You know, I still remember walking into my grandfather's small factory as a kid—the smell of fresh sawdust mixing with the metallic clanking of machinery. It was a humble furniture-making shop tucked away in a bustling town. Back then, I didn't understand much about what went on in that workshop. All I knew was that Grandpa crafted the most beautiful chairs, tables, and cabinets I'd ever seen.
The Goals of Process Logistics
Strategies for Optimizing Process Logistics
Benefits of Optimizing Process Logistics
Years later, as I ventured into the world of manufacturing myself, those memories resurfaced. I began to realize that behind every product—be it a simple wooden chair or a complex electronic device—there lies a web of processes intricately woven together. This web, my friends, is what we call process logistics. It's not just about moving stuff from point A to point B; it's about orchestrating every step to ensure that resources are used efficiently, costs are minimized, and quality is never compromised.
Understanding the Essence of Process Logistics
Before diving deeper, let's take a moment to understand what process logistics truly entails. At its core, process logistics is all about optimally managing resources to plan, coordinate, and execute the production of goods and services. It encompasses a range of activities—from inventory control, picking, packing, to the final shipping of products. In today's fast-paced manufacturing industry, process logistics isn't just a fancy term; it's the lifeblood that keeps the production line humming smoothly.
I recall my early days working in a mid-sized electronics manufacturing company. We faced a common challenge: high production costs and delayed delivery times. It didn't take us long to figure out that our supply chain management needed a serious overhaul. We weren't just dealing with supply and demand; we had to re-evaluate our entire process logistics to stay competitive.
The Goals of Process Logistics
Now, you might be wondering, what are we aiming for with process logistics? Well, it's quite straightforward.
Maximizing Efficiency
At the top of the list is efficiency. Efficiency, in this context, means reducing the time and resources required to produce a product. Think about it—if you can produce more with less, you're already ahead of the game. It's like baking cookies; if you can bake a dozen in half the time without compromising on taste, wouldn't you?
Enhancing Cost-Effectiveness
Next up is cost-effectiveness. This isn't just about cutting corners to save a buck. It's about strategically reducing the cost of resources and production time without sacrificing quality. When we managed to streamline our processes back at the electronics company, we saw a significant drop in overhead costs. It wasn't magic; it was smart supply chain management management.
Efficiency is achieved through organized process logistics in manufacturing, as in all other areas of life.
Streamlining Production
Lastly, there's the goal of achieving streamlined production. This involves creating the shortest and simplest process for manufacturing goods or services. It's about removing unnecessary steps that bog down the production line. And trust me, in the world of manufacturing, simplicity often equates to reliability and speed.
Strategies for Optimizing Process Logistics
So, how do we get there? How do we optimize process logistics to meet these lofty goals? Let me share some strategies that have worked wonders in my experience.
1. Systematizing and Digitizing Data
One of the first steps is to systematize and digitize data. When I was tasked with improving our manufacturing processes, I realized that our data was all over the place—some in paper files, others in disparate software systems. By organizing and cataloging all manufacturing data into a coherent and accessible system, we could track production processes in real-time and identify potential problems quickly.
2. Automating Manufacturing Processes
Automation is no longer a buzzword; it's a necessity. By automating repetitive tasks, manufacturers can operate promptly and efficiently with minimal human intervention. I remember implementing automated assembly lines that not only increased production speed but also reduced errors significantly.
3. Reducing Overhead Costs
Cutting down on overhead costs is crucial. This doesn't mean laying off staff or compromising on materials. It's about ensuring that all resources are used most effectively and efficiently. For instance, optimizing energy usage or negotiating better rates with suppliers can make a substantial difference.
4. Maximizing Resource Allocation
Lastly, maximizing resource allocation ensures that resources are directed where they're needed most. By analyzing production data, we can allocate manpower, machinery, and materials more effectively. This leads to a more resilient and responsive production process.
The Tangible Benefits of Optimizing Process Logistics
When we talk about optimizing process logistics, we're not just aiming for theoretical improvements. There are real, tangible benefits that organizations can reap.
Improved Production Efficiency
First and foremost is improved production efficiency. Products are produced faster, with fewer materials and less time. This was evident in our electronics manufacturing when production times dropped by 20% after optimization.
Enhanced Quality Control
Optimized process logistics allow for enhanced quality control measures. By having a streamlined and monitored process, defects can be spotted and rectified promptly. This not only saves costs but also enhances the brand's reputation.
Reduced Delivery and Lead Times
With a more efficient process, delivery and lead times are significantly reduced. Customers receive their products faster, leading to higher satisfaction levels.
Lower Inventory Levels
Optimizing process logistics can also lead to reduced inventory levels. By having a just-in-time production approach, we minimize the costs associated with storing excess inventory.
Improved Cash Flow
All these factors contribute to an improved cash flow. Faster production and delivery mean quicker payments and less capital tied up in inventory.
A Personal Anecdote on the Impact of Process Logistics
I can't help but think back to a project I was involved in a few years ago. We were tasked with improving the supply chain of a local food packaging company. Their main issue was delayed shipments and high spoilage rates. By applying process logistics optimization strategies, we managed to reorganize their entire supply chain activities.
We started by digitizing their inventory management. Using barcodes and a centralized database, we could track stock levels in real-time. Then, we automated their ordering processes so that raw materials were ordered based on actual demand forecasts. This not only reduced waste but also ensured that production never halted due to lack of materials.
