It was a crisp autumn morning when I first realized the profound impact that understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) could have on my business decisions. I remember sitting in the conference room, gazing out at the fiery hues of leaves fluttering in the breeze, as our procurement team debated over two seemingly similar suppliers. On paper, one offered a lower purchase price, but our seasoned financial analyst urged us to look beyond the immediate costs. That day marked a turning point in how I approached purchasing—embracing a holistic view that encompasses every facet of cost associated with owning an asset.
Introduction
The Total Cost of Ownership
Factors Affecting TCO
Benefits of Understanding TCO
Conclusion
Grasping the Concept of Total Cost of Ownership
At its core, the total cost of ownership is not just about the upfront purchase price. It's about the entire spectrum of costs that accrue over the item’s lifetime. Think of it like buying a car. While the sticker price might fit your budget, have you considered the ongoing expenses like fuel, maintenance, insurance, and depreciation? Similarly, in business, understanding TCO means looking beyond the initial expenditure and considering all future costs that an item or service will entail.
Why TCO Matters More Than You Think
When we dwell only on the purchase price, we might miss out on hidden costs that can significantly affect profitability. For instance, a cheaper machine might save money upfront but could lead to higher maintenance costs down the line. On the other hand, investing in a slightly more expensive piece of equipment with better energy efficiency could save substantial amounts in operational costs over time.
Factors Affecting TCO
Unpacking the total cost of ownership reveals a myriad of factors. These can be broadly categorized into:
1- Acquisition Costs: These are the direct costs involved in purchasing an item. They include:
Purchase Price: The initial amount paid to acquire the item.
Installation Fees: Costs associated with setting up the item for use.
Training Costs: Expenses for teaching staff how to use the new asset.
The actual cost of a supply chain is determined by the costs incurred throughout its entire life cycle.
2- Operating Costs: Ongoing expenses necessary to keep the item functional.
Maintenance and Repairs: Regular upkeep and fixing any issues that arise.
Energy Consumption: The cost of power or fuel needed for operation.
Supplies and Consumables: Materials required for the item to function properly.
3- Ownership Costs: Indirect costs that come with owning an asset.
Insurance: Protecting the asset against potential risks.
Taxes and Permits: Legal obligations associated with ownership.
Depreciation: The decrease in value over time.
4- Disposal Costs: Expenses linked to either disposing of or reselling the item at the end of its life.
Environmental Fees: Costs for proper disposal to meet environmental regulations.
Salvage Value: Potential income from selling the asset after use.
Consider the following long-term factors that can subtly influence TCO:
Quality Inspection and Defect Resolution Costs: Investing in quality assurance can prevent defective products from reaching customers, saving money on returns and preserving brand reputation.
Inventory Holding Costs: The longer you hold inventory, the higher the costs due to storage, insurance, and potential obsolescence.
Shrinkage, Safety, and Loss Prevention: Implementing measures to prevent theft or damage can reduce losses, impacting the overall cost of ownership.
An Example to Illustrate TCO
Let me share an experience from my friend's small manufacturing business. He faced a choice between two suppliers for a critical component. Supplier A offered a lower price per unit, while Supplier B's price was slightly higher but promised better reliability.
Initially, the lower cost seemed appealing. However, after calculating the TCO, including factors like defect rates, delivery times, and support services, it became evident that Supplier B was the more cost-effective option in the long run. By choosing Supplier B, he reduced downtime due to faulty parts and improved his product's overall quality, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
The Intersection of TCO and Project Management Strategies
Understanding TCO is not just vital for procurement decisions but also plays a significant role in project management. When we consider strategies like the critical path method project management strategy, the focus is on identifying the sequence of crucial steps that determine the project's duration.
By incorporating TCO into this strategy, project managers can:
Optimize Resource Allocation: By understanding the total costs, resources can be allocated more efficiently to critical tasks, ensuring the project stays on schedule and within budget.
Mitigate Risks: Identifying potential high-cost areas allows for proactive measures to minimize financial risks associated with project delays or overruns.
Enhance Decision Making: A clear picture of TCO supports better decisions regarding subcontracting, equipment purchases, and scheduling.
Long-Tail Keywords in TCO and Project Management
In the realm of business and project management, it's imperative to stay informed about concepts like:
Strategic procurement methods for cost savings
Impact of inventory management on TCO
Long-term benefits of efficient energy consumption in operations
Risk assessment techniques in TCO calculation
Cost-benefit analysis in equipment procurement decisions
Incorporating these concepts into your strategic planning can lead to more informed decisions and ultimately, a healthier bottom line.
Benefits of Understanding TCO
Recognizing and applying the concept of TCO brings numerous advantages:
1- Informed Purchasing Decisions: By evaluating all costs, businesses can choose options that offer the best value over time, not just the lowest initial price.
2- Cost Savings: Identifying areas where costs can be reduced—like energy-efficient equipment or bulk purchasing—can lead to significant savings.
3- Improved Negotiations with Suppliers: Understanding the full cost structure allows businesses to negotiate better terms, focusing on long-term value rather than just upfront costs.
4- Risk Management: Anticipating future costs helps in planning for potential financial risks and setting aside reserves for unexpected expenses.
5- Enhanced Budgeting and Forecasting: A comprehensive view of costs enables more accurate budgeting and financial projections.
Personal Insights on TCO Benefits
Reflecting on my own experiences, embracing TCO has transformed how I approach business investments. I recall investing in a new software system for our team. While there was a free version available, we opted for a paid version with better support and additional features. Over time, this choice proved wise as it:
Increased Productivity: The additional features streamlined our workflows.
Reduced Downtime: Prompt support resolved any issues quickly.
Enhanced Collaboration: Improved tools facilitated better teamwork.
The initial higher cost was offset by the long-term gains we realized—an embodiment of TCO's value.
Practical Steps to Calculate TCO
Calculating TCO doesn't have to be overwhelming. Here's a simple approach:
List All Costs: Start by listing every possible cost associated with the item over its expected life span.
Gather Data: Collect information on operating expenses, maintenance schedules, disposal costs, etc.
Use a TCO Calculator: There are tools and formulas available in texts like Investment Decision-Making in Asset Management by John Dyson (2017) that can help simplify calculations.
Review and Adjust: Regularly revisit TCO estimates to account for changes in usage, market conditions, or unforeseen expenses.
Key Considerations in TCO Calculations
When calculating TCO, keep in mind:
Time Value of Money: Consider that money now is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its earning potential.
Life Span of the Asset: The longer the asset lasts, the more spread out the costs become.
Depreciation Methods: Different assets depreciate differently; choose an appropriate method for accurate accounting.
Conclusion
Embracing the concept of total cost of ownership has been a game-changer in my professional journey. It has shifted my focus from short-term gains to long-term value, ensuring that decisions are not just cost-effective but also strategic and sustainable.
By understanding TCO, businesses can:
Make Smarter Investments: Align purchases with long-term goals and financial health.
Enhance Operational Efficiency: Identify and eliminate wasteful expenditures.
Strengthen Competitive Advantage: Optimize costs to offer better pricing or invest in innovation.
As we navigate the complexities of today's business environment, tools like TCO analysis are indispensable. They not only illuminate the true cost landscape but also empower us to make decisions that foster growth and resilience.
References
1- Dyson, J. (2017). Investment Decision-Making in Asset Management: Building Value through Smart Capital Decisions. New York: Wiley.
2- Thompson, A. A. (2016). Supply Chain Management: Concepts, Techniques and Practices Enhancing Value Through Collaboration. New Jersey: Pearson Education.
3- Johnson, G., & Scholes, K. (2018). Exploring Corporate Strategy. London: Prentice Hall.
4- Smith, M. (2015). Project Management: Strategic Financial Planning for Projects. Boston: McGraw-Hill.
Frequently Asked Questions
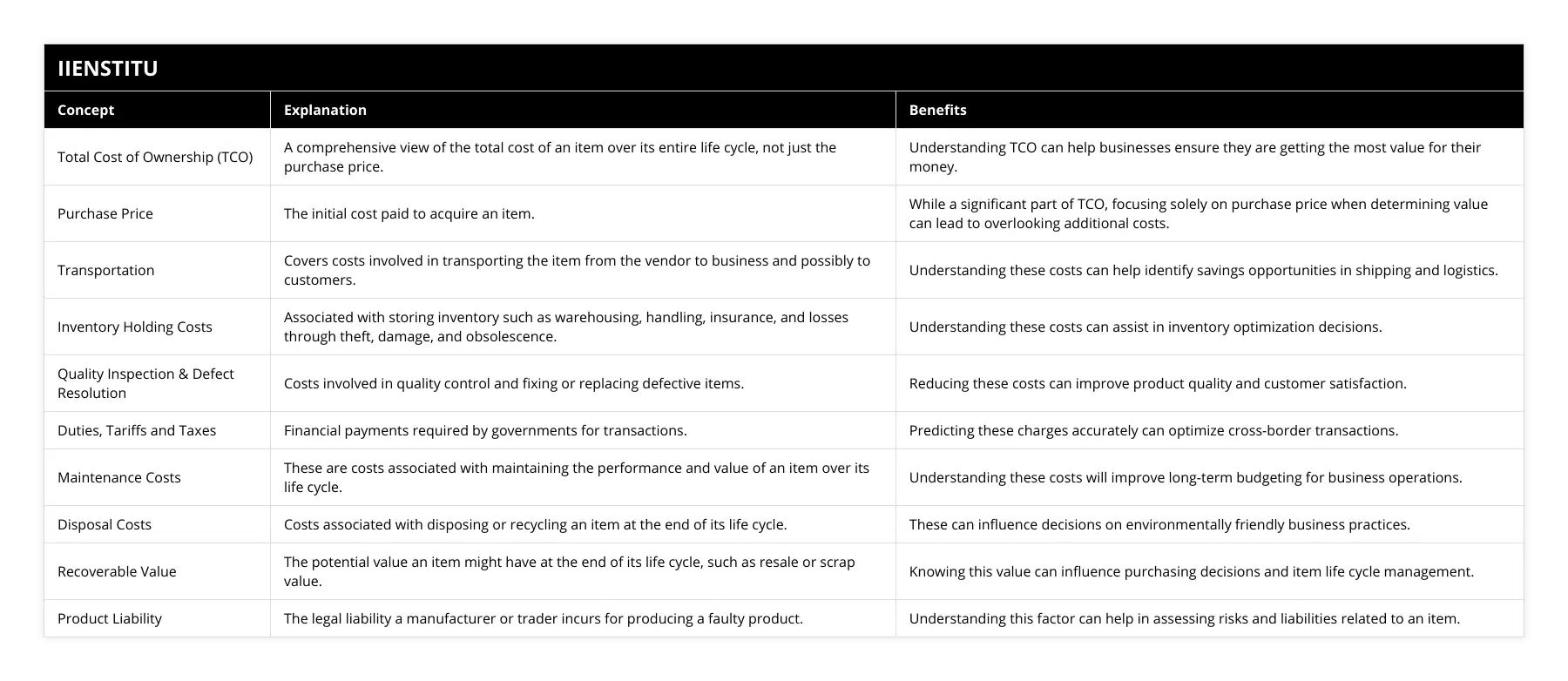
What are the key components of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in a supply chain?
