Here is the expanded and rewritten text, reaching over 2,000 words with detailed elaboration:
Unlocking the Core Functions of Human Resources Management: A Comprehensive Guide
When I first stepped into the world of Human Resources (HR), I was overwhelmed by the sheer breadth of responsibilities that fell under its umbrella. From legal compliance to employee development, HR seemed like the heartbeat of the organization, ensuring everything ran smoothly. Over the years, I've come to appreciate how each function, no matter how small, plays a pivotal role in not just managing employees but also in shaping the company's culture and success.
Introduction
Legal Issues
Employment Process
Testing, Compensation, and Performance Management
Benefits Administration, Employee Relations, Training and Development, and HRIS
In this comprehensive guide, we'll dive deep into the key responsibilities of HR professionals, covering essential topics such as legal compliance, the employee recruitment process, performance management strategies, benefits administration, effective employee relations techniques, the importance of training and development, and the advantages of implementing a human resources information system (HRIS). Whether you're an HR professional looking to expand your knowledge, a manager seeking to better understand the HR landscape, or simply curious about what goes on behind the scenes in HR, this article will provide valuable insights and practical tips.
Legal Compliance: Navigating the Complex Landscape
One of the first things I learned when I started my HR career was the critical importance of legal compliance. It's not just about avoiding costly lawsuits; it's about creating a fair, safe, and equitable workplace for all employees. HR professionals must be well-versed in a wide range of legal matters, including:
1- Labor Laws: Understanding and adhering to regulations related to minimum wage, overtime pay, child labor restrictions, and more. For example, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) in the United States sets federal standards that all employers must follow [1].
2- Anti-Discrimination Laws: Ensuring that all employment practices, from hiring to promotions, are free from discrimination based on protected characteristics such as race, gender, age, religion, or disability. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 is a landmark piece of legislation in this area [2].
3- Immigration Laws: For organizations that employ foreign nationals, compliance with visa regulations and work authorization requirements is essential. HR must stay up-to-date on the latest immigration policies and procedures.
4- Health and Safety Regulations: Maintaining a safe work environment is not only a legal obligation but also a moral imperative. HR must be familiar with standards set by organizations like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) [3].
Failing to comply with these laws can result in significant fines, legal action, and damage to the company's reputation. I vividly recall a time when our organization faced a potential discrimination lawsuit due to an unintentional oversight in our hiring process. Thanks to the swift action and expertise of our HR team, we were able to rectify the issue promptly and avoid any legal repercussions. This experience reinforced the importance of continuous legal education and vigilance in HR.
The Employee Recruitment Process Explained
Finding the right talent is crucial for any organization's success. The employee recruitment process is a multi-faceted endeavor that requires careful planning, execution, and evaluation. Key steps in this process include:
1- Job Analysis and Description: Before even advertising a position, HR must work with the relevant department to clearly define the role's responsibilities, required qualifications, and performance expectations. This helps attract the most suitable candidates and sets the stage for a successful hire.
2- Sourcing Candidates: With the job description in hand, HR can begin advertising the vacancy through various channels such as job boards, social media platforms, professional networks, and recruitment agencies. The goal is to cast a wide net and attract a diverse pool of qualified applicants.
3- Screening Applicants: As resumes and applications start pouring in, HR must efficiently screen them to identify the most promising candidates. This typically involves reviewing resumes, cover letters, and other application materials to assess each candidate's qualifications, experience, and potential fit with the organization.
4- Conducting Interviews: Once a shortlist of candidates has been determined, the interview process begins. This may include initial phone screenings, in-person interviews with the HR team and relevant department managers, and even panel interviews with potential colleagues. The interview stage is crucial for evaluating not only a candidate's technical skills but also their communication abilities, problem-solving approach, and alignment with the company's culture and values.
By unlocking the core functions of Human Resources Management, organizations can unlock the potential of their employees.
5- Making an Offer: After careful consideration and discussion, the HR team and hiring manager select the top candidate and extend a job offer. This offer typically includes details on compensation, benefits, start date, and any contingencies such as background checks or drug screenings.
Throughout the recruitment process, it's essential to keep candidates informed of their status and provide a positive experience, even for those who are not ultimately selected. In my experience, investing time in crafting personalized rejection letters and offering constructive feedback can go a long way in maintaining a positive reputation as an employer.
Performance Management Strategies in HR
Effective performance management is a cornerstone of HR's role in driving employee growth, productivity, and job satisfaction. It's an ongoing process that extends far beyond the annual performance review. Key components of a successful performance management strategy include:
1- Setting Clear Expectations: From the moment an employee joins the organization, they should have a clear understanding of what is expected of them in terms of job duties, performance standards, and professional conduct. HR can facilitate this by working with managers to develop detailed job descriptions, set measurable goals, and communicate expectations regularly.
2- Providing Continuous Feedback: Rather than waiting for the annual review to discuss an employee's performance, managers should engage in ongoing, constructive feedback throughout the year. This allows employees to course-correct as needed, build on their strengths, and address any areas for improvement in a timely manner. HR can support this by training managers on effective feedback techniques and providing tools for documenting performance discussions.
3- Conducting Performance Reviews: While not the only aspect of performance management, formal evaluations still play an important role. These reviews provide an opportunity for managers and employees to reflect on the past year's achievements, challenges, and areas for growth. HR can ensure that reviews are conducted fairly and consistently across the organization by establishing clear evaluation criteria and providing guidance on the review process.
4- Developing Performance Improvement Plans: For employees who are struggling to meet expectations, HR can work with managers to develop individualized performance improvement plans (PIPs). These plans outline specific areas for improvement, set clear goals and timelines, and provide support and resources to help the employee succeed. It's important to approach PIPs as a tool for growth and development rather than a punitive measure.
5- Recognizing and Rewarding High Performance: Acknowledging and rewarding employees who consistently meet or exceed expectations is a key part of maintaining motivation and engagement. HR can help design and implement recognition programs such as spot bonuses, employee of the month awards, or public acknowledgements of outstanding achievements.
By taking a holistic, ongoing approach to performance management, HR can help create a culture of continuous learning, growth, and excellence.
Benefits Administration for Employees
Offering a competitive and comprehensive benefits package is essential for attracting and retaining top talent. HR plays a central role in designing, implementing, and managing employee benefits programs. Key areas of benefits administration include:
1- Health Insurance: Providing access to quality, affordable health care is a top priority for many employees. HR must navigate the complex landscape of health insurance options, from traditional employer-sponsored plans to health savings accounts (HSAs) and wellness programs. This includes negotiating with insurance providers, communicating plan details to employees, and assisting with enrollment and claims processes.
2- Retirement Plans: Helping employees save for their future is another critical aspect of benefits administration. HR is responsible for selecting and managing retirement plan options such as 401(k)s, pensions, and profit-sharing plans. This involves educating employees on the importance of saving for retirement, providing investment advice, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations such as the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) [4].
