The article discusses the five key tasks of the supply chain, which are designing supply chains for strategic advantage, implementing collaborative relationships, forging supply chain partnerships, managing supply chain information, and making money from the supply chain. It explains how each of these tasks can help businesses create value, reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer service.
Additionally, it provides advice on how to build and sustain strong relationships with customers and suppliers.
Introduction: Introducing Five Supply Chain Tasks
Designing Supply Chains for Strategic Advantage
Implementing Collaborative Relationships
Forging Supply Chain Partnerships
Managing Supply Chain Information
Introduction: Introducing Five Supply Chain Tasks
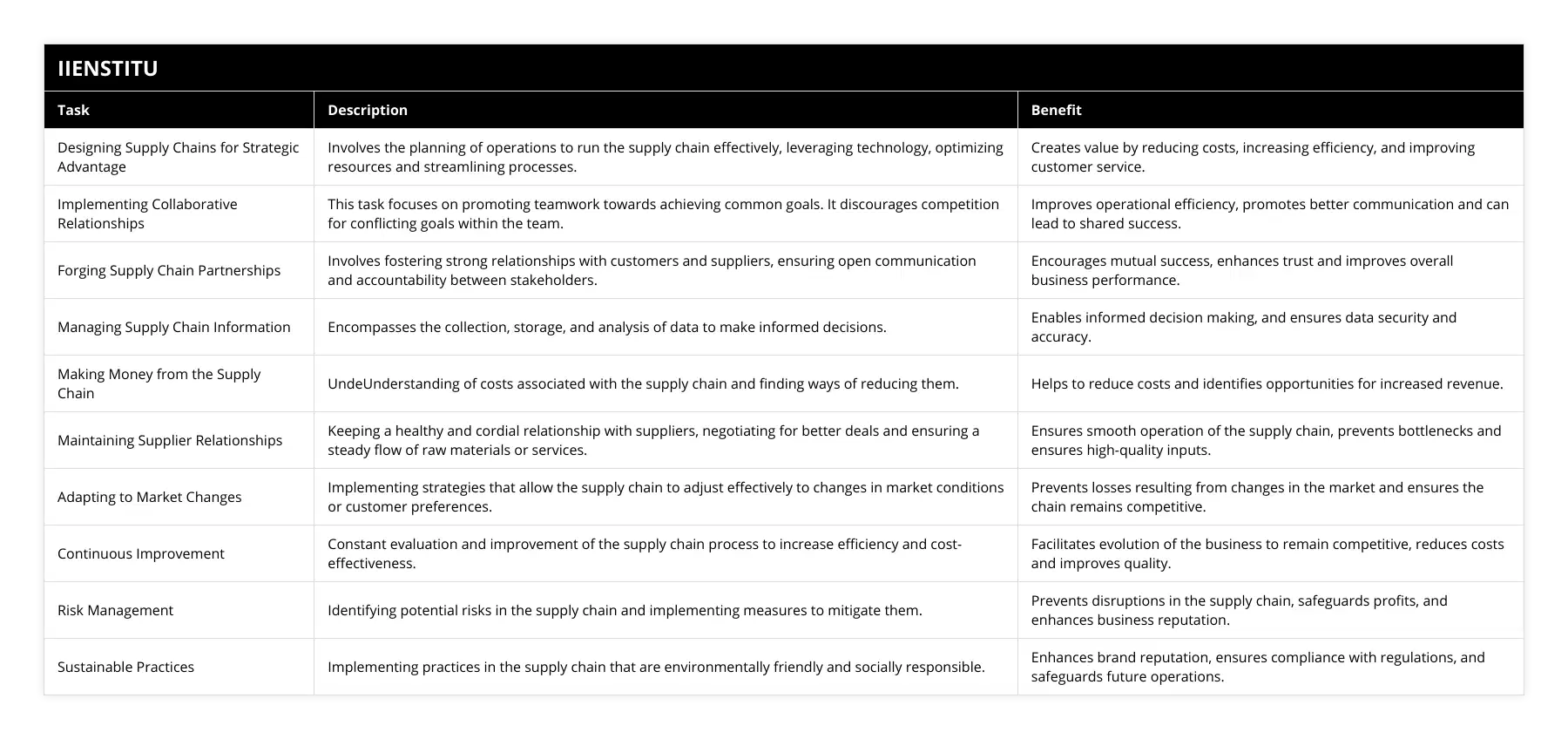
The supply chain is a complex system of activities that involves the coordination of resources and processes to deliver goods and services from supplier to customer. It is a critical component of any business and a key factor in its success. To ensure the success of a business, it is important to understand the five key tasks of the supply chain: designing supply chains for strategic advantage, implementing collaborative relationships, forging supply chain partnerships, managing supply chain information, and making money from the supply chain.
Designing Supply Chains for Strategic Advantage
Designing supply chains for strategic advantage is the first of the five key tasks of the supply chain. This involves considering how the supply chain can create value for the business. It is important to plan to operate the supply chain better, faster, and cheaper than the competition. This can be done by leveraging technology, streamlining processes, and optimizing resources. Additionally, it is important to consider how the supply chain can help to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer service.
Implementing Collaborative Relationships
Implementing collaborative relationships is the second of the five key tasks of the supply chain. This involves getting teams to work together toward a common goal rather than competing for conflicting goals. For example, if the sales team is trying to improve customer service by making sure that there is plenty of inventory available and the logistics team is trying to reduce inventory to lower costs, both teams need to work together to achieve their goals. Collaborative relationships can be implemented through communication, trust, and shared goals.
Forging Supply Chain Partnerships
Forging supply chain partnerships is the third of the five key tasks of the supply chain. This involves building and sustaining strong relationships with customers and suppliers. When companies understand that they depend on one another for their success, working well together becomes a priority. To do this, it is important to ensure that there is open communication, trust, and accountability between the two parties. Additionally, it is important to ensure that there are incentives in place to ensure that both parties are working towards the same goals.
Managing Supply Chain Information
Managing supply chain information is the fourth of the five key tasks of the supply chain. This involves collecting, storing, and analyzing data to make informed decisions. It is important to have access to accurate and up-to-date information in order to make the best decisions. Additionally, it is important to have systems in place to ensure that data is secure and protected.
Making Money from the Supply Chain
Making money from the supply chain is the fifth of the five key tasks of the supply chain. This involves understanding the costs associated with the supply chain and finding ways to reduce them. It is important to look for opportunities to reduce costs, such as negotiating better prices with suppliers or streamlining processes. Additionally, it is important to look for opportunities to increase revenue, such as introducing new products or services.
Conclusion
The five key tasks of the supply chain are essential for any business to be successful. It is important to understand the importance of designing supply chains for strategic advantage, implementing collaborative relationships, forging supply chain partnerships, managing supply chain information, and making money from the supply chain. By understanding and implementing these tasks, businesses can ensure that their supply chain is efficient, cost-effective, and profitable.
Success in supply chain management requires an effective balance of planning, execution, and adaptation.
In summarizing the text, the five essential tasks for effective supply chain management are detailed as designing supply chains for strategic advantage, implementing collaborative relationships, forging supply chain partnerships, managing supply chain information, and making money from the supply chain. All these tasks focus on optimizing efficiency, fostering beneficial relationships with suppliers and customers, and increasing profitability. To acutely understand and implement these tasks could significantly enhance a business's supply chain functionality and profitability. Understandably, gaining a supply chain management certificate would equip individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively navigate these tasks, potentially strengthening their company's competitive edge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the five tasks for achieving supply chain success outlined in the article?
The five tasks for achieving supply chain success outlined in the article are:
Designing supply chains for strategic advantage
Implementing collaborative relationships
Forging supply chain partnerships
Managing supply chain information
Making money from the supply chain.
