In today’s business world, effective logistics planning is vital for creating Supply Chains that are both efficient and cost-effective. Logistics planning analyzes and optimizes the flow of goods, services, information, and finance while also considering transportation costs, delivery lead times, and service-level requirements. With suitable analytical models and tools, businesses are better equipped to coordinate the movement of products and services, ultimately leading to a better customer experience.
Analytical Models
Regarding logistics planning, analytical models simplify and optimize complex supply chain problems. Such models come in step-by-step processes considering transportation costs, delivery lead times, and service-level requirements.
One of the most popular models is the step-by-step process model. This model involves establishing clear objectives, analyzing the supply chain network, and creating an optimized system for budget and logistics. This model helps businesses determine the most cost-effective shipping and delivery routes and the most efficient dispatch cycles.
Another popular model used in logistics planning is the multi-criteria decision analysis model. This model enables businesses to consider multiple criteria, such as delivery speed, costs, and environmental sustainability. The model is used to identify the optimal solutions for logistics planning challenges and can be continuously updated based on changes in the supply chain environment.
Analytical Tools
In order to effectively implement analytical models in logistics planning, businesses need to use analytical tools. The most commonly used tools include geographic information systems (GIS) and freight and transportation management systems (TMS).
Optimizing Logistics Management İn Manufacturing To Reduce Costs And İmprove Efficiency
Logistics Management Strategies To Maximize Efficiency And Reduce Costs
GIS is an analytical tool used to store and organize spatial, geographic, and demographic data. Such data can be used to create maps, analyze trends, and measure distances between locations. GIS is a valuable tool for logistics planning as it can identify potential risks and areas of inefficiency in the supply chain network.
TMS is an analytical tool used to coordinate the movement of goods and services. This tool enables businesses to track and monitor shipments easily, analyze delivery times and costs, and optimize fleet utilization. TMS is an invaluable resource for businesses, allowing them to automate the shipping and delivery process, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved customer service.
In conclusion, analytical models and tools are essential for effective logistics planning. Step-by-step process models are used to simplify and optimize complex supply chain problems. In contrast, multi-criteria decision analysis models identify the optimal solutions for logistical challenges. Additionally, GIS and TMS are two analytical tools used to coordinate the movement of goods and services while providing insights into potential inefficiencies in the supply chain network. With suitable analytical models and tools, businesses are better equipped to manage their logistics operations and create efficient, cost-effective supply chains.
Proper planning for logistics requires an analytical approach to ensure the most efficient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What analytical models and tools are commonly used for logistics planning?
Logistics planning is essential for efficient and effective business operations for all industries. To successfully plan for the movement of goods and resources in an organization, analysis of data and utilization of suitable analytical models and tools are necessary. In this article, the different analytical models and tools used in logistics planning will be discussed.
Linear programming is a widely used analytical model in logistics planning. It determines the cost-optimal allocation of resources and maximizes profit within a set of conditions. Linear programming models are used to identify an optimal solution for production, transportation, and scheduling problems. Additionally, these models are used to generate feasible and balanced production plans that are not overly sensitive to changes in demand and supply.
A standard analytical tool utilized for logistics planning is software simulations. Simulation programs allow for analyzing and evaluating possible events in a given system. These simulations generate data that can be used to optimize supply chain decisions, such as determining the best time to order more inventories. Furthermore, software simulations can recognize patterns and trends in a business environment and identify potential risks.
Optimization models, such as mixed-integer linear programming and constraint programming, are also used for logistics planning. These models are employed to determine an optimal transportation route and optimize the flow of goods through a distribution system. The models also help to identify the optimal locations for different types of resources, such as warehouses and transportation facilities. Additionally, they can be used to determine the most cost-efficient resources and production plans.
Finally, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are also increasingly used for logistics planning. AI can process large amounts of data and make complex decisions. AI can also identify patterns and trends in data, which can help to make logistics decisions that are more efficient.
In conclusion, several analytical models and tools are used to facilitate logistics planning. The correct selection of analytical models and tools is essential to ensure that decisions are based on accurate and reliable data. Furthermore, these analytical models and tools help optimize resource distribution and improve logistics operations' efficiency.
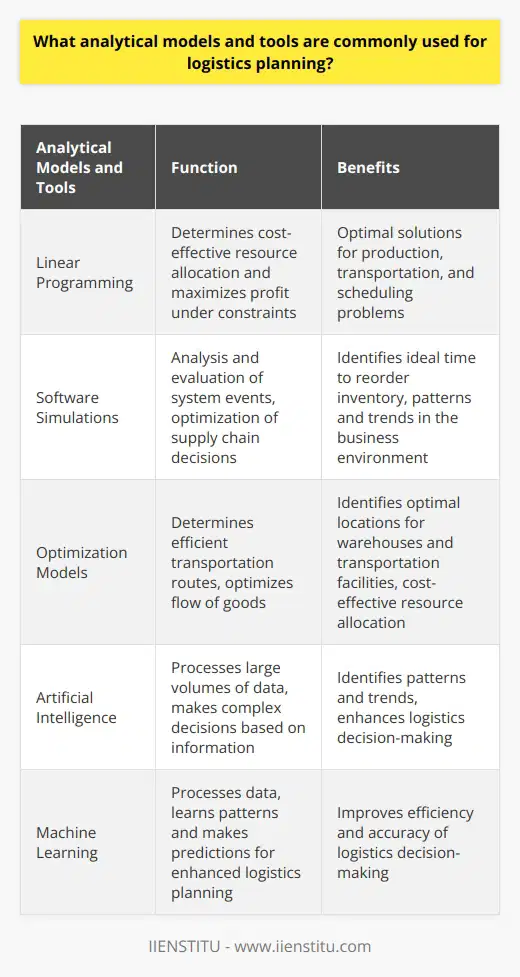
What techniques can be used to optimize the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of logistic planning?
Logistic planning is essential to any business, as it helps manage the resources and processes necessary to facilitate incoming and outgoing materials. Optimizing this process to ensure the most efficient and cost-effective outcomes is essential. To do this, various techniques can be used to assess and improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of logistic planning.
One of the essential techniques to implement when optimizing logistic planning is real-time tracking. Real-time tracking can monitor the progress of orders from where they are placed to where they arrive, allowing for better prediction of time delays and cost estimations. Furthermore, real-time tracking enables improved customer service and operational efficiency, making it a necessity for efficient logistics.
In addition, data analysis and mathematical models can be used to analyze the performance of logistics operations and their cost implications. By using data analysis and mathematical models, businesses can better comprehend the cost structure associated with the entire process, allowing for more accurate cost estimations and improved planning.
Another way to optimize the logistic planning process is to take advantage of technological advances, such as artificial intelligence (AI). AI tools can help analyze customer and market trends to predict supply chain requirements better and enable faster response times.
Finally, improved communication between different parties involved in the process can help to optimize logistic planning further. By establishing efficient lines of communication between vendors, manufacturers, and customers, businesses can better manage their resources and streamline their processes, improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
By implementing these techniques, businesses can optimize their logistic planning process and improve their operations' overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Real-time tracking, data analysis, mathematical models, the use of AI, and improved communication are all powerful techniques that should be leveraged to help enhance logistic planning.
How can data analysis be used to further improve the logistics planning process?
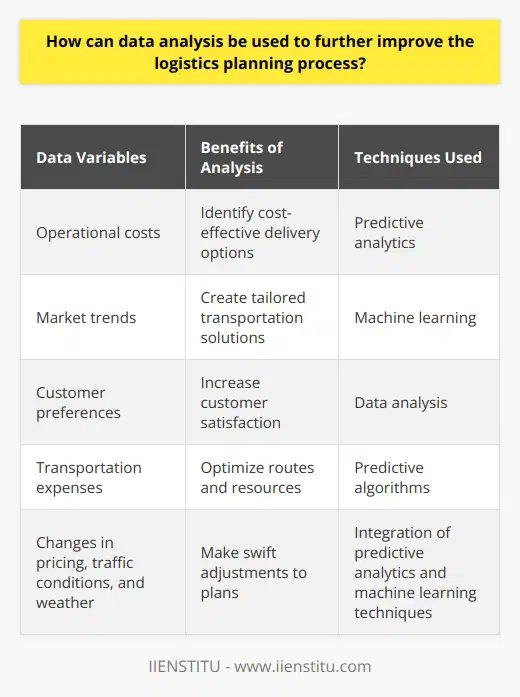
Data analysis has become an integral part of business operations and is often used to increase operational efficiency. Specifically, data analysis can further improve the logistics planning process. Logistics planning is critical for businesses to ensure goods and services are efficiently transported from origin to destination. It is a complex process that requires the optimization of numerous variables into a compelling end-to-end solution.
The use of data analysis to improve the logistics planning process requires the collection of large quantities of data regarding operational costs, market trends, customer preferences, transportation fees, and so on. Data analysis can be used to gain valuable insights into the best options to deliver goods and services cost-effectively. Data analysis provides visibility into the most efficient routes and identifies underperforming resources, including roads and personnel, that may need re-assignment. Additionally, accurate insights into customers’ preferences can be determined to tailor transportation solutions that best suit their needs.