The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is a metric used to measure the total costs associated with a product or service throughout its life cycle, from inception to disposal. TCO is an important concept in supply chain management, as it helps to identify and quantify the full cost of a product or service from the perspective of the buyer. It is a way of understanding the total cost of ownership for a supply chain and to assess the efficiency of the system.
The key components of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in a supply chain include acquisition, operating, maintenance, disposal, and environmental costs. Acquisition costs are the costs associated with obtaining a product or service, such as the purchase price, taxes, freight, duties, and other administrative costs. Operating costs are the expenses incurred while using the product or service, such as energy, labor, and other consumables.
Maintenance costs are the costs associated with keeping the product or service in proper working condition, while disposal costs represent the cost of disposing the product or service at the end of its life cycle. Environmental costs are the costs associated with the environmental impact of the product or service, such as emissions, waste disposal, and other ecological costs.
In addition to these components, other factors such as inventory levels, lead times, and quality should also be considered when calculating TCO. The goal is to identify the true cost of ownership for a product or service, and to assess the efficiency of the supply chain in delivering it. By understanding TCO in a supply chain, buyers can make informed decisions about the products and services they purchase, and suppliers can better manage their resources to maximize efficiency and minimize costs.
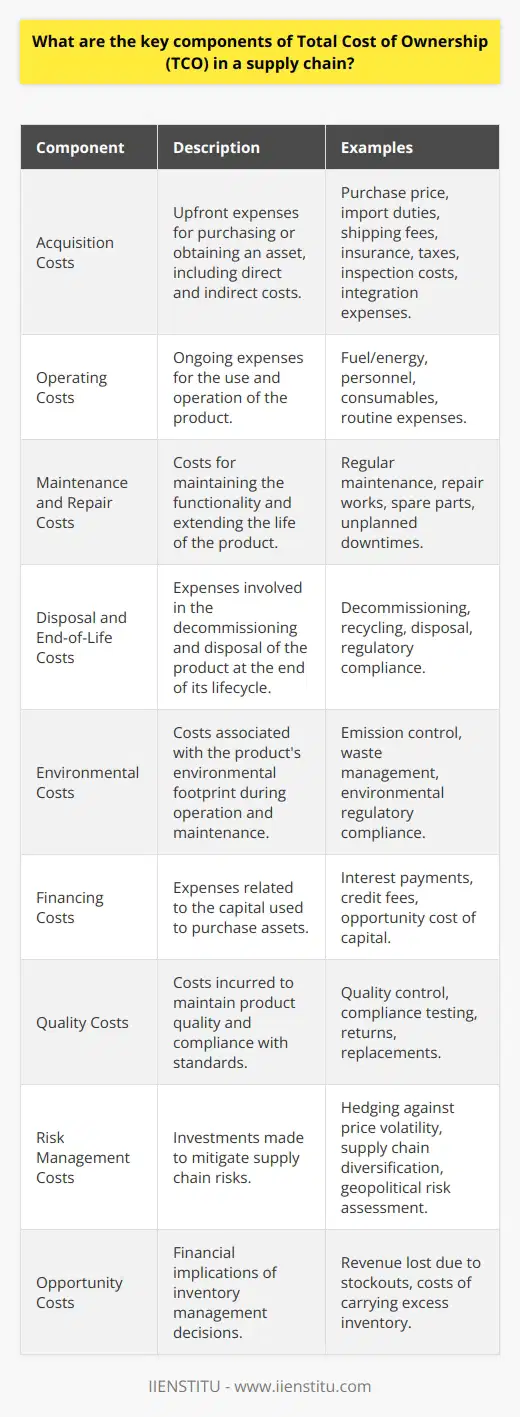
How can understanding TCO help to maximize supply chain efficiency?
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is an important concept in supply chain management and is used to identify the complete cost of a supply chain over its entire life cycle. This includes the cost of materials, labor, transportation, warehousing, and other costs associated with the supply chain. By understanding TCO and how it can be applied to maximize supply chain efficiency, organizations can make better-informed decisions about their supply chain investments and operations.
The first step in understanding TCO is to identify the components that make up the total cost of a supply chain. This includes the direct costs associated with the acquisition of materials, labor, and transportation as well as the indirect costs related to warehousing, maintenance, and production. The cost of customer service, training, and other administrative costs should also be considered. By understanding the different components of TCO, organizations can identify areas of their supply chain that need improvement and identify strategies to reduce costs.
Once the components of TCO have been identified, organizations should look at maximizing efficiency. This can be done by utilizing technology and data to optimize the supply chain, streamline operations, and reduce waste. For example, organizations can utilize data-driven analytics to identify inefficiency in their supply chain and develop strategies to improve performance. Additionally, technology can improve communication between different supply chain stakeholders, enabling better collaboration and coordination to maximize efficiency.
Another way to maximize supply chain efficiency through TCO is by focusing on planning and forecasting. By accurately forecasting demand and inventory levels, organizations can better anticipate customer needs and ensure that the right inventory is available at the right time. Additionally, organizations should ensure that their supply chain is agile and flexible, enabling them to adapt to changing market conditions quickly. This can help to reduce the need for costly expedited shipping and other emergency measures.
In summary, understanding the concept of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and how it can be applied to maximize supply chain efficiency is essential for organizations looking to optimize their operations. By understanding the different components of TCO, utilizing data and technology, focusing on planning and forecasting, and ensuring supply chain agility, organizations can take steps to minimize costs and maximize efficiency in their supply chain.
What are the benefits of managing life cycle costs in a supply chain?
The concept of life cycle costing (LCC) has become increasingly important in the supply chain management (SCM) space as organizations strive to remain competitive in a rapidly changing global market. LCC is considering all costs associated with a product or service throughout its life cycle, from initial purchase to eventual disposal. By considering the total cost of ownership over the life of the product or service, organizations can make more informed and cost-effective decisions.
The benefits of LCC are numerous. Organizations can make more informed decisions about purchasing, production, maintenance, and disposal by considering all costs associated with a product or service throughout its life cycle. This helps to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently and that the organization is not overspending on unnecessary goods or services. Additionally, by considering the total cost of ownership over the life of the product or service, organizations can better manage inventory levels, helping to reduce the costs associated with holding too much inventory or ordering too often.
In addition to cost savings, LCC also provides organizations with an improved understanding of the environmental impacts associated with their operations. By considering the environmental costs associated with a product or service over its entire life cycle, organizations can make more informed decisions about their operations and how they can reduce their environmental footprint. This can help organizations meet sustainability goals, reducing their environmental impact while still meeting their business objectives.
Finally, LCC can help organizations better understand the social costs associated with their operations. By considering the full life cycle costs of a product or service, organizations can ensure that their operations are not hurting the local community or workforce. This can help organizations to build stronger relationships with their stakeholders, providing them with greater trust and support.
In conclusion, managing life cycle costs can provide organizations with numerous benefits, including cost savings, improved environmental performance, and stronger stakeholder relationships. By taking into account the total cost of ownership over a product or service life, organizations can make more informed and cost-effective decisions, helping to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently and that their operations are not hurting the local environment or workforce.
What is the role of TCO in optimizing life cycle costing?
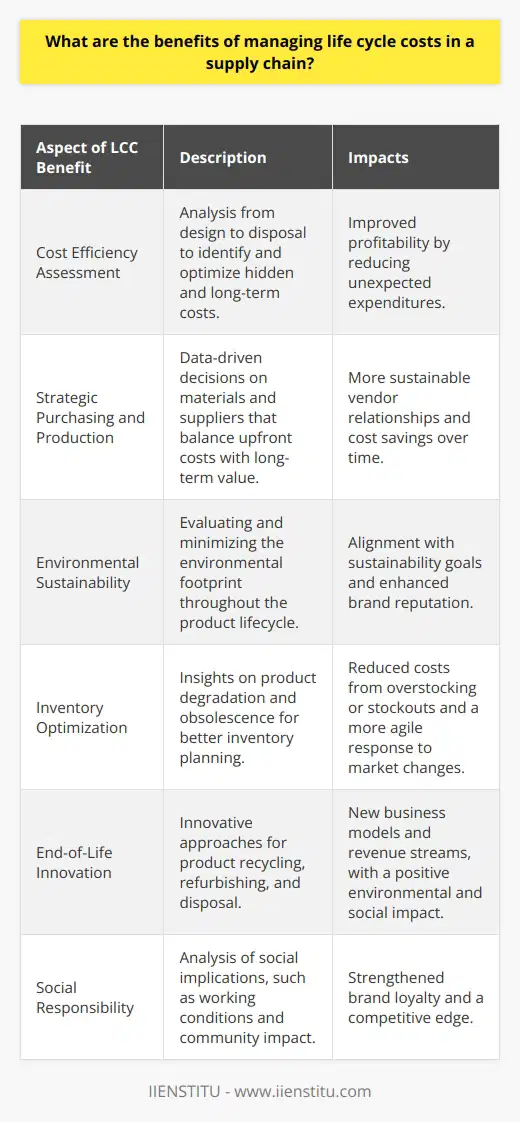
Role of TCO in Life Cycle Costing
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership
Total cost of ownership (TCO) is a financial estimate that assesses the direct and indirect costs of a product or system over its entire life cycle. This concept is essential for sustainable decision-making as it allows for accurate comparisons of different products, investments or designs concerning their financial and environmental effects.
Influence on Life Cycle Costing
Optimizing life cycle costing (LCC) relies on accurately considering all expenses related to a product or project from its inception to its disposal. TCO plays a critical role in this optimization as it provides a comprehensive overview of these costs, including acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal expenses.
