I remember the time when I was a kid, watching my grandfather run his small grocery store in the heart of our town. He knew every supplier by name, understood when the shipments would arrive, and always had the shelves stocked with what the locals needed most. Back then, I didn't realize it, but he was a master of supply chain planning on a micro scale. Today, businesses operate on a much larger stage, but the principles remain the same. Supply chain planning is the backbone of any successful enterprise, ensuring that products and services flow smoothly from producers to consumers.
In our rapidly evolving global economy, understanding the intricacies of what is supply chain planning in business isn't just for the big corporations. Whether you're running a local bakery or managing international shipments, the way you handle your supply chain resources and navigate supply chain constraints can make or break your business. Let's dive into what supply chain planning really means, explore the resources involved, and look at the constraints that businesses face every day.
Introduction
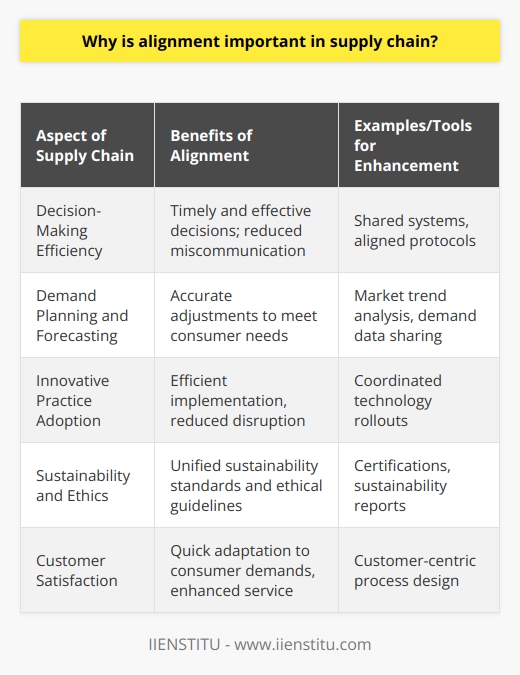
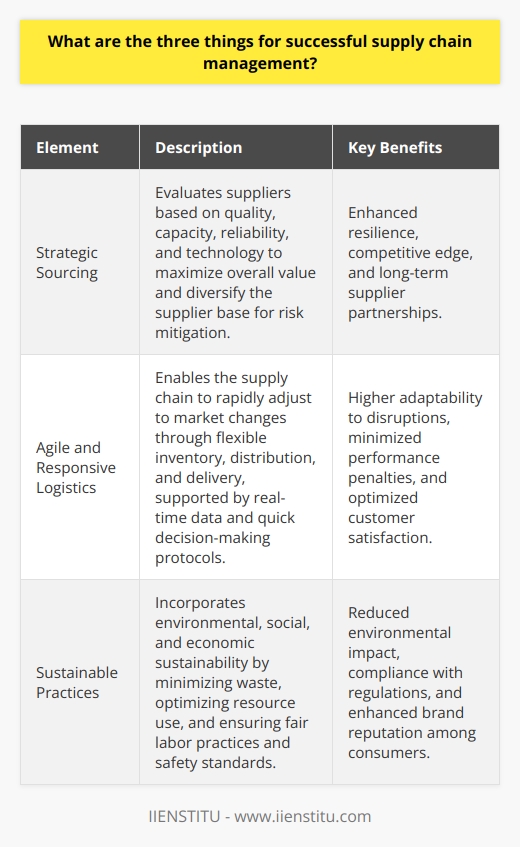
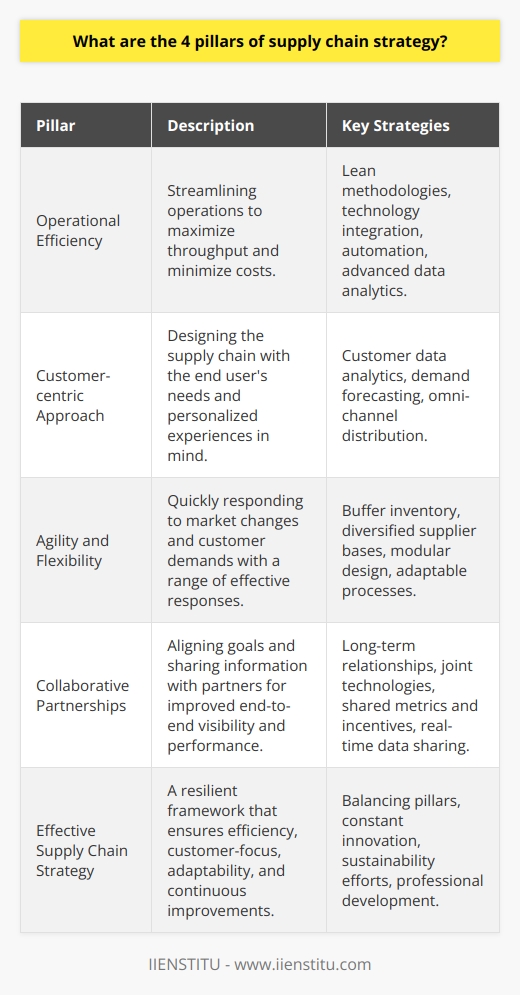
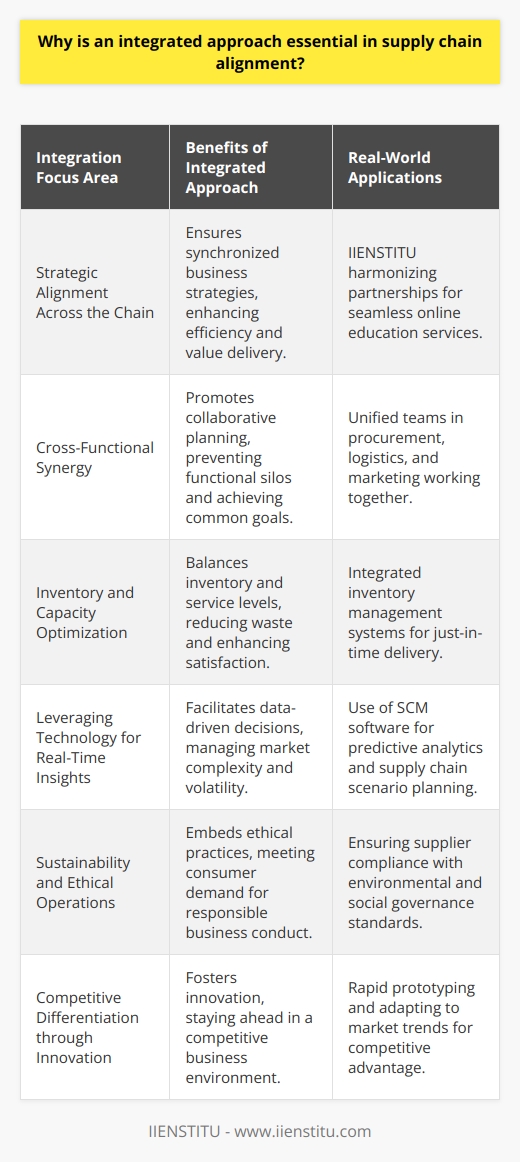
What is Supply Chain Planning?
What is Supply Chain Resources?
Examples of Supply Chain Constraints
Conclusion
What is Supply Chain Planning?
At its core, supply chain planning is all about optimizing the processes that get goods and services from point A to point B, aligning with the business's objectives and customer requirements. Imagine you're planning a road trip. You need to figure out the best route, where to stop for gas, and how to avoid traffic jams. In the business world, supply chain planning is similar but on a grander scale.
Supply chain planning involves:
1- Forecasting demand: Predicting what customers will want and when they'll want it. This is crucial for businesses to plan their production and inventory levels effectively. By accurately forecasting demand in supply chain management, companies can avoid stockouts or excess inventory, both of which can be costly.
2- Managing resources: Ensuring you have the right materials, people, and equipment in place. This includes managing supply chain resources such as raw materials, production capacity, and logistics capabilities.
3- Scheduling production: Deciding when and how much to produce. This involves balancing customer demand with available resources and constraints. Effective production scheduling can help minimize waste, reduce lead times, and improve overall efficiency.
4- Logistics coordination: Planning the movement of goods through various transportation modes. This includes selecting the most cost-effective and reliable shipping methods, optimizing routes, and ensuring timely delivery to customers.
By effectively planning these elements, businesses can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and provide better customer service. It's all about making informed decisions to optimize the flow of goods and services throughout the supply chain management process.
The Importance of Supply Chain Planning
You might be wondering, "Why is supply chain planning so crucial?" Well, consider this: A well-executed supply chain can be a significant competitive advantage. It can lead to:
1- Cost Savings: By optimizing inventory levels and transportation routes, businesses can save on storage and shipping costs. This is particularly important for companies operating in industries with tight profit margins, where even small cost reductions can have a significant impact on the bottom line.
