You know, I still remember the first time I walked into a bustling warehouse during my early days in supply chain management. The sheer scale of operations—the forklifts buzzing around, towering stacks of pallets, and the synchronized dance of workers—was nothing short of mesmerizing. It was in that moment I realized how critical efficient logistics are in getting products from manufacturers to customers. Over the years, I've come to appreciate the intricate web of supply chain activities that collectively ensure products reach their destinations safely and efficiently.
Advantages of Supply Chain Visibility
Utilizing Technology for Efficient Logistics
Implementing Strategies for Maximum Efficiency
Navigating the Complexities of Outbound Logistics
The Vital Role of Supply Chain Visibility
One of the biggest lessons I've learned is that visibility is the cornerstone of a successful supply chain. Without it, you're essentially flying blind. I remember a time when a lack of transparency led to a major hiccup in our operations. A shipment of essential components was delayed, and without real-time data, we couldn't provide accurate updates to our anxious customers. That experience underscored the importance of supply chain visibility.
Advantages of Enhanced Visibility:
Proactive Problem-Solving: Identifying and addressing bottlenecks before they escalate.
Improved Customer Satisfaction: Providing accurate delivery estimates boosts trust.
Optimized Inventory Levels: Balancing stock to meet demand without overstocking.
Streamlined Operations: Coordinating between different supply and chain partners effectively.
By investing in visibility tools, companies can monitor their supply chain mgmt in real-time, leading to more informed decisions and a smoother flow of goods.
Embracing Technology for Efficient Logistics
Technology has been a game-changer in the realm of logistics. Back in the day, tracking shipments involved heaps of paperwork and endless phone calls. Now, innovative solutions have revolutionized how we manage the supply chain.
Modern Tools Making a Difference:
1- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Implementing a robust warehouse management system allows for efficient handling of inventory, tracking goods from arrival to dispatch.
2- Inventory Management Software: These tools help in maintaining optimal stock levels, reducing holding costs and preventing stockouts.
3- GPS and Telematics: Utilizing GPS in logistics offers real-time tracking of shipments, enhancing lead time accuracy.
4- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms predict demand patterns, optimize routes, and manage scheduling.
Logistics Mgmt: System Approach to Transp, Route Plan, Mode Sel, & Vehicle Scheduling
An In-depth Study of Lean Logistics: Excellence in Supply Chains
Key Strategies and Principles for Effective Logistics Management
5- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices provide data on cargo conditions, ensuring products like perishables are transported under ideal conditions.
By leveraging these technologies, businesses can transform their logistics from a cost center into a competitive advantage.
Implementing Strategies for Maximum Efficiency
Efficiency doesn't happen by chance; it's the result of deliberate strategies and continuous improvement.
Planning for Volume Changes
Markets are unpredictable. A sudden surge in demand can catch businesses off guard, leading to delays and dissatisfied customers. To mitigate this:
Demand Forecasting: Use historical data and market analysis to predict future demand.
Flexible Supply Chains: Build adaptability into your supply and chain management to respond swiftly to market changes.
Scalable Operations: Ensure your systems and processes can scale up or down as needed.
Outsourcing to Experts
Sometimes, the most efficient move is to offload challenging tasks to third-party logistics providers. Partnering with specialized logistics companies can provide:
Expertise and Resources: Access to advanced technologies and experienced personnel.
Cost Savings: Reducing capital expenditure on logistics infrastructure.
Optimizing outbound distribution logistics can create a competitive edge and stay ahead of the rest.
Focus on Core Competencies: Allowing you to concentrate on what you do best while experts handle the logistics.
Back when our company decided to outsource certain logistics functions, we saw a significant improvement in delivery times and customer satisfaction.
Ethical Considerations in Supply Chain Management
In today's world, customers are more conscious about the ethical implications of their purchases. Addressing ethical dilemmas in supply chain management is not just a moral obligation but a business imperative.
Navigating Ethical Challenges
I once faced an ethical dilemma when we discovered a supplier was engaging in unfair labor practices. It posed a significant risk to our company's reputation.
Steps to Address Ethical Issues:
1- Conduct Thorough Audits: Regularly assess your suppliers and partners for compliance.
2- Establish a Code of Conduct: Set clear expectations regarding ethical standards.
3- Engage in Open Communication: Foster transparency with all stakeholders.
4- Provide Training: Educate your team on recognizing and addressing ethical issues.
By taking these steps, companies can ensure their supply chain management management aligns with their values and customer expectations.
Personal Experiences Shaping My Understanding
Over the years, several experiences have shaped my perspective on logistics and supply chain mgmt.
The Importance of Distribution Centers
I recall visiting one of our distribution centers during a particularly hectic holiday season. The energy was electric, but so was the potential for bottlenecks. By implementing an advanced warehouse management system, we streamlined operations, reducing errors and improving throughput.
Key Takeaways:
Automation Enhances Efficiency: Automated systems reduce manual errors.
Layout Matters: Organizing the warehouse for optimal flow minimizes delays.
Employee Training: Well-trained staff are crucial for smooth operations.
Overcoming Inventory Challenges
In one instance, poor inventory management led to overstocking, tying up capital that could have been better utilized. We learned the hard way the importance of balancing inventory levels.
Strategies Implemented:
Just-In-Time Inventory: Receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process.
ABC Analysis: Prioritizing inventory management based on the significance of items.
