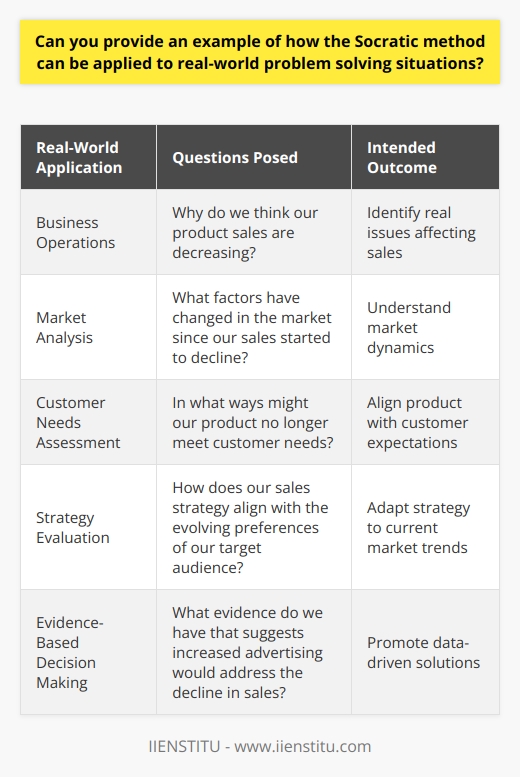
Socrates was a moral philosopher from the 5th century BC who believed in the power of reason and the importance of questioning one's beliefs. He developed the Socratic Method, a series of questions and answers to explore a subject and eliminate hypotheses.
This process involves asking a series of questions to identify the assumptions underlying a particular hypothesis, then testing each assumption by asking further questions. If the assumption is false, then the idea must be discarded. This process is repeated until all false beliefs have been eliminated and the truth is revealed. The Socratic Method is a powerful tool for discovering the truth and has been used ever since.
Introduction
Background on Socrates
Overview of the Socratic Method
Hypothesis Elimination
Conclusion
Introduction: Socrates is a renowned philosopher from the 5th century BC. He is famous for his Socratic Method, a series of questions and answers used to explore a subject and eliminate hypotheses. This article will discuss the background of Socrates, the overview of the Socratic Method, and the hypothesis elimination process.
Background on Socrates
Socrates was born in Athens, Greece, in 470 BC. He was a student of the philosopher Anaxagoras and a teacher of Plato. Socrates was a moral philosopher who believed in the power of reason and the importance of questioning one's beliefs. He was also a proponent of the Socratic Method, a series of questions and answers used to explore a subject and eliminate hypotheses.
Overview of the Socratic Method
The Socratic Method is a form of inquiry and discussion between individuals based on asking and answering questions to stimulate critical thinking and to draw out ideas and underlying presumptions. It is a method of hypothesis elimination in which a series of questions are asked to test the validity of a particular hypothesis. In this way, the Socratic Method can be used to identify and discard false assumptions and arrive at the truth.
Hypothesis Elimination
Unlocking Problem Solving Skills: Where Do Problems Come From?
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): A Comprehensive Guide to Improved Efficiency
The Socratic Method involves asking questions to eliminate false assumptions and arrive at the truth. The process of hypothesis elimination is as follows: First, a series of questions are asked to identify the assumptions underlying a particular hypothesis. Then, each assumption is tested by asking further questions to determine whether or not it is valid. If the belief is false, then the idea must be discarded. This process is repeated until all false assumptions have been eliminated and the truth is revealed.
Conclusion
The Socratic Method is an effective way of testing hypotheses and discarding false assumptions. It is based on the idea that knowledge can be gained through questioning and dialogue. Socrates was a proponent of this Method, and it has been used ever since as a powerful tool for discovering the truth. Using the Socratic Method, we can eliminate false assumptions and arrive at the truth.
The key to unlocking the power of problem-solving lies within the wisdom of Socrates.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Socratic Method and how does it relate to Socrates' problem solving skills?
The Socratic Method, also known as the Elenchus, is a problem-solving method attributed to the Greek philosopher Socrates. It involves a dialogue between two or more people in which questions are posed to draw a deeper understanding of the subject under discussion. The Socratic Method aims to arrive at a more precise and accurate account of the discussed issue.
In its simplest form, the Socratic Method involves questioning a statement or proposition. Socrates would often begin by asking the other person to define the information and then ask questions about the validity of the word. These questions would often reveal any inconsistencies or contradictions in the report. Through this process, Socrates was able to gain an in-depth understanding of the subject and arrive at a more accurate conclusion.
The Socratic Method is closely associated with Socrates’ problem-solving skills. Socrates was known for his ability to think critically and logically. He was able to identify inconsistencies and flaws in arguments and dissect complex problems and arrive at a more accurate solution.
The Socratic Method is still used today as a tool for problem-solving. It is often used in academic settings, such as in the classroom or law school. It has also been used in the business world, for example, in strategic planning.
The Socratic Method is an effective tool for problem-solving and critical thinking. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to identify inconsistencies and flaws in arguments and arrive at a more accurate understanding of a problem. It is an invaluable tool in the pursuit of knowledge and truth.
How does hypothesis elimination help to unlock Socrates' problem solving skills?
Socrates is renowned for his problem-solving skills, and his ability to systematically eliminate hypotheses to conclude has been the subject of much analysis. This article will examine how hypothesis elimination helps to unlock Socrates' problem-solving skills.
The Socratic Method is sometimes referred to as the process of systematically eliminating hypotheses to conclude. This Method was employed by Socrates in his famous dialogues and has become a cornerstone of philosophical inquiry. The process involves the interlocutor (usually Socrates) asking questions to lead the respondent to a logical conclusion. Through this process, Socrates can eliminate hypotheses and conclude systematically.
To unlock Socrates' problem-solving skills, it is essential to understand how his Method of hypothesis elimination works. First, Socrates begins by asking questions intended to lead the respondent to a logical conclusion. By asking questions, he can identify which hypotheses are viable and which are not. He then eliminates the ideas that are not viable, thus narrowing down the possibilities and leading the respondent to a logical conclusion.
The process of hypothesis elimination is a powerful tool in Socrates' problem-solving toolbox. By systematically eliminating hypotheses, Socrates can quickly and efficiently conclude. This process is especially effective when dealing with complex problems, as it allows Socrates to quickly identify which ideas are viable and which are not.
In summary, hypothesis elimination is essential to Socrates' problem-solving skills. By systematically eliminating hypotheses, Socrates can quickly and efficiently conclude. Furthermore, this process allows Socrates to identify which ideas are viable and which are not, thus allowing him to reach a logical conclusion efficiently.
What are the key components of the Socratic Method that can be used to improve problem solving skills?
The Socratic Method is a technique of inquiry and dialogue used to explore philosophical problems and help students think critically. The Socratic Method encourages students to reason and draw conclusions by posing and answering questions rather than relying on established rules or expert opinions. As a pedagogical technique, the Socratic Method has been widely used in various educational contexts to help students develop their problem-solving skills. In this article, we will discuss the critical components of the Socratic Method and how they can be used to improve problem-solving skills.
One of the main components of the Socratic Method is the use of open-ended questions. The teacher or facilitator should ask a series of open-ended questions which encourage students to think critically about the problem at hand. The questions should be structured so that they push students to explore different angles of the problem and consider alternative solutions. For example, a teacher might ask questions such as "What are the potential solutions to this problem?", "What are the advantages and disadvantages of each solution?" and "What are the implications of each solution?".
Another critical component of the Socratic Method is dialogue and discussion. The teacher should provide an environment that encourages students to engage with each other in meaningful conversation and to express their opinions and ideas. The conference should be structured to encourage students to challenge each other's ideas, consider different perspectives, and explore the implications of their solutions. By engaging in discussion, students can develop their problem-solving skills by seeing the problem from multiple perspectives and exploring different solutions.
Finally, the teacher should provide guidance and feedback throughout the discussion. The teacher should help to structure the meeting, provide clarification when needed, and guide students in their thinking. The teacher should also provide feedback on the solutions proposed by the students and help them evaluate their solutions' potential implications. By providing guidance and feedback, the teacher can help students to develop their problem-solving skills by encouraging them to think critically and consider different solutions.
Overall, the Socratic Method can be a powerful tool for helping students to develop their problem-solving skills. By posing open-ended questions, encouraging dialogue, and providing guidance and feedback, the teacher can help students think critically about the problem and explore different solutions. The Socratic Method is a valuable tool for any teacher or facilitator looking to help students develop their problem-solving skills.
What is the reasoning behind the Socratic method's emphasis on questioning as a problem solving strategy?
The Essence of the Socratic Method
The Socratic method greatly emphasizes the use of questioning as a problem-solving strategy, rooted in the ancient philosopher Socrates' belief in illuminating human ignorance. By engaging in a continuous process of questioning, individuals are encouraged to delve deeper into their thoughts and critically assess their understanding of ideas and concepts. This approach fosters analytical thinking and encourages individuals to evaluate their assumptions and beliefs to ultimately arrive at a less biased, more coherent conclusion.
Cognitive Benefits of Questioning
The process of questioning promotes intellectual engagement, as it requires individuals to actively analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information, thereby stimulating cognitive development. The act of formulating a question encourages the thinker to identify gaps in their understanding, while answering a question demands conceptual clarity and coherent reasoning. By exposing discrepancies in one's knowledge and challenging accepted assumptions, questioning supports intellectual growth and nurtures a spirit of intellectual curiosity.
Social Dynamics and Collaborative Inquiry
Employing questioning as a problem-solving strategy also has profound implications in the social dynamics of learning, as it promotes collaborative inquiry and fosters a culture of intellectual humility. When individuals engage in a Socratic dialogue, they explore ideas together, seeking to refine their thoughts and engage in a constructive exchange. This process enables individuals to appreciate various perspectives, challenge their preconceptions, and develop a more nuanced understanding of the matter at hand. Additionally, the questioning approach contributes to a respectful and open-minded environment that elevates the quality of intellectual discourse.
Scaffolding for Enhancing Understanding
The Socratic method, by virtue of its emphasis on questioning, serves as a powerful pedagogical tool for educators to aid students in deepening their understanding of complex subjects. By asking carefully crafted questions, educators can scaffold the learning process, guiding students to gradually build upon their prior knowledge to arrive at a more sophisticated understanding. This strategy allows educators to identify misconceptions and offer targeted feedback, resulting in an enhanced learning experience.
In conclusion, the reasoning behind the Socratic method's emphasis on questioning as a problem-solving strategy lies in its ability to stimulate cognitive development, promote collaborative inquiry, and provide an effective framework for enhancing understanding. By nurturing critical thinking skills and fostering a culture of intellectual openness, the Socratic method has maintained its relevance as an enduringly effective pedagogical approach.
How does the Socratic method encourage critical thinking and evaluation of ideas in the context of problem solving?
The Socratic Method and Critical Thinking
The Socratic method encourages critical thinking and evaluation of ideas within the context of problem-solving by promoting active engagement and constant questioning. By following this method, individuals are encouraged to approach every problem with skepticism and investigative curiosity. This promotes an open-minded disposition and a willingness to reconsider assumptions, allowing for a deeper understanding of the issue at hand.
Questioning and Dialogue
Fundamental to the Socratic method is the principle of interrogation, which pushes individuals to critically examine ideas by subjecting them to a series of logical and probing questions. Engaging in dialogue with others and continuously refining perspectives leads to the formation of well-reasoned and logical beliefs. This dialectical process highlights inconsistencies and ambiguities within one's understanding, allowing for continuous improvement in the evaluation of ideas.
Challenging Assumptions
The Socratic method also stimulates the examination of presuppositions and hidden assumptions that may influence our beliefs and decision-making processes. By identifying and investigating these underlying factors, we can address their limitations and build upon our existing knowledge. This process contributes to the development of an individual's critical thinking abilities, ensuring that problem-solving approaches remain strategic and informed.
Reflection and Intellectual Growth
Finally, the Socratic method fosters reflection and self-awareness, forcing individuals to confront their own beliefs and admit moments of uncertainty. This vulnerability encourages participants to take responsibility for their opinions, think critically, and embrace the potential for intellectual growth. Emphasizing the importance of adaptability and resilience in the face of evolving challenges, the Socratic method equips problem-solvers with the tools to navigate complex issues with intellectual rigor and creativity.