One of the significant changes was in their management chain supply. We collaborated closely with suppliers to ensure timely deliveries. We even implemented a Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) system, which was a game-changer.
The results were astounding:
Spoilage rates decreased by 35%.
Delivery times improved by 25%.
Overall production costs reduced by 15%.
Seeing these results firsthand reinforced my belief in the power of optimized process logistics.
Embracing Technology in Process Logistics
It's impossible to talk about process logistics without mentioning the role of technology. From SCM management software to IoT devices on the production floor, technological advancements are reshaping how we approach logistics.
The Role of SCM Software
Supply chain management software provides a holistic view of the entire supply chain. It allows for better planning, execution, and monitoring of supply chain mgmt activities. With features like demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and supplier collaboration, these tools are indispensable.
The Rise of Automation and Robotics
Automation isn't limited to software. Robotics on the production floor can handle tasks with precision and speed that humans can't match. This doesn't mean replacing human workers but rather augmenting their capabilities.
Data Analytics and AI
With the influx of data from various sources, data analytics and AI play a crucial role in making sense of it all. Predictive analytics can foresee potential bottlenecks, while AI algorithms can optimize resource allocation dynamically.
Challenges in Optimizing Process Logistics
Of course, it's not always smooth sailing. There are challenges that organizations face when attempting to optimize their process logistics.
Resistance to Change
One of the biggest hurdles is resistance to change. Employees accustomed to certain ways of working might be hesitant to adopt new processes or technologies.
Upfront Costs
Implementing new systems or technologies often requires a significant upfront investment. Convincing stakeholders of the long-term benefits is essential.
Complexity of Integration
Integrating new systems with existing ones can be complex. It requires careful planning to ensure that there's minimal disruption to ongoing operations.
Overcoming the Challenges
Despite these challenges, there are ways to navigate them effectively.
1- Engage Stakeholders Early: Involve employees and stakeholders from the beginning. Address their concerns and highlight the benefits.
2- Provide Training: Offer comprehensive training to ease the transition to new systems or processes.
3- Start Small: Implement changes in phases. Pilot projects can demonstrate value before a full-scale rollout.
4- Collaborate with Experts: Bringing in consultants or experts in SCM supply can provide valuable insights and ensure best practices are followed.
The Future of Process Logistics
Looking ahead, the field of process logistics is poised for exciting developments.
Sustainability and Green Logistics
With growing environmental concerns, there's a push towards sustainable logistics. This involves reducing carbon footprints, using eco-friendly materials, and optimizing routes to minimize emissions.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain has the potential to increase transparency and traceability in the supply chain. This can be particularly beneficial in industries where provenance is crucial.
Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning
As machine learning algorithms become more sophisticated, they will play a larger role in predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and dynamic optimization.
Final Thoughts
Efficiency is achieved through organized process logistics in manufacturing, as in all other areas of life. Whether you're running a small furniture shop like my grandfather or managing a vast manufacturing facility, the principles remain the same. By focusing on process logistics, embracing new technologies, and continually seeking improvement, organizations can stay ahead of the curve.
At the end of the day, it's not just about cutting costs or speeding up production. It's about delivering value—to your customers, your employees, and your stakeholders. And that, my friends, is a goal worth striving for.
