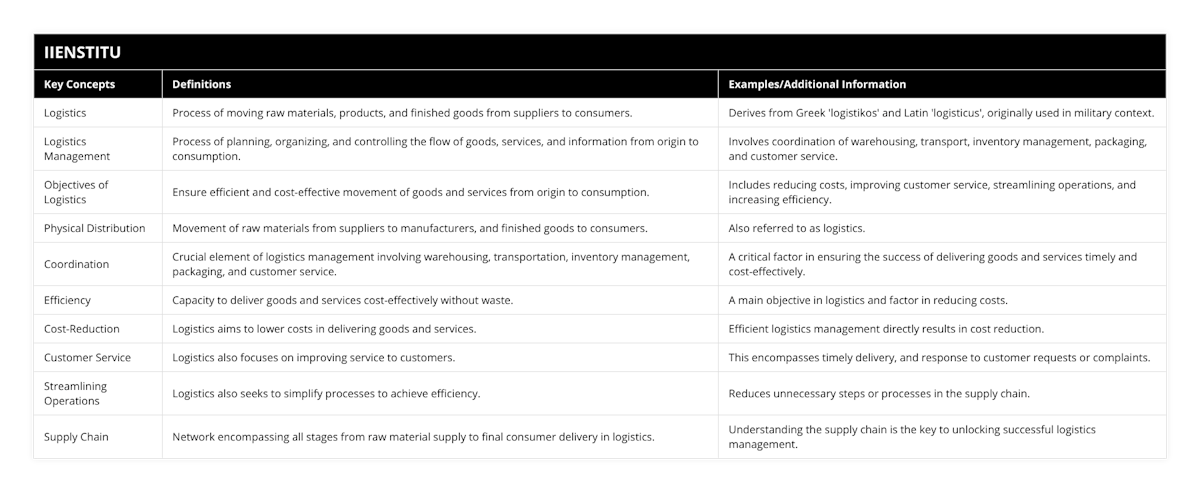
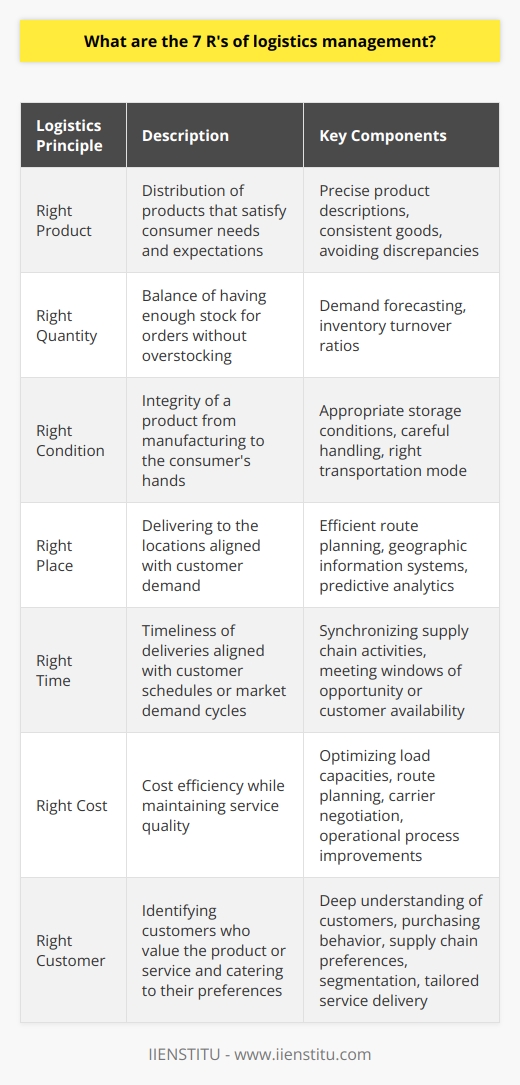
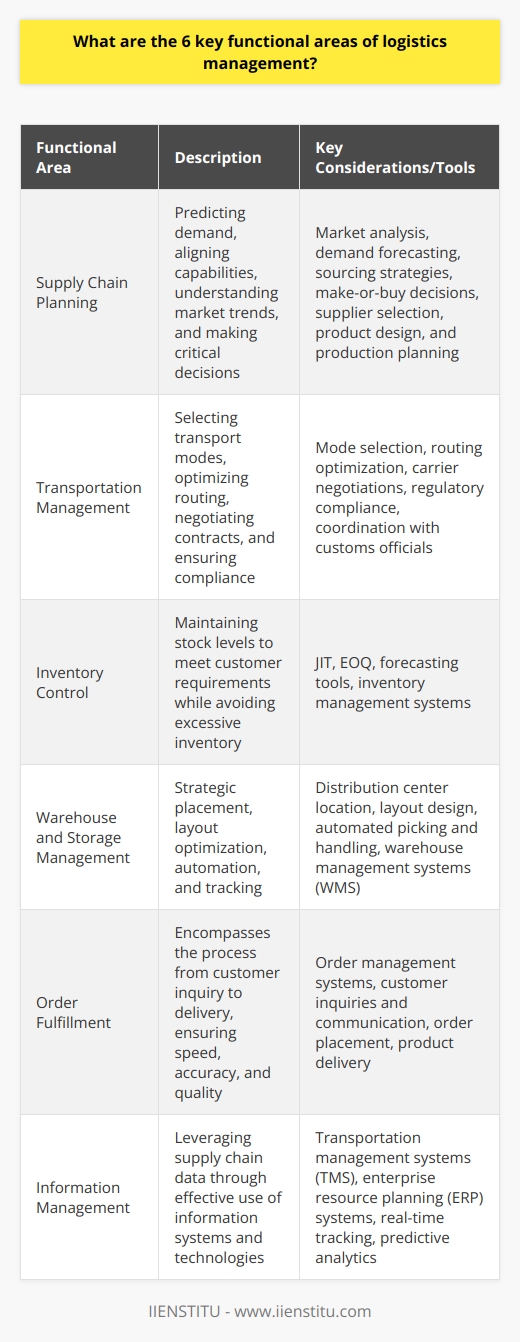
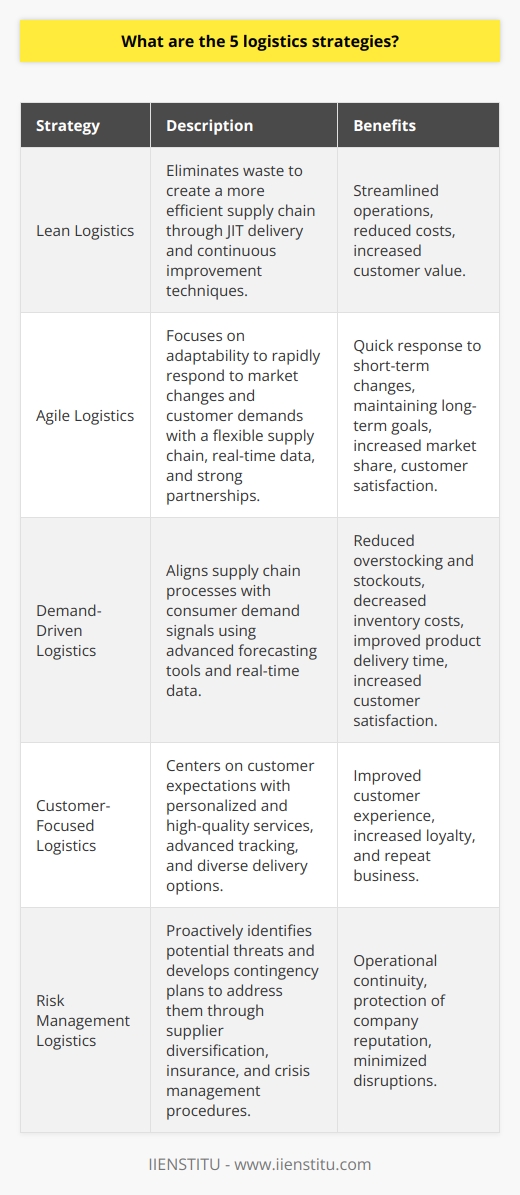
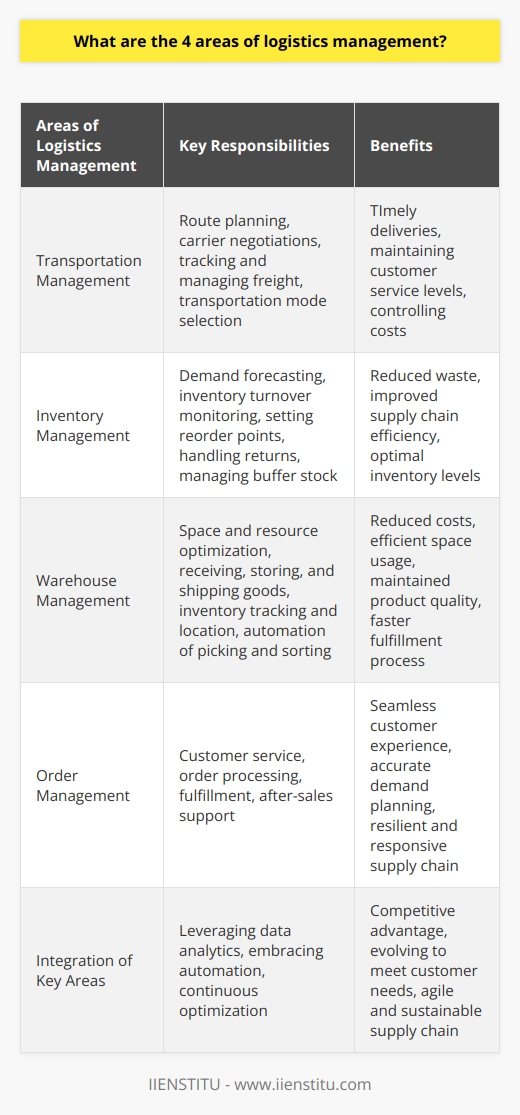
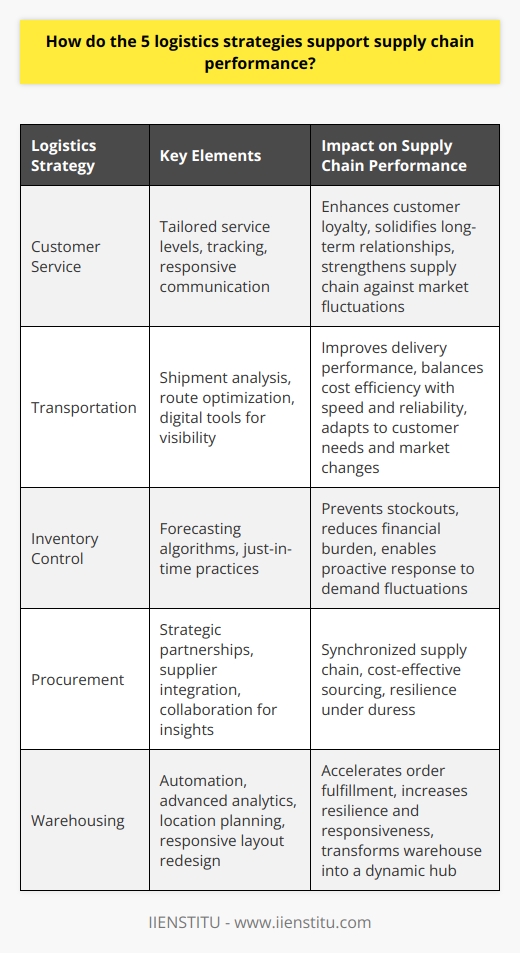
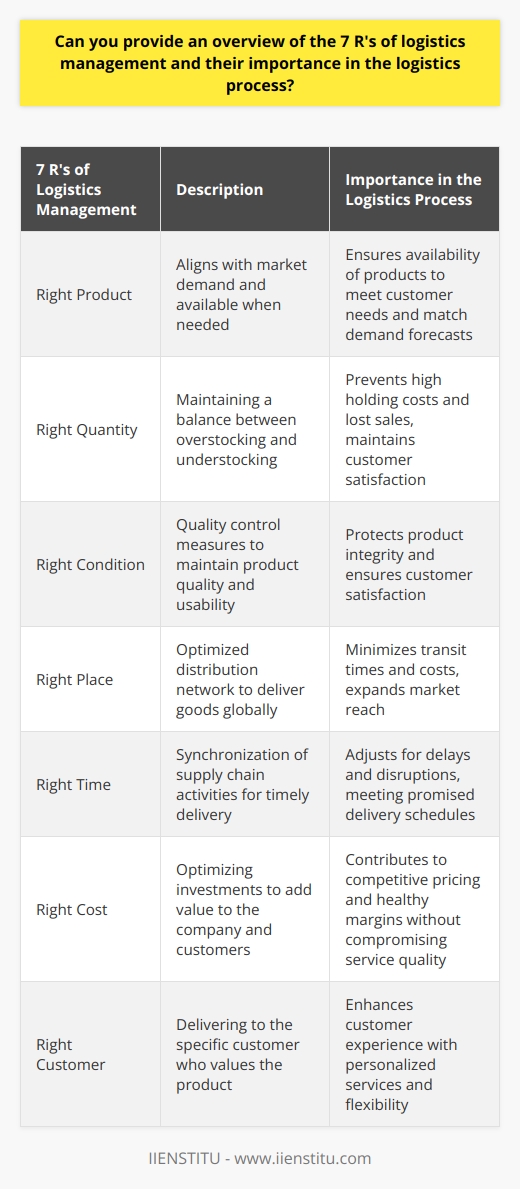
Logistics is an essential part of business operations, referring to the movement of raw materials, products, and finished goods from suppliers to consumers. Logistics management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the flow of goods, services, and information between the point of origin and the point of consumption. The main objective of logistics is to ensure the efficient and cost-effective movement of goods and services. In contrast, other purposes include reducing costs, improving customer service, streamlining operations, and increasing efficiency.
Related Course: Logistics Management Courses Online
Introduction
Definition of Logistics
Logistics Management
Objectives of Logistics
Conclusion
Introduction: Logistics is a term that has been used for centuries, but its meaning has evolved. Logistics plays an integral role in business, as it moves raw materials, products, and finished goods from suppliers to consumers. This article will discuss the definition of logistics, logistics management, and logistics objectives.
Definition of Logistics
Logistics is derived from the Greek word logistics and the Latin word logistics, which refer to the science of computing and calculating. Historically, logistics was used in connection with moving armies and supplies of food and armaments to the war front. However, during World War II, logistics gained importance in army operations as a term referencing the movement of supplies, men, and equipment across the border.
In the business world, logistics refers to the movement of raw materials from suppliers to manufacturers and, finally, the movement of finished goods to consumers. It is also referred to as physical distribution. According to Philip Kotler, logistics is “planning, implementing, and controlling the physical flows of materials.”
