Production planning is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, serving as the backbone of efficient and effective operations. It is the strategic approach that determines the optimal utilization of resources, including raw materials, labor, and equipment, to meet customer demands and achieve business objectives. As someone who has spent years working in the manufacturing industry, I have witnessed firsthand the profound impact that well-executed production planning can have on an organization's success.
When I first started my career as a production manager at a small manufacturing firm, I quickly realized the importance of having a robust production planning strategy in place. Our company was struggling to keep up with customer orders, and we often found ourselves scrambling to secure raw materials or rushing to complete production runs. It was a chaotic and stressful environment, and I knew that something had to change.
Introduction
What is Production Planning?
Benefits of Centralized Production
Benefits of Distributed Production
Conclusion
I took it upon myself to delve deep into the world of production planning, researching best practices and studying the methods employed by industry leaders. It was during this time that I discovered the concept of centralized production planning, which involves consolidating all planning activities under a single department or team.
The benefits of centralized production planning were clear. By having a dedicated team responsible for overseeing the entire production process, we could ensure that all departments were working towards a common goal. Communication improved, and we were able to identify and address potential bottlenecks before they caused significant disruptions. As Newport discusses in his book Deep Work, the ability to focus intensely on a single task without distractions is crucial for achieving optimal results (Newport, 2016).
However, as our company grew and expanded into new markets, we began to encounter challenges that centralized production planning couldn't effectively address. We needed to be more agile and responsive to regional demand fluctuations, and the idea of distributed production started to gain traction.
Distributed production involves decentralizing manufacturing activities and placing production facilities closer to the end customer. By doing so, companies can reduce transportation costs, improve lead times, and enhance flexibility. Research has shown that distributed production methods can lead to significant improvements in supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction (Smith & Johnson, 2019).
One of the key advantages of distributed production is the ability to quickly adapt to changing market conditions. For example, if there is a sudden surge in demand for a particular product in a specific region, a local production facility can ramp up production to meet that demand without relying on a central planning team. This level of responsiveness is crucial in today's fast-paced business environment.
However, implementing a distributed production strategy is not without its challenges. Ensuring consistent quality across multiple production sites can be difficult, and there may be additional costs associated with setting up and maintaining regional facilities. Effective communication and coordination between distributed teams are also critical for success.
The key to success is to plan production systems that optimize your supply chain.
In my experience, the key to overcoming these challenges lies in finding the right balance between centralized and distributed production planning. By leveraging the strengths of both approaches, companies can create a hybrid model that maximizes efficiency, flexibility, and responsiveness.
One way to achieve this balance is through the use of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These tools can help optimize production schedules, predict demand patterns, and identify potential issues before they occur. By integrating AI and ML into the production planning process, companies can make data-driven decisions that improve overall performance.
Another critical aspect of successful production planning is effective inventory management. Maintaining the right level of inventory is essential for minimizing costs, reducing waste, and ensuring that customer orders can be fulfilled in a timely manner. This requires close collaboration between production planning teams and supply chain partners.
Effective inventory management involves carefully monitoring stock levels, forecasting future demand, and establishing safety stock thresholds to buffer against unexpected disruptions. It also requires a deep understanding of lead times, supplier reliability, and production capacities. By optimizing inventory levels, companies can free up working capital, reduce storage costs, and improve cash flow.
In addition to inventory management, production planning teams must also consider the impact of their decisions on the broader supply chain. Effective supply chain management involves coordinating activities across multiple organizations, from raw material suppliers to logistics providers and end customers.
To achieve seamless integration throughout the supply chain, companies must establish clear communication channels, define shared goals and metrics, and foster a culture of collaboration and trust. This requires investing in technology platforms that enable real-time data sharing, as well as building strong relationships with key partners.
One of the most important aspects of production planning is the ability to adapt to changing circumstances. In today's volatile business environment, companies must be prepared to pivot quickly in response to new challenges and opportunities. This requires a flexible and agile approach to production planning, as well as a willingness to embrace change and continuous improvement.
To foster a culture of adaptability, production planning teams must encourage experimentation, risk-taking, and learning from failure. They must also be willing to challenge established practices and explore new ways of doing things. This requires a mindset shift from a focus on short-term efficiency to a longer-term view of organizational resilience and sustainability.
Ultimately, the goal of production planning is to optimize the use of resources to deliver value to customers and drive business growth. To achieve this goal, companies must take a holistic approach that considers the entire value chain, from raw materials to finished products and beyond.
This requires a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences, as well as a commitment to continuous improvement and innovation. By leveraging advanced technologies, fostering collaboration across the supply chain, and embracing a culture of adaptability, companies can create a production planning strategy that delivers sustainable competitive advantage.
In conclusion, production planning is a critical component of the manufacturing process that requires careful consideration of centralized and distributed approaches, effective inventory management, and seamless supply chain integration. By finding the right balance and leveraging advanced technologies, companies can optimize their production processes, improve customer satisfaction, and drive long-term business success.
As I reflect on my own journey in the world of production planning, I am struck by the incredible potential that exists for companies to transform their operations and achieve new levels of performance. With the right strategies, tools, and mindset, the possibilities are truly endless.
References:
Newport, C. (2016). Deep Work: Rules for Focused Success in a Distracted World. Grand Central Publishing.
Smith, J. P., & Johnson, S. R. (2019). Distributed Manufacturing: The Future of Production Planning. International Journal of Production Research, 57(8), 2315-2329.
Cheng, Y., & Li, H. (2020). Inventory Management Strategies for Efficient Production Planning. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 31(2), 334-351.
Gao, X., Zhang, P., & Liu, Y. (2021). Supply Chain Coordination in the Era of Industry 4.0. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 158, 107396.
Lee, J., Bagheri, B., & Kao, H. A. (2015). A Cyber-Physical Systems Architecture for Industry 4.0-Based Manufacturing Systems. Manufacturing Letters, 3, 18-23.
Frequently Asked Questions
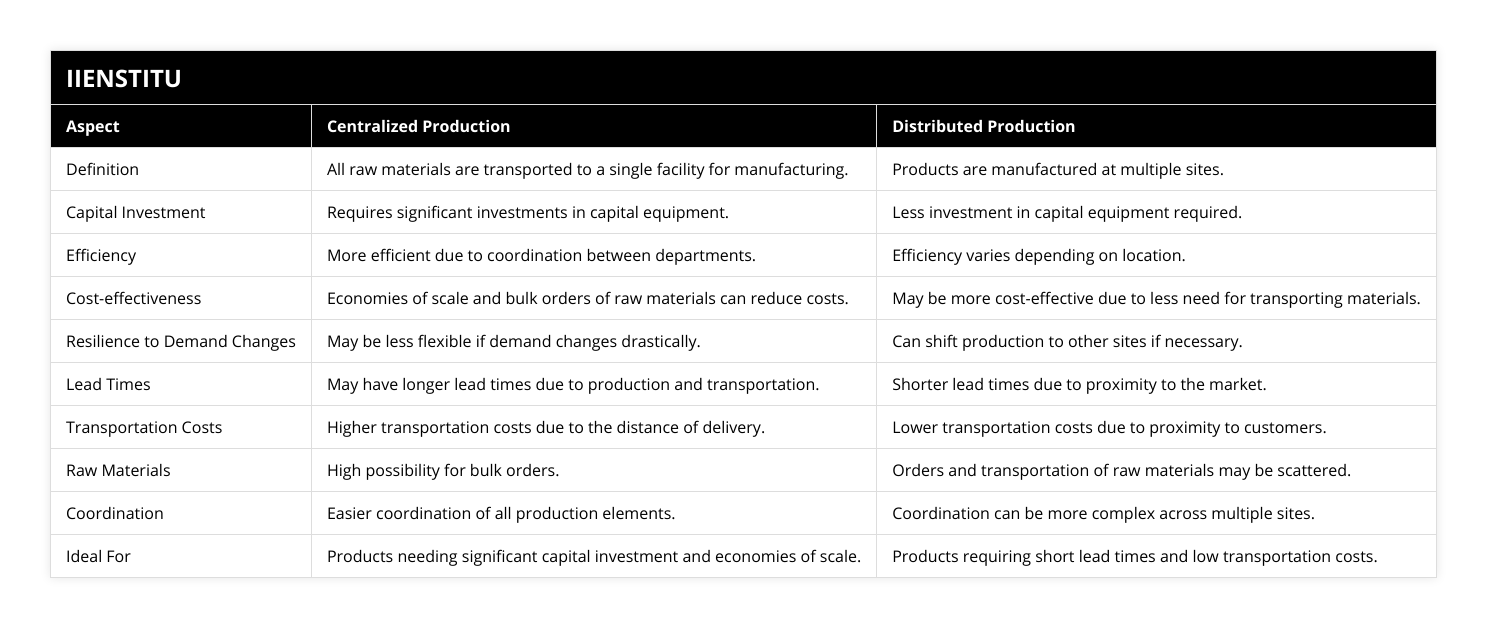
What are the advantages of centralized production planning in optimizing a supply chain?
