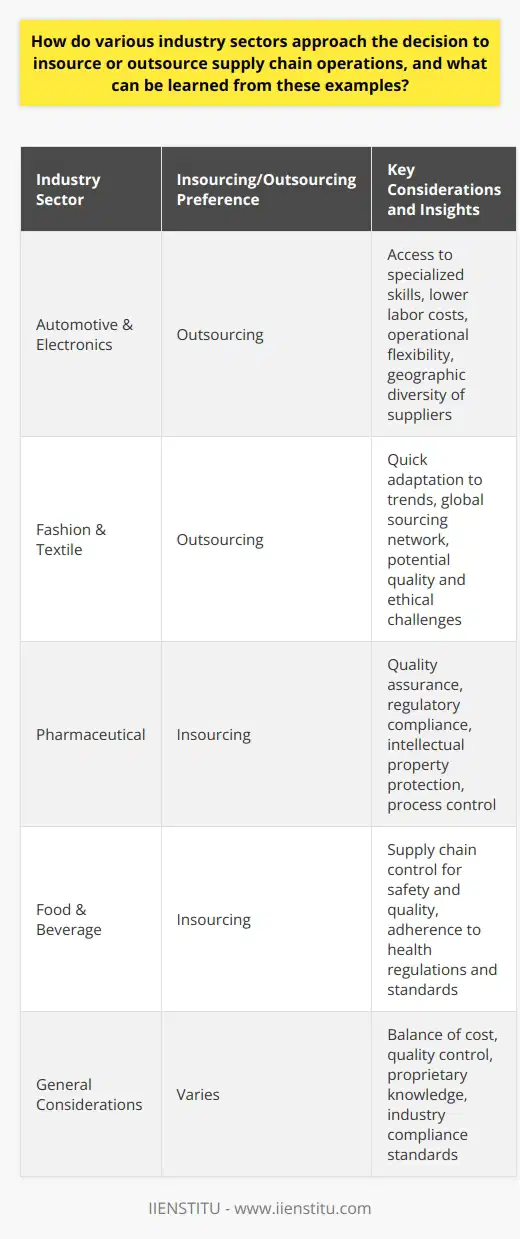
To what extent do companies employ a hybrid approach to insourcing and outsourcing in their supply chain, and what are the benefits of this strategy?
Hybrid Approach in Supply Chain Management
Companies increasingly adopt a hybrid approach in their supply chain management, combining both insourcing and outsourcing processes to effectively manage their business operations. This strategic approach allows companies to reap the benefits of both in-house production and external partnerships.
Balancing Costs and Control
One prime advantage of the hybrid method is its ability to balance cost efficiency and control over operations. Companies can minimize expenses by outsourcing certain tasks to specialized vendors, while maintaining control over key processes through insourcing.
Flexibility and Adaptability
The hybrid approach also enables businesses to maintain flexibility and adaptability in their supply chain, responding quickly to changing market demands and fluctuations in supply and demand. By combining outsourced and in-house production, companies can easily switch between different production methods or suppliers as needed, ensuring a continuous and uninterrupted supply despite external factors.
Risk Management and Efficacy
Effective risk management is another benefit of the hybrid approach. Companies can mitigate risks associated with single-vendor dependencies by diversifying their supply base and integrating multiple suppliers. This reduces the potential impact of supplier-related disruptions while ensuring maximum efficiency and quality.
Leveraging Expertise and Innovation
Collaborating with external partners allows companies to leverage specialized expertise and access to innovative technologies or processes to enhance their overall competitiveness. This, in turn, helps drive improvements in product quality, production efficiency, and overall customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, companies employing a hybrid approach to insourcing and outsourcing in their supply chain achieve significant benefits in the areas of cost management, flexibility, risk mitigation, and innovation. The combination and balance of these elements ultimately contribute to the business's competitive advantage and long-term sustainability, making the hybrid approach a popular strategy in today's globalized, fast-paced business environment.
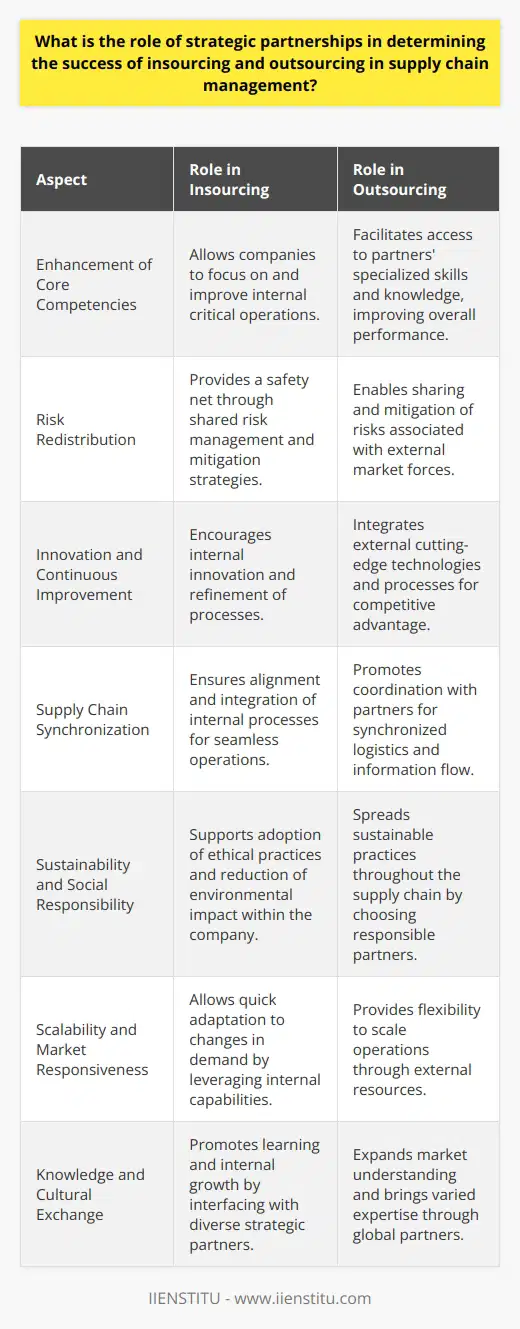
What is the impact of outsourcing in supply chain management?
Impact of Outsourcing on Supply Chain Management
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
Outsourcing in supply chain management has resulted in significant cost reductions and increased efficiency for many organizations. By delegating certain tasks such as manufacturing, procurement, and transportation to specialized external providers, companies can take advantage of economies of scale and streamlined processes, reducing operational expenses.
Global Expansion and Access to Markets
Through outsourcing, companies gain access to new markets and increased global reach. By partnering with suppliers and manufacturers in different regions, businesses can develop a more extensive network of distributors and consumers, allowing them to quickly respond to supply and demand changes and increase their market share.
Risk Management and Mitigation
Outsourcing helps businesses manage and mitigate risks associated with supply chain management. Through diversifying their supplier base, companies can reduce their reliance on a single source of supply, avoid potential disruptions, and ensure business continuity in the face of unforeseen events such as natural disasters or geopolitical tensions.
Leveraging Expertise and Innovation
Partnering with external providers enables companies to tap into their expertise in specific areas and benefit from their innovations. This collaboration can lead to improved products, services, and business processes, resulting in a more competitive and adaptive supply chain that can swiftly address market needs.
Challenges and Concerns
However, outsourcing in supply chain management can also create various challenges and concerns. It may result in loss of control over certain aspects of the supply chain, raising potential quality and compliance issues. Moreover, communication and coordination difficulties may arise due to geographical, cultural, and language barriers, potentially impacting the smooth functioning of the supply chain. Additionally, outsourcing may also lead to increased dependence on external providers, posing risks related to supplier stability and reliability.