References
1- Goldratt, E. M., & Cox, J. (2004). The Goal: A Process of Ongoing Improvement. North River Press.
2- Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & Supply Chain Management (5th ed.). Pearson.
3- Chopra, S., & Meindl, P. (2019). Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation (7th ed.). Pearson.
4- Ballou, R. H. (2003). Business Logistics/Supply Chain Management: Planning, Organizing, and Controlling the Supply Chain (5th ed.). Pearson.
5- Langley, C. J., Coyle, J. J., Gibson, B. J., Novack, R. A., & Bardi, E. J. (2008). Managing Supply Chains: A Logistics Approach. South-Western Cengage Learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
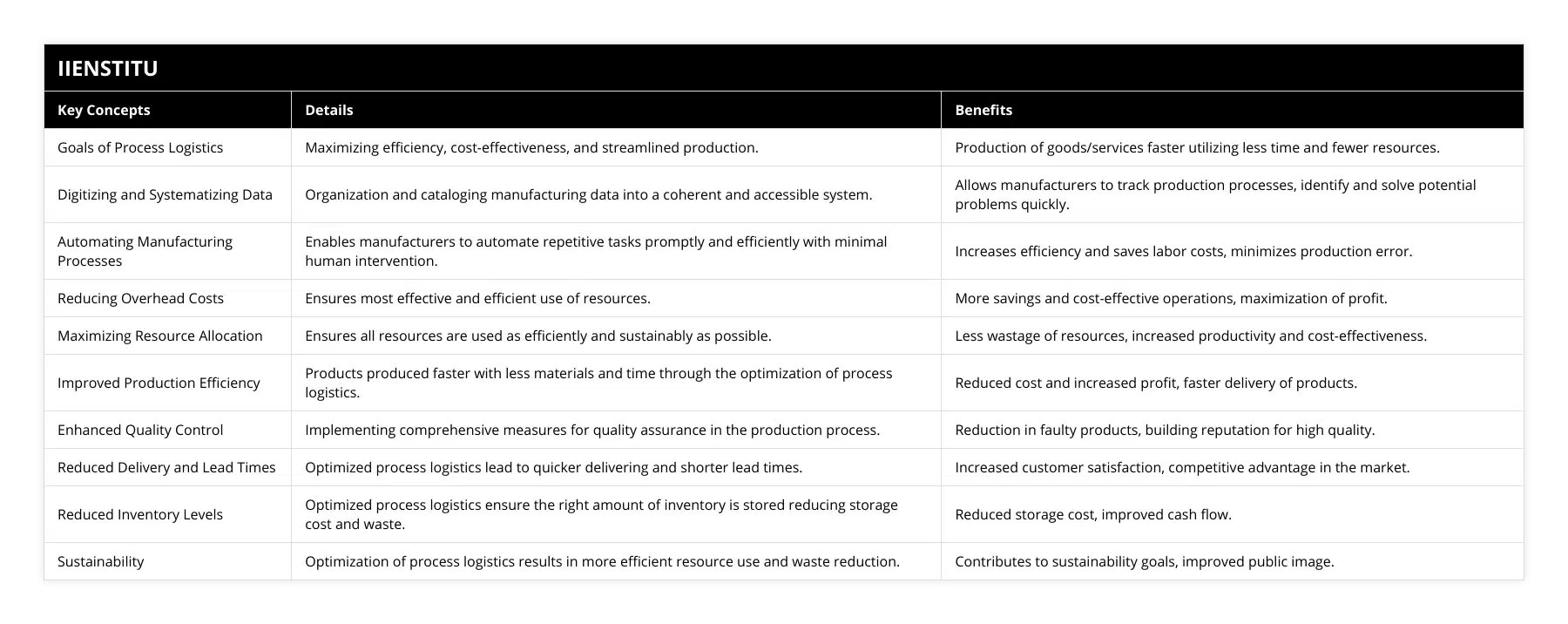
What strategies can be employed to optimize process logistics in manufacturing?
Process logistics play an essential role in the success of any manufacturing operation. To ensure the process's efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness, it is necessary to optimize the process logistics in manufacturing. This article discusses some strategies that can be employed to maximize process logistics in manufacturing.
One of the essential strategies to optimize process logistics in manufacturing is to analyze the existing process and identify areas for improvement. It is necessary to understand the workflow of the manufacturing process and its associated logistics, as well as current and future production needs. By thoroughly analyzing the system, areas where improvement can be made become more apparent. This includes scrutinizing individual processes, from purchasing raw materials to producing and delivering products, and considering combinations of techniques that could be improved upon.
Another strategy for optimizing process logistics in manufacturing is to eliminate or reduce waste. Manufacturing processes often feature various types of garbage that can result in poor product quality, excessive lead times for production, and unnecessary expenses. By identifying and eliminating such waste, it is possible to make the process smoother and more efficient. This can include reviewing and revising procedures, analyzing individual components of the process, or examining production machinery to ensure it delivers optimum performance.
A further strategy for optimizing process logistics in manufacturing is to use automation. Automation allows production processes to be completed more quickly and efficiently while reducing the required personnel. As a result, using robots and other automated systems can reduce the cost of manufacturing and improve product quality by ensuring consistent production. In addition, automation allows for processes that are not feasible for human labor to be completed, such as those that require exact and intricate movements.
Finally, it is essential to ensure that all personnel involved in manufacturing processes are well-trained and up-to-date on new developments and technologies. If personnel are not adequately trained, it can lead to mistakes and inefficiencies in the process that can prove costly and adversely affect production. Effective personnel utilization is critical to ensure they understand the processes and can adapt to new developments in the manufacturing landscape.
In conclusion, optimizing process logistics in manufacturing is essential for improving the process's efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. By thoroughly analyzing the process and eliminating or reducing waste, using automation, and adequately training personnel, it is possible to optimize process logistics in manufacturing.
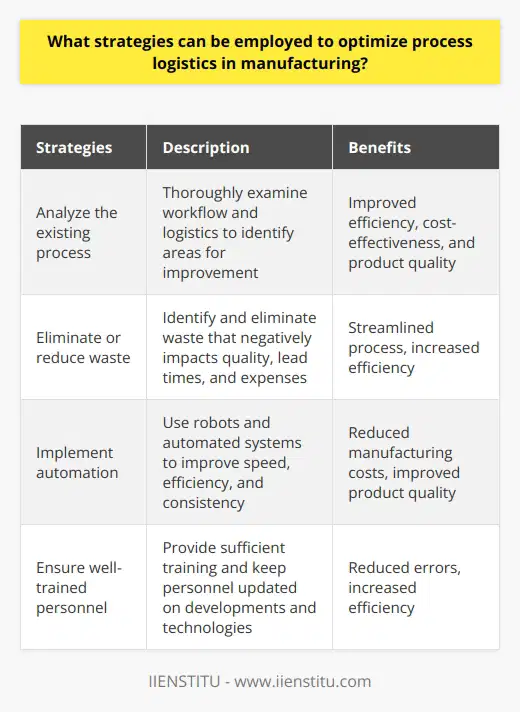
How can technology be used to streamline process logistics in manufacturing?
Technology innovation has revolutionized the traditional manufacturing industry by providing streamlined process logistics. With the advent of computerized automation, robots, and other systems, manufacturers can reduce costs while increasing quality and production cycle time. The logistics concept can be divided into three main categories: inventory management, production planning, and distribution. This article will discuss how technology can improve these essential logistics processes.