The key to successful supply chain management is aligning resources to maximize efficiency.
2- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Timely delivery and product availability enhance customer experience. In today's fast-paced, customer-centric business environment, meeting or exceeding customer expectations is crucial for building brand loyalty and driving repeat business.
3- Increased Flexibility: A responsive supply chain can adapt to market changes and unexpected disruptions. This agility allows businesses to quickly respond to shifts in customer demand, supply shortages, or other external factors, minimizing the impact on operations and profitability.
4- Risk Mitigation: Planning helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By proactively addressing risks such as supplier failures, transportation disruptions, or quality issues, companies can minimize the likelihood and impact of supply chain disruptions.
For example, during recent global events that disrupted supply chains worldwide, companies with robust planning processes were better equipped to handle shortages and delays. They had contingency plans in place, diversified their supplier base, and could quickly adapt their operations to mitigate the impact of the disruptions.
What are Supply Chain Resources?
Supply chain resources are everything that companies utilize to ensure their supply chain operates smoothly. These resources include:
People: The workforce, from factory workers to logistics managers. People are the driving force behind any successful supply chain operation. Their skills, knowledge, and experience are essential for planning, executing, and optimizing supply chain activities.
Facilities: Warehouses, factories, distribution centers, and offices. These physical assets provide the infrastructure necessary for storing, producing, and distributing goods. The location, capacity, and layout of these facilities can significantly impact supply chain efficiency and responsiveness.
Machines: Equipment used in production, packaging, and transportation. From assembly lines to conveyor belts to forklifts, machines play a critical role in automating and streamlining supply chain processes. Investing in the right machinery can help businesses increase productivity, reduce errors, and improve overall quality.
Inventory: Raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. Inventory management is a critical aspect of supply chain planning, as it directly impacts a company's ability to meet customer demand and manage costs. Effective inventory management involves striking a balance between having enough stock to avoid shortages and minimizing excess inventory that ties up capital and increases storage costs.
The key to successful supply chain management is aligning resources to maximize efficiency. This involves:
Ensuring the right people are in the right roles and have the necessary skills and training.
Optimizing facility layouts and locations to minimize transportation costs and lead times.
Selecting and maintaining the most appropriate machinery for each supply chain process.
Implementing inventory management systems and policies to maintain optimal stock levels.
By effectively managing and allocating supply chain resources , businesses can improve their supply chain efficiency and better meet customer needs.
People
People are the heart of supply chain management. Skilled employees ensure operations run efficiently. For instance, having certified operators for specialized equipment can prevent accidents and improve productivity. I recall a time when I visited a manufacturing plant and met an operator named Lisa. She was in charge of a critical machine that assembled components at high speed. Her expertise ensured minimal downtime and high-quality output. Without people like Lisa, even the most advanced machines wouldn't reach their full potential.
To optimize the role of people in the supply chain, companies should:
Invest in training and development programs to enhance employee skills and knowledge.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees to identify and solve problems.
Implement clear communication channels and collaboration tools to facilitate teamwork and information sharing.
Ensure safe and ergonomic working conditions to reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
By valuing and empowering their workforce, businesses can tap into the full potential of their human resources and drive supply chain success.
Facilities
Facilities are the physical locations where supply chain activities occur. This includes:
Warehouses: For storing inventory. The layout, equipment, and management of warehouses can significantly impact inventory accuracy, picking efficiency, and overall costs. Implementing best practices such as optimize inventory in supply chain management, can help businesses make the most of their warehouse resources.
Factories: Where products are manufactured. Factory layout, equipment, and processes directly influence production capacity, quality, and lead times. By applying lean manufacturing principles and investing in modern technology, companies can optimize their factory operations and improve overall supply chain performance.
Distribution Centers: Hubs that handle the sorting and shipping of goods. The location, size, and design of distribution centers can impact transportation costs, delivery times, and customer service levels. Strategically placing distribution centers near key markets or transportation nodes can help businesses reduce lead times and improve responsiveness.
Having strategically located facilities can reduce transportation costs and delivery times. For example, placing a warehouse closer to key markets can enhance customer service by shortening delivery lead times.
To optimize facility resources, companies should:
Regularly assess facility layouts and processes to identify improvement opportunities.
Invest in technology solutions such as warehouse management systems (WMS) and transportation management systems (TMS) to streamline operations.
Implement performance metrics and continuous improvement programs to drive operational excellence.