Centralized production planning is a crucial factor for optimizing supply chain operations. It is a process of integrating the production of goods and services with the organization's supply chain needs. By consolidating production planning, organizations can leverage the resources of the entire supply chain to ensure the most efficient and effective production possible.
One of the primary advantages of centralized production planning is the reduction of costs. Companies can reduce the resources needed to manage production and minimize the need for additional staff. By consolidating production planning into a central location, organizations can reduce the cost of raw materials, labor, and overhead. Additionally, by consolidating multiple production sites into one place, companies can reduce transportation costs since goods can be shipped to a single location rather than multiple locations.
Another advantage of centralized production planning is improved coordination of resources. By centralizing production planning, organizations can maximize the use of resources, such as labor, materials, and technology. This can help ensure that the most efficient use of resources is achieved, leading to the improved overall performance of the organization. Additionally, by consolidating production planning, organizations can reduce the time needed to develop production plans, allowing them to focus on other aspects of the supply chain.
Finally, centralized production planning can help organizations meet customer demand more effectively. By consolidating production planning, organizations can better anticipate customer needs and ensure that the right product is produced at the right time. This can help organizations meet customer demands in a timely and cost-effective manner.
In conclusion, centralized production planning is essential for optimizing supply chain operations. By consolidating production planning, organizations can reduce costs, improve the coordination of resources, and meet customer demands more effectively. This can help organizations achieve tremendous success in the global marketplace.
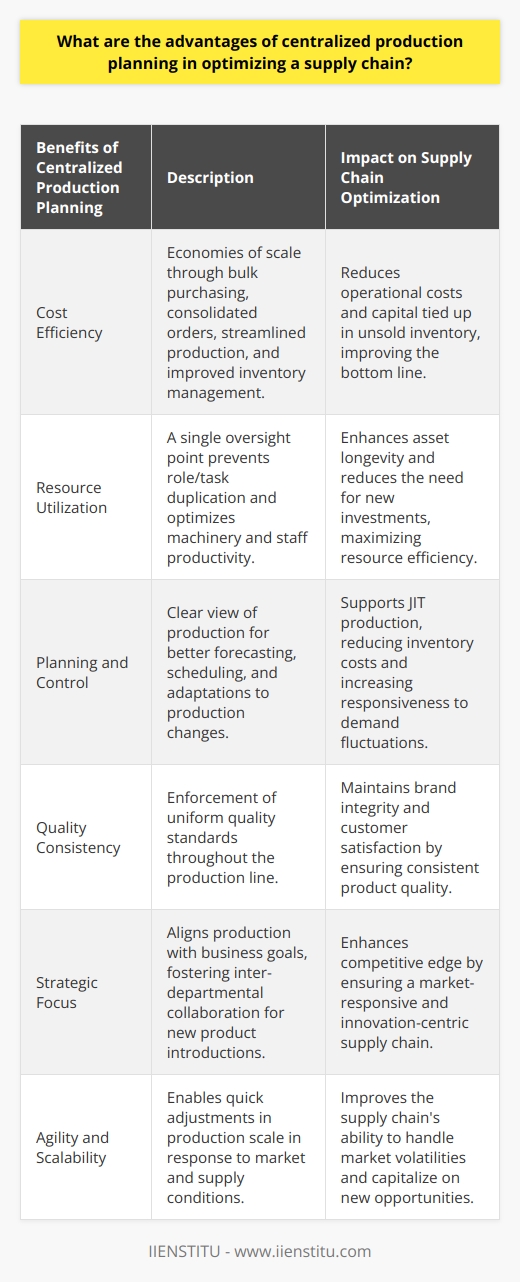
How can distributed production planning help to improve the efficiency of a supply chain?
Distributed production planning has become an increasingly popular approach to supply chain management in recent years. It is a method of planning and scheduling production activities across geographically dispersed sites to optimize the efficiency of the supply chain. This approach can bring several benefits, such as improved decision-making, reduced costs, and better visibility into the entire supply chain.
The primary benefit of distributed production planning is improved decision-making. By providing a comprehensive view of the entire supply chain, distributed production planning helps to make more effective decisions. This is because it considers the whole supply chain, from production to delivery. As a result, it helps to identify potential bottlenecks and to develop strategies to prevent them from arising. In addition, it allows for more accurate forecasting, enabling production planning to be more agile and respond to changing market conditions.
Distributed production planning can also result in reduced costs. Providing a more comprehensive view of the supply chain can help to identify areas where costs can be reduced. This can include reducing the number of warehouses, using more efficient transportation routes, or optimizing production processes. In addition, it can also help to reduce waste and improve the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
Finally, distributed production planning can improve visibility into the entire supply chain. This is because it provides a holistic view of the whole process, from production to delivery. This enables companies to have better control over their supply chain and to be more responsive to customer needs. In addition, it can help to identify potential risks and issues before they become a problem, allowing for proactive management of the supply chain.
In conclusion, distributed production planning can help to improve the efficiency of a supply chain in numerous ways. It can improve decision-making, reduce costs, and improve visibility into the entire process. By leveraging this approach, companies can optimize their supply chain and ensure they can meet customer needs promptly and cost-effectively.
What strategies can be used to ensure effective production planning in a supply chain?
Production planning is an essential part of the supply chain management process. It is the process of determining what products to produce, when and where to have them, and how to distribute them. Effective production planning can help supply chain organizations achieve their goals of cost savings, improved customer service, and increased profitability. In this blog post, we will discuss some strategies that can be used to ensure adequate production planning in a supply chain.