Moreover, using predictive analytics and machine learning in the data analysis process can make the logistics planning process even more efficient. By recognizing patterns and trends in the data, transport solutions with the lowest cost and the shortest routes can be identified quickly and accurately. Furthermore, predictive algorithms can also be used to anticipate changes in pricing, traffic, and weather conditions to make quick adjustments in the logistics plans for optimal results.
In conclusion, data analysis can significantly improve the logistics planning process. Through the application of predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms, businesses can gain valuable insights from data that can be used to identify the most cost-effective and efficient logistics solutions. Consequently, companies can significantly reduce their costs while also increasing customer satisfaction.
What are the key components and features of LMIS tools for effective logistics management?
Key Components of LMIS Tools
A Logistics Management Information System (LMIS) is an essential tool for effective logistics management, as it enables organizations to gather, analyze, and disseminate data to ensure efficient supply chain operations. The key components and features of LMIS tools for effective logistics management can be broadly categorized into three: data management capabilities, analytics tools, and end-user support.
Data Management Capabilities
Effective logistics management relies heavily on accurate, timely, and complete data. LMIS tools facilitate adequate data management through efficient data collection, storage, and validation mechanisms. These systems often offer data entry templates, automated validation checks, and support for various data formats, such as XML, CSV, and spreadsheets. Importantly, data confidentiality and security is maintained through access controls, encryption, and backup workflows, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected.
Analytics Tools
To streamline logistics operations and make informed decisions, organizations require powerful analytics tools. LMIS solutions offer a suite of analytics capabilities, including descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. Descriptive analytics helps visualize historical data through dashboards and reports, while diagnostic analytics identifies patterns and trends in the data. Predictive analytics enables organizations to forecast demand and supply requirements, and prescriptive analytics provides recommendations for optimal decision-making.
End-User Support
User-friendly interfaces and effective end-user support are imperative for the success of LMIS tools. Intuitive interfaces allow users to easily navigate the system, reducing the learning curve and ensuring efficient use of the tools. Furthermore, comprehensive training materials, responsive help desks, and ongoing support from software providers ensure that users have access to essential information and troubleshooting assistance when needed.
In conclusion, effective logistics management is highly dependent on the capabilities of LMIS tools. The key components that constitute successful LMIS solutions include data management capabilities, analytics tools, and end-user support. By implementing LMIS tools with these features, organizations can optimize their logistics operations and ensure efficient supply chain management.

How do the six supply chain models differ in terms of their structure, goals, and implementation?
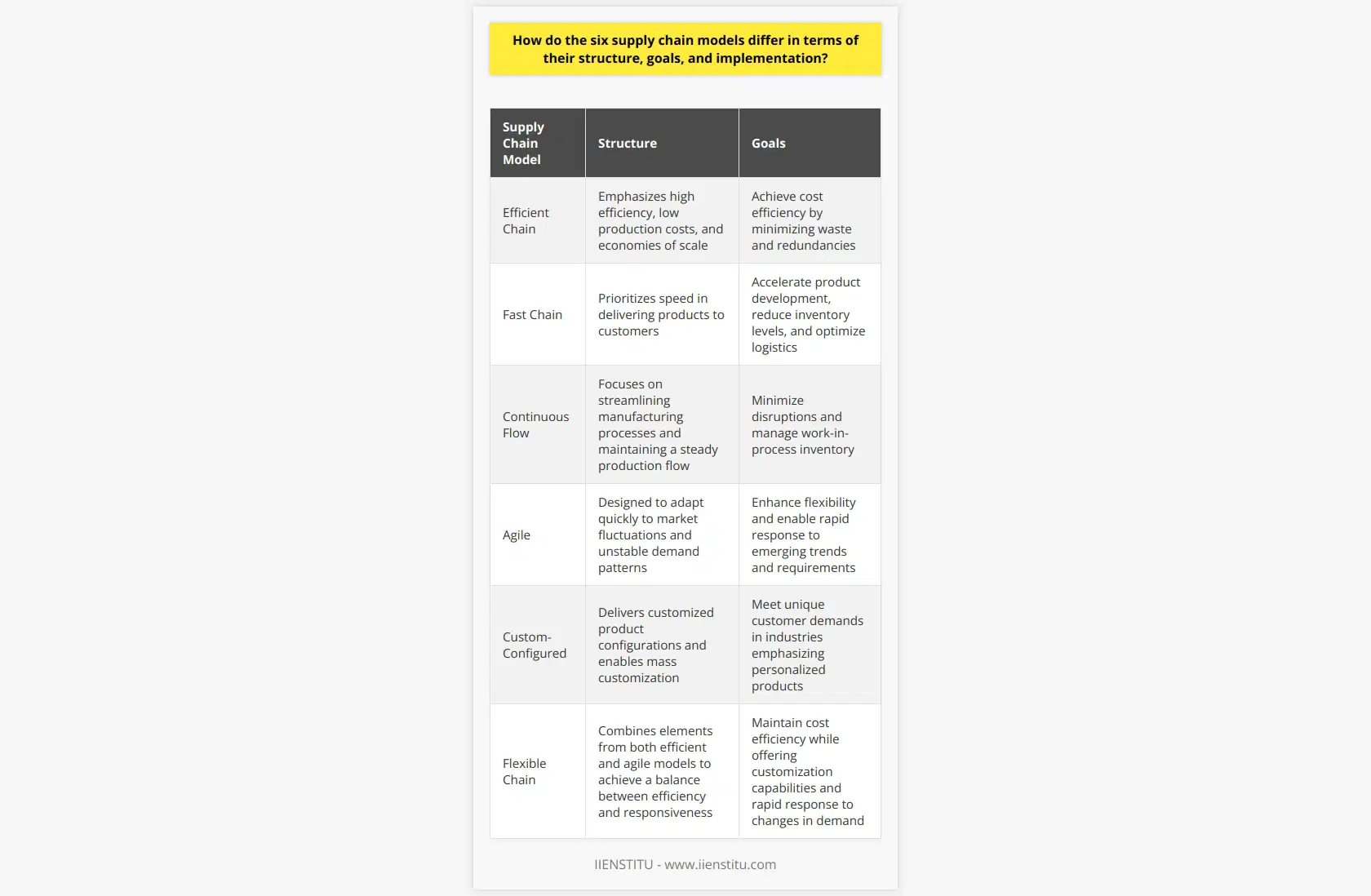
Diverse Structures in Supply Chain Models
The six supply chain models differ significantly in terms of their structure, goals, and implementation processes. These models are the efficient chain, fast chain, continuous flow, agile, custom-configured, and flexible chain models. Each model is designed to suit different industries and cater to specific customer requirements.
Efficient Chain: Achieving Cost Efficiency
The efficient supply chain model focuses on optimizing costs by minimizing waste and redundancies. It is typically used in stable and predictable markets, where demand patterns are well-established. This model is characterized by high efficiency, low production costs, and economies of scale, making it more suitable for industries with high production volumes and low product variety.
Fast Chain: Speed in Delivery
A fast supply chain prioritizes speed in delivering products to customers. It is typically employed in industries with short product lifecycles, such as fashion or electronics. The key goals of this model are to accelerate product development, reduce inventory levels, and optimize logistics to guarantee quick and rapid response to customer demands.
Continuous Flow: Streamlining Processes
Continuous flow supply chains focus on streamlining manufacturing processes to minimize disruptions and maintain a steady production flow. This model is employed in industries where products have limited customization and require high levels of automation. The central objective is to manage work-in-process inventory and sustain a smooth production flow.
Agile: Adapting to Market Changes
The agile supply chain model is designed to adapt quickly to market fluctuations and unstable demand patterns. It is ideal for industries experiencing constant change, such as technology or pharmaceuticals. The primary goal of this model is to enhance flexibility, allowing the supply chain to shift rapidly in response to emerging trends and requirements.
Custom-Configured: Personalizing Products
Custom-configured supply chains focus on delivering personalized products according to customer preferences. They are employed in industries where customization is paramount, such as automotive or furniture production. The central goals are to facilitate customer-driven product configurations and enable mass customization, thus meeting unique customer demands.
Flexible Chain: Balancing Efficiency and Responsiveness
Lastly, the flexible supply chain model strikes a balance between efficiency and responsiveness, combining elements from both the efficient and agile models. This model is suited for industries with variable demand patterns and varying levels of product customization. The primary goals are to maintain cost efficiency while simultaneously offering customization capabilities and rapid response to changes in demand.
In conclusion, the six supply chain models differ in their structures, objectives, and implementations to accommodate a diverse array of industries and customer needs. Companies should carefully assess their market conditions, product offerings, and customer expectations when selecting the most appropriate supply chain model to employ.
What are some widely-used logistics tools and models for improving supply chain efficiency and success?