Inventory management is essential in a manufacturing operation as it helps to ensure a constant supply of raw materials and components and products for sale. Technology can be used to identify and track items, improve inventory accuracy and visibility, and efficiently manage warehouses and other supply operations. For example, RFID tags and barcoding are often utilized to track inventory items. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can also be used to analyze and forecast sales demand, helping to optimize the inventory to get the most out of every product.
Manufacturers have traditionally used manual systems or programs such as Excel spreadsheets to plan, schedule, and control production in production planning. However, software tools such as production planning and scheduling (PPS) systems have automated the process, offering a more effective, efficient, and reliable means of production planning. In addition, PPS systems streamline production by tracking resources and materials, optimizing schedules, managing costs, and coordinating manufacturing activities.
Lastly, technology can also be used to improve distribution. With the right logistics software, manufacturers can track shipments and inventory in real-time, accurately forecasting demand, scheduling pickups and deliveries, and optimizing transportation strategies. Automated tracking systems can also provide customers with complete and up-to-date information about their orders, such as shipping costs, transit times, delivery estimates, and other vital aspects of the fulfillment process.
Overall, technology can significantly reduce costs and improve efficiency in the manufacturing industry by streamlining process logistics. From inventory management to production planning to distribution, technology solutions can automate the entire production cycle, helping to ensure that products are created, distributed, and sold efficiently. Given the many benefits of technological automation, it is clear that manufacturers must continue to invest in technology solutions to remain competitive in today's manufacturing landscape.
What challenges are typically encountered when optimizing process logistics in manufacturing?
Optimizing process logistics in manufacturing is essential to managing the manufacturing process and achieving operational excellence. However, the process is often riddled with everyday obstacles that can prevent optimal operational efficiency and cost optimization.
One major challenge inherent in the complex logistics of manufacturing is the so-called "dimensions of scale," in which production capacity must remain relevant and efficient despite the volatility of demand. To meet these capacity demands, manufacturers must carefully balance their available resources and assign labor and resources to the production efforts that provide the most efficient return on investment.
Furthermore, process optimization often requires industrial engineers and logistics professionals to reconcile complex production requirements and change regulations with the availability of labor, supplies, and materials. Intervening these components while providing the desired throughput to consumers requires considerable time, effort, and resources.
Furthermore, process optimization also demands considerable investment in information technology. For example, today's manufacturing processes require the delivery of material and information in real-time, which can be challenging when those processes span multiple entities, customers, and locations. Meeting these demands often requires considerable investments in networks, data systems, and digital infrastructure.
Finally, the manufacturing process is rife with risk, as any unexpected delays, shortages, or natural disasters can severely disrupt production. Therefore, achieving optimal logistics involves a level of risk management as well as creating backup plans that are simultaneously flexible and resilient.
In summary, manufacturers face a unique and multifaceted challenge when optimizing process logistics. Challenges often necessitate careful balancing of resources, reconciliation of components, and investments in organizational infrastructure and risk management. For manufacturers to succeed in optimizing the process, they must consider all relevant dimensions of the challenge to ensure that success is achieved efficiently and sustainably.
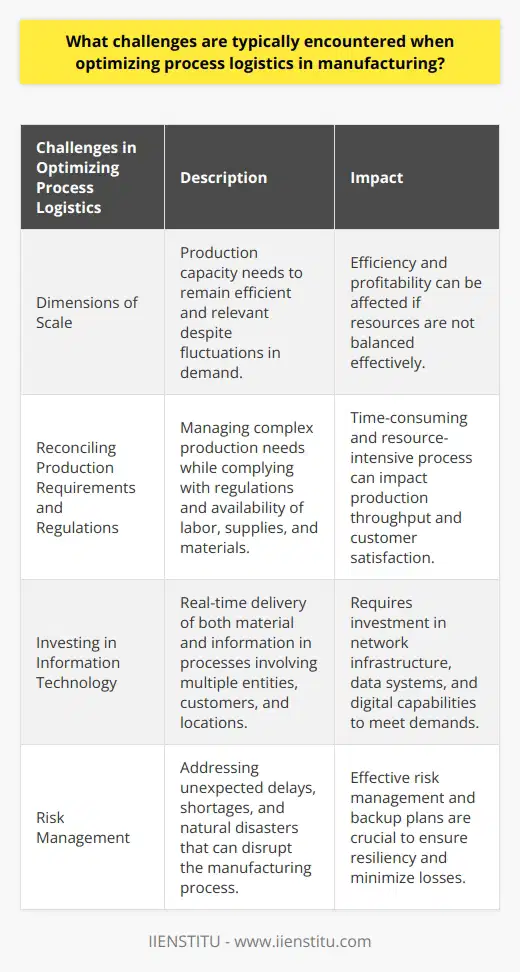
How are logistics processes optimized in addressing diverse customer needs and demands?
Logistics Process Optimization
To address the diverse needs and demands of customers, companies must optimize their logistics processes in several ways, ensuring efficient and effective operations. One crucial aspect of optimization involves the implementation of advanced technology systems, which can improve real-time analysis and information sharing between different departments and sections of a supply chain.