Regular Audits: Ensuring inventory records match physical stock.
The Human Element in Logistics
While technology and systems are vital, the human element remains at the heart of logistics.
Building Strong Relationships
Developing solid relationships with suppliers, partners, and even competitors can lead to collaborative opportunities.
Open Communication: Promotes trust and swift resolution of issues.
Shared Goals: Aligning objectives encourages cooperation.
Networking: Expanding your professional circle can open doors to new solutions.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The logistics landscape is ever-changing. Staying ahead requires a commitment to learning and flexibility.
Attend Industry Conferences: Keep abreast of the latest trends and technologies.
Professional Development: Invest in training and certifications.
Embrace Change: Be willing to adapt processes for better outcomes.
The Future of Supply Chain and Logistics
The future holds exciting possibilities for supply and chain operations.
Emerging Trends
Sustainability Focus: Eco-friendly practices are becoming standard.
Blockchain Technology: Enhances transparency and security in transactions.
Artificial Intelligence: Predictive analytics for demand forecasting and route optimization.
Preparing for Tomorrow
To stay competitive:
1- Adopt Innovative Technologies: Don't be left behind as the industry evolves.
2- Invest in People: Equip your team with the skills needed for the future.
3- Stay Customer-Centric: Ultimately, meeting customer needs is paramount.
Conclusion
Optimizing outbound distribution logistics is more than just an operational necessity—it's a strategic advantage. By enhancing supply chain visibility, leveraging technology, and addressing ethical considerations, businesses can achieve greater efficiency and customer satisfaction. Reflecting on my journey, the blend of technology, strategy, and human insight has been key to overcoming challenges and driving success.
By focusing on these areas, companies can not only create a competitive edge but also contribute positively to the industry and society at large. After all, a well-managed supply chain is the backbone of any successful business.
References
1- Chopra, S., & Meindl, P. (2019). Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation (7th ed.). Pearson.
2- Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & Supply Chain Management (5th ed.). Pearson UK.
3- Grant, D. B., Trautrims, A., & Wong, C. Y. (2017). Sustainable Logistics and Supply Chain Management (2nd ed.). Kogan Page Publishers.
4- Harrison, A., & Van Hoek, R. (2011). Logistics Management and Strategy: Competing Through the Supply Chain (4th ed.). Pearson Education Limited.
Note: The above references are based on widely recognized publications in the field of supply chain management and logistics.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can outbound distribution logistics enhance customer satisfaction?
Due to the current surge in online shopping, the logistics of outbound distribution have become more critical than ever. Outbound distribution involves the movement of goods to customers and the customer service associated with the shipment. To ensure customer satisfaction, outbound distribution procedures must be highly efficient and flexible.
The digitalization of the supply chain has made it easier for companies to track shipments, help customers with inquiries, and plan their outbound distribution logistics. Data management technology has enabled the ability to aggregate data from multiple sources and develop algorithms for transportation planning. Advanced analytics allow the creation of a reliable demand forecast and help the supply chain to plan shipments more cost-effectively and efficiently.
It is essential to make sure that customer satisfaction is the priority when it comes to outbound distribution logistics. To ensure customer satisfaction, companies should provide accurate delivery information and offer options for expedited delivery when appropriate. They should also provide real-time tracking information and be available to answer customer questions or concerns. It is also essential to provide personalized customer service by offering various delivery options that meet the customer's needs.
In addition, developing a reliable and efficient system for order processing and shipment is essential. An excellent outbound distribution logistics system should offer the ability to consolidate orders, optimize loads, and automate paperwork. In addition, the system should be able to generate accurate invoices and provide customers with an easy and secure way to pay for their orders.
Finally, it is essential to review the effectiveness of outbound distribution logistics regularly. Companies should measure customer satisfaction through surveys and online reviews and use the feedback to make improvements. This feedback can then be used to ensure that customer service remains top-notch. That outbound distribution is as efficient as possible.
In conclusion, outbound distribution logistics can and should be optimized to ensure customer satisfaction. Advanced technologies can provide the data and analytics needed to plan shipments cost-effectively and efficiently. Companies should also offer real-time tracking, personalized customer service, and reliable and efficient order processing and shipment systems. Lastly, companies should measure customer satisfaction and use feedback to make improvements. Together, these steps can help ensure customers have a positive experience and remain satisfied.
What are the benefits of implementing an effective outbound distribution logistics system?
An effective outbound distribution logistics system is invaluable for businesses to coordinate and manage to transport goods to their customers efficiently. The benefits of such a system encompass inter-organizational cost savings, improved customer service, and an overall reduction in communication complexity.
To begin with, one main benefit of having an effective outbound distribution logistics system in place is that it cuts down businesses’ expenditures. For instance, by having the necessary procedures to select an appropriate route for specific goods, companies can avoid going through traffic congestions or detours, reducing transportation time and thus cutting operational costs. Additionally, an effective outbound distribution system can help businesses to optimize the route for their outbound shipments due to having access to real-time information. This reduces operational costs such as fuel and labor, increasing their cost-saving potential.
Furthermore, an effective outbound distribution logistics system reduces the complexity of operations. By utilizing an efficient outbound delivery system with advanced tracking and communication capabilities, companies can keep track of their outbound shipments dynamically with greater accuracy, decreasing communication complexity. Furthermore, with suitable tracking systems, businesses can ensure that their outbound shipments are delivered to the right customers quickly and, most importantly, efficiently, improving customer service significantly.