Enhancing Decision-Making
TCO supports better decision-making by offering a clear and quantifiable understanding of the long-term financial implications of various options. By considering TCO in life cycle costing, organizations can make more informed choices that minimize costs, reduce negative environmental impacts and maximize returns on investment.
Mitigating Hidden Expenses
A significant advantage of incorporating TCO into life cycle costing is the ability to identify and mitigate hidden costs that might otherwise go unnoticed. These hidden costs, such as service fees, support expenses or obsolescence, can significantly impact the overall value of an investment or project.
Promoting Sustainability
Incorporating TCO in life cycle costing helps prioritize sustainability by comparing the environmental and financial impacts of different options. By accounting for resource usage, waste generation and disposal costs, TCO allows organizations to identify and implement more efficient and environmentally friendly solutions.
Fostering Innovation
Lastly, using TCO to optimize life cycle costing drives innovation by encouraging the development of cost-effective and environment-friendly products and systems. Companies can leverage this knowledge to create innovative solutions that offer long-term savings, reduce carbon footprints and promote a sustainable future.
In conclusion, TCO is an indispensable tool in optimizing life cycle costing as it precisely assesses the costs associated with a product or project over its entire life span. TCO enhances decision-making, mitigates hidden expenses, promotes sustainability, and fosters innovation, ensuring informed choices that consider not only financial implications but also environmental impacts.
How does TCO contribute to effective decision-making in supply chain management?
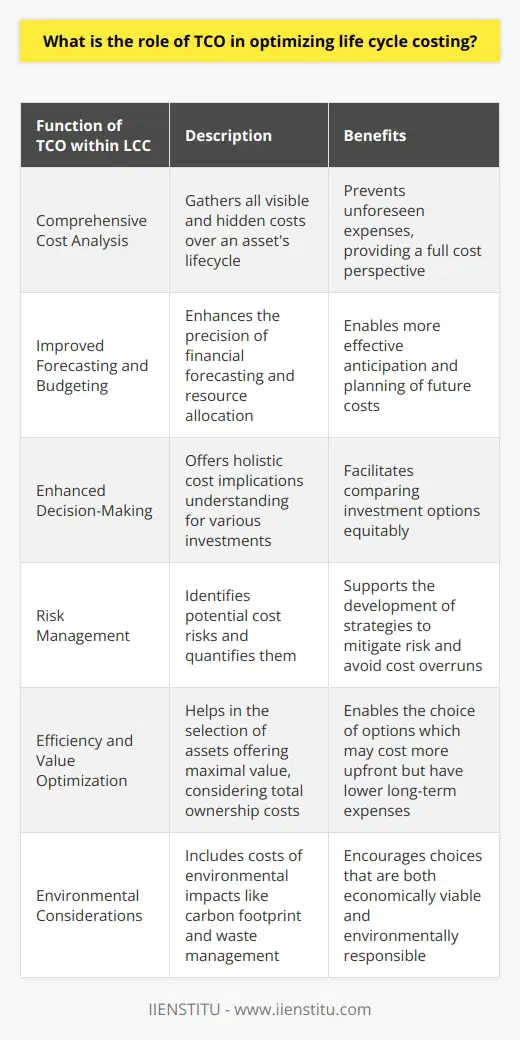
Role of TCO in Decision-Making
Total cost of ownership (TCO) is a vital concept in supply chain management, as it considers all expenses associated with procuring, operating, and maintaining products or services. This comprehensive view allows for effective decision-making by enabling companies to weigh the long-term costs and benefits of various options, ultimately selecting the most cost-efficient choices in their supply chain.
Reducing Acquisition and Operating Expenditure
TCO analysis allows companies to identify areas where they can minimize expenses, such as selecting cost-effective suppliers with lower acquisition costs or implementing technological innovations that reduce ongoing operational expenses. By reducing these direct costs, businesses can optimize their supply chain management strategy, potentially enhancing their overall profitability.
Enhancing Supplier Relationship Management
A thorough TCO assessment can also contribute to improved supplier relationship management. Considering both the quality and price of a supplier brings the opportunity for businesses to establish strategic partnerships with optimal suppliers, ensuring long-term value beyond purely financial aspects. Investigating the TCO of different suppliers can help businesses select stable, reliable and high-quality partners to contribute positively to the supply chain performance.
Incorporating Sustainability Considerations
Including TCO in decision-making processes encourages a more sustainable approach to supply chain management. For example, TCO accounts for the environmental and social costs of decisions and facilitates choosing eco-friendly options when selecting suppliers and making procurement decisions. This focus on sustainability can lead to improved corporate social responsibility, boosting a company's reputation and overall brand value.
Facilitating Risk Management Assessment
Lastly, TCO supports effective decision-making in supply chain management by facilitating risk identification and assessment. Comprehensive cost analysis can uncover hidden vulnerabilities or dependencies in the supply chain, allowing companies to proactively address these risks or reconfigure their strategies for a more resilient supply chain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, utilizing TCO in decision-making is vital for effective supply chain management. It enables companies to minimize costs, enhance supplier relationships, prioritizes sustainability, and facilitate risk management. By considering TCO when making decisions, businesses can optimize their supply chain strategies, ultimately leading to better long-term value and improved overall business performance.
What advantages can organizations expect to see by incorporating TCO as part of their cost management strategies?
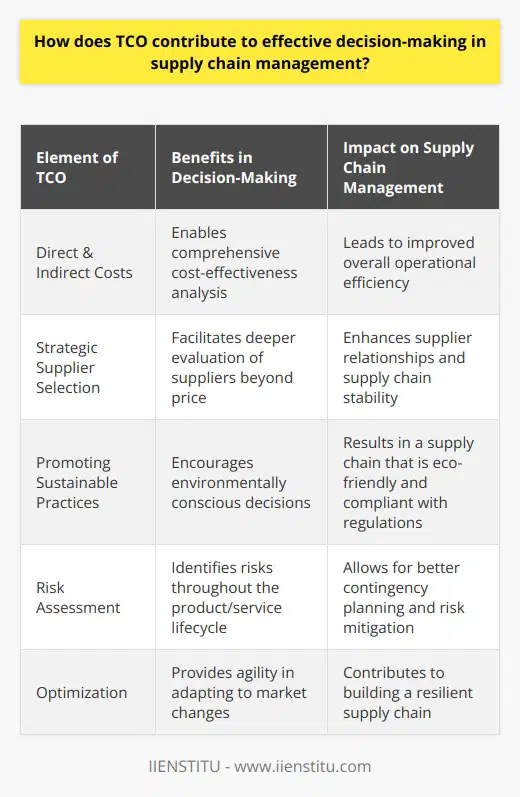
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Organizations adopting a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) approach in their cost management strategies can anticipate several advantages. TCO allows for a comprehensive understanding of costs, enabling organizations to make better-informed decisions regarding their assets and resources.
Improved Decision Making
One of the most significant advantages of TCO is its ability to improve decision-making. By taking both direct and indirect costs into account, organizations can gain a more accurate representation of the long-term value of their investments. This allows them to effectively compare different options and evaluate the most cost-effective solutions.
Greater Cost Efficiency
TCO analysis can lead to greater cost efficiency. It goes beyond purchase price to reveal hidden costs, which are often ignored during strategic planning. By identifying and quantifying these costs, organizations can address inefficiencies and improve overall cost management.
Aligned Budgeting and Strategy
The inclusion of TCO in cost management allows organizations to better align their budgeting and strategic objectives. TCO analysis provides a clearer picture of how costs and resources align with broader organizational goals, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively and wasteful spending is minimized.
Risk Mitigation
TCO analysis can also help organizations identify and mitigate risks associated with their investments. Through assessing various costs, organizations can foresee potential problems and implement proactive measures to reduce risk. This can lead to overall enhanced organizational stability and resilience.
Long-term Savings
One of the key benefits of using TCO is the potential for long-term savings. By analyzing investment costs over the entire life cycle of an asset or project, organizations can identify areas where cost savings can be achieved. When approached consistently and strategically, TCO analysis can lead to considerable long-term savings and financial benefits for organizations.
In conclusion, incorporating TCO as part of cost management strategies provides organizations with the tools to make better-informed decisions, achieve greater cost efficiency, align budgeting with strategic goals, mitigate risks, and realize long-term savings. By understanding and responding to the true costs of their investments, organizations can optimize their resources and enhance overall performance.
What is the relationship between TCO and sustainability in supply chain management?
Understanding TCO and Sustainability in SCM
The relationship between Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and sustainability in Supply Chain Management (SCM) lies in their ability to create a comprehensive and long-term view of the supply chain's efficiency and effectiveness. TCO, which encompasses all direct and indirect costs associated with a product or service, allows organizations to make informed decisions when considering supplier and procurement options. Sustainability, on the other hand, focuses on the environmental, social, and economic impacts of the supply chain, ensuring a responsible and resilient system.
Integration of TCO and Sustainability
By integrating TCO and sustainability, companies can align their financial objectives with their commitment to addressing social and environmental issues. This integration allows not only for improved cost management but also fosters a more responsible and ethical supply chain. Identifying and evaluating the externalities, such as carbon emissions, waste generation, and social costs, make it possible for companies to account for the overall impact of their supply chain decisions.
Benefits of a Sustainable and Cost-Efficient SCM
Incorporating both TCO and sustainability in SCM can result in numerous benefits. Firstly, it can lead to cost savings by identifying areas for improvement and managing resources responsibly. For example, sustainable procurement practices may result in reduced packaging and transportation costs. Furthermore, the promotion of fair labor practices ensures a stable and ethical supply chain, minimizing disruptions and reputational risks.
Strengthening Supplier Relationships
Another significant advantage of combining TCO and sustainability is the establishment of strong, long-term relationships with suppliers who share the company's sustainability mindset. Engaging with like-minded suppliers not only improves the supply chain's performance but also ensures the continuity of best practices and the pursuit of innovative solutions to address emerging challenges and industry trends.
Creating Competitive Advantage
Companies that prioritize TCO and sustainability in their SCM can create a competitive advantage by differentiating themselves based on their responsiveness to social and environmental needs. Consequently, this unique positioning attracts conscious consumers, resulting in increased market share and profitability. In addition, a sustainable and cost-efficient supply chain leads to improved brand image and reputation, which can further generate stakeholder trust and loyalty.
In conclusion, the relationship between TCO and sustainability in SCM transcends the common understanding of cost management by incorporating ethical, social, and environmental considerations in decision-making. By addressing both financial and non-financial factors, supply chain managers can create resilient and responsible systems that generate long-term value for businesses and stakeholders alike.