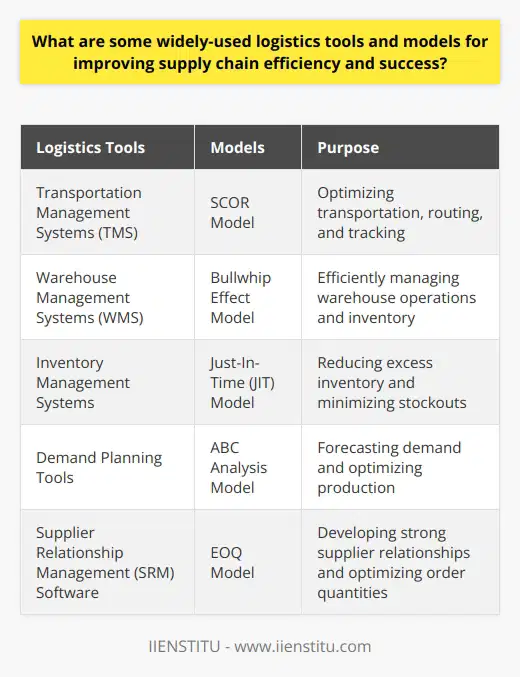
Logistics Tools for Supply Chain Efficiency
One widely-used logistics tool for improving supply chain efficiency is the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. This software integrates various business processes, such as procurement, inventory management, and sales forecasting, into a single platform to enhance decision-making and reduce inefficiencies.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Another essential tool for effective supply chain management is the Warehouse Management System (WMS). This software solution optimizes storage and retrieval operations, tracks inventory levels, and streamlines order fulfillment procedures, thus enhancing customer satisfaction.
Transportation Management Systems (TMS)
Transportation Management Systems (TMS) enable organizations to efficiently manage multiple modes of transportation, such as air, sea, and ground, to ensure timely delivery and minimize costs. These tools consider factors like route optimization, carrier selection, and freight monitoring, contributing to improved reliability and reduced expenses.
Inventory Optimization Models
Inventory optimization models like the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and Reorder Point (ROP) aid organizations in calculating the optimal order quantity and reorder threshold. These models help minimize inventory holding and stockout costs, thus optimizing the supply chain's financial performance and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain Network Design
Supply chain network design models, such as the location-allocation model, help organizations determine the optimal configuration of distribution centers, warehouses, and retail outlets. These models minimize supply chain costs and ensure timely product availability, contributing to the overall supply chain efficiency and success.
Demand Forecasting Techniques
Demand forecasting techniques, such as time-series analysis and regression models, assist businesses in predicting future demand fluctuations. Accurate demand forecasts enable organizations to optimize production plans, inventory levels, and resource allocation, leading to efficient supply chain management.
Data Analytics and Optimization
The integration of data analytics and optimization techniques, like linear programming and simulation modeling, supports supply chain professionals in identifying inefficiencies and evaluating potential improvement scenarios. By incorporating advanced data analysis, organizations can make informed decisions to enhance their supply chain processes.
In conclusion, various logistics tools and models, including ERP systems, WMS, TMS, inventory optimization models, supply chain network design, demand forecasting techniques, and data analytics, contribute to improved supply chain efficiency and success. By implementing these tools and techniques, organizations can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
What are the primary objectives and applications of LMIS tools in supply chain management?
Understanding LMIS Tools
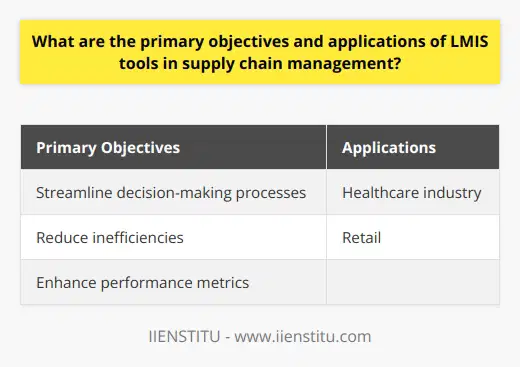
Logistics Management Information System (LMIS) tools are crucial components for efficient supply chain management. The primary objectives and applications of these tools are closely linked to enhancing decision-making processes, reducing inefficiencies, and improving the overall performance of supply chains.
Streamlining Decision-Making Processes
One primary objective of LMIS tools is to streamline decision-making processes. By providing accurate, up-to-date information on inventory levels, delivery times, and stock availability, these tools enable supply chain managers to make informed decisions. Consequently, this improves order processing, shipment tracking, and warehouse operations, leading to enhanced responsiveness and cost optimization.
Reducing Inefficiencies
Another important objective of LMIS tools is to minimize inefficiencies within the supply chain. These tools facilitate better communication and collaboration among stakeholders by providing them with real-time data on supply chain operations. This feature allows them to identify bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and optimize resource allocation. By eliminating redundancies and inconsistencies, LMIS tools ensure transparent, seamless, and efficient supply chain management.
Enhancing Performance Metrics
LMIS tools are designed to help supply chain managers monitor and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs). By tracking data on order fulfillment, transportation costs, and inventory turnover, these tools allow managers to assess the effectiveness of their strategies and identify areas for improvement. Continuous monitoring and evaluation of KPIs also help organizations in benchmarking their performance against industry standards and achieving a competitive advantage.
Application in Various Industries
The applications of LMIS tools span across multiple industries, ranging from healthcare to retail. In healthcare, for example, LMIS tools ensure the timely availability of essential medical supplies, thereby enhancing patient outcomes. In retail, they facilitate better demand forecasting, inventory management, and supplier partnerships, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In conclusion, the primary objectives and applications of LMIS tools in supply chain management involve streamlining decision-making processes, reducing inefficiencies, and improving performance metrics. By leveraging these tools, organizations can enhance their supply chain management efforts, overcome operational challenges, and ultimately, achieve a competitive edge in their respective industries.
How do different logistics models address the challenges and complexities of various industries and supply chain networks?
Logistics Models and Challenges
To address the challenges and complexities of various industries and supply chain networks, different logistics models aim to optimize processes and improve performance metrics. Specifically, these models focus on several aspects such as cost reduction, lead time reduction, inventory management, and risk mitigation.
Cost Reduction Strategies
Some logistics models, such as the network design model, focus on cost reduction by identifying the optimal distribution network for companies. This approach helps in cutting transportation, warehousing, and inventory costs while balancing service levels. Another model that addresses cost reduction is the transportation optimization model, which finds the best routing and shipment consolidation options to minimize transportation expenses.
Lead Time Reduction
Lead time reduction is another crucial aspect that logistics models address. For instance, the cross-docking model helps in reducing lead times by eliminating the need for storage and moving products directly from suppliers to customers. Additionally, the just-in-time model minimizes lead times by synchronizing the supply of materials with production schedules, resulting in lower inventory levels and faster customer response.
Inventory Management Solutions
Effective inventory management is essential for addressing the challenges of various industries and supply chains. Models such as the economic order quantity (EOQ) approach help organizations calculate the optimal order quantity to maintain minimal inventory costs. Similarly, the vendor-managed inventory (VMI) model enables suppliers to manage their customers' inventory levels, ensuring stock availability and reducing stock-outs.
Risk Mitigation Approaches
Logistics models can also mitigate risks associated with supply chain networks. For instance, the multi-echelon inventory model considers various factors such as lead times, demand variability, and service levels to optimize inventory allocation across multiple stages in a supply chain network. This approach reduces the risk of stock-outs and excess inventory. Moreover, sales and operations planning (S&OP) models integrate the sales, marketing, and operations functions within a company, enabling better demand forecasting and reducing execution risks.
In conclusion, different logistics models address the diverse challenges and complexities faced by various industries and supply chain networks. By focusing on key aspects such as cost reduction, lead time reduction, inventory management, and risk mitigation, these models provide organizations with the tools necessary to optimize their operations and improve overall performance.
What are the strategic and tactical benefits of implementing logistic tools and models in the planning and execution of supply chain operations?