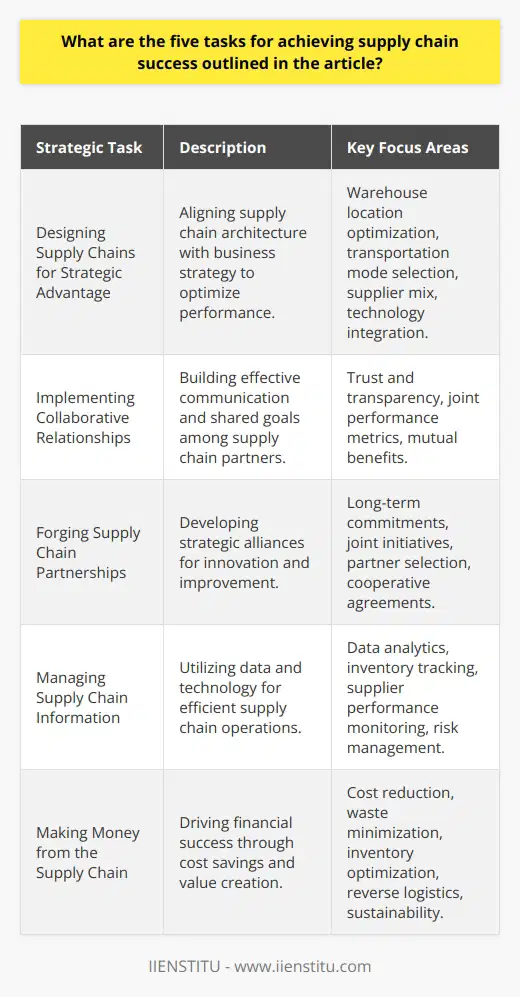
How can supply chain design be used to gain strategic advantage?
Supply chain design can be used to gain strategic advantage by optimizing the five key tasks of the supply chain. By designing supply chains effectively, businesses can create value, reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer service. Additionally, establishing collaborative relationships, forging supply chain partnerships, managing supply chain information, and making money from the supply chain can all help businesses gain a strategic advantage. Through these activities, businesses can realize the full potential of their supply chain and gain a competitive edge.
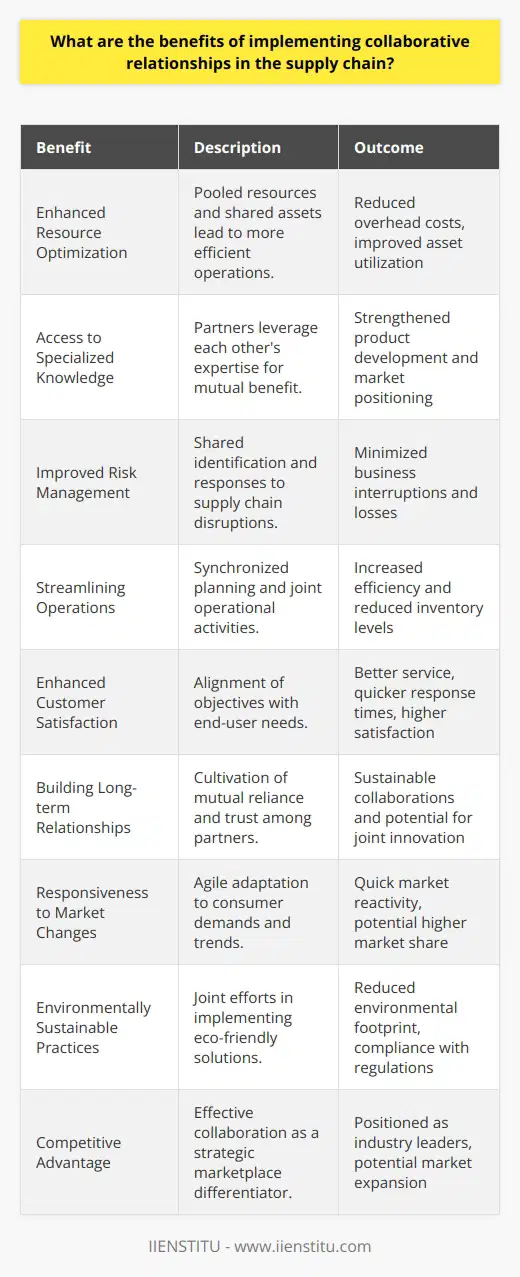
What are the benefits of implementing collaborative relationships in the supply chain?
The implementation of collaborative relationships in the supply chain can bring many benefits to a business. Collaboration can help to create value by allowing businesses to gain access to resources and expertise from different parties in the supply chain. It can also help to reduce costs by enabling businesses to share resources, reduce redundancy, and take advantage of economies of scale. Additionally, collaborative relationships can improve efficiency by streamlining processes and improving communication between supply chain members. Finally, collaboration can improve customer service by allowing businesses to better meet customer needs and expectations.
What are the five main functions of supply chain management?
Supply Chain Management Functions
**Integration of Key Business Processes**
The first primary function of supply chain management is to integrate and link the key business processes from end-to-end. This coordination ensures seamless flow of goods, information, and services across the supply chain, resulting in reduced lead time, improved efficiency, and better customer service.
**Strategic Sourcing and Procurement**
The second function of supply chain management is strategic sourcing and procurement. This process involves establishing strong relationships with suppliers, negotiating and finalizing contracts, and managing the optimal ordering and purchasing of raw materials and other inputs necessary for production and service delivery.
**Inventory Management and Forecasting**
The third important function of supply chain management is inventory management and forecasting. This facet involves balancing the need for product availability against the cost of carrying excess inventory. Accurate demand forecasts help manage and optimize inventory levels, anticipate fluctuations in demand, and adjust production and purchasing schedules accordingly.
**Logistics and Transportation**
The fourth key function of supply chain management is managing logistics and transportation. Effective movement and storage of goods play a critical role in the supply chain as these activities have direct impacts on product availability, delivery times, and customer satisfaction. Supply chain managers oversee the transportation, warehousing, and distribution of goods from suppliers to end customers.
**Quality and Performance Measurement**
The fifth vital function of supply chain management is to monitor quality and performance throughout the entire chain. This includes establishing and enforcing quality standards, ensuring regulatory compliance, and identifying opportunities for continuous improvement. Performance measurement and benchmarking are essential for evaluating and optimizing supply chain operations.
In conclusion, the primary functions of supply chain management include integration of key business processes, strategic sourcing and procurement, inventory management and forecasting, logistics and transportation, and quality and performance measurement. These functions are crucial for achieving reduced costs, improved efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction in today's fast-paced and competitive business environment.

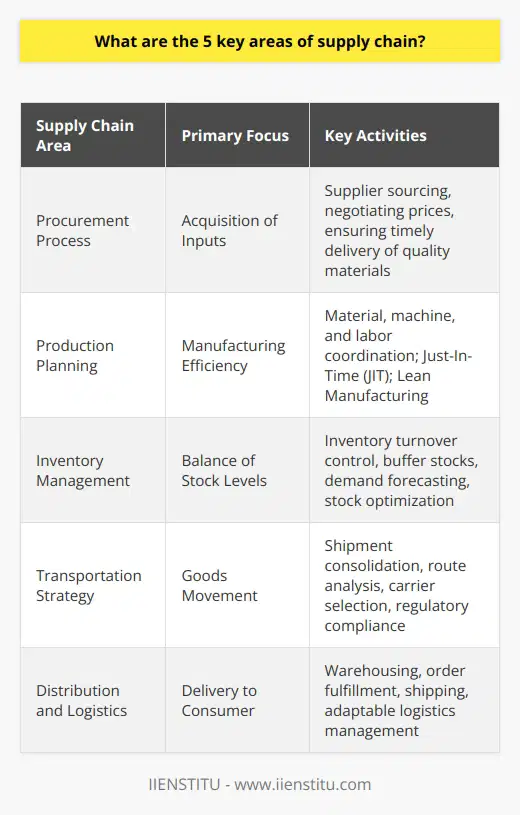
What are the 5 key areas of supply chain?