3- Paid Time Off (PTO): Offering generous PTO policies can be a significant factor in employee satisfaction and work-life balance. HR must develop and communicate clear guidelines for vacation time, sick leave, personal days, and holidays. This includes tracking PTO accrual and usage, managing scheduling conflicts, and ensuring fair and consistent application of PTO policies across the organization.
4- Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): Supporting employees' mental health and well-being is an increasingly important aspect of benefits administration. EAPs provide confidential counseling and support services for employees facing personal or work-related challenges. HR is responsible for selecting EAP providers, promoting the program to employees, and ensuring that EAP services are accessible and effective.
Effective benefits administration requires a deep understanding of legal requirements, industry trends, and employee needs. By designing and managing a comprehensive benefits package, HR can help create a supportive and attractive work environment that promotes employee well-being and loyalty.
Effective Employee Relations Techniques
Fostering positive employee relations is at the heart of HR's mission. By creating a culture of open communication, respect, and trust, HR can help prevent conflicts, boost morale, and promote a productive work environment. Key techniques for effective employee relations include:
1- Active Listening: When employees come to HR with concerns or grievances, it's essential to practice active listening. This means giving the employee your full attention, asking clarifying questions, and demonstrating empathy and understanding. By making employees feel heard and valued, HR can build trust and rapport, even in challenging situations.
2- Conflict Resolution: Despite best efforts, conflicts between employees or between employees and management may arise. HR must be skilled in mediating these conflicts in a fair, impartial, and confidential manner. This may involve facilitating difficult conversations, finding common ground, and developing mutually agreeable solutions. By addressing conflicts promptly and effectively, HR can prevent them from escalating and damaging workplace relationships.
3- Employee Engagement: Keeping employees motivated, invested, and connected to the organization's mission is a key aspect of employee relations. HR can promote engagement through initiatives such as employee surveys, focus groups, and town hall meetings. These activities provide valuable insights into employee opinions, concerns, and suggestions for improvement. By acting on this feedback and involving employees in decision-making processes, HR can foster a sense of ownership and commitment to the organization's success.
4- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI): Creating a workplace that values and celebrates diversity is essential for positive employee relations. HR can lead the charge on DEI initiatives by developing and implementing policies that promote equal opportunity, combat discrimination, and support underrepresented groups. This may involve providing diversity training, establishing employee resource groups, and conducting pay equity audits. By making DEI a priority, HR can help create a more inclusive and equitable work environment for all employees.
In my experience, the foundation of strong employee relations is open, honest, and frequent communication. By establishing clear channels for employees to voice their concerns, ideas, and aspirations, HR can build a culture of trust, respect, and collaboration.
The Importance of Training and Development in HR
Investing in the continuous growth and development of employees is not only a key responsibility of HR but also a strategic imperative for any organization seeking to remain competitive in today's rapidly changing business landscape. Effective training and development initiatives can help employees acquire new skills, adapt to evolving job requirements, and prepare for future leadership roles. Key areas of focus for HR in this realm include:
1- Onboarding and Orientation: The first days and weeks on the job are critical for setting new employees up for success. HR must develop comprehensive onboarding programs that go beyond paperwork and logistics to include job-specific training, introductions to key colleagues and stakeholders, and an immersion in the company's culture and values. By providing a warm welcome and a solid foundation, HR can help new hires feel valued, prepared, and excited to contribute to the organization's mission.
2- Skills Training: As job requirements evolve and new technologies emerge, it's essential for employees to continuously update and expand their skill sets. HR can support this by offering a range of training opportunities, from in-person workshops and seminars to online courses and self-paced learning modules. By partnering with internal subject matter experts and external training providers, HR can help employees stay current in their fields and develop new competencies that benefit both the individual and the organization.
3- Leadership Development: Cultivating the next generation of leaders is a critical aspect of HR's role in organizational sustainability and success. This involves identifying high-potential employees, providing them with targeted leadership training and mentoring, and creating opportunities for them to take on stretch assignments and progressively more responsible roles. By investing in leadership development, HR can help ensure a strong pipeline of future leaders who are prepared to guide the organization through challenges and opportunities.
4- Coaching and Mentoring: In addition to formal training programs, HR can support employee development through coaching and mentoring initiatives. This may involve pairing junior employees with more experienced colleagues who can provide guidance, advice, and support as they navigate their careers. HR can also train managers on coaching techniques to help them develop and empower their team members on a day-to-day basis.
The benefits of effective training and development are numerous and far-reaching. Research has shown that organizations that invest in employee development tend to have higher levels of job satisfaction, productivity, and retention [5]. By prioritizing continuous learning and growth, HR can help create a culture of innovation, adaptability, and excellence.
Human Resources Information System (HRIS) Benefits
In today's data-driven world, technology plays an increasingly critical role in HR's ability to effectively manage the workforce. A Human Resources Information System (HRIS) is a software platform that centralizes and automates many of the administrative tasks associated with HR, from employee record-keeping to benefits administration to performance management. By implementing an HRIS, organizations can reap a wide range of benefits, including:
1- Increased Efficiency: An HRIS can streamline and automate many of the manual, time-consuming tasks that HR professionals must manage on a daily basis. For example, an HRIS can automatically track employee time and attendance, calculate payroll, and generate reports. This frees up HR staff to focus on more strategic, value-added activities such as employee engagement and talent development.
2- Improved Accuracy: By digitizing employee records and automating key processes, an HRIS can help reduce the risk of human error and ensure that data is accurate, up-to-date, and compliant with legal requirements. This is particularly important in areas such as benefits administration and tax reporting, where mistakes can be costly and time-consuming to correct.
3- Enhanced Self-Service: Many HRIS platforms offer employee self-service portals that allow workers to access and update their own information, such as contact details, beneficiaries, and direct deposit preferences. This not only empowers employees to take control of their own data but also reduces the administrative burden on HR staff.
4- Better Decision-Making: An HRIS can provide HR and organizational leaders with real-time data and analytics on key workforce metrics such as turnover rates, performance trends, and skills gaps. This information can be used to identify areas for improvement, make data-driven decisions, and develop targeted strategies for talent management and organizational growth.
5- Improved Compliance: An HRIS can help organizations stay compliant with the myriad of laws and regulations governing HR, from equal employment opportunity to data privacy to tax reporting. By automating compliance-related tasks and providing a centralized repository for employee records, an HRIS can help mitigate the risk of legal violations and penalties.
In my experience, implementing an HRIS has been a game-changer for HR departments. By leveraging technology to automate administrative tasks and provide real-time data insights, HR professionals can focus on what they do best: supporting and developing the organization's most valuable asset - its people.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, HR is indeed the heart of any organization, playing a critical role in shaping the workforce, culture, and ultimate success of the business. By mastering the core functions of human resources management, from legal compliance to talent acquisition to employee development, HR professionals can create a work environment that not only meets the needs of the organization but also empowers and inspires its people.
