Supply chain risk management is an increasingly critical function within businesses that aims to identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks along the supply chain to ensure reliability and continuity of supply. In a globalized economy, an organization's supply chain can span multiple countries and involve various interdependent processes making it susceptible to a plethora of risks.
This article will explore the multi-faceted approach to managing these risks efficiently, underpinning the importance of robust strategies to maintain competitiveness and deliver value to customers.
Definition of Supply Chain Risk Management
Defined succinctly, supply chain risk management (SCRM) is the implementation of strategies designed to oversee and manage potential risks within the supply chain, including but not limited to inventory issues, supplier problems, logistic errors, and environmental factors that could interrupt or delay the flow of goods and services.
This process entails the proactive identification of potential risks, assessment of their possible impact, and development of strategies geared toward their mitigation. Effective SCRM is pivotal to ensuring smooth operational flow and upholding the integrity of a company's supply chain network.
Importance of Supply Chain Risk Management
In the dynamic and interconnected world of global trade, the importance of supply chain risk management cannot be overstated. Businesses face an array of challenges, from natural disasters disrupting transportation routes to cyber-attacks compromising data integrity.
These uncertainties necessitate a comprehensive understanding of potential vulnerabilities and the formation of robust SCRM strategies. The integration of logistics courses online and online certification courses greatly contributes to enhancing the knowledge and skills of professionals in this arena, equipping them with the expertise to cope with the complexities of supply chain risk.
Understanding the Risks in Supply Chain Management
Comprehending the myriad of risks pertinent to the supply chain is crucial in devising effective risk management strategies. These risks can broadly be classified into several types, each with the potential to adversely affect supply chain operations and compromise business performance.
Overview of the types of risks in the Supply Chain
Logistics and supply chain professionals often categorize risks into three main types: operational risks, disruption risks, and systemic risks. Operational risks are associated with the day-to-day management of the supply chain and can include vendor shortages, transportation delays, or inventory mismanagement.
On the other hand, disruption risks encompass unforeseen events like natural disasters, political instability, or labor strikes that can abruptly halt supply chain operations. Systemic risks cover macro-level events such as economic recessions or significant technological changes, which may require a complete rethink of supply chain strategy.
Operational risks
Disruption risks
Systemic risks
Examples highlighting the impact of unmanaged supply chain risks
The repercussions of ignoring supply chain risks can be severe. For instance, a key supplier's failure to deliver an essential component due to financial instability can cause a production standstill. Similarly, a retailer may face significant revenue loss in the occurrence of a cyber-attack that disrupts its distribution system. These examples underscore the absolute necessity for preemptive risk management measures in safeguarding supply chain operations.
Strategies for effective Supply Chain Risk Management
Addressing the challenges posited by potential risks requires strategic planning and action. Companies can develop an array of approaches to anticipate, prepare for, and neutralize supply chain risks.
Risk Identification and Assessment
The initial step of supply chain risk management is identifying and evaluating the potential risks that could affect the supply chain operations. This phase involves the use of predictive analytics for risk identification, wherein historical data, market trends, and current events are analyzed to forecast potential disruptions. Subsequently, organizations conduct an assessment of the impact and likelihood of identified risks to prioritize their attention and resources accordingly.
Predictive analytics for risk identification
Impact and likelihood assessment of risks
Risk Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
Upon assessing the risks, developing mitigation and prevention strategies is instrumental for risk management. Contingency planning plays a significant role in this, where alternative plans are in place in the event of supply chain disruptions. Moreover, prioritizing supplier diversity is vital to spread the risk and avoid over-dependence on a single source which can be a critical vulnerability.
The role of contingency planning
The importance of supplier diversity in risk reduction
Supply Chain Resilience Building
Building resilience into the supply chain is about creating a robust setup that can withstand and recover from unexpected disruptions. Replicating supply chains across different regions can mitigate risks associated with geographical limitations. Furthermore, proactive disruption management ensures swift reactive measures in response to supply chain threats, which minimizes impacts and accelerates recovery time.
Replicating supply chains for risk mitigation
Proactive disruption management
Role of Technology in Supply Chain Risk Management
The rapid advancement of digital tools has provided businesses with innovative opportunities to strengthen their supply chain risk management tactics. Utilizing cutting-edge technologies can significantly enhance the capability of organizations to predict, manage and mitigate risks more efficiently.
Advancement of Digital tools and techniques
Technological innovations such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Blockchain are revolutionizing supply chain risk management. AI algorithms can help predict potential disruptions before they occur, allowing for proactive measures to be implemented. Blockchain technology introduces a layer of transparency and security to supply chain transactions, which serves to build trust and traceability across the entire network.