Logistics Management
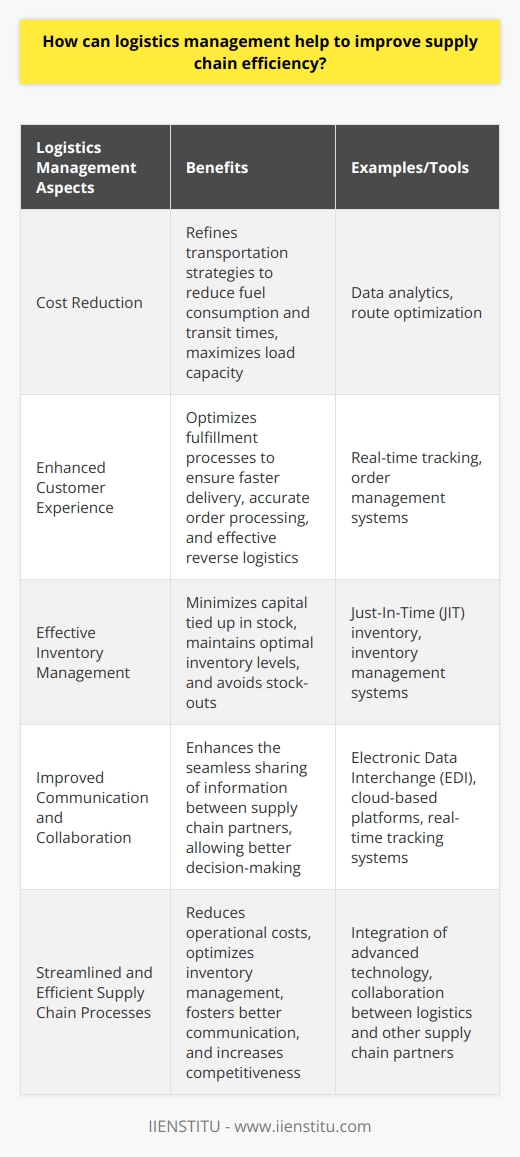
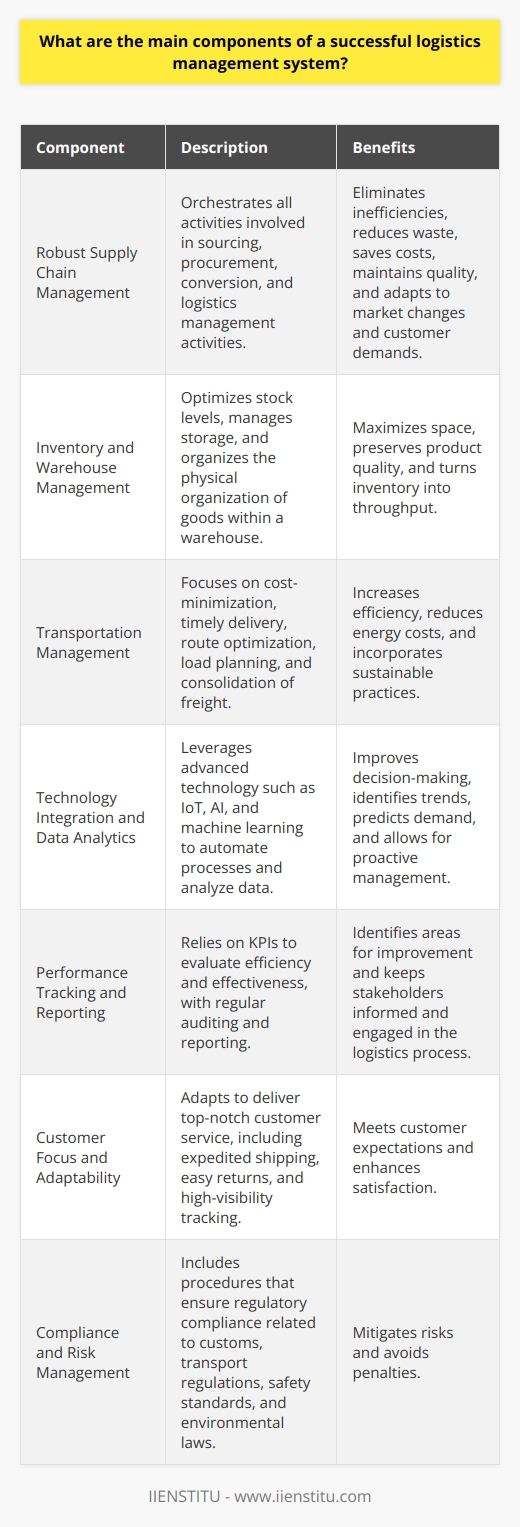
Logistics management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the flow of goods, services, and information between the point of origin and the point of consumption. It involves coordinating warehousing, transportation, inventory management, packaging, and customer service. Logistics management is essential for companies to ensure the timely and cost-effective delivery of goods and services.