In conclusion, implementing an effective outbound distribution logistics system can bring numerous benefits to any business which requires outbound transportation. Not only does it save inter-organizational money, but it also improves customer service and reduces communication complexity. This, in turn, can translate into higher customer satisfaction and increased business revenues.
What strategies can be used to ensure efficient and cost-effective outbound distribution logistics?
Outbound distribution logistics can play a critical role in the success of e-commerce businesses, as it involves transporting and delivering goods and services to customers. To maximize efficiency and cost-effectiveness, there are several strategies that companies can utilize.
First and foremost, businesses must select the correct shipping partner. This means considering delivery speed, cost, and service quality variables. In addition, evaluating packages from various shipping partners is essential to ensure the best possible outcome for customers and the business.
Companies should also consider the use of technology to streamline outbound distribution logistics. Implementing automated processes and solutions can reduce the time, effort, and resources required to complete logistical tasks and significantly enhance accuracy. For example, a computerized route planning system can ensure goods are delivered most efficiently, helping to reduce costs and improve customer service. In addition, automatic invoice processing and inventory tracking systems can decrease the likelihood of delivery issues.
When managing inventory, an effective strategy is implementing an inventory control system. This allows businesses to closely monitor stock levels, ensuring that goods aren’t overstocked or out of stock. This helps to reduce wastage and inventory handling costs. In addition, businesses should consider implementing a minimum stock level, which would trigger automatic restocking orders when the level drops below it.
Finally, businesses can maximize efficiency and cost-effectiveness by creating an accurate delivery schedule. This includes ensuring that goods are shipped in time so as not to delay delivery. By doing so, businesses can avoid additional charges and customer dissatisfaction due to delayed shipment.
In conclusion, several strategies can be utilized to ensure efficient and cost-effective outbound distribution logistics. For example, implementing automated solutions and technology, selecting the correct shipping partner, using an effective inventory control system, and creating an accurate delivery schedule can all help to optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
What is the role of outbound logistics in ensuring efficient product distribution management?
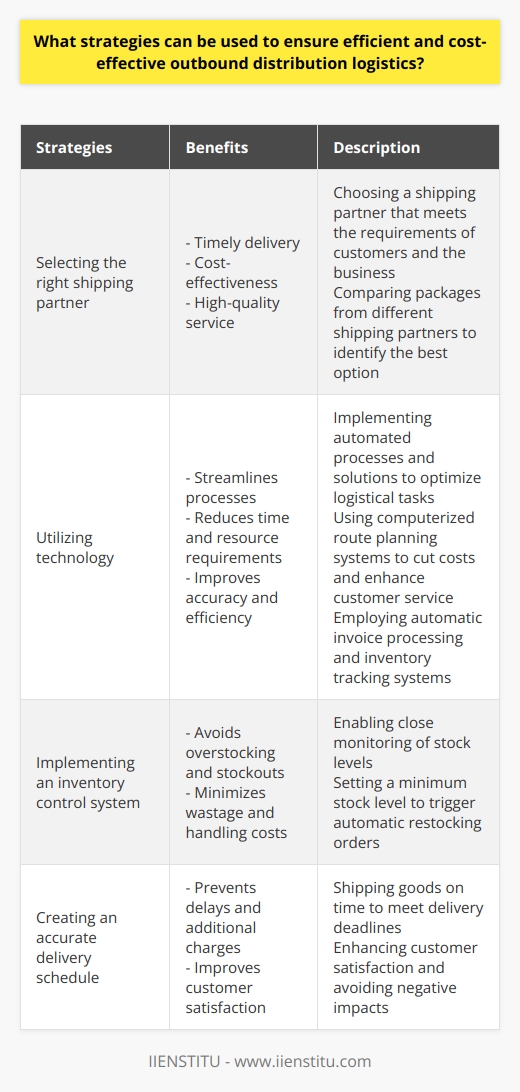
Role of Outbound Logistics in Distribution Management
Impact on Customer Satisfaction
Outbound logistics plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient product distribution management by directly impacting customer satisfaction. When a company's goods are efficiently and accurately managed through various distribution channels, they reach customers on time and in optimum conditions, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Optimizing Transport Operations
Effective outbound logistics management is essential in optimizing transportation operations. It involves selecting appropriate shipping options, routes, and carriers, while also minimizing costs and ensuring timely deliveries. This helps businesses to improve their distribution efficiency, reduce operational expenses, and provide a competitive advantage in the market.
Inventory Management and Warehousing
Another vital aspect of outbound logistics in distribution management is inventory management and warehousing. Companies must maintain appropriate stock levels, while also ensuring swift and accurate movement of goods from warehouses to distribution centers. This enables businesses to meet fluctuating demand requirements and reduce excess inventory holding costs, ultimately improving overall distribution efficiency.
Coordination with Distribution Partners
Efficient outbound logistics for distribution management demands seamless coordination among all supply chain partners, including suppliers, distributors, and retailers. Sharing relevant information and real-time data ensures streamlined processes and allows for quick adaptations to any changes in market conditions or demand patterns. As a result, businesses can better fulfill customer expectations and minimize disruptions in the distribution process.