Conclusion
Overall, outsourcing plays a significant role in modern supply chain management, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Companies must carefully evaluate the risks and benefits associated with outsourcing, striking a balance between cost reduction and control, leveraging external expertise while maintaining internal competencies, and safeguarding the integrity and resilience of their supply chains.
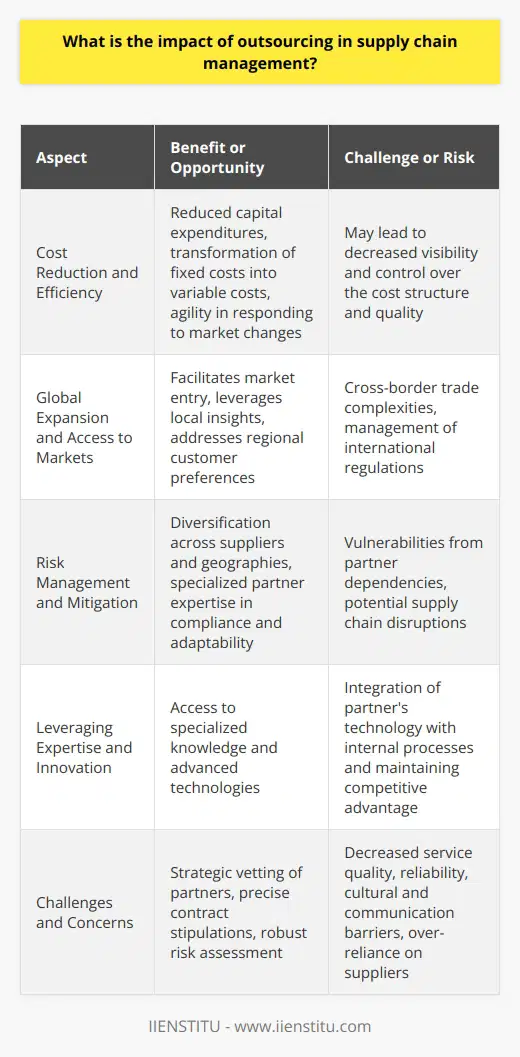
How does the decision to insource or outsource in supply chain operations affect a company's financial performance and flexibility?
Impact on Financial Performance
The decision to insource or outsource in supply chain operations greatly influences a company's financial performance. When a firm outsources, it can potentially reduce operating costs and overhead expenses. Outsourcing partners often possess economies of scale, providing cost-effective services due to their specialized knowledge and infrastructure. These savings can contribute to enhanced profitability and a stronger bottom line.
However, outsourcing may also introduce risks that can negatively affect financial results. For instance, issues such as quality control, communication barriers, and longer lead times may cause delays or unsatisfactory outcomes. Moreover, dependence on an external partner can limit the company's control over its supply chain, potentially harming its reputation and customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Flexibility through Outsourcing
Outsourcing can provide firms with increased flexibility, enabling them to better respond to market changes and shifting customer demands. This is particularly valuable during periods of uncertainty, when organizations must adapt quickly to stay competitive. By outsourcing non-core activities, companies can focus on their core competencies, allowing them to retain a strategic advantage in the marketplace.
Additionally, flexible outsourcing arrangements permit firms to scale their operations according to demand, avoiding the need for significant capital investments. This level of adaptability is crucial for growth, as it enables companies to expand and contract their supply chain as needed.
Risks to Flexibility in Insourcing
Conversely, insourcing can impose constraints on a company's flexibility. Retaining all supply chain operations in-house may require a more significant investment in infrastructure, staff, and technology - resources that are not easily adjustable to market changes. Insourcing may limit a company's capacity to promptly adapt to fluctuations in demand, with the potential for increased operating costs and reduced profit margins.
Furthermore, insourcing may hinder a firm's ability to access new markets, due to the limitations of in-house expertise and resources. Reliance on internally sourced capabilities can prevent a company from exploiting opportunities outside their core competencies.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the decision to insource or outsource in supply chain operations significantly affects a company's financial performance and flexibility. Outsourcing presents opportunities for cost savings and enhanced adaptability, while insourcing can provide greater control over quality and processes, albeit at the expense of limited flexibility. Organizations must carefully evaluate their strategic objectives and capacity for risk before making a decision on their supply chain management approach.
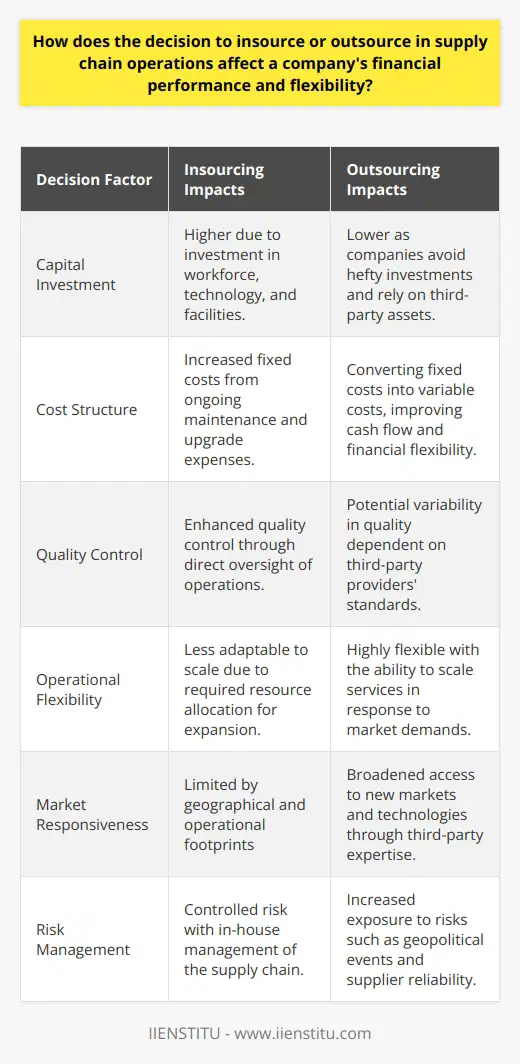
In what ways can companies optimize their insourcing and outsourcing decisions to better manage their global supply chain networks and achieve their strategic objectives?
Assessing Core Competencies and Resources
To begin with, organizations should focus on assessing their core competencies and resources to determine the functions that are best suited for insourcing or outsourcing. By identifying the capabilities that are essential for their strategic objectives, companies can then make informed decisions about which supply chain functions should be handled internally and which should be outsourced to external partners. This evaluation process helps the organization prioritize its investments and resources on the most critical areas of the supply chain.
Evaluating External Partner Capabilities
Additionally, companies must take into consideration the capabilities of external partners when determining the most effective outsourcing strategy. Companies should evaluate the expertise and resources possessed by potential partners, ensuring that the partner can effectively manage the outsourced supply chain functions. A thorough and comprehensive vetting process of potential partners can significantly mitigate the risks associated with outsourcing and ensure that the chosen partner is aligned with the company's strategic objectives.
Leveraging Technology and Data Analytics
Companies can further optimize their insourcing and outsourcing decisions by leveraging technology and data analytics. The use of advanced data analytics can help companies gain insights into their supply chain performance and identify potential areas of improvement. Companies can utilize this information to make strategic decisions about which supply chain functions should be insourced or outsourced, as well as to measure the effectiveness of existing outsourcing partnerships. Similarly, technology can be implemented to enhance communication and collaboration between internal and external supply chain stakeholders, ensuring a more streamlined and efficient process.
Maintaining Flexibility and Adapting to Changing Market Conditions
As global market conditions continue to evolve, organizations must maintain a flexible approach to their insourcing and outsourcing decisions. By continuously reassessing the effectiveness of their internal and external supply chain functions, companies can make adjustments as needed to respond to any shifts in market demand, consumer preferences, or industry trends. This adaptability allows companies to stay competitive and better align their global supply chain networks with their strategic objectives.
