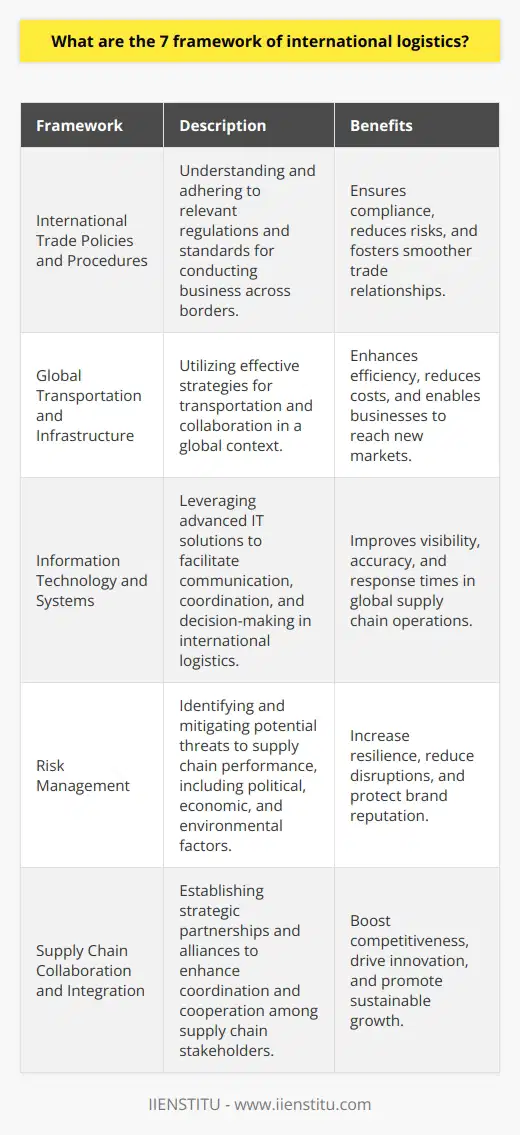
This article outlines the hierarchical framework of logistics planning, composed of strategic, tactical, and operational planning. Each of these planning horizons has distinct characteristics and requires different levels of resources and managerial time. Strategic planning involves making decisions that have the most significant impact on the organization’s long-term success; tactical planning involves making decisions that have a medium-term impact. Operational planning involves making decisions that have a short-term impact.
By implementing this hierarchical framework, organizations can ensure that their decisions are aligned with their long-term goals and objectives.
Introduction
Strategic Planning
Tactical Planning
Operational Planning
Conclusion
Logistics planning is a critical component of any business’s success. It involves making decisions about the resources, time, and cost associated with moving goods and services from one point to another. A hierarchical framework is necessary to effectively manage the range of activities and decisions related to logistics planning.
This framework is composed of strategic planning, tactical planning, and operational planning. Each of these planning horizons has distinct characteristics and requires different levels of resources and managerial time.
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is the most long-term of the three planning horizons. It involves making decisions that have the most significant impact on the organization’s long-term success. These decisions often require significant resources and managerial time.
Examples of strategic planning decisions include the location and size of a factory, the selection of suppliers and vendors, and the development of a global supply chain.
Balancing Capacity Responsiveness Flexibility And Cost İn Supply Chain
Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, And Replenishment Benefits İn Supply Chain Management
Tactical Planning
Tactical planning is the central planning horizon. It involves making decisions that have a medium-term impact on the organization’s success. These decisions require more resources and managerial time than operational planning decisions but less than strategic planning decisions. Examples of tactical planning decisions include inventory management, transportation schedules, and production scheduling.
Operational Planning
Operational planning is the shortest planning horizon. It involves making decisions that have a short-term impact on the organization’s success. These decisions require the least amount of resources and managerial time. Examples of operational planning decisions include warehouse layout, production line scheduling, and order fulfillment.
Logistics planning is a critical component of any business’s success. A hierarchical framework is necessary to effectively manage the range of activities and decisions associated with logistics planning. This framework is composed of strategic planning, tactical planning, and operational planning.
Each of these planning horizons has distinct characteristics and requires different levels of resources and managerial time. By implementing a hierarchical framework for logistics planning, organizations can ensure that their decisions are aligned with their long-term goals and objectives.
A Hierarchical Framework for Logistics Planning is the key to efficient and successful operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main components of the hierarchical framework for logistics planning?
Logistics planning is a crucial part of business operations. Without adequate planning, businesses cannot achieve desired results and may suffer losses. The hierarchical framework for logistics planning is a set of components organizations can use to develop and implement an effective logistics plan. This framework is based on a hierarchical approach, in which each component builds on the previous one.
The first component of the hierarchical framework for logistics planning is the problem definition. This involves analyzing the current situation and identifying the problems that need to be solved or improved. This component also includes a needs assessment to determine the best solutions to the identified problems.
The second component is strategy development. This component involves developing strategies and objectives to address the identified problems and needs. The strategy should be specific and measurable, and aligned with the organization's overall goals.
The third component is resource allocation. This component involves allocating resources to the strategies and objectives. This includes financial and non-financial resources, such as personnel, equipment, and technology.
The fourth component is process design. This component involves designing the processes and systems needed to implement the strategies and objectives. This includes defining personnel's tasks, roles, and responsibilities and identifying the technology and tools used.
The fifth component is performance analysis. This component involves measuring the performance of the strategies and objectives. This includes monitoring the effectiveness of the process and system design and assessing the effectiveness of the resource allocation.
The sixth component is review and refinement. This component involves analyzing the performance of the strategies and objectives and making adjustments as needed. This includes identifying new opportunities for improvement and making necessary changes to the process and system design.
The hierarchical framework for logistics planning is a valuable tool for organizations developing and implementing an effective logistics plan. By following the framework's components, organizations can ensure that their logistics plan is effective and efficient.

How does the hierarchical framework for logistics planning help to optimize logistics operations?
Logistics planning is a complex process that requires careful consideration of cost, efficiency, and customer service. A practical logistics planning framework can help organizations to optimize their logistics operations, improve cost efficiency, and provide better customer service.
A hierarchical framework for logistics planning is a practical approach for organizations to optimize their logistics operations. This framework is based on breaking down a task into its parts and then addressing each individually. This approach allows organizations to identify the most cost-effective solutions for their logistics operations.
