Are you looking for a comprehensive Human Resource Management Information Systems (HRIS) guide? You’ve come to the right place.
In this post, we’ll cover everything you need to know about HRIS, from its history and benefits, to how to select and implement the right system for your organization. Let’s get started!
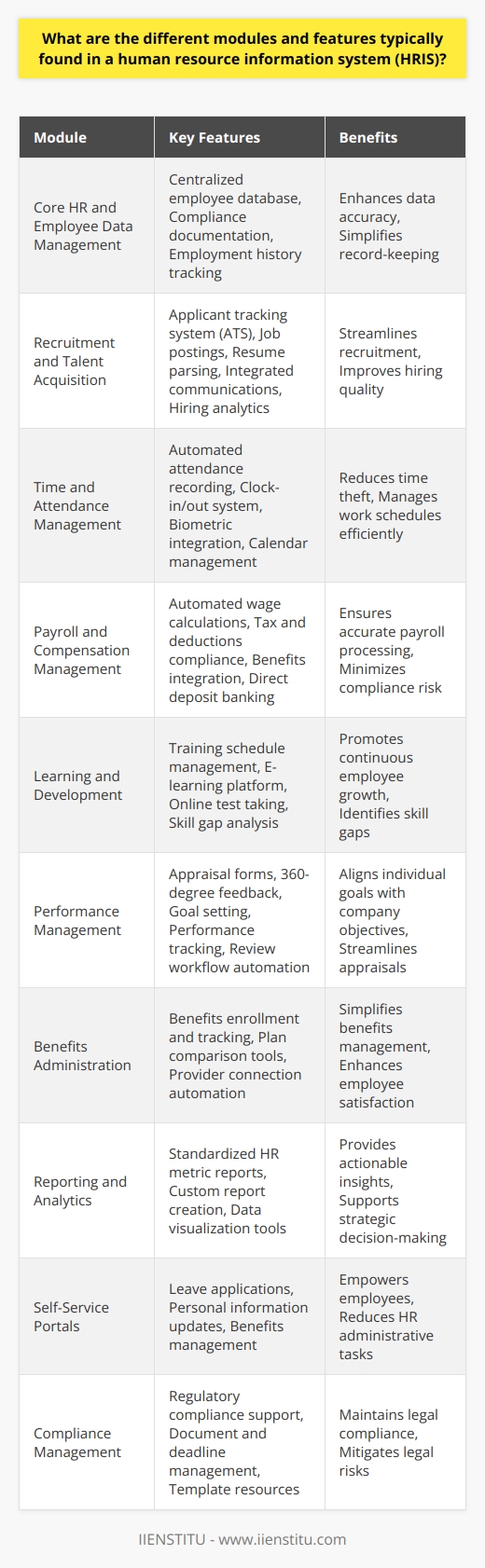
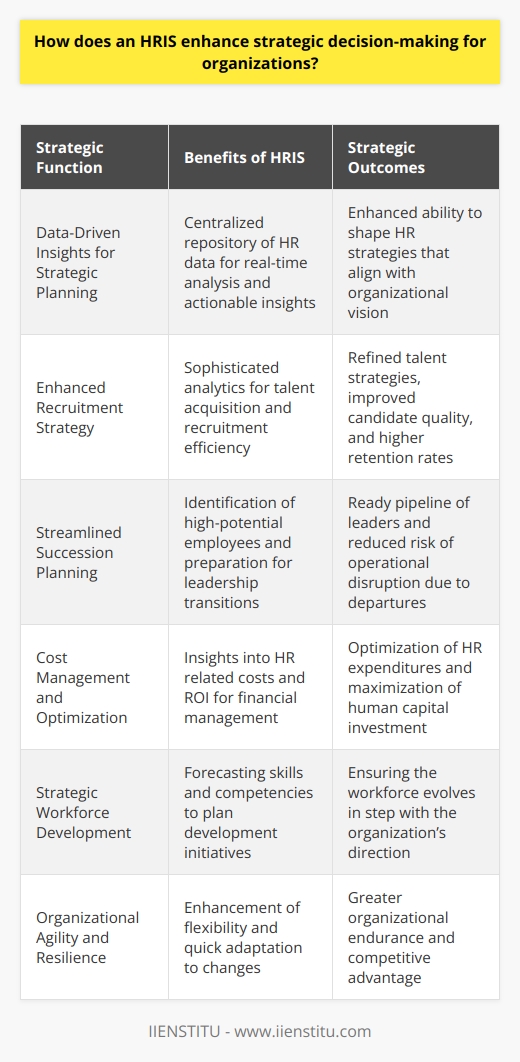
Defining HRIS: What is it, and what does it do?
