I remember the first time I heard about Total Quality Management (TQM). It was during a casual coffee break with a colleague who had just returned from a workshop. She was animatedly explaining how TQM had transformed her previous workplace, leading to happier employees and more satisfied customers. Her enthusiasm was contagious, and it piqued my interest in how TQM could be a game-changer in the corporate HR landscape.
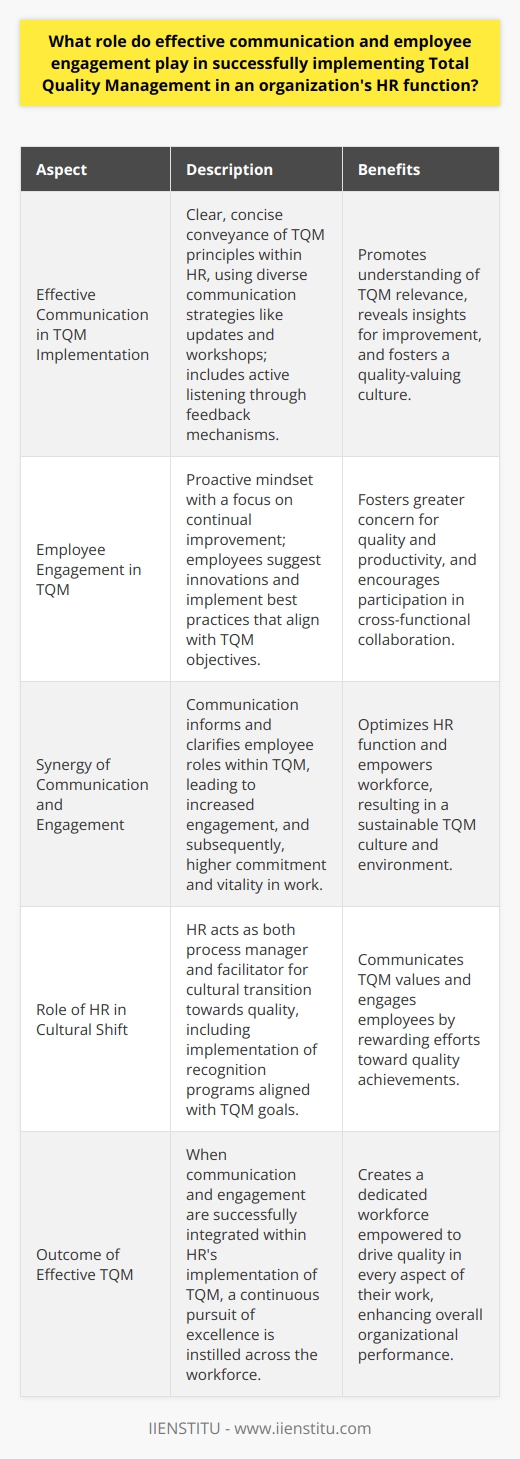
The Benefits of TQM
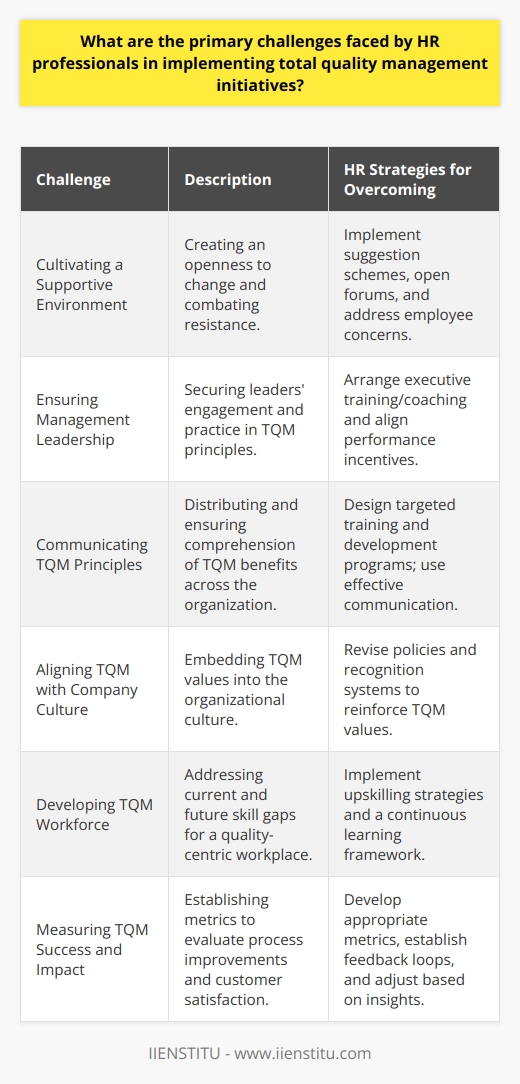
Challenges of Implementing TQM
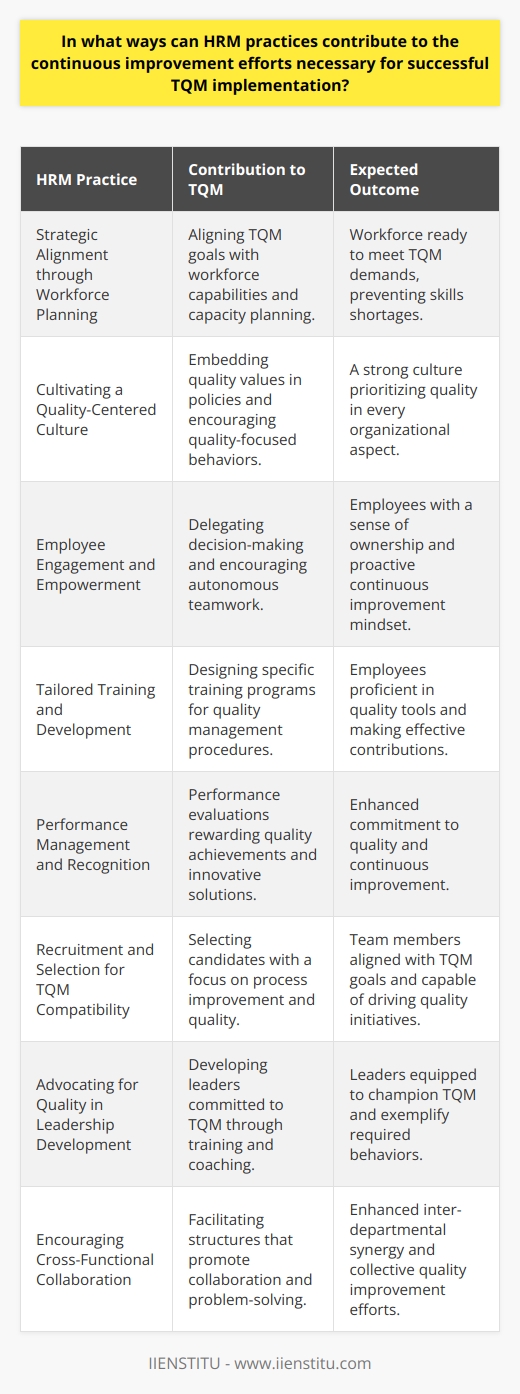
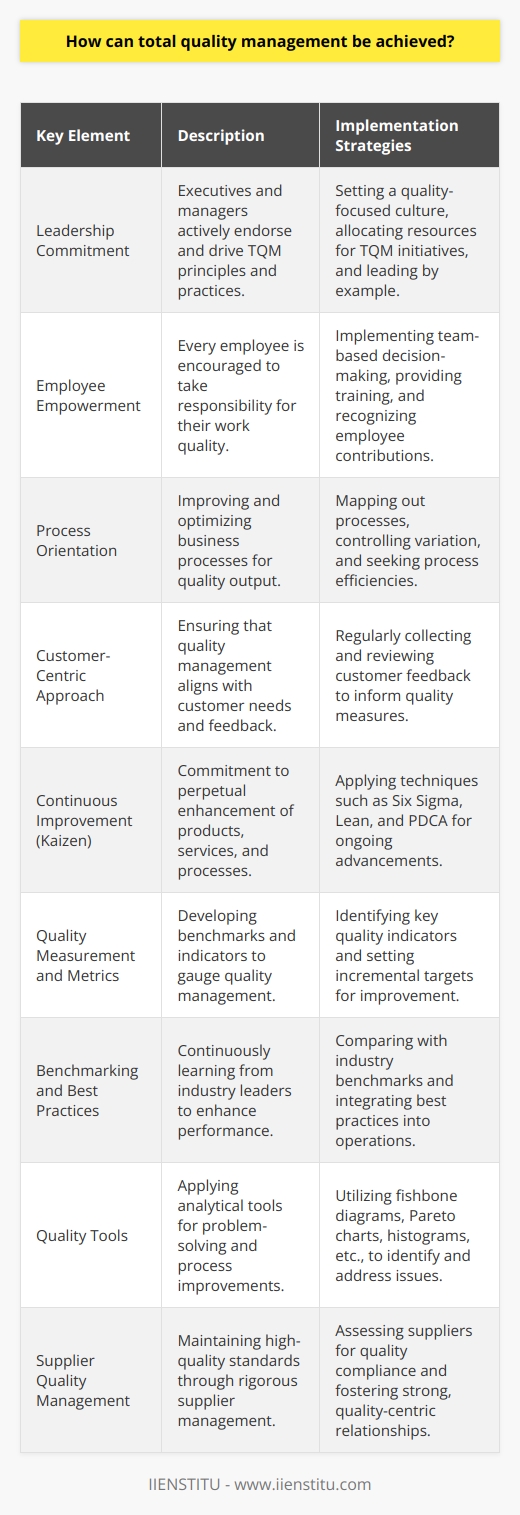
Strategies for Achieving TQM
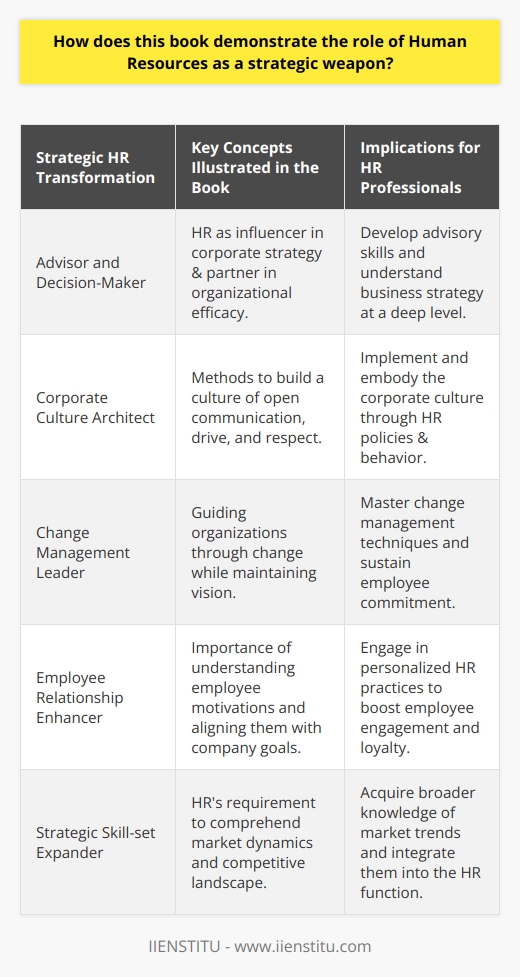
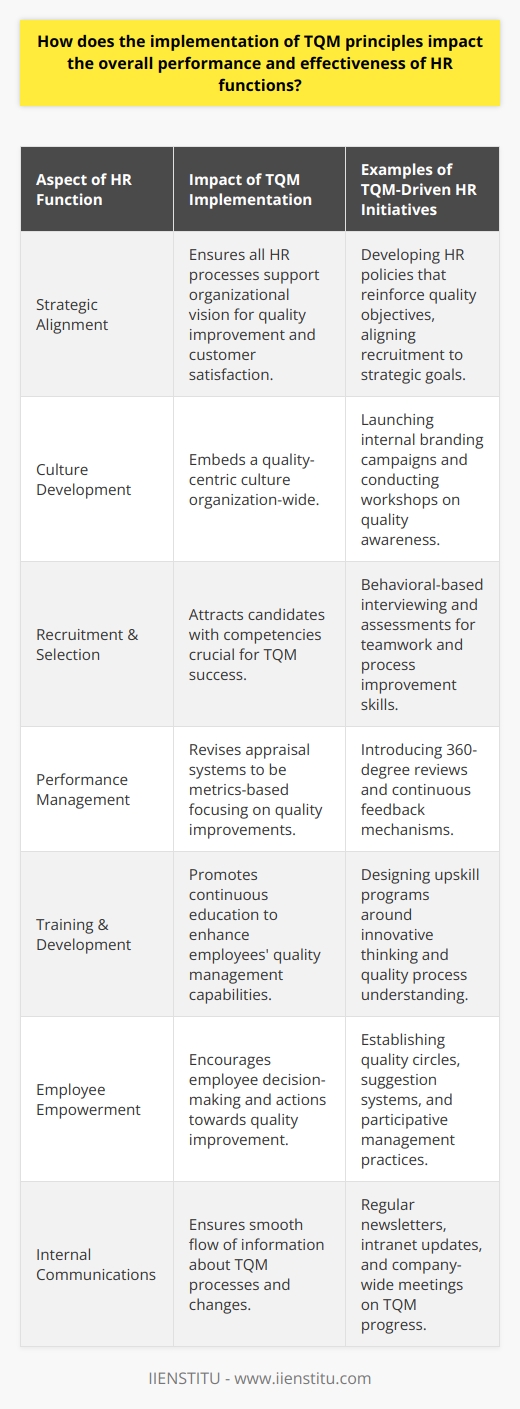
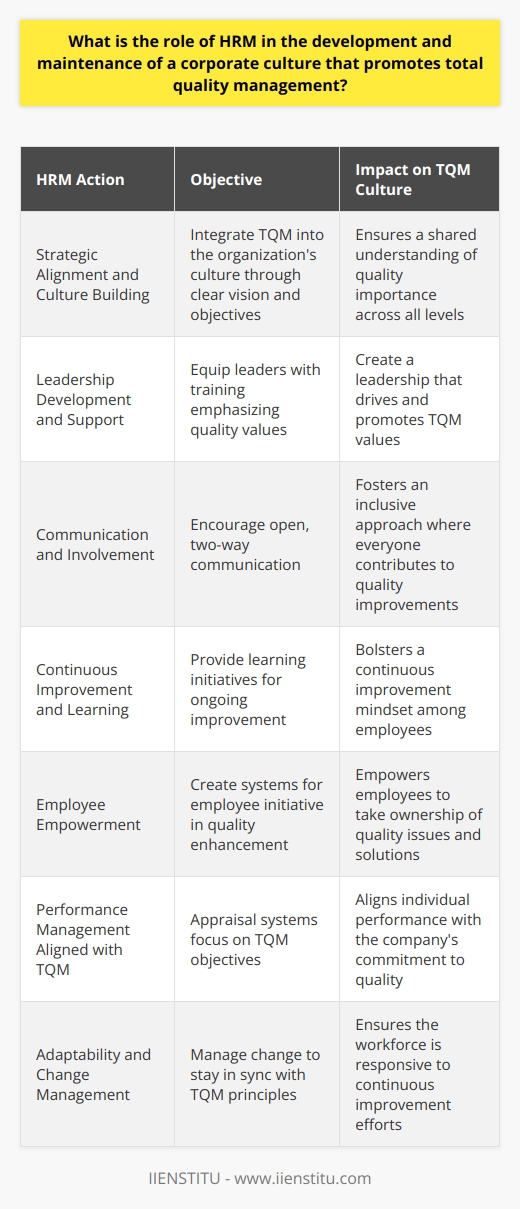