In conclusion, optimizing insourcing and outsourcing decisions is essential for organizations to effectively manage their global supply chain networks and achieve their strategic objectives. By carefully assessing core competencies, evaluating external partner capabilities, leveraging technology and data analytics, and maintaining flexibility, companies can successfully navigate the complexities of global supply chain management and secure a competitive advantage in today's dynamic market landscape.
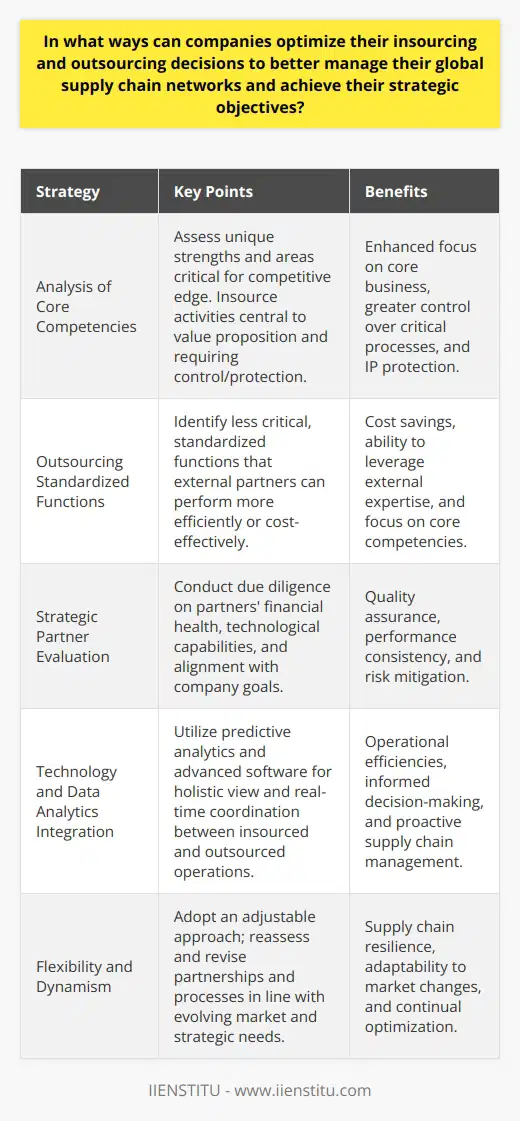
What is the role of strategic partnerships in determining the success of insourcing and outsourcing in supply chain management?
Role of Strategic Partnerships in Supply Chain Management
A crucial factor in successful insourcing and outsourcing within supply chain management is the establishment and maintenance of strategic partnerships. These partnerships dictate the efficacy and flexibility of the supply chain, ultimately impacting an organization's competitiveness in the market.
Benefits of Strong Strategic Partnerships
Improved Operational Efficiency.
Strategic partnerships foster seamless collaboration between organizations, enabling more efficient management of resources and streamlined operations. Consequently, both insourcing and outsourcing activities become more cost-effective, resulting in higher profit margins for businesses.
Access to Expertise and Resources.
When organizations form strategic partnerships, they can gain access to specialized skills, knowledge, and resources that may be unavailable in-house. This proves invaluable in the smooth execution of both insourcing and outsourcing projects.
Enhanced Risk Management.
Collaborating with trusted partners enables businesses to share risks associated with insourcing and outsourcing activities. This allows for more effective risk management strategies, mitigating potential adverse effects on the supply chain and overall business performance.
Competitive Advantage.
Strategic partnerships often result in innovative solutions, contributing to the attainment of a competitive edge in the marketplace. When organizations work together, they can better leverage their collective strengths to conquer market challenges and stay ahead of their competitors.
Flexible and Scalable Supply Chain.
Finally, strategic alliances enable the development of agile supply chains capable of growing and adapting to meet changing market dynamics. Such flexibility is essential for businesses seeking success in globalized and highly competitive environments.
In conclusion, strategic partnerships play a pivotal role in determining the success of insourcing and outsourcing activities in supply chain management. Establishing strong alliances with key partners not only enhances efficiency, but also provides access to valuable expertise, strengthens risk management strategies, and amplifies an organization's competitive advantage. Ultimately, fostering a robust network of strategic partnerships ensures the development of a highly flexible supply chain, crucial for thriving in today's fast-paced and ever-evolving market landscape.
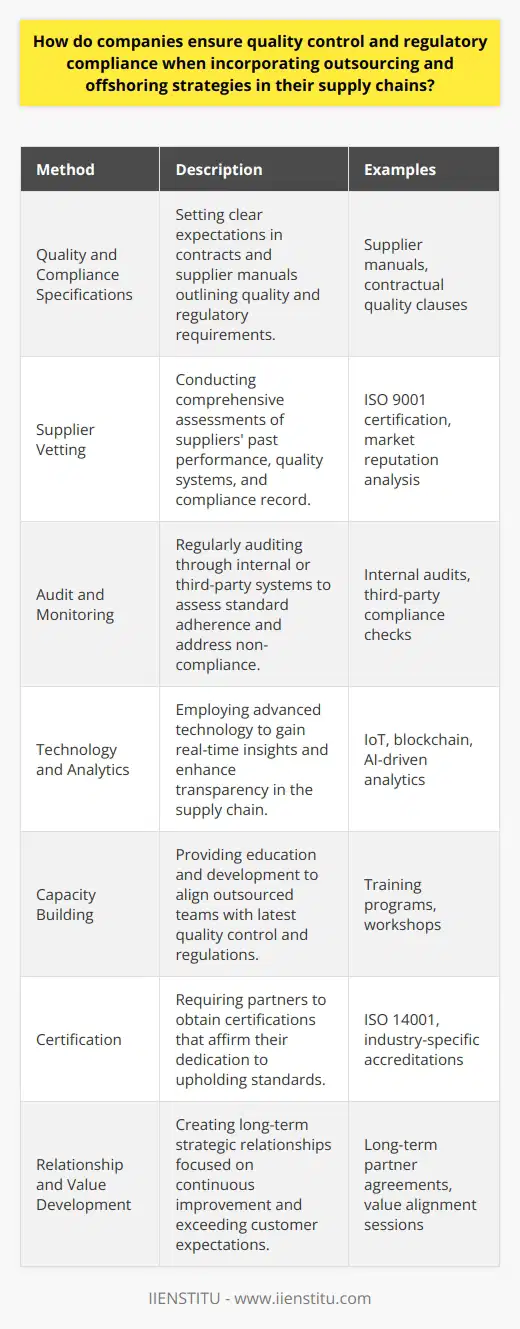
How do companies ensure quality control and regulatory compliance when incorporating outsourcing and offshoring strategies in their supply chains?
Quality Control Measures
Companies ensure quality control and regulatory compliance in their supply chains when integrating outsourcing and offshoring strategies through several approaches. Key among these is establishing comprehensive and clear requirements from the outset. Businesses communicate quality standards and specifications in contracts, ensuring that outsourcing and offshoring partners are well informed about the expectations.
Audit and Assessment of Suppliers
Another tactic involves consistently auditing and assessing supplier performance. Companies conduct regular, scheduled evaluations of their supply chain partners to ensure continuous adherence to quality standards and regulatory requirements. These audits help to identify potential issues early, allowing businesses to address concerns promptly and maintain optimum quality and compliance levels.
Training and Capacity Building
Businesses heavily invest in training and capacity-building programs for their outsourcing and offshoring partners. By providing the necessary resources and support, companies can ensure that their partners have sufficient knowledge and skills to deliver high-quality products and services while adhering to relevant regulations.
Technological Monitoring Tools
The use of technology further enhances quality control and regulatory compliance. Advanced monitoring tools help track and manage supply chain processes in real-time, making it easier for companies to identify and address any discrepancies. Moreover, these technologies enable businesses to share critical data with their partners in a secure and efficient manner, fostering collaboration and success in meeting quality standards.