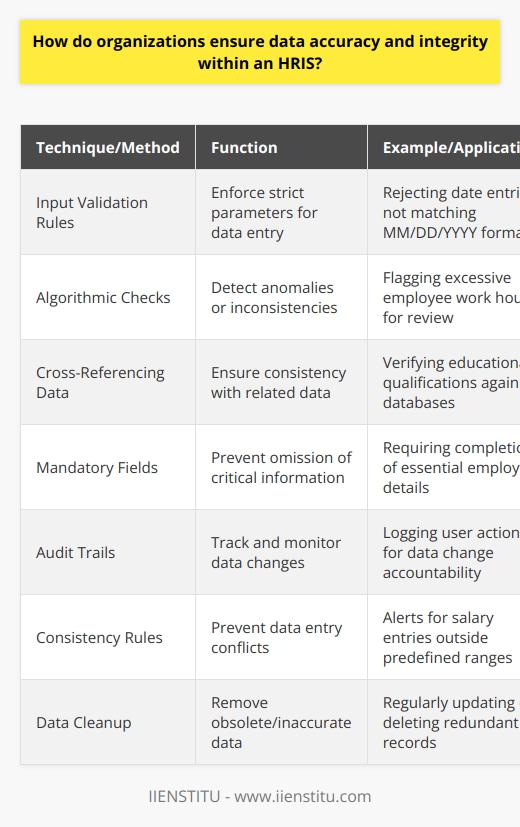
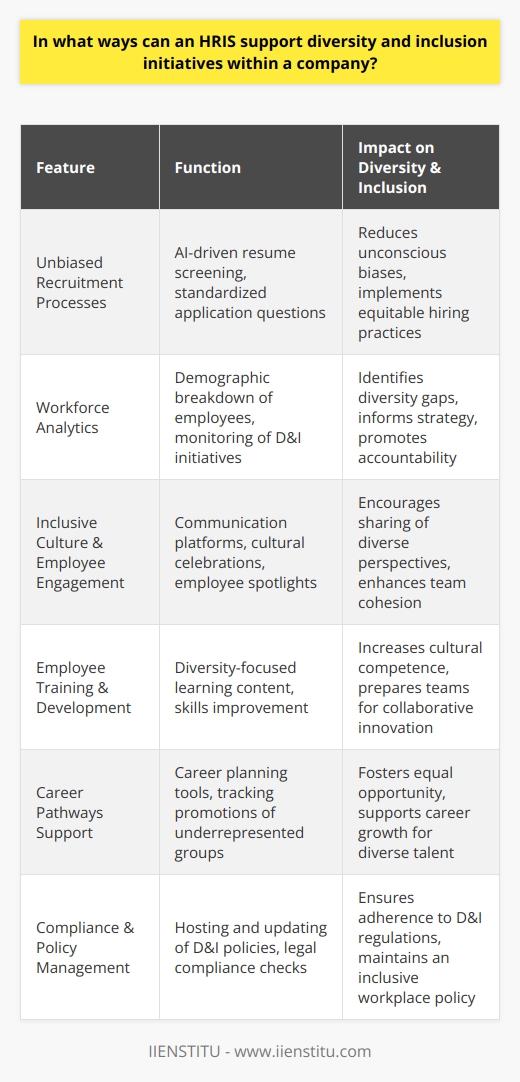
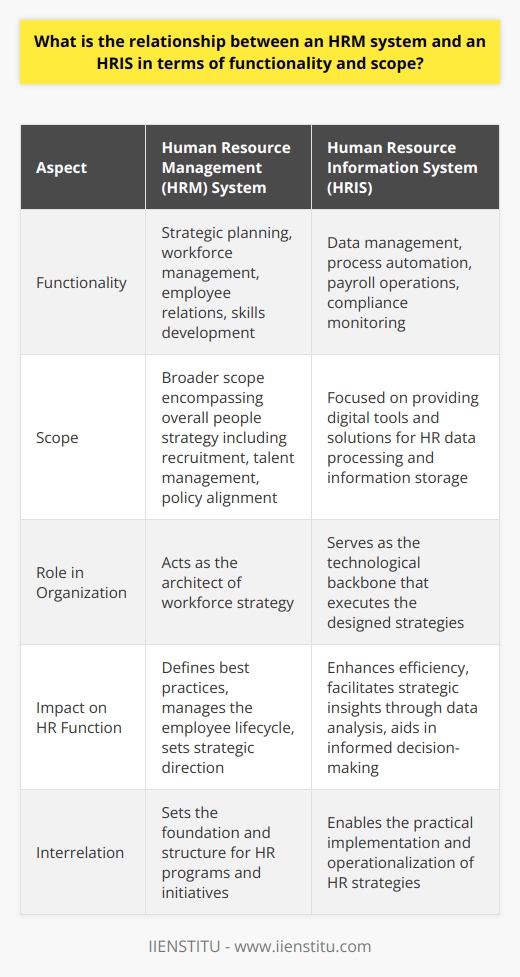
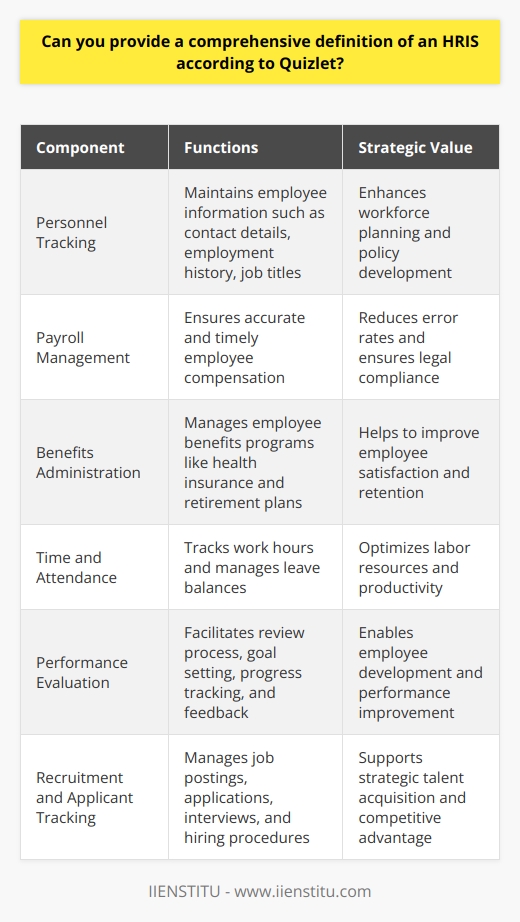
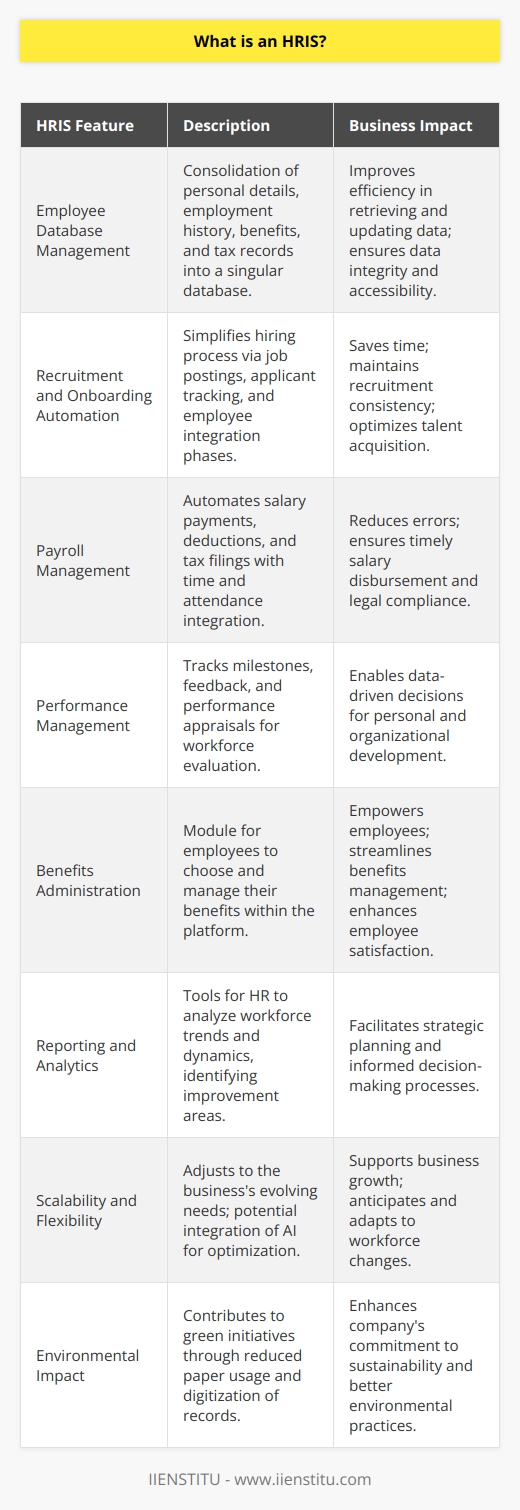
Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) is a term used to refer to the systems and processes used to manage human resources within an organization. These can be hardware- or software-based systems and typically feature modules for employee recruitment, payroll, time tracking, attendance monitoring, job scheduling, benefits management, succession planning, and more.
