As the business landscape becomes increasingly competitive and dynamic, the adoption of comprehensive strategies for maintaining quality and efficiency is crucial for organizational success. With the rise of consumer awareness and the demand for high-standard products and services, Total Quality Management (TQM) has emerged as a pivotal approach for achieving excellence in all facets of corporate operations.
This article endeavors to delve into the intricacies of TQM, exploring its historical context, principles, processes, benefits, and challenges, alongside real-world applications that underscore its significance. By harnessing the expert perspective reminiscent of W. Edwards Deming, this discussion will guide readers, especially business professionals and enthusiasts, to appreciate TQM as not merely a methodology, but as a strategic alignment towards persistent improvement and customer satisfaction.
Introduction to Total Quality Management (TQM)
Definition of Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management, a term that has become integral to corporate lexicons, is a management approach centered on the premise that the maintenance of quality within an organization is not solely the responsibility of a designated quality department, but of every individual associated with the establishment.
Strategies For Achieving Total Quality Management İn Corporate Hr
Principles Of Management Key Features For Effective Leadership
TQM postulates that long-term success is achieved through customer satisfaction and that all members of an organization should participate in ongoing quality improvement efforts. By cataloging and attempting to enhance every segment that could lead to higher standards and productivity, TQM underlines a holistic commitment to quality that is ingrained in the organization's culture.
Importance and relevance of TQM in modern business environment
The contemporary business environment is characterized by rapid technological advancements, volatile consumer behaviors, and the constant impetus for innovation. In this fast-paced arena, TQM represents a valuable asset. It not only helps to ascertain product and service excellence but also propagates a culture of systematic and continuous refinement across all sectors of an enterprise.
Increased globalization has further enhanced its relevance, as organizations must now uphold quality standards that satisfy the international market by integrating and respecting diverse viewpoints and methodologies within their management practices. Therefore, TQM is not just a set of guidelines but a strategic orientation towards operational resilience and Prosperity.
History and Evolution of Total Quality Management
Tracing the origins of Total Quality Management: The genealogy of TQM can be traced back to the post-World War II era when quality control techniques were paramount in the industrial manufacturing sector. Initially focused on statistical quality control, TQM has evolved from mere product inspection to an extensive quality management system. The emphasis on a comprehensive approach to quality was strongly influenced by the works of quality pioneers such as Deming, Juran, and Crosby, whose theories and practices form the bedrock of modern-day TQM principles.
Major contributors and milestones in the development of TQM: Significant contributors to the development and diffusion of TQM include W. Edwards Deming, whose philosophy revolutionized quality management in Japanese manufacturing and subsequently worldwide. His paradigm of Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) is a cornerstone in TQM methodologies, exemplifying the cycle of continuous improvement. Joseph M. Juran's emphasis on managerial aspects, which constitute the Juran Trilogy—planning, control, and improvement—further cultivated TQM's foundation. In their unique ways, these thought leaders ushered in a systemic and proactive quality environment within organizations across the globe.
Modern understanding and application of TQM: Today, TQM has transcended beyond the confines of manufacturing and is ubiquitously applied across various sectors, including services, healthcare, and education. Modern applications of TQM integrate technology and data analytics, providing a comprehensive platform for organizations to not only monitor but also predict quality issues before they arise. The fusion of traditional TQM frameworks with cutting-edge tools like Six Sigma and Lean Management has enriched the efficacy of TQM implementations, making them more adaptable to the evolving needs of contemporary markets.
Fundamental Principles of Total Quality Management
Detailed overview of TQM principles
The principles of Total Quality Management act as the compass for organizations on their journey towards quality enhancement. These principles include a customer-focused approach, where client satisfaction sits at the pinnacle of all strategic decisions; the cultivation of leadership that fosters a unifying purpose; and the engagement of employees at all levels, encouraging their participation and ownership in quality-oriented processes.
Explanation and analysis of each principle
Each TQM principle holds a specific purpose that, when synergistically applied, leads to a robust quality culture within an organization. Customer focus ensures that the products and services rendered closely align with consumer needs, driving loyalty and repeat business. Leadership's role in TQM is pivotal as it sets the tone for a supportive and collaborative work environment.
Employee engagement leverages varied insights and expertise, fostering innovation and establishing a proactive stance towards quality issues while promoting a sense of belonging and purpose within the team.