Supply Chain Components
The key areas of a supply chain encompass five important components: procurement, production, inventory management, transportation, and distribution.
Procurement Process
A critical aspect of the supply chain is the procurement process, which involves the sourcing and purchasing of raw materials and components needed for producing goods. It requires strategic supplier selection, negotiation of contracts, and effective management of supplier relationships to ensure the efficient supply of high-quality inputs while minimizing costs.
Production Planning
Production planning is the second key area and involves the manufacturing of finished goods from raw materials. This step requires efficient utilization of resources, optimal scheduling of manufacturing processes, and employing quality control measures. Production planning also involves coordination with other areas of the supply chain to ensure timely availability of materials and output distribution.
Inventory Management
The third component, inventory management, focuses on maintaining a balance between minimizing inventory costs and ensuring the availability of goods for customer demand. This area involves tracking inventory levels, optimizing safety stock levels, implementing inventory control techniques, and utilizing demand forecasting tools to prevent overstocks and stockouts.
Transportation Strategy
The fourth key area is transportation, which includes the movement of goods between various stages of the supply chain, such as from suppliers to manufacturing facilities and from production plants to distribution centers. The transportation strategy involves selecting appropriate transport modes, optimizing shipment schedules, and reducing transportation costs while ensuring timely and efficient movement of goods.
Distribution and Logistics
Lastly, the distribution and logistics aspect focuses on delivering finished products to customers, employing effective storage and warehousing strategies, and managing return processes. The goal in this area is to optimize the storage and movement of goods, ensuring the delivery of the right products, at the right time, and in the right condition, all while minimizing distribution costs.
In conclusion, the five key areas of supply chain—procurement, production, inventory management, transportation, and distribution—work together to enable efficient and cost-effective management of goods movement from their source to the end customer. A well-functioning supply chain can significantly contribute to a company's competitive advantage and overall success.
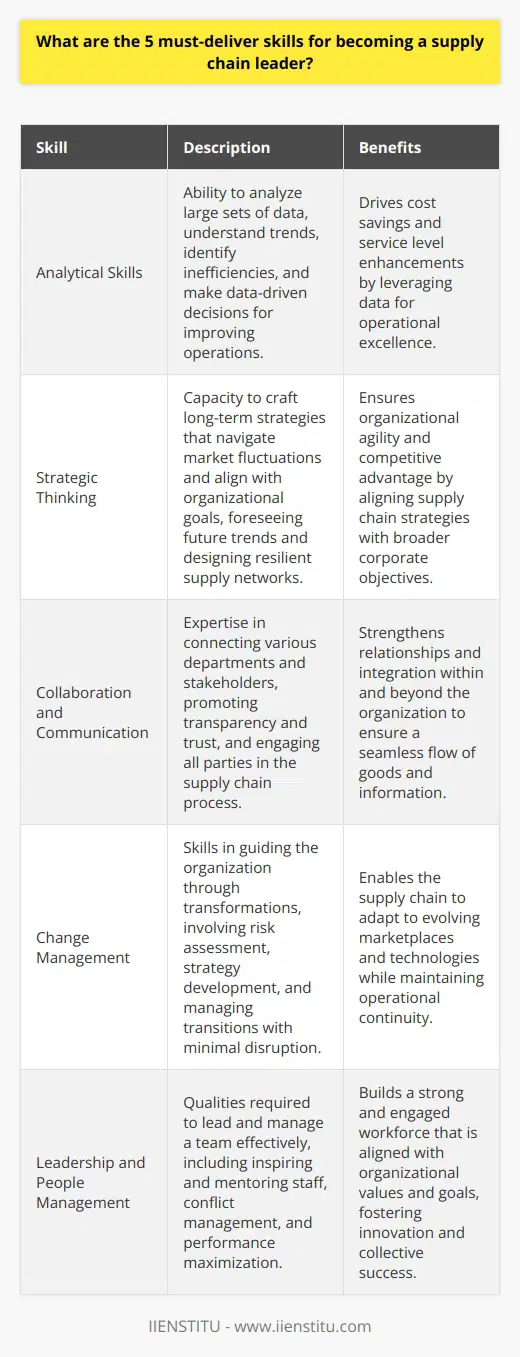
What are the 5 must-deliver skills for becoming a supply chain leader?
Analytical Skills
A supply chain leader must possess strong analytical skills, as they are integral to managing numerous aspects of a supply chain, including forecasting, inventory control, and transport logistics. Analytical skills facilitate data-driven decision-making to optimize end-to-end operations.
Strategic Thinking
Strategic thinking is essential, as supply chain leaders must create and execute plans that align with an organization's objectives. These individuals must have the foresight to identify potential challenges and opportunities and respond proactively to meet targets and reduce disruptions effectively.
Collaboration and Communication
Effective collaboration and communication skills enable supply chain leaders to work across various departments and build strong relationships with stakeholders. A strong supply chain leader must clearly articulate goals, expectations, and feedback to ensure all team members are aligned and working towards common objectives.
Change Management
Supply chain leaders must drive continuous improvement through efficient change management. This skill requires adaptability, resilience, and the ability to identify necessary changes to meet evolving market demand and organization goals. Change management involves the implementation of new strategies, methods, and technologies, ensuring smooth transitions and mitigating potential adverse effects on the supply chain.
Leadership and People Management
Lastly, strong leadership and people management skills are crucial in inspiring and motivating a high-performing supply chain team. Developing talent, managing performance, and creating a positive work culture contribute to increased employee satisfaction and reduced turnover. Excellent leadership skills boost overall productivity and efficiency within the supply chain.
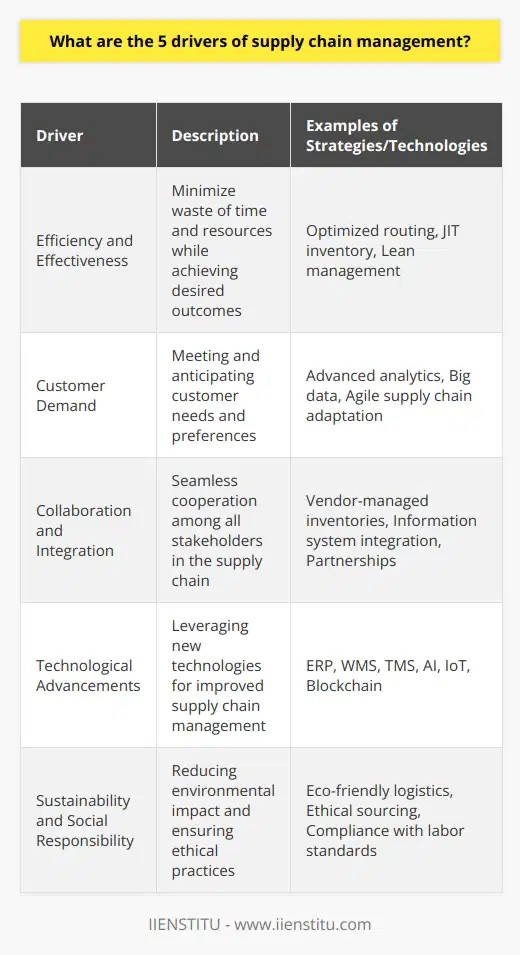
What are the 5 drivers of supply chain management?
Five Key Drivers
Efficiency and Effectiveness
One of the primary drivers of supply chain management is the pursuit of efficiency and effectiveness, which can be achieved through a streamlined approach to transportation and warehousing, as well as by the strategic management of inventory levels. By minimizing costs and maximizing customer satisfaction, organizations aim to optimize their supply chains and ensure overall competitiveness in their respective markets.
