In the symphony of modern business, supply chain management plays a crucial role in orchestrating the flow of goods, services, and information from source to consumer. It is the backbone of any product-based enterprise, weaving together suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and customers into a complex tapestry of commerce. At the heart of this intricate process lies supply chain modeling, a powerful tool that enables organizations to analyze, predict, and optimize their logistical operations. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the essentials of supply chain modeling, offering insights that are both in-depth and accessible for businesses striving to achieve operational excellence.
Understanding Supply Chain Modeling
Distribution Requirements Planning İmplementation Strategies
Optimization Of Multi-modal Transport İn Global Supply Chains
Definition and Explanation
Definition and Explanation
The supply chain is the lifeblood of any product-based business, a network weaving together suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and customers into a tapestry of commerce. Supply chain modeling, then, is the art of replicating this complex web in a conceptual or digital form, which allows organizations to analyze, predict, and enhance their logistical operations. It is a set of methods and tools designed to represent the supply chain's multiple layers and interconnections, transforming raw data into actionable insight.
Importance of Supply Chain Modeling
Identifying the core components that shape the effectiveness of a supply chain is not just good practice—it is a vital maneuver in a world ruled by efficiency and rapidity. The role of supply chain modeling in businesses of the modern age extends beyond mere mapping; it is an engine that drives decisions, reduces costs, and maximizes profitability. Through its predictive prowess, businesses gain foresight into potential disturbances and opportunities, laying the groundwork for preemptive action and strategic advantage.
Supply chain modeling is the art of replicating the complex network of a supply chain in a conceptual or digital form. It involves creating a representation of the supply chain's multiple layers and interconnections, allowing organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights. By modeling their supply chains, businesses can gain a holistic view of their operations, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions to improve efficiency and profitability.
Discussion on the Different Types of Supply Chain Models
Supply chain models come in several forms, each with its own focal point and purpose. Descriptive Modeling provides a snapshot of the supply chain's current state, offering a detailed view of its components and operations. Predictive Modeling, by contrast, leverages historical data to forecast future trends and outcomes, allowing for anticipatory adjustments. Lastly, Prescriptive Modeling advises on the best courses of action by analyzing the outcomes of various decisions, taking into account constraints and objectives.
Examples and Use Cases for Each Type of Model
Descriptive models are frequently employed to track inventory levels, monitor delivery status, and map supplier relationships. For example, a retailer might use a descriptive model to understand seasonal inventory fluctuations. Predictive models are integral for demand forecasting or assessing the impact of market changes, such as a manufacturing company predicting raw material needs based on sales trends. Prescriptive modeling finds its application in scenarios where optimization is key, perhaps in determining the best distribution routes to minimize shipping times and costs.
Step-wise Explanation of the Process
The genesis of effective supply chain modeling begins with meticulous Data Collection and Validation, ensuring that subsequent steps are built on a foundation of accuracy. Model Formulation is next, where the actual structure of the model is crafted, tailored to the complexities and nuances of the organization's supply chain. This then leads to Model Calibration and Validation, testing assumptions and fine-tuning to reflect reality as closely as possible. Finally, Implementation and Monitoring is where theory meets practice, and the model's efficacy is continuously assessed.
Best Practices in Model Creation and Implementation
Exceptional logistics management courses and certificate courses online stress the irrefutable significance of robust data quality and model precision. A model is only as good as the data feeding it, emphasizing the frequent updates necessary to keep the representation accurate. Additionally, the utilization of sophisticated software and modeling tools can remarkably streamline the process, supplying an agility and precision to decision-making that manual methods cannot match.
Case Study of a Firm that Effectively Used Supply Chain Modeling
Consider the case of a multinational electronics corporation that embraced supply chain modeling to navigate the tumultuous waters of global trade disruptions. By adopting a predictive modeling approach, the company was able to forecast demand surges in various markets and reallocate their manufacturing resources accordingly, preventing stockouts and sustaining customer satisfaction.
Lessons Learned and How Businesses Can Learn from It
This example underscores the transformative power of adept supply chain modeling. Organizations should take cues from such success stories, considering the integration of advanced models into their strategic planning not as an option but as a necessity to maintain competitive edge and operational resilience.