Relevance and implication of these principles in a business setup
The implications of these TQM principles within a business context are far-reaching. By adhering to these fundamental tenets, organizations can maintain consistent quality levels, improve efficiencies, and promote a sense of continuous improvement. This approach not only serves the immediate interests of the business, such as cost savings and market competitiveness but also contributes significantly to building a durable brand reputation. Furthermore, it arms businesses with the adaptive agility required to navigate the complex interconnections of the modern economic ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
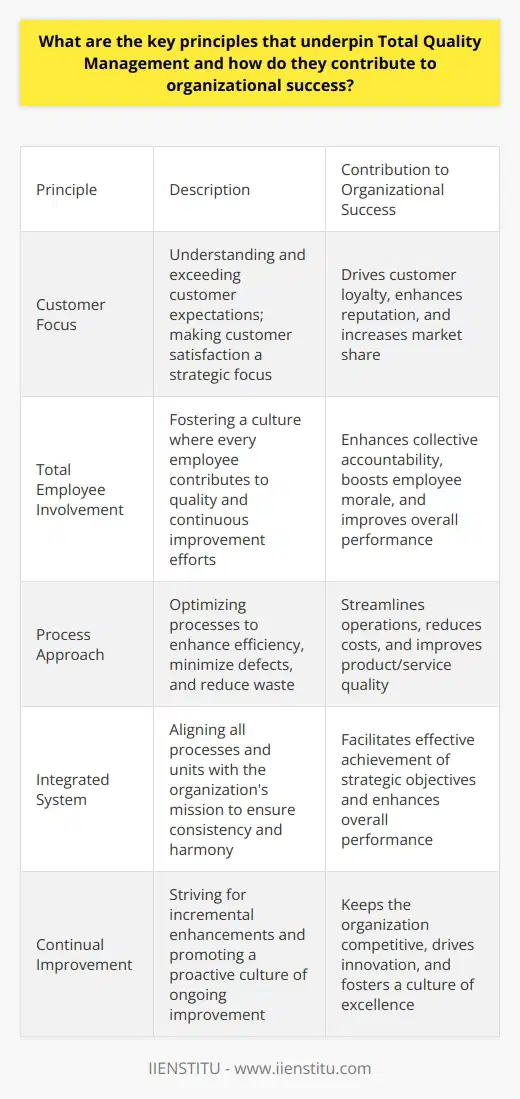
What are the key principles that underpin Total Quality Management and how do they contribute to organizational success?
Key Principles of Total Quality Management
Customer Focus
Organizations thrive on satisfied customers. Total Quality Management (TQM) hinges on understanding customer needs. It aims to exceed customer expectations. Meeting client demands becomes a strategic focus. Every business decision derives from customer-centric insights.
Total Employee Involvement
Success requires the commitment of all employees. TQM fosters a culture where every employee contributes. Employees at every level bear responsibility for quality. They participate in continuous improvement efforts. This inclusive approach drives collective accountability.
Process Approach
TQM views an organization as a collection of processes. It emphasizes the importance of optimizing these processes. Streamlining operations enhances efficiency. Emphasizing quality at each stage minimizes defects. This systematic approach prevents errors and reduces waste.
Integrated System
All processes and units must align with the organization's mission. TQM insists on an integrated system approach. This ensures consistency and harmony across the business. It helps in achieving strategic objectives more effectively.
Strategic and Systematic Approach
TQM requires a well-defined strategic plan. Strategic planning guides quality initiatives. It aligns quality goals with business objectives. This alignment ensures a systematic pursuit of improvement.
Continual Improvement
Continuous improvement is the cornerstone of TQM. Organizations must strive for incremental enhancements. Kaizen represents this philosophy of ongoing improvement. It promotes a proactive culture. And it keeps the business competitive.
Fact-Based Decision Making
Decisions must rely on data and analysis. TQM encourages evidence-based management. Organizations benefit from informed decision-making. It reduces uncertainty and guides strategic choices.
Communications
Effective communication is vital for TQM success. It ensures transparent knowledge sharing. Communication fosters strong relationships among stakeholders. It keeps everyone informed and engaged.
Recognition
Recognizing achievements motivates employees. TQM includes systems for acknowledging efforts. This encourages a culture of quality and continuous enhancement.
These principles contribute significantly to organizational success.
Customer focus ensures a loyal client base.
Total employee involvement optimizes workforce capabilities.
The process approach streamlines output quality.
An integrated system aligns all operations.
A strategic approach sets clear quality expectations.
Continual improvement keeps the organization agile.
Fact-based decisions enhance operational effectiveness.
Strong communication ensures consistency and clarity.
Recognition fosters a positive and committed workforce.
By adhering to these principles, organizations can achieve superior quality. Such quality drives competitive advantage. It unlocks higher profitability and market share gains. TQM thus forms an essential strategy for thriving in today's business landscape.
In the context of Total Quality Management, how should organizations approach continuous improvement and its role in strategic success?
Total Quality Management and Continuous Improvement
Total Quality Management, or TQM, stands as a cornerstone in the pursuit of strategic success for organizations. It demands a consistent commitment to quality in every organizational aspect. Continuous improvement functions as the lifeblood of TQM. It propels organizations to strive for operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Embracing an Improvement Culture
Organizations must foster a culture that embraces improvement. This culture should instill an unwavering persistence in enhancing processes, products, and services. Stakeholders at all levels need to commit to this ethos. They should consider quality a shared responsibility, not just a departmental task.
Principles for Effective Continuous Improvement
To navigate the journey of continuous improvement, organizations should:
Establish clear objectives: Without clear goals, direction lacks. Teams flounder.
Encourage employee involvement: Empowered employees innovate and improve processes.