Customer Demand
Another crucial driver is customer demand, as the focal point of any supply chain is to satisfy consumer needs. Developing a demand-driven supply chain is essential for organizations, as they need to forecast, manage, and respond to various fluctuations in customer preferences and requirements. By understanding and anticipating market needs, a company can create products and deliver services that meet customer expectations.
Collaboration and Integration
The third driver of supply chain management is collaboration and integration, which are necessary for efficient and effective operations throughout a supply chain. By fostering communication and cooperation between various departments within an organization as well as between external partners and suppliers, organizations can better coordinate their responses to changing market conditions and ensure the consistent delivery of high-quality products and services.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a significant role in driving supply chain management as they continuously offer new opportunities for organizations to improve and refine their operations. Emerging technologies such as RFID, blockchain, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) have the potential to enhance various aspects of supply chain management, including inventory management, demand forecasting, and real-time data analysis.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Lastly, sustainability and social responsibility are increasingly becoming drivers of supply chain management, as organizations face growing pressure from consumers, regulators, and shareholders to minimize the negative environmental and social impacts associated with their operations. By implementing sustainable practices and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations, companies can not only mitigate risks but also garner goodwill from customers and stakeholders, thus strengthening their overall supply chain and brand reputation.
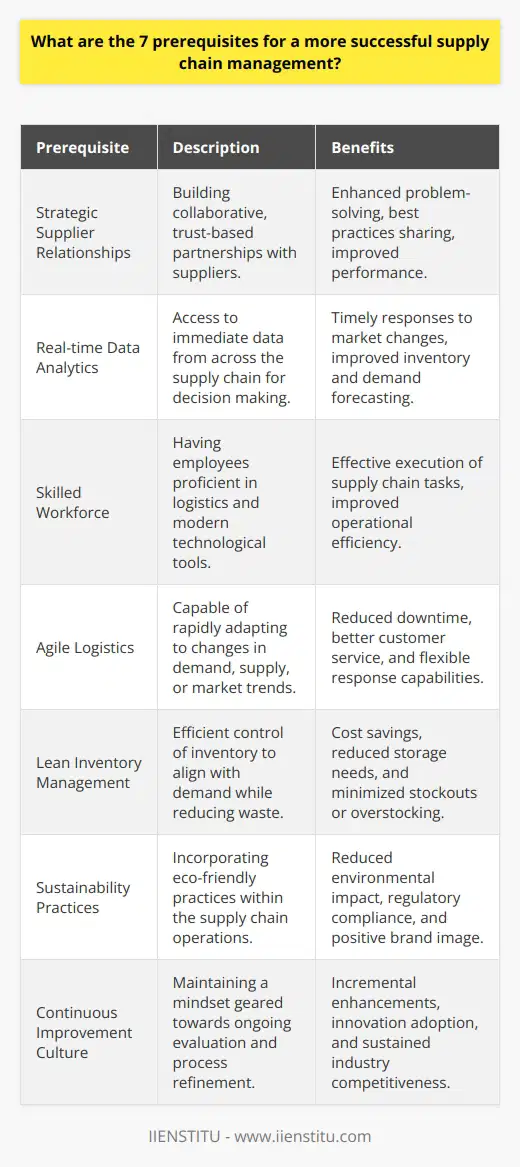
How do the 5 stages of a successful supply chain contribute to overall business strategy?
Stages of Supply Chain and Business Strategy
Supply Chain Stage 1: Planning
The first stage of a successful supply chain is planning, which involves developing a strategic approach to procurement, production, and distribution processes. By effectively aligning supply chain objectives with the overall business strategy, companies can streamline operations, reduce costs, improve efficiency, and meet customer demands more effectively.
Supply Chain Stage 2: Sourcing
The sourcing stage of a supply chain includes selecting suppliers that provide high-quality materials and services at competitive prices. This stage contributes to overall business strategy by ensuring that production costs remain low while maintaining optimal quality standards. Effective sourcing involves establishing long-term relationships with suppliers, which can lead to increased collaboration and reduced supply chain risks.
Supply Chain Stage 3: Production
Production is the stage during which materials are transformed into finished goods. Efficient production strategies support overall business goals by minimizing lead times and reducing production costs. Improvements in technology, such as automation and continuous improvement initiatives, help companies to increase productivity and better match customer demand. Additionally, implementing sustainable practices in the production stage can enhance brand reputation and contribute to overall business success.
Supply Chain Stage 4: Transportation and Logistics
The transportation and logistics stage of a supply chain involves the movement of materials and finished goods between locations. Efficiently managing this stage ensures timely and cost-effective delivery of products, directly contributing to customer satisfaction and overall business performance. By collaborating with reliable transportation partners and employing advanced technologies for transportation management, companies can effectively track shipments, optimize routes, and prevent potential disruptions.
Supply Chain Stage 5: Delivery and Returns
The final stage in the supply chain is delivery and returns, during which products reach the end customer. Proper management of this stage is critical to customer satisfaction and is directly linked to overall business success. Effective returns policies and processes can enhance customer loyalty, while efficient last-mile delivery services can lead to an improved customer experience.
In conclusion, the five stages of a successful supply chain each play a critical role in contributing to overall business strategy. By effectively managing and optimizing these stages, companies can create a competitive advantage, improve customer satisfaction, and drive growth. Integrating supply chain processes with overall business strategy ensures a cohesive approach to achieving organizational goals.
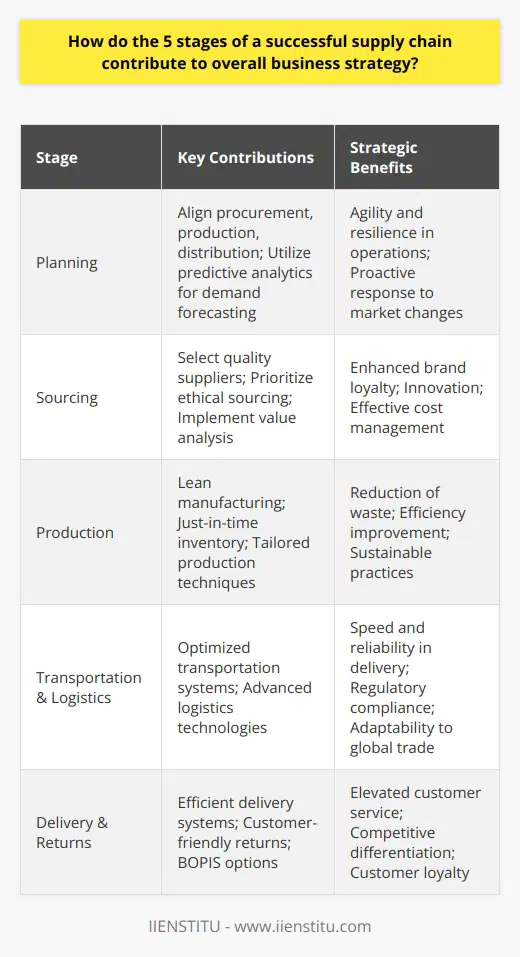
Which factors are critical for building a successful supply chain relationship model in a globalized economy?
Factors for Successful Supply Chain Relationships
Trust and Collaboration
Building trust and fostering collaborative relationships between partners are crucial in achieving a successful global supply chain relationship model. Trust mitigates potential risks and uncertainties while collaboration encourages information sharing, leading to improved decision making and operational efficiency.
Cultural Understanding
Effective communication and a deep understanding of diverse cultural practices and norms enable partners in the global supply chain to overcome potential misunderstandings or conflicts. It is important for businesses to develop cultural intelligence to foster better coordination and cooperation among supply chain partners.
Effective Information Sharing
Real-time, accurate, and transparent information sharing is vital for supply chain relationship success in a globalized economy. Effective information sharing helps increase responsiveness, reduce lead times, and lower inventory costs, allowing businesses to be more competitive and agile in a global market.