Identification of Possible Challenges in Implementing Supply Chain Modeling
While the benefits are plentiful, supply chain modeling is not without its hurdles. Companies may struggle with insufficient data quality, a lack of skilled analysts, or the enormity of integrating complex modeling systems with their existing operations. The dynamic and unpredictable nature of global markets further complicates the modeling.
Potential Solutions and Strategies to Overcome these Challenges
Proactive education through logistics management courses, disciplined data governance, and strategic partnerships can equip teams with the expertise and tools needed to leverage supply chain modeling successfully. Additionally, implementing scalable solutions and fostering a culture of continuous improvement will assist organizations in navigating these challenges.
Discussion on Emerging Trends and Technologies Influencing Supply Chain Modeling
With the continuous advancement of technology, the landscape of supply chain modeling is rapidly evolving. The infusion of Artificial Intelligence is already displaying its potential in enhancing predictive capabilities and decision-making processes. Meanwhile, the influx of Big Data Analytics is revolutionizing how companies handle and interpret the vast sea of information available to them.
As Chopra and Meindl explain in their book Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation, "A supply chain model is a simplified representation of a supply chain that captures the essential features and behavior of the system" (Chopra & Meindl, 2016, p. 45). This simplified representation enables businesses to understand the dynamics of their supply chain and make data-driven decisions.
Importance of Supply Chain Modeling
In today's fast-paced and competitive business landscape, identifying the core components that shape the effectiveness of a supply chain is not just good practice—it is a vital maneuver. Supply chain modeling serves as a powerful engine that drives decisions, reduces costs, and maximizes profitability. By leveraging the predictive capabilities of supply chain models, businesses can anticipate potential disruptions and opportunities, allowing them to take preemptive actions and gain a strategic advantage.
According to a study published in the International Journal of Production Economics, "Supply chain modeling and simulation can help organizations to reduce costs, improve customer service, and increase responsiveness to market changes" (Jain et al., 2019, p. 283). The study highlights the significant benefits that businesses can reap by incorporating supply chain modeling into their operations.
Types of Supply Chain Models
Discussion on the Different Types of Supply Chain Models
Supply chain models come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose and focusing on different aspects of the supply chain. The three main types of supply chain models are:
1- Descriptive Modeling: This type of modeling provides a snapshot of the current state of the supply chain. It offers a detailed view of the supply chain's components and operations, allowing businesses to understand how their supply chain functions at a given point in time.
2- Predictive Modeling: Predictive modeling leverages historical data to forecast future trends and outcomes. By analyzing past patterns and behaviors, predictive models enable businesses to anticipate future demands, identify potential risks, and make proactive adjustments to their supply chain operations.
3- Prescriptive Modeling: Prescriptive modeling takes supply chain optimization to the next level by providing recommendations on the best courses of action. It analyzes the outcomes of various decisions, taking into account constraints and objectives, and suggests optimal strategies for improving supply chain performance.
Examples and Use Cases for Each Type of Model
Descriptive models are commonly used to track inventory levels, monitor delivery status, and map supplier relationships. For instance, a retailer might employ a descriptive model to understand seasonal inventory fluctuations and adjust their ordering patterns accordingly.
Predictive models are essential for demand forecasting and assessing the impact of market changes. A manufacturing company, for example, can use a predictive model to estimate future raw material requirements based on sales trends and market dynamics.
Prescriptive modeling finds its application in scenarios where optimization is paramount. For example, a logistics company can utilize prescriptive modeling to determine the most efficient distribution routes, minimizing shipping times and costs while maximizing customer satisfaction.
The Process of Supply Chain Modeling
Step-wise Explanation of the Process
Creating an effective supply chain model involves a systematic approach that encompasses the following steps:
1- Data Collection and Validation: The foundation of any supply chain model is accurate and reliable data. This step involves gathering relevant information from various sources, such as inventory records, sales data, and supplier information. It is crucial to validate the collected data to ensure its accuracy and integrity.
2- Model Formulation: Once the data is collected and validated, the next step is to formulate the supply chain model. This involves defining the model's scope, identifying the key variables and parameters, and determining the relationships between different components of the supply chain. The model should be tailored to the specific needs and complexities of the organization's supply chain.
3- Model Calibration and Validation: After formulating the model, it is essential to calibrate and validate it to ensure its accuracy and reliability. This step involves testing the model's assumptions, comparing its outputs with real-world data, and fine-tuning the model parameters to minimize discrepancies. Validation helps to build confidence in the model's predictive capabilities.