Collaborate with suppliers and customers to align facility capabilities with supply chain requirements.
By effectively managing and optimizing their facility resources, businesses can create a more efficient and responsive supply chain.
Machines
Machines are essential for production and logistics. This includes:
Production Equipment: Machinery for manufacturing products. The selection, maintenance, and utilization of production equipment directly impact manufacturing capacity, quality, and costs. Investing in modern, reliable machinery can help businesses increase output, reduce defects, and improve overall efficiency.
Transportation Vehicles: Trucks, ships, planes, and trains. The choice of transportation mode and vehicle type can significantly impact shipping costs, lead times, and environmental impact. By optimizing transportation routes, consolidating shipments, and selecting the most appropriate vehicles, companies can reduce transportation costs and improve delivery performance.
Technology Systems: Software and hardware for managing supply chain activities. From enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to warehouse management systems (WMS), technology plays a critical role in automating and optimizing supply chain processes. Investing in the right technology solutions can help businesses improve visibility, reduce manual errors, and make data-driven decisions.
Investing in modern machinery can increase efficiency and reduce operational costs. However, machines also require maintenance and skilled operators, which are important considerations in planning.
To optimize machine resources, companies should:
Conduct regular maintenance and upgrades to ensure equipment reliability and performance.
Train operators to follow best practices and standard operating procedures.
Implement predictive maintenance programs to prevent unplanned downtime.
Leverage automation and robotics to reduce manual labor and improve consistency.
By effectively managing and maintaining their machine resources, businesses can improve their supply chain efficiency and competitiveness.
Inventory
Inventory management is a balancing act. Holding too much inventory ties up capital and incurs storage costs, while too little can lead to stockouts and lost sales. Effective inventory management ensures that the right products are available at the right time.
To optimize inventory resources, companies should:
Implement inventory tracking systems: Using barcodes, RFID tags, or other technologies to accurately track inventory levels and locations. This real-time visibility helps businesses make informed decisions about replenishment, allocation, and distribution.
Apply inventory optimization techniques: Such as economic order quantity (EOQ), safety stock calculations, and ABC analysis to determine optimal inventory levels and replenishment frequencies. These techniques help businesses balance the costs of holding inventory with the risk of stockouts.
Collaborate with suppliers and customers: Sharing information about demand forecasts, production plans, and inventory levels can help businesses better align supply with demand. This collaboration can reduce the need for excess inventory and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
Implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory management: Where raw materials and components are delivered just as they are needed for production. This approach reduces inventory holding costs and improves cash flow, but requires close coordination with suppliers and reliable transportation.
By effectively managing their inventory resources, businesses can optimize inventory in supply chain management, reduce costs, and improve customer service levels.
Examples of Supply Chain Constraints
In an ideal world, resources would be unlimited. However, in reality, businesses face numerous constraints that can impact their supply chain. Understanding and planning for these constraints is crucial.
Physical Limitations
1- Capacity Constraints: A machine can only produce a certain number of units per hour. Overloading equipment can lead to breakdowns and safety hazards. This is one of the most common examples of supply chain constraints in manufacturing. To address this, companies need to carefully plan production schedules, perform regular maintenance, and invest in additional capacity when necessary.
2- Labor Availability: If workers can only work 40 hours a week due to legal or company policies, overtime isn't an option without additional costs. This constraint can limit a company's ability to quickly ramp up production in response to demand spikes. To mitigate this, businesses can cross-train employees, implement flexible staffing strategies, and invest in automation.
3- Space Constraints: Limited warehouse space restricts the amount of inventory that can be stored. This can lead to stockouts or increased costs for external storage. To optimize space utilization, companies can implement lean inventory management practices, use vertical storage solutions, and consider third-party logistics providers.
Financial Constraints
1- Budget Limitations: Companies might not have the financial resources to purchase new equipment or expand facilities. This can hinder growth and limit a company's ability to respond to market opportunities. To overcome this, businesses can explore leasing options, seek external funding, or prioritize investments based on their strategic importance.
2- Cash Flow Issues: Delayed payments from customers can affect the company's ability to pay suppliers, leading to delays in production. This can create a domino effect throughout the supply chain. To mitigate this, companies can implement strict credit policies, offer early payment discounts, and explore supply chain financing options.
Security Constraints
1- Regulatory Compliance: Businesses must adhere to laws and regulations, such as handling hazardous materials or data protection requirements. Non-compliance can result in fines, legal action, and reputational damage. To ensure compliance, companies must stay up-to-date with regulatory changes, implement robust compliance programs, and regularly train employees.