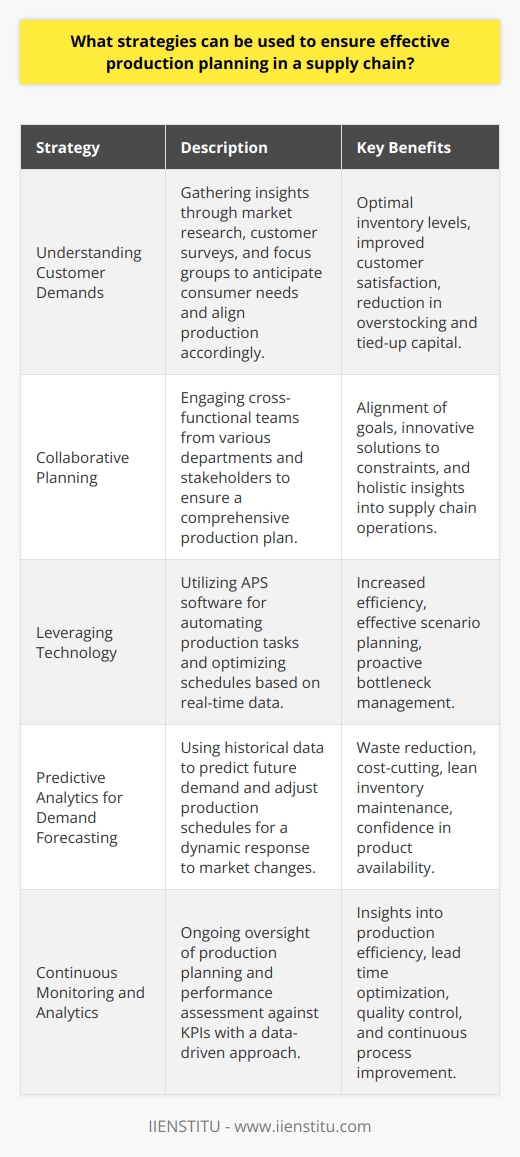
The first strategy is to understand the customer’s needs and wants. Effective production planning requires an understanding of customer needs and wants. This can be done through market research, customer surveys, and focus groups. Companies should also consider customer feedback when determining production schedules and inventory levels.
The second strategy is to adopt a collaborative approach to production planning. Companies should involve stakeholders across the supply chain in the production planning process. This will ensure that all stakeholders clearly understand the production plan and can provide valuable input and feedback.
The third strategy is to use technology to facilitate production planning. Technology can be used to automate the production planning process and make it more efficient. Advanced planning and scheduling (APS) software can track and analyze production data, optimize production schedules, and identify potential bottlenecks.
The fourth strategy is to use predictive analytics to anticipate demand. Predictive analytics can forecast customer demand and adjust production plans accordingly. This can help companies reduce inventory levels, improve customer service, and increase profitability.
Finally, companies should monitor the production planning process on an ongoing basis. This can help identify any problems or issues that may arise. Companies should also use analytics to track the success of their production plans.
By following these strategies, companies can ensure that their production plans are practical and efficient. This can help them reduce costs, improve customer service, and increase profitability.
How can you optimize the production process within a production chain?
Optimizing Production Strategies
Effective production optimization within a production chain involves employing tactical and strategic methods to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and boost productivity. To achieve these goals, manufacturers must adhere to the following measures:
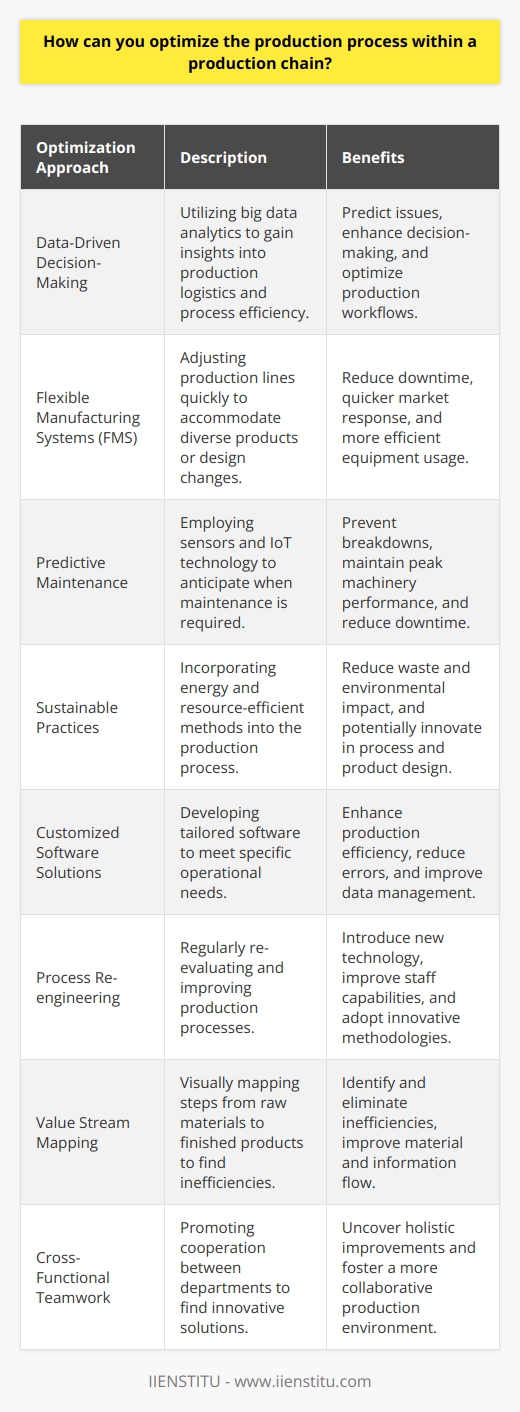
Embracing Automation
Integrating automation into the production process involves using cutting-edge technology, such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and advanced software systems. This not only accelerates the production process but also minimizes errors, resulting in higher product quality and lower costs.
Implementing Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing involves a systematic approach to identify and eliminate waste from the production process. By streamlining operations and reducing waste, companies can optimize their production chain, enhance product quality, and minimize manufacturing costs.
Conducting Process Audit
Auditing the production process identifies inefficiencies, redundancies, and bottlenecks that can hinder the production chain's performance. Periodic process audits enable companies to pinpoint and rectify these issues, allowing for continuous improvement and optimization of production processes.
Continuous Employee Training
Investing in employee training and skill development ensures that workers are up-to-date with current industry trends and technological advancements. Equipping staff with the latest knowledge and skills leads to increased workforce efficiency and productivity, ultimately enhancing the overall production process.
Supplier Collaboration
Forging strong relationships with suppliers can significantly improve the production process. Collaborating with suppliers enables companies to negotiate better prices and receive high-quality materials in a timely manner. This ensures that the entire supply chain functions more efficiently, driving down costs and augmenting production optimization.
Standardizing Work Processes
Creating standardized work processes reduces errors, promotes consistency, and enhances productivity. By developing and adhering to standard operating procedures, companies can optimize the production process by minimizing variations, reducing the risks of errors, and ensuring a smoother workflow.
In conclusion, optimizing the production process within a production chain necessitates a comprehensive approach that focuses on automation, lean manufacturing techniques, process audits, employee training, supplier collaboration, and standardization of work processes. By implementing these strategies, companies can achieve increased efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced productivity in their production chains.
What are the optimization techniques in supply chain management?