Alignment of Interests
To cultivate a successful supply chain relationship, businesses must identify and align common interests. Joint goals, risk-sharing, and mutual benefits help create a long-term, stable partnership, ensuring that all stakeholders are equally committed to the success of the supply chain.
Performance Measurement
Continuous performance measurement and monitoring are essential for maintaining relationships and achieving desired outcomes in the global supply chain context. Establishing clear performance metrics and conducting regular assessments allow businesses to make timely adjustments, identify areas for improvement, and refine strategies for long-term success.
Adaptive and Flexible Structures
A dynamic and adaptable supply chain relationship model is crucial for navigating the uncertainties and complexities of the global marketplace. Companies need to recognize and prepare for constant changes in demand, technologies, and regulations, and be willing to adapt their strategies accordingly.
Technology Integration
Leveraging advancements in technology, such as data analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain, can provide valuable insights and visibility into global supply chain operations. Technology-driven solutions help companies address various challenges, enhance performance, and promote the creation of a seamless and integrated supply chain network.
In conclusion, trust, collaboration, cultural understanding, effective information sharing, alignment of interests, performance measurement, adaptive structures, and technology integration are all critical factors for building a successful supply chain relationship model in a globalized economy. By focusing on these factors, businesses can forge more resilient, efficient, and sustainable global supply chain partnerships.
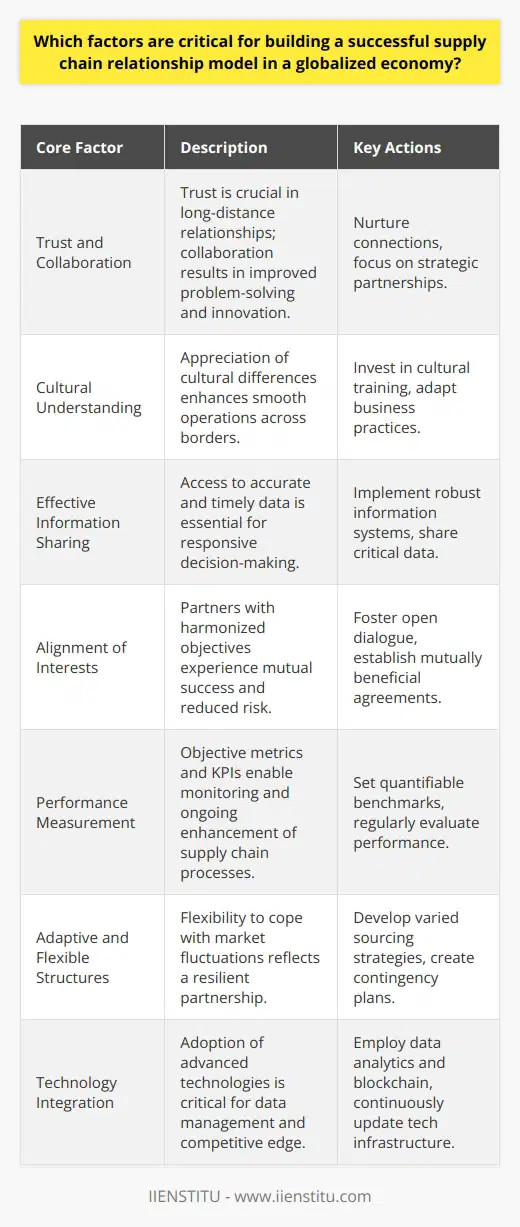
What are the 5 stages of a successful supply chain?
Supply Chain Stages Overview
A successful supply chain consists of five crucial stages, namely: planning, sourcing, manufacturing, delivery, and return. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring that products or services are delivered to customers efficiently and effectively, thus enabling businesses to achieve their goals.
Stage 1: Planning
Planning is the foundation of the supply chain process, wherein companies determine the best way to manage their resources, including raw materials, manufacturing processes, and logistics. Factors such as market demand, production capacity, and product specifications are considered to design an optimal supply chain framework that aligns with the organization's goals.
Stage 2: Sourcing
In the sourcing stage, businesses identify and negotiate with suppliers to obtain the materials and services required for producing their goods. This involves determining the right suppliers, assessing supplier performance, and managing procurement processes to ensure a consistent flow of raw materials at the best possible cost, quality, and delivery time.
Stage 3: Manufacturing
The manufacturing phase involves converting raw materials into finished products by utilizing various production techniques and following strict quality control standards. This includes determining the most cost-effective and efficient production processes, reducing waste, and continuously improving product quality to meet customer requirements and expectations.
Stage 4: Delivery
Delivery, also known as logistics, oversees transporting the finished products from manufacturers to customers. This stage focuses on managing effective transportation, warehousing, and distribution systems that aim to fulfill customer orders promptly and accurately. Additionally, companies must closely monitor inventory levels and maintain flexibility in supply chain operations to adapt to fluctuations in demand.
Stage 5: Return
The final stage in the supply chain process is managing product returns and addressing customer concerns. This involves handling returned goods, investigating the reasons for the return, and implementing corrective measures to improve the overall product or service quality. Companies must also prioritize effective communication and maintain a strong relationship with customers to facilitate a seamless return process and foster customer loyalty.
In conclusion, the five stages of a successful supply chain - planning, sourcing, manufacturing, delivery, and return - work together to ensure a company's products or services are delivered efficiently and effectively. By understanding and optimizing each stage, businesses can enhance their competitive advantage, minimize risks, and ultimately contribute to long-term success.
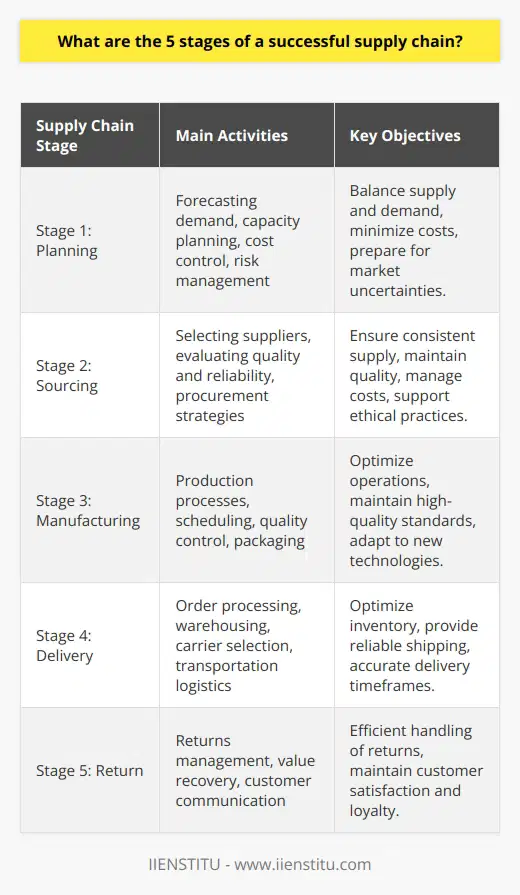
What are the 7 prerequisites for a more successful supply chain management?
**Effective Communication**
A successful supply chain management requires effective communication between all the stakeholders involved. This involves the sharing of information, timely updates, and transparency in operations to foster trust and collaboration.
**Well-defined Objectives**
Clear, well-defined objectives are crucial in guiding the supply chain management process. Establishing specific performance metrics and targets ensures all stakeholders are aligned in moving towards a common goal.
**Adaptable Supply Chain Strategy**
An adaptable supply chain strategy ensures the management process can flexibly respond to changing market conditions. It involves continuously monitoring trends, identifying potential disruptions, and implementing proactive measures to mitigate the risks involved.
**Seamless Integration of Technologies**
For a more successful supply chain management, seamless integration of technologies across different stages is vital. Data-driven tools, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation, support smarter decision-making, enhanced visibility, and dynamic optimization of resources.