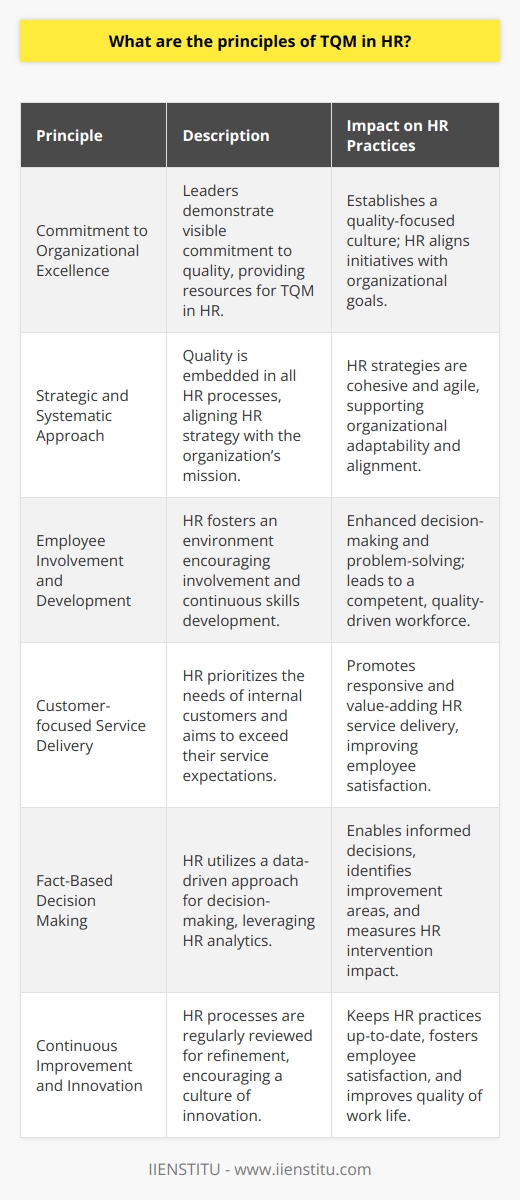
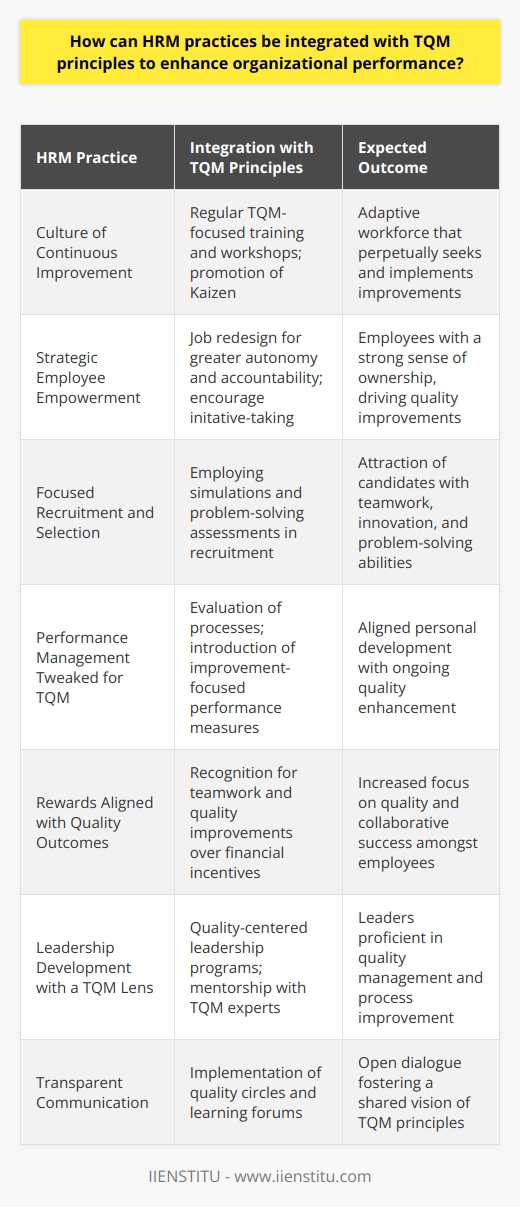
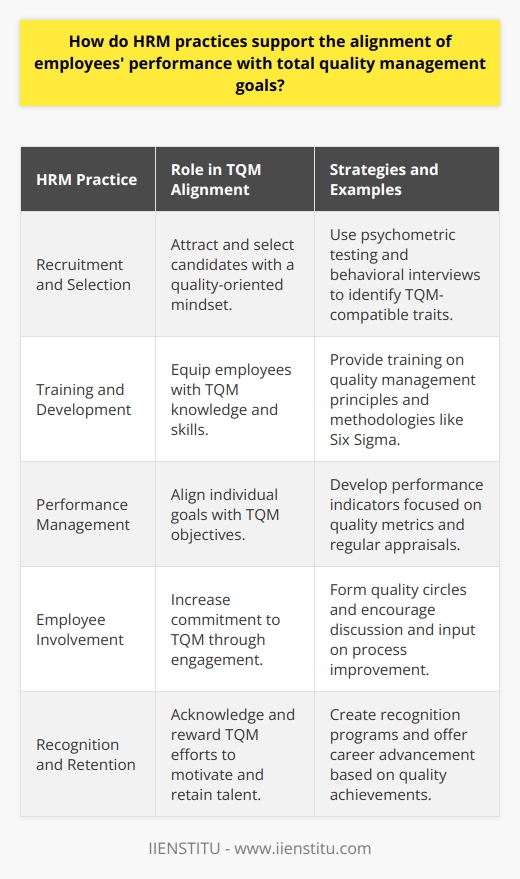
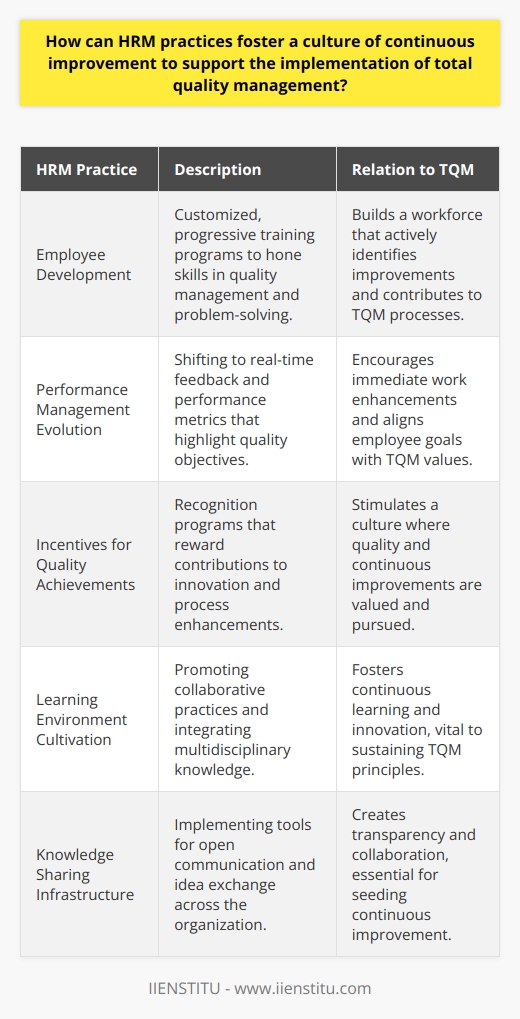
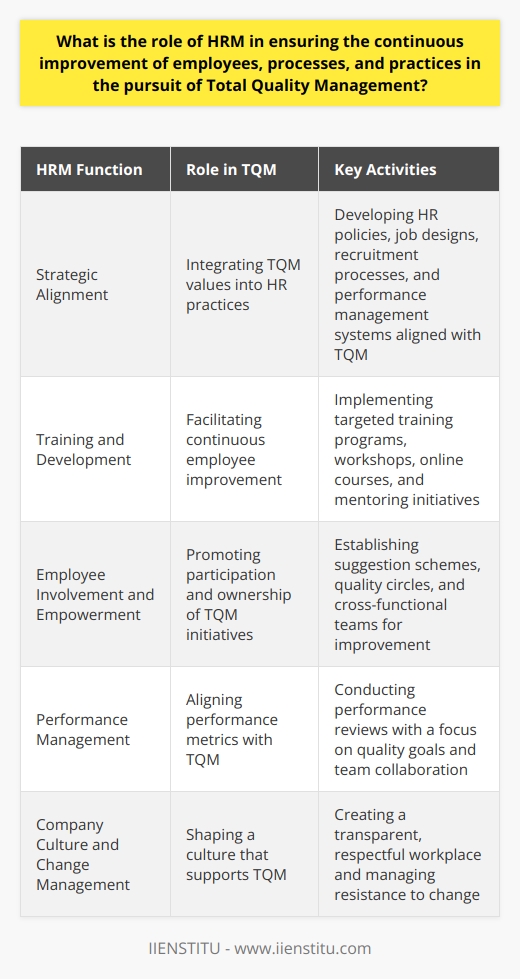
Embracing Total Quality Management in HR
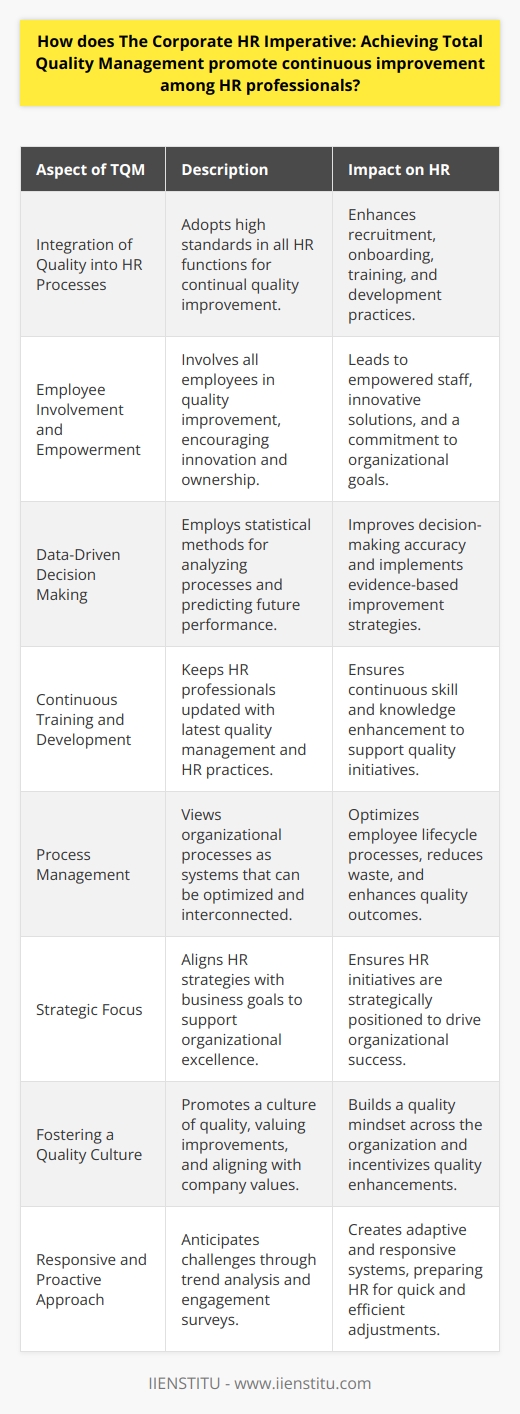
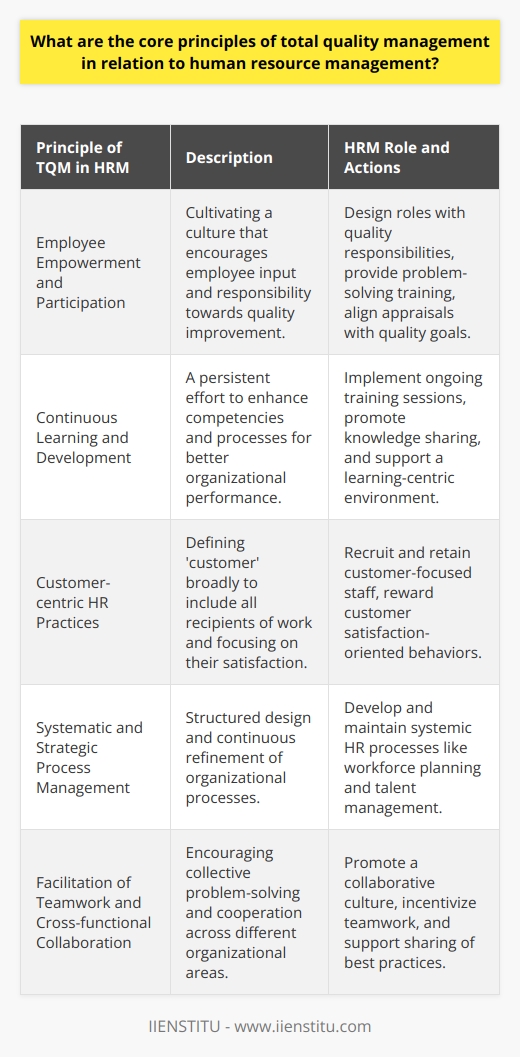
Implementing TQM isn't just about processes and procedures; it's about fostering