Mitigating Risk Factors
Outbound logistics also plays a critical role in mitigating risks associated with product distribution. Supply chain disruptions, such as natural disasters or global pandemics, can significantly impact distribution operations. However, a well-managed outbound logistics system can help businesses identify risk factors and adopt appropriate measures in advance, ensuring the continuous flow of products and minimum impact on customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, outbound logistics is a vital element in ensuring efficient product distribution management. It directly affects customer satisfaction and loyalty by optimizing transport operations, facilitating inventory management, enabling seamless coordination with distribution partners, and mitigating risk factors that could impact distribution processes. Effective outbound logistics management allows businesses to adapt to ever-changing market dynamics and maintain their competitive edge.
How can organizations optimize their outbound logistics processes for effective product distribution?
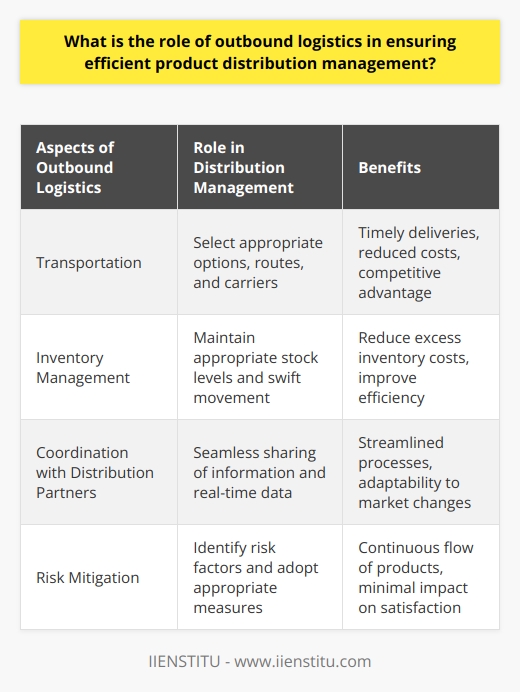
Outbound Logistics Optimization
Implementing Efficient Transportation Systems
Organizations can optimize their outbound logistics processes for effective product distribution by implementing efficient transportation systems. They can select the most suitable transportation modes, such as road, rail, air, or sea, based on factors like cost, speed, reliability, and environmental impact. Streamlining transportation operations and route planning can help reduce delivery times and fuel costs, consequently improving customer satisfaction.
Warehouse Management and Product Handling
Effective warehouse management and product handling are other crucial factors in outbound logistics optimization. Ensuring proper storage facilities, accurate inventory management, and efficient order picking systems can minimize errors and delays in the product dispatch process. Additionally, automating warehouse operations where possible can significantly enhance productivity and reduce labor costs, ultimately leading to more effective distribution.
Collaboration with Supply Chain Partners
Collaboration with supply chain partners, such as suppliers, freight carriers, and retailers, is essential for optimizing outbound logistics processes. By establishing open communication channels, organizations can better coordinate their supply chain activities and promptly respond to changing market demands. Sharing relevant data, such as product availability, transport capacity, and delivery schedules, can further improve supply chain efficiency and minimize disruptions.
Adopting Advanced Technologies
Organizations can also leverage advanced technologies, such as data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), to optimize their outbound logistics processes. These technologies can provide real-time visibility into the entire distribution process, enabling organizations to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, thereby allowing them to make informed decisions. For example, they can use predictive analytics to forecast demand accurately and effectively plan their inventory and transportation requirements.
Continuous Improvement and Performance Measurement
Lastly, embracing a culture of continuous improvement and regularly evaluating performance is crucial in ensuring optimized outbound logistics processes. Organizations should establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) related to outbound logistics, such as order accuracy, on-time delivery rate, and transport costs, to measure their success. By analyzing these KPIs, organizations can identify areas that require improvement and make strategic adjustments to enhance their overall product distribution effectiveness.
What are the best practices for improving outbound warehouse operations in distribution management?
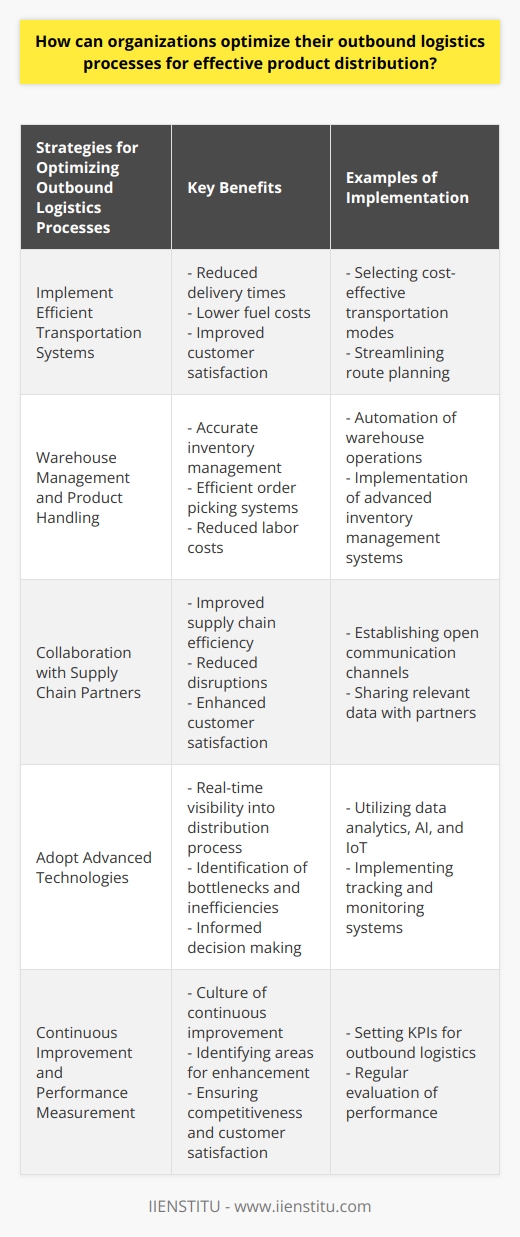
Efficient Picking Strategies
To optimize outbound warehouse operations in distribution management, implementing effective picking strategies is essential. Utilizing an appropriate picking technique, such as wave picking, batch picking, or zone picking, depending on the warehouse layout and product demand, can streamline the order process and enhance the overall efficiency.