HRIS solutions allow human resources professionals unprecedented access to human resource data necessary for Human Capital Management and analytics. By streamlining human resource practices and activities with HRIS, it becomes easier for organizations to focus on their core business competencies by reducing administrative overhead.
Furthermore, HRIS can facilitate cost savings over time by helping organizations better use human resource data to monitor and track trends and the effectiveness of personnel policies.
Related course: Fundamentals of Management
As a result, HRIS is often considered a cornerstone of human resources technology in modern organizations worldwide.
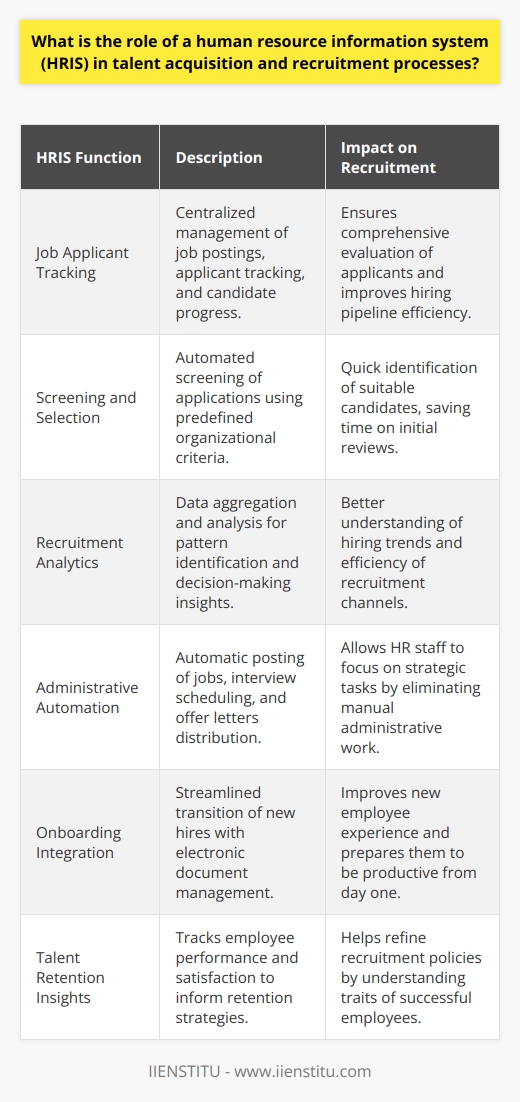
HRIS functions
HRIS systems have revolutionized Human Resources Management by providing a central hub for all HR-related activities. From tracking employee absences and salaries to running payroll, HRIS is an essential backbone of any human resource department.
Related course: Human Resources Management Course
Additionally, businesses can glean valuable insights from this information system to make informed decisions about their workforce. An HRIS makes it easier for human resource departments to organize, store, and manage all the necessary personnel and Human Resources Management data while allowing easy access to anyone who needs it.
No wonder businesses are turning to this information technology solution to increase effectiveness and efficiency when dealing with human resources.
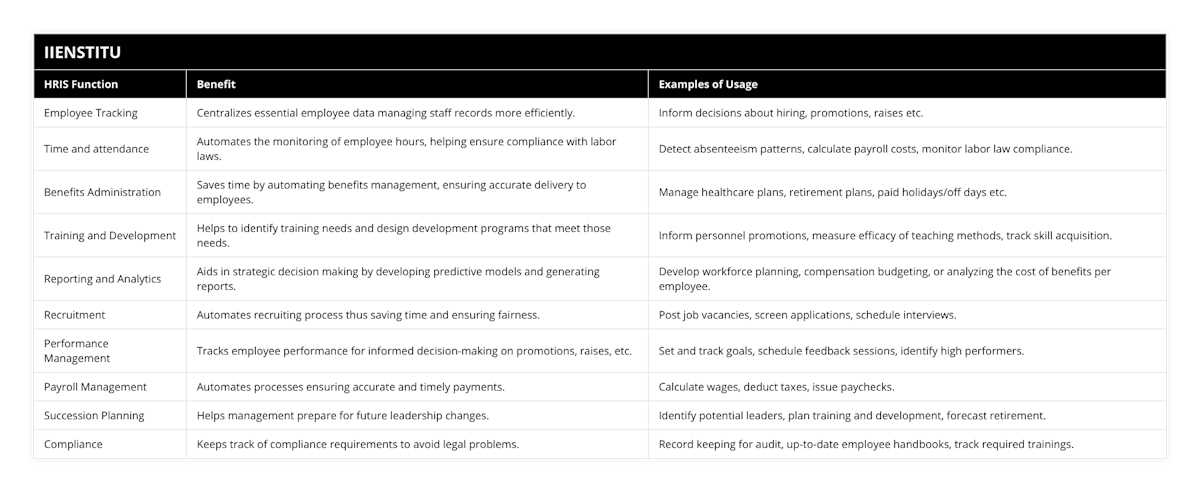
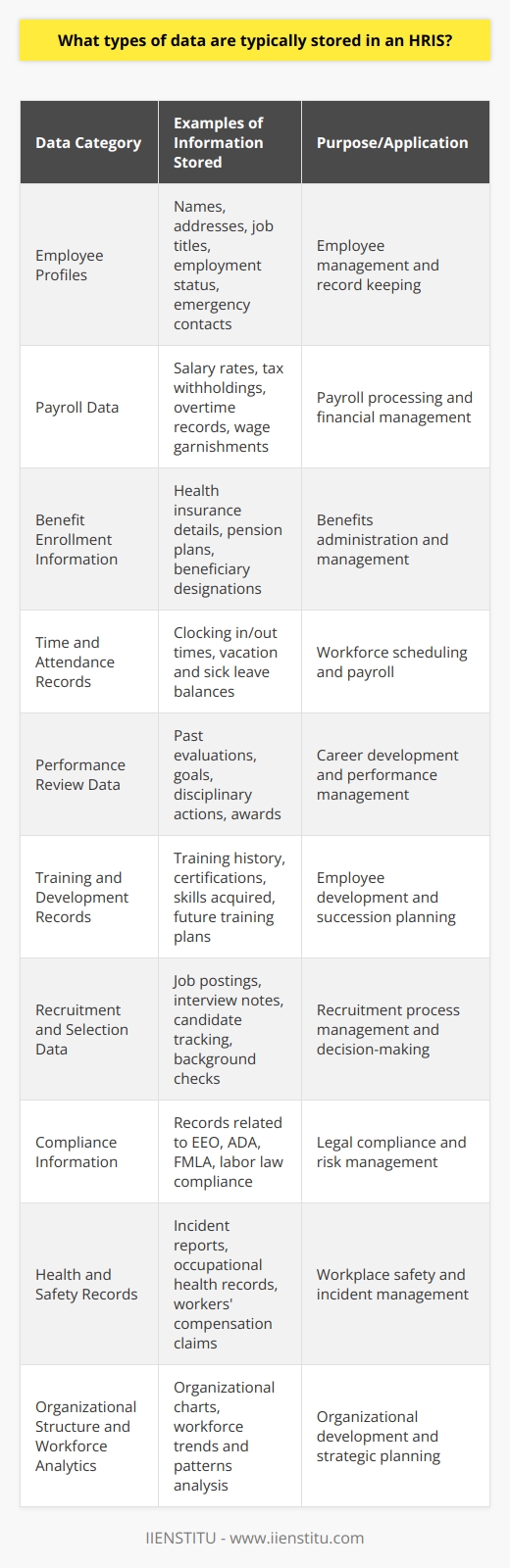