a culture of excellence. It's about everyone in the organization, from the CEO to front-line employees, committing to continuous improvement. Total Quality Management is more than a buzzword—it's a philosophy that, when embraced, can transform the very fabric of an organization.
The Heart of TQM: Employee Empowerment
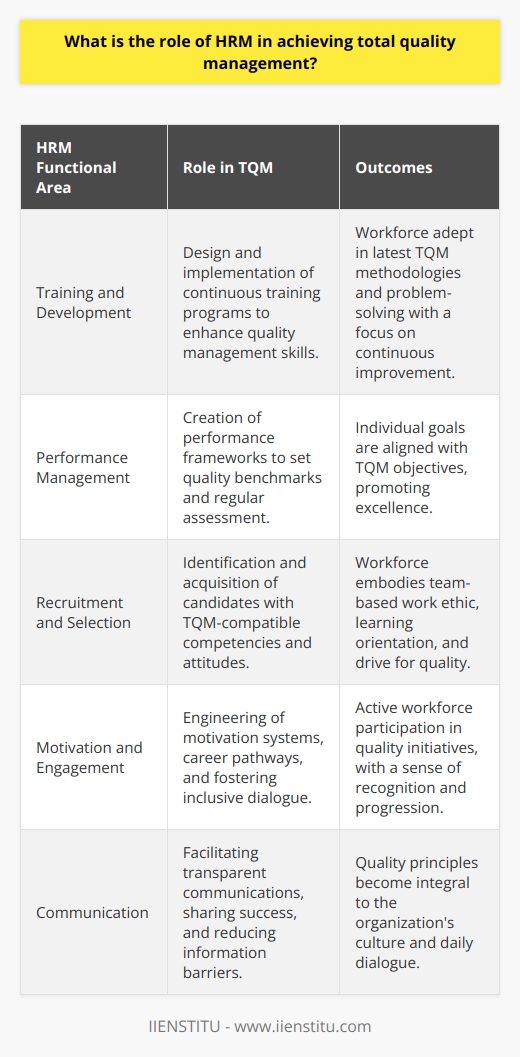
One of the core benefits of TQM is increased employee productivity. When employees feel valued and see that their well-being and development are prioritized, they're naturally more motivated. I once worked with a team where TQM principles were woven into our daily routines. We weren't just doing our jobs; we were actively seeking ways to improve our processes. This proactive approach led to:
Higher job satisfaction among team members.