The hierarchical framework for logistics planning begins with identifying the overall logistics requirements. This involves considering the size and scope of the organization, the type of goods or services it provides, and the customer base it serves. Once the requirements have been identified, the organization can identify the most efficient and cost-effective way to meet those requirements. This could involve choosing the right transportation mode, selecting a reliable carrier, and developing a reliable delivery schedule.
The hierarchical framework also allows organizations to identify potential problems and create solutions that can be implemented in the future. This can include anticipating customer needs, identifying areas of waste and inefficiency, and introducing new technologies that can improve the efficiency of their logistics operations.
Using a hierarchical framework for logistics planning allows organizations to optimize their logistics operations and make them more cost-effective. By breaking down the task into its parts, organizations can identify the most efficient solutions for their logistics operations. Additionally, the framework allows organizations to anticipate future needs and create solutions that can be implemented. In this way, the hierarchical framework for logistics planning helps organizations to optimize their logistics operations and improve their overall performance.
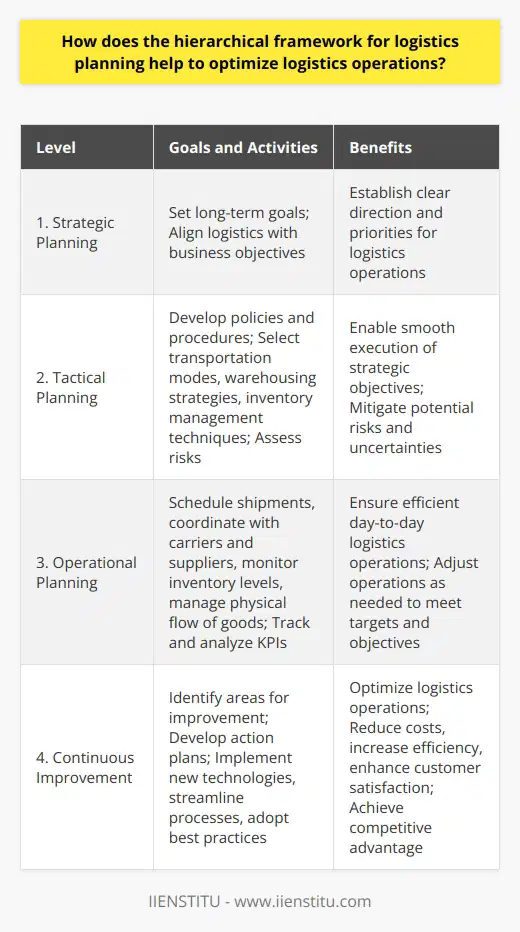
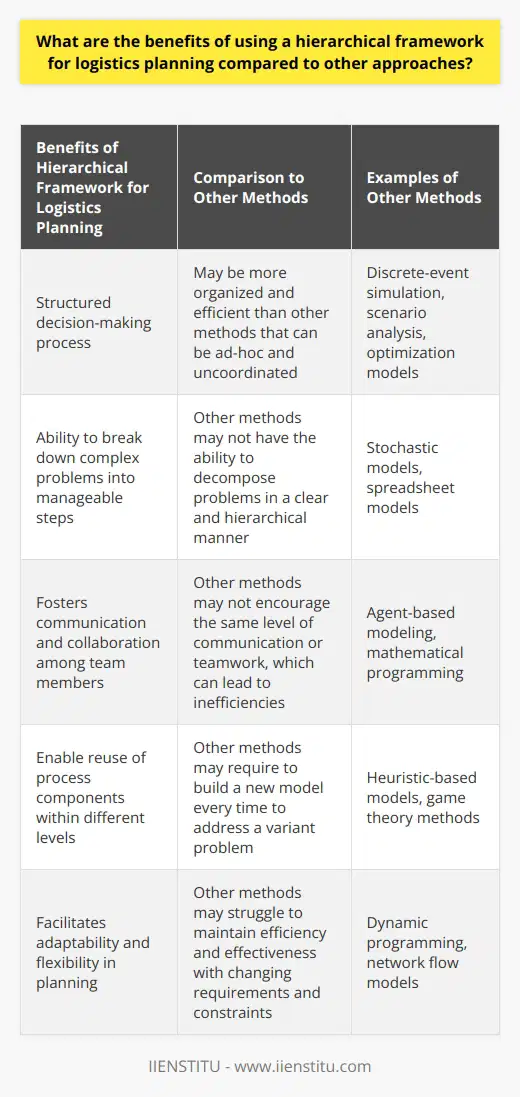
What are the benefits of using a hierarchical framework for logistics planning compared to other approaches?
Logistics planning is an essential part of any successful business venture. The need for a reliable and efficient system for managing the flow of goods, services, and resources cannot be understated. One of the most popular approaches to logistics planning is the hierarchical framework. This system of organizing tasks helps to simplify the process of getting goods and services to their intended destination in a timely and cost-effective manner. This article will explore the benefits of using a hierarchical framework for logistics planning compared to other approaches.
The hierarchical framework is a systematic approach to logistics planning. It involves the identification of tasks and the categorization of those tasks into hierarchical levels. This system allows for the mapping of tasks in a logical order, which helps reduce the plan's complexity. This approach makes it easier to identify the essential tasks and prioritize them accordingly. In addition, the hierarchical framework allows for better resource utilization, as tasks are grouped and assigned according to their importance.
Another advantage of the hierarchical framework is its scalability. This planning system can easily be adapted to different levels of complexity and can be used for small or large-scale operations. Furthermore, the hierarchical framework is flexible and can be adjusted to meet the needs of a particular organization or industry. This makes it an ideal solution for various logistics planning tasks.
The hierarchical framework also offers improved communication and collaboration between departments. Categorizing tasks into hierarchical levels makes it easier for different departments to understand their roles and responsibilities within the organization. This, in turn, leads to better collaboration and communication between departments, which can help to streamline the logistics planning process.
Finally, the hierarchical framework is a cost-effective solution for logistics planning. Reducing the plan's complexity makes it possible to reduce the amount of time and money spent on the process. In addition, the hierarchical framework helps to reduce the number of mistakes made in the process, resulting in fewer delays and higher quality output.
In conclusion, the hierarchical framework offers several benefits over other approaches to logistics planning. This organization system allows for improved resource utilization, scalability, better communication and collaboration, and cost-effectiveness. For these reasons, the hierarchical framework is an ideal solution for a wide range of logistics planning tasks.
What is a hierarchical supply chain framework?