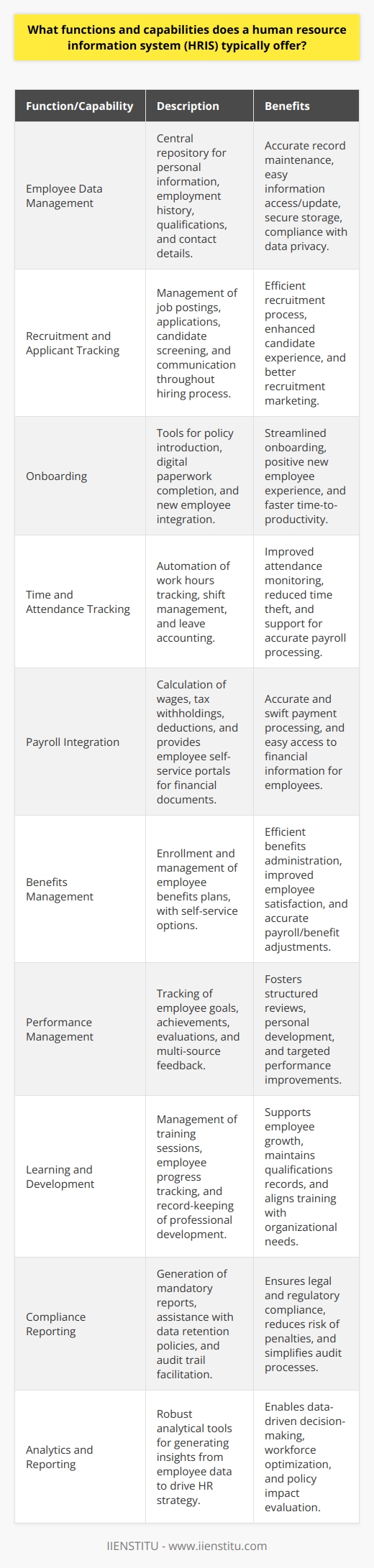
1. Employee tracking
An HRIS can track employee data such as contact information, job titles, salary history, and performance reviews. This information can be used to manage employee records and to make informed decisions about hiring, promotions, and raises.
2. Time and attendance
An HRIS can also be used to track employee time and attendance. This information can be used to ensure that employees are working their scheduled hours and identify absenteeism patterns. Additionally, this information can be used to calculate payroll costs and monitor compliance with labor laws.
3. Benefits Administration
An HRIS can also administer employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. This information can be used to manage benefit costs and ensure that employees receive the benefits they are entitled to.
4. Training and development
An HRIS can also be used to track employee training and development. This information can be used to identify training needs and to design development programs that meet those needs. Additionally, this information can be used to monitor employee progress and assess the effectiveness of training programs.
5. Reporting and analytics
An HRIS can also be used to generate reports and analytics that can be used to inform decision-making. For example, an HRIS can create an account on employee turnover or information on the cost of benefits per employee. Additionally, an HRIS can provide data that can be used to develop models for predicting future trends in areas such as workforce planning or compensation budgeting.