Certifications and Accreditations
Lastly, requiring outsourcing and offshoring partners to obtain appropriate certifications and accreditations contributes to quality control and regulatory compliance. Companies often mandate that their supply chain partners achieve specific, globally-recognized certifications to demonstrate a commitment to adhere to best practices, quality expectations, and relevant regulations. This approach provides an added layer of assurance regarding compliance and quality management.
In conclusion, businesses can successfully ensure quality control and regulatory compliance when incorporating outsourcing and offshoring strategies in their supply chains by adopting a multi-faceted approach. This process encompasses setting clear expectations, conducting regular audits, investing in training and capacity building, utilizing technological monitoring tools, and requiring certifications and accreditations from supply chain partners.
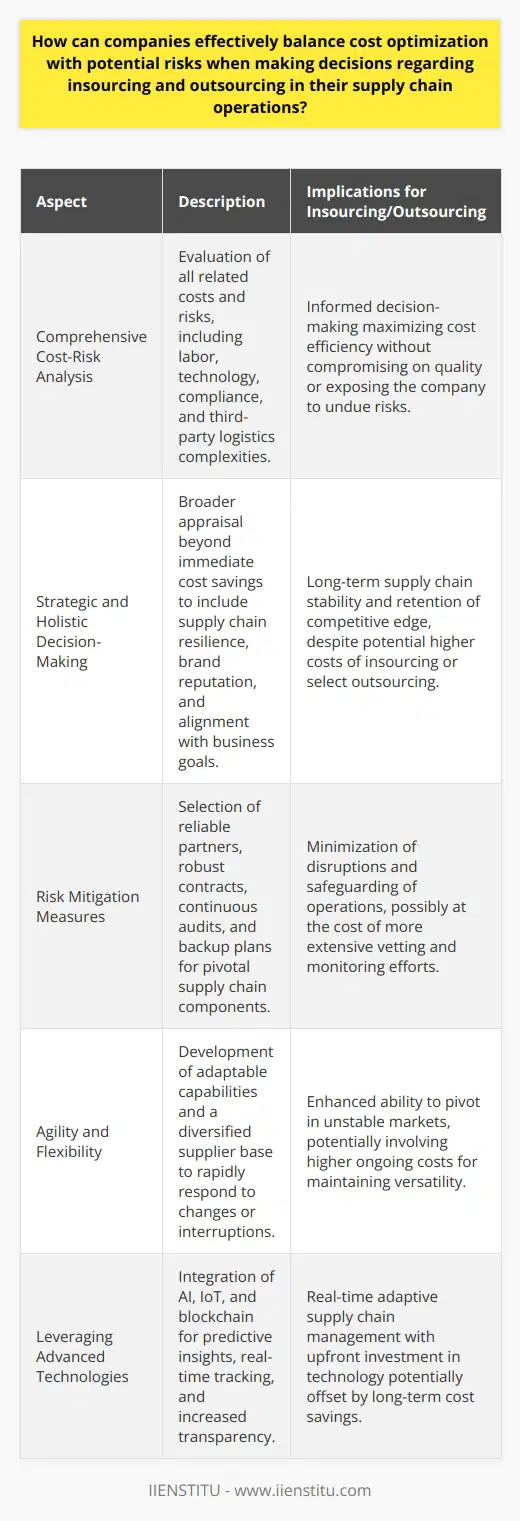
How can companies effectively balance cost optimization with potential risks when making decisions regarding insourcing and outsourcing in their supply chain operations?
Assessing Costs and Risks
To effectively balance cost optimization with potential risks in supply chain operations, companies should begin by conducting a thorough assessment of the costs and risks associated with insourcing and outsourcing. This involves analyzing factors such as labor costs, equipment costs, and regulatory compliance and comparing them with the costs and risks associated with working with external suppliers or partners.
Strategic Decision-Making
Upon analyzing cost and risk factors, companies need to implement strategic decision-making processes that enable them to choose between insourcing and outsourcing. The strategic decision-making process should take into account not only short-term cost savings but also long-term implications, including threats to supply chain resiliency, competitive advantages, and potential disruptions.
Mitigating Risks
If a company chooses to outsource a part of its supply chain operations, it is critical to select partners who are reliable, financially stable, and share similar business values. Engaging in due diligence, establishing performance metrics, and creating contingency plans can help mitigate potential risks associated with suppliers or partners. To ensure long-term success in either insourcing or outsourcing situations, companies should continuously monitor and evaluate their strategic decisions.
Maintaining Flexibility
A key aspect of balancing cost optimization and potential risks in supply chain operations involves maintaining flexibility within the organization. Companies should invest in developing and training internal resources while also building relationships with multiple suppliers or partners to hedge against potential supply chain risks.
Utilizing Technology
Leveraging technology is vital for both insourcing and outsourcing decisions in supply chain operations. Implementing appropriate management tools, monitoring systems, and data analytics can improve visibility across the supply chain, help predict potential risks, and optimize cost management.
In conclusion, to effectively balance cost optimization with potential risks in supply chain operations, companies must conduct a thorough assessment of associated costs and risks, implement strategic decision-making processes, continuously monitor and evaluate their choices, maintain organizational flexibility, and leverage technology. By considering these elements, companies can successfully navigate the complex landscape of insourcing and outsourcing and achieve their desired supply chain objectives.
What are the ethical implications of insourcing and outsourcing decisions in supply chain management, and how can companies navigate these complex issues?
Ethical Implications of Insourcing and Outsourcing
Insourcing and outsourcing are significant aspects of supply chain management that involve companies deciding to either retain operations in-house or contract with external suppliers or manufacturers. Both choices present ethical implications that can greatly affect a company's reputation, employees, and stakeholders. By understanding these complexities and implementing strategies to address them, firms can successfully navigate these issues and make more informed decisions in their supply chain management.
Social and Environmental Concerns
When outsourcing, companies often source products or services from locations with lower labor and material costs. However, this decision may inadvertently support labor exploitation or contribute to environmental damage, as suppliers in lower-cost countries may have less stringent labor and environmental regulations. To address these concerns, businesses need to perform thorough due diligence on potential suppliers and establish robust supplier codes of conduct to ensure that ethical and sustainable practices are maintained along the entire supply chain.
Internal Workforce Impact
For insourcing, the investment in a company's internal workforce, resources, and facilities can be seen as a commitment to employee well-being, community development, and long-term stability. Nonetheless, insourcing efforts may lead to challenges like job displacement, employee resentment, or communication breakdowns during the transition period. Companies can mitigate these risks by transparently communicating with employees about the changes, offering training and development opportunities, and providing support to affected personnel during the restructuring process.
Global Economic Effects
Both insourcing and outsourcing can have broader economic implications beyond the company itself, with potential impacts on global trade, local economies, and job opportunities in various regions. Companies must acknowledge these consequences and strive to balance their decisions with ethical considerations, such as ensuring job opportunities are fairly distributed and supporting communities affected by their supply chain choices.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Ultimately, companies have a responsibility to consider the broader ethical implications of their insourcing and outsourcing decisions. Integrating corporate social responsibility (CSR) priorities within supply chain management can help create sustainable and ethically responsible operations. This approach should include regularly assessing and measuring the effectiveness of in-house and external suppliers, prioritizing continuous improvement, and fostering transparent communication with stakeholders about supply chain practices.
In conclusion, companies must carefully evaluate the ethical implications of their insourcing and outsourcing decisions in supply chain management, taking into account the potential social, environmental, and economic consequences. By adopting a corporate social responsibility mindset and implementing sound strategies and practices, they can navigate these complex issues and operate ethically throughout their supply chain.