Defining Hierarchical Supply Chain Framework
A hierarchical supply chain framework is an organizational structure that categorizes and systematizes supply chain processes into distinct levels of prioritization and management. This enables companies to optimize their operations, improve coordination among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, and achieve better visibility and control over the entire supply chain network.
Primary Levels of Hierarchical Framework
Typically, a hierarchical supply chain framework divides the entire process into three primary levels: strategic, tactical, and operational. Each level serves a specific purpose, addressing varying aspects of supply chain management, and interacts with the others for seamless integration.
Strategic Level: Long-Term Approach
At the strategic level, companies focus on long-term objectives, such as market expansion, supplier selection, and network design. Decisions made at this level have a significant impact on the organization’s overall performance and involve in-depth analysis, foresight, and innovative thinking.
Tactical Level: Medium-Term Planning
The tactical level involves medium-term planning, including inventory management, transportation, and production policies. The primary goal at this stage is to balance supply and demand while maintaining cost efficiency and mitigating risks. Tactical decisions often emerge from the strategic level and act as a bridge between long-term goals and day-to-day operations.
Operational Level: Short-Term Execution
The operational level encompasses the detailed execution of daily supply chain activities and the implementation of decisions made at the tactical level. Tasks include scheduling production runs, fulfilling customer orders, and managing transportation and delivery routes. Operational level actions directly impact customer satisfaction and operational efficiency, making it vital for the success of the overall supply chain.
Benefits of Hierarchical Framework in Supply Chain Management
Implementing a hierarchical supply chain framework enables organizations to attain various benefits. By segregating processes into different levels, businesses can distribute responsibilities, ensuring an efficient and organized management approach. Additionally, this structure enhances communication and collaboration across departments, allowing each level to contribute to decision-making and foster a better understanding of the overall network. Ultimately, employing a hierarchical framework streamlines supply chain management, driving improved performance, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
What are the levels of logistics planning?
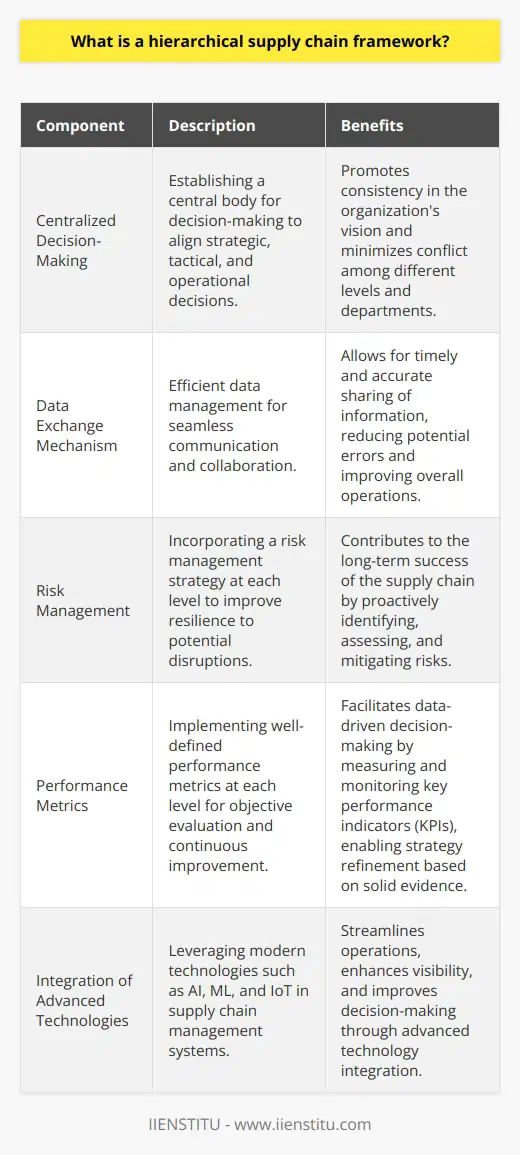
Levels of Logistics Planning
Strategic Level
The strategic level of logistics planning deals with long-term decisions that shape the overall direction of an organization's logistics operations. These critical choices include the selection and development of distribution networks, transportation modes, inventory management systems, and outsourcing partners.
Operational Level
Operational logistics planning revolves around the day-to-day management of an organization's logistics functions. At this level, logistical managers focus on executing and supervising essential tasks such as procurement, warehousing, transportation, and customer service. They also monitor and ensure regulatory compliance and risk mitigation.
Tactical Level
Tactical logistics planning involves making adjustments and modifications to existing logistics plans based on the analysis of specific market trends, customer demand variations, and situational factors. This requires managers to evaluate the effectiveness of the existing logistics strategies and adapt them based on the recognition of inefficiencies, constraints, or opportunities.
Contingency Level
The contingency level of logistics planning is designed to prepare an organization to face unexpected events, such as natural disasters, labor strikes, or political disturbances. It includes developing backup plans and robust strategies that ensure the continuity of logistics operations during emergencies. This planning can minimize disruptions, maintain customer satisfaction, and protect profitability.
In conclusion, effective logistics planning requires a thorough understanding of the varying levels involved, including strategic, operational, tactical, and contingency planning. Competent logistics managers adapt their approach depending on the situation and the changing needs of the organization, ultimately ensuring efficient and resilient supply chains.
What are the 7 pillars of logistics?
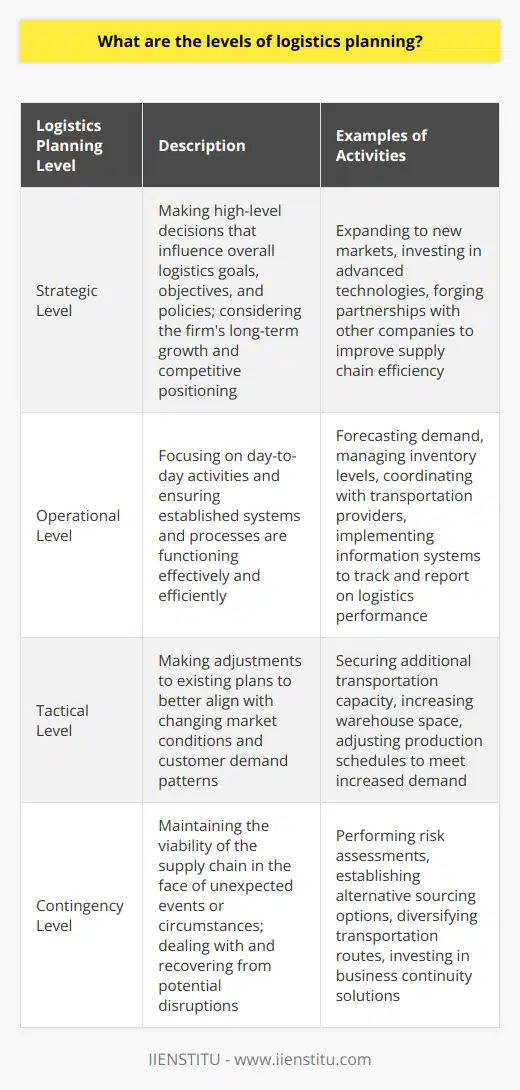
**Pillar 1: Customer Service**
The first pillar of logistics is customer service, which entails meeting customer expectations and providing satisfaction. It is crucial because it defines the overall scope and objective of logistics.
