In the intricate web of modern supply chain operations, Distribution Requirements Planning (DRP) emerges as a critical element in achieving a seamless flow of goods from suppliers to customers. As someone who's spent over a decade in supply chain management, I've witnessed firsthand the transformative power of DRP when implemented correctly. It's not just an operational tactic; it's a game-changer that can make or break a company's efficiency and customer satisfaction levels.
I remember when I first encountered DRP in my early career. I was working for a mid-sized electronics distributor, and we were constantly struggling with inventory issues. We'd either have too much stock gathering dust in our warehouses or face frustrating stockouts that left customers disappointed. It was a constant balancing act that seemed impossible to perfect. That's when our management decided to implement a DRP system, and let me tell you, it was like night and day.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll dive deep into the world of Distribution Requirements Planning. We'll explore its history, understand its core components, and discover how it's shaping the future of supply chain management. Whether you're a seasoned professional looking to refine your knowledge or a newcomer trying to grasp the basics, this article will provide valuable insights to help you master DRP.
Understanding the Concept of Distribution Requirements Planning
Definition and Explanation of DRP
Distribution Requirements Planning, or DRP, is a systematic approach to determining the optimal inventory levels and replenishment schedules across a multi-echelon distribution network. It's like a conductor orchestrating a symphony, ensuring that every instrument (or in this case, every node in the supply chain) plays its part at the right time and with the right intensity.
At its core, DRP aims to:
Forecast demand accurately
Optimize inventory levels
Reduce transportation costs
Improve customer service
Role of DRP in Supply Chain Management
In the grand scheme of supply chain management, DRP acts as a crucial link between demand planning and supply execution. It takes into account various factors such as:
Historical sales data
Seasonal fluctuations
Market trends
Lead times
Transportation constraints
By considering all these elements, DRP helps create a holistic view of the entire distribution network, allowing for more informed decision-making and better resource allocation.
Brief History and Evolution of DRP
The concept of DRP isn't new. It has its roots in the 1970s when companies started realizing the limitations of traditional inventory management systems. The term was first coined by André Martin, who developed the concept while working at Abbott Laboratories.
Over the years, DRP has evolved significantly:
1970s: Basic time-phased order point systems
1980s: Integration with Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
1990s: Incorporation of advanced forecasting techniques
2000s: Integration with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems
2010s onwards: Adoption of AI and machine learning for more accurate predictions
Components of DRP
Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is the bedrock of effective DRP. It's like trying to predict the weather – you need to consider multiple factors and use sophisticated tools to get it right. In my experience, combining statistical models with human insight often yields the best results.
Some key aspects of demand forecasting include:
Time series analysis
Causal models
Collaborative forecasting with customers and suppliers
Incorporation of external factors (e.g., economic indicators, competitor actions)
Order Processing
Efficient order processing is crucial for DRP success. It involves:
Order entry
Order validation
Credit checks
Inventory allocation
Order picking and packing
Shipping and delivery
A well-oiled order processing system can significantly reduce lead times and improve customer satisfaction.
Warehouse and Distribution Center Management
Effective warehouse management is the unsung hero of DRP. It ensures that the right products are in the right place at the right time. Key aspects include:
Layout optimization
Inventory tracking
Pick and pack efficiency
Cross-docking
Returns management
I once worked with a company that reduced its warehouse operating costs by 15% simply by optimizing its layout and implementing a more efficient picking system. It's amazing how much impact small changes can have when multiplied across an entire distribution network.
The Mechanics of Distribution Requirements Planning
Process and Stages Involved in DRP
Identification of Demand
The first step in DRP is accurately identifying demand. This involves:
Analyzing historical sales data
Considering market trends
Factoring in promotional activities
Accounting for seasonality
It's crucial to involve various departments in this process. Sales teams often have valuable insights that can't be captured by data alone.
Resource Procurement and Allocation
Once demand is identified, the next step is to procure and allocate resources accordingly. This includes:
Determining optimal order quantities
Scheduling production runs
Allocating warehouse space
Planning transportation routes
The goal is to ensure that resources are used efficiently while meeting customer demand.
Supply and Distribution Planning
This stage involves creating a detailed plan for moving products through the distribution network. It includes:
Determining safety stock levels
Setting reorder points
Planning inter-facility transfers
Optimizing transportation routes
The key is to find the right balance between cost efficiency and service level.