In conclusion, the Socratic method encourages critical thinking and evaluation of ideas in the context of problem-solving by engaging individuals in regular questioning, challenging assumptions, and promoting reflection. By adopting this approach, individuals refine their critical thinking skills and develop an open-minded, engaged, and adaptive approach to addressing complex problems.
In what ways do the principles and steps of the Socratic method align with collaborative problem solving approaches?
Alignment of Socratic Method with Collaborative Problem Solving
Shared Inquiry
Both the Socratic method and collaborative problem-solving approaches emphasize the importance of shared inquiry within a group. Through asking questions and engaging in critical discussions, participants collectively explore a problem or topic in depth, clarifying various perspectives and better understanding each other’s thought processes.
Mutual Respect
In both approaches, participants exhibit mutual respect to contribute effectively to the conversation. This encourages open-mindedness, active listening, and the willingness to adapt or reevaluate one’s position as new insights emerge. Consequently, individuals cooperate in fostering an atmosphere conducive to the progress of intellectual exploration.
Generating Alternatives
Both approaches involve generating multiple solutions to problems by engaging multiple perspectives. Rather than seeking the fastest resolution or working in isolation, participants in the Socratic method and collaborative problem-solving deliberately pursue various strategies and solutions, acknowledging that the collective wisdom of the group often outpaces the capabilities of a single individual.
Pursuit of Understanding
In both the Socratic method and collaborative problem-solving, the primary focus is not merely to reach a solution but to deepen understanding. Participants actively seek to grasp the underlying principles and concepts that contribute to the problem at hand. This intellectual curiosity fosters an environment where the journey toward the solution is viewed as valuable as the destination itself.
Iterative Process
An alignment between the Socratic method and collaborative problem-solving can also be seen in the iterative nature of their processes. Both involve cycling through multiple stages of inquiry, refinement, and reflection, allowing participants to build upon each other’s insights and systematically move toward a common goal.
In conclusion, the principles and steps of the Socratic method and collaborative problem-solving approaches align in their emphasis on shared inquiry, mutual respect, generating alternatives, pursuit of understanding, and iterative processes. By integrating these approaches, individuals and groups can foster an environment conducive to more effective problem-solving and deeper intellectual exploration.
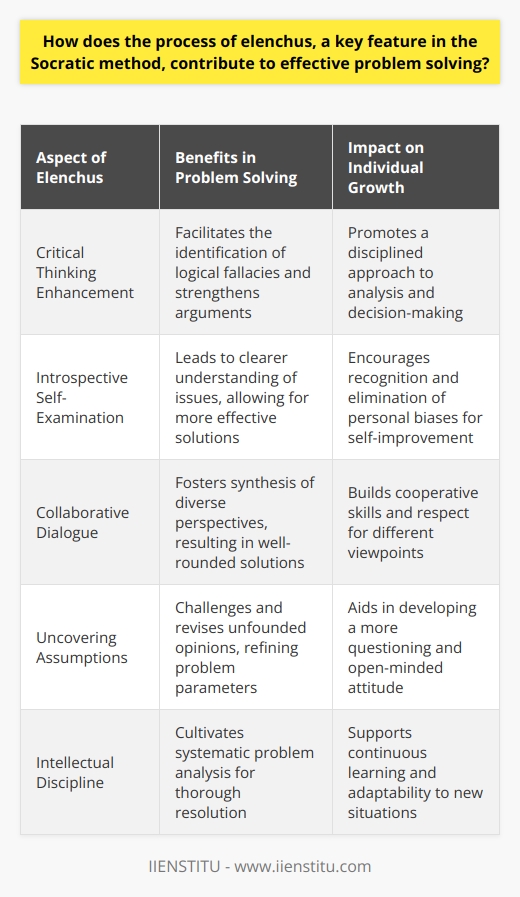
What is the significance of employing the Socratic method in contemporary problem-solving contexts?
The Role of the Socratic Method Today
The significance of employing the Socratic method in contemporary problem-solving contexts lies in its potential to foster critical thinking and intellectual growth. By engaging in a process of questioning and dialogue, participants expose assumptions, clarify concepts, and scrutinize arguments, leading to a deeper understanding of the issue at hand.
Promoting Critical Thinking
The Socratic method encourages individuals to examine their own beliefs and assumptions, which is crucial for developing a well-rounded perspective on a given problem. Critical thinking empowers participants to make well-informed decisions and avoid relying solely on intuition or preconceived notions.
Enhancing Intellectual Growth
Through the practice of continuous questioning and logical reasoning, the Socratic method promotes intellectual growth. Participants refine their thought process, increase their mental agility, and become better equipped to tackle complex problems.
Clarification of Concepts
Employing the Socratic method in problem-solving allows for a clearer view of the concepts involved. By engaging in a dialogue, participants identify areas of ambiguity or confusion and work together to arrive at a shared understanding.
Evaluation of Arguments
The Socratic method enables participants to scrutinize the quality of arguments presented, assessing their logical coherence and validity. This process helps reveal any potential flaws and ensures well-founded conclusions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Socratic method continues to be a valuable tool in contemporary problem-solving because it cultivates critical thinking, promotes intellectual growth, clarifies concepts, and evaluates arguments. By engaging in this process, individuals are better equipped to approach complex problems with a more refined and well-rounded understanding.
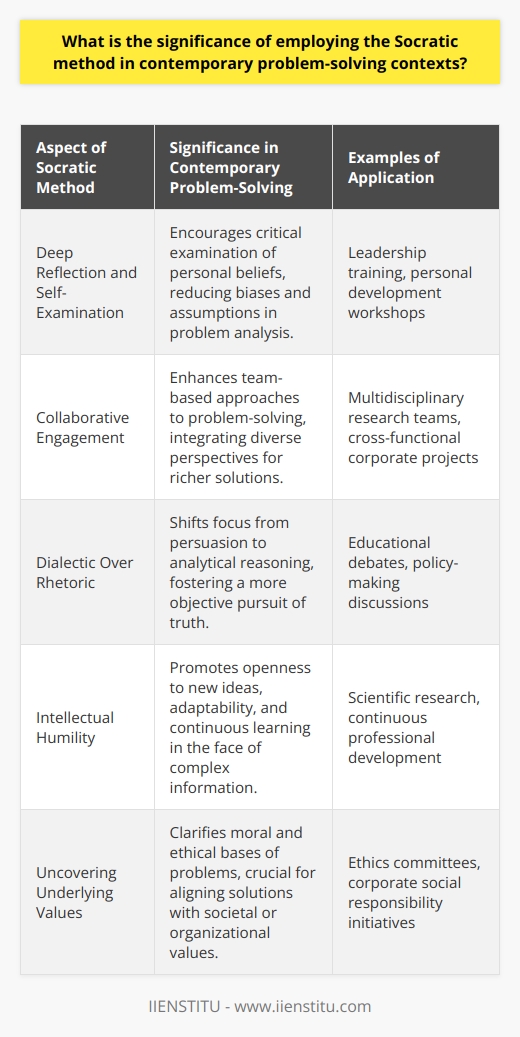
How can the use of the Socratic method promote the development of essential problem-solving skills in various disciplines and professions?
Socratic Method in Problem-Solving
The Socratic method, characterized by dialogues and question-driven discussions, cultivates essential problem-solving skills in various disciplines and professions. By encouraging critical thinking and effective communication, this approach contributes to the development of essential competencies and abilities demanded in diverse fields.
Cultivating Critical Thinking
The Socratic method fosters critical thinking by prompting participants to examine and evaluate their own beliefs and assumptions. Through continuous questioning and constructive dialogue, individuals are encouraged to develop analytical thinking, identify inconsistencies, and formulate logically coherent arguments. As a result, participants within a Socratic dialogue refine their ability to discern false assumptions or misleading information, honing their problem-solving skills.
Enhancing Effective Communication
Engaging in Socratic discussions fosters effective communication, an indispensable skill in any discipline or profession. Participants learn to articulate thoughts clearly, listen actively, and respond thoughtfully. Through this process, they develop the ability to communicate complex ideas and negotiate diverse perspectives, which is essential for resolving problems collaboratively and reaching well-informed decisions.
Fostering Creative Problem-Solving
Participating in Socratic dialogues stimulates creative problem-solving by encouraging participants to consider diverse viewpoints and novel ideas. By examining multiple perspectives, individuals develop flexibility in their thinking and adaptability, crucial traits for problem-solving in rapidly changing environments. This practice, grounded in open inquiry, encourages intellectual curiosity, innovation, and adaptability, qualities essential for addressing complex challenges in various fields.
Applicability Across Domains
The Socratic method extends beyond philosophical inquiry and can be effectively applied in various disciplines and professions. For instance, in science, researchers can engage in Socratic dialogues to question the validity of their hypotheses or design more rigorous experiments. In law, attorneys can use this method to strengthen their legal arguments, while educators can develop deeper understanding of their subjects and foster critical thinking among students.
In conclusion, the Socratic method promotes the development of essential problem-solving skills across disciplines and professions by nurturing critical thinking, effective communication, and creative problem-solving abilities. Its applicability in diverse domains suggests its enduring value as an effective approach to problem-solving, teaching, and learning.
In light of modern cognitive and educational theories, how does the Socratic method contribute to fostering critical thinking and complex problem-solving abilities in learners?
The Socratic Method and Cognitive Theories
Modern cognitive theories posit that critical thinking and complex problem-solving abilities are developed through active engagement and reflection. The Socratic method, an instructional approach based on guided questioning, aligns with these theories by fostering critical thinking through dialogue, encouraging learners to question their assumptions and beliefs.
Divergent Thinking and Socratic Dialogue
According to cognitive theorists, divergent thinking plays a significant role in problem-solving, as it allows individuals to generate multiple alternatives, examine potential consequences, and make informed decisions. The Socratic method aligns with this notion, as its emphasis on dialogue between teacher and learner encourages the exploration of various perspectives and viewpoints. This dialogue fosters the development of divergent thinking skills, as learners engage in questioning and analyzing the validity of their thoughts and ideas.
Conceptual Change and Deep Learning
Educational theories emphasize the importance of deep learning, which is the process of altering one's understanding of concepts and constructing new mental models. The Socratic method contributes to this process by providing a supportive environment for learners to identify and challenge their preconceived notions, promoting constructive reasoning and conceptual change.
Metacognition and Reflective Inquiry
Metacognition, or the awareness and understanding of one's thought processes, is a key component of effective critical thinking and problem-solving. The Socratic method encourages learners to engage in metacognitive processes by prompting them to reflect on their reasoning and consider alternative viewpoints. Through reflective inquiry, learners become more adept at recognizing gaps in their knowledge and understanding, ultimately cultivating their critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Peer Interaction and Collaborative Learning
Modern educational theories also emphasize the value of social interaction and collaborative learning in fostering critical thinking and problem-solving. Adopting the Socratic method in group settings helps facilitate peer interaction, enabling learners to challenge and learn from one another. Additionally, this collaborative environment supports the development and refinement of communication and persuasion skills, which are key components of problem-solving.
In conclusion, the Socratic method aligns with modern cognitive and educational theories by fostering critical thinking and complex problem-solving abilities in learners. By facilitating dialogue, promoting divergent thinking, encouraging conceptual change, nurturing metacognitive skills, and supporting collaborative learning, the Socratic method provides a versatile and effective approach to instruction that enhances learners' cognitive abilities.