4- Implementation and Monitoring: The final step is to implement the supply chain model and integrate it into the organization's decision-making processes. It is important to establish a monitoring framework to track the model's performance over time. Regular monitoring enables businesses to identify any deviations from expected outcomes and make necessary adjustments to keep the model aligned with the dynamic nature of the supply chain.
Best Practices in Model Creation and Implementation
To create and implement effective supply chain models, businesses should adhere to the following best practices:
Ensure Data Quality: The accuracy and reliability of a supply chain model heavily depend on the quality of the input data. Businesses should invest in robust data collection and validation processes to ensure that the model is built on a solid foundation. Regular data updates are necessary to keep the model representative of the current state of the supply chain.
Leverage Advanced Modeling Tools: Utilizing sophisticated software and modeling tools can significantly streamline the modeling process and enhance the model's accuracy. These tools offer advanced capabilities such as simulation, optimization, and scenario analysis, enabling businesses to make informed decisions with greater agility and precision.
Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration: Supply chain modeling should not be a siloed effort. Effective model creation and implementation require close collaboration among various functions, including supply chain management, operations, finance, and information technology. Cross-functional teams bring diverse perspectives and expertise, leading to more comprehensive and realistic models.
Continuously Monitor and Refine: Supply chain models are not static entities. As the business environment evolves and new data becomes available, it is crucial to continuously monitor the model's performance and refine it accordingly. Regular model updates and calibration ensure that the model remains relevant and accurate in the face of changing market dynamics.
Case Study: The Use of Supply Chain Modeling in Real-world Scenarios
Case Study of a Firm that Effectively Used Supply Chain Modeling
To illustrate the practical application of supply chain modeling, let's consider the case of XYZ Corporation, a multinational electronics manufacturer. XYZ Corporation faced significant challenges in managing its global supply chain, including long lead times, inventory imbalances, and frequent stockouts. To address these issues, the company decided to implement a comprehensive supply chain modeling approach.
XYZ Corporation began by collecting and analyzing historical sales data, inventory records, and supplier information. They collaborated with a team of supply chain experts and data scientists to formulate a predictive model that could forecast demand patterns and identify potential risks. The model incorporated advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and simulation, to provide accurate and reliable predictions.
The company then used the insights generated by the model to optimize their inventory management strategies. They implemented a data-driven approach to determine optimal safety stock levels, reorder points, and replenishment frequencies. The model also helped XYZ Corporation to identify the most critical suppliers and develop contingency plans to mitigate potential disruptions.
By leveraging supply chain modeling, XYZ Corporation achieved significant improvements in their operations. They reduced inventory carrying costs by 20%, improved on-time delivery rates by 15%, and minimized stockouts by 30%. The company also gained greater visibility into their supply chain, enabling them to make proactive decisions and respond quickly to changing market conditions.
Lessons Learned and How Businesses Can Learn from It
The success story of XYZ Corporation highlights the transformative power of effective supply chain modeling. Businesses can learn valuable lessons from this case study:
1- Embrace Data-Driven Decision Making: Supply chain modeling enables businesses to make decisions based on data-driven insights rather than intuition or guesswork. By leveraging historical data and advanced analytics, companies can gain a deeper understanding of their supply chain dynamics and make informed decisions that drive operational excellence.
2- Foster Collaboration and Expertise: Implementing supply chain modeling requires a collaborative effort among various functions and stakeholders. Businesses should assemble cross-functional teams that bring together supply chain expertise, data science skills, and domain knowledge. Collaborating with external experts, such as consulting firms or academic institutions, can also provide valuable insights and best practices.
3- Continuously Monitor and Adapt: Supply chain modeling is not a one-time exercise. Businesses should establish a continuous monitoring and improvement process to ensure that their models remain accurate and relevant. Regular model updates, performance tracking, and scenario analysis are essential to adapt to the ever-changing business landscape.
4- Leverage Technology and Tools: Advanced modeling software and tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of supply chain modeling. Businesses should invest in the right technology infrastructure and tools that align with their specific needs and goals. Cloud-based solutions, simulation platforms, and optimization engines are some examples of tools that can streamline the modeling process and provide valuable insights.