Integration of Technologies
Incorporating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) in logistics processes enables companies to improve their demand forecasting and inventory management. These technologies assist in decision-making, allowing businesses to better anticipate customer needs and adjust their procurement and production processes accordingly.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Using data analytics can significantly enhance the efficiency of logistics processes by identifying patterns and trends in customer demands. By analyzing historical and real-time data, companies can make informed decisions about resource allocation, transportation, and distribution, ultimately improving their ability to meet clients' needs.
Collaborative Platforms
The implementation of collaborative platforms is essential for optimizing logistics processes, as they facilitate information exchange among various stakeholders, such as suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers. This increased transparency and communication enable businesses to adapt their strategies to meet diverse customer needs more effectively.
Customized Solutions
Providing tailored solutions to clients is a vital aspect of addressing diverse customer needs. Companies that invest in configurable products and offer flexibility in their services, such as multiple shipping options or personalized packaging, are better positioned to meet the specific demands of their target market.
Continuous Improvement
Finally, adopting a continuous improvement mindset can significantly contribute to logistics process optimization. By routinely evaluating and refining the existing processes, companies can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, developing targeted solutions to address them. This iterative approach ensures that organizations are always striving for excellence and improvement, enhancing their ability to meet the ever-evolving demands of their customers.
In conclusion, optimizing logistics processes to address diverse customer needs and demands requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on technology integration, data-driven decision-making, collaboration, customization, and continuous improvement. In doing so, companies can not only adapt to the ever-changing landscape of customer expectations but also ensure efficiency and competitiveness within their operations.
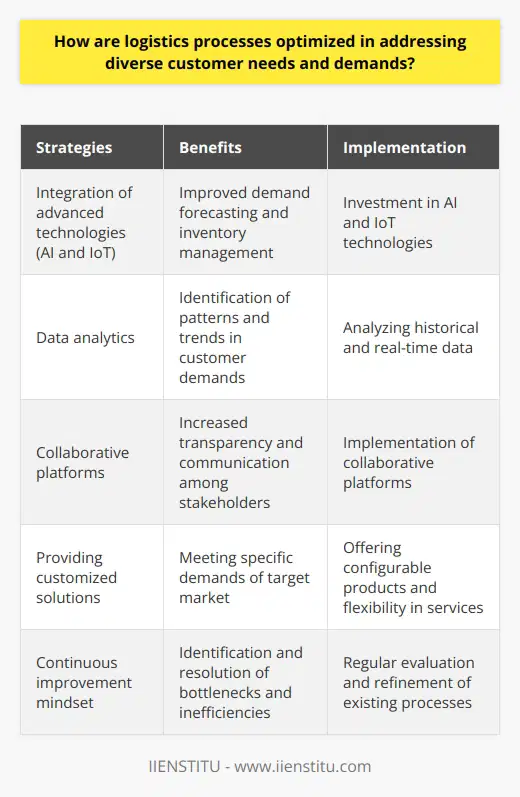
What is the impact of optimizing logistics on overall business performance and sustainability?
The Influence of Optimized Logistics
Optimizing logistics is a crucial component to maintain a competitive edge in modern business environments. The impact on overall business performance and sustainability can be substantial, particularly when addressing costs, customer satisfaction, and environmental concerns.
Cost Savings
One significant benefit of optimizing logistics is the potential cost savings. Efficiently managing transportation, warehousing, and inventory can result in reduced overhead expenses, thereby improving a company's bottom line. Such cost reductions allow businesses to invest more in other areas, such as research and development, employee training, and marketing, further strengthening their market position.
Customer Satisfaction
Another impact of optimizing logistics is the improvement in customer satisfaction. When a business can deliver products and services more quickly and accurately, customers are more likely to remain loyal and recommend the company to others. Implementing effective logistics systems ensures that customers receive orders on time and with fewer errors, which is essential in maintaining and improving a company's reputation.
Environmental Responsibility
Furthermore, optimizing logistics has a considerable effect on a business's sustainability efforts. By improving transportation efficiency, reducing waste, and lowering energy consumption, companies can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and impact on the environment. Embracing sustainability initiatives is not only ethically responsible but can also lead to long-term cost savings and an enhanced public image.
Supply Chain Resilience
Optimized logistics also contribute to a company's ability to establish a resilient supply chain. A robust and adaptable supply chain is vital for businesses to respond to disruptions effectively, such as natural disasters, economic crises, or manufacturing issues. Fostering resilience in logistics processes can mitigate risks and ensure a company's continued operation and success in challenging circumstances.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Lastly, optimizing logistics helps businesses make more informed decisions through the use of data analysis. Collecting and analyzing data on transportation, inventory, and other logistical aspects enable companies to identify trends, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. By leveraging these insights, businesses can make targeted adjustments to increase efficiency and performance across their entire operation.
In conclusion, optimizing logistics plays a critical role in enhancing overall business performance and sustainability. Through cost savings, increased customer satisfaction, environmental responsibility, supply chain resilience, and data-driven decision making, companies can improve their competitiveness, achieve sustained growth, and ensure long-term success in the marketplace.