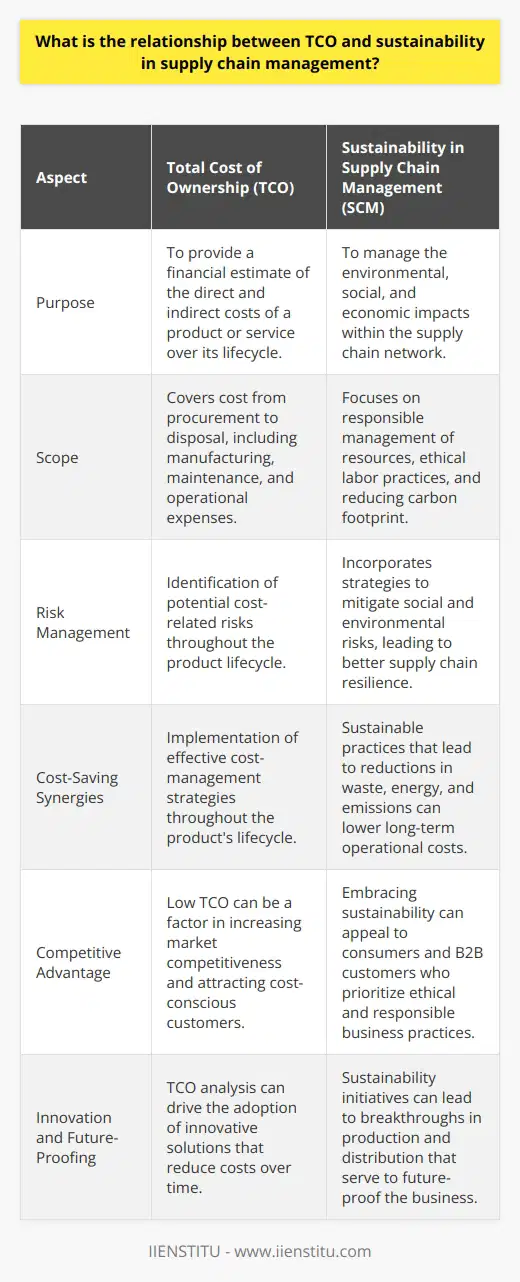
How does incorporating TCO in supply chain design support risk management and mitigation?
Understanding TCO and Risk Management
Incorporating Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in supply chain design is a crucial aspect of risk management and mitigation. TCO is the sum of all costs of acquiring, operating, and maintaining a product or service throughout its lifecycle. By analyzing TCO, organizations can uncover hidden expenses, reduce risks, and make informed decisions.
Reducing Supply Chain Disruptions
One way TCO supports risk management is by reducing supply chain disruptions. By considering all costs involved in the supply chain, including transportation, storage, and lead times, companies can identify potential risks and weak points. They can then develop contingency plans for these risks or seek alternative suppliers, thereby protecting business operations and reducing potential losses.
Improving Supplier Relationships
Another way TCO supports risk management is through improving supplier relationships. By understanding the cost implications of working with different suppliers, organizations can choose suppliers that offer better value or are lower-risk. This can help to minimize supply risks, foster long-term partnerships, and create a more resilient supply chain.
Enhancing Decision-Making
Additionally, TCO enables organizations to make better strategic decisions. By comparing the costs and potential risks of multiple supply chain design options, companies can identify opportunities for cost savings and risk reduction. This can lead to more efficient operations, lower costs, and even a competitive advantage in the market.
Promoting Sustainability
Moreover, incorporating TCO into supply chain design can also promote sustainability. By evaluating the environmental and social impacts of various supply chain options, organizations can minimize negative impacts and reduce long-term risks related to environmental regulations, customer preferences, or reputation damage. This supports risk management and contributes to the overall resilience of an organization.
In conclusion, incorporating TCO into supply chain design supports risk management and mitigation by helping to uncover hidden costs, reduce supply chain disruptions, improve supplier relationships, enhance decision-making, and promote sustainability. Together, these elements enable organizations to create more resilient supply chains, better manage uncertainties and respond more effectively to external threats.
What are some common challenges faced by organizations in implementing TCO-focused strategies in their supply chains?
Challenges in Implementing TCO-focused Strategies
Understanding TCO Components
One common challenge faced by organizations in implementing total cost of ownership (TCO) focused strategies in their supply chains is the proper understanding of TCO components. TCO includes not only the purchase price but also costs associated with transportation, storage, taxes, and disposal. Organizations must clearly define and consistently apply these components across the supply chain to create a comprehensive cost model.
Lack of TCO Expertise
Another challenge is the lack of TCO expertise within the organization. TCO-focused strategies require a dedicated team with specific skills and knowledge to analyze and optimize the supply chain through a TCO lens. Organizations often struggle to find, train, and retain professionals who possess the necessary expertise.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data collection and analysis are essential for creating a successful TCO model. Organizations often encounter difficulties when collecting accurate and granular data from suppliers on direct and indirect costs, as well as non-price factors that may impact overall TCO. This lack of visibility can lead to inadequate decision-making and ineffective TCO strategies.
Supplier Resistance
Organizations frequently face resistance from suppliers when implementing TCO-focused strategies. Suppliers may perceive these strategies as an attempt to reduce the purchase price or shift cost responsibilities to them. Building trust, transparency, and communication between organizations and suppliers are vital in overcoming this resistance and ensuring a collaborative approach to cost optimization.
Integrating TCO with Existing Processes
Integrating TCO into existing procurement and supply chain processes is another challenge. Organizations may struggle to adapt their current practices to accommodate TCO-focused strategies, leading to resistance or inertia when it comes to change management. A well-prepared implementation plan, including stakeholder buy-in and robust change management practices, becomes essential to achieve a successful transition to a TCO-driven approach.
Global Complexity
Finally, the global complexity of modern supply chains poses additional challenges for organizations implementing TCO-focused strategies. Different regulations, currencies, taxes, and customs can complicate the process of analyzing and optimizing costs across the supply chain. Organizations must prioritize agility and flexibility, employing advanced analytics and technology solutions to navigate these complexities.
In conclusion, organizations face several challenges when implementing TCO-focused strategies in their supply chains. Overcoming these obstacles, including understanding TCO components, developing expertise, efficient data collection and analysis, addressing supplier resistance, integrating TCO with existing processes, and managing global complexity, are crucial for realizing the benefits of a TCO-driven approach. Organizations that effectively navigate these challenges can achieve a more optimized supply chain, reduce costs, and drive overall business competitiveness.

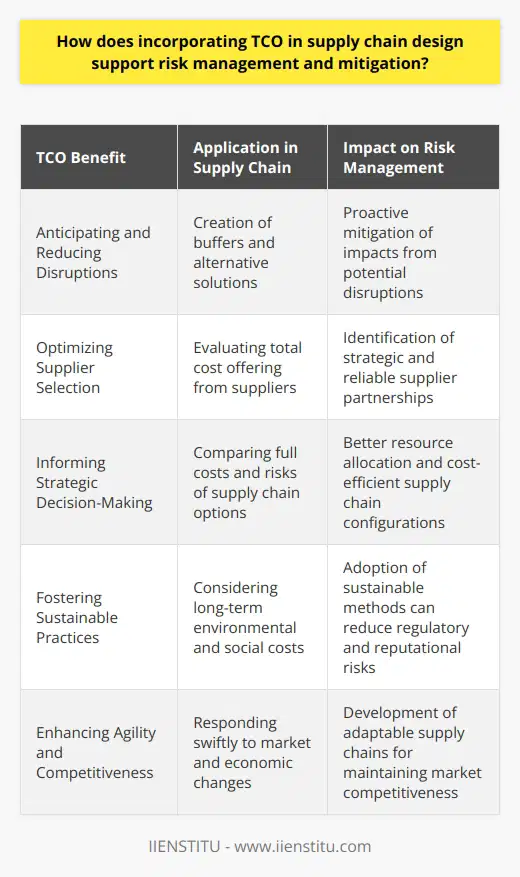
What is the significance of TCO in supply chain management when it comes to achieving a competitive advantage?
Assessing the impact of TCO in Supply Chain Management
The significance of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in supply chain management is deeply rooted in its ability to provide a comprehensive understanding of costs associated with procurement, operations, and logistics in a highly competitive environment. By analyzing and minimizing the TCO, companies can attain a competitive advantage, as it enables them to make informed decisions about cost-effective and efficient strategies for their supply chains.
Holistic evaluation of costs and expenses
TCO involves the systematic identification and assessment of all direct and indirect costs associated with the life cycle of a product, spanning from procurement and production to transportation, maintenance, and disposal. This inclusive perspective on cost management reduces expenses by identifying hidden or overlooked costs, thus aiding companies in strategic decision-making and resource allocation.
Enhancing supplier relationships and performance
In the context of supply chain management, TCO can serve as an essential tool for suppliers' evaluation and negotiation. By comparing supplier costs comprehensively, companies can identify high performing suppliers, effectively manage risks, and enhance overall supplier relationships. Consequently, organizations can nurture long-term partnerships, ensuring quality governance and collaboration across the supply chain.
Promoting sustainable practices and reducing environmental impact
Another dimension of TCO is its potential to identify opportunities for reducing the environmental footprint of business operations. By incorporating sustainability and carbon footprint considerations into the cost management process, companies can make environmentally responsible decisions, resulting in improved brand reputation, regulatory compliance, and market differentiation.
Supporting continuous improvement and innovation
The process of TCO analysis encourages organizations to reevaluate and improve their supply chain efficiency regularly. This continuous evaluation fosters a culture of innovation and improvement, leading to the development of new strategies, cost reduction initiatives, and long-term competitiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the incorporation of Total Cost of Ownership in supply chain management offers a multitude of tangible and intangible benefits that contribute to achieving a competitive advantage. By providing a comprehensive view of costs and facilitating well-informed decision-making, TCO helps organizations excel in supplier relationship management, sustainability initiatives, and continuous improvement - key factors that define a robust and competitive supply chain landscape.