Warehouse Layout Optimization
A well-designed warehouse layout is critical for improving material handling and minimizing travel time for pickers. By employing techniques like slotting optimization, which places high-demand items near the shipping area, and rearranging the warehouse according to product popularity, warehouses can ensure smoother operations and shorter lead times.
Use of Technology
Employing technology in warehouse operations is beneficial for minimizing human errors and boosting productivity. Implementing warehouse management systems (WMS) allows for better inventory control and tracking, which in turn ensures accurate and timely order fulfillment. Additionally, the use of automated systems such as AGVs, robotics, and advanced picking technologies like pick-by-light or pick-by-voice can significantly improve warehouse efficiency.
Employee Training and Incentives
Proper training of employees ensures their familiarity with warehouse systems and efficient picking techniques, leading to enhanced productivity. Providing ongoing training, refreshers, and addressing gaps in knowledge or performance can maintain a high level of workforce competence. Additionally, implementing incentive programs and recognition schemes can motivate workers, increase job satisfaction, and further improve outbound warehouse operations.
Continuous Improvement
Adopting a continuous improvement mindset can lead to ongoing enhancements in warehouse operations. Regularly analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and conducting assessments, such as time and motion studies or value-stream mapping, allows for the identification of bottlenecks and areas requiring improvement. Implementing changes based on these findings and continuously reassessing the results contributes to the warehouse's long-term success.
In conclusion, improving outbound warehouse operations in distribution management requires a multifaceted approach, including efficient picking strategies, warehouse layout optimization, the use of technology, proper employee training, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By implementing these best practices, warehouses can achieve increased productivity, accuracy, and overall operational efficiency.
What is the importance of outbound logistics in achieving a competitive advantage?
Significance of Outbound Logistics in Competitive Advantage
Efficient Delivery System
Outbound logistics, which refers to the process of storing, transporting, and distributing goods to customers, plays a crucial role in achieving a competitive advantage. An efficient delivery system ensures that products reach consumers in a timely and cost-effective manner. This directly affects customer satisfaction and, ultimately, a company's long-term success in the market.
Cost Reduction and Profit Maximization
By optimizing outbound logistics, businesses can minimize transportation and storage expenses, leading to lower overall costs. These cost savings can be passed on to consumers in the form of lower prices, making the company's products more attractive and boosting its market share. Moreover, effective outbound logistics management allows for profit maximization through strategic resource allocation and reduced wastage.
Inventory Management and Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting and effective inventory management are essential components of a successful outbound logistics strategy. By predicting customer needs and managing inventory levels accordingly, companies can avoid stockouts, maintain high product availability, and minimize holding costs. This further enhances the company's competitive advantage by ensuring consistent product availability and meeting a variety of customer expectations.
Customization and Flexibility
A strong outbound logistics operation allows companies to offer enhanced customization and flexibility in their product offerings. By meeting unique customer requirements and catering to specific market segments, businesses can differentiate themselves from competitors and strengthen customer loyalty. Furthermore, a responsive outbound logistics system can adapt to market fluctuations, enabling rapid shifts in product offerings to meet evolving customer needs and preferences.
Environmental Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility
Lastly, a sustainable and responsible approach to outbound logistics contributes to a company's competitive advantage by aligning with customer demands for environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices. Green logistics initiatives such as reducing transportation emissions, using eco-friendly packaging materials, and optimizing delivery routes can enhance a company's reputation and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
In conclusion, the importance of outbound logistics in achieving a competitive advantage cannot be underestimated. Implementing efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable outbound logistics practices can lead to satisfied customers, increased market share, and long-term business success.
How do technological advancements impact the efficiency of outbound logistics processes?