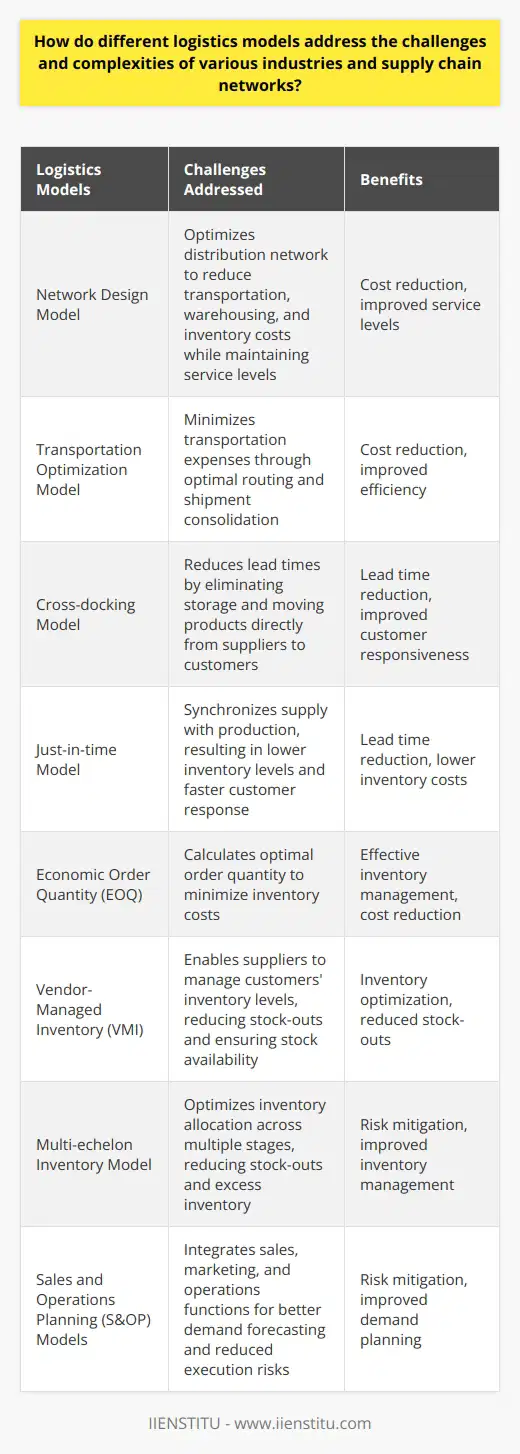
Strategic Advantages of Logistic Tools
One of the strategic benefits of implementing logistic tools and models in the planning and execution of supply chain operations lies in enhanced decision-making capabilities. With the aid of advanced analytic tools, managers can analyze various aspects of their supply chain to improve forecasting, optimize inventory levels, and streamline their transportation networks. These tools also enable organizations to align their supply chain objectives with their overarching business strategies, leading to a more integrated and effective operational framework.
Increased Efficiency through Tactical Advancements
Tactically, logistic tools and models provide essential support for supply chain operations through real-time visibility and performance monitoring. Integration of these tools into daily processes allows organizations to improve resource utilization, reduce waste, and minimize costs. For instance, transportation management systems (TMS) can optimize route selection, leading to decreased fuel consumption, shorter transit times, and ultimately, reduced delivery costs. Furthermore, warehouse management systems (WMS) can enhance the flow of goods within storage facilities, improving order accuracy and turnaround times.
Risk Mitigation and Improved Resilience
Another vital aspect of using logistic tools is their ability to help organizations identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks in their supply chains. With the support of these tools, companies can develop contingency plans to address potential disruptions, such as supplier bankruptcies or natural disasters. As a result, organizations can maintain a high degree of supply chain resilience, enabling them to recover more quickly from unforeseen setbacks and maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
Facilitating Collaboration and Communication
Logistic tools and models often incorporate features that support cross-functional collaboration, both internally and externally, giving all stakeholders access to critical information in real-time. By providing a shared platform for communication, these tools contribute to a more synchronized approach to supply chain management, leading to improved relationships with suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. Improved collaboration also enables organizations to react rapidly to changes in demand or disruptions in the global marketplace, ensuring that their supply chain networks remain agile and responsive.
In conclusion, the implementation of logistic tools and models offers companies significant strategic and tactical benefits in managing their supply chain operations. These advantages include improved decision-making capabilities, increased operational efficiency, risk mitigation and resilience, and enhanced collaboration and communication. Ultimately, employing these tools can help organizations achieve a more integrated, agile, and cost-effective supply chain, giving them a critical competitive edge in today's fast-paced global market.
What are the specific advantages and disadvantages of each of the six supply chain models?
Analyzing Each Supply Chain Model
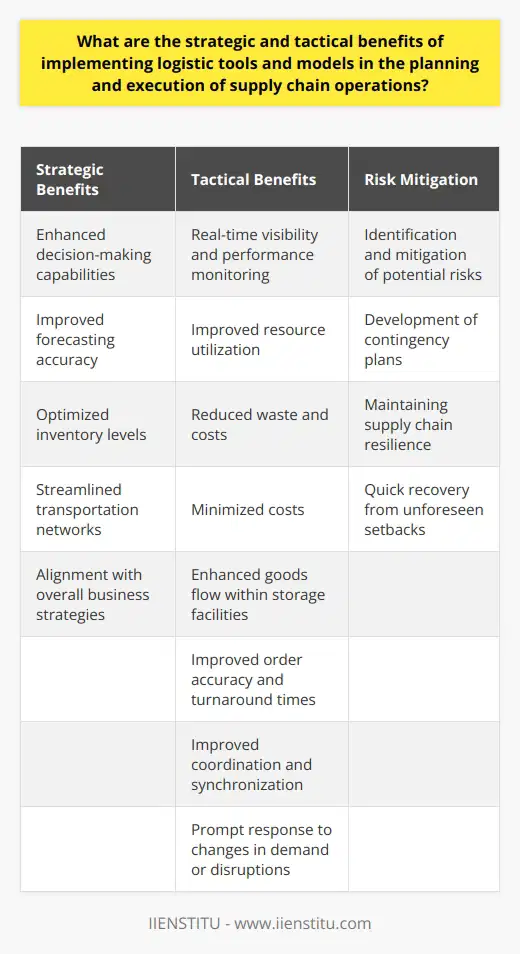
Advantages of the Efficient Chain Model
The Efficient Chain model is designed for functional products with stable, predictable demand. This model has low production costs primarily due to economies of scale. Additionally, operational excellence through low lead time and minimal stockouts is achieved through effective information sharing and forecasting methods.
Disadvantages of the Efficient Chain Model
However, the Efficient Chain model could suffer from low flexibility due to its primary focus on cost reduction. Furthermore, product variety is limited, making it less appealing for customers with diverse preferences. In some cases, this approach may lead to long lead times for new products.
Advantages of the Agile Chain Model
Aimed at unpredictable and innovative markets, the Agile Chain model can quickly respond to market changes. This approach focuses on flexibility and adaptability, allowing companies to rapidly adjust inventory levels and production schedules. Moreover, collaboration between suppliers and customers is strengthened, leading to better end-to-end visibility.
Disadvantages of the Agile Chain Model
Nonetheless, the Agile Chain model may come with higher operational costs, as rapid response and frequent changes often require additional resources. This model might also face challenges in supporting large-scale, high-volume production due to its emphasis on flexibility and responsiveness.
Advantages of the Continuous Replenishment Chain Model
This model ensures continuous product availability by maintaining constant inventory replenishment. It helps effectively manage customer service levels and inventory turnover. Companies adopting this model can develop closer relationships with suppliers and streamline supply chain processes, resulting in reduced operational costs.
Disadvantages of the Continuous Replenishment Chain Model
On the flip side, this model might not be suitable for industries with significant fluctuations in demand or short life cycles, as continuous replenishment could lead to excess inventory or stockouts. It could also be less effective in managing complex product portfolios.
Advantages of the Hybrid Push-Pull Chain Model
The Hybrid Push-Pull Chain model combines the benefits of both push and pull strategies within a single supply chain. This model achieves an optimized balance between production efficiency and customer responsiveness by incorporating demand-driven and forecast-based approaches.
Disadvantages of the Hybrid Push-Pull Chain Model
However, implementing this model can be complex, as it requires efficient coordination and integration between the two supply chain strategies. The need for sophisticated technology and advanced forecasting methods could increase implementation costs and challenges.
Advantages of the Leagile Chain Model
Based on the principles of Lean and Agile, the Leagile Chain model aims to offer a high level of flexibility while maintaining cost efficiency. This model promotes waste reduction, process improvements, and quick responsiveness, enabling it to satisfy diverse customer demands.
Disadvantages of the Leagile Chain Model
Nevertheless, achieving the right balance between agility and leanness may prove challenging due to the inherent tradeoffs. Moreover, organizational alignment and effective implementation might be demanding, considering the comprehensive transformation the Leagile Chain model entails.
Advantages of the Synchronized Chain Model
The Synchronized Chain model focuses on integrating all supply chain components and aligning them strategically. The benefits lie in enhanced end-to-end transparency, better resource utilization, improved decision-making, and increased innovation potential due to cross-functional collaboration.
Disadvantages of the Synchronized Chain Model
Despite the advantages, synchronization across an entire supply chain can be a complex, time-consuming endeavor. It requires extensive communication, data sharing, and collaborative efforts with all involved parties, which could be a daunting task for large organizations with numerous stakeholders.
How do LMIS tools and logistics models contribute to the overall strategic planning and decision-making process in an organization?