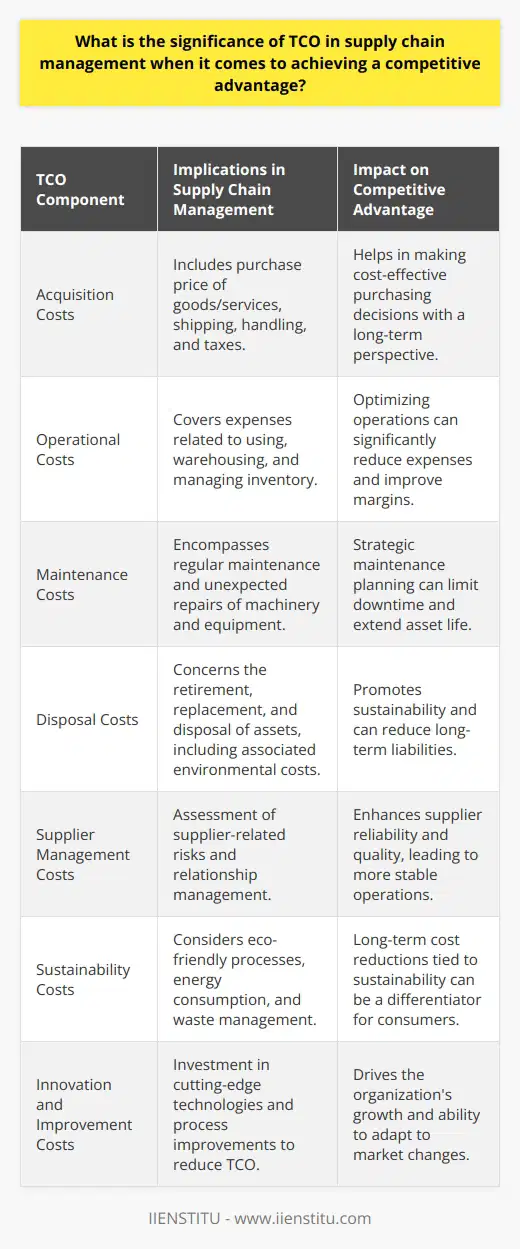
How can organizations ensure accurate and comprehensive TCO analysis to inform their supply chain decisions?
**Understanding the TCO Framework**
In order to ensure accurate and comprehensive Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis, organizations need to understand the TCO framework thoroughly. The TCO framework encompasses not only the direct costs connected to the procurement of a product or service but also the indirect and hidden expenses that arise in the entire lifecycle of the product or service. Knowing the key components of the framework aids in conducting a reliable and accurate TCO analysis.
**Identifying Relevant Costs**
Organizations can improve TCO analysis accuracy by carefully identifying all relevant costs. These costs include tangible costs like materials, labor, and transportation, as well as intangible costs such as product quality, customer satisfaction, and risks associated with supply chain disruptions. A comprehensive list of cost elements enables decision-makers to have a clear view of the complete supply chain and make better-informed decisions.
**Establishing a Cross-Functional Team**
Having a cross-functional team in place helps organizations get accurate TCO analysis results. This team comprises professionals from different departments, such as purchasing, finance, logistics, and operations, contributing their respective expertise to derive a holistic understanding of the TCO. A diverse team stands better equipped to identify and measure all relevant direct and indirect costs, as well as to evaluate risks and opportunities associated with the supply chain.
**Using Standardized Methods and Tools**
Organizations should rely on standardized methods and tools for TCO analysis to ensure accuracy and comprehensibility. Such methods can include Activity-Based Costing (ABC) to allocate indirect costs or a standardized TCO template that organizations can adapt to fit their specific context. By choosing the right methods and tools, organizations can maintain consistency in their TCO analysis and improve the quality of supply chain decision-making.
**Continuous Improvement and Learning**
Lastly, adopting a continuous improvement mindset is crucial for organizations to keep refining their TCO analysis process. Conducting regular reviews and audits of the TCO analysis methods enables identification of any gaps, discrepancies or errors. This, in turn, allows the organization to improve its understanding of supply chain costs and make more informed decisions.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the TCO framework, identification of relevant costs, cross-functional collaboration, standardized methods and tools, and continuous improvement are essential steps for organizations to ensure an accurate and comprehensive TCO analysis. By incorporating these best practices, organizations can make more precise, data-driven decisions in their supply chain management.
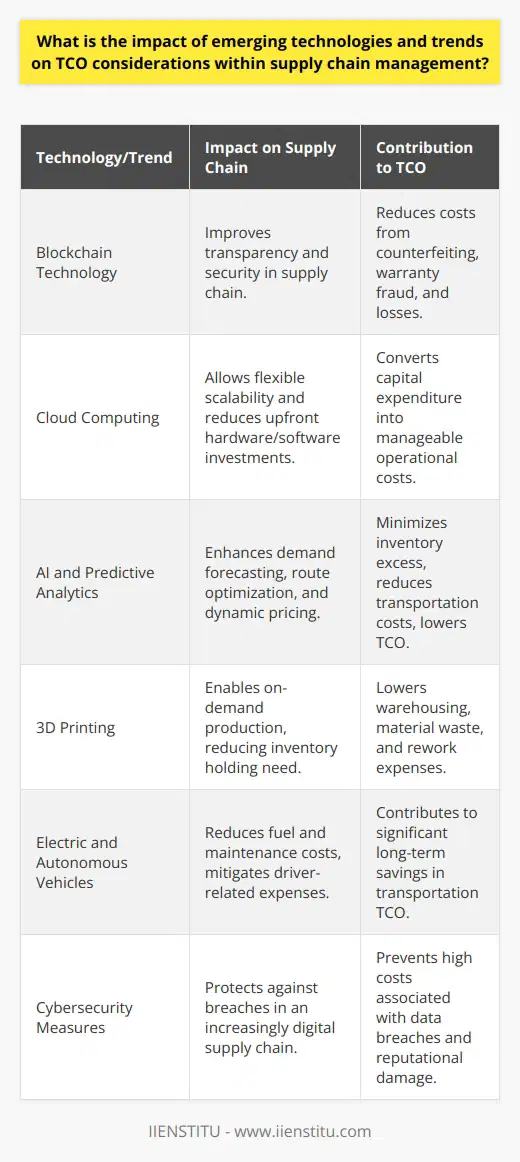
What is the impact of emerging technologies and trends on TCO considerations within supply chain management?
Impact on TCO Considerations
Emerging technologies and trends significantly reshape the landscape of supply chain management, directly impacting Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) considerations. By understanding these impacts, organizations can streamline their supply chain processes and leverage novel technologies to reduce overall costs.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics play a critical role in reducing manual labor expenses, thereby reducing TCO. When companies implement automated material handling systems, warehouse management, and packaging processes, they can effectively minimize labor costs and the risk of human error, ultimately enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Advanced Analytics
The integration of advanced analytics into supply chain operations enables better decision making, planning, and forecasting. Organizations can leverage these insights to identify inefficiencies, optimize processes, and reduce costs throughout the supply chain. Consequently, adopting advanced analytics contributes to more informed TCO considerations and strategic decision making.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices allow for real-time tracking and monitoring of inventory, asset utilization, and transportation. This capability results in improved visibility, accuracy, and control within the supply chain. Increased efficiency through IoT lends itself to reduced TCO by optimizing resource allocation, minimizing delays, and mitigating potential disruptions.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices are becoming increasingly relevant for organizations due to environmental concerns and changing consumer preferences. Incorporating sustainability into supply chain management can not only reduce emissions and waste but can also impact TCO by generating cost savings through waste reduction, energy efficiency, and compliance with evolving regulations.
Collaborative Platforms
Collaborative supply chain platforms have emerged to foster communication, transparency, and cooperation among supply chain partners. These platforms streamline processes, reduce lead times, and optimize inventory levels, ultimately leading to reduced carrying costs and an overall lower TCO.
To conclude, the integration of emerging technologies and trends is essential for organizations to remain competitive and maintain a low TCO amidst a rapidly changing supply chain landscape. By embracing automation, advanced analytics, IoT, sustainable practices, and collaborative platforms, businesses can optimize their supply chain operations and intelligently make TCO considerations, leading to cost savings and increased efficiency.
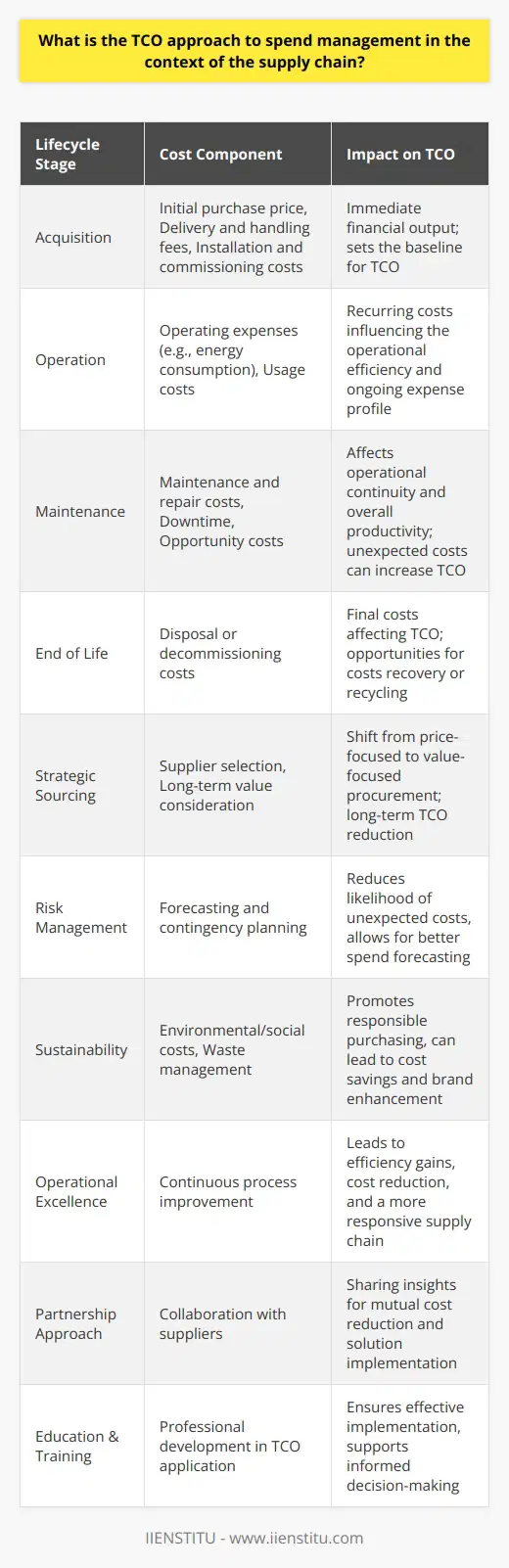
What is the TCO approach to spend management in the context of the supply chain?