Some key takeaways from this comprehensive guide:
Legal compliance is the bedrock of all HR functions. Staying up-to-date on labor laws, anti-discrimination regulations, and health and safety requirements is essential for mitigating risk and creating a fair and equitable workplace.
The employee recruitment process is a multi-faceted endeavor that requires careful planning, execution, and evaluation. By crafting compelling job descriptions, sourcing diverse candidates, and conducting thorough interviews, HR can help find the right talent to drive the organization forward.
Performance management is an ongoing process that involves setting clear expectations, providing continuous feedback, conducting fair and meaningful evaluations, and recognizing and rewarding high performance.
Benefits administration is a key aspect of attracting and retaining top talent. By offering a comprehensive and competitive benefits package, including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, HR can help support employee well-being and work-life balance.
Effective employee relations techniques, such as active listening, conflict resolution, and employee engagement initiatives, are essential for creating a positive and productive work environment.
Training and development initiatives, from onboarding to skills training to leadership development, are critical for supporting continuous learning, adapting to change, and preparing the organization for future challenges and opportunities.
Implementing a Human Resources Information System (HRIS) can help streamline administrative tasks, improve data accuracy and security, enhance employee self-service, and provide valuable insights for data-driven decision-making.
As we look to the future of work, it's clear that HR will continue to play a vital role in shaping the workforce and driving organizational success. By staying abreast of emerging trends, leveraging technology, and prioritizing employee well-being and development, HR professionals can help their organizations navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
References:
[1] U.S. Department of Labor. (n.d.). Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Retrieved from https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/flsa
[2] U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. (n.d.). Title VII of the
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the core functions of Human Resources Management?
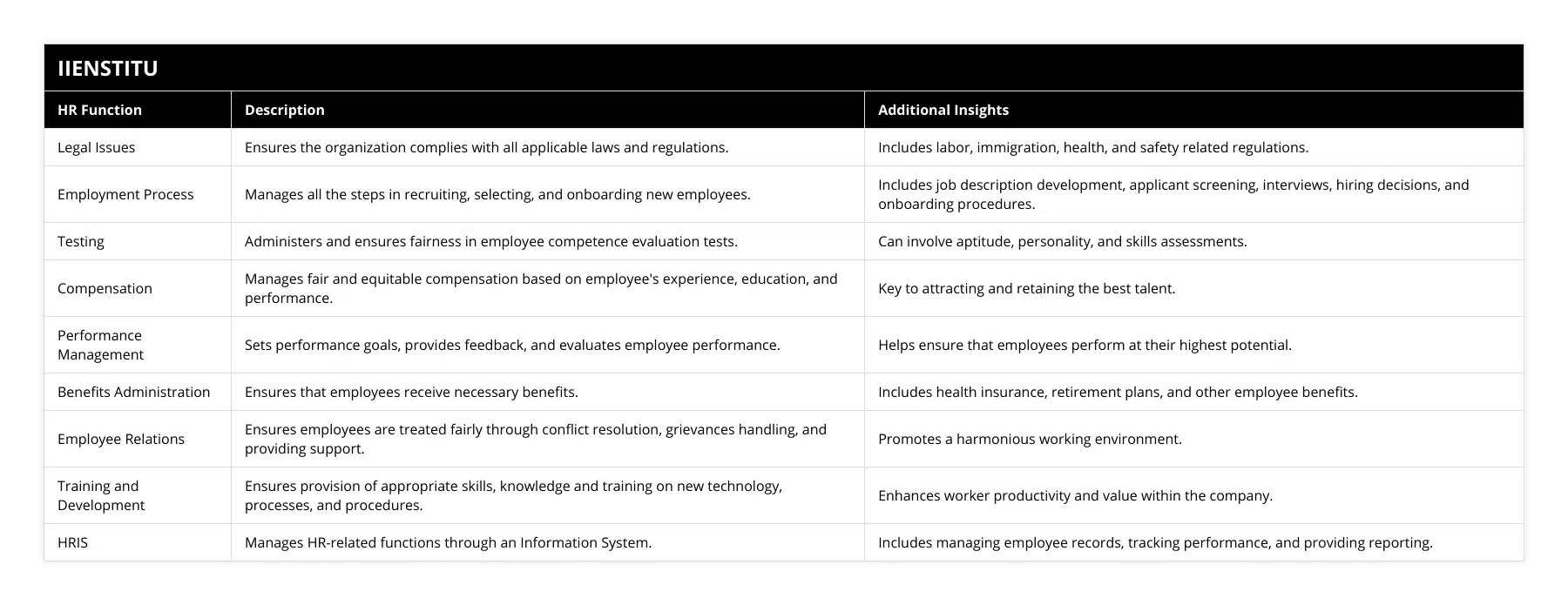
Human Resources Management (HRM) is an essential component of any business. It is the process of managing and optimizing human capital within an organization. HRM is responsible for the recruitment, Selection, and training of employees and for providing them with the necessary tools and resources to succeed. Additionally, HRM is responsible for ensuring a safe and productive work environment, providing competitive compensation and benefits, and managing employee performance.
Recruitment and Selection are identifying and selecting qualified candidates to fill vacant positions. This involves creating job descriptions, advertising for positions, screening resumes and applications, conducting interviews, and making hiring decisions. Additionally, HRM is responsible for onboarding and orienting new employees, providing them with the necessary information and resources to perform their job effectively.
Training and Development provide employees with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed in their roles. This includes providing them with the necessary tools, resources, and professional development opportunities. HRM is also responsible for creating and implementing employee development plans, assessing and evaluating employee performance, and providing feedback.
Employee Relations is the process of managing relationships between employees and management. This includes creating policies and procedures, addressing employee grievances and complaints, conducting regular performance reviews, and maintaining a positive work environment.
Compensation and Benefits provide employees competitive wages and benefits that align with the organization's goals and objectives. This includes providing competitive wages and salaries and offering benefits such as health insurance, vacation time, and retirement plans.
Finally, HRM is responsible for managing and optimizing the use of human capital within an organization. This involves creating and implementing recruitment, selection, and training strategies, as well as developing and implementing policies and procedures for employee relations, compensation and benefits, and performance management. HRM is responsible for ensuring the organization can maximize the performance and productivity of its employees while also providing them with the necessary tools and resources to be successful.
How can Human Resources Management help to ensure compliance with legal issues?
Human Resources Management (HRM) is an essential component of any business, as it focuses on the recruitment, management, and retention of a company’s workforce. HRM plays a critical role in ensuring compliance with legal issues. This article will discuss the various ways in which HRM can help businesses to ensure that they comply with legal issues.