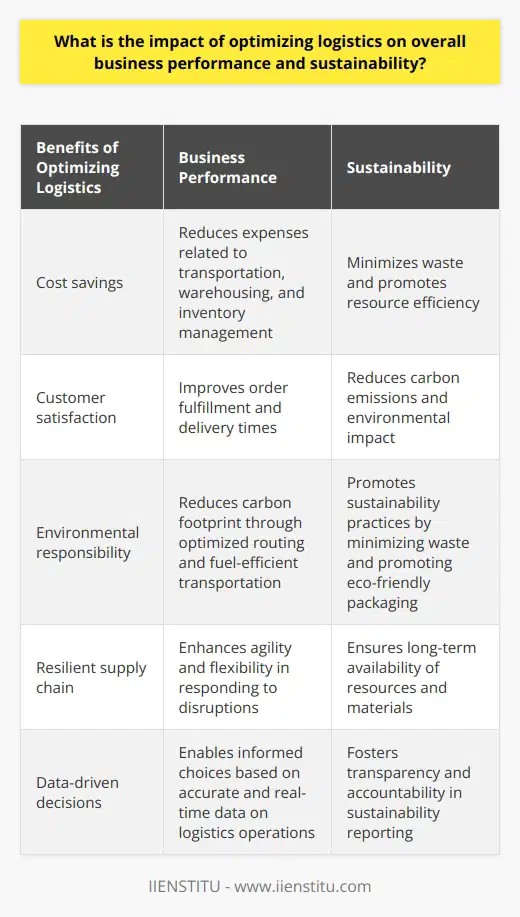
How do you optimize logistics in supply chain to ensure resilience and adaptability in times of disruption?
Assessing Risks and System Vulnerabilities
To optimize logistics in supply chain, resilience and adaptability must be prioritized during times of disruption. A vital approach to achieving this is to assess risks and identify system vulnerabilities. Evaluating potential disruptions and their impacts on supply chain operations helps organizations create effective contingency plans.
Building Strategic Partnerships
Another crucial step is to establish strategic partnerships with suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. These relationships facilitate information sharing and enhance collaboration during crisis management. Working closely with partners allows for flexibility in the supply chain and effective communication when mitigating risks.
Diversifying Supply Sources
To further enhance resilience, supply chain managers should diversify their sources of supply. Engaging with multiple suppliers in different geographic locations can minimize the detrimental effects of localized disruptions. By reducing dependency on single-source suppliers, organizations can better navigate interruptions without compromising their operations.
Implementing Technology and Automation
Utilizing technology and automation can significantly improve supply chain adaptability. Advanced systems, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, can help predict disruptions and optimize decision-making processes. Additionally, digital tools can facilitate real-time communication and data exchange among supply chain stakeholders, promoting coordination and fast response to changing circumstances.
Emphasizing Inventory Management
Proper inventory management techniques, such as just-in-time (JIT) and safety stock, contribute to supply chain resilience. Balancing optimal inventory levels with the ability to respond to unpredictable demands minimizes potential disruptions resulting from stock-outs or overstocking. Efficient inventory management also supports cost optimization and reduces waste.
Investing in Workforce Training
Ultimately, the workforce plays a crucial role in optimizing supply chain logistics. Investing in training programs that enhance employees' skills and knowledge in risk management, advanced technologies, and crisis response can empower them to make informed decisions. Moreover, a well-prepared workforce can adapt quickly to disruptions, ensuring business continuity.
In conclusion, optimizing logistics in supply chain to ensure resilience and adaptability requires a multi-faceted approach. Evaluating risks, fostering partnerships, diversifying supply sources, adopting technology, managing inventory, and investing in workforce training are essential strategies for navigating supply chain disruptions effectively.
How do you optimize logistics processes to reduce lead times and increase efficiency?
Assessing the Supply Chain
Optimizing logistics processes involves a comprehensive assessment of the entire supply chain, identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and potential improvement areas. This enables organizations to modify and enhance their systems and procedures, consequently reducing lead times and increasing efficiency.
Implementing Lean Practices
A crucial approach for optimization is embracing lean practices, which involves eliminating waste from the process. These practices include just-in-time inventory, minimizing transportation time, consolidating shipment loads, and reducing handling operations. Lean practices can also streamline the supply chain by promoting cross-functional collaboration and centralizing decision-making processes.
Utilizing Technology Solutions
Technology plays a vital role in enhancing logistics processes. Implementing advanced tools such as warehouse management systems, transportation management systems, and demand forecasting software helps organizations track inventory levels, monitor shipments, and anticipate fluctuations in demand. This allows organizations to make informed decisions, optimizing their operations, and reducing overhead costs.
Improving Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is essential for supply chain optimization. Improved forecasting allows organizations to anticipate changes in demand, allocate resources efficiently, and avoid stock-outs and overstock situations. Machine learning algorithms and historical data analysis aid in enhancing forecasting accuracy, enabling organizations to minimize inefficiencies and reduce lead times.
Establishing Performance Metrics
Measuring and monitoring performance is key to identifying areas for improvement. Organizations should establish performance metrics such as order cycle time, delivery accuracy, and inventory holding costs to track progress and make necessary adjustments. Regularly evaluating and benchmarking these metrics enables companies to detect inefficiencies, implement corrective actions, and optimize their logistics processes.
Building Strategic Partnerships
Collaborating with suppliers, distributors, and other stakeholders can contribute significantly to supply chain optimization. Strategic partnerships facilitate information sharing, enable joint problem-solving, and promote a sense of shared responsibility. This collaboration results in reduced lead times, enhanced process efficiency, and better overall performance.