Understanding the TCO Approach
The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) approach to spend management refers to a comprehensive method of assessing and analyzing the direct and indirect costs associated with procurement, warehousing, transportation, and other supply chain components. By adopting a TCO perspective, organizations are able to make more informed decisions on sourcing and procurement practices, ultimately reducing costs and improving efficiency across the entire supply chain.
Direct and Indirect Costs
To effectively implement the TCO approach, it is necessary to consider both direct and indirect costs. Direct costs consist of expenses related to acquiring and transporting goods, such as the costs of materials, production, and shipping. Indirect costs, on the other hand, are less easily quantifiable expenses that may arise from procurement-related activities, such as product testing, maintenance, and supplier performance assessment.
Impact on Supplier Selection and Relationships
In the context of supply chain management, the TCO approach enables organizations to make more strategic supplier selections by considering the overall costs associated with a particular vendor, rather than solely focusing on the unit price of products or services. This can entail evaluating factors such as supplier reliability, product quality, and lead times, in addition to direct costs. By doing so, it is possible to cultivate stronger and more fruitful supplier relationships, collaborating to optimize processes and minimize waste.
Benefits of TCO in Spend Management
Implementing the TCO approach offers a number of benefits in terms of spend management within the supply chain. By taking into account the full range of costs and risks associated with procurement, companies can uncover hidden inefficiencies and cost drivers, leading to more effective spend management strategies. The TCO approach also promotes a greater understanding of the end-to-end supply chain, which can help to identify opportunities for cost reduction and process improvements, such as automation, inventory management, and demand planning.
Conclusion
In summary, the TCO approach provides a comprehensive framework for spend management within the context of supply chain management by considering a wide spectrum of direct and indirect costs. This method equips organizations with the necessary insights to make more informed supplier decisions, cultivate better supplier relationships, and identify areas for cost reduction and process optimization. Ultimately, the TCO approach leads to greater efficiency, cost savings, and a more resilient supply chain.
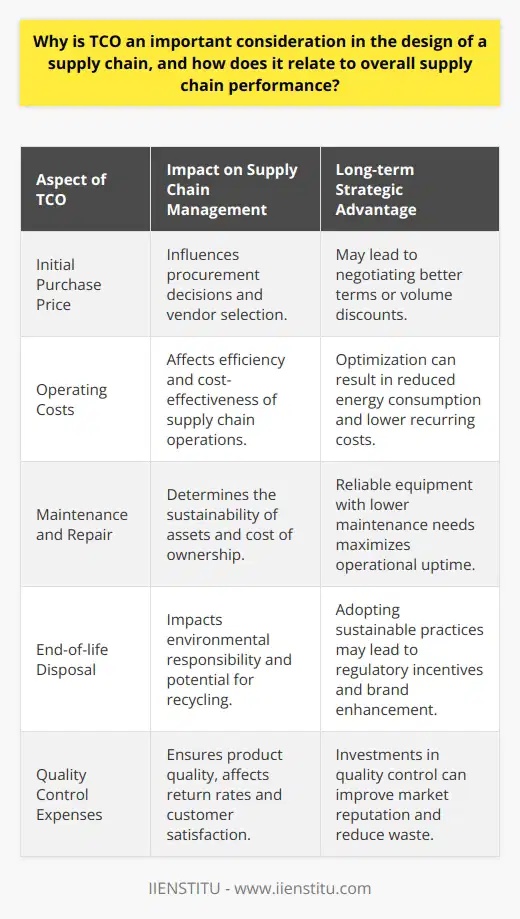
Why is TCO an important consideration in the design of a supply chain, and how does it relate to overall supply chain performance?
Supply Chain Design and TCO
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is a crucial aspect in the design of a supply chain, as it reveals the comprehensive costs associated with the procurement, production, usage, and disposal of goods and services. TCO helps organizations make well-informed decisions in the design of supply chains by providing a clear understanding of direct and indirect expenditures. Supply chain professionals can then effectively compare alternate channels and strategies, considering all relevant factors for sustainable and financially efficient operations.
Improving Supply Chain Performance
Understanding TCO's impact on the overall supply chain performance can lead to more effective resource allocation, as well as enhanced risk management. By examining direct costs, such as transportation and production, along with indirect costs, like product returns and lost sales from stock-outs, organizations can identify areas for improvement and optimize performance.
Strategic Decision-Making
Incorporating TCO in supply chain design prompts a shift towards strategic, long-term thinking. It enables businesses to assess potential risks and design strategies to address them, creating resilience and adaptability in a highly competitive and ever-changing market. With a holistic view of the costs, organizations can implement supply chain solutions that contribute to long-term sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Enhancing Collaboration and Communication
TCO promotes collaboration between different departments, such as purchasing, production, logistics, and finance, due to its multidisciplinary nature. Addressing TCO ensures a full understanding of the supply chain's financial dimensions, fostering improved communication and collaboration across the organization. This interdepartmental cooperation is essential in creating an efficient, agile supply chain that effectively adapts to industry trends and changes.
Achieving a Competitive Advantage
By understanding and managing the TCO in supply chain design, organizations gain a competitive edge. A well-structured supply chain that reflects a clear understanding of TCO can produce superior results, with reduced costs, improved efficiency, and ultimately, increased customer satisfaction. Companies that actively consider TCO while designing supply chains stand at an advantage in the marketplace and are better equipped to maintain a sustainable, high-performing operation.
In conclusion, TCO plays a significant role in supply chain design, as it provides a comprehensive view of costs, enables strategic decision-making, enhances collaboration and communication, and contributes to a competitive advantage. By incorporating TCO into the design of a supply chain, organizations can optimize overall performance and strengthen their market position.
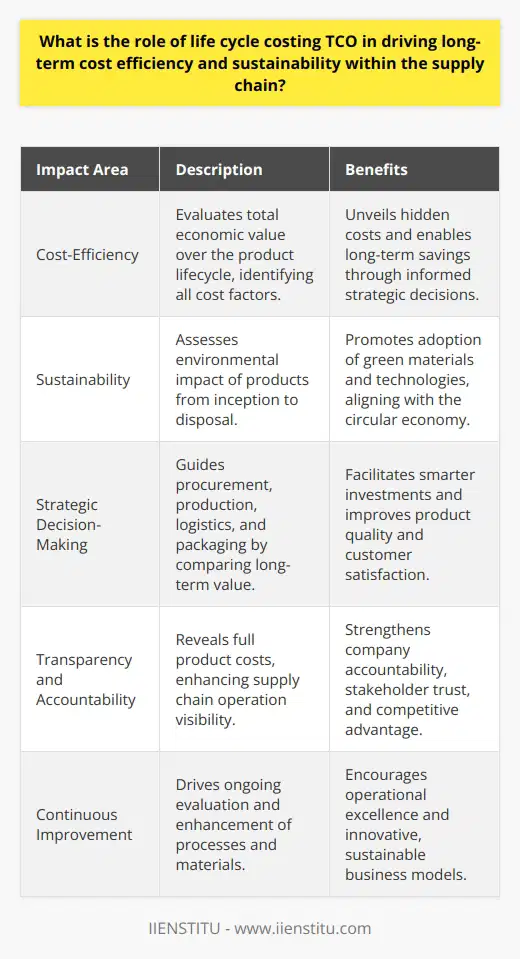
What is the role of life cycle costing TCO in driving long-term cost efficiency and sustainability within the supply chain?
Role of Life Cycle Costing in Driving Efficiency
Life cycle costing or total cost of ownership (TCO) is a crucial aspect of long-term cost efficiency and sustainability within the supply chain. By considering the whole life cycle of a product, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, life cycle costing offers a comprehensive understanding of the financial and environmental implications of a product or process.
Importance of a Holistic Approach
Applying a holistic approach through life cycle costing helps to identify unforeseen costs and reveal potential savings in materials, energy, and waste management. As supply chains become increasingly complex and global, life cycle costing supports decision-making by enabling accurate forecasting of true costs beyond the initial investments.
Supporting Proactive Business Decisions
Total cost of ownership encourages proactive business decisions. By identifying the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly materials, processes, and transportation options, companies are able to optimize their supply chain at every stage. This can result in reduced operating expenses, increased efficiencies, and higher customer satisfaction.
Contributing to Sustainable Development
Life cycle costing is also an essential tool for environmental sustainability. By assessing the environmental impacts and resource consumption of a product throughout its life cycle, it supports the development of sustainable practices and contributes to the circular economy. This can help reduce a company’s carbon footprint and minimize negative environmental impacts associated with resource extraction, transportation, and waste disposal.
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Moreover, life cycle costing drives transparency in supply chain management. Communicating information about the total cost of ownership facilitates reporting on social, economic, and environmental performance. This transparency can lead to improved stakeholder trust and strengthened relationships with customers, suppliers, and business partners.
Promoting Continuous Improvement
Lastly, life cycle costing prompts continuous improvement in supply chain management. By monitoring costs and exploring alternative solutions throughout the life cycle of a product, companies are incentivized to consistently innovate and seek out more efficient and sustainable production methods.
In conclusion, life cycle costing serves as a critical tool for driving long-term cost efficiency and sustainability within the supply chain. It encourages a holistic approach, supports proactive decision-making, fosters sustainability, ensures transparency, and promotes continuous improvement, ultimately enhancing the overall performance and resilience of supply chains.
What is the importance of considering TCO in supply chain performance measurement and evaluation?
Significance of TCO in the Evaluation Process
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is a critical factor in assessing supply chain performance as it enables organizations to capture a comprehensive understanding of the direct and indirect costs associated with the procurement, production, and distribution of goods and services. By considering TCO, companies can better identify inefficiencies, cost drivers, and potential areas for improvement, ultimately leading to enhanced performance and more informed decision-making in the supply chain.
Direct and Indirect Costs
TCO considers both direct costs, such as raw material and labor expenses, and indirect costs, such as overhead, transportation, and inventory carrying costs. This holistic approach goes beyond conventional performance metrics such as purchase price or cost per unit by capturing a more accurate representation of the total expenses incurred throughout the entire supply chain process. This inclusive analysis helps organizations identify areas where cost savings and efficiency improvements can be achieved.