Optimization Techniques in Supply Chain Management
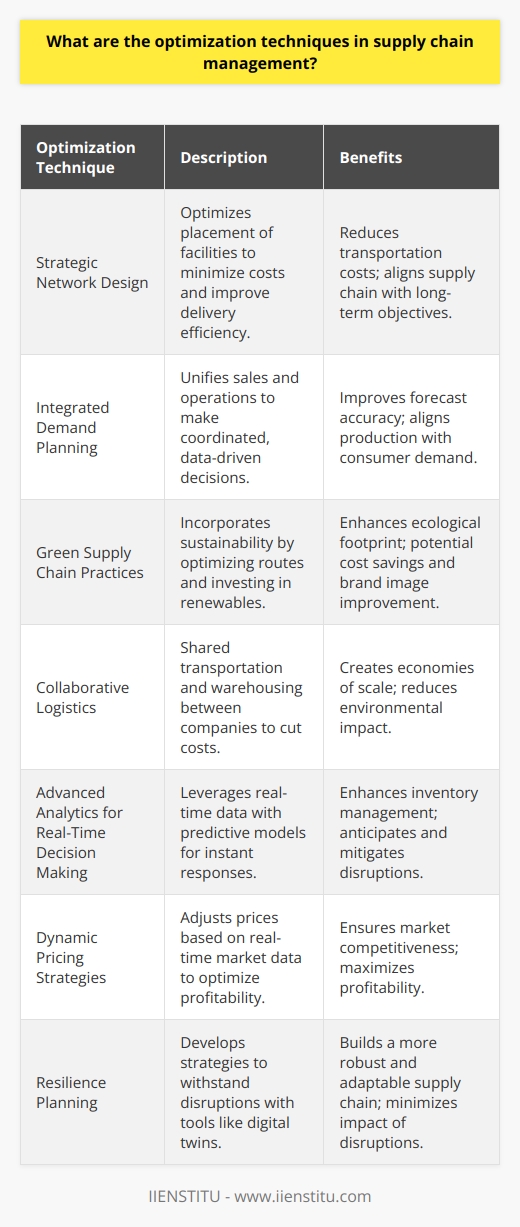
Data Analysis and Forecasting
In supply chain management, optimization techniques involve using data analysis and forecasting tools to understand trends, predict demands, and improve overall efficiency. An important aspect of this is utilizing historical data to analyze demand patterns and develop accurate forecasts, reducing inventory costs while maintaining high service levels.
Inventory Management
Another optimization technique involves effectively managing inventory levels, focusing on reducing storage and carrying costs without sacrificing product availability. Optimized inventory management strategies include safety stock calculations and just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems, which aim to balance the need for stock availability against the costs associated with keeping inventory on hand.
Transportation Planning
Effective transportation management is another key aspect of supply chain optimization. It involves the strategic selection of carriers, transportation modes, and routing to achieve the lowest possible transportation costs. This includes consolidating shipments, implementing multimodal transportation solutions, and utilizing advanced scheduling techniques to minimize delays and enhance delivery accuracy.
Supplier Relationship Management
Developing strong relationships with suppliers is crucial in optimizing supply chain operations. This involves strategic sourcing, supplier selection, and continuous evaluation to ensure that suppliers deliver high-quality products on time and at competitive prices. Supplier relationship management also includes understanding suppliers' capacity constraints and working with them to develop plans to address these challenges, thus ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma
These two methodologies, Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma, contribute significantly to the optimization of supply chain processes. Lean Manufacturing focuses on the reduction of waste and streamlining operations to minimize lead times and costs. Six Sigma, on the other hand, concentrates on reducing process variability and enhancing overall product quality. Integrating these methodologies results in constantly improving and efficient supply chain operations.
Technology and Automation
Incorporating advanced technology and automation in supply chain management has been a major driver for optimization. For instance, implementing modern software to manage inventory, warehouse operations, transportation, and procurement helps streamline processes and improve decision-making. The use of technology like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) also plays a valuable role in monitoring performance, predicting disruptions, and making real-time adjustments.
Risk Management and Visibility
Lastly, supply chain optimization requires proactive risk management and increased visibility into all aspects of the supply chain. Identifying and mitigating potential risks, such as disruptions from natural disasters or political unrest, helps ensure the stability and resilience of supply chain operations. Enhancing visibility within the supply chain allows for better collaboration, faster response times, and improved overall efficiency.
What is supply chain production planning?
Supply Chain Production Planning Overview
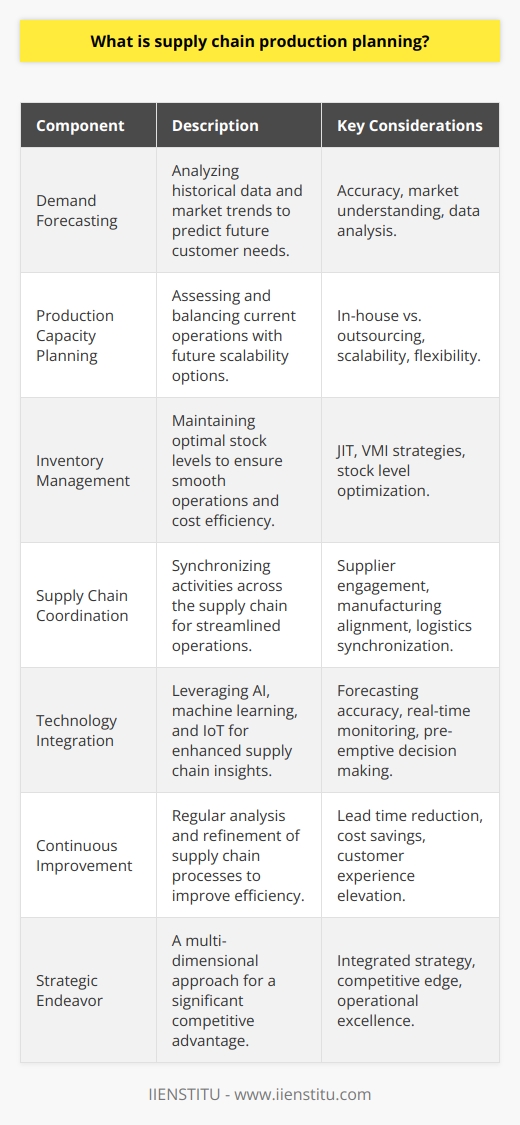
Supply chain production planning is a crucial process in managing and organizing the resources necessary for producing goods or providing services to meet customer demands. It coordinates various operations and decisions, including staffing, inventory levels, vehicle routing, and order fulfillment.
Role of Demand Forecasting
In this planning process, demand forecasting is essential. Accurate predictions of customer needs help companies determine the required production volume, allocate resources efficiently, and prevent possible delays or stockouts. Long-term forecasts also enable businesses to plan investments, such as expanding capacity or procuring new equipment.
Strategic Planning and Capacity
Strategic planning involves determining the optimal production capacity that balances current demand and future growth expectations. Companies need to decide whether to invest in facilities, outsource production, employ temporary workers or a combination of these methods. These decisions significantly impact long-term competitiveness and profitability.
Inventory Management
A key aspect of supply chain production planning is inventory management. Companies must establish suitable inventory levels to meet the anticipated demand, avoid overstocking, minimize holding costs, and maintain customer satisfaction. They employ various strategies such as just-in-time (JIT), safety stock or vendor-managed inventory (VMI).
Coordination of Activities
Another essential element is the coordination of all activities and stakeholders throughout the supply chain, from raw material procurement to customer delivery. Seamless communication and cooperation between suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers are vital for efficient production processes and minimizing disruptions.
Role of Technology
Technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the internet of things (IoT), have significantly improved supply chain production planning. These technologies enable real-time data analysis and accurate forecasting, optimize routing and scheduling, and monitor equipment and inventories.
Continuous Improvement Efforts
Lastly, companies require continuous improvement efforts to enhance their supply chain production planning processes. They regularly monitor their performance regarding costs, lead times, and customer satisfaction levels. Furthermore, they identify areas of improvement and develop strategies to achieve better results.
In conclusion, supply chain production planning is a multi-faceted approach that enables efficient production and ensures customer demands are met. It involves several key components such as demand forecasting, strategic planning, inventory management, coordination of activities, technology, and continuous improvement efforts.