Objectives of Logistics
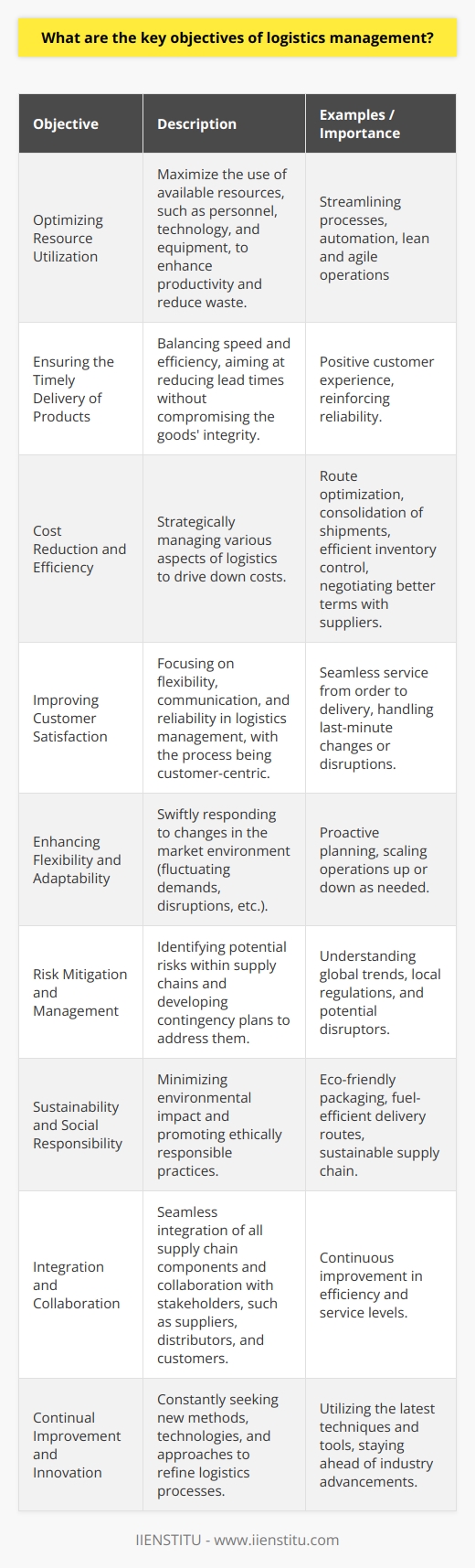
The main objective of logistics is to ensure the efficient and cost-effective movement of goods and services from the point of origin to the end of consumption. This involves coordinating warehousing, transportation, inventory management, packaging, and customer service. Other logistics objectives include reducing costs, improving customer service, streamlining operations, and increasing efficiency.
Conclusion: Logistics is an essential part of business operations, as it is responsible for moving raw materials, products, and finished goods from suppliers to consumers. Logistics management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the flow of goods, services, and information between the point of origin and the point of consumption.
The main objective of logistics is to ensure the efficient and cost-effective movement of goods and services from the point of origin to the end of consumption. Other logistics objectives include reducing costs, improving customer service, streamlining operations, and increasing efficiency.
The key to successful logistics management is to unlock the mysteries of the supply chain.