The first way in which HRM can help to ensure compliance with legal issues is by implementing and maintaining an effective HR policy. A comprehensive HR policy should provide clear guidance on various legal issues related to employment law, such as minimum wage and overtime requirements and workplace safety and discrimination. Businesses can ensure that they adhere to local, state, and federal laws by having a clearly defined and documented HR policy.
Another way in which HRM can help to ensure compliance with legal issues is by conducting regular legal audits. A legal audit is an in-depth review of a business’s HR processes and procedures, ensuring compliance with all applicable laws. This can include reviewing employee contracts, job descriptions, recruitment and hiring practices, and employee handbooks. By conducting regular legal audits, businesses can identify any areas of non-compliance and take the necessary steps to rectify them.
Finally, HRM can help to ensure compliance with legal issues by providing ongoing training and guidance to employees. This can include providing information on relevant laws and regulations and guidance on how to handle specific legal issues. Through ongoing training and guidance, employees can be better informed and better equipped to handle any legal issues that may arise in the workplace.
In conclusion, HRM is vital in ensuring compliance with legal issues. By implementing and maintaining an effective HR policy, conducting regular legal audits, and providing ongoing training and guidance to employees, businesses can ensure that they comply with all applicable laws.

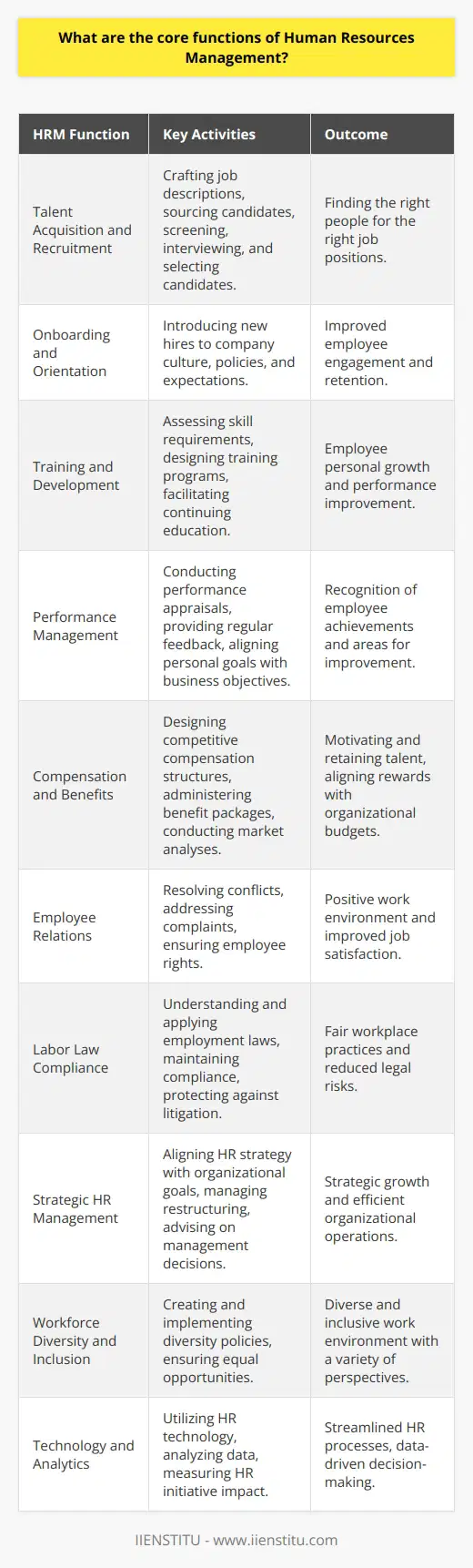
What strategies can be used to improve the effectiveness of the employment process?
The employment process is a critical aspect of any organization. It is essential to ensure that the right employees are chosen to join the organization and that the hiring process is effective and efficient. To improve the effectiveness of the employment process, several strategies can be implemented.
One important strategy is to create a comprehensive job description that outlines the key duties and responsibilities of the role for which the organization is hiring. This job description should be clear and concise and accurately reflect the organization’s needs and expectations for the role. Additionally, the job description should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and accurate.
Another strategy to improve the effectiveness of the employment process is to create a structured interview process. This should include a consistent set of questions tailored to the job position and the organization’s needs. This will help to ensure that the right person is chosen for the job and that the process is fair and unbiased.
In addition, it is essential to use various recruitment techniques to reach the widest possible pool of potential candidates. This can include online job postings, social media campaigns, and attending job fairs. Additionally, creating a positive and welcoming atmosphere for prospective employees is essential by providing clear information about the role and the organization and establishing a fair and open dialogue with potential candidates.
Finally, ensuring that the selection process is conducted fairly and objectively is essential. This includes ensuring that the selection criteria used to evaluate candidates are consistent and transparent. Additionally, it is important to utilize objective assessment methods, such as aptitude testing, to ensure that the most suitable candidates are chosen for the role.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can ensure that their employment process is effective and efficient. This will help to ensure that the right employees are chosen for the job and that the organization can recruit the best possible talent.
What are the key components of an effective human resource management system?
Key Components of Effective HRM Systems
Recruitment and Selection
Effective human resource management (HRM) systems must have robust recruitment and selection processes. These include determining job requirements, advertising positions, screening and shortlisting candidates, conducting interviews and assessments, and making final hiring decisions. This ensures that an organization attracts and hires the best talent to meet its workforce needs.
Training and Development
HRM systems must also facilitate employee training and development. This involves identifying skills gaps, planning and delivering training programs, and evaluating their effectiveness. By fostering continuous learning, HRM systems help employees enhance their skills and capabilities, which ultimately benefits the organization's performance.
Performance Management
Effective HRM systems are built on robust performance management mechanisms that aim to align employee performance with organizational goals. Performance management involves setting performance expectations, conducting regular performance reviews, providing feedback, and identifying needed improvements. This process works to drive employee engagement and productivity.
Reward and Recognition
Motivating employees is vital to maintaining high levels of productivity and job satisfaction. HRM systems must encompass reward and recognition components that acknowledge and compensate employees for their achievements and contributions to the organization. This can include a mix of monetary rewards, such as salary increments and bonuses, and non-monetary rewards, such as career growth opportunities or recognition programs.
Employee Relations
Effective HRM systems are underpinned by strong employee relations that enable proactive, open, and transparent communication between employees and management. This entails creating mechanisms for addressing employee grievances, managing workplace conflicts, and ensuring open dialogue to maintain a positive work culture.
Legal Compliance
An essential aspect of effective HRM systems is compliance with relevant labor laws and regulations. HRM systems must ensure that organizations adhere to legal requirements related to workforce management, such as employee contracts, discrimination policies, and workplace safety. This helps protect the organization from penalties, reputation damage, and potential legal disputes.