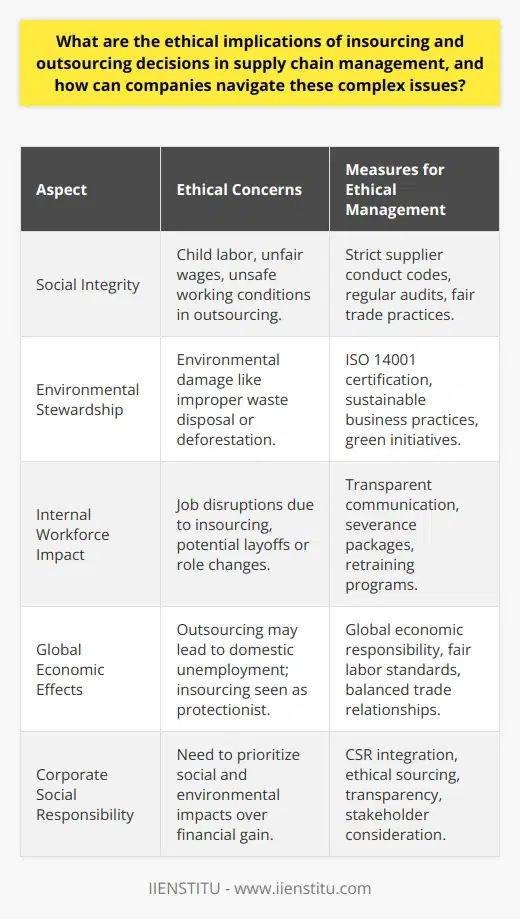
How can companies effectively incorporate environmental and social sustainability criteria in their insourcing and outsourcing decision-making processes?
Incorporating Sustainability Criteria in Decision-Making Processes
Evaluate Environmental and Social Impacts
Companies can begin by assessing the environmental and social impacts of their insourcing and outsourcing decisions. They should consider factors such as carbon emissions, waste management, energy consumption, and resource use across their supply chains. Furthermore, attention must also be paid to social aspects, such as labor rights, community relations, and employee health and safety.
Set Sustainability Goals and Prioritize Actions
After identifying key sustainability factors, companies should establish clear targets and prioritize actions to achieve these goals, by incorporating them into their strategic planning. This can be achieved by setting time-bound targets and working collaboratively with internal and external stakeholders to ensure alignment with business objectives and broader sustainability initiatives.
Integrate Sustainability in Vendor Selection
When outsourcing, companies should include sustainability criteria in their vendor selection process. By evaluating potential partners on their environmental and social performance, businesses can ensure that they are working with suppliers who share their sustainability values. This can be done by scrutinizing vendor corporate social responsibility (CSR) reports or certifications and conducting due diligence on their practices.
Monitor and Report Progress
In order to ensure effective integration of sustainability criteria, companies need to regularly monitor and measure their progress. Metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) should be utilized to demonstrate progress on sustainability targets and assess performance across the supply chain. Furthermore, regular reporting of sustainability achievements can help maintain accountability and communicate successes to stakeholders.
Engage and Educate Employees
Finally, fostering a culture of sustainability within the organization is key to embedding these considerations in decision-making processes. Employees should be educated and trained on the importance of environmental and social sustainability and empowered to contribute their ideas to the process. By actively engaging and encouraging employees to participate in sustainability discussions, companies can ensure that these criteria are integrated into their sourcing and procurement decisions.
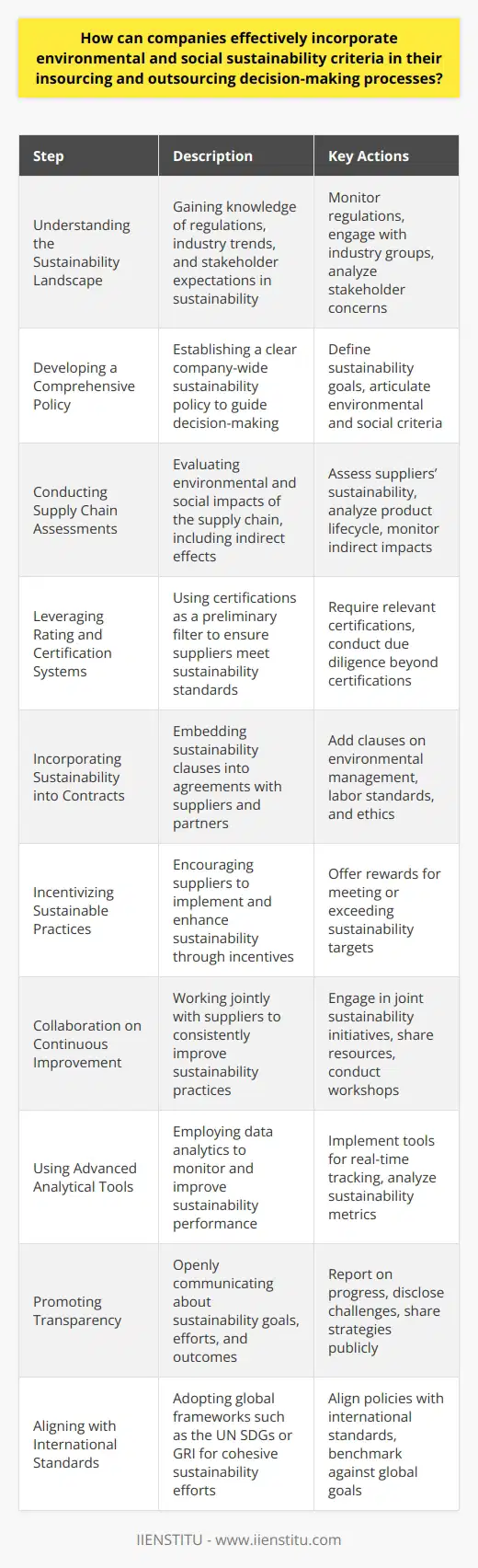
What role do governance structures and performance measurement systems play in managing and evaluating insourcing and outsourcing initiatives within a company's supply chain?
Governance Structures Impact
Effective governance structures significantly influence insourcing and outsourcing decisions within a company's supply chain. By establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes, governance structures provide a framework for evaluating and managing these initiatives. This framework ensures alignment with the company's overall strategy and objectives, while promoting collaboration and communication among stakeholders. Additionally, governance structures help in mitigating risks and addressing challenges related to insourcing and outsourcing, such as supplier selection, contract negotiation, and potential disruptions.
Performance Measurement Systems
Performance measurement systems play a crucial role in managing and evaluating insourcing and outsourcing initiatives by ensuring the effectiveness and efficiency of the supply chain. These systems involve the use of key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor and assess the performance of both internal and external suppliers. By identifying trends and patterns, KPIs can be used to support decision-making processes and drive continuous improvement efforts within the supply chain.
Benefits of Effective Governance and Performance Measurement
Implementing robust governance structures and performance measurement systems offers several benefits in managing insourcing and outsourcing initiatives within a company's supply chain. These include improved strategic alignment, risk management, accountability, transparency, and cost control. Additionally, effective governance and performance measurement can lead to enhanced supplier performance and better control over operational and financial outcomes, ultimately contributing to the company's overall success.
In conclusion, governance structures and performance measurement systems are vital for successfully managing and evaluating insourcing and outsourcing initiatives within a company's supply chain. By providing a clear framework for decision-making and enabling continuous monitoring of supplier performance, these mechanisms support effective risk management, strategic alignment, and process optimization, leading to a more efficient and competitive supply chain.