LMIS Tools and Operational Efficiency
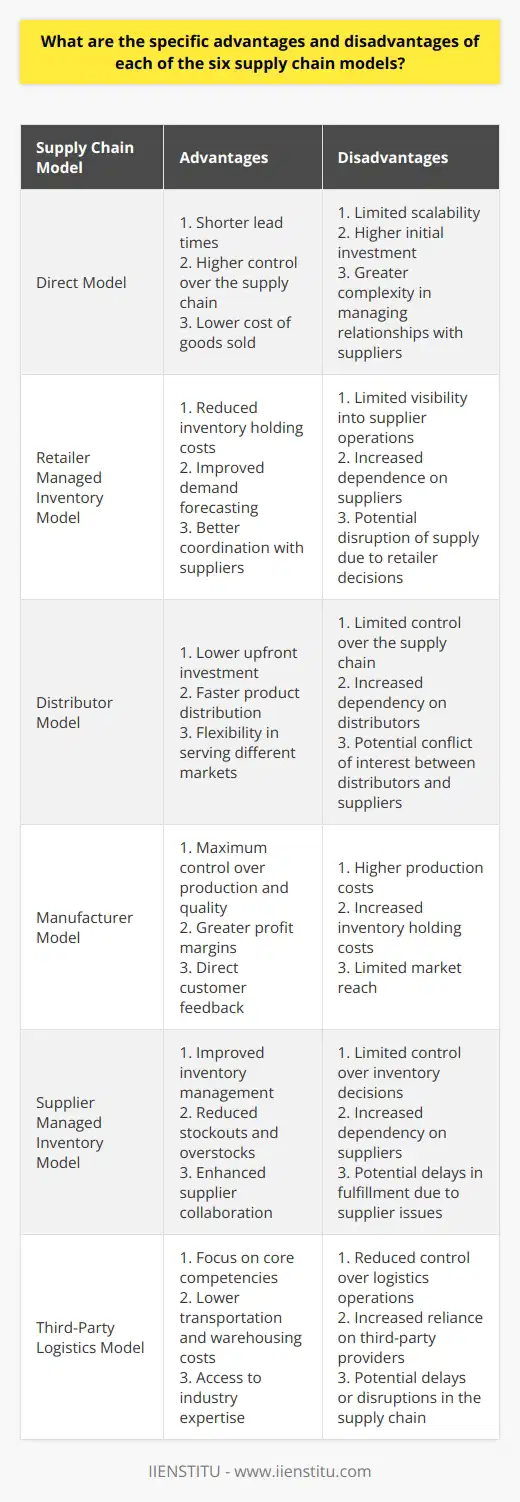
LMIS (Logistics Management Information Systems) tools contribute significantly to an organization's strategic planning and decision-making process by enabling efficient data management and streamlined logistics operations. These tools facilitate the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data relevant to supply chain management, which helps organizations identify areas for improvement and capitalize on opportunities.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Furthermore, by providing accurate and timely data, LMIS tools support data-driven decision-making within organizations. This allows managers and executives to make informed choices, backed by concrete evidence, which can lead to better alignment of strategic goals and increased operational efficiency. This effect is particularly pronounced when used in conjunction with advanced logistics models, which provide a comprehensive and detailed analysis of the organization's supply chain.
Enhanced Forecasting and Planning
The integration of LMIS tools and logistics models allows organizations to improve strategic planning through enhanced forecasting and inventory management. By analyzing historical data, these tools can help predict future demand patterns and assist in optimal inventory management. Consequently, this aids organizations in avoiding stockouts and reducing excess inventory, resulting in decreased costs and improved customer satisfaction.
Optimizing Resource Allocation
Additionally, the combined use of LMIS tools and logistics models helps organizations optimize resource allocation, ensuring resources are utilized efficiently and effectively. This encompasses the allocation of human resources, facilities, and transportation assets, all of which are critical components of a successful logistics system. The ability to allocate resources strategically is essential for organizations to maintain a competitive edge in today's global marketplace.
Risk Management and Mitigation
Lastly, through the use of LMIS tools and logistics models, organizations can better identify and manage potential risks within their supply chain. By providing insights into potential disruptions and vulnerabilities, these tools help organizations develop contingency plans and strategies to mitigate potential losses. Consequently, this mitigates risks and strengthens overall supply chain resilience.
In conclusion, the utilization of LMIS tools and logistics models significantly contributes to an organization's strategic planning and decision-making process. They enhance operational efficiency, support data-driven decision-making, and promote optimal inventory management, resource allocation, and risk mitigation. The integration of these tools and models is therefore essential for organizations aiming to achieve a competitive edge in today's dynamic business landscape.
What are the key factors to consider when selecting an appropriate logistics management model for a specific industry or supply chain network?
Selection Criteria for Logistics Management Models
Supply Chain Characteristics
The first key factor to consider when selecting an appropriate logistics management model is the characteristics of the supply chain network. Different industries have distinct supply chain structures and require unique approaches to logistics management. The length, size, and complexity of the supply chain play a crucial role in determining the most suitable model to adopt.
Nature of Products and Services
Another essential factor to take into account is the nature of the products or services being handled. This includes the size, weight, and perishability of goods, as well as their specific storage, handling, and transportation requirements. Certain logistics management models are more effective for perishable goods, while others may be better suited for high-value items.
Technological Compatibility
Ensuring the compatibility of the logistics management model with existing or planned technological infrastructure is imperative. The model should be able to integrate seamlessly with current systems and operational processes to facilitate efficient data exchange, process integration, and real-time visibility of supply chain activities.
Demand and Supply Volatility
In industries with fluctuating demand and supply conditions, it is essential to consider the responsiveness and flexibility of the logistics management model. A model that allows for rapid adaptation to changing market conditions will help organizations in maintaining an agile, customer-centric supply chain that can respond effectively to demand shifts and supply disruptions.
Cost Considerations
The cost implications of implementing and maintaining a specific logistics management model should be thoroughly assessed. The selected model must strike a balance between offering the required functionality and providing cost savings through efficiency improvements, streamlined operations, and reduced waste.
Environmental and Social Impact
Finally, the environmental and social implications of adopting a particular logistics management model should be considered. Companies must opt for sustainable and socially responsible models that prioritize reducing environmental footprints and eliminating unethical practices, supporting the global push towards more sustainable and ethical supply chain management.
In conclusion, selecting an appropriate logistics management model hinges on a comprehensive understanding of the specific industry, supply chain network, and organizational needs. By considering factors such as supply chain characteristics, product nature, technological compatibility, demand volatility, cost implications, and environmental and social impact, companies can identify the most suitable logistics management model to drive supply chain performance and deliver customer value.
What are the primary functions and capabilities of LMIS tools in streamlining logistics operations and decision-making?
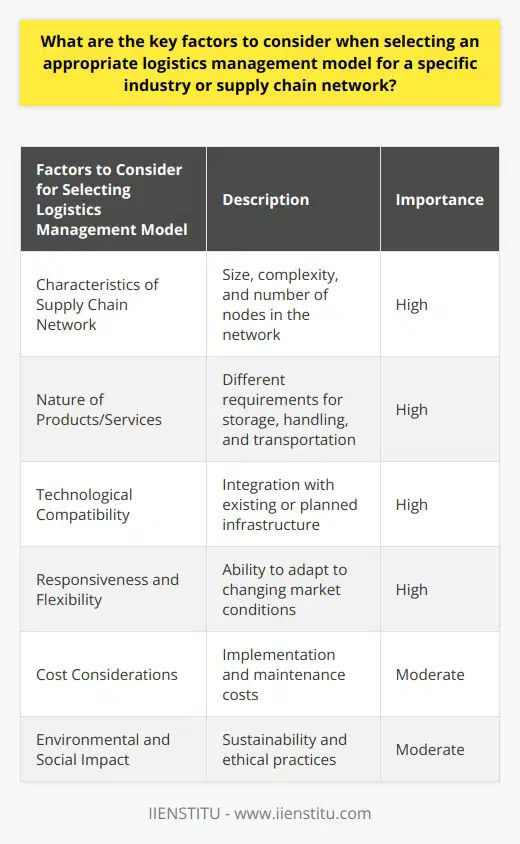
**Functions of LMIS Tools**
The primary functions of Logistics Management Information System (LMIS) tools include data collection, analysis, and reporting. They facilitate the tracking of resources, such as inventory levels and location, transportation, and distribution. These tools are essential for effective coordination and decision-making in logistics operations.
**Capabilities for Streamlining Operations**
LMIS tools offer several capabilities that help streamline logistics operations. Firstly, they provide real-time information, enabling organizations to monitor and control supply chain activities effectively. This allows for efficient adjustments to meet changing market demands and avoid disruptions. Secondly, LMIS tools support automation of routine tasks, such as order processing, inventory management, and shipment tracking, reducing manual effort and increasing accuracy.
**Supporting Decision-Making Processes**
In addition to streamlining operations, LMIS tools also support decision-making by offering predictive analytics and decision support features. These tools analyze historical and current data to identify trends and patterns, allowing organizations to make informed decisions regarding inventory levels, transportation routes, and distribution channels. Furthermore, they enable scenario planning, allowing logistics managers to study the impact of various strategies and choose the most effective approach.
**Enhanced Collaboration and Communication**
LMIS tools play a crucial role in improving collaboration and communication among stakeholders involved in the logistics process. By providing a central platform for sharing information, these tools enhance visibility and transparency across the supply chain. This fosters trust and cooperation, resulting in more efficient and effective logistics operations.