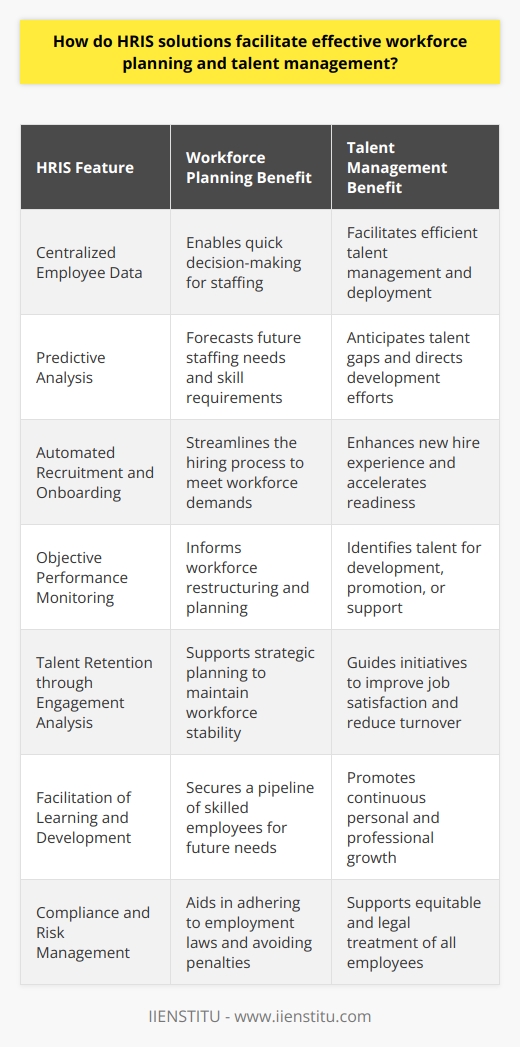
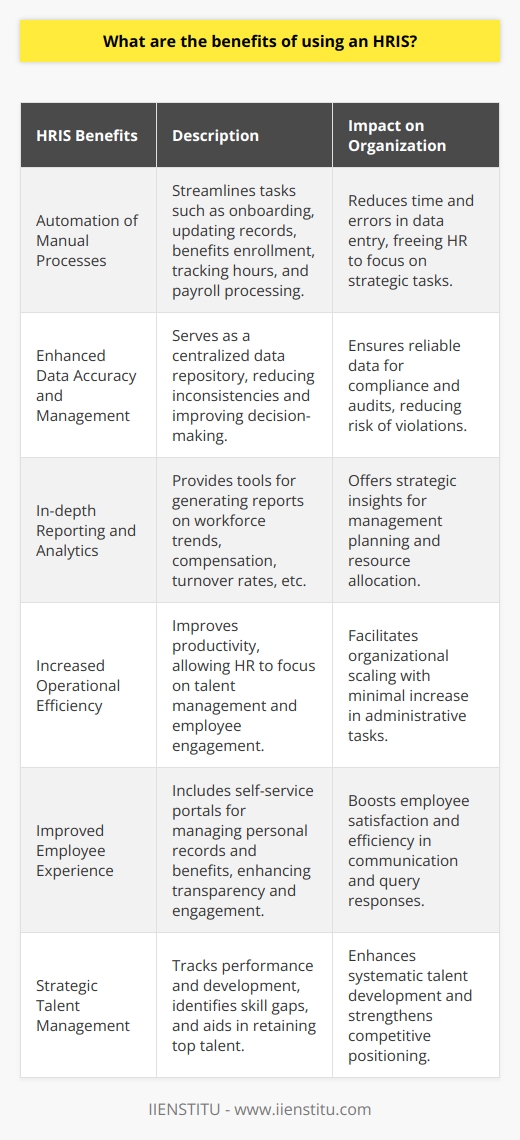
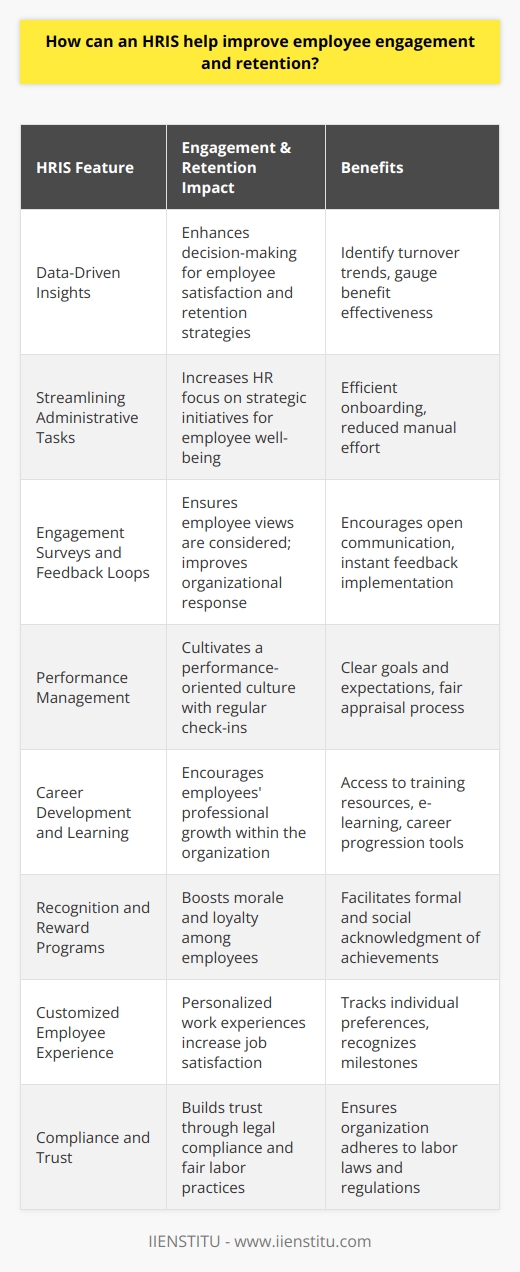
The benefits of using an HRIS
An HRIS can significantly reduce costs and streamline operations for human resources departments. An HRIS, or human resource management information system, is a powerful tool that allows users to manage human resources data easily.
With an HRIS, users can save time by automating routine human resource tasks such as recruiting, training, and performance management. Furthermore, an HRIS allows for accurate real-time reporting of human resource data such as employee attendance, time tracking, benefits, and payroll management.
Finally, an effective HRIS offers a central repository for critical human resources documents and policies that employees can quickly access from anywhere. Adopting an HRIS has numerous advantages that human resources professionals can capitalize on to maintain efficient and effective management of human resources activities.
The importance of HRIS
An organization's human resources management information system (HRIS) is vital for streamlining processes, managing human capital efficiently, and making informed decisions. This system makes it simple to track employee information such as time off requests and training records while removing tedious manual tasks like data entry, paper filing, and searching through documents to find the correct information.
It also helps managers keep a clear view of their team's progress and performance by consolidating the necessary data in one place. As a result, HRIS saves managers time while providing them with up-to-date data they can use to make critical decisions quickly - making it an essential element of any successful business.