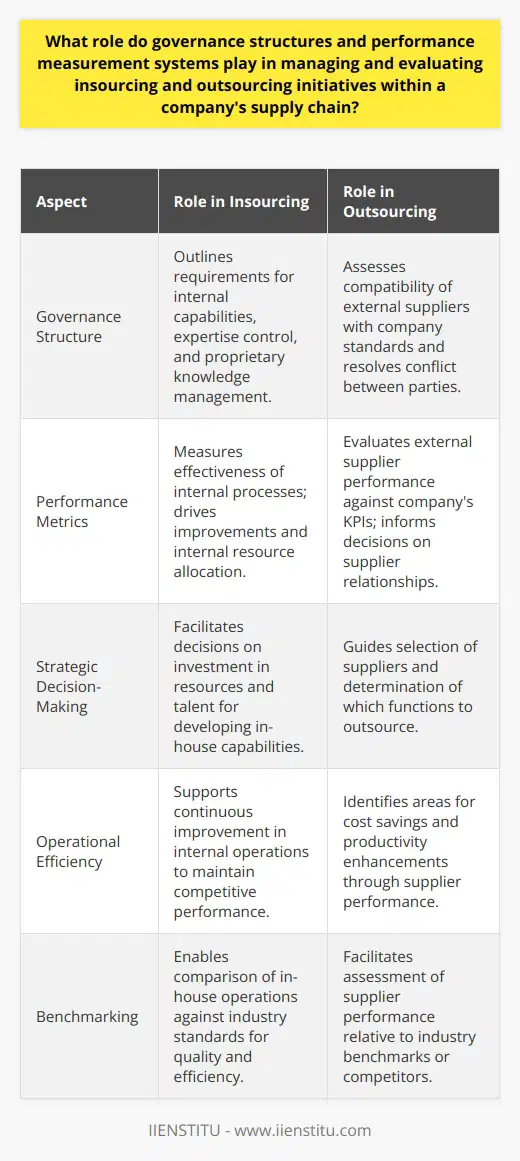
What are the long-term strategic implications of insourcing and outsourcing decisions on supply chain management?
Impact on Supply Chain Flexibility
Insourcing and outsourcing decisions have a significant impact on a supply chain's ability to adapt to change. Organizations that choose to outsource production, for example, often benefit from a more flexible supply chain through lower fixed costs and greater access to external resources. In contrast, insourcing can result in higher fixed costs and reduced responsiveness to market fluctuations. Consequently, companies must evaluate the trade-offs between these two options in terms of long-term flexibility.
Influence on Innovation
When considering the implications of insourcing and outsourcing on supply chain management, it is crucial to examine how these decisions affect innovation. Outsourcing can provide organizations with access to specialized knowledge and skills, enabling them to stay competitive and up-to-date with the latest technologies. However, insourcing can foster a more collaborative environment by promoting internal knowledge sharing and creating synergies among different departments. Ultimately, companies need to balance the benefits and drawbacks of both approaches to maximize innovation.
Costs and Efficiency
Insourcing and outsourcing decisions play a crucial role in shaping a supply chain's cost structure and overall efficiency. Outsourcing can lead to cost savings, especially in labor-intensive industries, by utilizing lower-cost or specialized service providers. However, insourcing can offer greater control over critical production processes, leading to improved efficiency, quality, and margins. Therefore, long-term strategic decisions should consider the cost and efficiency implications of insourcing and outsourcing.
Risk Management
One of the most significant factors to consider when evaluating the long-term strategic implications of insourcing and outsourcing on supply chain management is risk management. Outsourcing can expose companies to risks such as supplier bankruptcy, geopolitical issues, and lack of visibility into production processes. On the other hand, insourcing might expose organizations to technological obsolescence, capacity constraints, and labor issues. As a result, effective risk management should be an essential consideration when making insourcing and outsourcing decisions.
In conclusion, the long-term strategic implications of insourcing and outsourcing decisions on supply chain management encompass factors such as flexibility, innovation, cost and efficiency, and risk management. Companies should carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each approach to achieve a balance that best aligns with their long-term business objectives. A successful supply chain strategy will result from a thoughtful and comprehensive analysis of the intersection between these critical factors.
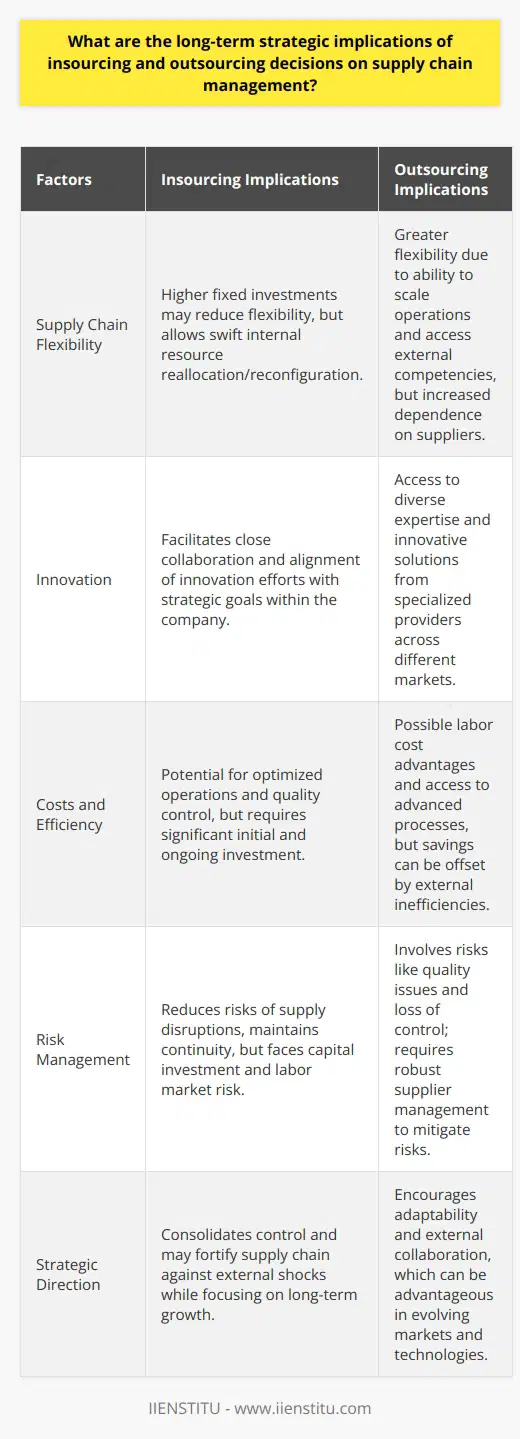
How does a company's competitive landscape influence the choice to insource or outsource supply chain activities?
Influence of Competitive Landscape on Insourcing vs Outsourcing
Market Dynamics and Supply Chain Decisions
A company's competitive landscape directly impacts its choice to insource or outsource supply chain activities. The competitive landscape encompasses multiple factors, such as market dynamics, industry trends, and competitor strategies. Businesses must carefully evaluate these elements to determine the most cost-effective and efficient approach to managing their supply chains.
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
In some cases, a company's competitors may have already outsourced their supply chain processes, potentially reaping benefits in terms of reduced costs and increased operational efficiency. Such a scenario may induce a firm to follow suit, hoping to improve competitiveness and maintain market share. Alternatively, a company may decide to insource to preserve control, accelerate decision-making, and customize supply chain processes more adeptly.
Technology and Innovation Factors
A key aspect of the competitive landscape is the role of technological advancements and innovation in supply chain management. Businesses may undertake insourcing if they believe that their in-house capabilities surpass those of third-party providers, enabling the development and implementation of cutting-edge solutions. Conversely, some companies may opt for outsourcing to leverage external expertise and access innovative tools and techniques that can enhance their supply chain operations.
Risk Mitigation and Adaptability
The level of risk inherent in a company's supply chain also plays a significant role in the choice between insourcing and outsourcing. If potential risks are high, such as with fluctuating demand, intellectual property concerns, or potential disruptions, a firm may favor insourcing as a means to better manage and mitigate these uncertainties. In contrast, firms may outsource to improve flexibility, allowing them to adapt more readily to changing market conditions.