**Conclusion**
In summary, the primary functions and capabilities of LMIS tools in streamlining logistics operations and decision-making include data collection, analysis, reporting, real-time information, automation, predictive analytics, decision support, and enhanced collaboration. By leveraging these functionalities, organizations can significantly improve their logistics efficiency and effectiveness, ensuring the successful movement of goods and services to meet customer demands.
How do analysis methods in logistics inform the development and refinement of efficient supply chain management strategies?
Analyzing Logistics Data
Efficient supply chain management strategies depend on accurate logistics data analysis. Utilizing quantitative and qualitative methods, supply chain managers can reduce costs, mitigate risks, and improve operational performance. In this blog post, we will examine how analysis methods in logistics inform supply chain strategy development and refinement.
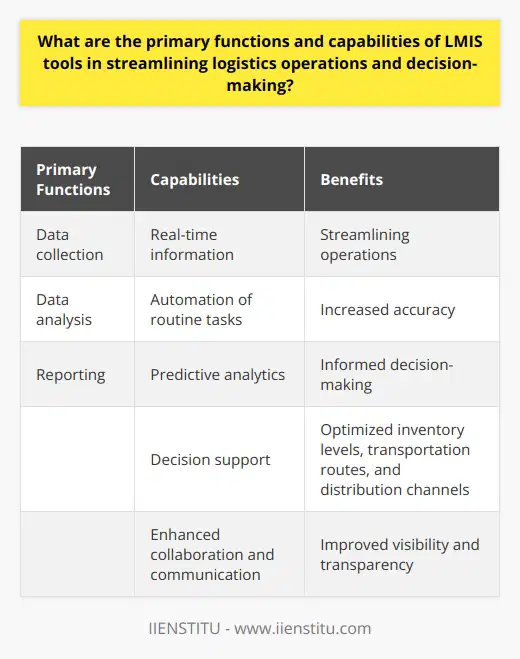
Quantitative Techniques
One key component of logistics analysis is applying quantitative techniques, such as data mining, optimization models, and simulation. Data mining identifies patterns and relationships within large data sets, providing insights into customer behavior, inventory management, and transportation efficiency. These can help supply chain managers to better allocate resources and plan for demand fluctuations. Optimization models, such as the traveling salesman problem and facility location problem, allow decision-makers to find the most cost-effective routes and locations for warehouses, distribution centers, and transport networks. Simulation models enable supply chain managers to test various scenarios, evaluate the potential impact of disruptions, and identify bottlenecks in the system.
Qualitative Approaches
Complementing quantitative methods are qualitative approaches, such as expert interviews, focus groups, and case studies. Expert interviews offer in-depth knowledge and experience-based insights, which can be invaluable for understanding the dynamics of the supply chain environment. Focus groups allow for the gathering of opinions and ideas from various stakeholders, helping to ensure that supply chain strategies are grounded in practical concerns. Case studies provide real-world examples of successful strategies, offering supply chain managers the opportunity to learn from the experiences of others and adapt best practices to their particular context.
Continuous Improvement
Adopting a continuous improvement mindset is critical in leveraging analysis methods to enhance supply chain management strategies. By regularly evaluating and monitoring performance metrics, organizations can track progress, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments. Implementing a systematic approach, such as the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, can assist in driving improvements on an ongoing basis. Essentially, supply chain managers should use the insights gained from logistics analysis to set attainable goals, implement strategic initiatives, measure results, and refine strategies as necessary.
In conclusion, effective analysis methods in logistics play a pivotal role in the development and refinement of supply chain management strategies. Quantitative techniques facilitate data-driven decision making, while qualitative approaches ensure consideration of practical concerns and real-world examples. A continuous improvement mindset ensures that strategies evolve in response to changing circumstances and performance outcomes. Ultimately, combining these elements allows supply chain managers to construct and adapt strategies for maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
In what ways do the various models in logistics management address the unique needs and challenges of diverse industries and logistical environments?
Models in Logistics Management
Addressing Unique Industry Needs
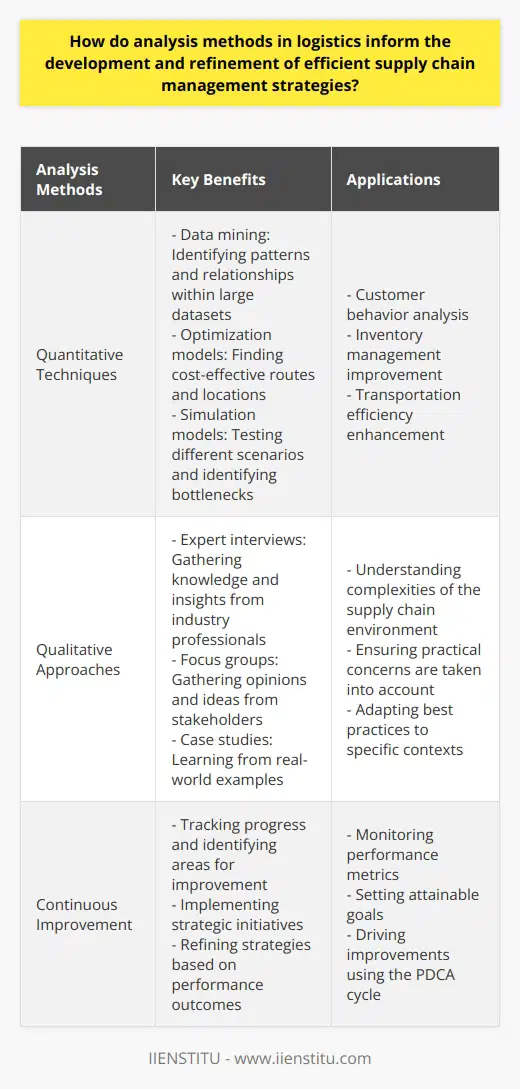
The various models in logistics management address the unique needs and challenges of diverse industries by incorporating specific strategies that cater to each sector. For instance, Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management is frequently used in the automotive industry, where components must be available precisely when needed during production. This technique helps reduce lead times, inventory carrying costs, and warehouse space requirements, making it an ideal approach for this industry.
Customized Solutions for Logistical Environments
In contrast, the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model is designed for environments with more predictable and consistent demand patterns. By calculating the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, this model addresses the needs of industries like retail, which rely on cost-efficient replenishment strategies to maintain high service levels. In addition, the EOQ model can adapt to various logistical environments, such as those with lead times and other constraints, with modifications like the Reorder Point model.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Another way that logistics management models address diverse challenges is through cross-functional collaboration. The Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR®) model, for example, identifies and optimizes performance metrics in terms of reliability, responsiveness, agility, and cost, thus facilitating collaboration among various stages of a supply chain. This approach is particularly beneficial for diverse industries in which supply chain stakeholders must coordinate their efforts to achieve optimal results, such as the electronics or pharmaceutical sectors.
Incorporating Advanced Technologies
Lastly, several logistics management models integrate advanced technologies like automation, artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, which can help address unique industry-specific needs. For instance, the Digital Twin concept allows companies to simulate complex logistical environments and test different scenarios before implementing them in real life, thereby reducing risk and uncertainty. Such technologies can also enhance inventory management and demand forecasting, enabling industries to adapt to fast-changing environments more effectively.
In conclusion, the various models in logistics management tackle the unique needs and challenges of diverse industries and logistical environments through the utilization of industry-specific strategies, customized solutions, cross-functional collaboration, and advanced technologies. As a result, organizations can optimize their operations, enhance efficiency, and meet the dynamic demands of their respective markets.
What are the different types of logistics analysis and their respective applications in supply chain management?
Logistics Analysis Types
In supply chain management, logistics analysis plays a significant role in enhancing performance and customer satisfaction. Different types of logistics analysis cater to specific requirements in supply chain management, encompassing demand forecasting, network design and optimization, transportation management, and inventory control.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting involves predicting future customer demand to adjust production, inventory levels, and resource allocation. Accurate demand forecasts enable organizations to optimize production planning and reduce stockouts or excess inventory, resulting in lower carrying costs and improved customer service levels. Various methods, such as time-series analysis, causal models, and qualitative techniques, are employed to generate demand forecasts based on historical data, market trends, and expert opinions.
Network Design and Optimization
This type of logistics analysis focuses on determining the optimal network configuration to minimize costs and improve service levels. It examines factors such as facility location, transportation modes, and capacity utilization to identify the most efficient network structure. Network design and optimization often leverage advanced mathematical models and analytical tools, such as linear programming and mixed-integer programming, to solve complex supply chain problems.
Transportation Management
Transportation management addresses the selection, coordination, and execution of transportation activities to ensure the smooth movement of goods between supply chain participants. It entails analyzing various transportation modes and routes, selecting the most suitable carriers, and optimizing cargo consolidation and delivery schedules. Additionally, transportation management incorporates performance evaluation through key performance indicators (KPIs), such as on-time delivery and transportation cost per unit, to continuously monitor and improve transportation activities.