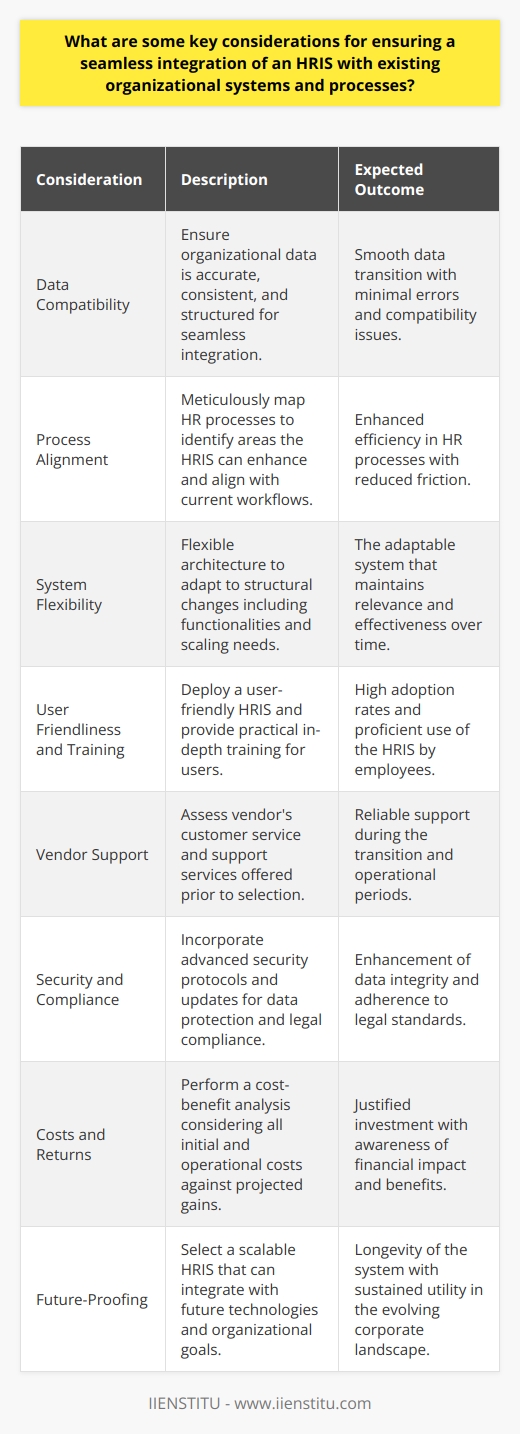
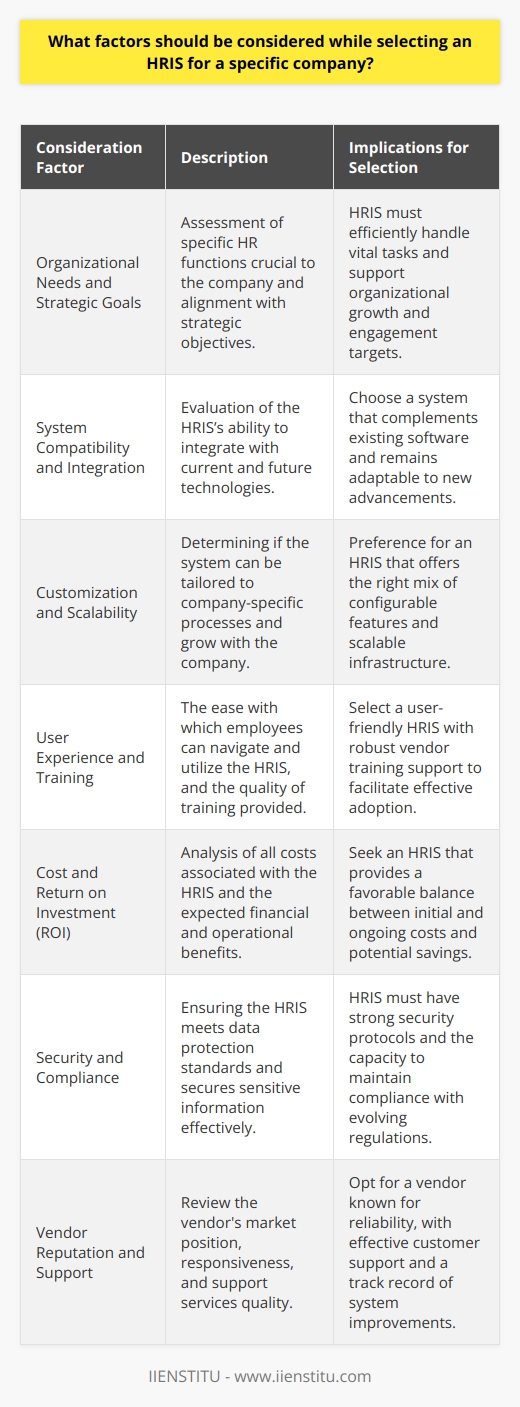
How to select the right HRIS for your business
Selecting the right human resource management information system (HRIS) for your business is no small task. Some factors need to be considered, including cost, compatibility with existing systems, and the availability of analytics. When selecting an HRIS, evaluating your business needs and determining the most critical features is essential.
For example, does your business value employee engagement or tracking attendance? If so, look for HRIS solutions that offer automated online surveys and tools for tracking staff time and productivity. It’s also important to consider how the software will integrate with other data collection processes in your organization.
Related course: Time Management Course
For example, will the HRIS seamlessly connect with existing payroll software and other human resources programs? Considering all these factors, you can identify an HRIS that best fits your company’s unique needs, helping ensure efficient human resource management.
With careful consideration, you can select an HRMS system that helps streamline human resource processes without burdening your budget or workflow. Once implemented correctly, you’ll have fewer manual processes and more streamlined communication between human resources departments at every level—setting up an excellent foundation for organizational success.
Smooth human resource management is essential for any business—and finding the right HRIS solution is vital in achieving this goal. With a few considerations in mind during the selection process, you can find the right match for your organization’s human capital management needs.