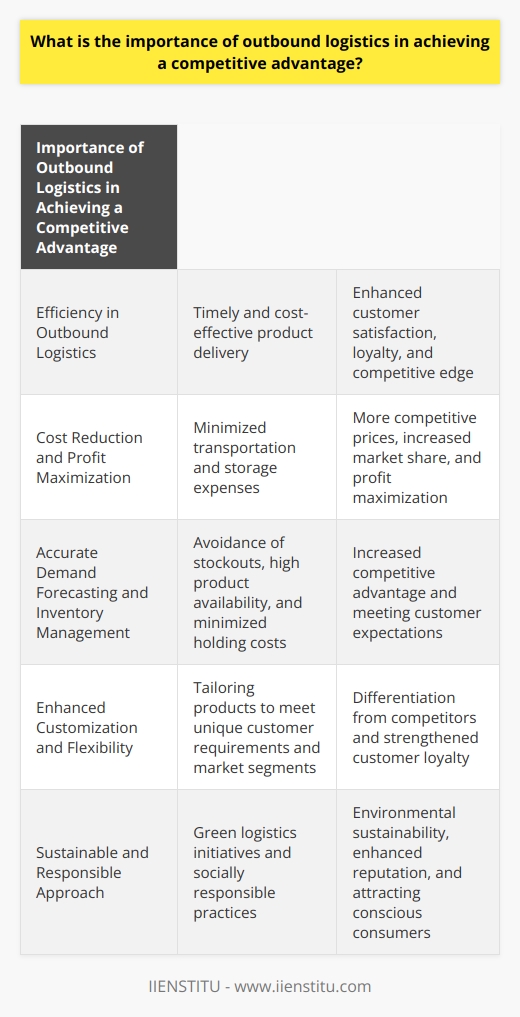
**Impact on Speed and Accuracy**
Technological advancements have significantly improved the speed and accuracy of outbound logistics processes. The use of automation, IoT, and AI has led to a reduction in manual labor, minimizing the scope of human errors and enhancing overall productivity. Faster and more precise processes enable companies to pick, pack, and ship their products quickly, helping them to meet consumer expectations and deliver orders on time.
**Data-Driven Decision-Making**
Technology has facilitated the rise of data-driven decision-making in outbound logistics management. Real-time tracking, data analysis, and predictive analytics provide essential insights into various aspects of the logistics process, such as inventory management, route optimization, and delivery times. These data-driven insights allow companies to optimize their operations and swiftly respond to any changes in market demand or external factors, leading to increased efficiency.
**Collaboration and Communication**
Many technological advancements have enhanced collaboration and communication between different players involved in outbound logistics processes. Cloud-based software solutions and digital platforms allow companies to work seamlessly with partners, suppliers, and customers worldwide. This enhanced connectivity allows for rapid sharing of information, better coordination of tasks, and improved decision-making, contributing to more efficient logistics processes.
**Cost Efficiency**
Embracing technology may lead to cost savings in various stages of outbound logistics processes. Through the use of automated warehouse systems, robotics, and IoT devices, companies can minimize labor costs and save on their warehouse operational expenses. Similarly, by utilizing advanced technologies such as route optimization and real-time tracking, organizations can minimize transportation expenses, ensuring efficient fuel consumption and reduced carbon emissions.
**Customization and Personalization**
Technological advancements have also allowed companies to offer a higher level of customization and personalization in their logistical processes. Customers can now place orders tailored to their preferences and track their shipment throughout its journey. These customer-centric capabilities allow businesses to differentiate themselves from their competitors by delivering an exceptional customer experience, which ultimately boosts the efficiency of their outbound logistics processes.
In conclusion, technological innovations have greatly contributed to the efficiency, speed, and cost-effectiveness of outbound logistics processes. The enhanced accuracy, data-driven decision-making, improved collaboration, and personalization have allowed companies to achieve better performance and deliver superior customer value.
What are the key challenges faced by organizations while managing outbound logistics in a global distribution network?
Challenges in Global Distribution Networks
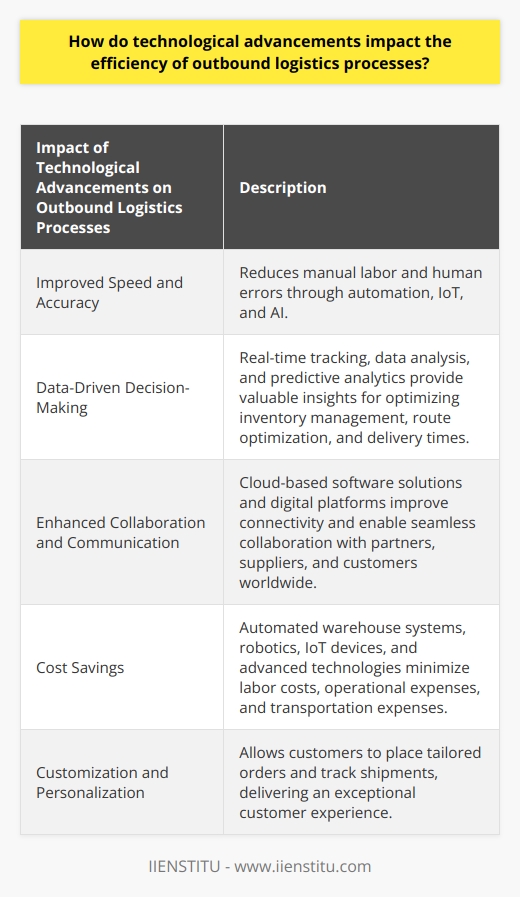
Complexity of Operations
The foremost challenge faced by organizations in managing outbound logistics in a global distribution network is the increasing complexity of operations. International trade involves dealing with multiple regulatory environments, tax regimes, and legal frameworks. This necessitates a thorough understanding of international laws, cultural practices, and bureaucratic processes in different countries, which often requires hiring local experts and specialized staff.