Talent and Workforce Considerations
Lastly, the availability of skilled talent can sway a company's decision to insource or outsource. If a firm has access to a competent workforce with relevant domain expertise, it may choose insourcing to capitalize on this human capital. However, if there is a lack of skilled workers, partnering with a specialized outsourcing provider may present a more viable option.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a company's competitive landscape significantly influences the decision to insource or outsource supply chain activities. Businesses must weigh aspects such as cost and efficiency, technological advancements, risk management, and talent availability when assessing their options, ultimately selecting an approach that optimizes their competitive positioning within the market.
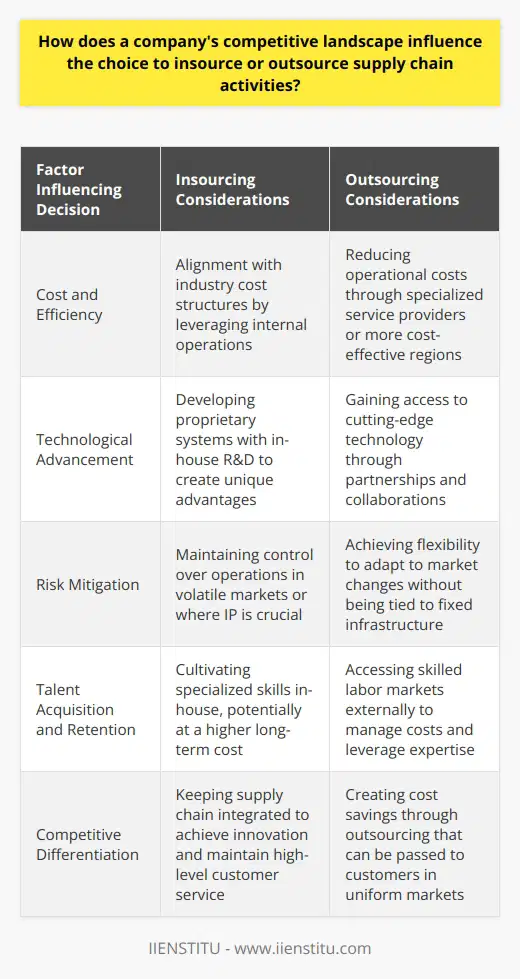
In what ways can insourcing and outsourcing contribute to supply chain resilience and adaptability in the face of global disruptions and uncertainties?
**Insourcing and Supply Chain Resilience**
Insourcing bolsters supply chain resilience by enabling organizations to maintain control over critical operations. By insourcing vital functions, companies can closely monitor their activities, anticipate disruptions, and swiftly respond to uncertainties. In doing so, they reduce dependence on external parties and improve their ability to handle unexpected events.
**Outsourcing and Adaptability**
Conversely, outsourcing contributes to supply chain adaptability by increasing flexibility and diffusion of risks. Companies can select from a diverse range of suppliers, adopt a multi-sourcing approach, and quickly adjust their strategies in response to shifting environments. By delegating specific operations to specialized providers, organizations can tap into industry expertise while focusing on their core competencies.
**Supplier Diversification**
Both insourcing and outsourcing strategies can benefit from supplier diversification. By working with various suppliers, businesses can reduce concentration risk and strengthen their resilience against unforeseen disruptions. Additionally, diversification allows for a greater ability to reconfigure operations, enhancing adaptability in the face of global uncertainties.
**Information Sharing and Collaboration**
Effective information sharing and collaboration between insourced and outsourced partners can lead to improved resilience and adaptability in supply chains. Companies that openly share information and collaborate with their partners are better equipped to identify emerging risks and exploit opportunities for innovation. This collaborative approach can foster a more profound understanding of the supply chain landscape, ultimately enabling businesses to navigate disruptions more efficiently.
**Technological Integration**
Both insourcing and outsourcing strategies can benefit from employing advanced technology to enhance supply chain resilience and adaptability. By implementing technologies such as automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, companies can optimize their operations, minimize bottlenecks, and improve overall visibility. By leveraging technological capabilities, businesses can also enable faster decision-making and adapt more quickly to disruptions.
In conclusion, insourcing and outsourcing both contribute to supply chain resilience and adaptability by offering distinct advantages in the face of global disruptions and uncertainties. Companies can employ these strategies individually or in combination, according to their specific requirements and goals, to build robust, agile, and adaptable supply chains that can withstand the unpredictable nature of today's global environment.
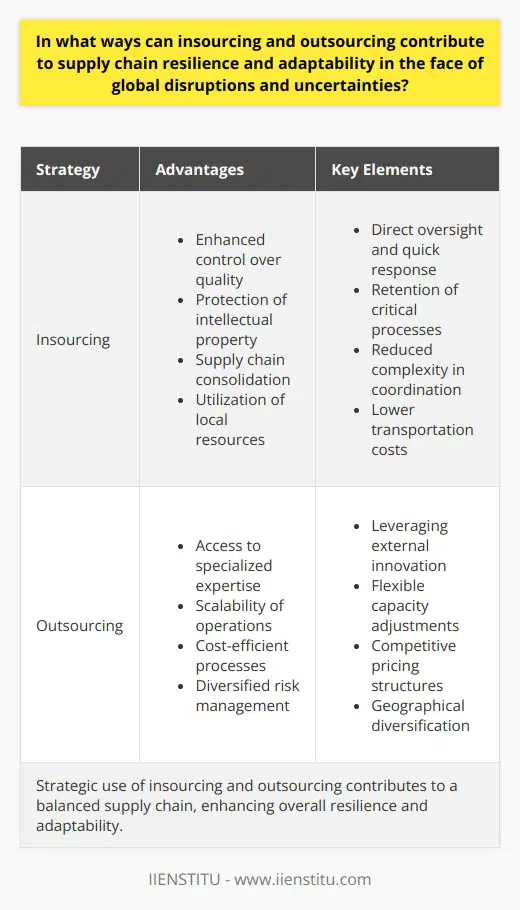
What is the relationship between insourcing, outsourcing, and supply chain performance metrics such as efficiency, flexibility, and responsiveness?
Relationship Between Insourcing and Outsourcing
The relationship between insourcing, outsourcing, and supply chain performance metrics can be understood by examining their individual impact on efficiency, flexibility, and responsiveness. Insourcing refers to the process of engaging internal resources in addressing business processes or requirements, while outsourcing involves engaging external organizations or vendors to perform specific tasks or functions.
Impact on Efficiency
Both insourcing and outsourcing can contribute to improved efficiency in the supply chain. When a company decides to insource, it leverages the existing competencies of its workforce to address operational needs. This may lead to a reduction in lead times, improved resource utilization, and faster problem resolution, which increases efficiency. On the other hand, outsourcing can enhance supply chain efficiency by availing specialized expertise and cost-effective solutions through industry-best practices and global delivery centers.
Influence on Flexibility
Supply chain flexibility involves the ability of a company to adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands. Insourcing can provide greater flexibility and control, as internal teams can swiftly modify processes or reallocate resources to accommodate fluctuating requirements. Outsourcing, however, may result in contractual rigidity that limits the extent of adjustments that can be made to outsourced processes. It may also lead to a dependency on external providers, making it difficult for a company to change course quickly in response to market dynamics.
Impact on Responsiveness
Responsiveness in the supply chain context implies the ability to react quickly to changes in customer needs and preferences. Insourcing allows for more direct communication and collaboration between different functional areas within a company, potentially leading to quicker response times. On the other hand, outsourcing can also enhance responsiveness by leveraging the vast experience and innovative solutions of specialized service providers, which can aid in addressing new challenges or fulfilling customer expectations more efficiently. However, a potential drawback with outsourcing is the potential for communication breakdowns or cultural differences that may affect response times negatively.