What are the 5 key areas for setting up a supply chain plan?
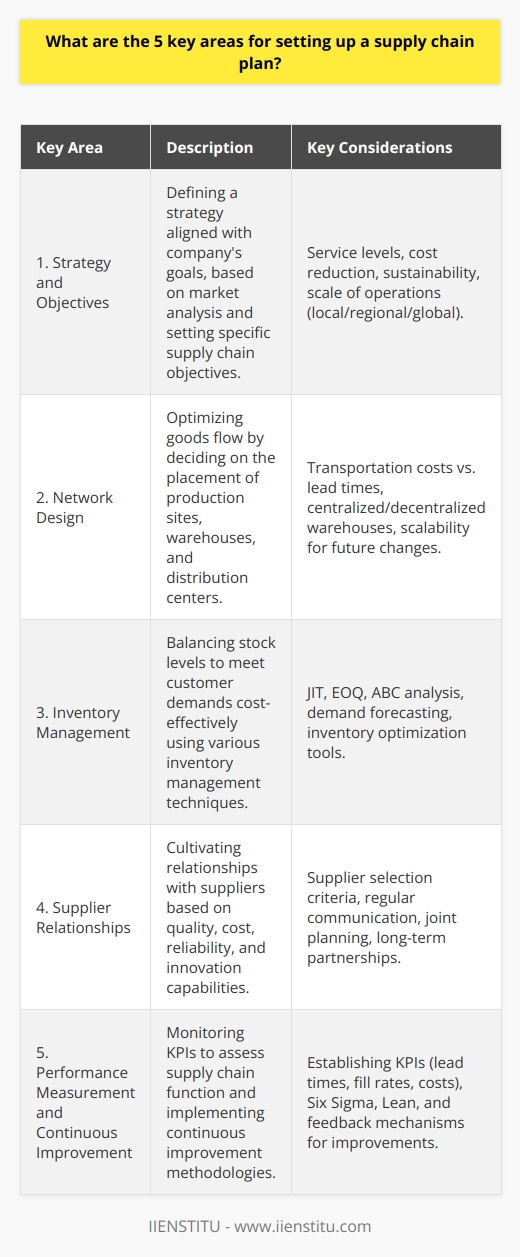
Key Area 1: Strategy and Objectives
A successful supply chain plan must begin with a clear and comprehensive strategy, outlining the goals and objectives to be achieved. This involves identifying the target market, understanding customer needs, and aligning supply chain operations with the overall business strategy.
Key Area 2: Network Design
Network design involves determination of the structure and layout of the supply chain, including the number and location of facilities such as distribution centers, and the flow of materials through the network. Selection of transportation modes and establishment of relationships with carriers and logistics providers are also crucial factors at this stage.
Key Area 3: Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is essential for maintaining optimal stock levels and ensuring product availability. This encompasses accurate demand forecasting, utilizing safety stocks, and implementing inventory control systems. Furthermore, determining the appropriate inventory policies and replenishment strategies supports the organization in meeting customer requirements while minimizing carrying costs.
Key Area 4: Supplier Relationships
Developing strong relationships with suppliers is key to establishing a well-functioning supply chain plan. Supplier relationships entail selecting the appropriate vendors based on various criteria, such as quality, cost, and delivery performance. Additionally, it involves fostering collaboration and communication, keeping suppliers informed of any changes in demand or product requirements to ensure uninterrupted supply of materials.
Key Area 5: Performance Measurement and Continuous Improvement
Lastly, monitoring the performance of the supply chain against established key performance indicators (KPIs) and benchmarks is vital to ensuring its ongoing effectiveness. This process necessitates tracking metrics such as on-time delivery, order accuracy, and inventory turnover. Regular review and refinement of the supply chain plan, supported by analysis of performance data, enable continuous improvement to adapt to changing market conditions and drive competitiveness.
How can organizations utilize data analysis and forecasting methods for effective supply chain planning?
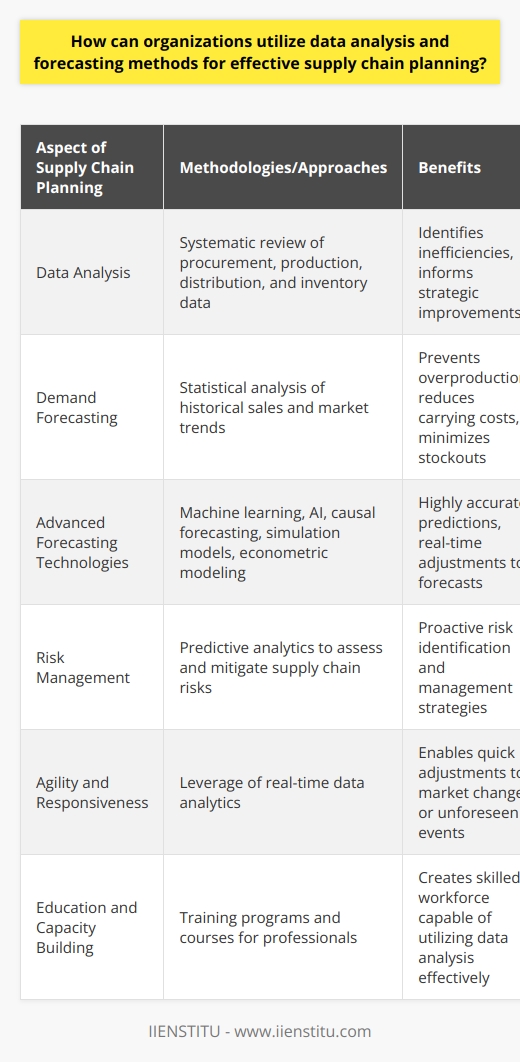
**Understanding Data Analysis and Forecasting Methods**
Organizations can utilize data analysis and forecasting methods to enhance their supply chain planning processes. Data analysis involves examining, cleaning, and transforming raw data to extract valuable insights, whereas forecasting predicts future trends based on historical data patterns. These methods enable organizations to make informed decisions, optimizing their supply chains and improving overall efficiency.
**Benefits of Data Analysis in Supply Chain Planning**
One key advantage of data analysis in supply chain planning is improved demand forecasting. By evaluating historical sales data and identifying patterns, organizations can better predict future customer demand, minimizing stock shortages or excess inventory. Implementing a robust demand forecasting system ensures the right products are available when needed, enhancing customer satisfaction and increasing the potential for repeat business.
**Leveraging Forecasting Techniques**
Utilizing appropriate forecasting techniques can significantly impact supply chain planning. Time series analysis, for example, focuses on analyzing data points collected over time to identify patterns, trends, and seasonality. This method can help organizations predict future sales, inventory requirements, and resource allocation, enabling better anticipation of market fluctuations and more effective planning strategies.
**Incorporating Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence**
The integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) into supply chain planning provides a more advanced approach to data analysis and forecasting. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large volumes of data more efficiently than traditional methods, producing more accurate predictions. As a result, supply chain decisions can be based on reliable data analysis, reducing the likelihood of stockouts, surplus inventory, and delivery delays.
**Data-Driven Decision Making**
By leveraging data analysis and forecasting methods, businesses can shift towards data-driven decision-making, enhancing the efficiency of their supply chain planning. This approach reduces reliance on intuition or guesswork and allows for more accurate inventory management, resource allocation, and demand forecasting. Consequently, organizations can improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and increase their competitiveness in the market.
In conclusion, data analysis and forecasting methods hold significant potential for enhancing supply chain planning processes within organizations. By integrating these techniques into their decision-making processes, businesses can optimize their supply chains, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
What role does inventory management play in optimizing the production process within a supply chain?