In conclusion, optimizing logistics processes to reduce lead times and increase efficiency involves a holistic approach that addresses all aspects of the supply chain. By implementing lean practices, utilizing technology solutions, improving demand forecasting, establishing performance metrics, and building strategic partnerships, organizations can achieve significant improvements in their logistics operations. Investing in these efforts not only enhances supply chain performance but also contributes to an organization's overall competitiveness and long-term success.

What are the crucial factors to consider when implementing optimization strategies for logistics processes in manufacturing?
Crucial Factors for Optimization Strategies
When implementing optimization strategies for logistics processes in manufacturing, several crucial factors contribute to a successful outcome. Understanding these factors is essential for identifying potential areas for improvement and driving efficiency gains.
Supply Chain Visibility
The first crucial factor is supply chain visibility. Manufacturers must be able to track all components, raw materials, and finished products throughout the production process. Implementing real-time tracking technologies, such as RFID-tags and GPS-tracking systems, improves accuracy and timeliness of information, enabling better decision-making and faster responsiveness to changes in demand.
Resource Allocation
Effective resource allocation is another essential factor for optimizing logistics processes in manufacturing. This includes assigning the right team members and equipment to specific tasks, such as production, assembly, and transportation. Manufacturers must also understand their production capacities, flow rates, and storage capacities to allocate resources efficiently and minimize bottlenecks.
Inventory Management
Proper inventory management is critical for optimizing logistics in manufacturing. It involves understanding the optimal inventory levels of raw materials and finished products, which help to prevent stockouts or overstocking situations. Techniques such as just-in-time (JIT) production and vendor-managed inventory (VMI) can prevent excess inventory while ensuring a continuous supply of materials.
Process Integration
Integrating logistics processes within the manufacturing facility can lead to significant improvements in efficiency. Organizations should aim for seamless coordination between different departments, such as procurement, production, and distribution. Adopting technologies like enterprise resource planning (ERP) helps streamline processes and reduce human errors, ultimately improving overall logistics performance.
Continuous Improvement
Recognizing the importance of continuous improvement allows manufacturers to adjust and fine-tune their optimization strategies. Regularly reviewing and analyzing logistics processes helps identify gaps and opportunities, enabling timely changes and further optimization. Embracing principles such as lean manufacturing and Six Sigma can support this process.
In conclusion, successful implementation of optimization strategies in manufacturing logistics relies on supply chain visibility, effective resource allocation, proper inventory management, process integration, and continuous improvement. By addressing these crucial factors, manufacturers can significantly boost their logistics performance, driving cost savings and enhancing competitiveness within their industry.

How can data analysis and forecasting techniques be utilized to optimize logistics processes and decision-making?
Understanding Data Analysis and Forecasting
Data analysis and forecasting are essential tools in optimizing logistics processes and decision-making. To understand their application, one must first grasp their basic principles. Data analysis refers to the process of extracting useful information from raw data to identify trends, patterns, and relationships. Forecasting, on the other hand, involves using historical and current data to make predictions about future events or trends.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
One way data analysis and forecasting can optimize logistics processes is through the identification of patterns and trends in historical data. By analyzing large datasets from various operations, businesses can pinpoint similarities and variations between different products, services, and markets. Consequently, these insights can help optimize logistics operations, such as transportation routes and inventory management, by providing data-driven decision-making on operational changes and improvements.
Predictive Analytics for Decision-making
Predictive analytics, a subset of data analysis and forecasting, uses advanced techniques, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to predict future outcomes. In logistics management, predictive analytics can enhance decision-making by forecasting demand, estimating lead times, and predicting equipment failures. For instance, by using historical sales data and external factors like seasonality and market trends, companies can forecast demand for specific products and adjust their production and inventory levels accordingly.
Improving Resource Allocation
Another application of data analysis and forecasting in optimizing logistics processes is improving resource allocation. Effective resource management is crucial for reducing operational costs and enhancing efficiency. By analyzing real-time data from operations, companies can detect inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement, allowing them to align their resources with the most critical areas. Forecasting makes it possible to predict future resource needs, enabling better planning and allocation of resources, such as labor, warehouse space, and transportation assets.
Mitigating Risk and Uncertainties
Data analysis and forecasting techniques also play an essential role in mitigating business risks and uncertainties related to logistics operations. By identifying patterns and trends in historical data, managers can make informed decisions in anticipation of potential disruptions, such as natural disasters, supply chain disruptions, and changing regulations. Moreover, forecasting allows businesses to identify potential bottlenecks or future risks in their operations, enabling them to take proactive measures to avoid or minimize negative impacts.
In conclusion, data analysis and forecasting techniques contribute significantly to optimizing logistics processes and decision-making. By harnessing information found in historical and real-time data, businesses can identify trends and patterns, make accurate predictions, allocate resources effectively, and mitigate risks. Consequently, this leads to improved efficiency, reduced operational costs, and increased competitive advantage.
What is the role of strategic planning in optimizing logistics processes?
Role of Strategic Planning
Strategic planning plays a critical role in optimizing logistics processes by providing guidance on resource allocation, identifying areas for improvement, and setting objectives to achieve operational efficiency. By developing a comprehensive strategy, organizations can streamline their logistics operations, enhance their competitiveness, and boost overall performance.
Resource Allocation
Effective resource allocation is essential in optimizing logistics processes. Through strategic planning, organizations can identify and prioritize their most critical resources, such as human capital, technology, and finances. This prioritization helps maximize the value derived from these resources, ensuring optimal decision-making and reducing overall operational costs.