**Robust Risk Management**
To minimize disruptions and improve overall supply chain performance, robust risk management systems must be in place. Identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and prioritizing them based on severity enables organizations to develop effective risk mitigation strategies.
**Synchronized Demand and Supply Planning**
Successful supply chain management relies on synchronized demand and supply planning. Accurate demand forecasting and efficient inventory management help to reduce excess stock, avoid stockouts, and optimize the overall product flow while balancing costs.
**Strong Collaboration and Partnerships**
Lastly, fostering strong partnerships and collaborations across all stakeholders is essential to a more successful supply chain management. Building trust and pooling expertise not only improves efficiency but also leads to better decision-making and innovation in supply chain processes.
In conclusion, effective supply chain management requires a well-coordinated approach, encompassing effective communication, well-defined objectives, adaptable strategy, integrated technologies, robust risk management, synchronized planning, and strong collaboration. With these prerequisites in place, organizations are better positioned to achieve greater success in their supply chain management.
What are the five main functions of supply chain management?
Main Functions of Supply Chain Management
Planning and control:
One primary function of supply chain management is to strategize and oversee the entire supply chain process. This includes identifying potential risks, reallocating resources when necessary, and ensuring that the entire process runs smoothly from procurement to delivery.
Sourcing and procurement:
By identifying, selecting, and contracting various suppliers, supply chain management can maintain a consistent flow of materials, goods, and services. The main objective is to select the most suitable suppliers, negotiate and maintain long-lasting collaborations, and formulate pricing strategies.
Inventory management:
Effective supply chain management requires the careful regulation of inventory levels. This involves balancing the need to meet customer demand with the financial implications of maintaining high inventory levels. This function includes warehousing, transportation, and order processing of finished goods and raw materials.
Order fulfillment and distribution:
Ensuring accurate and timely delivery of products and services to customers is central to supply chain management. This entails determining the most effective and cost-efficient distribution channels, ensuring proper transportation and delivery schedules, and implementing an efficient order-processing and tracking system.
Collaboration and coordination:
Finally, supply chain management ensures seamless collaboration and coordination among all stakeholders, such as suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. By fostering strong communication channels, the entire process can be monitored and optimized to provide maximum value to both the customers and the organization.

What are the essential components of an effective supply chain risk management strategy?
Assessing Risks and Vulnerabilities
An effective supply chain risk management (SCRM) strategy begins by thoroughly identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks and vulnerabilities present across the entire supply chain. This phase involves evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of various scenarios, such as supply disruptions, demand fluctuations, and supplier insolvencies, on business operations, financial performance, and overall competitiveness.
Developing Risk Mitigation Plans
The second key component is the crafting of concrete risk mitigation plans designed to address the identified risks and vulnerabilities. Companies must devise measures to prevent, mitigate, or transfer risks, depending on their likelihood and potential impact. These risk mitigation tactics may include diversification of suppliers, geographic locations, and transportation modes; maintaining safety stocks; selecting reliable suppliers; and establishing robust supplier monitoring and evaluation systems.
Implementing Risk Monitoring and Control Systems
A successful SCRM strategy requires continuous monitoring and adjustment to remain relevant and effective as risks evolve. Implementing comprehensive risk monitoring and control systems is crucial for detecting changes in the risk landscape and ensuring that the management strategy remains responsive to new threats. Among these systems are automated real-time data collection and analysis tools that help to identify new risks and vulnerabilities, and also provide early warning signals to enable prompt and informed decision-making.
Engaging Stakeholders and Integrating Supply Chain Efforts
Additionally, an effective strategy must foster collaboration and communication between the various stakeholders in the supply chain, including suppliers, customers, regulators, and other relevant parties. This coordinated effort ensures that risks are managed holistically, rather than in silos, and that all parties share a common understanding of the risks facing the supply chain and their role in addressing them.
Promoting a Risk-Aware Culture
Lastly, a vital component of an effective SCRM strategy is promoting a risk-aware culture throughout the organization. This entails leadership actively demonstrating a commitment to making risk management an integral part of all business decisions, employees recognizing the importance of proactively identifying and addressing potential risks, and continuous improvement through learning and adapting from risk-related incidents.
In summary, an effective supply chain risk management strategy must be built on a solid foundation of risk assessment, mitigation planning, continuous monitoring, stakeholder engagement, and a risk-aware culture. These elements flow together to create a systemic approach that can be adapted to changing conditions and ultimately enhances the overall performance, resilience, and competitiveness of the organization.
How do the principles of demand-driven supply chain management contribute to improving overall performance?
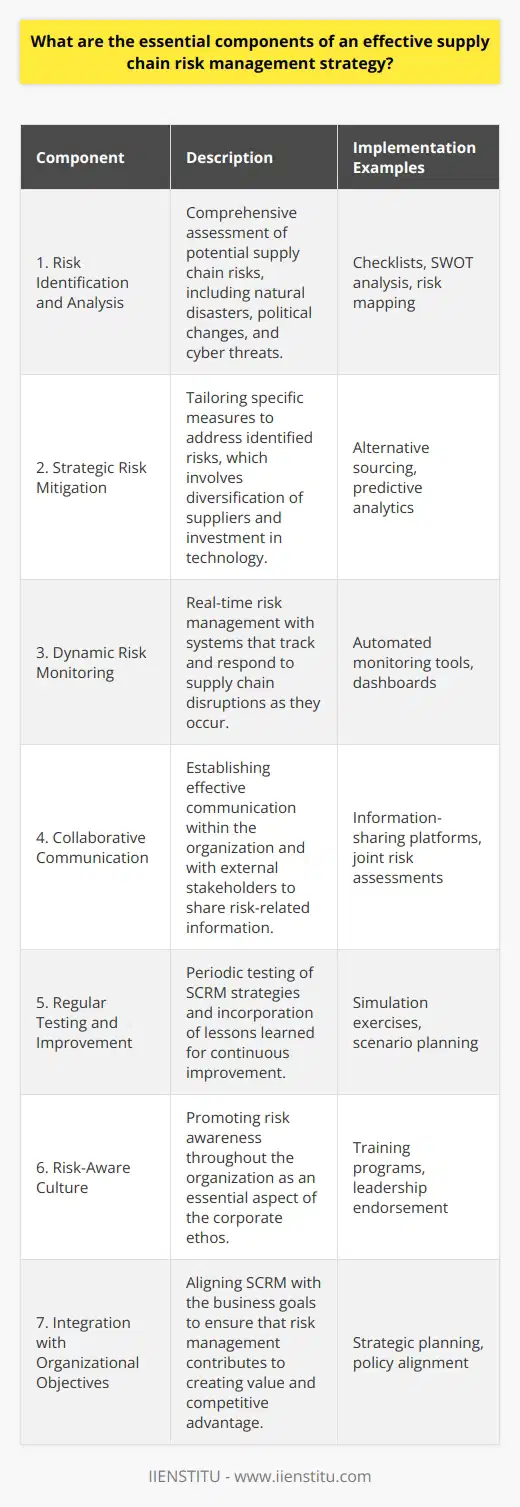
Enhanced Responsiveness
The principles of demand-driven supply chain management (DDSCM) significantly improve overall performance by enhancing responsiveness to changes in customer demand. By focusing on consumer needs, DDSCM allows businesses to better adjust their supply chains and allocate resources efficiently, ultimately improving customer satisfaction. This agile approach ensures the delivery of the right products, at the right time, and in the right quantities, driving increased sales and business growth.
Optimized Inventory Management
DDSCM also contributes to improved performance by optimizing inventory management. Companies can achieve leaner inventories by accurately forecasting demand, avoiding stockouts, overstocking, or scrapping obsolete products. Consequently, businesses save on warehousing and storage costs, reduce capital tied up in inventory, and minimize the risks associated with stock obsolescence. Optimized inventory management also allows companies to allocate resources more effectively and strategically invest in emerging trends or evolving customer needs.