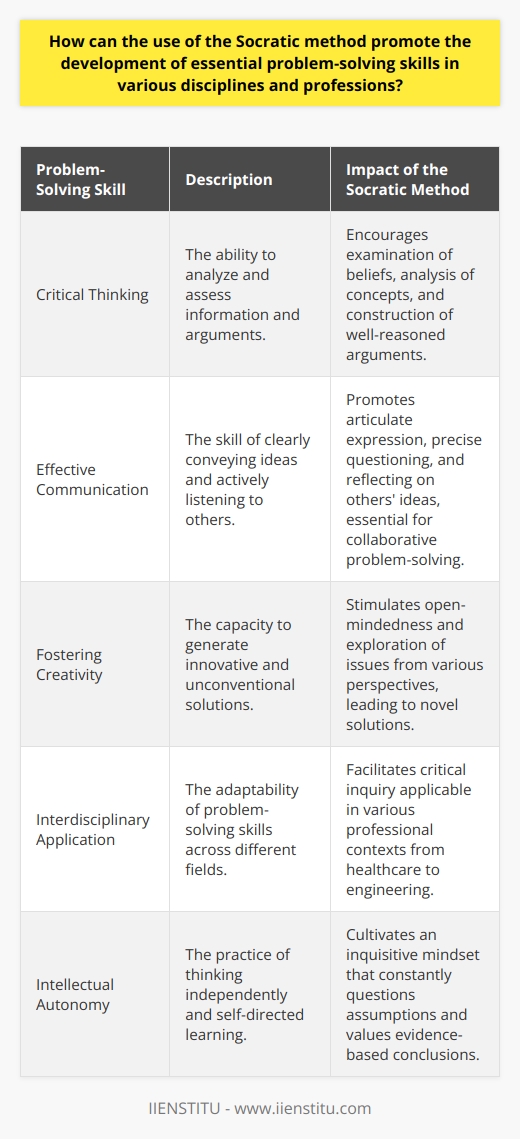
What is the relationship between the Socratic method and the development of problem-solving skills in various contexts?
**Socratic Method as a Foundational Approach**
The Socratic method, a dialectical approach to inquiry, plays a significant role in fostering problem-solving skills in various contexts. Originating from the teachings of the Greek philosopher Socrates, this method involves the use of questions and dialogue to stimulate critical thinking, analyze complex ideas, and reveal underlying assumptions.
**Fostering Critical Thinking**
The primary objective of the Socratic method is to develop critical thinking skills in learners, which in turn fosters problem-solving abilities. Engaging in this method facilitates the deconstruction of complex ideas, thereby allowing individuals to discern key aspects of a given problem and analyze it from diverse perspectives. This systematic questioning promotes deeper understanding and comprehension, equipping learners with the cognitive tools necessary to tackle challenges.
**Promoting Analytical Skills**
The Socratic method imparts learners with essential analytical skills by encouraging them to identify and question underlying assumptions present in any given problem. In this process, individuals are urged to challenge various viewpoints, leading to a more nuanced understanding of the issue at hand. Consequently, such analytical skills can be applied across diverse contexts, opening up new avenues for problem-solving.
**Adapting to Various Contexts**
The flexibility and adaptability of the Socratic method make it particularly suited for developing problem-solving skills in multiple contexts. While initially applied to philosophical inquiries, this approach has been adopted in various educational settings such as law, medicine, and business. Its application in these different disciplines demonstrates how the Socratic method can be adapted for specific problem-solving requirements while retaining its essence of fostering critical and analytical thinking.
**Encouraging Collaboration and Active Learning**
Active participation is another prominent feature of the Socratic method that contributes to improved problem-solving abilities. This collaborative approach requires learners to actively engage in discourse, encouraging them to articulate their thoughts and contribute to the collective understanding of a problem. By cultivating such an environment, the Socratic method fosters the development of both individual and group problem-solving skills.
In summary, the Socratic method plays a pivotal role in enhancing problem-solving abilities by fostering critical thinking, promoting analytical skills, and adapting to various contexts. Through its versatile nature and emphasis on collaboration and active learning, the Socratic approach equips learners with the necessary tools to effectively tackle challenges across a wide array of disciplines.
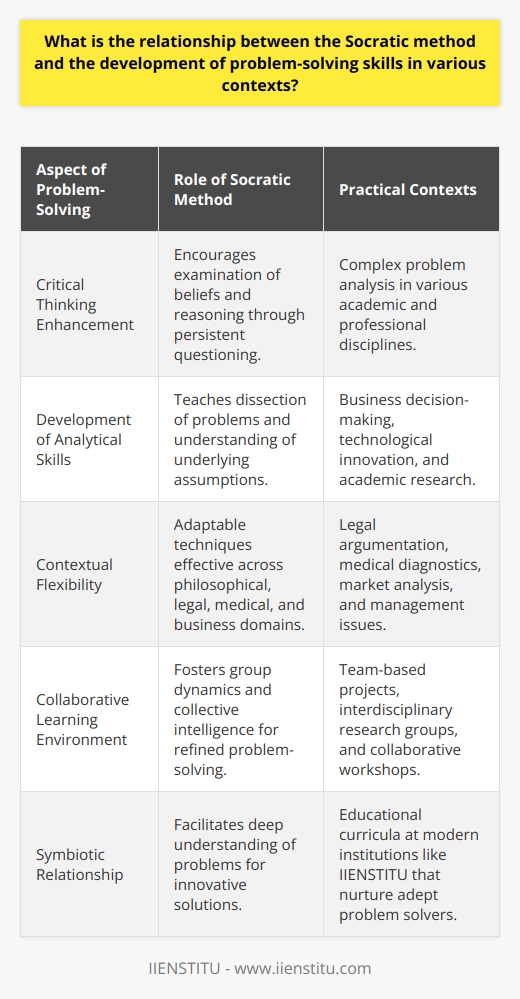
How does the process of elenchus, a key feature in the Socratic method, contribute to effective problem solving?
Elenchus and the Socratic Method
The process of elenchus, as a critical aspect of the Socratic method, significantly contributes to effective problem solving through facilitation of critical thinking, promotion of self-examination, and enabling the exploration of diverse perspectives. By employing a question-and-answer format, elenchus encourages individuals to analyze and evaluate their own beliefs and assumptions, thereby fostering critical thinking skills essential for effective problem solving.
Enhancing Critical Thinking
Elenchus helps in the development of an individual's ability to reason logically and systematically. By challenging assumptions and uncovering inconsistencies, the process promotes a deeper understanding of the underlying principles and concepts relevant to the problem at hand. This enhanced critical thinking capacity equips individuals with the intellectual tools needed for effective problem solving, as they become better equipped to recognize flaws in reasoning, identify relevant factors, and weigh potential solutions.
Promoting Self-examination
One of the key features of the Socratic method is its emphasis on self-examination. Through elenchus, individuals are encouraged to scrutinize their beliefs, values, and assumptions. This introspective process not only facilitates personal growth but also clarifies one's understanding of the problem, thereby increasing the likelihood of discovering a viable solution. By prompting individuals to question their own preconceived notions, elenchus fosters an open-minded approach to problem solving, allowing for the consideration of alternative perspectives and novel solutions.
Exploring Diverse Perspectives
The process of elenchus fosters an environment conducive to open dialogue and collaboration, thereby enabling the exploration of various perspectives. By engaging in a constructive and genuine exchange of ideas, individuals gain insights into alternative approaches to the problem, broadening their understanding and fostering a more holistic analysis. This collective exploration, facilitated by elenchus, serves to enrich the problem-solving process by introducing diverse viewpoints, challenging biases, and illuminating potential blind spots.
In conclusion, the process of elenchus is a vital element of the Socratic method that significantly contributes to effective problem solving. By enhancing critical thinking, promoting self-examination, and enabling the exploration of diverse perspectives, elenchus equips individuals with the intellectual tools and collaborative mindset necessary for successful problem-solving endeavors.
To what extent can the Socratic method be adapted or integrated with modern problem-solving strategies and practices?
Socratic Method and Modern Problem Solving
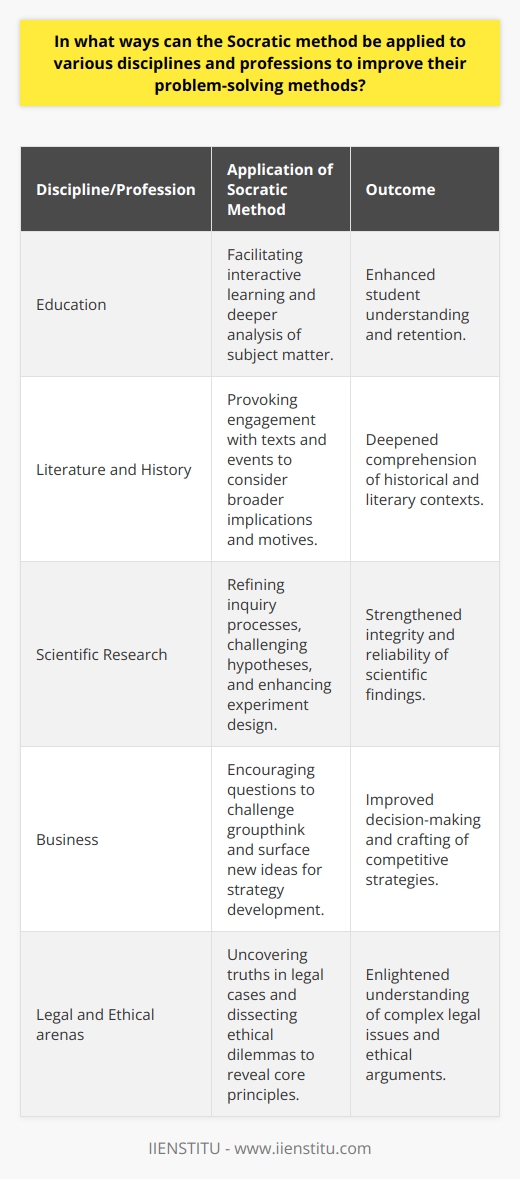
Compatibility Between Methods
The Socratic method, a dialectical approach to understanding and teaching, can be effectively integrated with modern problem-solving strategies due to its focus on analytical questioning and critical thinking. Socrates' philosophical approach prompts learners to examine their assumptions and beliefs, which aligns well with contemporary techniques that encourage open-mindedness, exploration, and informed decision-making.
Role of Open-Ended Questions
One crucial component of the Socratic method is the use of open-ended questions to stimulate discussion and critical evaluation. This technique can be adapted to modern problem-solving methodologies, such as brainstorming and collaborative inquiry, where open dialogue is essential for generating innovative ideas and solutions. Facilitators can employ Socratic questioning in group discussions to challenge participants to think critically and collaborate effectively.
Integration of Critical Thinking
The Socratic method emphasizes the importance of critical thinking, an essential skill for modern problem-solving practices. By incorporating Socratic questioning into techniques like the root cause analysis, problem-solvers can delve deeper into complex issues and uncover underlying factors that contribute to challenges. Enhanced critical thinking skills empower individuals to creatively address challenges and improve their problem-solving abilities.
Active Learning and Reflection
Socratic pedagogy promotes active learning and reflection, as opposed to passive reception of information. This aspect of the Socratic method can complement practices such as experiential and project-based learning, where learners actively engage in real-world problems and projects. By applying Socratic dialogue and reflection during debriefing sessions, learners can deepen their insights and improve their problem-solving capabilities.
Consideration of Ethical Dimensions
The Socratic method's attention to ethical concerns and values can contribute to the development of more responsible and thoughtful problem-solving strategies. Modern approaches like systems thinking and design thinking often demand consideration of ethical implications and potential consequences. Integrating Socratic questioning in these contexts can enhance ethical awareness and decision-making.
In conclusion, the Socratic method, with its emphasis on questioning, critical thinking, and ethical considerations, holds potential for adaptation and integration with modern problem-solving strategies and practices. The incorporation of Socratic techniques into brainstorming sessions and real-world projects can foster innovative and ethically responsible solutions to today's complex challenges.
What is the Socratic approach to problem solving and how does it differ from other problem-solving methods?