Artificial Intelligence in supply chain risk management
Usage of Blockchain for Supply Chain transparency
Case Studies showing implementation of technology for risk management
An examination of case studies where companies successfully incorporated technology to manage their supply chain risks can offer valuable insights. These practical examples showcase the effectiveness of digital tools in real-world applications, reinforcing the argument for their wider adoption in SCRM strategies.
The field of supply chain risk management remains paramount to the success and resilience of organizations worldwide. The continuous evolution of risks makes it imperative for businesses to stay vigilant, be adaptive, and incorporate robust risk management processes into their supply chain operations.
Recap of the importance of managing risks in supply chains
It is crystal clear that the significance of identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks cannot be understated. The employment of practices like engaging in logistics courses online and obtaining online certification courses invigorates the knowledge base and skill set of those overseeing and managing supply chains, equipping them to handle potential risks successfully.
Future trends and challenges in Supply Chain Risk Management
Looking forward, the domain of SCRM is set to encounter new challenges and trends such as the growing significance of sustainability, digitization, and geopolitical shifts. Companies need to remain proactive and innovative in crafting their risk management strategies to stay ahead of these evolving dynamics.
Optimizing supply chain risk management is a strategic imperative that transcends operational efficiency and encompasses the broader scope of sustaining business growth and customer satisfaction. By embracing comprehensive risk management practices, including the augmentation of professional capabilities through continued learning and the adoption of advanced technologies, companies can fortify their supply chains against an unpredictable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
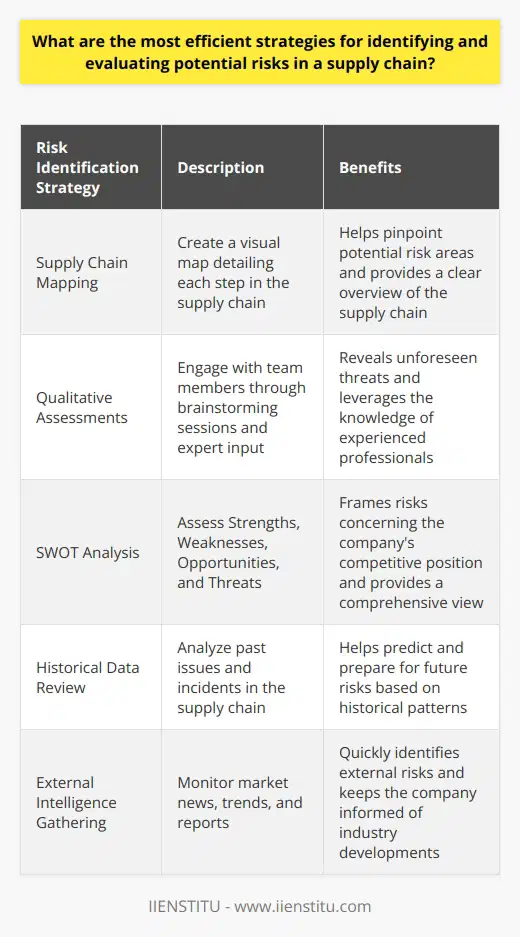
What are the most efficient strategies for identifying and evaluating potential risks in a supply chain?
Identifying Potential Risks
Supply chains face myriad risks. These range from supplier insolvency to natural disasters. Sound risk management begins with rigorous identification. Here are several strategies to pinpoint those risks effectively.
Map the Supply Chain
First, create a visual map. This chart should detail each step in the chain. It helps pinpoint where risks might arise.
Use Qualitative Assessments
Next, engage with your team. Conduct brainstorming sessions. Identify risks via expert input. This often reveals unforeseen threats.
Conduct a SWOT Analysis
Perform a SWOT analysis. Assess Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This frames risks concerning your competitive position.
Review Historical Data
Historical data is invaluable. It shows where past issues occurred. Use this to predict and prepare for future risks.
Collect External Intelligence
Keep an eye on the market. Monitor news, trends, and reports. This will point to external risks quickly.
Evaluating Supply Chain Risks
Once identification is complete, evaluation follows. The goal is to measure each risk's potential impact.
Categorize the Risks
Begin by categorizing risks. Common groups are operational, financial, strategic, and compliance-related. This organizes risks by nature.
Assign Probability and Impact
Every risk has a chance of occurrence. Assess this probability. Also, estimate each risk's impact if it materializes.
Use Risk Matrices
Risk matrices are a simple tool. Place each risk within a matrix based on its score. This shows clear priorities.
Perform a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Consider the costs. Weigh them against the benefits of mitigation. This illuminates which risks justify investment.
Carry Out Scenario Planning
Plan for various outcomes. Simulate different scenarios. How does each risk affect your operation? This will prepare you for different eventualities.