Challenges in Supply Chain Modeling
Identification of Possible Challenges in Implementing Supply Chain Modeling
While the benefits of supply chain modeling are significant, businesses may face several challenges during the implementation process. Some of the common challenges include:
1- Data Quality and Availability: Accurate and reliable data is the foundation of effective supply chain modeling. However, many organizations struggle with poor data quality, inconsistent data formats, and incomplete information. Ensuring data integrity and availability across multiple systems and sources can be a daunting task.
2- Complexity and Dynamism: Supply chains are inherently complex and dynamic, with numerous variables and interdependencies. Capturing all the relevant factors and relationships in a model can be challenging, especially in the face of rapidly changing market conditions and supply chain disruptions.
3- Lack of Skilled Resources: Implementing supply chain modeling requires specialized skills and expertise in areas such as data analytics, modeling techniques, and supply chain management. Organizations may face difficulties in finding and retaining skilled resources who can effectively develop and maintain supply chain models.
4- Integration with Existing Systems: Supply chain models need to be integrated with existing enterprise systems, such as ERP, WMS, and TMS, to ensure seamless data flow and decision-making. Integrating disparate systems and ensuring data compatibility can be a complex and time-consuming process.
5- Resistance to Change: Implementing supply chain modeling often requires significant changes in organizational processes and decision-making approaches. Overcoming resistance to change and building buy-in from stakeholders can be a challenge, especially if the benefits of modeling are not clearly communicated and demonstrated.
Potential Solutions and Strategies to Overcome these Challenges
To overcome the challenges associated with supply chain modeling, businesses can adopt the following strategies:
1- Invest in Data Governance: Establishing a robust data governance framework is crucial for ensuring data quality and consistency. This involves defining data standards, implementing data validation processes, and establishing data ownership and accountability. Investing in data cleansing and integration tools can also help in improving data quality and availability.
2- Adopt a Phased Approach: Implementing supply chain modeling can be overwhelming, especially for large and complex supply chains. Adopting a phased approach, starting with pilot projects and gradually scaling up, can help in managing complexity and mitigating risks. Prioritizing critical areas of the supply chain and focusing on high-impact use cases can deliver quick wins and build momentum for broader adoption.
3- Build Internal Capabilities: Developing internal capabilities in supply chain modeling is essential for long-term success. Organizations should invest in training and development programs to upskill their workforce in areas such as data analytics, modeling techniques, and supply chain management. Collaborating with external experts and consulting firms can also provide valuable knowledge transfer and best practices.
4- Leverage Standardized Interfaces: To facilitate integration with existing systems, businesses should leverage standardized interfaces and APIs. Adopting industry-standard data formats and protocols can help in streamlining data exchange and ensuring interoperability across different systems. Partnering with technology vendors who offer pre-built connectors and integration solutions can also accelerate the integration process.
5- Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Overcoming resistance to change requires a cultural shift towards continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making. Engaging stakeholders throughout the modeling process, communicating the benefits of modeling, and celebrating successes can help in building buy-in and driving adoption. Establishing a culture of experimentation and learning can also foster innovation and continuous improvement in supply chain modeling practices.
Future Trends in Supply Chain Modeling
Discussion on Emerging Trends and Technologies Influencing Supply Chain Modeling
The field of supply chain modeling is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing business requirements. Some of the emerging trends and technologies that are shaping the future of supply chain modeling include:
1- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML techniques are increasingly being applied to supply chain modeling to enhance predictive capabilities and automate decision-making. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate accurate demand forecasts. AI-powered optimization engines can also help in optimizing inventory levels, transportation routes, and production schedules.
2- Big Data Analytics: The proliferation of data from various sources, such as IoT sensors, social media, and transactional systems, is creating new opportunities for supply chain modeling. Big data analytics techniques, such as data mining and predictive analytics, can help in uncovering hidden patterns, identifying risk factors, and generating actionable insights. Leveraging big data can enable businesses to make more informed decisions and respond quickly to changing market conditions.
3- Cloud-based Solutions: Cloud computing is transforming the way supply chain modeling is implemented and delivered. Cloud-based modeling platforms offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it easier for businesses to access advanced modeling capabilities without significant upfront investments. Cloud solutions also facilitate collaboration and data sharing across different stakeholders and geographies.
4- Digital Twin Technology: Digital twin technology involves creating a virtual replica of the physical supply chain, enabling businesses to simulate and optimize supply chain operations in a virtual environment. Digital twins can help in testing different scenarios, identifying bottlenecks, and evaluating the impact of changes before implementing them in the real world. This technology can significantly enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of supply chain modeling.