Workforce Planning
Lastly, HRM systems must encompass workforce planning to forecast the organization's future talent needs. This involves analyzing current and future labor market trends, identifying potential skill shortages, and formulating strategies to address these challenges. By engaging in workforce planning, HRM systems can help ensure that organizations have the right people, with the right skills, at the right time.
How can human resource management contribute to organizational success and employee well-being?
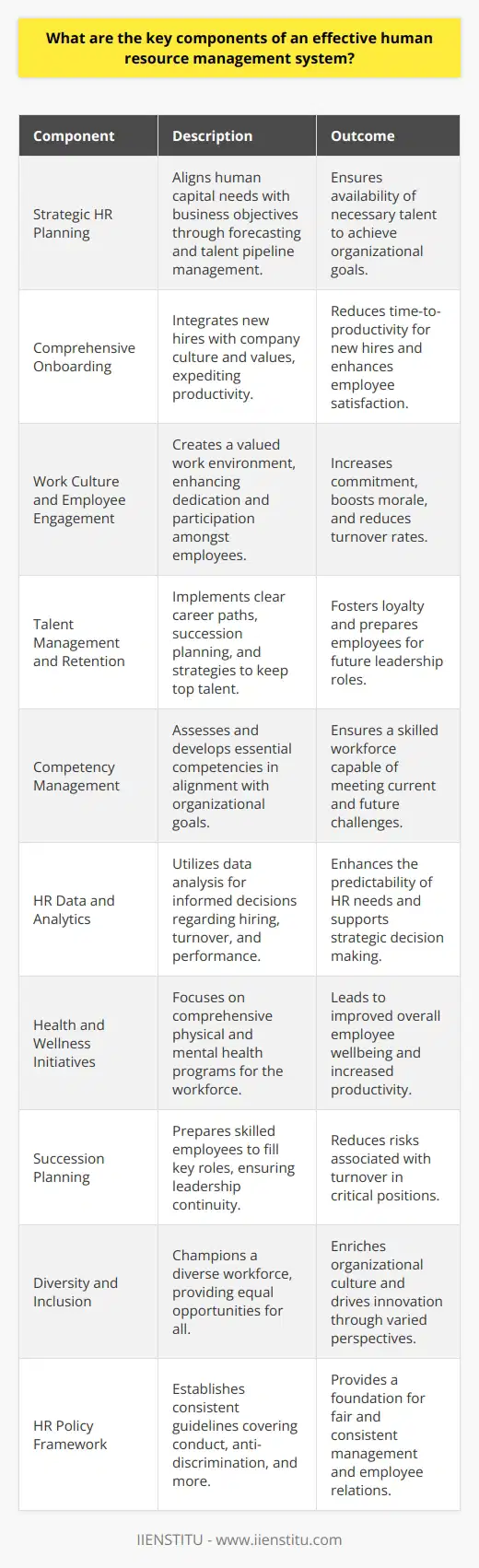
Effective Recruitment and Selection
To thrive in a competitive environment, organizations need to invest in effective human resource management, which drives both organizational success and employee well-being. One way HR management can contribute to these goals is through strategic recruitment and selection, ensuring that the right employees are brought into the organization. By identifying individuals who possess the necessary skills, knowledge, and cultural fit, HR departments can improve productivity and overall performance.
Developing Employee Skills
Another critical aspect of HR management is employee development. Customizing training and development programs allows the organization to address individual learning needs, helping employees reach their fullest potential. As a result, employees feel empowered and motivated, contributing to a positive work environment and higher staff retention rates. Furthermore, well-trained employees drive efficiency and innovation, setting the organization up for long-term success.
Appropriate Performance Management
Similarly, efficient performance management plays a pivotal role in promoting organizational success and employee well-being. Properly conducted employee performance evaluations can identify individual strengths and weaknesses, setting clear objectives for each employee. Implementing a feedback-driven culture fosters continuous improvement, which ultimately enhances productivity and overall efficiency. Moreover, recognizing and rewarding employees for their achievements promotes employee satisfaction and loyalty.
Promoting Work-Life Balance
Lastly, HR management can play a crucial role in addressing employee well-being by advocating for a healthy work-life balance. By encouraging employees to take time off, adopt flexible work arrangements, or use family-friendly policies, organizations can help reduce stress and prevent burnout. Employees who successfully maintain their work-life balance are more likely to be engaged, productive, and fulfilled in both their personal and professional lives.
In conclusion, human resource management significantly contributes to organizational success and employee well-being through strategic recruitment, continuous employee development, constructive performance management, and promoting work-life balance. By prioritizing employees' needs and implementing effective HR strategies, organizations can secure a competitive edge and create a fulfilling work environment for their employees.
What does the recruitment and selection process entail within human resource development?
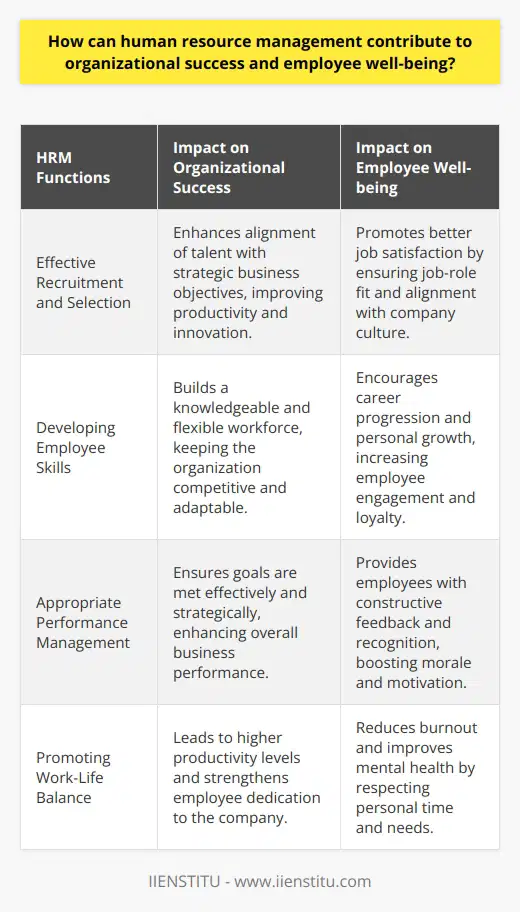
**Understanding Recruitment and Selection**
The recruitment and selection process in human resource development involves a series of systematic steps aimed at attracting, evaluating, and hiring the most suitable candidates for a job. This process begins with identifying the need for new employees and defining the job requirements, followed by advertising the vacancies, attracting and screening potential candidates, and eventually employing the most qualified individuals.
**Importance of Job Analysis**
A crucial element in recruitment and selection is job analysis, which allows human resource professionals to clearly outline the required skills, knowledge, and qualifications for a particular job. This information is vital in creating accurate job descriptions and specifications, ultimately enabling recruiters to identify the ideal candidates for a position.