**Pillar 2: Transport Management**
Transport management focuses on the movement of goods from their origin to their destination. This pillar involves planning, coordination, and execution of efficient and cost-effective transportation solutions for products.
**Pillar 3: Inventory Control**
Controlling inventory is essential to maintaining the right balance between stock availability and holding costs. Effective management of inventory involves accurate forecasting, efficient reordering processes, and proper storage.
**Pillar 4: Warehouse Management**
Warehouse management deals with optimizing the storage, retrieval, and handling of goods within a facility. Efficient warehouse management practices ensure that products are stored and organized properly for smooth movement and timely delivery.
**Pillar 5: Order Processing**
Order processing is the compilation and execution of purchase orders. A streamlined order processing system minimizes errors, expedites order confirmation and delivery, and ultimately enhances customer satisfaction.
**Pillar 6: Information Technology**
Information technology plays a vital role in modern logistics. IT systems improve communication, data management, and visibility throughout the supply chain. Technology solutions facilitate efficiency, accuracy, and cost reduction in logistics operations.
**Pillar 7: Supply Chain Integration**
The final pillar, supply chain integration, is the collaboration and coordination of all parties involved in the supply chain. It seeks to optimize processes, reduce redundancies, and improve overall performance through data sharing and coordinated decision-making.
What is the role of strategic planning in the hierarchical logistics framework?
Role of Strategic Planning
Strategic planning holds a paramount role in the hierarchical logistics framework, primarily serving as the backbone for organizing and coordinating logistics operations. It enables businesses to achieve their long-term objectives by outlining their visions and goals in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
Setting the Objectives
The planning process commences with the establishment of clear objectives, which provide direction and a sense of purpose for the organization. These objectives steer the logistics operations, aligning them with the overarching business goals. By setting quantifiable targets, organizations can better evaluate their progress and promptly adjust their strategies if necessary.
Analyzing the Environment
An essential aspect of strategic planning involves conducting a thorough analysis of the internal and external environment. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the organization and the opportunities and threats in the market is crucial for formulating an effective logistics strategy. This analysis helps decision-makers identify barriers, foresee potential disruptions, and allocate resources optimally to maximize efficiency and minimize costs.
Formulating Logistics Strategies
Developing logistics strategies is a crucial step in the strategic planning process. These strategies are devised to ensure the efficient use of resources and the smooth functioning of the logistics framework. They encompass the design, implementation, and continuous improvement of various processes like procurement, transportation, warehousing, and distribution.
Coordination and Integration
In a hierarchical logistics framework, strategic planning plays a vital role in coordinating and integrating different logistics functions. By fostering collaboration among various departments and stakeholders, it promotes seamless information flow and effective decision-making. This coordination and integration result in a more agile and responsive logistics system, capable of handling complex situations.
Performance Measurement and Control
Strategic planning also includes performance measurement and control mechanisms, which allow organizations to monitor their logistics efficiency and effectiveness continually. By employing key performance indicators (KPIs) and benchmarking their results, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement necessary corrective actions. This data-driven approach fosters continuous learning and enhances the overall resilience of the logistics framework.
In conclusion, strategic planning is indispensable in a hierarchical logistics framework, as it steers logistics operations towards their objectives through comprehensive analysis, formulation of strategies, and continuous performance evaluation. Ultimately, it enables organizations to maintain a competitive edge in a dynamic and challenging landscape.

How do different levels of planning and decision-making interact within a logistics planning hierarchy?
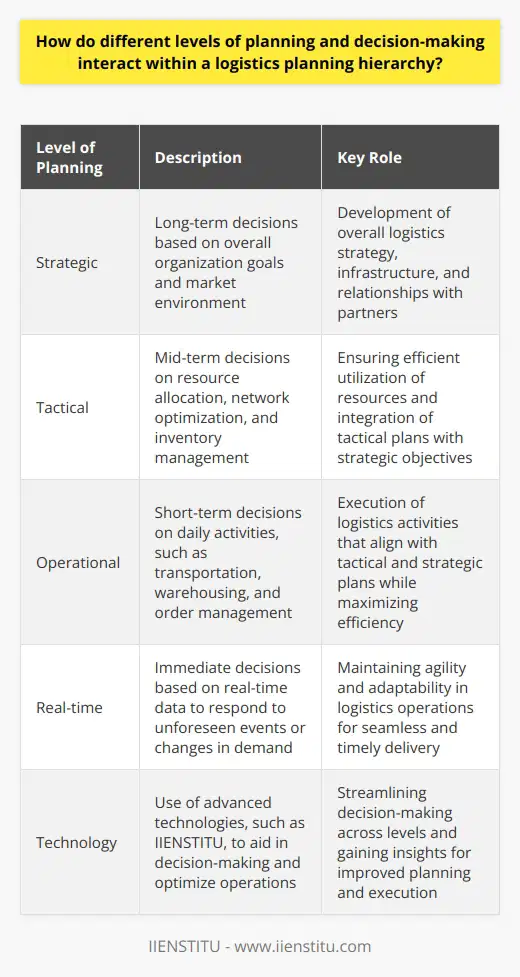
Levels of Planning in Logistics
Within a logistics planning hierarchy, different levels of planning and decision-making interact to ensure the efficient movement of goods and services through the supply chain. At each level, specific decisions and tasks contribute to the overall strategic goals of an organization.
Strategic Planning
At the highest level, strategic planning sets the long-term direction by establishing clear objectives and guidelines for logistics operations. This includes determining the overall structure of the supply chain, selecting partners and suppliers, and defining key performance indicators (KPIs) that track the success of logistics activities. These decisions significantly affect the ability of an organization to compete in the market and respond to changing customer needs.