5- Blockchain Integration: Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize supply chain transparency and traceability. By integrating blockchain with supply chain modeling, businesses can gain real-time visibility into the movement of goods, ensure data integrity, and enable secure information sharing among supply chain partners. Blockchain-based modeling can also facilitate smart contracts and automate decision-making based on predefined rules and conditions.
Predictions on the Future of Supply Chain Modeling
As technology continues to advance and business needs evolve, the future of supply chain modeling looks promising. Some predictions for the future of supply chain modeling include:
1- Increased Adoption of AI and Automation: AI and automation will become increasingly prevalent in supply chain modeling, enabling businesses to make faster and more accurate decisions. AI-powered models will be able to self-learn and adapt to changing conditions, reducing the need for manual intervention and improving overall supply chain performance.
2- Real-time Modeling and Simulation: With the proliferation of IoT devices and real-time data streams, supply chain modeling will shift towards real-time monitoring and simulation. Businesses will be able to continuously update their models based on live data feeds, enabling them to respond quickly to disruptions and optimize operations in real-time.
3- Collaborative and Networked Modeling: Supply chain modeling will become more collaborative and networked, with multiple stakeholders contributing to the modeling process. Blockchain technology will enable secure and transparent data sharing among supply chain partners, facilitating joint decision-making and optimization. Collaborative modeling will help in aligning incentives and driving overall supply chain efficiency.
4- Prescriptive and Autonomous Decision-Making: As prescriptive modeling techniques mature, supply chain models will increasingly provide autonomous decision-making capabilities. AI-powered models will be able to analyze multiple scenarios, evaluate trade-offs, and recommend optimal actions without human intervention. This will enable businesses to make faster and more consistent decisions, improving supply chain agility and responsiveness.
5- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Supply chain modeling will continue to integrate with emerging technologies such as augmented reality, 5G networks, and edge computing. These technologies will enable real-time data collection, enhanced visualization, and faster decision-making, further enhancing the capabilities of supply chain models.
Conclusion
In conclusion, supply chain modeling is a critical tool for businesses seeking to optimize their operations and gain a competitive edge in today's complex and dynamic business environment. By leveraging the power of data analytics, advanced modeling techniques, and emerging technologies, businesses can gain deep insights into their supply chain dynamics, make informed decisions, and drive operational excellence.
However, implementing effective supply chain modeling is not without its challenges. Businesses must overcome data quality issues, manage complexity, build internal capabilities, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. By adopting best practices, leveraging standardized interfaces, and collaborating with external experts, businesses can successfully navigate these challenges and realize the full potential of supply chain modeling.
As technology continues to evolve and business needs change, the future of supply chain modeling looks bright. The increasing adoption of AI, automation, real-time modeling, and collaborative decision-making will transform the way businesses manage their supply chains. By staying at the forefront of these trends and embracing innovation, businesses can position themselves for long-term success and build resilient and agile supply chains.