The use of Technology in DRP
The Role of DRP Software
Modern DRP systems leverage advanced software to handle complex calculations and provide real-time insights. Some key features of DRP software include:
Demand forecasting algorithms
Inventory optimization tools
What-if scenario planning
Real-time visibility across the supply chain
Integration with other business systems (ERP, CRM, etc.)
Advancements and Future Prospects in DRP Technology
The future of DRP is exciting, with emerging technologies promising to make it even more powerful:
Artificial Intelligence for more accurate demand forecasting
Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time inventory tracking
Blockchain for improved supply chain transparency
Advanced analytics for deeper insights and better decision-making
Benefits and Challenges of Implementing DRP
Advantages of Using DRP
Improved Inventory Management
One of the most significant benefits of DRP is improved inventory management. By accurately forecasting demand and optimizing replenishment schedules, companies can:
Reduce excess inventory
Minimize stockouts
Improve cash flow
Reduce warehouse costs
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
DRP directly contributes to improved customer satisfaction by:
Ensuring product availability
Reducing lead times
Improving order accuracy
Enabling better communication about product availability and delivery times
Increased Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
DRP can lead to significant cost savings and efficiency improvements:
Reduced transportation costs through optimized routing
Lower inventory holding costs
Improved labor productivity in warehouses
Better utilization of production capacity
Potential Hurdles in DRP Implementation
Understanding the Complexity of DRP Systems
Implementing DRP can be challenging due to its complexity. It requires:
A deep understanding of supply chain dynamics
Significant changes to existing processes
Integration of various data sources
Extensive training for staff
Challenges with Data Accuracy and Consistency
The effectiveness of DRP heavily relies on data quality. Common challenges include:
Inconsistent data across different systems
Inaccurate inventory counts
Delays in updating information
Lack of historical data for accurate forecasting
Integration Issues with Existing Operations
Integrating DRP with existing systems and processes can be a significant hurdle. It often requires:
Overcoming resistance to change
Aligning different departments (sales, operations, finance)
Upgrading or replacing legacy systems
Ensuring seamless data flow between different systems
Real-world Examples and Case Studies
Success Stories of Companies Implementing DRP
Walmart: The retail giant uses DRP to manage its vast network of stores and distribution centers, resulting in lower inventory costs and improved product availability.
Amazon: Their sophisticated DRP system enables them to offer fast delivery times and maintain high customer satisfaction levels.
Procter & Gamble: P&G implemented DRP to streamline its global supply chain, resulting in significant cost savings and improved service levels.
Lessons Learned from DRP Failures
A major electronics manufacturer failed to account for seasonal demand fluctuations in their DRP system, leading to significant stockouts during peak periods.
A food distributor struggled with data accuracy issues, resulting in frequent inventory discrepancies and customer dissatisfaction.
A fashion retailer's DRP implementation failed due to poor change management and inadequate staff training.
Recap of the Importance and Benefits of DRP
Distribution Requirements Planning is not just a tool; it's a strategic approach that can transform your entire supply chain. By accurately forecasting demand, optimizing inventory levels, and streamlining distribution processes, DRP can lead to significant cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and a more resilient supply chain.
Future Trends and Expectations in DRP
Impact of Emerging Technologies (like AI, IoT, etc.) on DRP
As we look to the future, emerging technologies promise to make DRP even more powerful:
AI and machine learning will enable more accurate demand forecasting
IoT devices will provide real-time visibility into inventory levels and product movement
Blockchain technology will improve supply chain transparency and traceability
Advanced analytics will offer deeper insights and enable more proactive decision-making
Predictions for Future Changes in DRP Approaches and Strategies
We can expect to see:
Increased focus on sustainability in distribution planning
Greater emphasis on risk management and supply chain resilience
More collaborative planning across the entire supply chain ecosystem
Integration of DRP with other advanced planning systems for end-to-end optimization
In conclusion, mastering Distribution Requirements Planning is crucial for any business looking to thrive in today's competitive landscape. While the journey may be challenging, the benefits far outweigh the costs. As someone who has seen the transformative power of DRP firsthand, I can confidently say that it's an investment worth making.
Remember, the key to successful DRP implementation lies in understanding your unique business needs, investing in the right technology, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. With the right approach, DRP can be your secret weapon in building a world-class supply chain.
References:
Martin, A. (1990). Distribution Resource Planning: The Gateway to True Quick Response and Continuous Replenishment. John Wiley & Sons.
Chopra, S., & Meindl, P. (2016). Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation (6th ed.). Pearson.
Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & Supply Chain Management (5th ed.). Financial Times/Prentice Hall.
Stadtler, H., & Kilger, C. (Eds.). (2015). Supply Chain Management and Advanced Planning: Concepts, Models, Software, and Case Studies (5th ed.). Springer.
Simchi-Levi, D., Kaminsky, P., & Simchi-Levi, E. (2008). Designing and Managing the Supply Chain: Concepts, Strategies, and Case Studies (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Frequently Asked Questions
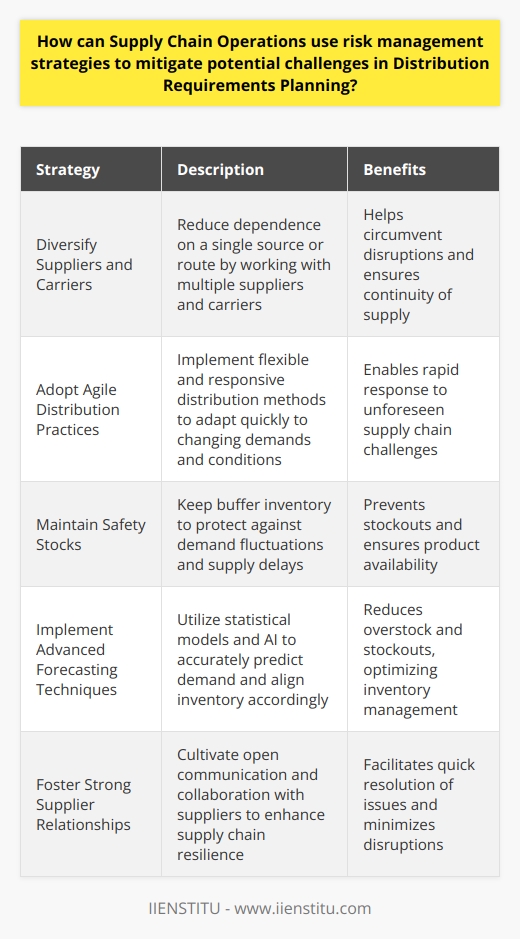
What are the fundamental elements required for successful Distribution Requirements Planning in Supply Chain Operations?
Understanding Distribution Requirements Planning (DRP)
Distribution Requirements Planning, or DRP, stands as a critical component of supply chain management. It entails the process of ensuring the right products reach the right destinations at the right time. Success in DRP hinges on meticulous planning and execution. It involves various fundamental elements for effective operation.
Accurate Forecasting Is Key
Forecasting demand is foundational. It predicts customer demand with precision. Companies use past data, market trends, and statistical tools for this. Accurate forecasts enable effective distribution planning. They set the stage for all subsequent DRP activities.
Inventory Control Optimizes Stock Levels
Inventory control ensures optimal stock levels. It minimizes capital tied up in inventory. Yet, it prevents stockouts. Balancing these two aspects is a delicate undertaking. Regular review and adjustment keep inventory at ideal levels.
Efficient Resource Management
Resource allocation is critical. It spans across warehouse space, personnel, and transportation. Proper resource management reduces bottlenecks. It streamlines the flow of goods.
Robust Information Systems
Advanced information systems serve as the backbone. They provide real-time data sharing. This aids in decision-making and coordination. Information integrity and accessibility are pivotal for DRP success.
Supplier and Manufacturer Coordination
Collaboration with suppliers and manufacturers is essential. Synchronized production and delivery schedules align with distribution needs. This coordination fosters a seamless supply chain.
Transportation Logistics Is a Linchpin
Efficient transportation logistics are a linchpin. They comprise route planning, load optimization, and carrier selection. These factors together make for timely and cost-efficient product distribution.
Continuous Improvement Culture
A culture of continuous improvement drives DRP. Regularly reviewing and refining processes improve efficiency. It also boosts responsiveness to market changes.
Customer-Centric Approach
Finally, a customer-centric approach shapes DRP activities. It ensures that distribution aligns with customer needs and expectations. Ultimately, it contributes to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
DRP is a complex yet critical component of supply chain operations. Integrating these fundamental elements fosters a resilient and responsive distribution network. A successful DRP system supports a company's competitive edge in a dynamic market.