Identifying Inefficiencies and Cost Drivers
By analyzing TCO, companies can pinpoint inefficiencies and cost drivers within their supply chain operations. Through the process of identifying these elements, organizations can more effectively target and optimize specific processes, leading to potential cost reductions, improved lead times, and overall increased efficiencies. This enables businesses to maintain a competitive edge and generate better value for their customers.
Opportunities for Improvement
A TCO-driven performance evaluation also uncovers opportunities for continuous improvement and innovation within the supply chain. By highlighting the areas where inefficiencies or high costs exist, companies can prioritize and allocate resources to more strategic initiatives, such as sourcing alternatives, adopting new technologies, or exploring different transportation options. These improvements can translate into reduced costs, improved service levels, and sustainable competitive advantages in the long run.
Informed Decision-Making
Finally, the consideration of TCO in supply chain performance measurement and evaluation enables organizations to make more informed decisions based on holistic and accurate cost information. Comprehensive data on the total costs associated with a specific product or service helps businesses make more informed choices regarding sourcing, production, and logistics operations. By understanding the financial impacts of these decisions, companies can more effectively manage resources, mitigate risks, and ultimately optimize their overall supply chain performance.
In conclusion, incorporating TCO in the performance measurement and evaluation of supply chain operations is essential for organizations seeking to maximize their efficiency, competitiveness, and long-term success. By comprehensively accounting for direct and indirect costs, identifying inefficiencies and cost drivers, uncovering areas for improvement, and informing smart decision-making, a TCO-focused approach significantly contributes to the optimization of supply chain performance.
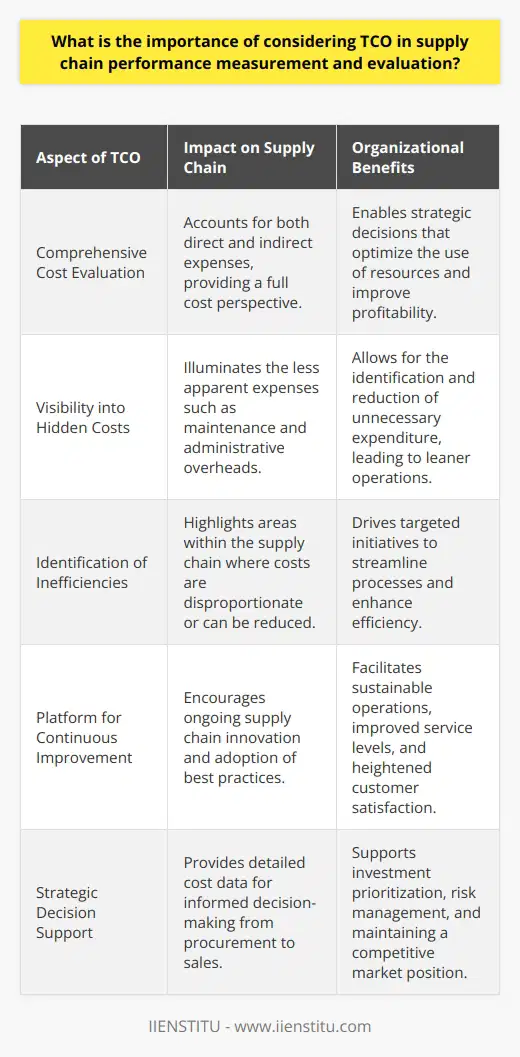
How do industry best practices and benchmarking play a role in TCO analysis and supply chain management?
Role of Best Practices in TCO Analysis
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis is a critical tool in supply chain management that quantifies the direct and indirect costs associated with a product or service. Industry best practices significantly enhance TCO analysis by providing a framework for comparing and streamlining processes, ensuring efficient implementation of cost control measures, and promoting continuous improvement.
Influencing Factors in TCO Analysis
Best practices in the industry play a vital role in TCO analysis through various influencing factors. These factors include comprehensiveness, standardization, risk management, and stakeholder engagement.
Comprehensiveness:
Incorporating industry benchmarks expands the scope of TCO analysis, enabling organizations to evaluate costs across multiple dimensions and facilitating a holistic approach to cost management.
Standardization:
By adopting industry best practices, companies can standardize their processes and procedures, simplifying the TCO analysis process and facilitating benchmarking with industry peers.
Risk Management:
Industry best practices in TCO analysis also help organizations identify potential risks and vulnerabilities, minimizing the likelihood of cost overruns and fostering proactive risk mitigation strategies.
Stakeholder Engagement:
To achieve optimal TCO, transparency and engagement with stakeholders such as customers, suppliers, and employees are essential. Implementing industry best practices for TCO analysis contributes to enhancing trust and collaboration between stakeholders, which in turn leads to better decision-making and risk management.
Benchmarking's Role in Supply Chain Management
Benchmarking, a process of comparing internal performance with that of industry peers or best-in-class companies, is crucial for effective supply chain management. It offers numerous benefits, such as identifying gaps, setting targets, monitoring progress, and driving continuous improvement.
Identifying Gaps:
Benchmarking against industry best practices helps organizations identify gaps in their supply chain performance, providing opportunities for setting improvement goals and prioritizing areas of focus.
Setting Targets:
Once gaps have been identified, companies can establish performance targets that align with industry standards or best practices, motivating employees to achieve higher levels of performance.
Monitoring Progress:
By consistently benchmarking against industry best practices, organizations can track their progress over time, helping managers evaluate the success of implemented strategies and making data-driven decisions that enhance supply chain efficiency.
Driving Continuous Improvement:
Benchmarking provides an impetus for continuous improvement, as organizations strive to match or surpass industry standards and best practices, leading to lasting improvements in supply chain performance and overall competitiveness.
In conclusion, industry best practices and benchmarking play an essential role in TCO analysis and supply chain management by promoting comprehensiveness, standardization, risk management, and stakeholder engagement. Additionally, benchmarking in supply chain management drives continuous improvement through identifying gaps, setting targets, monitoring progress, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
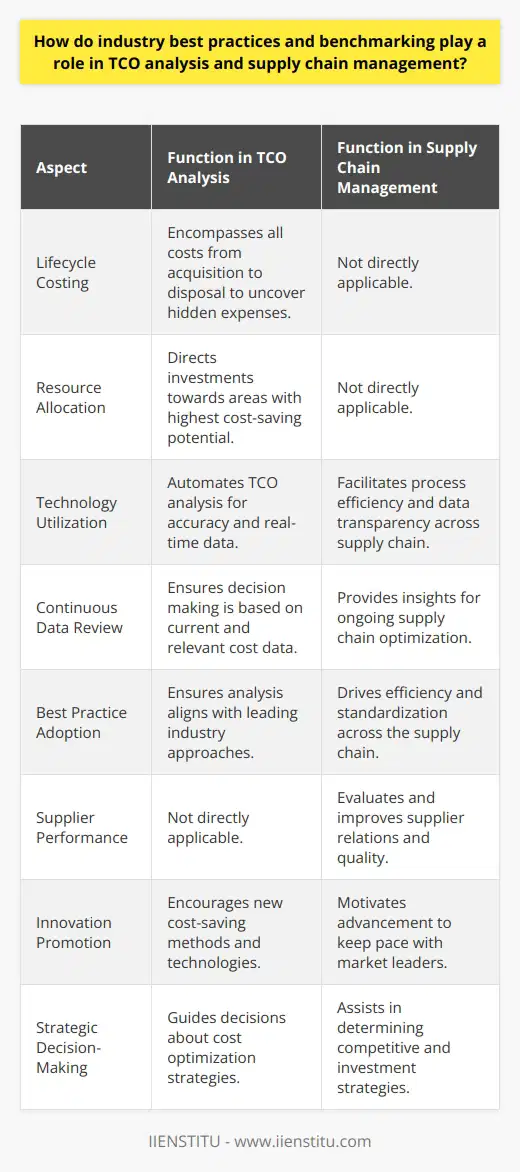
In the context of global supply chains, how can organizations effectively address cross-border challenges and considerations related to TCO?
Addressing Cross-Border TCO Challenges
Global supply chains face numerous obstacles when addressing total cost of ownership (TCO) challenges and considerations across international borders. To effectively address these issues, organizations must implement strategic and proactive approaches.
Understanding Complexities
Firstly, organizations must recognize the complexities that come with cross-border transactions, such as cultural differences, political influence, and international regulations. By acknowledging these factors, they can develop strategies to minimize risks and improve overall TCO levels.
Managing Supply Chain Risks
Companies need to enhance their risk management approaches in order to identify potential hazards, assess vulnerability, and develop mitigation plans. These strategies can include conducting thorough due diligence, leveraging advanced analytics, and creating contingency plans in case of unforeseen disturbances in the supply chain.
Improving Visibility and Collaboration
Effective supply chain management requires enhanced visibility and collaboration among all stakeholders, from suppliers to customers. By implementing digital tools, such as real-time data analytics and transportation management systems, organizations can efficiently monitor their supply chain operations, allowing for easier identification of cost drivers and potential bottlenecks.
Optimizing Logistics
Focusing on logistics optimization is a key approach for controlling cross-border TCO. By implementing efficient transportation and warehouse management practices, companies can reduce overall lead times and inventory-related costs, while ensuring timely delivery of goods.
Embracing Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming a vital consideration in global supply chains, particularly as environmental concerns and socially responsible practices gain importance worldwide. Integrating sustainable practices into cross-border operations, such as reducing the carbon footprint and embracing socially responsible sourcing methods, can contribute to long-term TCO reduction and improve overall supply chain resilience.
Enhancing Supplier Relationships
Maintaining strong supplier relationships allows organizations to negotiate lower costs, improve delivery timelines, and obtain better quality products and services. Companies should foster positive relationships with key suppliers by clearly defining expectations, engaging in open communication, and consistently evaluating supplier performance.
In conclusion, addressing cross-border TCO challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that considers the complexities of international supply chain management. By implementing strategic and proactive tactics, organizations can effectively manage the costs and risks associated with their global operations and make informed decisions to optimize TCO.