Coordination and Communication
Another significant hurdle is the coordination and communication among various entities in the supply chain, including suppliers, customers, transportation providers, and government agencies. Organizations face substantial challenges in ensuring that all parties deliver their responsibilities on time and as per the agreed-upon standards. Moreover, transparency and information sharing among stakeholders are crucial for maintaining efficiency in global distribution networks, and language barriers may aggravate the situation.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Organizations also confront the issue of supply chain vulnerabilities in the form of disruptions, delays, and uncertainties. These may arise due to natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or economic fluctuations, among other factors. Coping with such vulnerabilities requires robust contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies to minimize negative impacts on the global distribution network.
Lead Time Management
Global distribution networks typically involve longer lead times, which demand accurate demand forecasting and inventory management. Miscalculations can adversely affect customer satisfaction and overall operational efficiency. To address this challenge, organizations may invest in advanced technological solutions such as data analytics and predictive tools to ensure accurate demand forecasting and avoid stockouts or excess inventory in the distribution network.
Transportation and Warehousing
Lastly, efficient transportation and warehousing are vital components of managing outbound logistics in a global distribution network. Organizations must select the most appropriate transportation modes and warehouse locations while balancing cost, delivery time, and environmental sustainability factors. Additionally, ensuring the capability of transportation and warehousing partners to handle regulatory compliance, customs clearance, and storage requirements is essential for seamless movement of shipments across borders.
In conclusion, organizations operating in a global distribution network face challenges such as complexity of operations, coordination and communication, supply chain vulnerabilities, lead time management, and efficient transportation and warehousing. Addressing these challenges necessitates investments in human resources, technology solutions, and strategic partnerships to develop a robust and efficient outbound logistics management system.
What is the outbound logistics strategy?
Outbound Logistics Strategy Defined
An outbound logistics strategy is a vital component of a company's supply chain, focused on the storage, transportation, and distribution of finished products from a production facility to their final destinations, such as wholesalers, retailers, and end consumers. Implementing an efficient and effective outbound logistics strategy is crucial in ensuring customer satisfaction while optimizing costs and resources involved in the process.
Components of Outbound Logistics Strategy
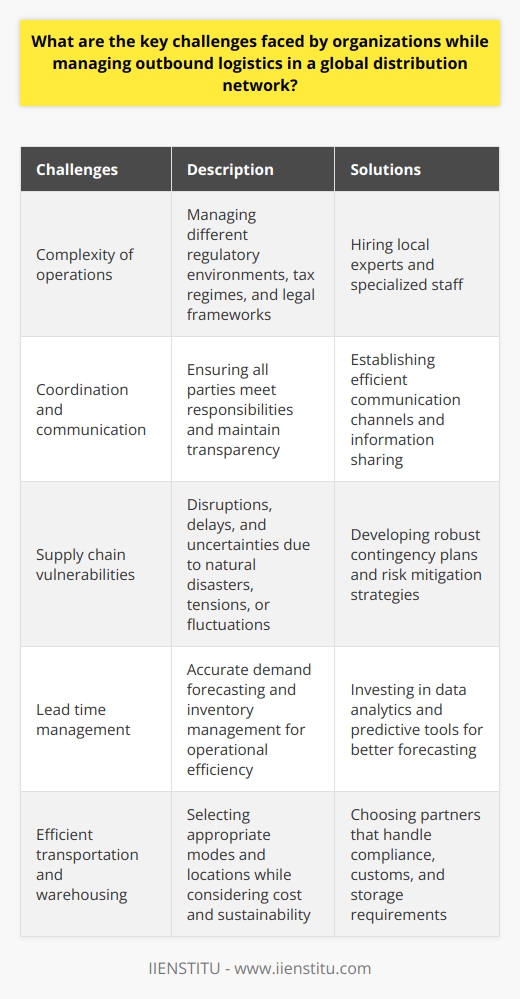
Warehousing and Storage
The primary aspect of an outbound logistics strategy is the warehousing and storage of finished products. Companies need to identify suitable warehousing solutions that ensure product safety, mitigate risks, and maintain appropriate inventory levels to prevent stockouts or overstocking.
Order Processing and Management
Efficient order processing and management are crucial in ensuring timely deliveries, preventing miscommunication, and improving customer satisfaction. Companies must invest in reliable order management systems to streamline communication and coordination between departments, warehouse teams, and third-party logistics partners.
Transportation and Delivery
Selecting the appropriate transportation and delivery methods is a critical consideration when developing an outbound logistics strategy. Companies must choose between various transportation modes, including road, rail, air, and sea, while considering factors such as costs, transit times, and environmental impact.
Distribution Networks
Establishing a well-planned distribution network ensures products reach their intended destinations efficiently and cost-effectively. Companies must consider factors such as geographic coverage, customer proximity, and delivery timelines to develop an optimized distribution network.
Customer Service and Returns
Effective customer service and returns management are essential in building a positive brand reputation and maintaining customer loyalty. An outbound logistics strategy should involve developing a robust returns policy and implementing customer support systems that promptly address customer concerns and queries.
Performance Metrics and Continuous Improvement
Monitoring and evaluating the performance of an outbound logistics strategy is vital in identifying areas for improvement and ensuring competitiveness in the market. Key performance indicators such as delivery lead times, transportation costs, and order accuracy can be used to benchmark the success of the strategy and identify areas for potential optimization. Companies should frequently engage in data-driven analysis and incorporate feedback from stakeholders to drive continuous improvement in their outbound logistics processes.