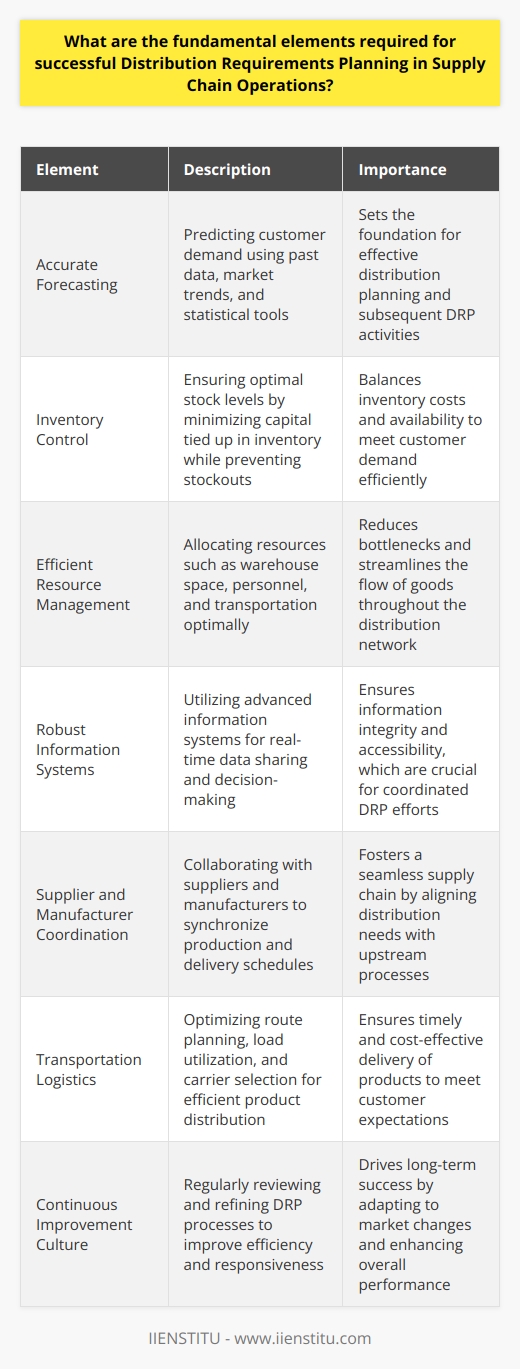
How can technology and software solutions be effectively implemented to enhance Distribution Requirements Planning?
Effective Implementation of Tech Solutions in DRP
Understanding DRP
Distribution Requirements Planning, or DRP, is a critical function. It ensures product distribution efficiency. DRP balances inventory levels, supply chain processes, and customer demand. For optimal DRP, businesses need robust tech solutions.
Key Elements for Tech Integration
Integration is vital for technology in DRP. Software must communicate across systems. Real-time data flow is a must. It empowers informed decision-making. Integration removes silos for seamless operation.
Scalability is equally important. Systems must grow with business needs. Small-scale solutions can hinder growth. Aim for platforms that expand easily.
Enhancing DRP with Specific Solutions
Cloud-based platforms simplify scalability. They offer flexibility in data management. Access is possible from anywhere. This fosters collaboration across the supply chain.
Advanced analytics bolster DRP strategies. These platforms interpret vast data streams. They reveal trends and forecast demands. This ensures better stocking and distribution decisions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) takes analytics further. AI predicts market changes more accurately. It automates complex decision processes. Integration into DRP systems cuts human error.
Internet of Things (IoT) enables smarter inventories. Sensors track goods and update systems automatically. This results in real-time inventory visibility.
Mobile technology supports DRP on the move. Staff accesses DRP systems via smartphones. Updates can happen in transit. Real-time data adjustments improve efficiency.
Ensuring Software Effectiveness
Training is crucial for new technology adoption. Employees should understand software utility. Adequate training ensures faster onboarding. It encourages system use to its full potential.
Continuous Improvement keeps DRP systems relevant. Tech evolves continuously. So should DRP solutions. Regular updates and reviews keep systems optimal.
Support from software vendors is a must. It ensures issues resolve quickly. This minimizes downtime.
Data Security must be a priority. Reliable cybersecurity protects supply chain data. DRP solutions must include robust security measures.
Conclusion
Effective technology in DRP is achievable. It involves careful planning and execution. Start with integration and scalability. Choose tech solutions that match business needs. Ensure staff are well-trained and supported. Keep data secure. This approach enhances DRP systems significantly. It benefits the entire supply chain.