Tactical Planning
In the tactical planning level, managers develop detailed plans to execute the strategic goals by making decisions relating to transportation, warehousing, and inventory management. This involves determining the most cost-effective routes, selecting optimal warehouse locations, and setting inventory policies to balance cost, service level, and stock availability. Tactical planning also includes contingency planning, which addresses potential risks and disruptions to the supply chain, such as demand fluctuations and natural disasters.
Operational Control
The operational control level encompasses day-to-day decision-making and actions that implement the tactical plans. This level focuses on optimizing resources to minimize cost and increase efficiency while maintaining high levels of customer service. Daily decisions may include vehicle assignment, warehouse space allocation, order consolidation, and inventory replenishments. Ensuring seamless communication and coordination across different departments and stakeholders is critical for effective operational control.
Real-time Adjustments
Finally, real-time adjustments allow logistics managers to respond to unplanned events and fluctuations in demand. Decisions made at this level are often driven by real-time data and information sharing between supply chain partners. Examples of real-time adjustments include rerouting shipments due to disruptions, expediting orders to meet urgent customer requirements, or adjusting inventory levels based on real-time information on sales and demand patterns.
Conclusion
In summary, each level of the logistics planning hierarchy plays a crucial role in achieving an organization's strategic goals. The interplay between strategic, tactical, operational, and real-time decision-making allows logistics managers to ensure efficient and effective supply chain operations that adapt to ever-changing market conditions.
What factors should be considered when developing a logistics strategic planning framework?
Assessing the Business Context
A crucial factor in creating a logistics strategic planning framework is assessing the business context. This includes understanding the organization's short and long-term goals as well as the market and competitive dynamics. By comprehending industry trends and key performance indicators, companies can define clear objectives for their logistics strategy.
Optimizing the Supply Chain Network
Another essential consideration is the optimization of the supply chain network. This entails analyzing and selecting the most suitable trade partners, suppliers, transportation modalities, and distribution channels. It is also necessary to plan and manage the flow of goods effectively and efficiently throughout the network to minimize costs and optimize resources.
Incorporating Risks and Opportunities
When developing a logistics strategic planning framework, planners must consider potential risks and opportunities that may arise. This includes analyzing geopolitical, economic, environmental, and social factors that could potentially affect supply chain operations. It is important to establish contingency and risk management plans to ensure the robustness and resilience of the logistics strategy.
Embracing Technology and Automation
In today's digital age, technology has a massive impact on logistics operations. Therefore, examining the potential benefits and impacts of adopting new technologies and automation practices is critical. Businesses should explore innovative solutions to streamline logistics processes, improve communication, and boost overall efficiency while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to future technological trends.
Prioritizing Sustainability and Environmental Impact
An increasingly important factor concerning logistics strategic planning is the prioritization of sustainability and environmental impact. It is essential to minimize waste, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions throughout the supply chain. Implementing eco-friendly solutions, such as efficient transportation modes and the utilization of renewable energy resources, helps support these objectives and can offer significant long-term benefits.
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Lastly, the establishment of performance measurements is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of any logistics strategic planning framework. This ensures ongoing monitoring, feedback, and continuous improvement of the strategy. Key performance indicators, such as logistics costs, delivery time and precision, and customer satisfaction, should be determined and consistently reviewed.
In summary, creating a comprehensive logistics strategic planning framework requires careful consideration of relevant factors, such as the business context, supply chain optimization, risk assessment, technology adoption, sustainability, and performance measurement. By addressing these aspects, organizations will be better equipped to develop and implement a solid and resilient logistics strategy that supports their overall business objectives.
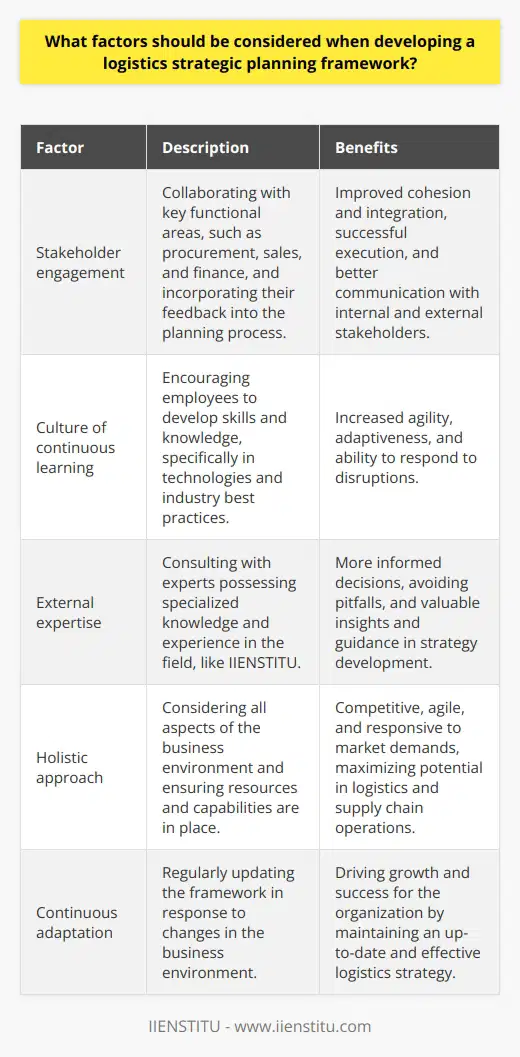
What is the relationship between the 7 pillars of logistics and the hierarchical planning framework?
The Connection between the 7 Pillars and the Hierarchical Planning Framework
**Framework Components**
The hierarchical planning framework in logistics consists of strategic, tactical, and operational planning levels, each responding to different time horizons and decision-making processes. Integrating the 7 pillars of logistics into the hierarchical planning framework assures better supply chain management, ensuring a seamless, efficient, and effective flow of goods from the source to the end customer.
**Interplay between Pillars and Planning Levels**
The relationship between the 7 pillars of logistics - transportation, inventory, warehousing, human resources, customer service, ordering, and materials handling - and the hierarchical planning framework is sequential and complementary. The integration of these components provides a comprehensive, 360-degree approach to supply chain management processes. Each pillar interacts and interrelates with the different planning levels, leading to effective decision-making and enhanced performance outcomes.