Inventory Control
Inventory control involves determining the appropriate levels of stock to be maintained at various stages of the supply chain to meet customer requirements while minimizing inventory holding costs. Techniques used for inventory control include economic order quantity (EOQ), safety stock calculations, and just-in-time (JIT) inventory management. Moreover, inventory control involves utilizing analytical tools to classify items based on their importance, such as ABC analysis, to allocate resources effectively and reduce stock obsolescence risks.
In conclusion, logistics analysis, including demand forecasting, network design and optimization, transportation management, and inventory control, contributes to enhancing supply chain efficiency, responsiveness, and flexibility. By applying these analytical techniques, businesses can reduce costs, improve service levels, and adapt to changing market conditions, resulting in a competitive advantage and increased customer satisfaction.
How do logistic tools assist in addressing the unique challenges and requirements of various industries and optimize overall supply chain performance?
Logistic Tool Applications
Logistic tools play an essential role in streamlining supply chain management across diverse industries. By implementing innovative approaches and technologies, these tools provide customized solutions tailored to sector-specific challenges and requirements. Consequently, they facilitate the optimization of overall supply chain performance.
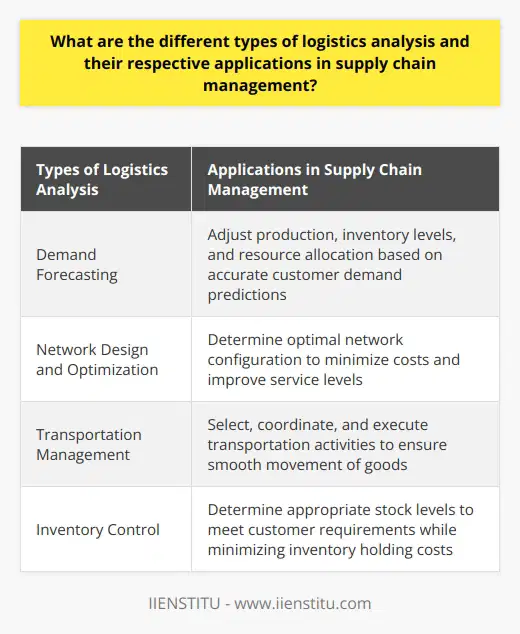
Inventory and Warehouse Management
One critical aspect in which logistic tools assist various industries is inventory and warehouse management. Utilizing advanced technologies such as RFID tracking, drone inspections, and barcode scanning, logistics software helps manage inventory levels and storage facilities more efficiently. This in turn leads to reduced operational costs, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased profitability.
Transportation and Distribution Planning
Logistic tools also contribute significantly to transportation planning and distribution efforts. They enable shippers to streamline their route planning and optimize delivery schedules by integrating real-time traffic and weather data. This ensures cost-effective transportation of goods, adherence to delivery deadlines, and improved customer service.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Another vital area where logistic tools prove beneficial is risk management and contingency planning. With predictive analytics and real-time monitoring, these tools help companies identify potential disruptions and implement proactive measures to minimize their impact on the supply chain. This leads to increased operational reliability and reduced risk exposure.
Integration and Collaboration
Logistic tools foster integration and collaboration among supply chain stakeholders by enabling information sharing, effective communication, and coordinated decision-making. By bringing together multiple parties such as suppliers, manufacturers, retailers, and carriers, these tools help create a more efficient and unified supply chain ecosystem.
Sustainability and Compliance
Furthermore, logistic tools contribute to promoting sustainable practices and ensuring regulatory compliance across the supply chain. By providing companies with insights into their environmental footprint and carbon emissions, these tools enable industries to adopt greener approaches, adhere to international standards, and demonstrate their commitment to corporate social responsibility.
In conclusion, logistic tools address the unique challenges and requirements of various industries. By enhancing inventory control, transportation planning, risk management, collaboration, sustainability, and compliance, they help optimize overall supply chain performance and lead to a more competitive market position.
What are the main characteristics and features of the six supply chain models, and how do they cater to the diverse needs of different industries in terms of structure, goals, and implementation strategies?
Supply Chain Model Characteristics
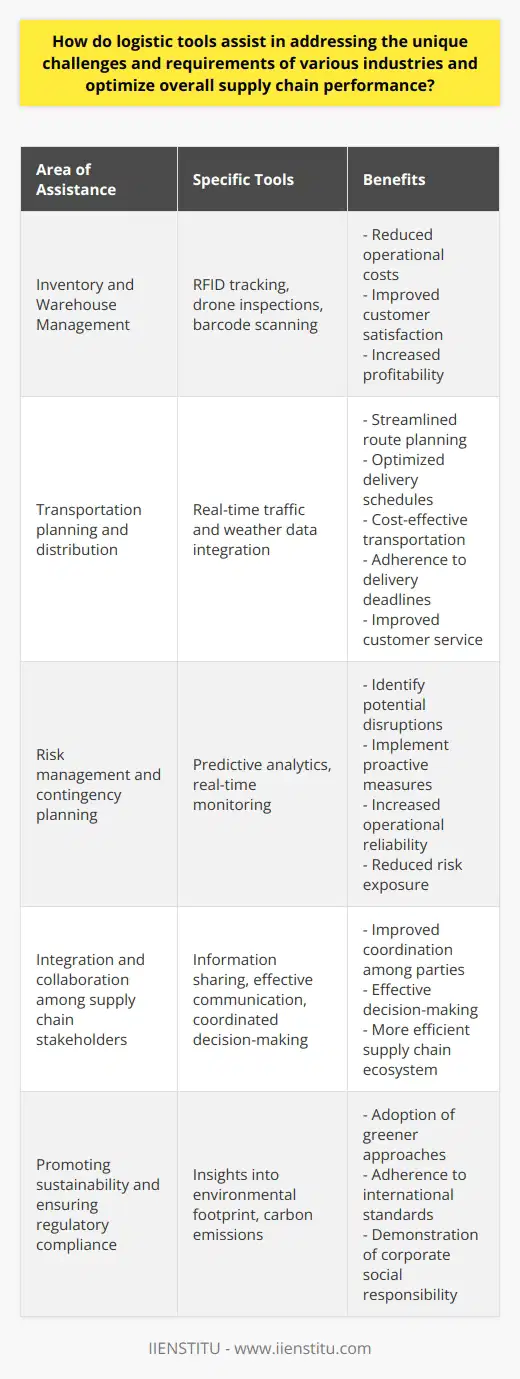
The six supply chain models are the efficient chain, the fast chain, the continuous flow, the discontinuous innovation, the agile chain, and the custom-configured product chain. Despite the varying attributes, these models address the diverse needs of industries when it comes to structure, goals, and implementation strategies.
Efficient Chain Model
The efficient chain, also known as the lean supply chain, emphasizes minimizing costs and reducing waste. This model is ideal for industries with stable demand, where standardization, low production costs, and high-quality products are essential.
Fast Chain Model
The fast chain model is highly responsive, with short lead times to cater to volatile markets. It’s suitable for industries with fluctuating product demand, requiring rapid adaptation in the manufacturing and distribution processes to remain competitive.
Continuous Flow Model
The continuous flow model focuses on process streamlining and efficiency through high-volume production. This model is ideal for industries like automotive, chemicals, and refining, where uninterrupted flow of products from raw materials to finished goods is critical to success.
Discontinuous Innovation Model
The discontinuous innovation model thrives in industries where technological advancements occur at a rapid pace. It encourages innovation and rapid product development, making it perfect for industries like telecommunications, software, and semiconductors.
Agile Chain Model
The agile chain combines the best of both the efficient and fast chain models. It emphasizes quick response times to market demands while also prioritizing cost-efficiency, making it ideal for industries like consumer electronics and apparel that face unpredictable demand patterns and a high level of customization.
Custom-Configured Product Chain
Lastly, the custom-configured product chain enables tailored solutions for niche markets. It decouples assembly and order fulfilment processes, allowing manufacturers to deliver highly customized products at relatively low costs. This model is well-suited for industries like automotive, home appliances, and furniture.
In conclusion, these six supply chain models address different industry requirements in terms of structure, goals, and implementation strategies. By understanding and applying the most suitable model, businesses can establish and maintain a competitive advantage in an ever-evolving marketplace.
What are the key principles and methodologies underlying the development and application of LMIS tools in logistics management?