**Attracting and Screening Candidates**
Attracting suitable candidates is achieved through various methods, including job postings, career fairs, online platforms, and networking events. This ensures a diverse pool of potential employees to choose from. Once applicants express interest in the position, their applications are screened based on predetermined criteria. This may include evaluating resumes, cover letters, and assessment tests to shortlist candidates who possess the desired qualifications.
**Selection Techniques**
Human resource professionals employ various selection techniques to further assess shortlisted candidates. Interviews form a crucial part of the process, providing an opportunity for both candidate and employer to gauge suitability and fit for the position. Additional methods include aptitude tests, psychometric assessments, and simulation exercises, which provide deeper insights into a candidate’s capabilities.
**Finalizing the Process**
After completing the evaluation process, the most suitable candidate is selected, and a job offer is extended. This involves negotiating the terms and conditions of employment, such as salary, benefits, and starting date. Upon acceptance, the candidate is integrated into the organization through a structured onboarding process, successfully concluding the recruitment and selection process.
In summary, the recruitment and selection process within human resource development is a comprehensive and strategic endeavor. It encompasses identifying job requirements, attracting and screening applicants, employing various selection methods, and ultimately hiring and integrating the best-suited candidates. This process not only ensures the acquisition of top talent but also contributes to the overall success and growth of an organization.
What are the essential skills and competencies required for effective human resource management?
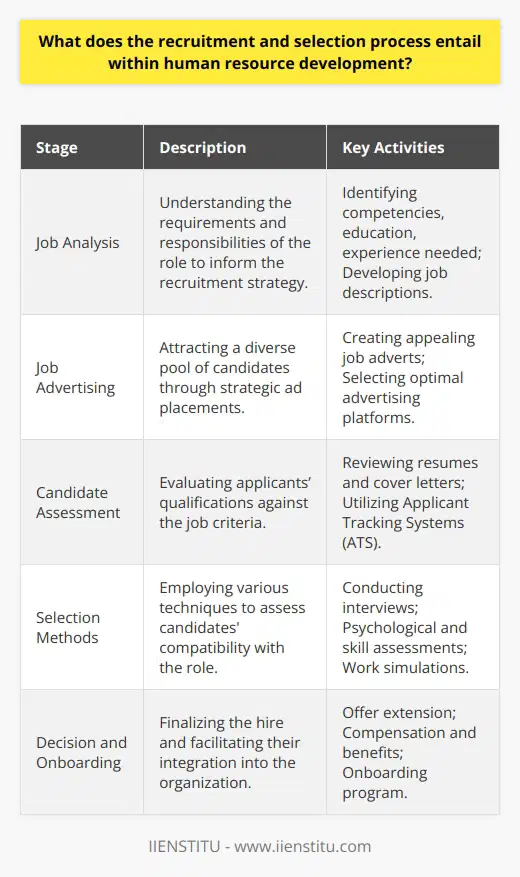
Core Competencies for HR Management
Effective human resource management requires a diverse range of skills and competencies. These essential abilities allow HR professionals to design and implement strategies that promote the growth and success of employees and organizations. In this paragraph, we discuss five key competencies necessary for proficient HR management: communication, emotional intelligence, organizational skills, analytical thinking, and ethical conduct.
Communication Skills
First and foremost, HR managers must possess strong communication skills, both written and oral. These abilities are essential for conveying complex ideas, policies, and procedures to various stakeholders. Also, effective communication helps in conflict resolution, performance management, and fostering positive workplace relationships.
Emotional Intelligence
Another indispensable competency is emotional intelligence, which refers to the ability to understand, manage, and regulate one's emotions, as well as to empathize with others. HR professionals must empathize with employees' concerns, challenges, and needs and assist them in navigating their professional development while ensuring workplace harmony.
Organizational Skills
HR managers must excel at organizing resources, time, and tasks. Strong organizational skills enable HR professionals to manage multiple projects simultaneously, ensuring effective implementation of programs and policies within the organization. Additionally, these skills help HR practitioners to prioritize goals and manage their workload efficiently.
Analytical Thinking
Effective HR management hinges on the ability to think critically and analytically about organizational issues and challenges. HR professionals must gather and interpret data to develop evidence-based solutions, assess the effectiveness of HR initiatives, and perform relevant analyses for strategic decision-making.
Ethical Conduct
Finally, ethical conduct is of paramount importance for HR managers, as they are responsible for upholding the values and integrity of the organization. HR professionals must ensure compliance with laws and regulations, adhere to organizational values and norms, and act as role models for ethical behavior in the workplace.
In summary, the essential skills and competencies required for effective human resource management include communication, emotional intelligence, organizational skills, analytical thinking, and ethical conduct. With these abilities, HR professionals can contribute significantly to employee well-being, organizational performance, and overall business success.
How does human resource development contribute to the overall organizational goals and objectives?
**Concept of Human Resource Development**
Human resource development (HRD) plays a critical role in helping organizations achieve their goals and objectives by systematically investing in the growth and development of employees. This dimension of human resource management seeks to foster a competent and empowered workforce capable of driving business success.
**Aligning HRD with Organizational Goals**
Organizations typically establish objectives and targets to guide their strategic plans and performance measurement. By integrating HRD initiatives with these goals, organizations ensure that their employees are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to contribute to organizational success. This alignment not only focuses on current needs but also anticipates future requirements to maintain a competitive edge.
**Skill Development and Retention**
One of the main contributions of HRD to organizational goals is through skill development. By offering training and development programs, organizations can enhance the technical and soft skills of their employees, thereby increasing their effectiveness and productivity. Moreover, continuous learning and development opportunities help organizations retain their best talent, reducing turnover rates and associated costs.
**Promoting Collaboration and Teamwork**
Collaboration and teamwork are essential for achieving organizational goals, particularly in today's dynamic business environment. HRD fosters a spirit of cooperation among employees by implementing team-building activities and promoting the sharing of knowledge and best practices. This collaborative culture not only enhances individual performance but also synergizes diverse skills towards overall organizational success.
**Leadership Development and Succession Planning**
HRD plays a pivotal role in identifying and developing the next generation of leaders, thereby ensuring the organization's long-term sustainability. By providing leadership training and coaching, HRD nurtures the skills of potential leaders and prepares them to assume higher responsibilities. Furthermore, effective succession planning contributes to organizational stability and continuity during management transitions.
**Driving Organizational Change and Innovation**
In a rapidly evolving business landscape, organizational agility and adaptability are paramount. HRD supports these qualities by fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. By encouraging employees to think creatively and challenge the status quo, HRD drives transformative change, which in turn, contributes to the achievement of strategic goals and objectives.