Reduced turnover rates, saving the company recruitment costs.
Enhanced collaboration, as everyone was encouraged to share ideas.
The Ripple Effect on Organizational Effectiveness
An organization practicing TQM doesn't just improve internally; it becomes more effective as a whole. According to Juran's Quality Handbook (Juran, J.M., 1998), organizations that implement TQM see tangible benefits such as:
1- Improved customer satisfaction, resulting from higher quality products and services.
2- Cost reductions through more efficient processes and less waste.
3- Enhanced market reputation, which can lead to increased market share.
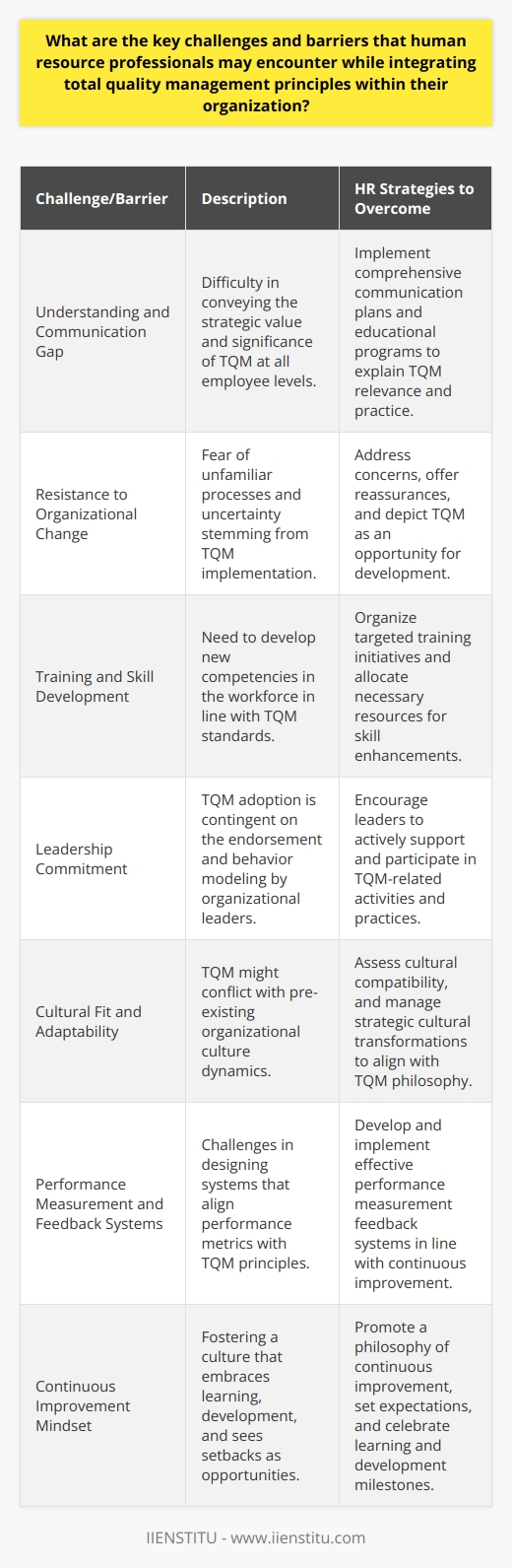
Overcoming the Challenges of Implementing TQM
As with any significant change, implementing TQM isn't without its hurdles. Aligning corporate culture with TQM practices can be like turning a massive ship—it requires time, patience, and a clear direction.
Transforming Attitudes Across the Board
One of the biggest challenges is transforming the attitudes of all stakeholders. When I was part of a TQM implementation team, we faced resistance from some long-time employees who were set in their ways. They saw TQM as just another management fad. To address this, we:
Held open forums where employees could voice concerns.
Total Quality Management is the key to unlocking the HR potential of any corporate organization.
Shared success stories from other departments to show real-world benefits.
Provided ongoing support and training to ease the transition.
Resourcing for Change
Another significant challenge is ensuring the organization is adequately resourced for change. TQM requires investment—not just financially, but also in terms of time and effort. It's essential to have the right tools, training programs, and support systems in place.
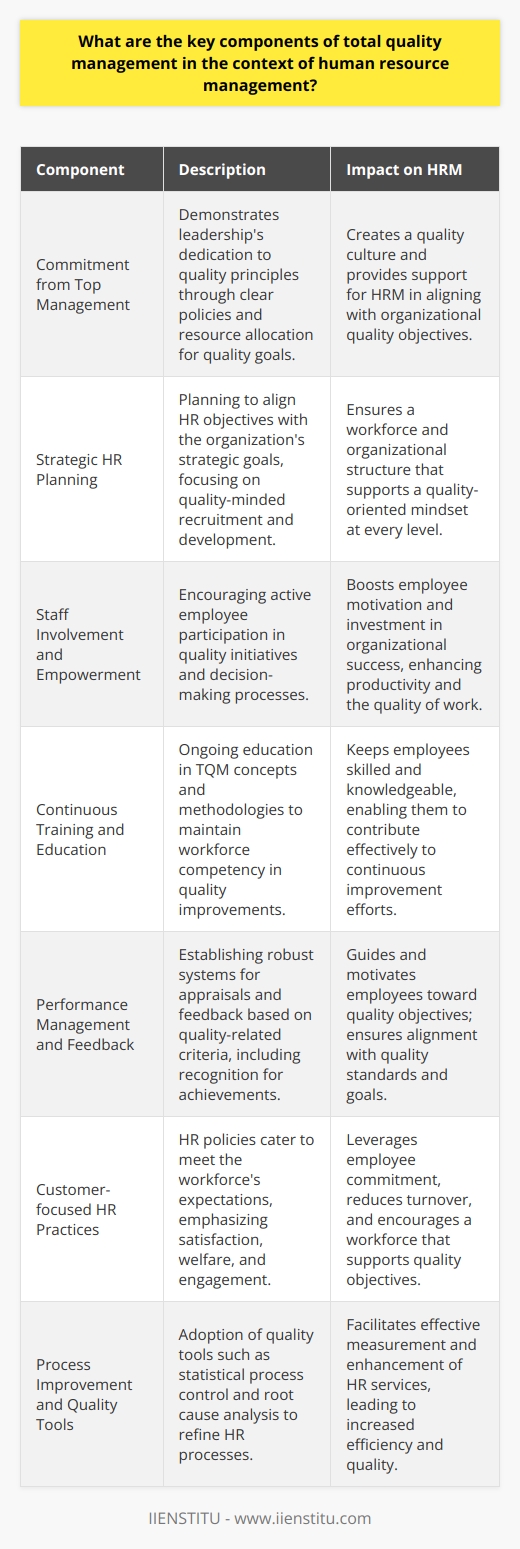
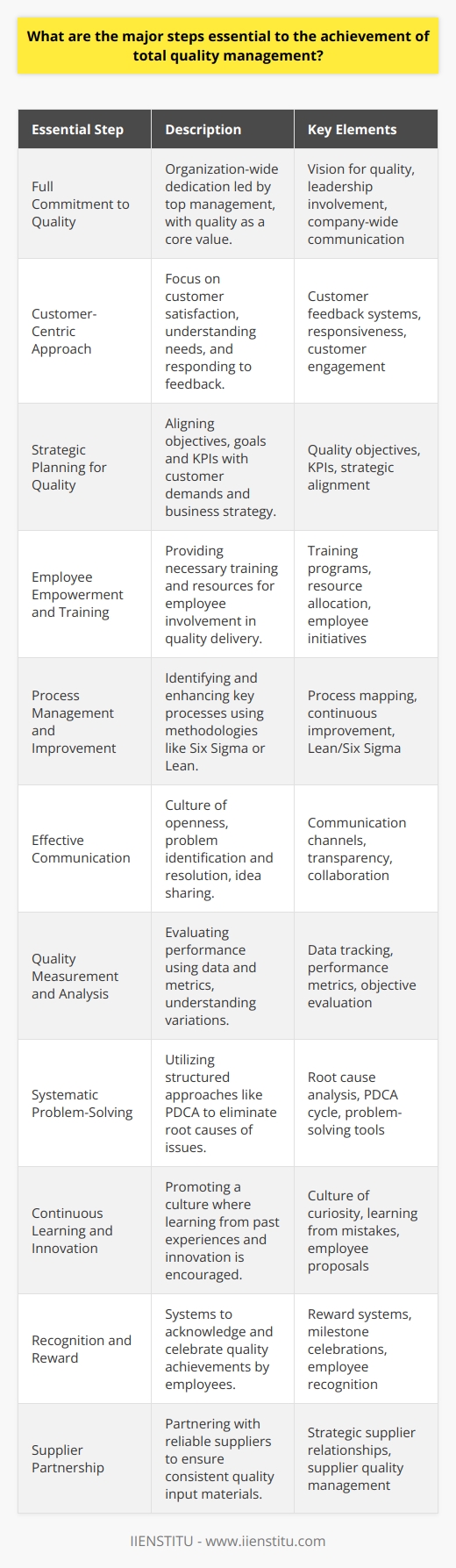
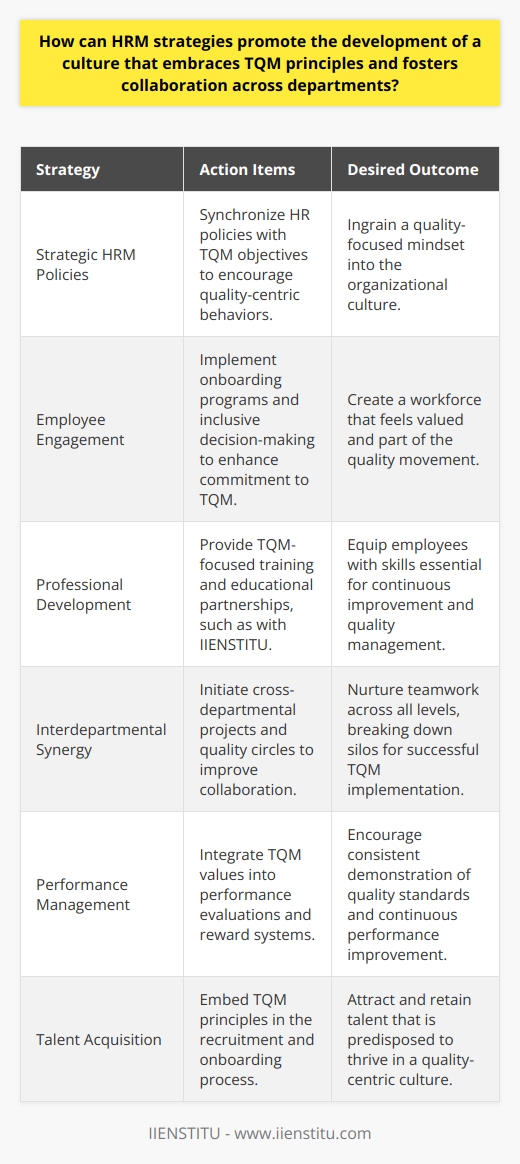
Strategies for Achieving Total Quality Management
So, how does an organization successfully navigate these challenges and achieve TQM? It boils down to intentional strategies and consistent efforts.
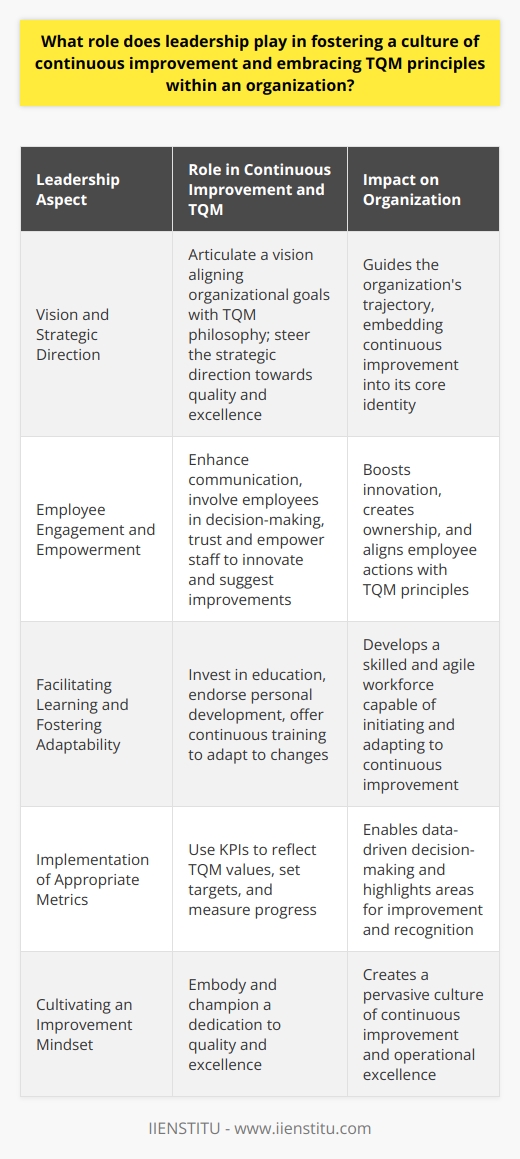
Purposeful Leadership: Setting the Tone from the Top
Leadership plays a pivotal role in TQM implementation. Leaders must model the behaviors and attitudes they wish to see throughout the organization. This means:
1- Communicating the vision clearly and consistently.