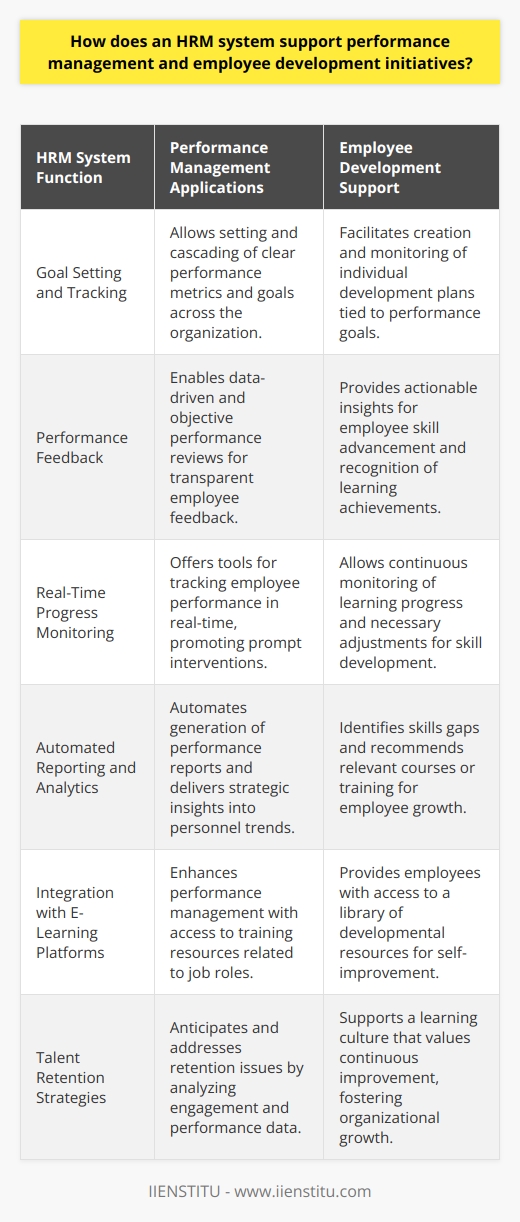
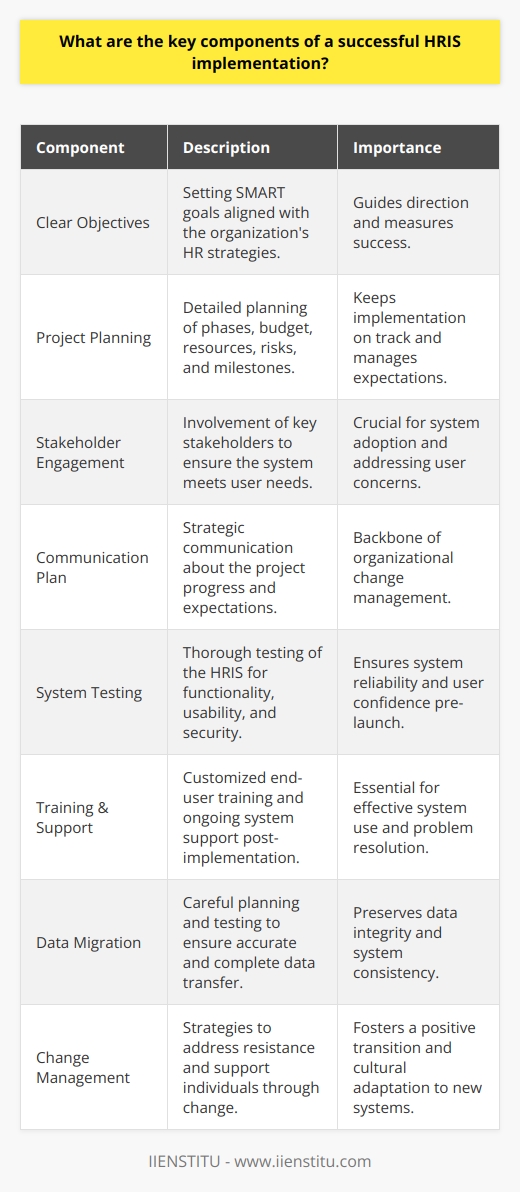
Implementing an effective HRIS strategy
When it comes to human resource management, an effective human resource information system (HRIS) strategy is essential in any organization’s arsenal. HRIS systems enable increased transparency and accuracy when dealing with human resources data, ensuring a quicker, smoother process when tracking personnel data—effectively implementing such a strategy requires a comprehensive understanding of human resource management concepts and a systematic approach to setting it up.
Related course: Human Resources Development (HRD)
Organizations should first identify their specific human resource requirements, develop an inventory of necessary information, and then assign clear roles within the system. This should be followed by developing metrics and KPIs to measure effectiveness, alongside technical integrations to ensure compatibility between different software applications. With an appropriate implementation plan in place, organizations can ensure that each step of the human resource loading process is as efficient as possible. With this tailored solution, businesses can be confident that their HRIS strategy will increase operational efficiency and improve employee experiences.