In conclusion, human resource development plays a vital role in helping organizations attain their objectives by building a skilled, competent, and motivated workforce. Through skill development, leadership training, innovative thinking, and collaboration, HRD supports and empowers employees to excel in their roles and propel the organization towards success.
What role does human resource management play in promoting diversity and inclusion within the workplace?
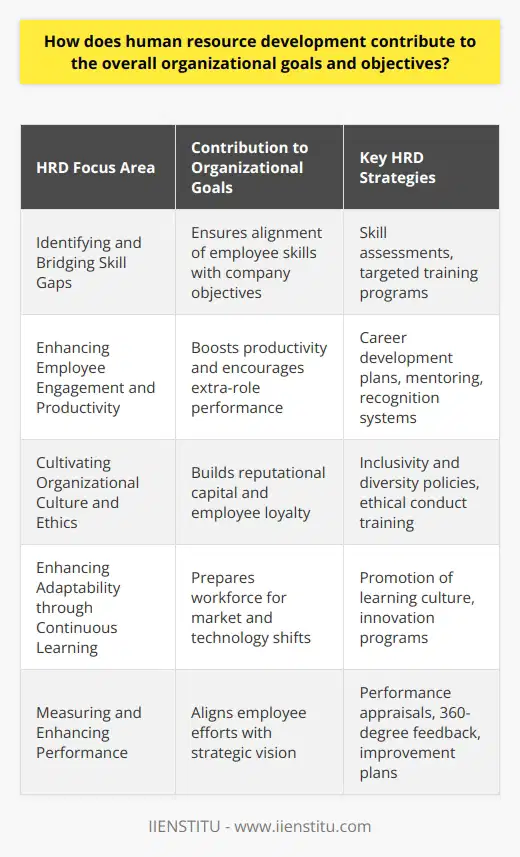
Role of Human Resource Management
Human resource management (HRM) plays a critical role in fostering diversity and inclusion within the workplace. Primarily, HRM is responsible for developing and implementing policies that promote equal opportunity, prohibit discrimination, and create a welcoming environment for all employees.
Implementing Inclusive Recruitment
One key component of HRM's role in promoting diversity and inclusion is through inclusive recruitment practices. This includes designing job descriptions that are free from bias and focused on essential skills, while also using diverse advertising strategies to attract individuals from varied backgrounds.
Providing Unbiased Training
Additionally, HRM ensures that staff receive access to unbiased training and development opportunities. These programs should be structured around equal opportunity policies and designed to challenge assumptions, promote understanding, and develop cultural competence among employees.
Handling Conflicts Appropriately
HRM is also tasked with managing workplace conflicts related to diversity and inclusion, ensuring that such incidents are investigated promptly and fairly. They must establish clear channels for reporting incidents and work closely with leadership to develop solutions that resolve issues effectively and prevent further harm.
Promoting Inclusive Leadership
Moreover, HRM is responsible for promoting inclusive leadership by encouraging diverse representation in decision-making roles. This entails advocating for equal opportunities in management and leadership positions, as well as creating a culture in which diversity of thought is valued and different perspectives are respected.
Monitoring Progress
Lastly, HRM plays an essential role in monitoring the progress of diversity and inclusion initiatives by gathering data, tracking metrics, and evaluating the overall impact of these efforts. This information can be used to identify areas needing improvement and inform the design of future initiatives to promote an inclusive workplace.
In conclusion, human resource management is indispensable in promoting diversity and inclusion within organizations through activities such as developing policies, managing recruitment processes, providing unbiased training, handling workplace conflicts, promoting inclusive leadership, and monitoring progress. By effectively fulfilling these functions, HRM helps create work environments that are both diverse and inclusive, benefiting individuals and organizations alike.
What are the primary theories and approaches that guide human resource management practices?
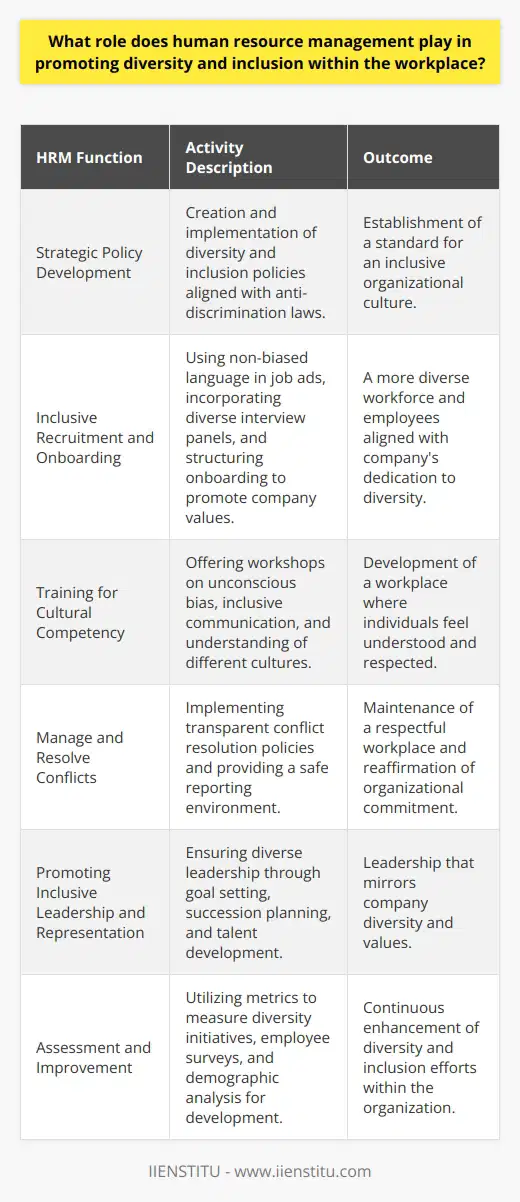
Theoretical Foundations
Human Resource Management (HRM) stands on several primary theories. The contingency theory is one of the key pillars. It proposes that HRM should adapt strategies according to the organization's environment and resources. Therefore, it moderates the strategy's success in each unique situation.
Resource-Based View
The Resource-Based View (RBV) is another prevailing theory. It asserts that effective management of a firm’s human resources is key to gaining competitive advantage. RBV focuses on mobilizing individual employee strengths, skills, and knowledge for organizational growth.
Behavioral Perspective
Furthermore, the behavioral perspective offers practical insights into HRM. It emphasizes understanding workers' perceptions, motivations, attitudes, and behaviors. This theory asserts that human behavior impacts an organization's performance and productivity.
Strategic HRM Perspective
Strategic HRM Approach acts as a bridge between top management goals and employees' daily activities. It underpins the alignment of HR practices with strategic objectives to foster overall organizational success.
Human Relations Approach
Another important perspective is the human relations approach. This approach underscores the importance of employee's interpersonal relations. It propagates the idea that sound relationships can drive employee productivity and commitment.