In light of the insights shared in this blog post, we encourage businesses to embrace supply chain modeling as a strategic imperative. By investing in the right tools, talent, and processes
Frequently Asked Questions
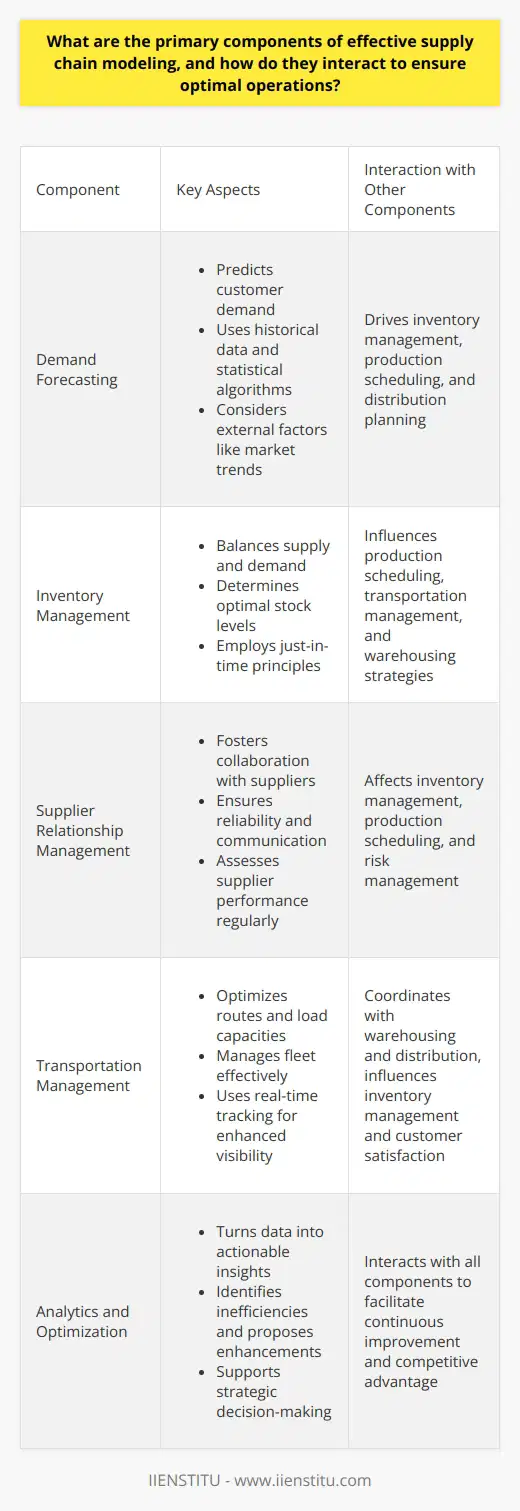
What are the primary components of effective supply chain modeling, and how do they interact to ensure optimal operations?
Effective Supply Chain Modeling Components
Effective supply chain modeling requires precision. It hinges on multiple components. These components must integrate seamlessly. Together they ensure optimal operations. Let us delve into these primary components.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting predicts customer demand. Accurate forecasting drives the entire supply chain. It uses historical data. It applies statistical algorithms. External factors like market trends matter. Effective forecasting reduces inventory costs. It also improves production planning.
Inventory Management
Inventory management balances supply and demand. It includes determining optimal stock levels. It employs just-in-time principles. The goal is to minimize holding costs. Nonetheless, it ensures product availability. Inventory data allows for real-time insights. Agile responses to demand shifts become possible.
Supplier Relationship Management
Strong supplier relationships prove crucial. They affect quality, delivery, and costs. Supplier relationship management (SRM) fosters collaboration. SRM ensures reliability and communication. It assesses supplier performance regularly. Long-term partnerships can reduce procurement costs. They also can improve innovation.
Transportation Management
Efficient transportation is a key component. It moves goods within the supply chain. It affects delivery times and costs. Transportation management optimizes routes and load capacities. It also manages the fleet effectively. Use of real-time tracking enhances visibility. It promotes better coordination.
Production Scheduling
Production scheduling coordinates manufacturing activities. It ensures resources are available. It aligns production with demand forecasts. Efficient scheduling maximizes throughput. It reduces bottlenecks and downtime. Production scheduling must remain flexible. It adapts to demand fluctuations and capacity changes.
Warehousing and Distribution
Warehousing involves storing goods strategically. Distribution ensures timely delivery. Together, they affect customer satisfaction. Efficient warehousing reduces retrieval times. It minimizes storage costs. Smart distribution networks speed up delivery. They also extend reach. Warehousing and distribution must align with transportation strategies.
Risk Management
Supply chains face various risks. These include disruptions, demand uncertainty, and regulatory changes. Risk management identifies potential issues. It plans for contingencies. It aims to minimize the impact of unforeseen events. Robust risk management fosters resilience. It allows continuous supply chain functioning.
Technology Integration
Technology underpins every component. It includes enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. It also includes advanced analytics and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Technology facilitates data sharing. It enhances transparency across the supply chain. Integrated technology allows for informed decision-making. It enables automation of complex processes.
Customer Relationship Management
Customers are at the supply chain's end. Customer relationship management (CRM) understands customer needs. It ensures their expectations are met. CRM interacts with other components. It influences forecasting, inventory levels, and distribution networks. Strong CRM leads to customer retention. It drives long-term profitability.
Analytics and Optimization
Analytics turn data into insights. Optimization uses those insights to improve operations. Together, they support strategic decisions. They identify inefficiencies. They propose enhancements. Analytics and optimization offer a competitive edge. They facilitate continuous improvement.