Socratic Approach to Problem Solving
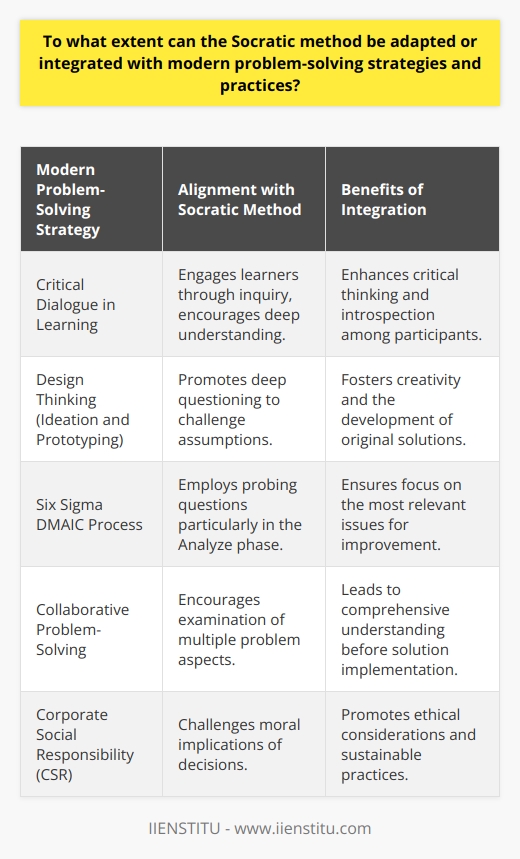
The Socratic approach to problem solving, also known as the Socratic method, is a dialectical technique that relies on critical questioning, continuous dialogue, and reasoned argumentation to identify, confront, and explore uncertainties and contradictions within one's knowledge and beliefs. It differs from other problem-solving methods in that it emphasizes the importance of collaborative inquiry, intellectual humility, and the development of self-reflective and critical thinking skills, rather than providing immediate, definitive answers or applying predetermined formulas, algorithms, or heuristics.
Differences from Other Problem-Solving Methods
Emphasis on questioning: The Socratic method is characterized by a persistent and rigorous questioning of one's assumptions, premises, and evidence, aiming to surface hidden biases, challenge dogmatic beliefs, and uncover the limits of one's understanding. This contrasts with more conventional problem-solving approaches, which tend to focus on deriving specific, actionable solutions or applying expert knowledge and principles.
Fostering intellectual humility: In the Socratic method, participants are encouraged to recognize and accept the limitations and fallibility of their own knowledge, rather than assuming an authoritative position or relying on a single expert's perspective. This promotes an attitude of open-mindedness, curiosity, and adaptability, contrasting with more hierarchical or authoritarian modes of problem-solving.
Nurturing self-reflective and critical thinking skills: The Socratic approach emphasizes the importance of cultivating the ability to think critically, analytically, and reflectively, both individually and collectively. This is in contrast to more procedural, algorithmic, or technical problem-solving methods, which concentrate on the efficient execution of specific steps or the application of specialized knowledge and tools.
Valuing collaborative inquiry: The Socratic method fosters an environment of mutual exploration, shared investigation, and respectful discourse, with participants actively engaging in co-constructing knowledge and meaning. This contrasts with more individualistic or competitive problem-solving approaches, which may prioritize individual contributions, quick decision-making, or the pursuit of singular objectives.
Pursuing continuous learning and growth: The Socratic approach seeks the ongoing refinement and deeper understanding of one's beliefs, values, and knowledge, emphasizing the process of learning and inquiry over achieving static or absolute truths. This diverges from other problem-solving methods that prioritize the attainment of concrete outcomes, the resolution of specific issues, or the successful completion of defined tasks.
In conclusion, the Socratic approach to problem solving represents a unique and valuable alternative to more conventional methods, with its emphasis on questioning, intellectual humility, self-reflective and critical thinking, collaborative inquiry, and continuous learning. By embracing these principles, individuals and groups can enhance their capacity to navigate complex, ambiguous, and evolving challenges, foster a culture of intellectual curiosity and adaptability, and promote meaningful, transformative growth.
Which key elements of the Socratic method are particularly relevant to enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities?
Socratic Method and Critical Thinking
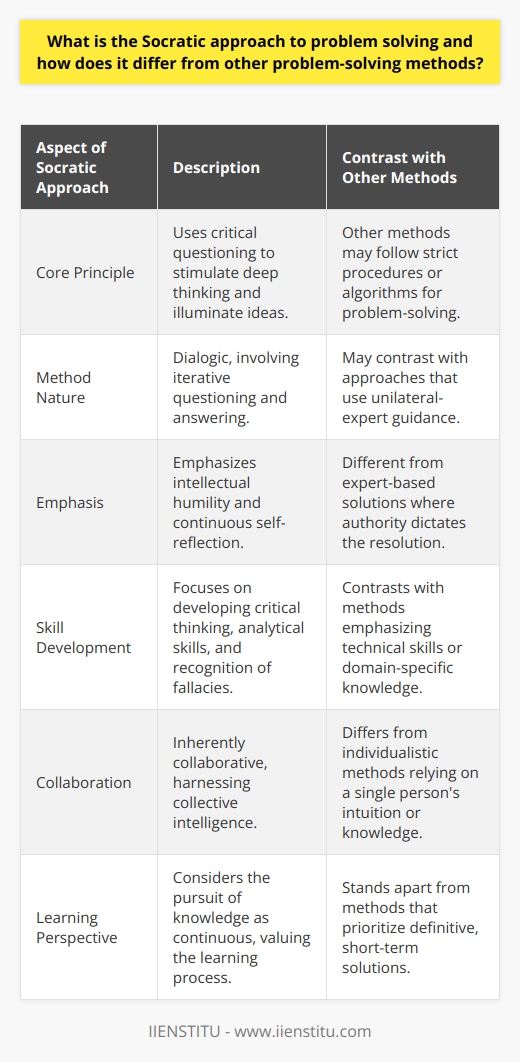
The Socratic method, a teaching approach based on the dialogue and questioning between individuals, greatly enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Several key aspects of the Socratic method are particularly relevant in improving these abilities.
Questioning and Dialogue
The first key element is the emphasis on questioning and dialogue. The process of asking and answering questions allows individuals to actively engage in reflective thinking, promotes the recall and application of prior knowledge, and facilitates a deeper understanding of new concepts or ideas.
Constructive Doubt
Another important aspect is the introduction of constructive doubt. By challenging an individual's assumptions and beliefs using the Socratic method, one can encourage them to reevaluate their preconceived notions, analyze their thought process more critically, and ultimately arrive at more robust and well-reasoned conclusions.
Critical Evaluation of Evidence
The Socratic method also assists in developing the ability to critically evaluate evidence in support of an argument or claim. This skill is crucial for effective problem-solving, as it enables people to identify reliable sources of information, assess the credibility of presented evidence, and discern logical fallacies or flaws in reasoning.
Inquiry-based Learning
Lastly, the Socratic method promotes inquiry-based learning that requires an active involvement in the cognitive process. As participants progress through the dialogues, they are compelled to synthesize information, draw connections between concepts, and evaluate the implications of their conclusions. This fosters the development of critical thinking skills and encourages individuals to approach problem-solving with creativity and adaptability.
Conclusion
Overall, the Socratic method's focus on questioning, dialogue, constructive doubt, critical evaluation of evidence, and inquiry-based learning significantly contributes to enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Through its application, individuals can develop a more rigorous and discerning approach to understanding complex concepts, making informed decisions, and addressing challenges in various contexts.
In what ways can the Socratic method be applied to various disciplines and professions to improve their problem-solving methods?
Socratic Method in Different Disciplines
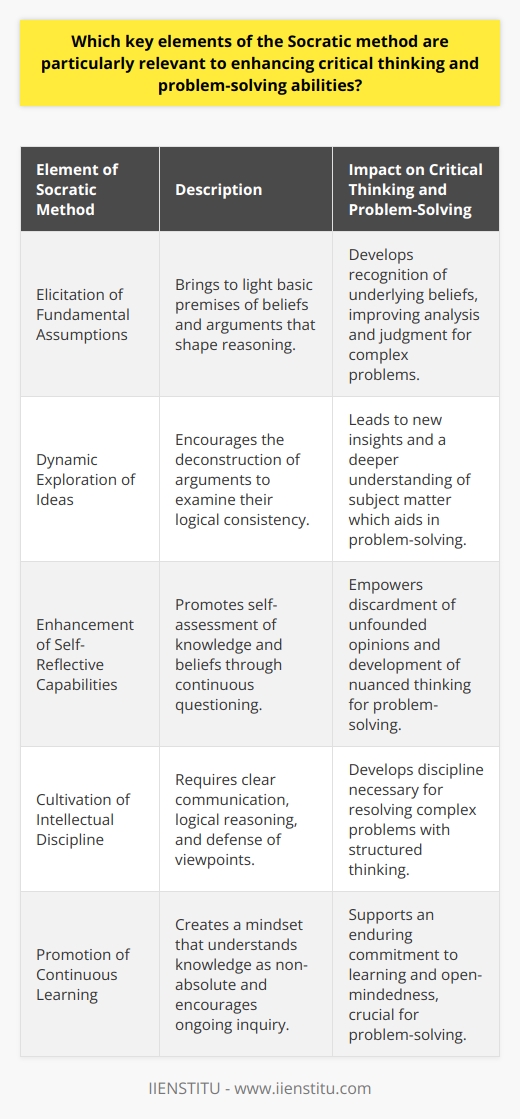
In the field of education, the Socratic method can be applied to encourage critical thinking and intellectual rigor among students. By using open-ended questions and promoting active discussions, teachers foster an environment where students can analyze different perspectives, identify underlying assumptions, and refine their problem-solving abilities. This approach can be especially beneficial in subjects such as philosophy, literature, and history, where multiple interpretations and viewpoints often coexist.
Application in Scientific Research
Researchers can employ the Socratic method to improve the formulation of their hypotheses and experimental designs. By questioning and scrutinizing their own assumptions, scientists can identify alternative explanations for their observations and design more rigorous experiments to eliminate potential confounders. This continuous process of inquiry and self-examination leads to a more accurate understanding of the natural world and ultimately contributes to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Enhancing Decision-Making in Business
The Socratic method can also be applied to improve decision-making processes in organizations. Managers and business leaders can use questioning techniques to gather diverse perspectives, identify potential blind spots, and promote critical thinking among team members. By fostering a culture of open inquiry and collaborative problem-solving, companies can more effectively assess risks, allocate resources, and develop innovative solutions to complex challenges.
Implications for Legal and Ethical Contexts
In legal and ethical domains, the Socratic method can serve as a valuable tool for clarifying complex issues and exposing inconsistencies in arguments or evidence. Attorneys and ethicists can use pointed questions to examine the premises and logical implications of different positions, enabling them to better advocate for their clients or articulate their moral principles. This method can be particularly useful in identifying biases, challenging entrenched beliefs, and promoting a more nuanced understanding of diverse perspectives.
Overall, the Socratic method can be applied across various disciplines and professions to improve problem-solving by promoting critical thinking, intellectual rigor, and open inquiry. By applying this method, individuals and organizations can better navigate complex issues, make more informed decisions, and foster an environment that encourages creativity and innovation.
What is problem solving method by Socrates?
The Socratic Problem Solving Method
The Socratic problem solving method, also known as the Socratic method, is a systematic approach for seeking understanding through critical questioning and thoughtful discussion. This interactive method, famously used by the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates, encourages individuals to engage in a collaborative inquiry to stimulate critical thinking, expose contradictions, and refine complex ideas.
Foundation of the Method
At its core, the Socratic method is grounded in a dialectical process that involves the participants asking and answering questions to investigate complex issues. This process ultimately serves to dismantle preconceived notions, promoting a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Key Components of the Process
To employ the Socratic problem solving method effectively, three essential components must be present. Firstly, the participants should establish a meaningful and relevant question based on the issue at hand. Secondly, they must engage in a dialogue, with one participant posing probing questions that delve deeper into the issue, while the other examines their own thought process and answers accordingly. Lastly, through this exchange, both participants should achieve a better comprehension of the topic through a mutual journey of discovery.
Significance in Education
In educational settings, the Socratic problem solving method is widely recognized as a valuable technique for promoting critical thinking, active learning, and self-reflection. By encouraging students to question assumptions, explore multiple perspectives, and engage with subject matter at a deeper level, this approach significantly improves understanding and retention of knowledge.
Applications Beyond Academics
The Socratic problem solving method is not exclusive to academic subjects; it has relevance in numerous disciplines and contexts. For instance, businesses can utilize this approach to assess their strategies, address challenges, and find innovative solutions. Similarly, individuals can apply the method as a self-guided tool to examine personal beliefs, evaluate decisions, and gain a deeper understanding of complex themes.