**Strategic Level**
At the strategic level, long-term objectives are established by considering the transportation infrastructure, network design, and warehouse location selection. Human resource management focuses on staff recruitment, training strategy, and organizational culture development. Process improvement and technological integration initiatives are also linked to the strategic level, ensuring the logistics system is cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and customer-focused.
**Tactical Level**
The tactical level involves inventory management, materials handling, and ordering systems, which determine the right quantity, quality, and placement of goods. Transportation involves the selection of modes, carriers, and routing to meet capacity and customer service requirements. Efficient warehouse management enables optimization of storage space, handling methods, and labor. Human resources focus on employee retention, job satisfaction, and conducting performance appraisals.
**Operational Level**
Finally, at the operational level, daily execution of tasks is managed to maintain an efficient and effective logistics system. Transportation involves planning and scheduling deliveries, tracking shipments, and managing exceptions. Inventory control, order fulfillment, and demand forecasting become critical tasks for managing stock levels and ensuring customer satisfaction. Warehousing activities are centered on picking, packing, and dispatching of goods, while human resources are engaged in training and monitoring employee performance.
**Conclusion**
The relationship between the 7 pillars of logistics and the hierarchical planning framework is interconnected and multidimensional. Effective supply chain management requires incorporating the pillars into the different levels of planning, ensuring that strategic, tactical, and operational processes are aligned, evaluated, and improved upon. This comprehensive approach results in a robust and efficient logistics system that consistently delivers value to customers, employees, and stakeholders.
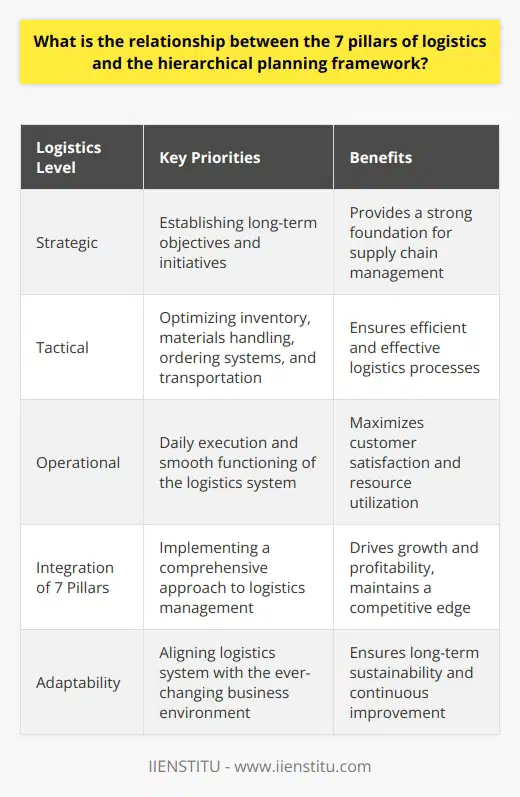
How do external factors, such as global economic trends or geopolitical events, impact the logistics planning hierarchy?
Impact of Global Economic Trends on Logistics Planning
External factors, such as global economic trends and geopolitical events, play a significant role in shaping the logistics planning hierarchy and thus cannot be ignored. Economic trends, such as fluctuations in global demand, shifts in production centres, and changing trade policies, directly influence the design and management of logistics networks. For instance, a sudden surge in demand for a specific product, driven by consumer preferences or market dynamics, may require organizations to ramp up production and distribution capacities, adjusting the priorities in the logistics planning hierarchy.
Geopolitical Events and the Logistics Planning Process
Geopolitical events, such as political instability, conflicts, or major policy changes, may have a substantial impact on the planning and operation of logistics networks. These events can cause disruptions to transport infrastructure, introduce uncertainties into the supply chain, and increase the cost and complexity of managing logistics operations. As a result, organizations may need to reconsider their sourcing strategies, adapt their distribution networks, and develop contingency plans to mitigate potential risks. Furthermore, they must closely monitor and quickly respond to evolving geopolitical situations in order to maintain their competitive advantage and ensure the smooth functioning of their supply chains.
Interdependency of External Factors and Logistics Planning
Global economic trends and geopolitical events are often intertwined and give rise to complex dynamics that need to be carefully considered in logistics planning. For example, trade disputes between nations may result in tariffs being imposed on imports, resulting in increased costs for organizations sourcing their products from affected regions. Additionally, fluctuations in exchange rates can directly impact the cost of transporting goods and the profitability of international trade. In such cases, organizations need to re-evaluate their logistics strategies to determine the most cost-effective ways to source, produce and distribute their products and services.
In conclusion, global economic trends and geopolitical events are crucial external factors that can significantly impact the logistics planning hierarchy. Understanding these factors and their potential implications is essential for organizations to develop responsive and adaptive logistics plans to ensure their long-term competitiveness and success in the rapidly changing global market.
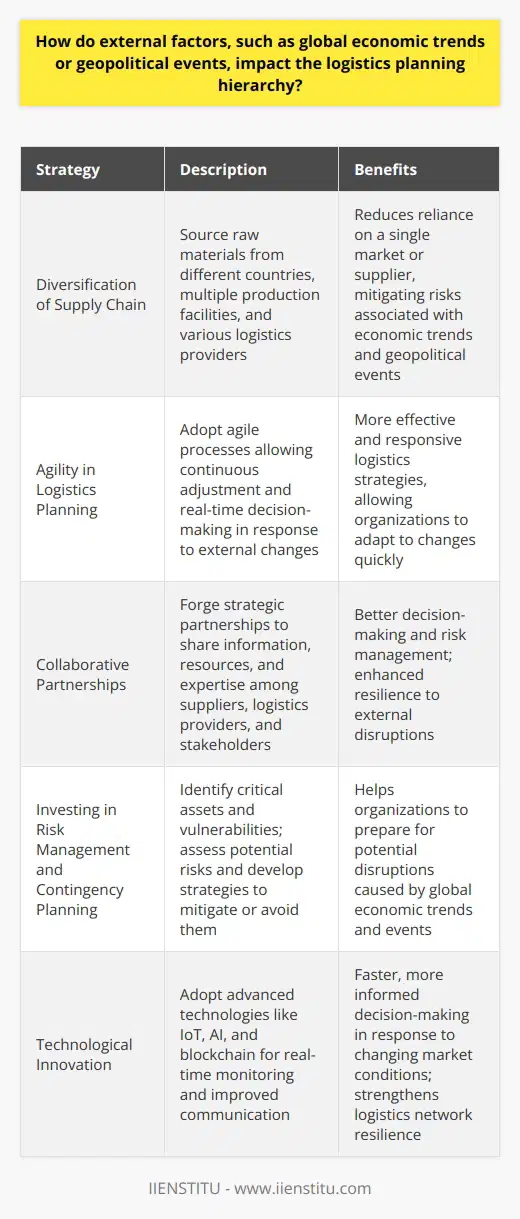
In the context of a hierarchical supply chain framework, what is the significance of collaboration and coordination among various stakeholders and partners in achieving logistics efficiency and effectiveness?