In conclusion, the relationship between insourcing, outsourcing, and supply chain performance metrics is complex and multifaceted. Both approaches can have positive and negative effects on efficiency, flexibility, and responsiveness, depending on the specific processes being considered, the company's capabilities, and the overall business context. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to weigh the pros and cons of both insourcing and outsourcing before determining the best approach to optimize their supply chain performance.
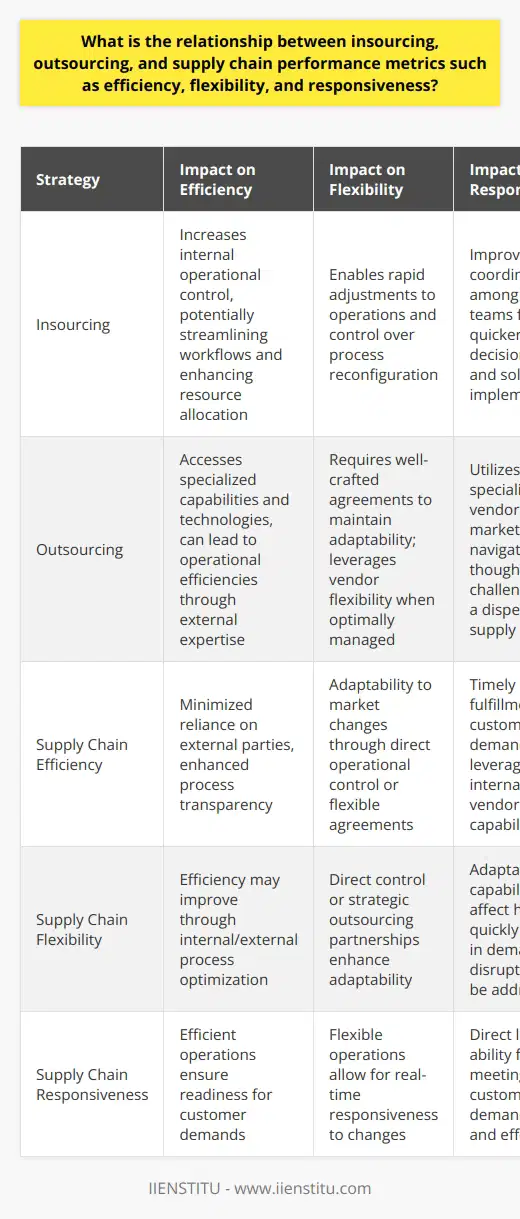
How do changes in customer demands and market dynamics influence the decisions to insource or outsource supply chain activities?
Influence of Market Dynamics and Customer Demands
Changes in customer demands and market dynamics greatly influence the decision to insource or outsource supply chain activities. Companies must adapt to ever-changing market conditions and customer expectations, while also maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Shifts in Customer Demands
As preferences shift, businesses must revisit their supply chain arrangements to align with these new requirements. Consequently, the need for specialized production capabilities, cultural or geographical proximity to the target market, or swift response times might lead companies to outsource tasks to service providers possessing the desired expertise. On the other hand, aiming to maintain direct control over customer experience, firms may insource certain activities back.
Evolving Market Dynamics
Similarly, evolving market dynamics can necessitate adjustments in supply chain management. Relocating manufacturing operations to regions where production costs are lower, they often decide to outsource. Conversely, protectionist trade policies or external shocks, like natural disasters or pandemics, can induce trade restrictions, thereby pushing companies to mitigate risks and insource their operations.
Technological Advancements
Additionally, advancements in technology affect the choice between insourcing and outsourcing. As automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and digitalization become more prevalent, businesses may consider insourcing due to the potential reduced labor costs and improved productivity. At the same time, outsourcing to technology-focused providers could offer specialized expertise and resources without considerable upfront investments.
Competitive Advantage and Necessity
Lastly, the need for a competitive edge and the businesses' necessity to focus on core competencies can determine the decision. Insourcing allows firms greater control and customization of key processes crucial to their competitive advantage. In contrast, outsourcing provides access to industry specialists and their expertise, freeing up resources for companies to focus on their primary areas of strategic value.
Conclusion
In conclusion, changes in customer demands and market dynamics play a pivotal role in shaping the decision to insource or outsource supply chain activities. Firms must continually reassess their arrangements, considering factors such as specialization, market trends, technological advancements, risk mitigation, and competitive advantage. Furthermore, striking a balance between insourcing and outsourcing to maximize benefits and adaptability is crucial for successful supply chain management.
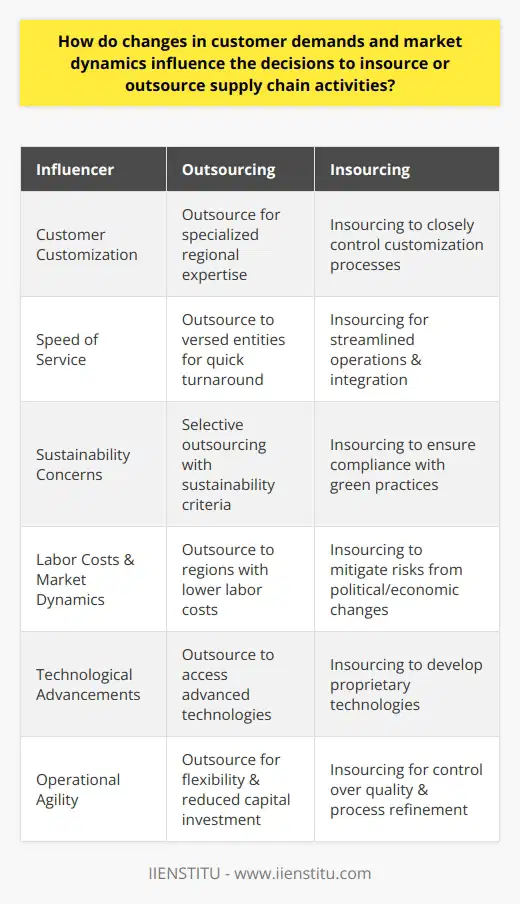
What are the success factors for driving innovation and continuous improvement in supply chain management through insourcing and outsourcing strategies?
Integrating Insourcing and Outsourcing
Successful innovation and continuous improvement in supply chain management require a strategic integration of insourcing and outsourcing strategies. Key success factors for driving such improvements include:
Understanding Core Competencies
Identifying core competencies enables organizations to strategically insource crucial areas in which they excel while outsourcing non-core functions to external specialists. This fosters agility and flexibility.
Developing Collaborative Partnerships
Strengthening relationships with suppliers and outsourcing partners is essential for ensuring that both parties fully understand the organization's expectations and process requirements, contributing to overall supply chain efficiency.
Leveraging Technological Advancements
Harnessing cutting-edge digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, big data, and the Internet of Things, can drive innovation through data-driven decision-making, optimized logistics, and enhanced inventory management.
Promoting Continuous Learning
Encouraging a culture of continuous learning and improvement within the organization fosters a more proactive approach to enhancing supply chain management. This can include training programs and employee development initiatives to ensure that staff can adapt to changing conditions in the industry and technological landscape.
Monitoring Performance Metrics
Establishing quantifiable performance metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of insourcing and outsourcing strategies enables a systematic assessment of the overall supply chain. Regular monitoring and analysis can help identify areas for improvement and drive continuous innovation.
Implementing Risk Management Strategies
Proactively identifying and mitigating potential risks in supply chain management through robust risk management planning can help organizations foresee and prepare for potential disruptions, ensuring business continuity and smoother operations.
In conclusion, driving innovation and continuous improvement through insourcing and outsourcing strategies is reliant upon a balanced approach that leverages an organization's core competencies, collaborative partnerships, technology advancements, and continuous learning while monitoring performance metrics and managing potential risks. By combining these key success factors, organizations can achieve a more resilient, flexible, and efficient supply chain management process capable of adapting to the ever-changing business environment.