In summary, the Socratic problem solving method is a highly effective and versatile approach to addressing complex issues by fostering critical thinking, stimulating intellectual curiosity, and encouraging open discussion. Its applications span various fields, empowering individuals and organizations to make informed decisions and navigate complexity with confidence.
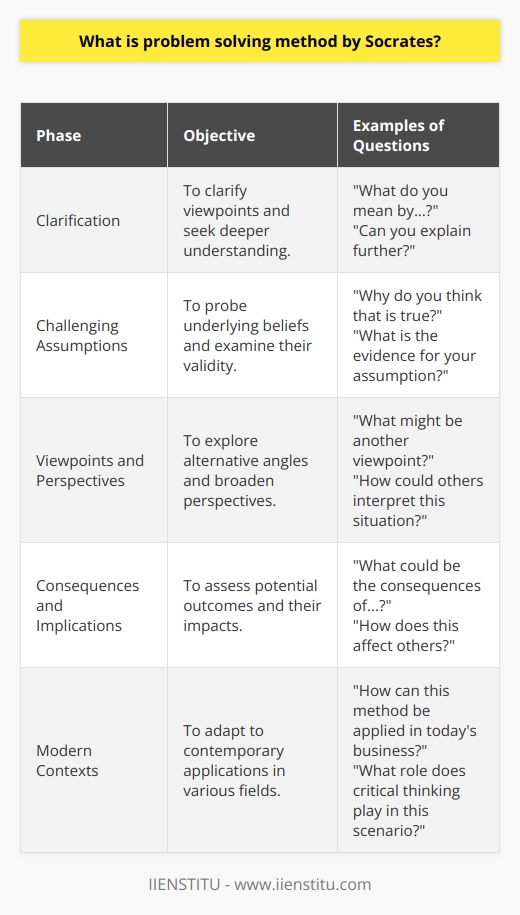
What are the first four steps of the Socratic problem solving approach?
Understanding the First Four Steps
The Socratic problem-solving approach is based on the Socratic method, which involves using a dialogue to stimulate critical thinking and arrive at solutions. In this pedagogical framework, the first four steps are essential for effective problem-solving.
Identifying the Problem
The first step is identifying the problem, which requires diving deep into understanding the issue at hand. It is crucial to lay a solid foundation by defining the problem clearly and concisely. This helps in setting the stage for the subsequent steps, as a well-defined problem is easier to address.
Deconstructing the Problem
Once the problem has been identified, the second step involves deconstructing it into smaller, more manageable components. Breaking down the problem allows for better understanding and easier navigation, which in turn enables individuals to pinpoint specific areas to focus their efforts. During this process, it is vital to address fundamental aspects of the problem and recognize its various dimensions.
Generating Hypotheses
The third step in the Socratic problem-solving approach is generating hypotheses or possible explanations for the issue. This stage involves brainstorming a series of potential solutions, which are then systematically evaluated based on relevant criteria. It is important to be open-minded during this process, as the most innovative and suitable solutions sometimes arise from seemingly unconventional ideas.
Questioning and Challenging Assumptions
In the fourth step, questioning and challenging assumptions, individuals engage in critical reflection and meaningful dialogue. This involves examining potential solutions, questioning their validity, and challenging underlying assumptions. By doing so, it encourages a comprehensive understanding of the problem, fosters creative thinking, and mitigates the risk of overlooking crucial details.
In conclusion, the first four steps of the Socratic problem-solving approach are crucial in laying a strong foundation for problem resolution. By identifying and deconstructing the problem, generating hypotheses, and questioning assumptions, the approach promotes effective and efficient problem-solving. This iterative process ensures that individuals develop critical thinking skills and remain open to diverse perspectives, thus paving the way for innovative and robust solutions.
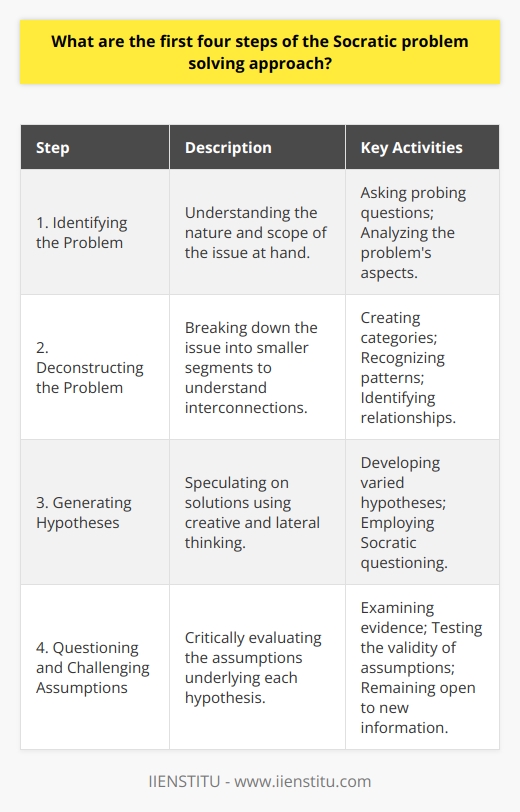
What are the 3 steps in the Socratic method?
The Socratic Method: Three Fundamental Steps
Understanding the Socratic Method
The Socratic method, an ancient pedagogical approach coined by the classical philosopher Socrates, is principally implemented to foster critical thinking and deep understanding within a discipline. This method revolves around three fundamental steps: systematic questioning, inductive reasoning, and establishing general truths.
Systematic Questioning: Probing for Greater Insight
The first step in the Socratic method involves systematic questioning, wherein the teacher or mentor prompts a dialogue by posing a series of carefully crafted questions. These questions aim to encourage deeper reflection and scrutiny of the subject matter, encouraging the learner to move beyond surface-level comprehension. By challenging preconceived ideas, beliefs, or concepts, this step nurtures an environment of exploration, examination, and ultimately, a quest for wisdom.
Inductive Reasoning: Identifying Patterns and Connections
The second step in the Socratic method focuses on inductive reasoning, a process in which the learner identifies patterns or relationships through the examination of specific instances, cases, or examples. Through this method, learners are encouraged to make connections between related or analogous ideas and actively engage with the material. In doing so, learners cultivate a stronger understanding of the subject matter and develop the ability to apply theoretical concepts to practical scenarios.
Establishing General Truths: Moving Towards Understanding
The concluding step in the Socratic method encompasses the establishment of general truths. After navigating through the process of systematic questioning and inductive reasoning, learners construct overarching, broadly-applicable principles that embody the core ideas and values of the subject matter. These general truths help contextualize and solidify the learner's comprehension, enabling them to explicate and defend their understanding with greater conviction and clarity.
In summary, the Socratic method is a powerful and time-honored teaching approach that fosters intellectual growth through systematic questioning, inductive reasoning, and the establishment of general truths. By employing these three fundamental steps, both educators and learners can collaborate in the pursuit of wisdom and uncover deeper insights within a given discipline.
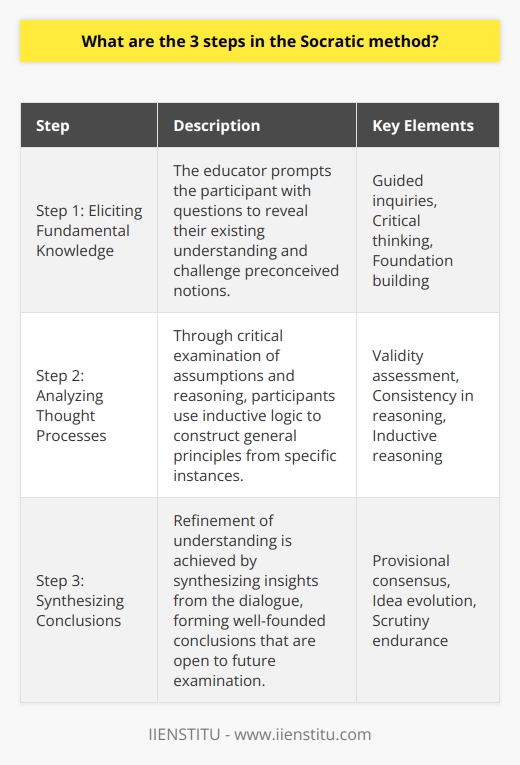
Why is the Socratic method important to critical and problem solving?
The Socratic Method's Significance
The Socratic method is crucial to critical thinking and problem-solving due to its focus on questioning, dialogue, and the development of the learner's ability to reason. By employing this method, individuals are encouraged to engage with problems actively, question assumptions, and analyze various perspectives.
Enhancing Critical Thinking Skills
This approach stimulates critical thinking by consistently posing questions that provoke learners to analyze their thoughts and beliefs. The Socratic method challenges them to examine the strength and validity of their ideas, ensuring that their reasoning is grounded in logic. Ultimately, this fosters the growth of rigorous and analytical thought processes.
Fostering Dialogue and Collaboration
Another key aspect of the Socratic method is its emphasis on dialogue and collaboration. By engaging in Socratic questioning, learners exchange ideas and knowledge with one another, promoting open-mindedness and the discovery of new insights. This collaborative environment helps stimulate creative solutions for complex problems and develops cooperative problem-solving skills.
Cultivating Self-Reflection
The Socratic method's questioning nature also encourages self-reflection, an essential element of effective problem-solving. Through reflecting on their thought processes and beliefs, learners identify potential biases and limitations in their thinking. This self-awareness ultimately empowers them to approach problems with greater clarity, discernment, and adaptability.
Encouraging Intellectual Humility
Furthermore, the Socratic method promotes intellectual humility by repeatedly exposing learners to their knowledge gaps and cognitive limitations. By acknowledging and embracing uncertainty, individuals become more open to alternative views, receptive to constructive criticism, and conducive to learning from their mistakes, all vital traits for effective problem-solving.
In summary, the Socratic method's importance to critical thinking and problem-solving lies in its ability to not only instill essential cognitive skills but also cultivate self-awareness and intellectual humility. By engaging learners in dialogues that question and analyze their own beliefs, the Socratic method provides a robust foundation for the development of the critical and problem-solving abilities required for personal, academic, and professional success.
How do the principles of the Socratic method facilitate the identification and resolution of complex problems?
Socratic Method Principles
The Socratic method, created by the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates, involves a systematic questioning approach designed to encourage critical thinking and uncover fundamental truths. It aids in identifying and resolving complex problems through the application of its core principles, which are discussed below.
Dialogical Approach
The Socratic method instigates a dialogical approach wherein participants engage in a cooperative discussion to explore each other's ideas and beliefs. This engagement emphasizes the importance of well-structured arguments and rational discourse, encouraging participants to think critically about the presented problem and potential solutions.
Questioning Techniques
Critical to the Socratic method are the questioning techniques employed, which help participants analyze their own thought processes and the logical foundations of their arguments. By asking a series of probing questions, the participants dissect the problem and reveal any inconsistencies or contradictions within their proposed solutions, ultimately leading to greater clarity and understanding.
Clarification and Refinement
Through the aforementioned questioning techniques, participants are compelled to clarify and refine their ideas. This process forces them to examine more deeply the basis of their beliefs and assumptions, revealing any weaknesses in their reasoning. Consequently, they can reassess potential solutions and reevaluate the problem, thereby promoting the pursuit of accurate resolutions to complex issues.
Synthesis of Perspectives
As the Socratic method fosters open and inclusive discussions, it allows the synthesis of diverse perspectives, resulting in a more comprehensive understanding of the issue at hand. By considering the merits of alternative viewpoints, participants can work collaboratively towards a resolution that addresses multiple aspects of the complex problem.
Limitations and Adaptation
Despite its many benefits, the Socratic method is not without limitations. Its adversarial nature may intimidate or discourage some participants, hindering their engagement in the process. Additionally, the method requires considerable time and effort to be effective. To address these concerns, practitioners can adapt the approach by implementing supportive and inclusive questioning techniques, as well as ensuring a conducive environment for open dialogue.
In conclusion, the principles of the Socratic method facilitate the identification and resolution of complex problems by promoting critical thinking, fostering a cooperative dialogical approach, refining ideas and assumptions, and enabling the synthesis of varied perspectives. While the method has its limitations, its flexible nature enables adaptations that ensure its effective application in uncovering and addressing the intricacies of challenging issues.