Provide training and resources: These enable staff to effectively contribute to improvement efforts.
Implement a systematic approach: For example, Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) can structure improvement activities.
Use data to guide decisions: Measurable results highlight problems and track progress.
Every function within the organization must align with the continuous improvement philosophy. This alignment ensures that the strategic objectives integrate fully with quality initiatives.
Measuring Progress
Quantifiable metrics help organizations to gauge improvement efforts. Regular audits and assessments maintain accountability. They also foster a results-oriented culture necessary for sustained excellence.
Continuous Improvement and Strategy
At the strategic level, continuous improvement influences long-term planning. Organizations must adapt their strategies to respond to market demands and technological advances. Continuous improvement provides the framework to respond effectively.
The Role of Leadership
Leaders play a crucial role in championing continuous improvement. They must communicate its importance and ensure it permeates organizational values. This leadership commitment inspires a quality mindset throughout the workforce.
Customer Focus
Organizations should listen attentively to customer feedback. It serves as a vital input for continuous improvement processes. Aligning improvements with customer needs guarantees that quality enhancements resonate with the market.
Conclusion
Continuous improvement in TQM is more than just a principle. It is an operational imperative that drives strategic success. By embedding quality into the fabric of organizational culture, entities can not only meet but exceed the expectations of customers and stakeholders alike. Thus, continuous improvement stands not as an option but as a strategic necessity in the pursuit of excellence.

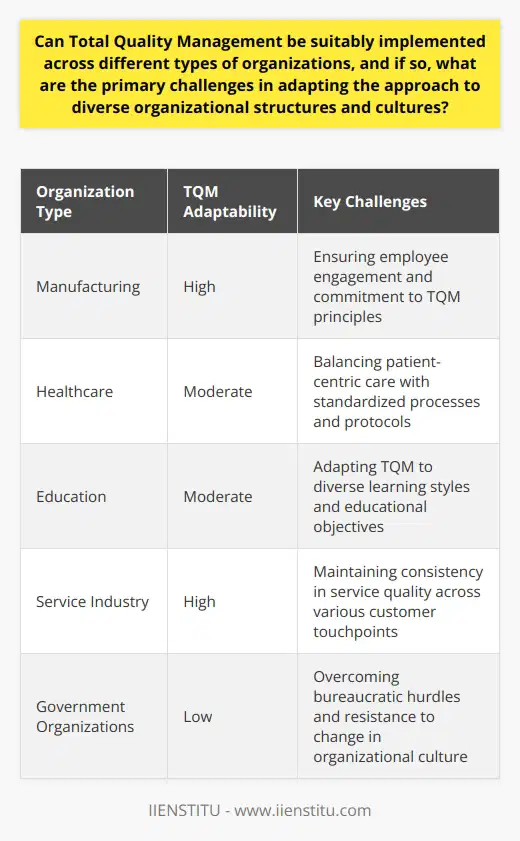
Can Total Quality Management be suitably implemented across different types of organizations, and if so, what are the primary challenges in adapting the approach to diverse organizational structures and cultures?
Understanding Total Quality Management
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive approach. It focuses on long-term success. This success comes through customer satisfaction. In TQM, all members of an organization participate. They improve processes, products, services, and the culture.
TQM Across Different Organizations
TQM can adapt to various organizations. It suits manufacturing, healthcare, education, and more. Its principles are universal. However, the adaptability does not assure easy implementation.
Challenges in Adaptation
Culture and Structure Variations pose challenges for TQM implementation. Each organization has unique cultural nuances. Structures differ vastly.
The hierarchy plays a role.
As does the existing quality culture.
Employee willingness to change matters.
Communication Patterns affect TQM success. Effective communication is crucial. It facilitates collaboration. It enables process improvements. Diverse organizations have unique communication channels.
Leadership Commitment is another determinant. Leaders must support TQM. They should allocate resources. They also need to champion the TQM initiative.
Adapting TQM
To adapt TQM:
Understand organizational culture.
Align TQM with strategic objectives.
Tailor TQM practices to specific needs.
In training, context is key. Customized training helps. It addresses unique organizational challenges.
Employee involvement varies. So does commitment across different organizations. Engaging employees at all levels is a must. They need to understand the benefits. They must see how TQM affects their roles.
Feedback mechanisms are essential. They track progress. They also identify areas for improvement. Feedback should be prompt. It should also be constructive.
Resource allocation needs careful planning. TQM is resource-intensive. It needs time, money, and people. Appropriate resources at the right time are critical for success.
Continuous improvement is a TQM cornerstone. Processes evolve. So should TQM approaches. Adaptation is not a one-time effort. It is continuous.
Conclusion
TQM can spread across various organizations. Yet, challenges in adaptation do arise. Culture, structure, and commitment level play huge roles. Adapting TQM requires understanding. It demands a tailored approach. Success lies in continuous improvement and adaptability. Support from leaders and engagement from employees is crucial. And so is the right allocation of resources. TQM, when carefully adapted, can indeed lead to excellence across diverse organizational landscapes.