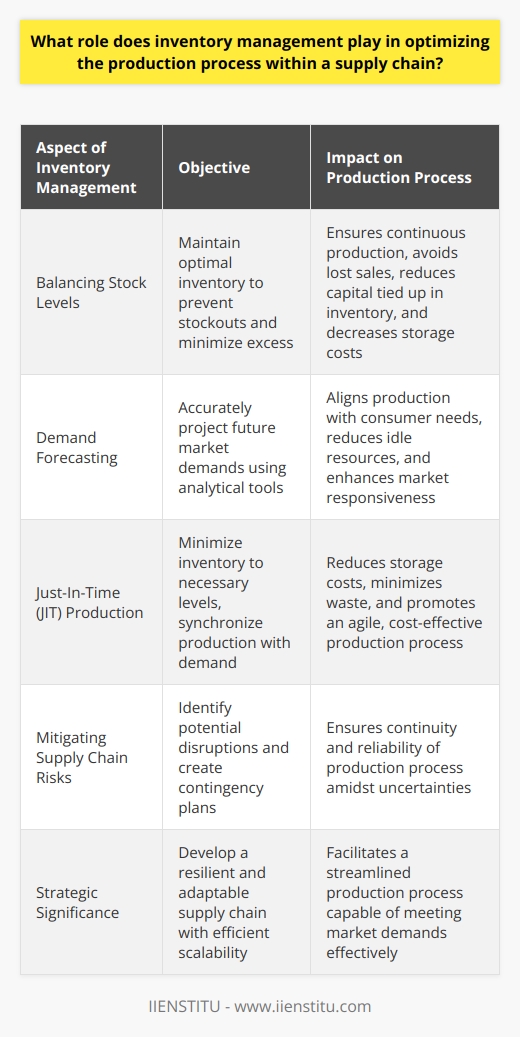
Role of Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management plays a crucial role in optimizing the production process within a supply chain. Proper inventory control ensures that adequate stock levels are maintained, stabilizing production and allowing businesses to meet various demand patterns effectively.
Balancing Stock Levels
An essential aspect of inventory management is balancing stock levels to prevent stockouts and overstocking. Stockouts can disrupt production and lead to unsatisfied customers, while overstocking increases storage costs and the risk of obsolete inventory. Thus, maintaining optimal inventory levels avoids these issues, enhancing production efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is another critical function of inventory management that impacts the production process. By predicting future demand, businesses can adjust their production levels accordingly, ensuring that the right amount of products is manufactured at the right time to meet customer requirements. Consequently, accurate demand forecasting helps reduce lead times, minimize stockouts, and decrease excess inventory.
Just-In-Time Production
Just-in-time (JIT) production is a widely-used inventory management technique that can optimize the production process. By producing products when customer orders are received, JIT minimizes stocked inventory and decreases holding costs. This approach requires tight coordination between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to ensure that raw materials and components are readily available for production when needed. As a result, JIT fosters efficient resource allocation and reduces waste within the supply chain.
Mitigating Supply Chain Risks
Inventory management also plays a crucial role in mitigating risks within the supply chain. By monitoring supplier performance, businesses can proactively identify potential bottlenecks or disruptions and take corrective action. Additionally, implementing contingency plans and holding safety stock can help manage fluctuations in demand and supply, ensuring that production continues smoothly despite unexpected events.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inventory management plays a vital role in optimizing the production process within a supply chain. By balancing stock levels, accurately forecasting demand, employing JIT production, and managing supply chain risks, businesses can achieve cost savings, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction. Therefore, effective inventory management should be a key focus for any organization looking to optimize its supply chain operations.
What is the importance of demand forecasting in supply chain optimization?
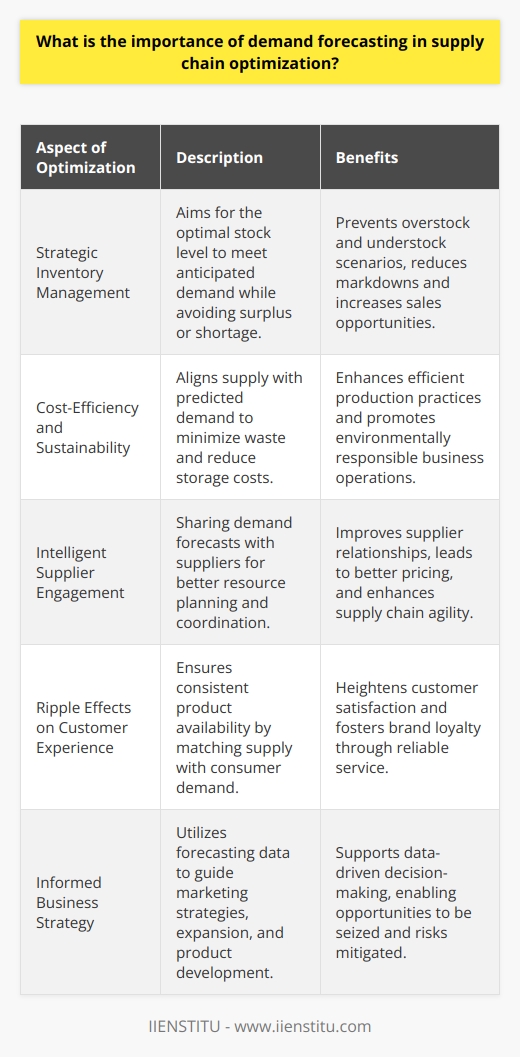
Understanding Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting plays a pivotal role in the optimization of the supply chain. It acts as the critical component in predicting customer demand. Accurate forecasting aids in understanding market trends, enabling effective decision making and planning.
Reducing Costs and Wastage
An accurate demand forecast directly influences the effective management of inventory levels, thus minimizing costs. On top of this, it reduces the prospect of waste due to surplus stock. It also ensures an operational balance between supply and demand, thus averting inventory stockouts or excesses.
Improved Supplier Relationships
Accurate forecasting bolsters supplier relationships. When suppliers have clear insights into future demand, they can streamline their own production schedules. This harmony fosters a more collaborative and efficient supply chain partnership.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Demand forecasting enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability. Predicting demand allows businesses to meet customer needs promptly. This reduces the chance of losing sales due to shortages, thereby increasing customer loyalty.
Supporting Strategic Decisions
Finally, accurate demand forecasting supports strategic decision making. It provides data that can guide businesses in product development, budget allocation, and sales target setting. The right forecasting capabilities result in better business strategies and increased revenues.
In conclusion, demand forecasting remains an essential tool for supply chain optimization. It aids cost reduction, boosts customer satisfaction, enhances supplier relations, and supports robust strategic decision-making processes. Consequently, understanding and effectively employing demand forecasting constitutes a significant advantage in modern supply chain management.
How do companies implement effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders in the supply chain planning process?