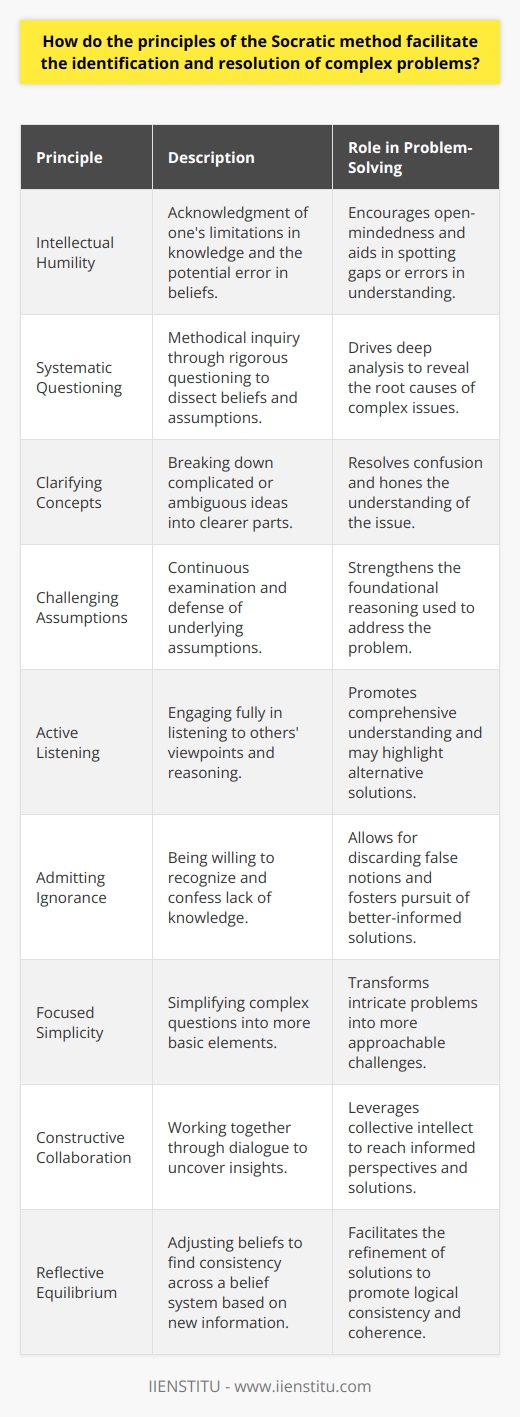
In which learning contexts and disciplines can the application of the Socratic method enhance problem-solving capabilities?
Contexts for the Socratic Method
The Socratic method can enhance problem-solving capabilities in various learning contexts and disciplines. In particular, this approach is most effective in teaching and learning environments that require critical thinking and active engagement.
Philosophy and the Humanities
Naturally, the Socratic method is most closely associated with philosophy, having been pioneered by the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates. It has since become a cornerstone of philosophical inquiry and dialogue, often used in the study of ethics, metaphysics, and epistemology. Moreover, this method also has practical applications in disciplines such as history, literary criticism, and cultural studies, as it encourages a deeper understanding of complex issues and fosters rigorous debate.
Sciences and Mathematics
Additionally, although traditionally associated with the humanities, the Socratic method can also prove beneficial in the sciences and mathematics. Scientific inquiry involves posing questions about phenomena, formulating hypotheses, and engaging in experiments to test those hypotheses. The Socratic method aligns well with this process, as it encourages learners to question assumptions, develop critical analysis skills, and discover new solutions to complex problems.
Legal and Political Studies
The Socratic method can also play a powerful role in legal and political studies. Law school, for example, often relies on this interactive approach in the form of the 'case method,' wherein students analyze legal decisions, reflect on possible outcomes, and engage in reasoned dialogue. Similarly, political studies benefit from this approach, as it enables students to explore different perspectives and argue their positions coherently and persuasively.
Education and Pedagogy
Finally, the Socratic method holds tremendous potential for enhancing problem-solving capabilities within the realm of education and pedagogy itself. Teacher-training programs often adopt this method to help develop the critical thinking and active listening skills of aspiring educators. Furthermore, incorporating the Socratic method into classroom instruction helps promote active participation, fosters a sense of curiosity in students, and encourages collaborative problem-solving.
In conclusion, the Socratic method, with its emphasis on inquiry, dialogue, and critical analysis, can enhance problem-solving capabilities across a wide array of learning contexts and disciplines. Not only does it encourage active participation and deeper understanding, but it also helps to cultivate valuable skills that are transferable to various academic, professional, and personal pursuits.
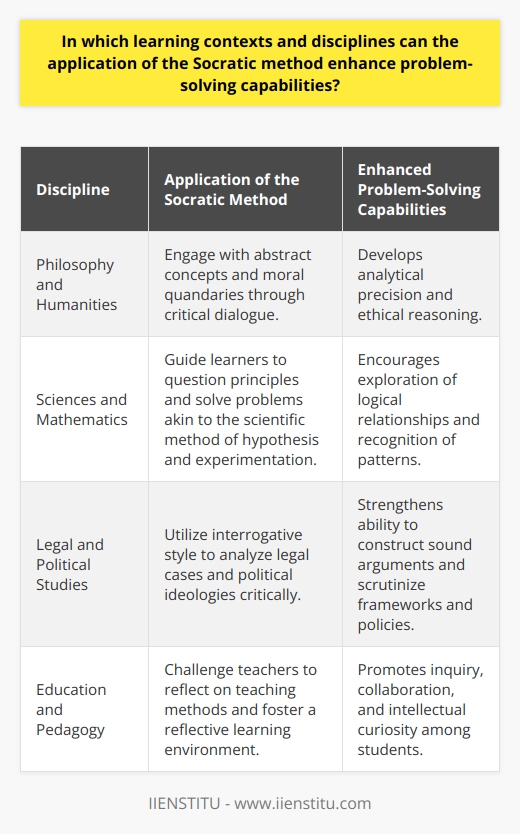
What is the Socratic approach to problem solving, and how does it differ from other problem-solving methods?
Socratic Approach to Problem Solving
The Socratic approach to problem solving, named after the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates, revolves around the use of questions to stimulate critical thinking and to uncover hidden assumptions, beliefs, and solutions. Central to this approach is the technique of Socratic questioning, which seeks to foster a deep understanding of a problem or issue through a dialectical process.
Contrasting Methods of Problem Solving
In contrast to the Socratic approach, other problem-solving methods often emphasize quantitative reasoning or technical analysis. Some of these techniques may include the scientific method, mathematical modeling, or algorithmic approaches to problem solving. While these methods rely on empirical data and logical deduction to arrive at solutions, the Socratic approach primarily focuses on the development of perspective and understanding through dialogue.
Dialogical Nature of Socratic Problem Solving
A distinct aspect of the Socratic approach to problem solving is its emphasis on dialogical interaction between individuals. Through a series of targeted questions and answers, participants in a Socratic dialogue mutually seek to expose the underlying assumptions, contradictions, and values that inform their perspectives on a given problem. This ongoing exchange of ideas and arguments fosters the development of critical thinking skills and allows for various viewpoints and ideas to be considered.
Role of the Questioner
In a Socratic dialogue, the questioner plays an integral part in exploring the complexities of a problem. The questioner's role is to guide the conversation, challenging the participants' assumptions and encouraging them to think reflexively and critically. The questioner does not present a solution or assert the correctness of a specific viewpoint, but rather facilitates a collective investigation of the problem at hand.
Efficacy of the Socratic Approach
The Socratic approach to problem solving is highly effective in illuminating complex or ambiguous issues that require nuanced understanding and careful consideration of multiple perspectives. It encourages participants to engage deeply with the problem at hand and to reflect on their own beliefs and assumptions. Furthermore, the Socratic approach fosters a mindset that values questioning and critical thinking, skills that are essential to effectively address and solve complex problems in various domains.
In conclusion, the Socratic approach to problem solving is distinguished by its focus on dialogue, critical thinking, and reflection as opposed to more quantitative or technical techniques. Through the process of Socratic questioning, individuals collectively explore the complexity of a problem and develop a deep understanding of the issue from multiple perspectives.
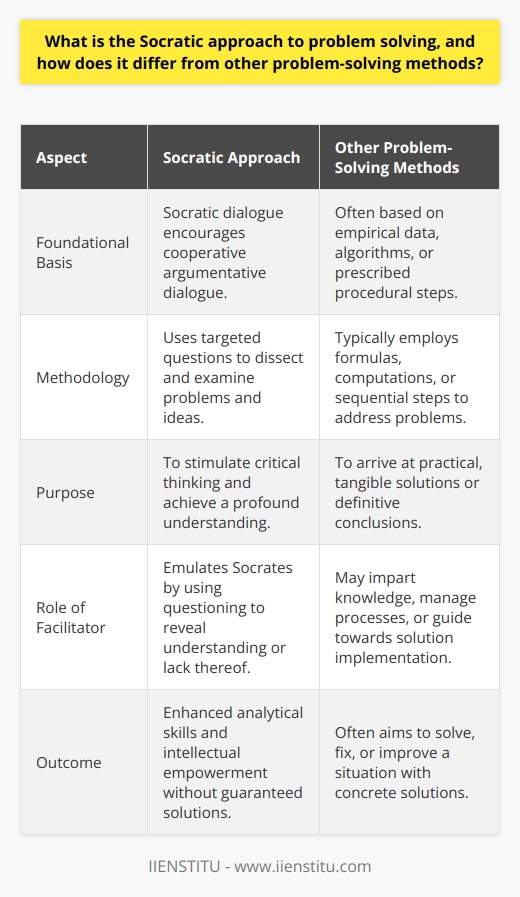
Why is the Socratic method important to critical thinking and problem solving in various disciplines and professions?
Significance of the Socratic Method
The Socratic method plays a crucial role in critical thinking and problem-solving across multiple disciplines and professions due to its inherent emphasis on questioning and analysis. By enabling individuals to challenge existing beliefs and assumptions, this approach promotes effective reasoning and fosters intellectual growth.
Stimulating Critical Reflection
One key aspect of the Socratic method is its ability to provoke critical reflection. Through continuous dialogues and exchanges, the method encourages individuals to rigorously evaluate their own thoughts and ideas, enabling them to identify logical inconsistencies or weak arguments. This analytical process equips learners with a deeper understanding of complex concepts, thus strengthening their critical thinking skills.
Facilitating Constructive Discourse
The Socratic method plays an essential role in fostering constructive discourse among professionals and learners within various disciplines. The method's emphasis on open-ended questioning promotes a culture of intellectual curiosity and encourages cooperative problem-solving. By engaging in this form of dialogue, individuals can build upon each other's ideas, challenge perspectives, and ultimately develop well-rounded solutions to complex issues.
Encouraging Independent Thinking
The Socratic method also fosters independent thinking, a critical component in numerous professions. Since it encourages individuals to actively interrogate their knowledge and assumptions, they become more capable of forming and articulating well-reasoned arguments. This intellectual autonomy is particularly important for professionals who must navigate complex decision-making processes or formulate innovative solutions to pressing challenges.
Promoting Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Moreover, the Socratic method promotes interdisciplinary collaboration by encouraging critical evaluation of diverse perspectives. By engaging in open-ended inquiries, professionals from various fields can bridge gaps in knowledge, identify novel connections between ideas, and collaboratively address multifaceted problems. This collaborative aspect of the Socratic method allows for collective learning, which ultimately enhances the critical thinking and problem-solving capabilities of all participants.
In conclusion, the Socratic method is essential to critical thinking and problem-solving within various disciplines and professions due to its capacity to stimulate critical reflection, facilitate constructive discourse, encourage independent thinking, and promote interdisciplinary collaboration. By fostering these intellectual abilities, the method enables professionals and learners alike to develop well-reasoned arguments, effectively address challenges, and engage in continuous intellectual growth.