Regularly Review and Update
Risks change. Review your assessments often. Update them to reflect new information. This ensures your risk profile remains current.
Map the supply chain
Use qualitative assessments
Conduct a SWOT analysis
Review historical data
Collect external intelligence
In short, efficient supply chain risk identification and evaluation call for a structured approach. Map out the chain, assess qualitatively and quantitatively, and keep your information updated. Use tools such as risk matrices and scenario planning to keep a clear focus on where to direct your mitigation efforts. With these strategies, businesses can better prepare for the unpredictable and mitigate risks in their supply chains.
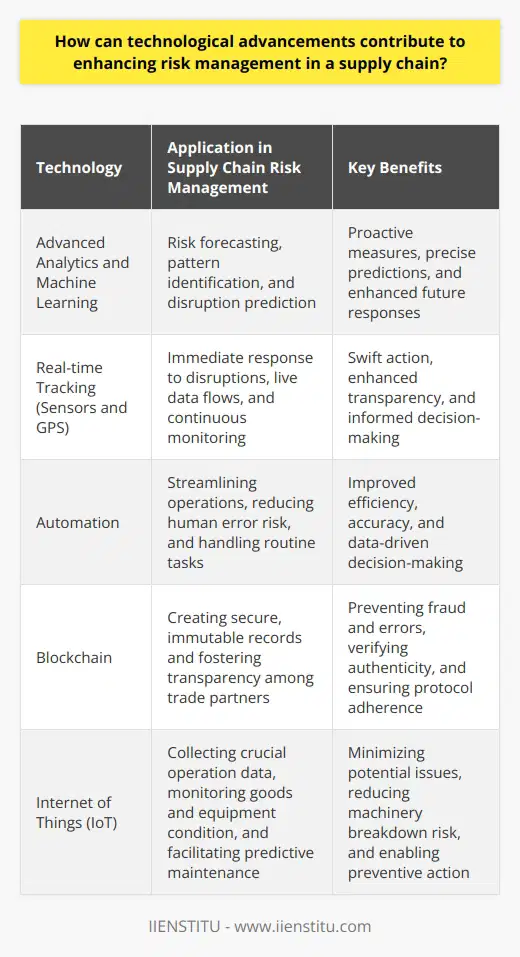
How can technological advancements contribute to enhancing risk management in a supply chain?
The Interplay of Technology and Risk Management in Supply Chains
In today's fast-paced market, managing supply chain risk is vital. Companies face numerous uncertainties. Technological advancements provide tools to mitigate these risks. Key benefits stem from technology's role in supply chain oversight.
Technology as a Predictor
Advanced analytics aid risk forecasting. They help identify patterns and predict disruptions. Machine learning algorithms process vast datasets. This analysis discerns potential problems early. It thereby supports proactive measures. Risk prediction turns more precise over time. The tech learns from each event, enhancing future responses.
Real-time Visibility Aids Swift Action
Real-time tracking is critical. It allows for immediate response to disruptions. Sensors and GPS generate live data flows. Companies monitor shipments around the clock. Any deviation triggers alerts. Thus, stakeholders can take quick, informed action. Real-time visibility also means enhanced transparency across the chain.
Automation Improves Efficiency and Accuracy
Automation streamlines operations. It reduces human error risk in routine tasks. Automated systems handle order processing and inventory updates. They provide accurate data for decision-making. Better data means better risk management. Time-sensitive decisions benefit from automation's speed.
Enhanced Communication through Technology
Effective communication underpins risk mitigation. Digital platforms enable instant data sharing. Stakeholders remain aware of any changes or issues. Collaboration tools facilitate rapid strategy adjustments. Partners synchronize their response efforts. Instant communication is crucial in crisis scenarios.
Cybersecurity Protects Critical Data
Amidst technological reliance, data breaches pose significant risks. Robust cybersecurity measures are indispensable. They protect sensitive information integral to supply chains. Secure data transmission and storage are priorities. Cybersecurity efforts safeguard against costly data-related disruptions.
The Impact of Blockchain for Transparency
Blockchain technology offers unparalleled transparency. It creates secure, immutable records. Each transaction adds a new 'block' to the 'chain.' Every party can access this unalterable ledger. Blockchain prevents fraud and errors. It thus fosters trust among trade partners. Blockchain makes verifying authenticity simpler. It further ensures that all participants follow agreed-upon protocols.
The Role of Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices collect crucial operation data. They monitor goods and equipment condition. IoT sensors can track temperature, movement, and more. Alerts notify managers of deviations from norms. Managers can then take preventive action. This minimizes the impact of potential issues. The IoT also facilitates predictive maintenance. It reduces the risk of machinery breakdowns.