Each component plays a specific role. They interact closely. They combine to create a cohesive system. Together, they balance efficiency with responsiveness. They strive for cost-effectiveness without compromising service levels. Effective supply chain modeling creates a dynamic, responsive system. It is adaptable to the ever-changing business landscape. It remains customer-focused. It ensures long-term success.
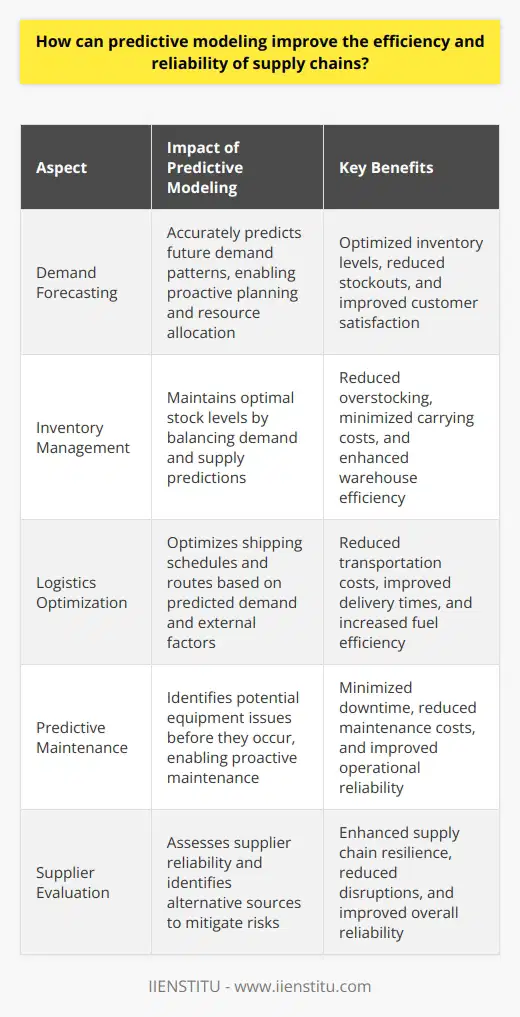
How can predictive modeling improve the efficiency and reliability of supply chains?
Predictive Modeling and Supply Chain Enhancements
Understanding Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling harnesses data. It anticipates outcomes. The method employs statistics. Data analytics are key. It fundamentally reshapes decision-making. Core to this is machine learning. Algorithms learn from data. They identify patterns. They inform future actions.
Predictive Modeling in Supply Chains
Supply chains are complex. They can be unpredictable. Many variables exist. Demand fluctuates. Supply can be erratic. Logistics networks are intricate. External factors, such as weather, impact them. Predictive modeling intervenes here. It offers foresight. Decisions improve.
Improving Efficiency
Efficiency means doing more with less. It requires smart resource utilization. Predictive modeling aids here. It forecasts demand accurately. Inventory management benefits from this. It keeps stock optimal. Overstocking and stockouts reduce. Warehouse operations become smooth. Shipping schedules align with predictions. Route optimization saves time and fuel. Predictive maintenance flags potential equipment issues. Operations face fewer interruptions.
Enhancing Reliability
Reliability builds trust. Customers expect consistent service. Predictive modeling makes this possible. It predicts disruptions. Planning mitigates these risks. Suppliers are evaluated. Their reliability gets assessed. Alternative sources are identified. Risk management strengthens. Delivery times become more accurate. Customer satisfaction improves.
Benefits of Predictive Modeling
Accurate Demand Forecasts: This enables better planning.
Optimized Inventory: Carrying costs lessen.
Effective Route Planning: It saves time and costs.
Maintenance Schedules: Unexpected breakdowns decrease.
Risk Management: Predictive modeling identifies risks early.
Customer Satisfaction: Reliable deliveries make happy customers.
Supplier Evaluation: Partners' performance gets predicted and monitored.
Each benefit feeds into a more robust system. Reliability and efficiency underpin this. Indeed, predictive modeling is not just beneficial; in today's fast-paced global economy, it might be essential.