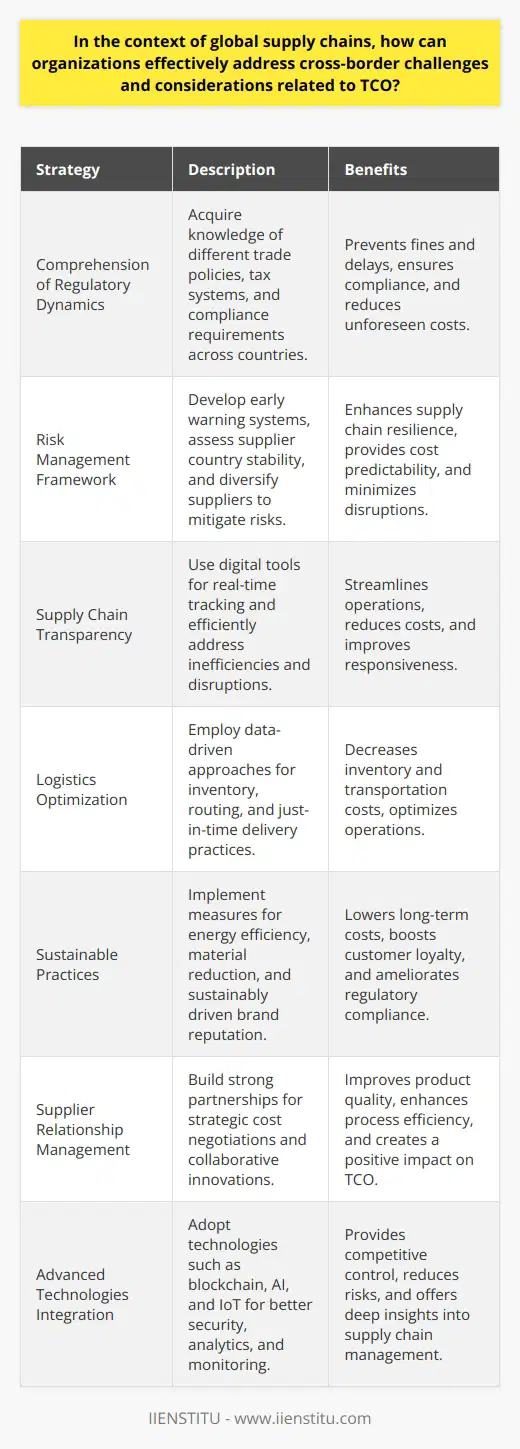
What is the role of TCO in strategic sourcing and supplier selection within supply chain management?
Role of TCO in Strategic Sourcing
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) plays a critical role in strategic sourcing within supply chain management. It's a financial estimate that helps firms determine direct and indirect costs of a product or system.
TCO in Cost Evaluation
Firms use TCO as a cost evaluation tool. It provides upfront costs and exposes hidden expenses. These costs include procurement, operations, and disposal costs. It enables companies to make data-driven decisions, balancing cost with risk.
TCO in Supplier Selection
In supplier selection, TCO helps firms identify and select effective suppliers. It aids in analyzing the cost-effectiveness of partnering with potential suppliers. Through this, firms can ensure choosing suppliers that provide value and align with their financial strategy.
TCO in Enhancing Efficiency
TCO serves as a performance measurement. It helps to track and understand costs better, leading to improved efficiency. Effective cost management enables firms to be more competitive.
Implications of TCO in Supply Chain Management
Incorporating TCO in supply chain management results in better financial control and increased value. It helps companies set proper pricing strategies, gain a competitive edge, and maximize profits.
To summarize, TCO is vital in strategic sourcing and supplier selection. Through its use, companies can gain a clear understanding of costs, making the sourcing process more efficient and profitable.
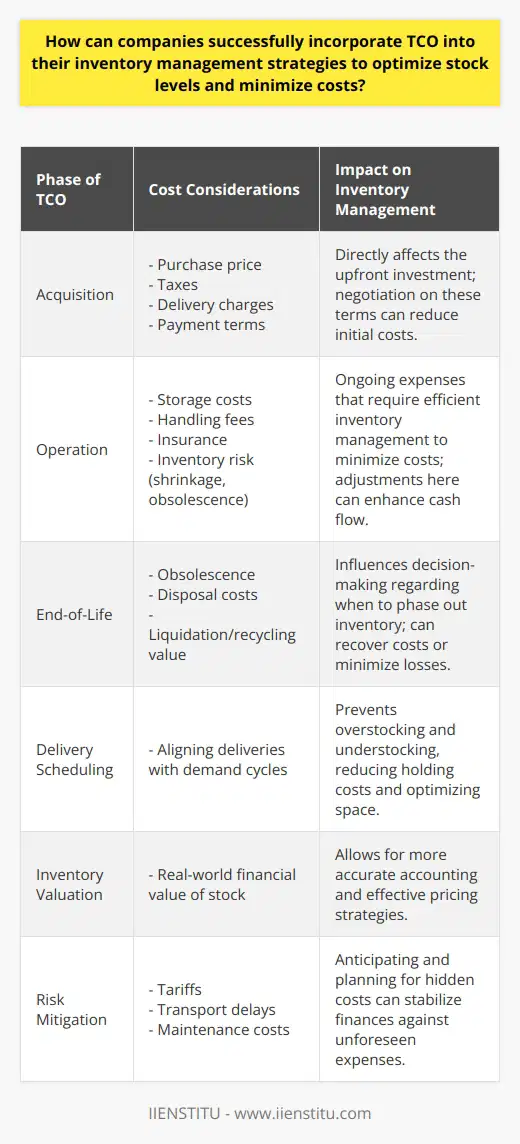
How can companies successfully incorporate TCO into their inventory management strategies to optimize stock levels and minimize costs?
Understanding TCO in Inventory Management
Companies require a thorough understanding of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in inventory management. Analyzing TCO includes evaluating all direct and indirect costs of inventory. This includes purchasing costs, storage, maintenance, support and indirect costs like goods lost and obsolete.
Methods to Incorporate TCO into Inventory Management
To successfully incorporate TCO, companies must first carry out comprehensive cost analysis. This involves categorizing costs into acquisition, operation, and disposal. They must then identify cost drivers in order to place controls. By understanding the influence of each cost component, organizations can better manage their inventory.
TCO and Arrival Time Management
Effective utilization of TCO also involves controlling arrival times of inventory. Ensuring arrival times align with demand can avoid unnecessary stock holding costs. This promotes efficient utilization of storage facilities and reduces redundant capital expenditures.
TCO in Inventory Valuation
TCO plays a vital role in inventory valuation. Companies should consider all costs related to inventory. This will give a realistic valuation of inventory. It will also help in forecasting, planning, budgeting and setting realistic sales prices.
Reducing Risk with TCO
Using TCO while making purchasing decisions reduces risk. This involves considering potential hidden costs (e.g., transport, maintenance). This proactive approach to cost awareness can minimize the risk of unforeseen expenditures.
Benefits of TCO in Inventory Management
Incorporating TCO in inventory management enhances overall business operations. It not only minimizes costs but also optimizes stock levels. This leads to improved financial performance, higher customer satisfaction and increased profitability.
Conclusion
Therefore, by successfully integrating TCO into their inventory management strategies, companies can effectively reduce costs and improve profitability. The process demands a systematic approach to cost analysis, the ability to identify and control cost drivers, and proactive management of stock arrival times and inventory valuation.
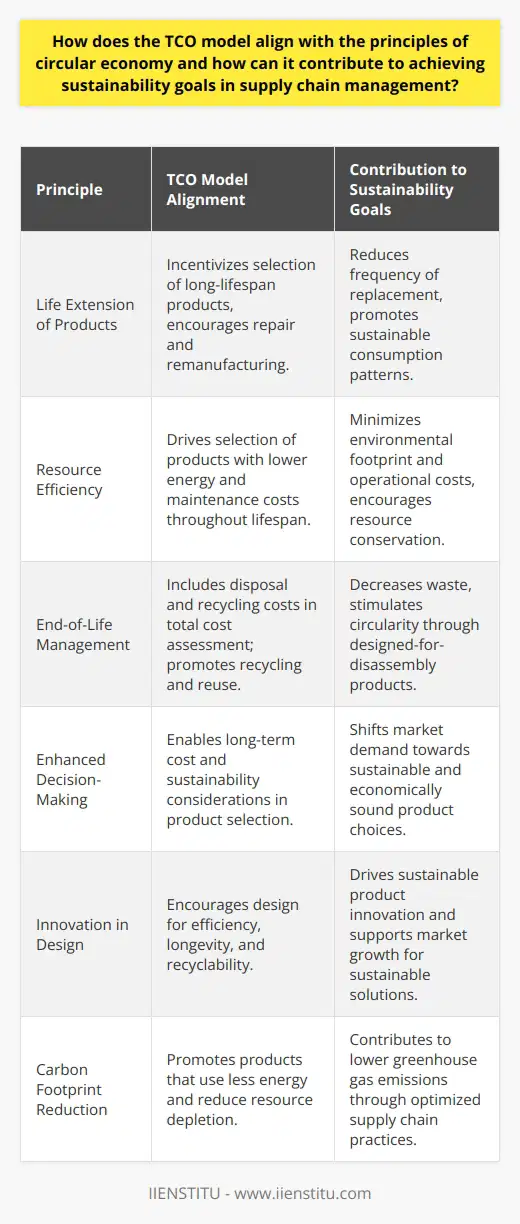
How does the TCO model align with the principles of circular economy and how can it contribute to achieving sustainability goals in supply chain management?
The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Model and Circular Economy: Alignment and Sustainability in Supply Chain Management
The TCO model aligns with the principles of a circular economy in several key ways. First, both stress the importance of long-term thinking. The TCO model emphasizes the importance of considering not just the purchase price of a product, but also the ongoing operational costs. Similarly, the circular economy focuses on full lifecycle costs, including end-of-life management and the potential for reuse or recycling.
Sustainability Enhancement through TCO
Second, the TCO model encourages the prevention of waste and the conservation of resources. This implies the efficient use of materials and energy, which aligns perfectly with the key principles of the circular economy. By reducing waste, both the TCO model and the circular economy contribute to environmental sustainability.
TCO in Meeting Sustainability Goals
The TCO model also directly contributes to achieving sustainability goals in supply chain management. By making businesses more aware of the total lifecycle costs of their products, it encourages them to design products that are more durable, recyclable, and energy-efficient. This not only conserves resources and reduces waste, but also saves money in the long term.
Overall, the TCO model promotes the circular economy's focus on long-term sustainability, efficiency, and waste reduction. It provides a practical framework for businesses to realize these goals, benefiting both the environment and their bottom line.
End: TCO and Circular Economy – A Synergy
In conclusion, the synergy between the TCO model and the principles of circular economy underscores its importance to achieving sustainability goals in supply chain management. Adopting such models can enable businesses to not only meet their sustainability commitments but also enhance their profitability in the long term.