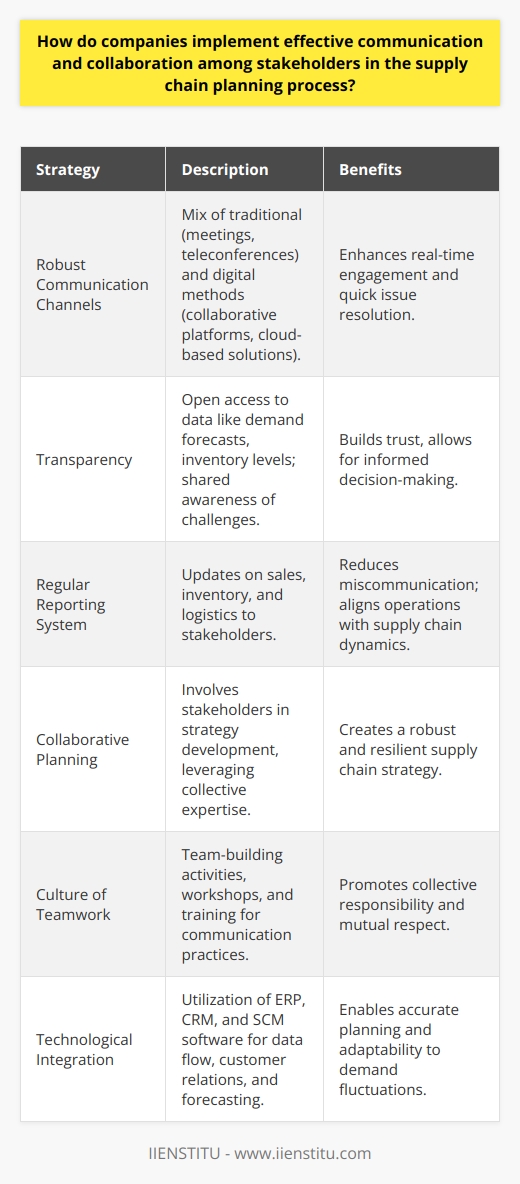
Building Communication Channels
Companies implement effective communication among supply chain stakeholders through well-structured communication channels. They utilize traditional methods like emails, meetings, and teleconferences. With advanced technology, they employ collaborative platforms, cloud-based solutions, and real-time tracking systems.
Promoting Transparency
Transparency plays a vital role in fostering an effective collaboration. Companies ensure open access to information about demand forecasts, sales data, and inventory levels. Sharing this information strengthens mutual trust and understanding between suppliers, manufacturers, and customers.
Establishing Regular Reporting
Regular reporting is another way companies establish effective communication. Pre-determined intervals for reporting enhance the predictability and consistency of information flow. The reporting often involves sharing progress on assigned tasks, updating on changes or delays, and outlining the next steps.
Implementing Collaborative Planning
Collaborative planning is a formidable tool in promoting stakeholder involvement. Involving stakeholders in planning and decision-making processes enhances their commitment. It allows them to provide valuable input and feedback, ensuring a more efficient and smooth process.
Cultivating a Culture of Teamwork
Companies foster a culture of teamwork to encourage collaboration. They train employees on the importance of collective responsibility and mutual respect. Such a culture diminishes individual silos and promotes a shared vision, leading to more productive collaboration.
Integrating Technological Tools
Lastly, companies rely on the integration of technological tools to facilitate communication and collaboration. Tools such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, and other Supply Chain Management (SCM) software allow for effective and efficient information sharing. They also improve decision-making by providing real-time data.
In conclusion, effective communication and collaboration in supply chain planning can be achieved through structured channels, promoting transparency, regular reporting, collaborative planning, fostering teamwork, and integrating technological tools. These strategies ensure a streamlined process, prevent misunderstandings, and ultimately, lead to enhanced supply chain performance.
In what ways can sustainable practices contribute to supply chain optimization and planning?
Boosting Efficiency in Processes
Sustainable practices can dramatically optimize supply chain procedures. They reduce raw material utilization, consequently minimizing waste production. This eco-friendly approach maximizes efficiency and diminishes running costs. By streamlining their use of resources, businesses can improve profitability.
Ensuring Resource Longevity
Another key benefit is the longevity it brings to resources. Sustainable practices include the prudent usage and conservation of raw materials. It ensures resource longevity and reduced supply disruptions. Thus, businesses practicing sustainability can greatly reduce their risks related to supply chain shortages.
Improving Brand Image
Sustainable practices contribute positively to a company's Brand Image. The increased corporate social responsibility augments the company's brand reputation among consumers, stakeholders, and industry peers. Subsequently, it gives a firm competitive advantage, enjoying improved consumer loyalty and stakeholder support.
Boosting Innovation
Finally, sustainable practices inspire innovation. Implementing green alternatives within the supply chain system can lead to the discovery of new, improved methods and processes. It fosters a spirit of creativity and innovation within the organization, enhancing their overall operational efficiency.
Sustainability in supply chain optimization, with its multifaceted benefits, thus propels companies towards sustainable growth in an environment conscious world. The thoughtfully engineered practices minimize risk, increase efficiency, and establish a firm as a responsible entity contributing positively to the global ecosystem. This proves that sustainability not only benefits the planet but also significantly aids supply chain optimization and business planning.

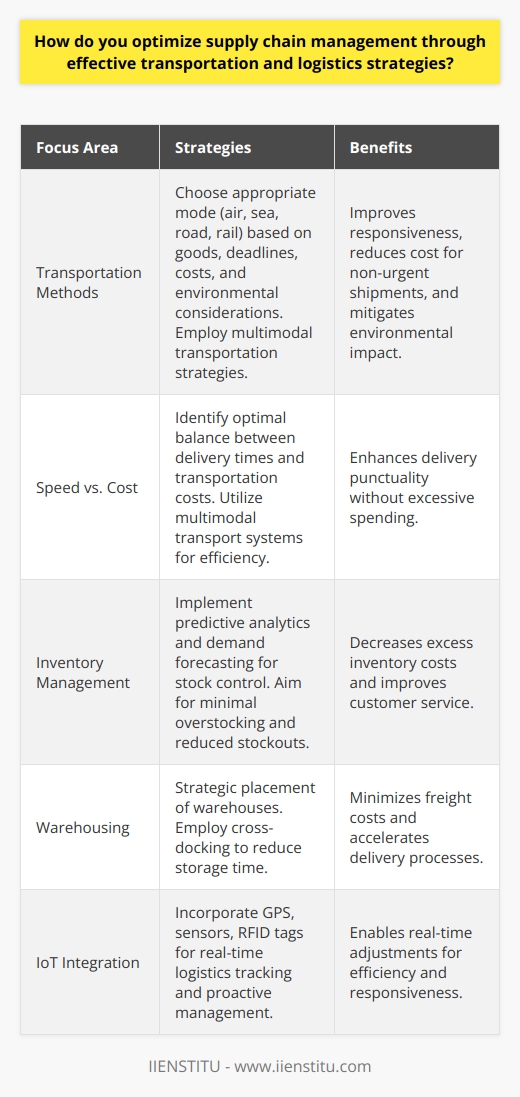
How do you optimize supply chain management through effective transportation and logistics strategies?
Efficient Transportation Methods
Optimizing supply chain management involves incorporating efficient transportation strategies. This includes selecting the optimal transport modes tailored to the nature of products and the urgency of delivery. Shippers should consistently review transportation costs and delivery times to ensure they match the supply and demand trends.
Balancing Speed and Costs
This process isn't solely about speed but also cost efficiency. For instance, air transport offers swift delivery but high costs. In contrast, using ship freight can cut costs significantly, but time is extended. Ideally, one should implement a mix of both to balance speed and costs while satisfying customer needs.
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management can optimize operations as well. Use of advanced technological tools such as predictive analytics to manage stock levels can remarkably reduce inventory costs. This approach prevents both understocking and overstocking, ensuring a seamless flow of goods along the supply chain.
Strategic Warehousing
Strategic warehousing is another means to enhance supply chain management. Centralizing warehouses reduces transportation costs and time. Meanwhile, using distribution centers close to major markets speeds up delivery while mitigating risks related to delays or disruptions.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Lastly, leveraging the Internet of Things (IoT) transforms supply chain management by providing real-time visibility into the location and status of shipments. This allows quick responses to any disruptions, ensuring smooth and prompt delivery.