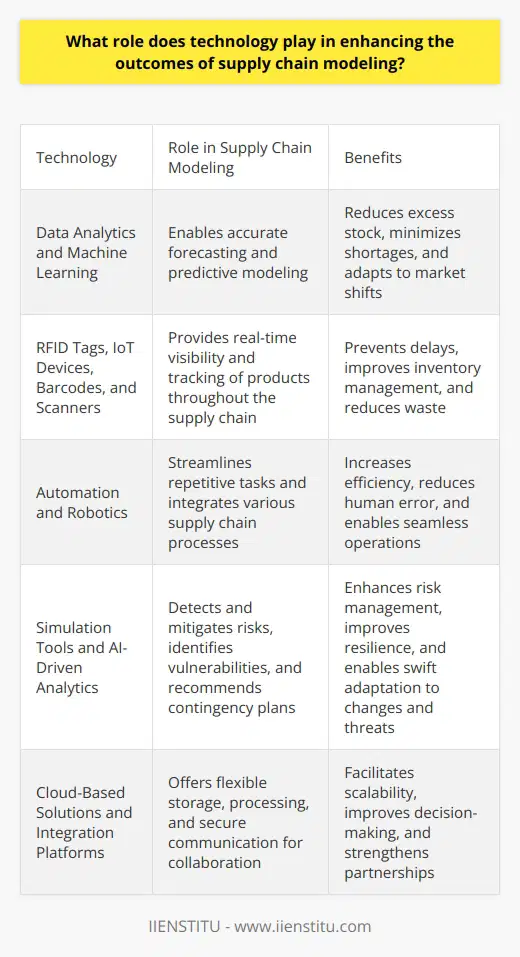
What role does technology play in enhancing the outcomes of supply chain modeling?
Technology's Role in Supply Chain Modeling
Supply chain modeling stands as the architecture of how products move from concept to consumer. It encompasses the journey of materials through production, delivery, and sales. Here, technology serves as both the foundation and the innovator.
Accurate Forecasting and Planning
Data analytics play a crucial role in predictive modeling. Algorithms can forecast demand with precision. They analyze vast data expanses quickly. Forecasting informs production, distribution, and inventory. This accuracy reduces excess stock and minimizes shortages.
Machine learning refines these forecasts over time. It adapts to patterns and shifts in consumption. Resultantly, supply chains can react before markets shift.
Real-Time Visibility and Tracking
Technology delivers transparency throughout the supply chain. RFID tags and IoT devices monitor products in real-time. Stakeholders can track shipments precisely. Delays become visible, action quickly follows.
Inventory systems now operate with unprecedented efficiency. Barcodes and scanners update stock levels instantly. This real-time data prevents overproduction and waste.
Automation and Efficiency
Automated systems streamline repetitive tasks. They free human labor for complex analysis and strategy. Robots in warehouses sort products and manage inventories. Efficiency soars, human error falls.
Software systems integrate various supply chain processes. They connect suppliers, warehouses, distributors, and retailers. This integration enables seamless operations. With one command, a complex array of actions unfolds.
Risk Management and Resilience
Advanced technologies detect and mitigate risks. Simulation tools forecast potential disruptions. Supply chains can prepare for such disturbances. Contingency plans are ready, resilience strengthens.
AI-driven analytics identify vulnerabilities. They can recommend diversification of suppliers and routes. Supply chains thus become more agile. They adapt to changes and threats swiftly.
Green Supply Chain Initiatives
Sustainability gains importance in supply chain modeling. Technology assists in establishing green initiatives. Data analysis spots inefficiencies and waste. It then guides the reduction of carbon footprints.
Electric and autonomous vehicles promise greener logistics. They aim to reduce emissions and energy use. Supply chains move towards a sustainable future.
Scalability and Growth
Technology allows supply chains to scale effectively. They can handle increased demand without faltering. Systems upgrade and expand with few disruptions. Growth becomes manageable and controlled.
Cloud-based solutions offer flexible storage and processing. Companies pay for the capacity they use. This scalability is crucial in adapting to market shifts.
Collaboration and Integration
Information sharing is vital in supply chains. Technology enables secure, fast communication. Stakeholders from across the globe collaborate efficiently.
Integration platforms like ERP and SCM software are key. They ensure all players have access to necessary data. Decision-making improves, partnerships strengthen.
Technology stands at the core of modern supply chain modeling. It enables accuracy, efficiency, and resilience. Analytics, real-time tracking, and automation lead these advancements. Additionally, it supports sustainability and scalability. Technology not only improves operations but also fortifies against future challenges. It is clear that technology will continue to shape efficient, robust supply chains.