Streamlined Operations
Adopting demand-driven principles encourages streamlined operations, resulting in cost savings and increased operational efficiency. DDSCM fosters greater collaboration among various stakeholders, such as suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, leading to better coordination and reduced lead times. By synchronizing processes and adjusting production schedules based on real-time demand information, companies can reduce waste, avoid excess inventory, and maintain high quality standards. This operational excellence contributes to improved performance by reducing costs, increasing profitability, and allowing companies to respond promptly to market changes.
Improved Supplier Relationships
Finally, DDSCM promotes strong supplier relationships, which play a crucial role in enhancing overall performance. With demand-driven supply chain management, businesses can communicate effectively with their suppliers and share vital information regarding customer demand and market trends. This open communication fosters trust and long-term partnerships, allowing suppliers to better plan their production and manage their own supply chains proactively. In turn, this improves supplier performance, reduces risks related to disruptions, and ensures a steady supply of high-quality materials and components.
In conclusion, adopting demand-driven supply chain management principles significantly contributes to improving overall performance by fostering enhanced responsiveness, optimizing inventory management, streamlining operations, and promoting strong supplier relationships. These benefits result in cost savings, increased operational efficiency, and higher customer satisfaction, enabling businesses to remain competitive in today's ever-changing marketplace.
Can you elaborate on the role of advanced analytics and digital transformation in optimizing supply chain operations?
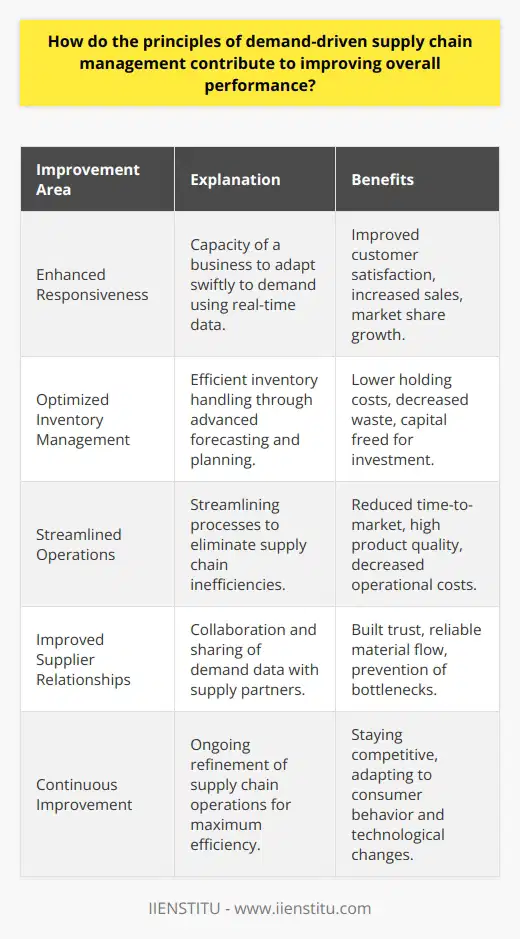
Role of Advanced Analytics
Advanced analytics play a critical role in optimizing supply chain operations by providing deeper insights into various aspects of the supply chain, including demand forecasting, inventory management, and operational efficiency. By leveraging advanced statistical models, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, organizations can gain a better understanding of current and future market trends, customer preferences, and potential risks in their supply chain operations.
Digital Transformation in Supply Chain Operations
Digital transformation further enhances supply chain optimization by automating various processes, integrating data from different sources, and ensuring real-time visibility of the supply chain. This digitalization helps organizations to make data-driven decisions, streamline operations, and reduce overall costs. Key elements of digital transformation in supply chain operations include the adoption of cloud-based platforms, internet-of-things (IoT) devices, and advanced robotics for material handling and transportation.
Driving Efficiency and Collaboration
Digital transformation and advanced analytics foster supply chain collaboration by enhancing communication, information sharing, and coordination among various supply chain partners, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. This increased connectivity enables organizations to accurately predict demand, ensure optimal inventory levels, and reduce lead times, thus resulting in optimized production planning and scheduling. Furthermore, advanced analytics facilitate proactive decision-making, enabling supply chain managers to minimize disruptions and mitigate potential risks.
Improving Sustainability and Compliance
Beyond efficiency gains, advanced analytics and digital transformation also contribute to enhancing sustainability and compliance within supply chain operations. By monitoring and analyzing the environmental impact of various supply chain processes, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce their carbon footprint. Additionally, digital transformation enables better visibility into global regulatory requirements, ensuring that organizations remain compliant with trade regulations and industry standards.
Conclusion
In summary, advanced analytics and digital transformation play a pivotal role in optimizing supply chain operations by providing valuable insights, driving efficiency, enhancing collaboration among partners, and improving sustainability and compliance. By embracing these technological advancements, organizations can gain a competitive advantage in the market, reduce costs, and ensure the long-term success of their supply chain operations.
What are the 5 tasks of supply chain management and how do they contribute to overall business efficiency?
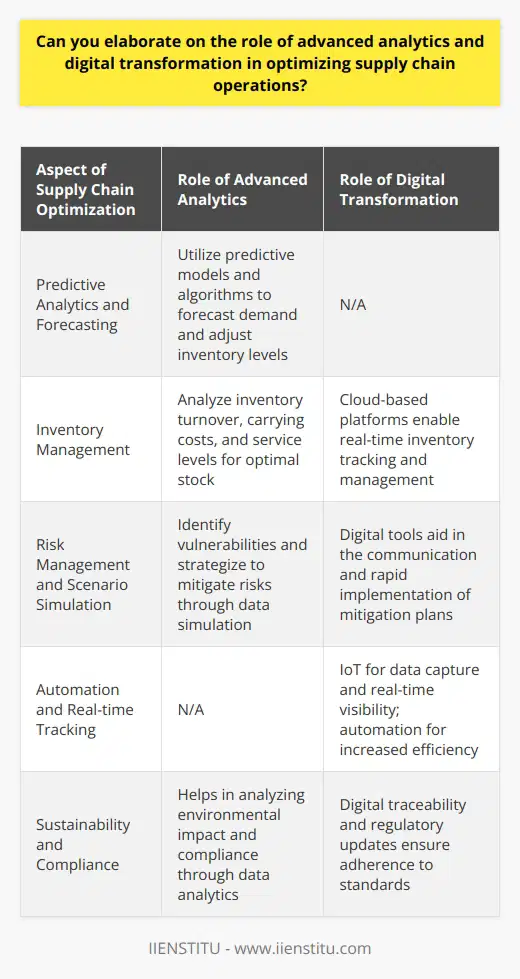
Supply Chain Strategy Design
The first task is designing a well-structured supply chain strategy. This involves identifying the best methods of product delivery from manufacturers to end users. Effective strategy design increases efficiency by minimizing costs and delivery time.
Supply Chain Operations Planning
Next is planning supply chain operations. This involves scheduling production, inventory management, and transportation. A well-planned operation reduces wastage, ensuring the business is cost-effective.
Supply Chain Operations Management
Thirdly, supply chain management entails managing the operations of the supply chain. This involves overseeing the production, transportation and delivery processes. Efficient management optimizes business operations.
Logistics Coordination
Subsequently, the fourth task is logistics coordination which involves managing transportation and warehousing. Effective coordination ensures timely, safe, and cost-efficient delivery of products.
Performance Measurement
Lastly, supply chain management involves measuring and monitoring performance. Through this, businesses can identify areas of inefficiency for improvement. Continuous performance measurement enhances overall business operations.