2- Demonstrating commitment by allocating resources and time.
3- Recognizing and rewarding efforts and achievements in quality improvements.
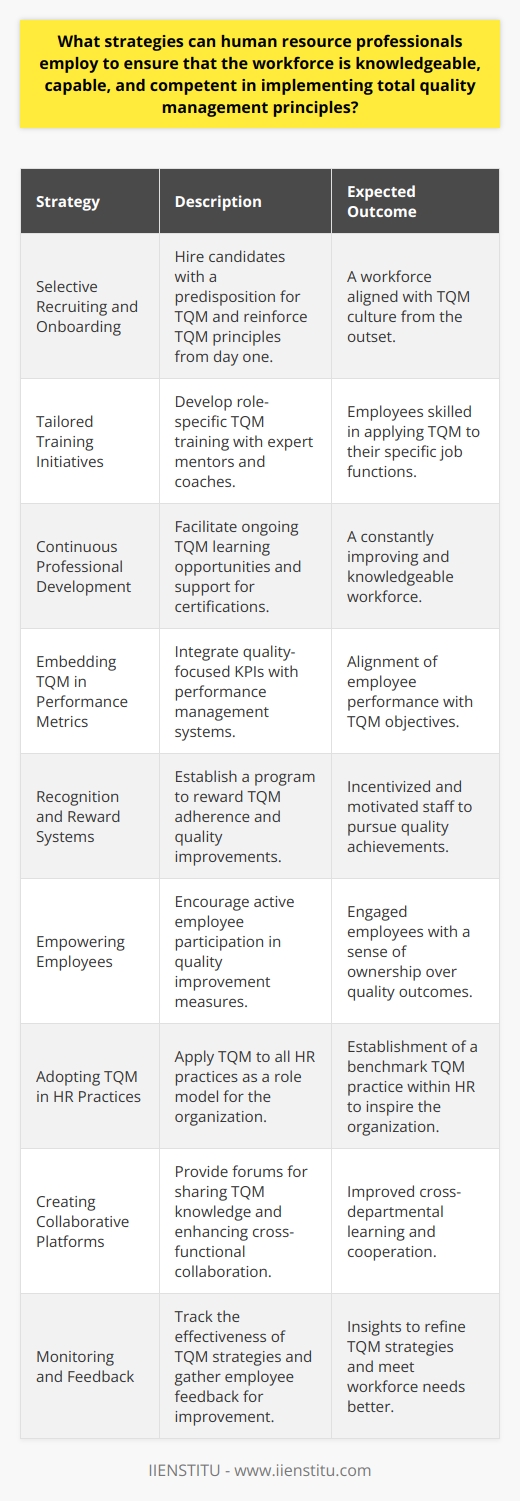
Empowering Through Training and Development
Employees need to understand not just the "what" but the "why" behind TQM. Adequate training and development are crucial. In my experience, the most effective training programs:
Are interactive, allowing employees to engage with the material actively.
Provide practical examples relevant to their specific roles.
Encourage continuous learning, not just one-off sessions.
Cultivating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
TQM isn't a one-time project; it's an ongoing commitment. Organizations must cultivate a culture where continuous improvement is the norm. This can be achieved by:
Implementing suggestion programs where employees can contribute ideas.
Conducting regular assessments to identify areas for improvement.
Celebrating small wins, reinforcing the value of ongoing efforts.
The Unexpected Link: Reassignment Request Letter Tips and Information
You might wonder how TQM relates to something like reassignment request letter tips and information. Well, in a TQM-driven organization, processes—even those related to HR requests—are continuously improved for efficiency and employee satisfaction. For instance, improving the process of submitting reassignment requests can:
Reduce processing time, leading to quicker responses.
Enhance employee satisfaction, as they feel heard and valued.
Streamline HR operations, making them more effective.
This attention to detail and commitment to quality in every aspect of the organization is what sets TQM apart.
Personal Reflections on TQM's Impact
Looking back, adopting TQM philosophies had a profound impact on my professional life. I recall a time when our department was struggling with project deadlines and quality issues. By applying TQM principles, we:
Identified bottlenecks in our processes.
Implemented standard operating procedures to ensure consistency.
Fostered a team environment where everyone felt responsible for the outcome.
The result? We not only met our deadlines but also received commendations for the quality of our work. It was a turning point that showcased the power of TQM in action.
Conclusion: Unlocking HR Potential Through TQM
In wrapping up, Total Quality Management isn't just about improving products or services—it's about unlocking the full potential of an organization's human resources. By aligning HR practices with TQM principles, companies can:
1- Boost employee productivity and satisfaction.
2- Enhance organizational effectiveness, leading to better business outcomes.
3- Navigate challenges by fostering a culture open to change.
Taking the steps necessary to achieve TQM can transform an organization into an effective and successful institution. It's about making quality a way of life, not just a set of guidelines.
References
Deming, W. Edwards. Out of the Crisis. MIT Press, 1986.
Juran, J.M. Juran's Quality Handbook. McGraw-Hill, 1998.
Ishikawa, Kaoru. What Is Total Quality Control? The Japanese Way. Prentice Hall, 1985.
Note: The journey to TQM may be challenging, but the rewards are well worth the effort. Just as my colleague's enthusiasm sparked my interest, I hope this exploration inspires you to consider how TQM can benefit your organization.