The Development of LMIS Tools
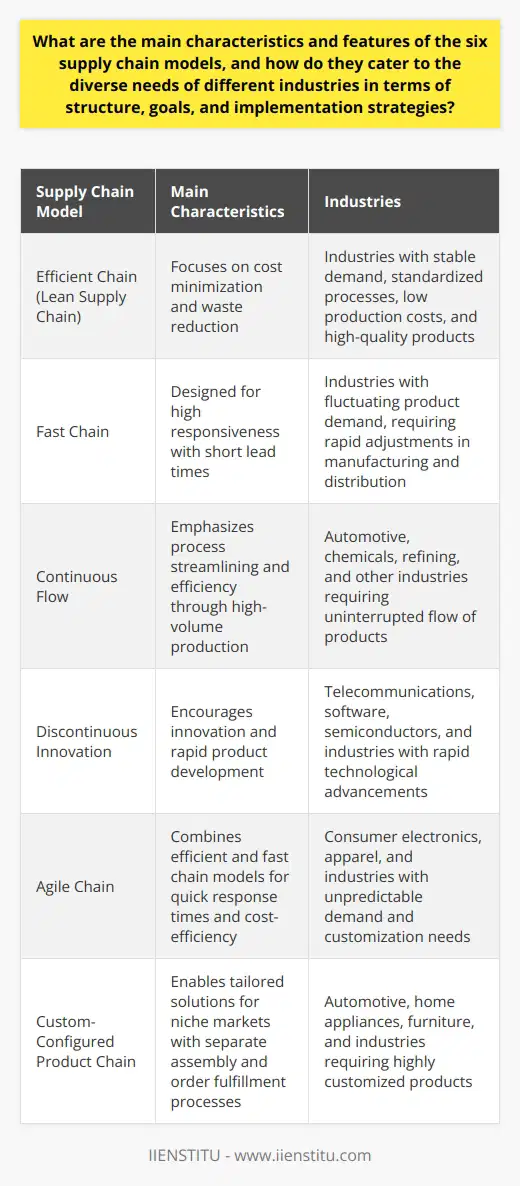
The development and application of Logistics Management Information Systems (LMIS) tools rest on a few key principles. Firstly, the principle of integration advocates for interconnected systems, facilitating broad insights across the supply chain. This might include procurement planning, inventory management, and distribution tracking.
End-User Accessibility
Next, the principle of end-user accessibility suggests that LMIS tools must not only be user-friendly but also scalable corresponding to the increasing complexity of supply chains. It emphasizes presenting data clearly and straightforwardly, so everyone in the supply chain can understand and act on this information.
Data-Driven Decision Making
A central concept underpinning LMIS is data-driven decision-making, which encourages responders to make decisions grounded on real-time and accurate data rather than intuition. This can influence quicker response times, enhance efficiency and accuracy, and mitigate potential risks in logistics management.
FMCG and JIT Methodologies
Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) and Just-In-Time (JIT) are two key methodologies that influence the development of LMIS tools. The FMCG methodology emphasizes high turnover rates, requiring tools that can evaluate and operate at rapid speeds. Conversely, the JIT methodology necessitates tools capable of precise coordination and synchronization in order to minimize waste and maximize efficiency.
Agile and Lean Methodologies
Moreover, Agile and Lean methodologies also play a key role. Agile methodologies require adaptability and flexibility, prompting tools that can swiftly recalibrate as per supply chain changes. Meanwhile, Lean methodologies demand efficiency and waste reduction, necessitating tools that identify and eliminate unproductive elements in the logistics process.
In conclusion, understanding these principles and methodologies is key for designing effective LMIS tools that can streamline logistics management, leading to increased operational efficiency and cost reduction.
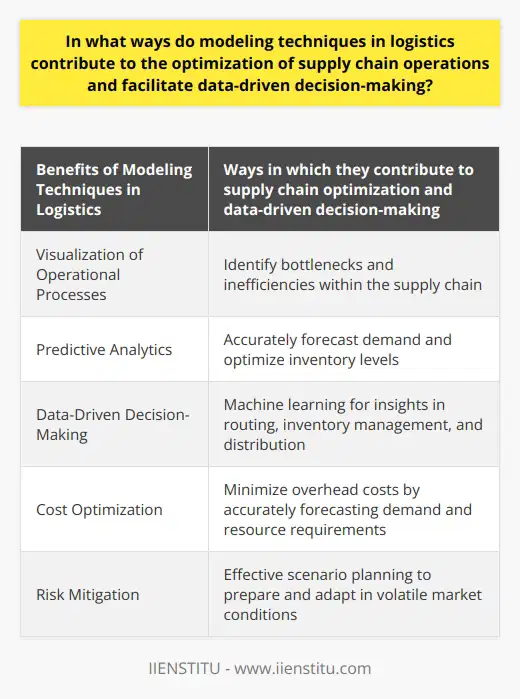
In what ways do modeling techniques in logistics contribute to the optimization of supply chain operations and facilitate data-driven decision-making?
Modeling Techniques Enhancing Supply Chain Operations
The use of modeling techniques in logistics drives the optimization of supply chain operations. Such techniques visualize operational processes, thereby, aiding understanding and improvement. The primary outcome is impressive cycle time reduction. By visualizing the interconnected links in a supply chain, potential bottlenecks become evident. Quickly addressing these prevents unnecessary delays or surplus inventory accumulation.
Predictive Analytics for Improvement
Further, predictive analytics, a type of modeling technique, forecasts demand patterns. Utilizing past trends and real-time data, this technique refines accuracy in demand forecasting. Efficient demand prediction prevents stockouts or excesses, managing inventory efficiently. It also aids firms in strategically planning production schedules, allocating resources more efficiently.
Towards Data-Driven Decisions
Additionally, modeling allows for algorithmically-driven, data-based decision-making. Machine learning, for instance, provides valuable insights drawn from the analysis of large datasets. This helps guide decision-making regarding routing, inventory, and distribution to enhance productivity.
Cost Optimization and Risk Mitigation
Modeling techniques also assist in cost optimization by aiding resource planning, thereby minimizing overheads. They enable risk mitigation in volatile market conditions through effective scenario planning. By evaluating diverse potential scenarios of market changes, these tools help firms prepare and adapt more effectively.
In conclusion, modeling techniques in logistics revolutionize supply chain operations. Their contribution is fundamental to streamlining processes, efficient resource use, risk management, and insightful, data-driven decision-making. They create robust, adaptable, and high-performing supply chains, a competitive advantage in today's marketplace.
How can logistics tools and models be integrated into existing supply chain management systems to enhance efficiency and effectiveness across various industry sectors?
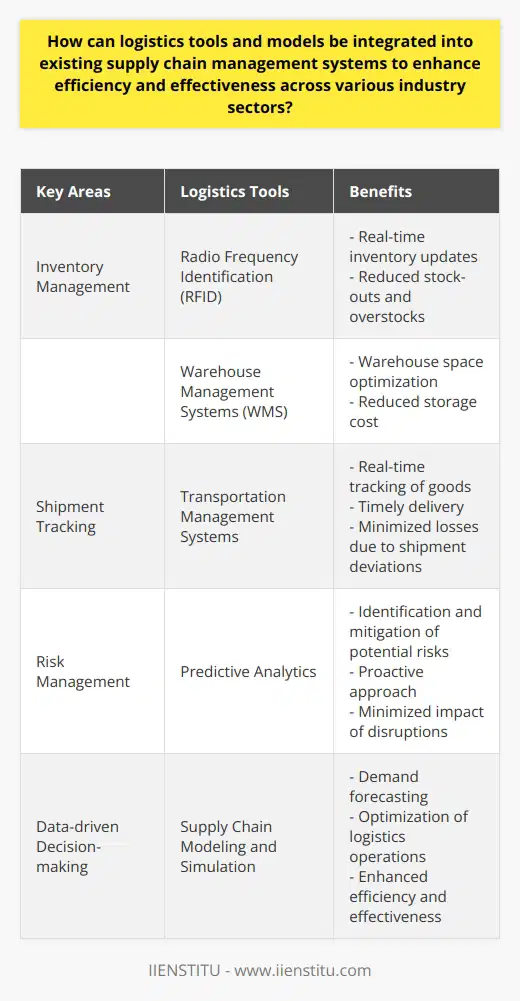
Integrating Logistics Tools into Supply Chain Systems
Logistics tools and models can enhance supply chain management by streamifying operations. Often, these tools help manage inventory, track shipments, and analyze delivery performance. Their integration within existing supply chain systems can aid in predicting demand, ensuring inventory availability, and mitigating potential disruptions.
Facilitating Efficient Inventory Management
For instance, logistic tools like Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) enhance inventory management. RFID ensures real-time inventory status updates, reducing stock-outs and overstocks. Meanwhile, WMS allows for warehouse space optimization, impacting overall storage cost.
Improving Shipment Tracking
Moreover, logistics tools can improve shipment tracking, a crucial aspect of supply chain management. Tools such as Transportation Management Systems allow real-time tracking of goods, ensuring timely delivery and customer satisfaction. It also enables quicker reaction to shipment deviations, reducing potential losses.
Enhancing Risk Management
Furthermore, the integration of these logistic tools can enhance risk management in supply chain systems. Predictive analytics enable identification and mitigation of potential risks before they escalate, improving the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
Driving Decision-Making with Data Analytics
In addition, analytic tools and models can drive data-driven decision making. Tools such as Supply Chain Modeling and Simulation can forecast demand and optimize logistics operations, enhancing both efficiency and effectiveness.
In conclusion, integrating logistics tools and models into existing supply chain systems has significant potential to enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness across various industries. These benefits span from improved inventory and shipment management to enhanced risk management and data-driven decision-making. Thus, organizations should consider adopting and integrating these tools within their supply chain systems.