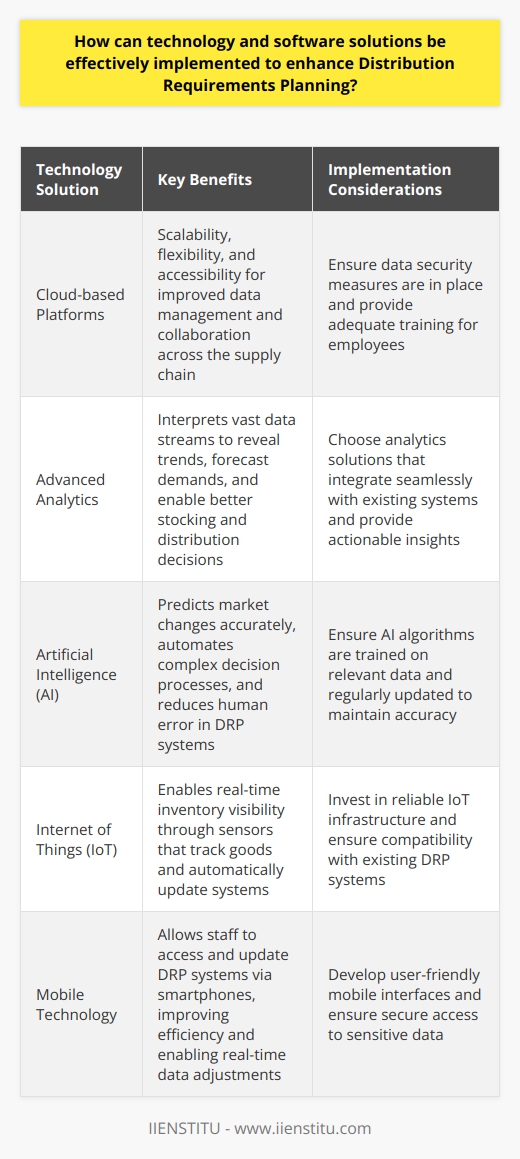
How can Supply Chain Operations use risk management strategies to mitigate potential challenges in Distribution Requirements Planning?
Understanding Distribution Requirements Planning
Distribution Requirements Planning (DRP) is critical. It ensures the right products reach the right places at the right time. Challenges in DRP can disrupt supply chain operations. These disruptions can lead to customer dissatisfaction, increased costs, and inventory issues.
Risk Management in Supply Chain
Risk management is a structured approach. It involves identifying, assessing, and responding to risks. In supply chains, risks can range from supplier failures to transportation disruptions. Effective risk management in supply chains ensures business continuity and reliable performance.
Strategies for Risk Mitigation in DRP
Diversify Suppliers and Carriers
Do not rely on single suppliers or carriers. Diversification is key. It reduces dependence on one source or route. Multiple suppliers and carriers can help circumvent disruptions.
Adopt Agile Distribution Practices
Agility in distribution is crucial. It allows rapid response to changing demands and conditions. Agile practices can help companies adapt quickly to unforeseen supply chain challenges.
Maintain Safety Stocks
Keep safety stock levels. They serve as buffers against demand fluctuations. Safety stocks can prevent stockouts when forecasting errors or supply delays occur.
Implement Advanced Forecasting Techniques
Use advanced forecasting. This includes statistical models and AI. Accurate forecasts help in aligning inventory with demand, reducing overstock and stockouts.
Foster Strong Supplier Relationships
Cultivate strong relationships with suppliers. This enhances communication and collaboration. It also increases supply chain resilience during disruptions.
Utilize Technology for Real-Time Tracking
Invest in real-time tracking technology. It provides visibility into the movement of goods. This helps in identifying and addressing issues promptly.
Regularly Review and Update DRP
Review processes often. Revise as necessary. This ensures that DRP strategies remain relevant and effective against emerging supply chain risks.
Ensure Compliance with Regulations
Stay compliant with trade regulations and laws. Compliance helps in avoiding costly fines and delays in the supply chain.
Plan for Contingencies
Prepare contingency plans. They should cover various risk scenarios. Planning helps in quick recovery from supply chain disruptions.
Train Employees on Risk Awareness
Educate employees about risk management principles. Empowered employees can better recognize and mitigate risks within the supply chain.
Supply Chain operations can use these risk management strategies to enhance DRP. They contribute to minimizing the impact of potential challenges. This proactive approach to managing risks can lead to a more robust and resilient supply chain. With careful planning and execution, companies can navigate uncertainties and maintain customer satisfaction and profitability.