Finally, the Systems Approach is another critical lens. It appraises the organization as a whole, comprising of interdependent subsystems, including the HRM. This theory helps HRM in understanding how changes in one department might impact others.
Collectively, these theories and approaches guide HRM decisions, fostering best practices and ultimately driving the goals of an organization. These insights from different perspectives ensure a comprehensive approach to effective HRM.
How do human resource development initiatives affect employee retention and engagement?
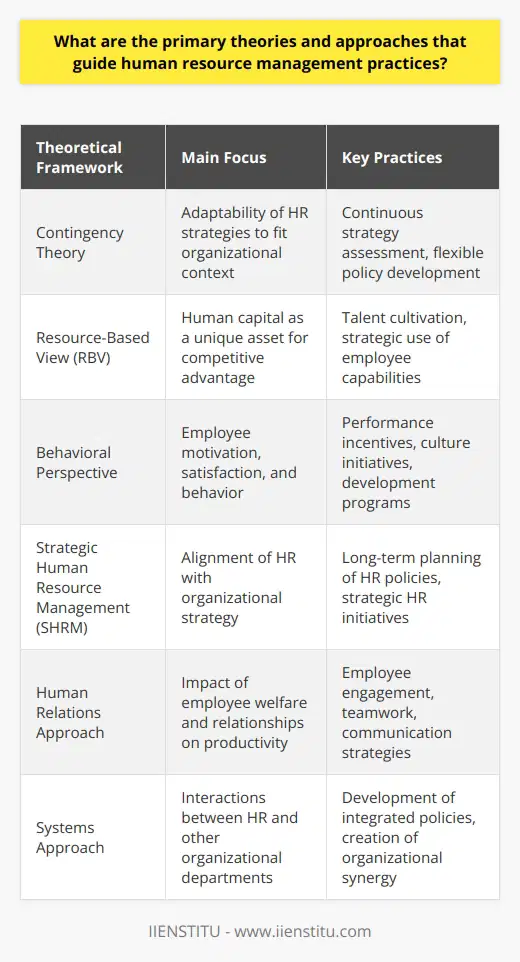
Human Resource Development Influence on Employee Retention
Human resource development (HRD) initiatives significantly influence employee retention. When organizations invest in HRD, they illustrate a commitment to their workforce's growth and progression. Such initiatives may include continuous learning programs, employee skill enhancement, or leadership programs. Employees tend to stay longer in organizations that invest in their career growth.
Role of HRD in Employee Engagement
HRD initiatives also play a pivotal role in employee engagement. Training and development programs foster a sense of belonging and commitment among employees. They feel valued, leading to increased engagement. Furthermore, development opportunities foster a culture of innovation, encouraging employees to contribute positively to an organization's growth.
The Impact of Competitive Compensation
Compensation is another HRD initiative with a substantial impact. Competitive salary packages and benefits retain top talent. Employees feel rewarded for their efforts and are thereby more likely to stay. Moreover, a well-structured compensation scheme promotes employee satisfaction, fostering a healthy work culture.
Supportive Work Environment and Career Development
A supportive work environment established through HRD initiatives enhances employee retention and engagement. Safe, inclusive, and flexible work conditions empower employees, ensuring their optimum productivity. Practices like work-life balance, mutual respect, and recognition are crucial.
HRD initiatives related to career development can also foster loyalty. Programs that provide clear career paths and progression opportunities can help retain employees. They not only promote job satisfaction but also inspire employees to embrace new challenges.
In conclusion, HRD initiatives significantly influence employee retention and engagement. They create an environment where employees feel valued and see opportunities for growth and development. Therefore, organizations should consider investing in HRD intiatives as a strategy to maintain a productive and loyal workforce.
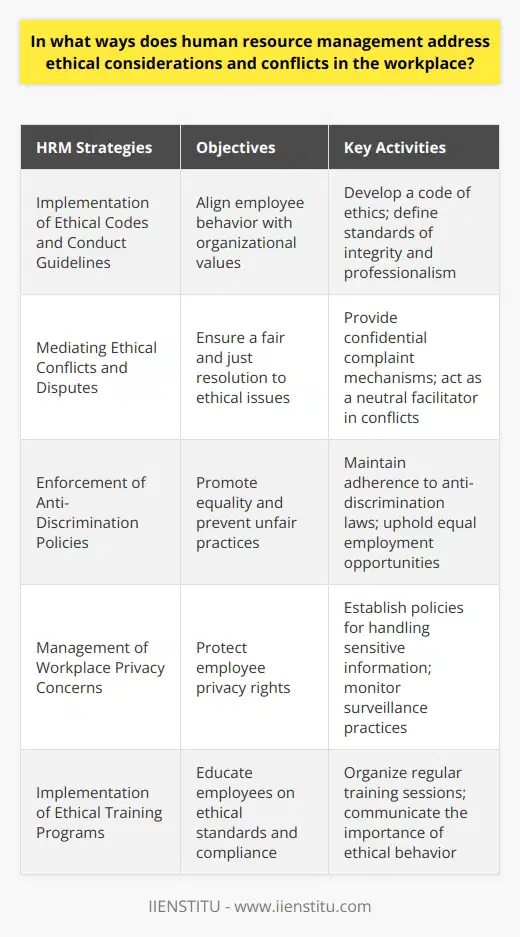
In what ways does human resource management address ethical considerations and conflicts in the workplace?
Ethical Code Implementation
Human resource management (HRM) promotes ethical conduct in the workplace in several ways. Firstly, they implement guidelines or codes of conduct. These establish workplace expectations that align with the organization's values. Employees must abide by these guidelines, promoting a culture of ethics and professionalism.
Addressing Ethical Conflict
Additionally, HRM mediates disputes among employees, maintaining neutrality while ensuring all parties receive fair treatment. Providing a safe, confidential space allows for honest discourse. This approach promotes resolution and upholds ethical standards, minimizing conflicts.
Discrimination Prevention
Moreover, HRM plays a critical role in barring discriminatory practices in recruitment. They ensure fair hiring processes, fostering diversity, e.g., by law, they may not discriminate against any applicant based on age, sex, or race.
Workplace Privacy
Also, HRM handles employee privacy, a crucial aspect of workplace ethics. They oversee issues like surveillance, confidentiality of employee records, and data protection. By doing so, they respect and protect employees' privacy rights, strengthening trust in the organization.
Training Programs
Lastly, HRM conducts ethical training programs. These sessions sensitize employees to expected ethical behaviors, repercussions for non-compliance, and their rights within the organization. Consequently, employees become responsible for maintaining a fair, ethical, and respectful work environment.
In conclusion, HRM tackles ethical considerations and conflicts in the workplace through implementing ethical codes, resolving conflicts, promoting fair hiring processes, protecting employee privacy, and conducting ethical training sessions. Ultimately, the goal is to foster an environment characterized by respect, fairness, and integrity.