2- Certification Requirements: Operators might need specific certifications to run certain equipment, limiting who can perform specific tasks. This can create staffing challenges and increase training costs. To address this, businesses can partner with local educational institutions, offer in-house training programs, and develop succession plans for critical roles.
Policy Constraints
1- Company Policies: Internal policies might restrict certain actions, such as prohibiting overtime or requiring multiple approvals for expenditures. While these policies are intended to control costs and maintain quality, they can sometimes limit flexibility and responsiveness. To balance control with agility, companies should regularly review their policies, involve employees in the policy-making process, and allow for exceptions when justified.
2- Supplier Contracts: Long-term contracts with suppliers might limit flexibility in sourcing materials. While these contracts can provide stability and cost savings, they can also prevent companies from taking advantage of new opportunities or responding to changing market conditions. To maintain flexibility, businesses can negotiate shorter contract terms, include provisions for renegotiation, and develop a diverse supplier base.
Navigating Constraints
To navigate these constraints, businesses often:
Prioritize Tasks: Focusing on the most critical activities first. This helps ensure that limited resources are allocated to the areas that have the greatest impact on the business.
Optimize Processes: Implementing lean principles to reduce waste. By eliminating non-value-added activities, streamlining processes, and improving quality, companies can maximize the efficiency of their constrained resources.
Invest in Training: Enhancing employee skills to improve efficiency. Well-trained employees can work more productively, reduce errors, and adapt to changing conditions more effectively.
Negotiate with Suppliers: Working with suppliers to adjust terms or delivery schedules. By collaborating with suppliers to find mutually beneficial solutions, companies can often find ways to work around constraints and maintain a smooth flow of materials.
Personally, I've seen companies transform their operations by re-evaluating their constraints. One business I worked with realized that by adjusting their production schedule and cross-training employees, they could increase output without additional costs. This demonstrates the power of creative problem-solving in overcoming supply chain constraints.
Strategies for Effective Supply Chain Planning
Effective supply chain planning isn't just about recognizing resources and constraints; it's about developing strategies to optimize operations. Here are some tips to optimize your supply chain management process:
Implement Technology Solutions
1- Supply Chain Management Systems: Utilize SCM software to integrate various supply chain activities. These systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, production schedules, and transportation status, enabling better decision-making and coordination across the supply chain.
2- Real-Time Tracking: Implement RFID and GPS technologies for tracking inventory and shipments. This allows companies to monitor the movement of goods in real-time, identify potential delays or disruptions, and take proactive measures to mitigate their impact.
3- Data Analytics: Use analytics to forecast demand and identify trends. By leveraging historical data, market intelligence, and statistical models, companies can generate more accurate demand forecasts, optimize inventory levels, and make informed pricing and promotion decisions.
Foster Strong Relationships
1- Supplier Collaboration: Build strong relationships with suppliers to improve communication and reliability. By sharing information, aligning goals, and working together to solve problems, companies can reduce supply risks, improve quality, and drive innovation.
2- Customer Feedback: Incorporate customer feedback to adjust production and inventory levels. By actively seeking and acting on customer input, businesses can better understand evolving needs, preferences, and expectations, and adapt their supply chain strategies accordingly.
Embrace Lean Principles
1- Reduce Waste: Identify areas of waste in processes and eliminate them. This includes overproduction, waiting, unnecessary transportation, over-processing, excess inventory, unnecessary motion, and defects. By systematically eliminating these wastes, companies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer value.
2- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and improve supply chain activities. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, businesses can encourage employees to identify and implement incremental changes that lead to significant improvements over time.
Diversify Supply Chain
1- Multiple Suppliers: Avoid relying on a single supplier to reduce risk. By sourcing from multiple suppliers, companies can mitigate the impact of supply disruptions, price fluctuations, and quality issues. This also provides greater flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions.
2- Alternative Transport Routes: Plan for alternative logistics options in case of disruptions. By identifying and pre-qualifying alternative transportation routes and providers, businesses can quickly respond to unexpected events such as natural disasters, labor strikes, or infrastructure failures, minimizing their impact on the supply chain.
Invest in Training
1- Employee Development: Provide ongoing training to enhance skills. By investing in employee training and development, companies can improve productivity, reduce errors, and foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. This also helps to attract and retain top talent in a competitive market.
2- Cross-Functional Teams: Encourage collaboration across different departments. By bringing together employees from various functions such as procurement, production, logistics, and sales, companies can