In conclusion, the optimization of supply chain management is achievable through the sensitive integration of efficient transportation methods, inventory management, strategic warehousing, and IoT. These strategies ensure cost efficiency, speed of delivery, inventory accuracy, risk mitigation, and real-time visibility.
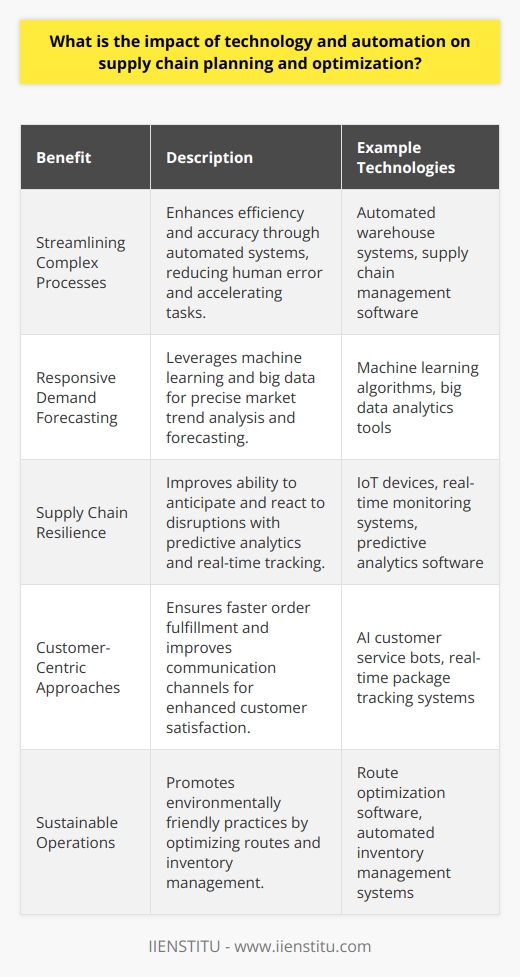
What is the impact of technology and automation on supply chain planning and optimization?
Enhancing Efficiency
Technology and automation have significantly improved efficiency in supply chain planning. They've automated complex tasks that could consume considerable time and resources if done manually. With automated systems, companies can more accurately predict demand and manage inventory, reducing waste and cost.
Minimizing Supply-Demand Mismatch
Technology aids in supply and demand reconciliation. Through advanced analytics and real-time data, businesses can respond quickly to changes in demand, reducing the likelihood of supply-demand mismatches. Hence, it minimizes the risk of overproduction or underproduction.
Increasing Transparency
Integration of technology has increased transparency in supply chains. Digital solutions like blockchain offer real-time visibility, ensuring stakeholders are aware of every stage of the supply chain. This increased visibility improves trust and collaboration among participants.
Risk Management Improvement
Automation helps in risk management. Advanced analytics and predictive modelling enable companies to identify potential disruptions and risks early, allowing for timely mitigation. It also improves resilience, as companies can swiftly adapt supply chain plans to respond to unexpected events.
Improving Customer Satisfaction
Lastly, technology and automation improve customer satisfaction. Faster, more accurate supply chain management means businesses can deliver goods on time and with fewer mistakes. This increased efficiency improves customer experience, which boosts brand reputation and loyalty.
Thus, the impact of technology and automation on supply chain planning and optimization is vast and positive. They enhance efficiency, minimize supply-demand mismatch, increase transparency, improve risk management, and boost customer satisfaction. As such, their integration is no longer considered a luxury, but a necessity for any business wishing to thrive in the modern marketplace.
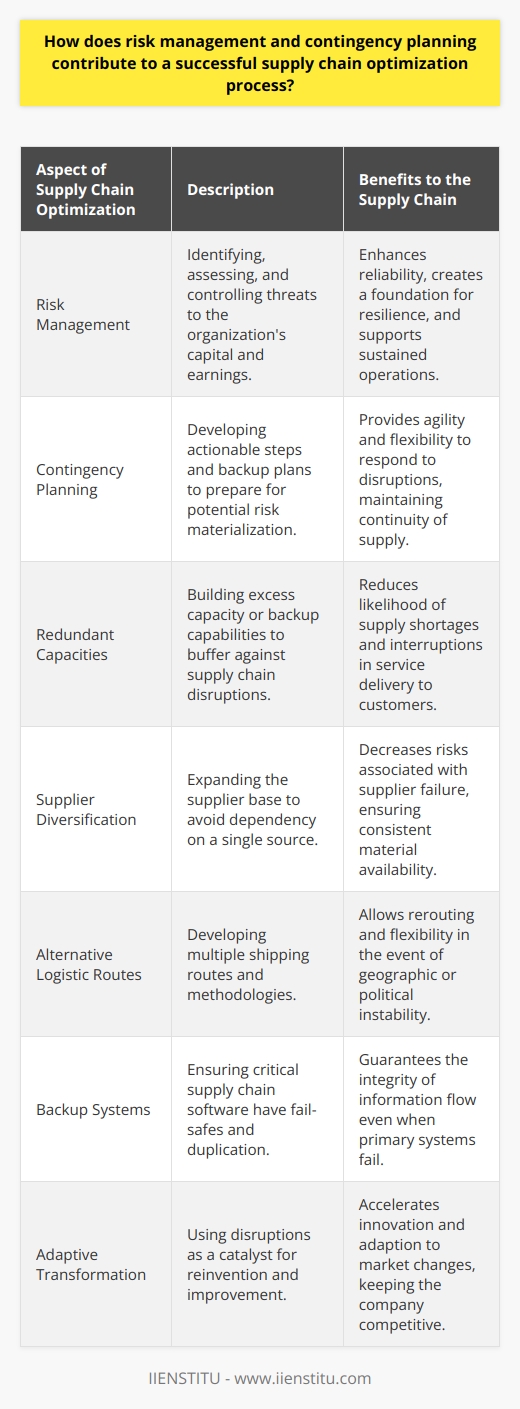
How does risk management and contingency planning contribute to a successful supply chain optimization process?
Prioritizing Risk Management in Supply Chain Optimization
Risk management plays an instrumental role in the supply chain optimization process. It helps anticipate potential disruptions, hence, eradicating disastrous outcomes. The proactive approach identifies and mitigates risks, thereby enhancing efficiency and reliability within the supply chain.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency with Contingency Planning
Contingency planning is an equally essential component of a successful supply chain optimization process. It prepares organizations for unexpected incidents. The planning involves continuous updating and testing of contingency plans, ensuring companies can promptly address supply chain interruptions.
Boosting Supply Chain Reliability
An adept combination of risk management and contingency planning boosts the reliability of the supply chain. Organizations, by anticipating possible risks and planning for them, can optimize their operations, thus increasing dependability. These processes, therefore, act as security buffers, ensuring seamless supply chain operations, regardless of the circumstances.
Adding Resilience to Supply Chain
Above all, risk management and contingency planning contribute resilience to the supply chain optimization process. They empower businesses to weather adverse events and quickly bounce back, maintaining efficiency and profitability. Such resilience turns disruptions into opportunities, enabling businesses to thrive even during uncertainty.
In conclusion, risk management and contingency planning are indispensable avenues of a successful supply chain optimization process. They augment operational efficiency, reliability, and resilience, thus ushering in success and competitiveness for businesses. Companies wishing to optimize their supply chain should, therefore, incorporate risk management and contingency planning into their operations. Doing so will ensure continuous delivery of products and services, satisfying customers, ultimately leading to business growth and prosperity.