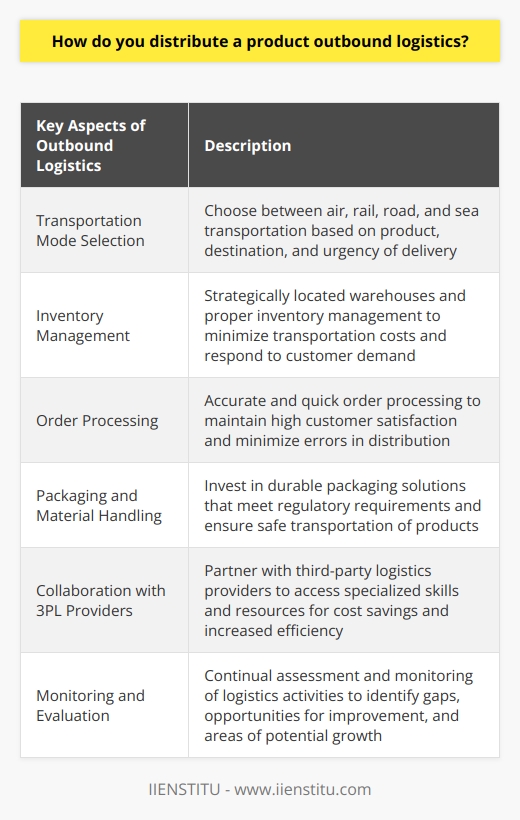
How do you distribute a product outbound logistics?
Outbound Logistics Strategy
The distribution of a product through outbound logistics involves several key steps and strategies to ensure the efficient movement of goods from a manufacturer to end customers. Firstly, planning and organization are crucial for successful product distribution.
Transportation Modes
A company must carefully select the appropriate transportation mode or a combination of modes, such as air, rail, road, and sea, depending on the product, destination, and urgency of delivery. The choice is crucial to minimize transit time and transportation costs while ensuring the product's safety and quality.
Warehousing and Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management and warehousing are essential factors for smooth outbound logistics. Companies need to store products in strategically located warehouses that minimize transportation costs and quickly respond to customer demand. They must also manage inventory levels to avoid stockouts or excess inventory, as both may result in financial and brand reputation losses.
Order Processing
Accurate and quick order processing is necessary to maintain high customer satisfaction and reduce the risk of errors in the distribution process. Companies need streamlined order tracking and confirmation systems to ensure proper communication and reduce the chances of delays and mistakes in delivering products to customers.
Packaging and Material Handling
Appropriate packaging and material handling are vital for a product's safety and quality preservation during transportation. Companies must invest in durable packaging solutions that meet regulatory requirements and ensure that products are satisfactorily protected from damage or spoiling. Material handling equipment and policies are equally crucial for efficient loading and unloading processes, ensuring staff safety, and reducing the risk of damage during transportation.
Relationships with Third-Party Providers
Companies often collaborate with third-party logistics (3PL) providers, who offer specialized skills and resources. Establishing strong relationships with trustworthy and experienced 3PL providers can lead to cost savings and enhanced efficiency in the distribution process. This partnership can also help a company to access updated technology and industry expertise without heavy investment.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Finally, continuous assessment and monitoring of outbound logistics activities are essential for identifying gaps in the distribution process, opportunities for improvement, and areas of potential growth. By frequently evaluating logistics performance, a company can make informed adjustments and investments that align with its overall business objectives and ensure that they continue to deliver products effectively and efficiently to customers.
What is the importance of outbound logistics in distribution management?
Outbound Logistics Significance
Outbound logistics plays a crucial role in distribution management by ensuring the efficient and timely delivery of finished goods from production facilities to customers. A well-managed distribution system is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction, managing costs, and staying ahead in a competitive market.
Customer Satisfaction
Maintaining a top-notch outbound logistics system guarantees that customers receive their orders promptly and in good condition. A streamlined distribution process reduces the chances of delivery delays or damaged products, resulting in increased customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. By meeting customers' expectations consistently, businesses can establish a positive reputation and attract new clients.
Cost Management
Efficient outbound logistics management not only enhances customer satisfaction but also helps companies manage their costs effectively. By optimizing the distribution process, organizations can reduce transportation expenses, minimize product wastage, and lower warehouse storage costs. An effective distribution management system also prevents the need for costly measures such as expedited shipping and extra warehouse staff to handle backlogs.
Competitive Advantage
In a highly competitive environment, an exceptional outbound logistics system can provide businesses with a significant competitive edge. By ensuring speedy delivery of high-quality products, companies can differentiate themselves from competitors, secure repeat business, and increase market share. Moreover, efficient logistics management enables organizations to scale and adapt to market changes rapidly, allowing them to seize new opportunities and outpace competitors.
Innovation and Technology
Incorporating modern technology and innovative practices is essential for developing strong outbound logistics. Utilizing advanced tracking systems, data analytics, and automation can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of distribution management processes. By embracing these technologies, businesses can ensure their logistics systems remain agile and responsive to ongoing market demands.
Conclusion
In summary, outbound logistics is a vital component of distribution management that directly impacts customer satisfaction, cost management, and competitive positioning. By prioritizing the development of an efficient and reliable outbound logistics system, businesses can enhance customer loyalty, mitigate costs, and maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace. Embracing innovation and technology will further optimize distribution processes for continued success.