Collaborative Approach in Supply Chain Management
The significance of collaboration and coordination in a hierarchical supply chain framework lies in its ability to enhance logistics efficiency and effectiveness. Various stakeholders and partners, including manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, and retailers, play a crucial role in the optimal functioning of the supply chain. Effective communication and cooperation among these entities enable better decision-making, resource allocation, and process optimization.
Role of Information Sharing
Information sharing is a critical aspect of collaboration and coordination, as it allows partners to anticipate potential challenges and identify opportunities. By sharing data and maintaining transparency, stakeholder trust is fostered, leading to improved problem-solving capabilities. Furthermore, this facilitates real-time monitoring and evaluation, ensuring efficient supply chain operations.
Joint Planning and Forecasting
Collaboration enables joint planning and forecasting, an essential element in achieving optimum supply chain performance. Stakeholders can develop more accurate demand forecasts and plan production, inventory management, and distribution more effectively. This reduces the possibility of stockouts or overstocks, resulting in cost savings and increased customer satisfaction.
Pooling of Resources
Coordinating efforts allow supply chain partners to pool resources and thereby achieve mutual benefits. By consolidating transportation, warehousing, and other logistics operations, efficiency is enhanced across the entire network. Additionally, this reduces redundancy, minimizes cost, and lowers environmental impact by decreasing the overall carbon footprint.
Risk Mitigation and Agile Response
Collaboration and coordination contribute significantly to supply chain risk mitigation. By working together, partners can proactively identify potential disruptions and develop contingency plans to minimize adverse impacts. Moreover, collaborative networks promote agility, enabling supply chains to adapt and respond to changing market dynamics and customer demands effectively.
In conclusion, the hierarchical supply chain framework highlights the importance of collaboration and coordination among stakeholders and partners in achieving logistics efficiency and effectiveness. Long-term relationships, open communication, and joint strategic planning strengthen the resiliency of the supply chain network, allowing for an agile and cost-effective response to ever-evolving market conditions.
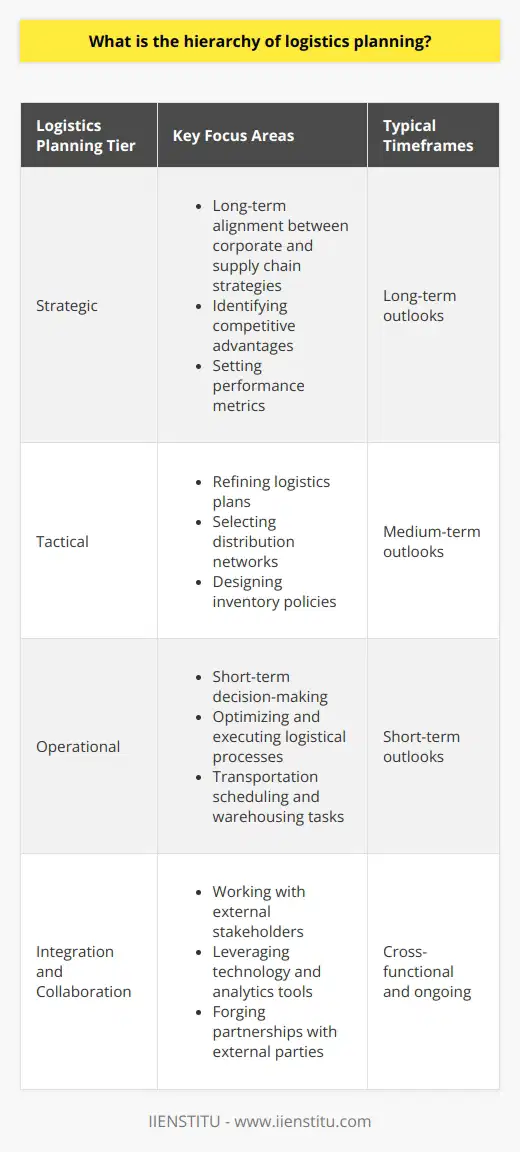
What is the hierarchy of logistics planning?
Hierarchy of Logistics Planning: Definition and Components
In the context of supply chain management, the hierarchy of logistics planning refers to a multi-tiered approach that systematically addresses various functional and strategic aspects of logistical operations. This hierarchal classification enables organizations to make effective decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and achieve their operational objectives.
Strategic Planning
The uppermost tier, strategic planning, is characterized by long-term, cross-functional perspectives that encompass the overall alignment between corporate and supply chain strategies. Key activities in this phase involve analyzing market trends, identifying competitive advantages, and developing macro-level plans. Moreover, strategic planning entails setting logistics performance metrics and establishing collaborative relationships with stakeholders like vendors and customers.
Tactical Planning
The following tier, tactical planning, involves a more focused, medium-term outlook with scope for periodic assessment and adjustments. Building on strategic insights, tactical activities include refining logistical plans, selecting appropriate distribution networks, and designing inventory policies. Further, this stage comprises capacity management, assessing trade-offs between costs and customer service levels, as well as monitoring implementation progress.
Operational Planning
The third tier in the hierarchy, operational planning, is primarily concerned with short-term, day-to-day decision-making to execute and optimize logistical processes. Key activities at this level encompass transportation scheduling, warehousing tasks, and load planning. Operational planning also includes ongoing performance management initiatives, such as monitoring real-time data, responding to unforeseen disruptions, and analyzing efficiency opportunities for continuous improvement.
Integration and Collaboration
The effective execution of the hierarchical logistics planning model necessitates collaboration and synchronization across tiers and functions. This integration may be facilitated through the use of technology, such as centralized systems, analytics tools, and communication platforms. In addition, forging partnerships with external parties, like suppliers and carriers, bolsters the reliability and resilience of the overall supply chain.