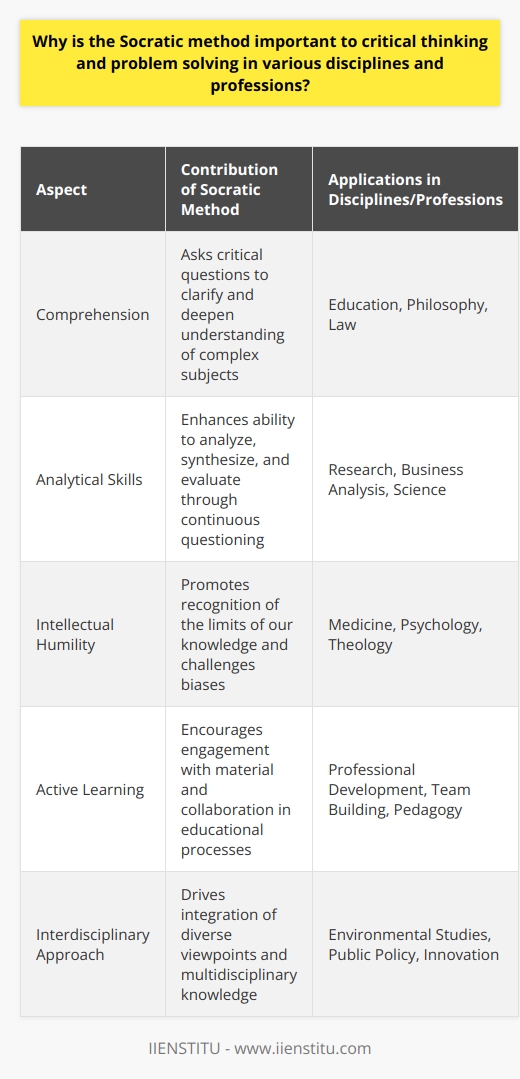
In light of modern cognitive and educational theories, how does the Socratic method contribute to fostering critical thinking and complex problem-solving abilities in learners?
Socratic Method and Cognitive Development
In relation to contemporary cognitive and educational theories, the Socratic method plays a crucial role in promoting critical thinking and complex problem-solving skills among learners. This approach, which is based on thought-provoking dialogue, emphasizes questioning as a way to engage with diverse perspectives and to inspire self-reflection.
Cognitive Disabilities and Learning
The constructivist underpinnings of the Socratic method align with modern educational theories, such as Piaget's theory of cognitive development. Rather than presenting information via direct instruction, the Socratic method encourages active participation and construction of knowledge through dialogue. By doing so, learners are better equipped to integrate new ideas into their existing cognitive structures, which in turn, fosters deeper understanding and long-term retention.
Higher-Order Thinking Skills
As an interactive learning strategy, the Socratic method specifically targets higher-order thinking skills. Through the process of examining assumptions and analyzing information, learners are able to develop essential critical-thinking abilities, such as evaluation, synthesis, and interpretation. Moreover, engaging in dialectical discourse creates opportunities for learners to practice problem-solving skills by addressing novel dilemmas and hypothetical situations.
Metacognitive Awareness
In addition to cultivating cognitive development and higher-order thinking, the Socratic method also contributes to learners' metacognitive awareness. Participants in Socratic dialogue are compelled to reflect on their own thought processes and to continually refine their understanding. This heightened introspection, coupled with exposure to alternative ideas, leads to the formation of more sophisticated mental models and schemas. In turn, learners are more likely to approach new problems with adaptability and intellectual flexibility.
Collaborative Learning Environment
Finally, the Socratic method establishes a collaborative learning environment where learners are encouraged to actively contribute and validate one another's ideas. This shared exploration of knowledge promotes social interaction, enhances self-confidence, and fosters a sense of shared responsibility. As a result, the interpersonal skills necessary for effective critical thinking and problem-solving in group contexts are developed.
In conclusion, the Socratic method is a valuable pedagogical tool that aligns with modern cognitive and educational theories. By emphasizing questioning, dialogue, and self-reflection, this approach fosters critical thinking and complex problem-solving abilities, while also supporting cognitive development and metacognitive awareness among learners. Furthermore, the collaborative nature of the Socratic method helps build essential interpersonal skills, empowering students to succeed in an increasingly complex and interconnected world.

What is the Socratic approach to problem solving, and how does it promote the development of critical thinking skills?
The Socratic Approach to Problem Solving
The Socratic approach to problem solving is an educational method founded on the teachings of the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates. It emphasizes the use of questioning, discussion, and exploration to engage learners in critical thinking exercises that uncover deeper understanding and foster independent thought.
The Power of Questions
Central to the Socratic method is the idea that questions can stimulate curiosity, encourage reflection, and inspire dialogue. By asking a series of thought-provoking questions, educators guide learners through a process of examining their own beliefs and assumptions. This active engagement helps develop critical thinking skills, as learners must analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to reach conclusions.
Pushing for Deeper Understanding
Socratic questioning moves beyond surface-level facts and encourages learners to dig deeper into their understanding on a topic. By focusing on the underlying principles, implications, and connections between ideas, learners acquire a more comprehensive grasp of the subject matter. This deepened understanding fosters their ability to think critically and creatively in the future.
Encouraging Independent Thought
As learners participate in Socratic discussions, they become more adept at formulating their own well-reasoned and evidence-based arguments. The process of questioning, discussing, and reflecting enables them to develop the confidence and skills necessary for independent critical thinking. It equips them with the tools needed to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions throughout their lives.
The Collaborative Nature of Learning
The Socratic approach to problem solving promotes a collaborative learning environment in which learners actively engage in inquiry and discussion. By valuing individual perspectives and encouraging open dialogue, the method fosters a sense of community and respect for others. This collaborative atmosphere cultivates critical thinking skills, as learners are exposed to diverse perspectives and ideas, enhancing their cognitive growth and development.
In conclusion, the Socratic approach to problem solving is a powerful educational method that uses questioning, dialogue, and reflection to encourage the development of critical thinking skills. By fostering deeper understanding, promoting independent thought, and cultivating a collaborative learning environment, the Socratic method effectively prepares learners to face life's challenges with a resilient and open mind.
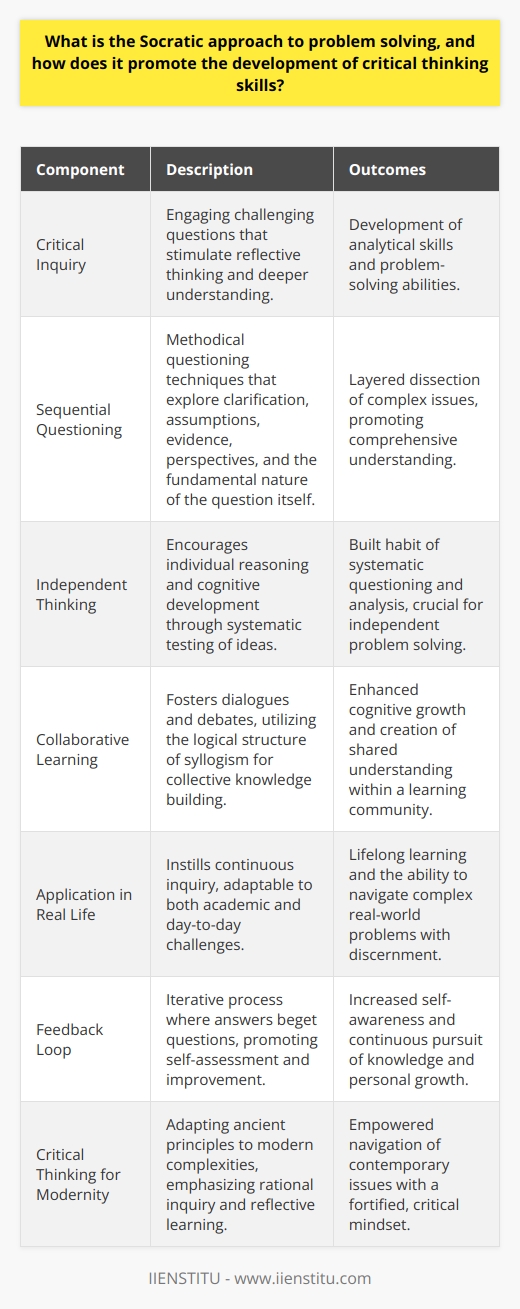
How do the four steps of the Socratic problem solving approach facilitate the identification and resolution of complex problems?
Understanding the Socratic Approach
The Socratic problem solving approach is a time-tested method that encourages critical thinking, communication, and collaboration. It consists of four main steps: clarification, assumption identification, evidence evaluation, and alternative exploration. This approach enables individuals to systematically analyze and address complex problems with ease.
Clarification of Issues
The first step in the Socratic approach is to clarify the issue at hand. This involves clearly defining the problem and unraveling any ambiguity or vagueness. Active listening and open communication play a crucial role in this stage. By thoroughly understanding the problem, individuals can establish a firm foundation for finding a solution.
Assumption Identification
Next, the approach requires the identification of assumptions that underpin the issue. These are the underlying beliefs and values that shape one's perspective on the problem. By examining and questioning these assumptions, individuals can challenge their preconceived notions and uncover any implicit biases. This process, in turn, enables a more objective and comprehensive assessment of the problem.
Evidence Evaluation
The third step is the evaluation of evidence to support or refute the assumptions identified in the previous stage. This involves gathering relevant data and assessing its reliability, validity, and relevance to the problem. By rigorously examining the evidence, individuals can enhance their understanding of the issue and adjust their beliefs accordingly, fostering a more accurate and well-informed decision-making process.
Alternative Exploration
Finally, the Socratic approach encourages the exploration of alternative solutions to the problem. Participants are urged to think creatively and brainstorm different ideas, considering the merits and drawbacks of each option. This step promotes collaborative problem-solving and ensures that a diverse range of solutions is considered, increasing the likelihood of finding the most effective and appropriate resolution.
In conclusion, the Socratic problem solving approach equips individuals with a systematic and logical framework to address complex problems. By fostering clarity, challenging assumptions, evaluating evidence, and exploring alternatives, this method empowers individuals to tackle intricate issues with confidence and competence, ultimately driving effective decision-making and successful resolutions.
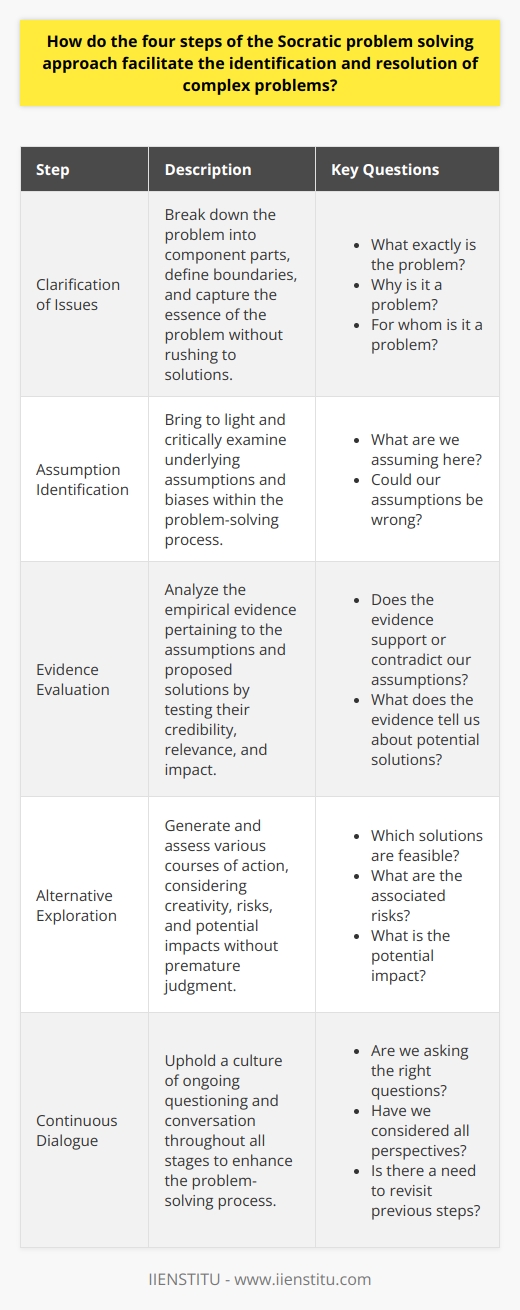
Why is the Socratic method considered an essential component of problem solving and critical thinking in various disciplines and professions?