Cloud Computing Centralizes Information
Cloud computing centralizes data storage. It grants access from anywhere, anytime. Supply chain parties can retrieve vital information on demand. Decision-making becomes more informed and timely. Cloud computing supports scalability and collaboration. It offers robust backup solutions. These are crucial in disaster recovery scenarios.
AI and Machine Learning Refine Risk Assessment
AI and Machine Learning enhance risk assessment. They can model complex risk scenarios. These technologies offer insights into potential impact. Firms can assess various risk strategies efficiently. AI-powered tools also assist in supplier evaluation. They can predict supplier reliability and performance.
Drones and Autonomous Vehicles for Safer Logistics
Drones and autonomous vehicles promise safer logistics. Drones inspect hard-to-reach areas. They can check for hazards without endangering workers. Autonomous vehicles can reduce accidents caused by human error. They promise to make the transportation of goods safer.
Technology is reshaping supply chain risk management. Firms that adopt these advancements may gain competitive edges. They do so through enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness. Technology's role will only grow. It will keep transforming risk management and supply chains.
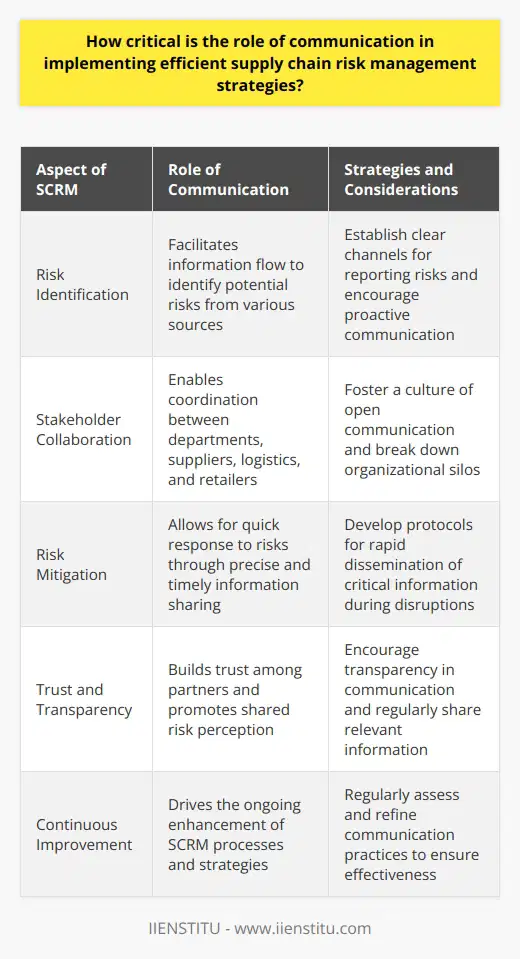
How critical is the role of communication in implementing efficient supply chain risk management strategies?
Understanding Supply Chain Risk Management
Supply chain risk management (SCRM) involves handling disruptions. It is crucial for business sustainability. Risks can occur at any moment. They can emerge from various sources. These include natural disasters, economic shifts, or technological failures. Efficient SCRM mitigates the impact of these disruptions. It ensures continuity and resilience.
Communication's Role in SCRM
Communication drives successful SCRM. It does so by facilitating information flow. Stakeholders stay informed through clear communication. It enables quick response to risks. Information must be precise. It must also be timely.
Effective communication promotes collaboration. Different departments must work together. Suppliers, logistics, and retailers also need to coordinate. Good communication makes this possible. It breaks down silos within organizations.
Transparency is essential in communication. It builds trust among partners. It allows for shared risk perception. Understanding risks becomes easier. So does finding solutions.
Implementation of Communication Strategies
Implementing communication strategies involves several steps. These steps ensure that communication is efficient and effective. Here are some critical considerations:
Establish Protocols: Define clear communication channels. This ensures that messages reach the right people.
Regular Updates: Keep all parties informed with frequent updates. It ensures that everyone is on the same page.
Train Employees: Teach staff how to communicate during disruptions. Prepared teams manage risks better.
Technology Utilization: Use technology to enhance communication. Digital tools can provide real-time data sharing.
Challenges to Communication
Several barriers can impede communication. These challenges include:
Cultural Differences: Global supply chains face this. It can lead to misunderstandings.
Information Overload: Too much information can confuse stakeholders. Distill it to what is necessary.
Resistance to Change: Some may resist new communication methods. They need convincing of the benefits.
Leadership commitment is important for overcoming these challenges. Leaders must champion open communication. They inspire their organizations. They guide them toward efficient SCRM.
Communication is not just critical. It is the backbone of SCRM. It empowers organizations to face uncertainties. It builds resilient supply chains. It should, therefore, receive the attention it deserves. Continuous improvement is key. Organizations must strive for better communication to manage their supply chain risks effectively.