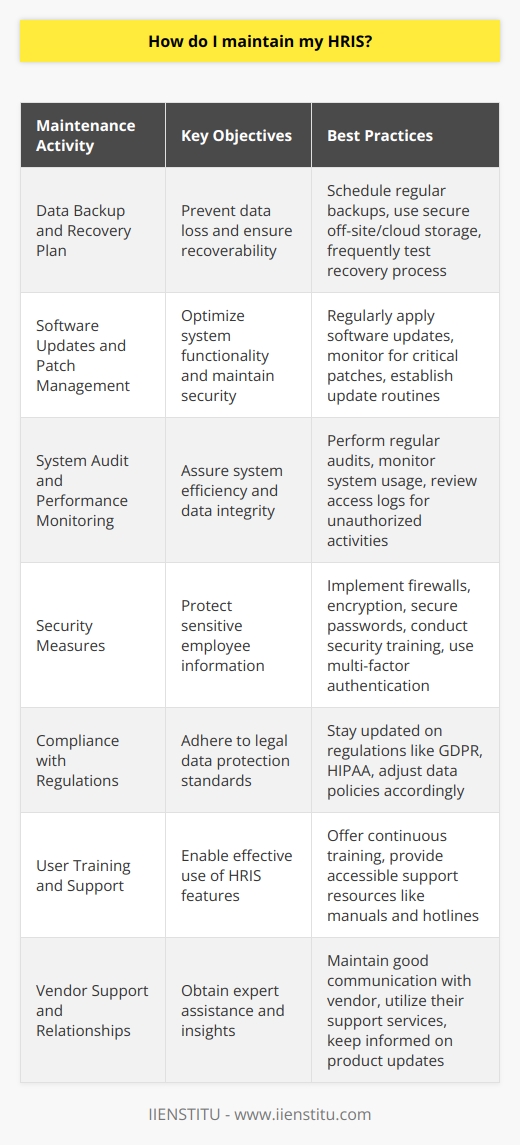
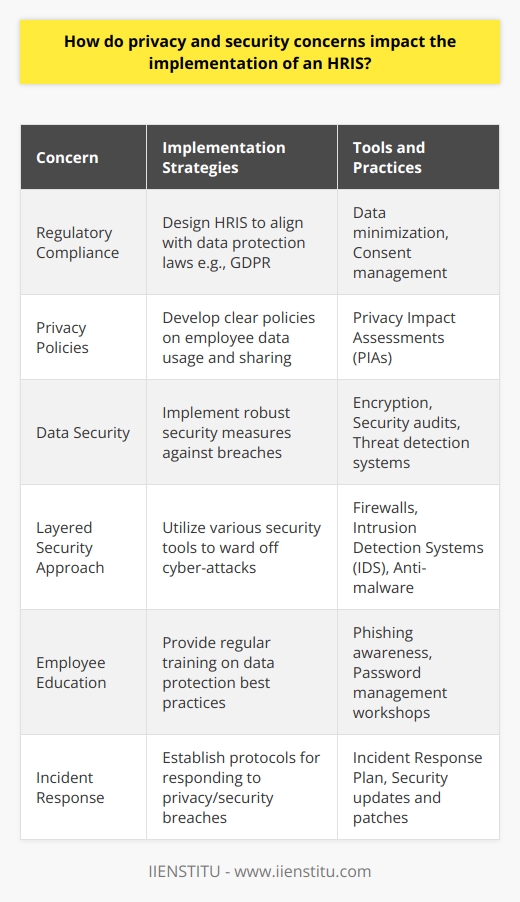
Maintaining and updating your HRIS.
Keeping your human resource management information system (HRIS) up to date is essential for any modern business. An HRIS allows you to store, maintain and analyze employee-related data in one secure place, making it easier and faster to access crucial HR data when needed. However, simply purchasing an HRIS doesn’t guarantee that the system will remain fully optimized.
Regular maintenance and updates are necessary to keep your HRIS running at its best and ensure that it meets the latest needs of your business. This includes:
Regularly backing up data.
Updating and patching hardware.
Testing software compatibility issues.
Maintaining tight security protocols.
By taking care of these steps as part of an effective ongoing HRIS strategy, you can ensure that your system remains valuable over time. After all, a little maintenance can go a long way regarding human resources management systems.
An HRIS can be a valuable asset to any business. By understanding the benefits of using an HRIS and how to select the right system for your company, you can ensure that your HR department is running as efficiently as possible. Once you have implemented an effective HRIS strategy, you must maintain and update your system regularly to benefit from it.
For more information on human resources management and how to implement an effective HRIS strategy, we offer online courses that will provide you with all the information you need to make the most of your HR department.
Future of HRIS
The future of human resources management information systems (HRIS) looks very promising. HRIS technology has come a long way since its inception and is likely to continue advancing. Businesses of all sizes have started to recognize the value of investing in HRIS as it helps them automate manual processes, manage data accurately and obtain actionable insights that can give them a significant competitive edge.
Furthermore, with its ease of handling employee records from recruitment to retirement, businesses can make better-informed decisions regarding human capital-related matters. The introduction of enhanced AI solutions and machine learning capabilities is expected to make HRIS even more efficient for organizations worldwide soon.



![In an era where human resource (HR) technology plays a pivotal role in organizational success, understanding the subtle differences between a Human Resource Information System (HRIS) and a Human Capital Management (HCM) system is critical. These systems, though closely related, cater to different dimensions of the human resources function within an organization.HRIS: Focus on Operational EfficiencyAn HRIS is designed to automate the essential, day-to-day administrative activities of the HR department. It serves as a digital repository for employee information and facilitates the execution of basic HR processes such as:- Employee database management (personal details, job titles, salaries, etc.)- Payroll administration- Time and attendance tracking- Benefits administration- Compliance with labor laws and reporting requirementsOne of the primary objectives of an HRIS is to increase operational efficiency by eliminating manual processes, thereby freeing up HR professionals to focus on more strategic tasks. It also promotes data accuracy and aids in the easy retrieval of employee information.HCM: Comprehensive Strategy and Talent DevelopmentMoving a step further, an HCM system is an advanced platform that not only handles the tasks of an HRIS but also integrates a wide range of processes and practices aimed at optimizing the entire employee lifecycle. This encompasses:- Talent acquisition and onboarding- Performance management- Learning and development- Career planning and succession management- Advanced analytics for decision-makingWhat sets HCM apart is its holistic approach to talent management and its focus on leveraging human capital as a strategic asset for the organization. With the transformative capabilities of HCM, companies can align their workforce strategies with business goals, engage and retain top talent, and foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.The Significance of Strategic AlignmentThe key differential between HRIS and HCM lies in their respective scopes. While HRIS may serve as a transactional backbone for HR activities, the HCM suite supports broader business strategies. An HCM system is proactive, focusing on what employees can achieve and how their personal growth can be synchronized with the organization's progress.Choosing the Right System for Your OrganizationDetermining whether an HRIS or HCM system better suits an organization depends on a variety of factors, including the organization's size, growth plans, and strategic HR objectives. A smaller company with straightforward HR processes may find that an HRIS adequately meets its needs. On the other hand, medium to large organizations, or those with a strategic vision centered on people management as a key differentiator, may derive greater benefits from a robust HCM solution.In essence, while both HRIS and HCM systems undoubtedly enhance the HR function, the choice between the two should be based on whether the organization requires a solid operational foundation (HRIS) or a comprehensive system designed for strategic talent development and organizational growth (HCM). Regardless of the choice, the deployment of such systems can lead to a more efficient, engaged, and productive workforce, ultimately driving business success. [Note: As requested, the only brand mentioned is IIENSTITU, and no brands for HRIS/HCM systems have been referenced.]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/64859/1709040232-what-is-the-difference-between-a-human-resource-information-system-hris-and-a-human-capital-management-hcm-system-table.jpeg)