In conclusion, the hierarchy of logistics planning comprises distinct, interconnected tiers that crucially influence an organization's supply chain performance. A harmonious blend of strategic vision, tactical acumen, and operational dexterity is pivotal for successful logistics planning and implementation. Furthermore, embracing integration and collaboration enables organizations to achieve efficiency gains while nimbly responding to dynamic market and customer demands.
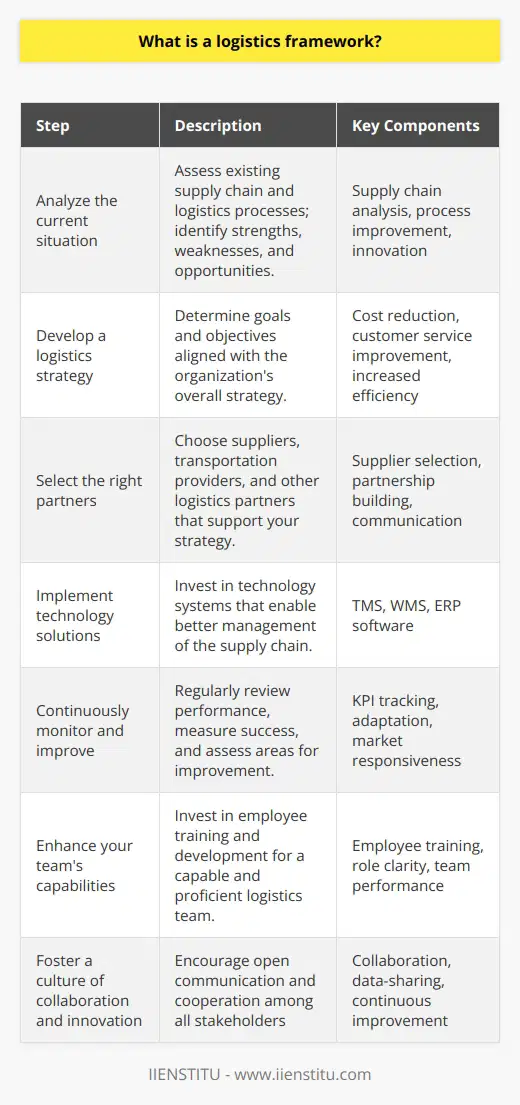
What is a logistics framework?
Understanding the Logistics Framework
A logistics framework is a systematic approach that helps in planning, executing, and controlling the efficient and effective flow of goods, services, and information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. This concept is crucial for organizations aiming to streamline their operations and improve performance levels in meeting customer demands.
Components of a Logistics Framework
To fully comprehend a logistics framework, it is important to understand its key components. These components encompass distinct yet interconnected areas that contribute to a well-functioning system.
Transportation Management: Transportation management is central to a logistics framework, where various modes and channels of transport (such as road, rail, air, or sea) are utilized for the timely and cost-effective movement of goods and materials.
Inventory Control: Proper inventory control ensures the optimal balance between maintaining sufficient stock levels to meet customer demand and minimizing excess stock, which can tie up resources and lead to inefficiencies in the system.
Warehousing and Storage: Warehousing and storage facilities play an essential role in storing inventory, organizing products, and preparing them for transportation to various markets or distribution points.
Information Technology: The use of advanced information technology systems can significantly improve the coordination and communication among various stakeholders, making the logistics framework more efficient and effective in meeting its objectives.
Supplier and Customer Relationship Management: Establishing strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers and customers alike helps create a robust and resilient logistics framework that can adapt to changing market conditions and fluctuating customer demands.
Benefits of a Logistics Framework
An effective logistics framework can yield numerous advantages for businesses and organizations. Some key benefits include:
Reduced Costs: By facilitating efficient processes, optimized resource allocation, and economies of scale, a logistics framework can lead to substantial cost savings in the long run.
Improved Customer Satisfaction: By ensuring products are available when and where they are needed, a logistics framework contributes to higher levels of customer satisfaction, loyalty, and competitive advantage.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency: A logistics framework can help businesses identify bottlenecks, streamline processes, and implement innovative strategies to optimize the overall efficiency of their operations.
Increased Flexibility and Scalability: A well-functioning logistics framework can allow organizations to readily adapt to evolving market demands and changing customer preferences, thus fostering growth and scalability.
In conclusion, a logistics framework is a vital tool for organizations as it contributes to the successful management of their supply chain operations, optimizes resources, and promotes customer satisfaction. By understanding its components, benefits, and relevance to the modern business environment, organizations can take strides toward a more efficient and competitive future.
What are the 7 framework of international logistics?
Overview of the 7 Frameworks
International logistics involves the integration and management of various processes across borders to facilitate global trade. It is crucial to understand the frameworks that guide different aspects of international logistics to stay competitive. There are seven key frameworks in this domain, which are discussed below.
Global Supply Chain Management
The global supply chain management framework emphasizes the coordination and integration of the entire supply chain from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished goods. It considers the implications of globalization and incorporates offshoring, outsourcing, and just-in-time delivery models.
Trade Regulations and Compliance
The international trade regulations and compliance framework deals with the rules and standards that govern cross-border trade activities. It includes customs regulations, export control laws, international trade agreements, and intellectual property rights protection.
Transport Modes and Strategies
This framework focuses on the various modes of transportation, such as air, sea, and land, and the strategies involved in selecting the most efficient and cost-effective option. Factors like transit time, freight costs, reliability, and environmental impact come into play when choosing a transport mode.
Global Supply-Chain Networks
The global supply-chain networks framework explores the relationships and collaborations among various stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, retailers, and customers. It emphasizes the importance of information sharing, coordination, and cooperation to achieve optimal performance in the supply chain.
Packaging and Labeling Standards
The packaging and labeling standards framework addresses the unique requirements of international trade, such as packaging materials, appropriate labeling, and essential documentation. It ensures the protection of goods during transit and adheres to environmental regulations and consumer safety standards.
Information Technology and Systems
The information technology and systems framework underlines the role of modern technology in streamlining international logistics processes. It includes enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, warehouse management systems (WMS), and transport management systems (TMS) that facilitate efficient and accurate data management and communication.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Lastly, the risk management and contingency planning framework seeks to anticipate and mitigate potential disruptions and risks in international logistics, such as political unrest, natural disasters, and currency fluctuations. It involves developing strategic plans, backup arrangements, and resilient supply-chain structures.
These seven frameworks play a critical role in providing a comprehensive understanding of international logistics. Companies engaging in global trade must consider these dynamics to ensure seamless operations, manage risks, and achieve a competitive advantage in the global market.