In conclusion, the tasks of supply chain management contribute to business efficiency by optimizing operations. They minimize costs, improve delivery times, and provide a mechanism for continuous improvement. This results in an efficient, effective, and competitive business infrastructure.
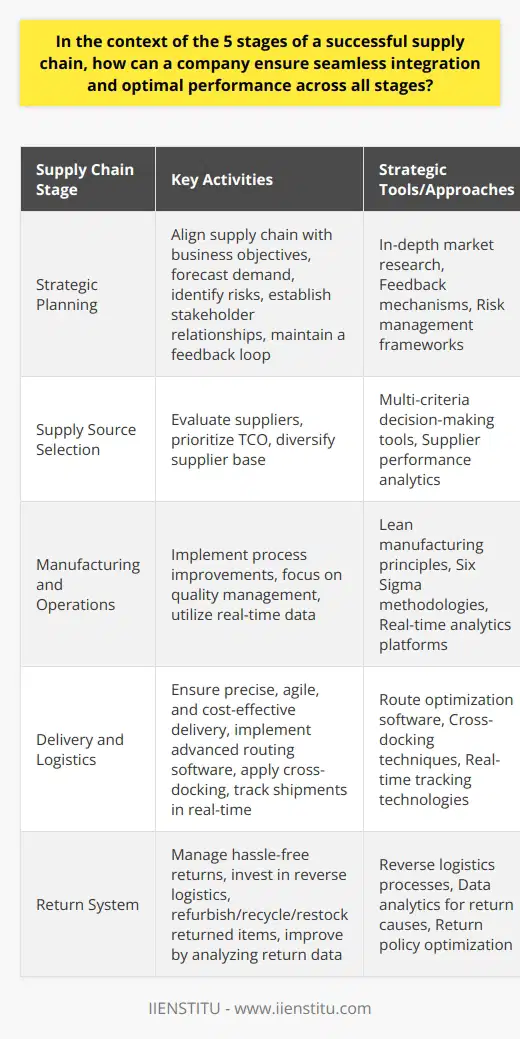
In the context of the 5 stages of a successful supply chain, how can a company ensure seamless integration and optimal performance across all stages?
Strategic Planning Stage
A company can ensure seamless integration and optimal performance at the strategic planning stage by developing robust plans. These strategies should be comprehensive, involving all relevant participants. This early involvement can solidify effective collaboration across all other stages.
Supply Source Selection
Choosing the correct sources of supply is critical. A thorough analysis of potential vendors, including their reliability, quality, and cost, is essential. Transparent and effective communication channels with suppliers will ensure a smooth flow of supplies.
Manufacturing and Operations
Effective management of the manufacturing process is crucial for reducing waste and maximizing efficiency. This involves monitoring production closely, anticipating problems, and swiftly implementing solutions. Clear communication, training, and support for employees can lead to higher productivity and better performance.
Delivery and Logistics
At this stage, efficient management of logistics makes a significant difference. This includes coordinating transportation, handling inventory, and monitoring warehousing. Technology, such as application software and tracking systems, can significantly improve integration and efficiency.
Return System
Managing returns can be a challenging aspect of a supply chain. A company can streamline this process by setting up clear policies and procedures for returns and exchanges. Additionally, a robust system should be in place to analyze returns, providing valuable feedback to improve future production and distribution.
In summary, a company can achieve seamless integration and optimal performance in its supply chain by developing strategic plans, thoroughly selecting suppliers, effectively managing their manufacturing process and logistics, and implementing a sound return policy. Effective use of technology can also enhance integration and performance across all stages. Regular review and adaptive adjustment of these elements are essential for continuous improvement.
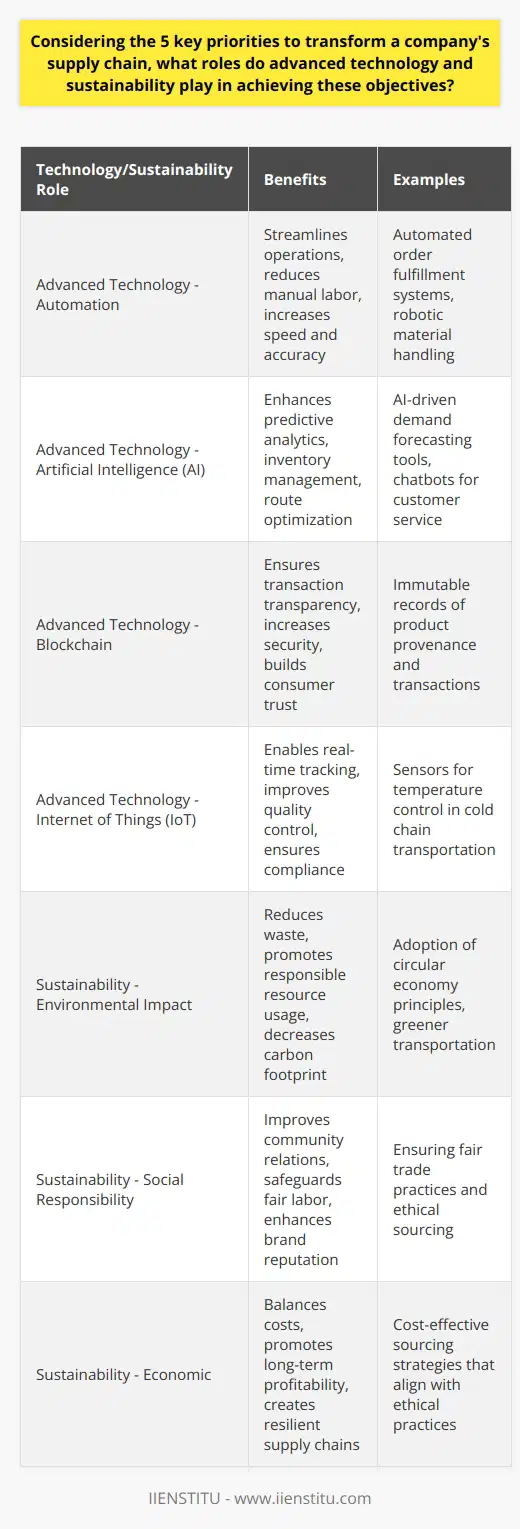
Considering the 5 key priorities to transform a company's supply chain, what roles do advanced technology and sustainability play in achieving these objectives?
Implementing Advanced Technology
One overriding priority to transform a company's supply chain revolves around implementing advanced technology. These advanced technologies include automation, artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and Internet of Things (IoT). They contribute to overhauling supply chain processes by enhancing transparency, accountability, and cyber secure data storage and sharing. Automation technology improves process efficiency, minimizes human errors, and achieves time conservation in supply chain management.
Role of Artificial Intelligence
AI, when used in supply chain management, helps predict and mitigate potential risks and disruptions. AI’s ability to process large volumes of data makes it possible to anticipate trends, optimize logistics, and reduce costs. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, provides a reliable means of recording transactions, thus promoting trust and transparency in the organization’s supply chain. IoT enhances real-time monitoring of product movement and storage in the supply chain.
Incorporation of Sustainability
Aside from technology, sustainability is another essential aspect of supply chain transformation. This means ensuring the supply chain processes are environmentally friendly, socially adequate, and economically viable. The company should aim to minimize carbon emissions, waste and excessive exploitation of natural resources. These can be achieved through employing eco-friendly means of production and distribution, proper waste management, and sustainable sourcing.
Importance of Social Responsibility
Social responsibility entails ensuring workers' welfare and human rights are safeguarded within the company and across the supply chain. It also includes strengthening relations with stakeholders. Economically, a sustainable supply chain model underpins long-term profitability and resilience. It ensures the company can withstand shocks, be it economic or environmental.
In conclusion, advanced technology and sustainability play critical roles in transforming a company's supply chain. They not only assure efficient and transparent operations but also contribute towards the company's social, environmental responsibility and long-term economic viability.