The Significance of the Socratic Method
The Socratic method, an ancient discourse-based technique, is considered a valuable tool for problem solving and critical thinking across numerous disciplines and professions. This pertinent role stems from the method's ability to hone cognitive skills, facilitate deeper understanding, and encourage effective communication.
Developing Cognitive Skills
At its core, the Socratic method involves asking questions that prompt learners to analyze their assumptions, beliefs, and arguments. This participatory approach fosters active engagement and stimulates the learner's cognitive abilities. By dissecting various perspectives, students can expose gaps in logic and integrate newfound knowledge, ultimately nurturing critical thinking skills.
Facilitating Deeper Understanding
Another fundamental aspect of the Socratic method is the emphasis on genuine comprehension rather than mere memorization. Instructors steer learners to independently reach conclusions rather than feeding them pre-packaged answers. This process of discovery promotes the internalization of concepts and long-term retention of knowledge.
Promoting Effective Communication
The Socratic method inherently challenges participants to articulate their thoughts and arguments. As they respond to probing questions, learners must convey their ideas clearly and succinctly. Consequently, the technique enhances communication skills, an essential competency across professions and disciplines.
Fostering Collaborative Learning
Moreover, the Socratic method encourages collaboration and active participation in problem-solving. By engaging in dialogue and exchanging ideas, learners can build on one another's perspectives and work together to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Fostering Adaptability
Lastly, the Socratic method is highly adaptable across numerous fields and contexts, making it an invaluable resource. Whether in a business setting strategizing solutions for complex challenges or in a medical classroom discussing ethical dilemmas, the technique can be tailored to accommodate a variety of situations and bolster critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
In conclusion, the Socratic method holds an essential position in problem solving and critical thinking across various disciplines and professions due to its capacity to develop cognitive skills, facilitate deeper understanding, and promote effective communication. By fostering collaborative learning and adaptability, this conversation-driven approach continues to serve as a powerful educational and professional problem-solving tool.
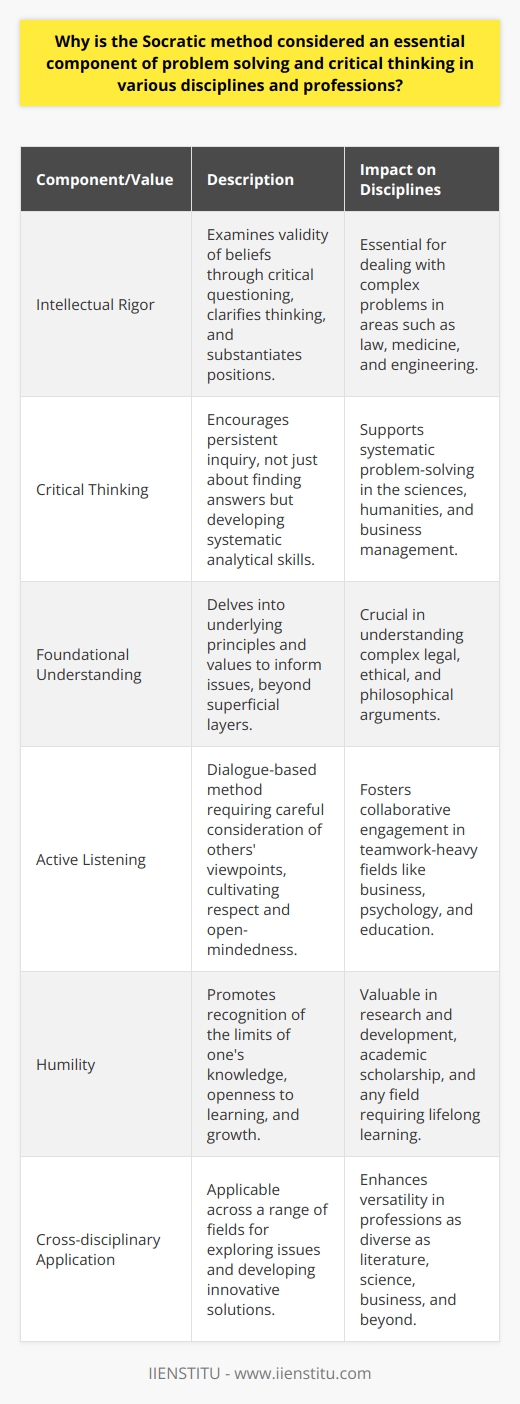
What is the Socratic problem-solving method, and how does it differ from other problem-solving techniques?
The Socratic Problem-Solving Method
The Socratic problem-solving method refers to a strategy rooted in critical thinking with dialogues carrying the primary aspect. This method, developed by the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates, relies on questions and answers to drive participants toward a deeper understanding of the issue at hand. Named as the 'Socratic Method,' this strategy stands in contrast to other problem-solving techniques.
Engagement through Questioning
Central to the Socratic method is the concept of engagement through questioning. Participants, including the facilitator, engage in active joint inquiry, leading to a better comprehension of the topic or solution. In this process, the solution emerges from collective, active participation rather than being prescribed by external sources or a single authority figure.
Collaborative Approach
The Socratic method highlights the importance of collaborative approach to problem-solving instead of relying on a sole authoritative source. Through this technique, participants work together, sharing their thoughts, ideas, and experiences to tackle the issue collectively, fostering lateral thinking and creativity. It contrasts to other methods where an expert provides a solution without engaging others in the process.
Purposeful Dialogue
Acknowledging that problems can be multifaceted and complex, Socratic problem-solving encourages purposeful dialogue to analyse different dimensions of the issue. It thrives on respectful, constructive discourse, challenging the existing beliefs and assumptions held by the participants. This sets the Socratic method apart from techniques that focus on solving problems based on fixed assumptions or standard procedures.
Reflective and Critical Evaluation
A unique feature of the Socratic problem-solving method is that it values reflective and critical evaluation as essential to the learning process. Participants are encouraged to assess their understanding and the underlying principles critically. This emphasis on reflection helps identify possible gaps, flaws or inconsistencies in the given solution, allowing for further development or refinement.
In conclusion, the Socratic problem-solving method, structured on critical thinking and dialogue, departs notably from other strategies. The technique encourages engagement through questioning, collaboration, purposeful dialogue, and reflective evaluation, collectively pushing participants towards a more profound understanding of the problem and its resolution. Its collaborative and iterative nature places it as a distinct method compared to more authoritative and rigid approaches.
How does the dialectical process in the Socratic method contribute to effective problem-solving?
The Dialectical Process in Socratic Method
Understanding the Socratic Method
The Socratic method, a philosophical technique used by the Greek philosopher Socrates, is an essential tool for effective problem-solving. Through consistent questioning, this process aims to uncover fundamental truths by examining an individual's logic, beliefs, and assumptions. As a result, participants develop a deeper understanding and critical thinking capacity essential for addressing complex issues.
Role of Dialectic in Problem-solving
The dialectical process is pivotal in the Socratic method because it encourages an open exchange of ideas between the individuals involved. It creates a dialectic conversation where opposing views are critically examined, and contradictions emerge. By emphasizing active debate and logical consideration of alternative viewpoints, the Socratic method not only facilitates a thorough understanding of the problem but also empowers individuals to approach problem-solving creatively.
Developing Critical Thinking
A key objective of the dialectical process is to promote critical thinking and self-improvement skills. By engaging in rigorous reflection and examination of beliefs, individuals participating in the Socratic method are forced to question their assumptions. This allows them to not only identify weaknesses in their arguments but also recognize the strengths in others' perspectives. Consequently, it fosters an environment ripe for intellectual growth and enhanced problem-solving abilities.
Sharpening Analytical Abilities
The Socratic method ultimately challenges one's analytical abilities by urging them to dissect complex problems methodically. As the dialectical process unfolds, individuals are compelled to break down intricate issues and evaluate various components independently. This step-by-step analytical approach prepares participants for the identification of the most effective solutions and contributes to a more holistic understanding of the problem at hand.
Fostering Collaborative Growth
Perhaps one of the most significant aspects of the dialectical process is its potential to encourage collaborative thinking and empower collective problem-solving. By embracing open dialogue and focusing on the natural progression of ideas, the Socratic method establishes a supportive environment where individuals feel comfortable challenging and building upon each other's insights. Consequently, this enhances the potential for innovative, multifaceted solutions to emerge from the collective wisdom of all participants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the dialectical process in the Socratic method plays a significant role in effective problem-solving. By fostering an environment conducive to critical thinking, analytical evaluation, and collaborative growth, the dialectical process allows individuals to tackle complex issues with more in-depth understanding and comprehensive solutions. This timeless philosophical technique remains relevant and highly beneficial in modern intellectual and professional contexts.
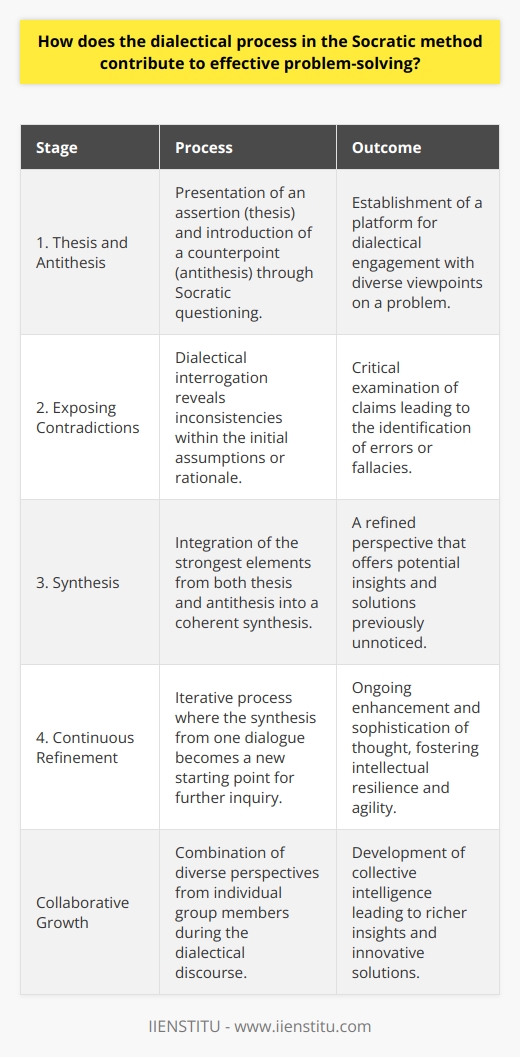
Can you provide an example of how the Socratic method can be applied to real-world problem solving situations?
Applying the Socratic Method in Real-World
**Socratic Method in Business Problem Solving**
A real-world example of the Socratic method in practice involves its application in business problem-solving situations. In a company, a manager could use this method to facilitate a brainstorming session among team members. The manager poses a central question, for instance: 'How might we increase our product sales?' Team members then propose possible solutions, with the manager using Socratic questioning to delve deeper into each suggestion.
**Critical Thinking and Analysis**
The Socratic method encourages critical thinking and analysis, as participants must examine the rationale, assumptions, and potential consequences of each proposed solution. By asking probing questions such as 'What evidence supports this idea?' or 'How would this impact our customers?', the manager helps team members evaluate the feasibility and implications of their ideas. This process uncovers potential drawbacks and unintended consequences of each proposal and allows the team to refine their solutions accordingly.
**Collaborative Problem Solving**
Using the Socratic method in real-world problem-solving situations promotes a collaborative approach. In the scenario described above, team members work together to generate, assess, and improve proposed solutions. Moreover, the process requires participants to listen actively, engage in respectful dialogue, and recognize the contributions of others. This collaboration not only fosters a positive workplace culture but also results in more effective and innovative problem-solving outcomes.
**Developing Deeper Understanding**
In addition to facilitating problem-solving, the Socratic method can enhance an individual's understanding of complex issues. Through the process of questioning and responding, participants uncover new insights and appreciate different perspectives on the problem at hand. This deeper understanding helps build a strong foundation for informed decision-making in real-world situations.
**Conclusion**
In summary, the Socratic method can be employed effectively in real-world problem-solving situations, such as in business contexts. By stimulating critical thinking and fostering collaboration, the method enables individuals and teams to generate, evaluate, and refine solutions in pursuit of a shared goal. Furthermore, the method nurtures better understanding of complex issues, ultimately enhancing the decision-making process in real-world contexts.