Continuous Improvement
Identifying areas for improvement is another critical function of strategic planning in optimizing logistics processes. Organizations need to continuously assess and evaluate their logistics operations to identify performance gaps and inefficiencies. By setting targets and benchmarks, logistics operations can be improved incrementally and strategically, leading to sustained optimization and growth.
Setting Objectives
Strategic planning provides a framework for setting objectives, which are crucial in driving improvements in logistics processes. By setting clear, achievable, and measurable goals, organizations can enhance accountability, motivate their workforce, and drive innovation throughout the logistics value chain.
Risk Management
Strategic planning also aids in risk management, which is vital in optimizing logistics processes. By assessing potential risks and developing contingency plans, organizations are better prepared for any disruptions or challenges that may arise, ultimately mitigating the impact of unforeseen events on logistics operations.
Innovation and Technology
In today's ever-changing business landscape, innovation and technology are integral to achieving optimization in logistics processes. Strategic planning enables organizations to identify the latest trends, adopt relevant technology solutions, and stay ahead in the competitive landscape, all of which are essential in achieving optimization.
In conclusion, strategic planning is a vital component in optimizing logistics processes. By focusing on resource allocation, continuous improvement, setting objectives, risk management, and embracing innovation and technology, organizations can drive efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance in their logistics operations. With the right strategic approach, logistics processes can be optimized, leading to significant competitive advantages in an increasingly demanding business environment.

How can collaboration between various stakeholders contribute to logistics process improvement?
Collaborative Approach in Logistics
Collaboration between various stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, retailers, and transportation companies, significantly enhances logistics process improvement. Each stakeholder's unique perspective and expertise enable the development of innovative, efficient, and cost-effective logistics solutions.
Data Sharing and Integration
One crucial aspect of stakeholder collaboration is the sharing and integration of data. By making information about inventory levels, order statuses, lead times, and demand forecasts accessible, the logistics process becomes more transparent and streamlined. Additionally, data sharing allows the stakeholders to make informed decisions, minimize errors and delays, and achieve operational excellence.
Coordination and Synchronization
When stakeholders collaborate, they can better coordinate and synchronize their operations, leading to significant improvements in the logistics process. For example, suppliers and manufacturers can work together to optimize production schedules and inventory levels, while transportation providers can ensure timely and efficient delivery of goods. This level of coordination leads to reduced lead times, optimized inventory levels, and cost savings.
Innovative Solutions Development
The collaboration also encourages the creation and implementation of innovative logistics solutions. Combining the expertise of each stakeholder, parties can design new distribution strategies, implement technology-driven solutions, and adopt best practices found within and outside of their industries. These innovations, in turn, help to maximize service levels and reduce operating costs.
Performance Monitoring and Feedback
Collaboration fosters a continuous feedback loop among stakeholders, enabling them to monitor and evaluate the logistics process's performance. Through performance analytics and regular communication, they can identify deficiencies, areas in need of improvement, and opportunities for further enhancement. This iterative approach ensures that the logistics process remains agile and responsive to evolving market conditions.
To sum up, collaboration between various stakeholders plays a critical role in improving the logistics process. Collective efforts in data sharing, coordination, innovation, and performance monitoring yield synergistic benefits that lead to increased efficiency, cost savings, and overall competitiveness.
What measures can be taken to ensure continuous improvement in the four key processes of logistics?
Supply Chain Visibility
To ensure continuous improvement in the four key processes of logistics – transport, warehousing, forecasting, and distribution – organizations can employ various measures. One such measure is enhancing supply chain visibility, which requires the adoption of advanced tracking and communication technologies. With better visibility, businesses can monitor and analyze their operations in real-time, enabling swift decision-making and the ability to adapt to market changes.
Demand Forecasting Accuracy
Improving demand forecasting accuracy is another crucial aspect in optimizing logistics processes. By employing sophisticated forecasting tools and techniques, such as predictive analytics and machine learning, companies can generate more accurate estimates of future demands and adjust their operations accordingly. This helps with inventory management, reduces stock-outs and overstocking, and streamlines the entire supply chain.
Resource Optimization
Efficient use of resources, including manpower, equipment, and transportation, is essential in improving logistics operations. This involves eliminating redundancies, adopting advanced resource management systems, and enhancing employee skills through regular training and development programs. Resource optimization minimizes wastage, ensures timely deliveries, and ultimately improves the bottom line of the business.
Collaborative Partnerships
Establishing cooperative partnerships with suppliers, customers, and third-party logistics (3PL) providers is a vital component of boosting logistics performance. Collaborative relationships foster information sharing, improve decision-making, and encourage innovation as partners jointly develop solutions for common challenges. They align interests across the supply chain, enabling greater operational efficiency and customer responsiveness.
Performance Measurement and Evaluation
Regularly monitoring and evaluating logistics performance indicators is a necessary measure for continuous improvement. This can be achieved through the implementation of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that track the efficiency, effectiveness, and cost of operations. By continuously assessing their performance, organizations can identify bottlenecks and areas of improvement, allowing them to make necessary adjustments in their logistics processes strategically.
In conclusion, the continuous improvement of logistics processes can be ensured through various measures, including increased supply chain visibility, accurate demand forecasting, resource optimization, collaborative partnerships, and regular performance measurement and evaluation. These approaches not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to overall business success.
How do you optimize logistics processes to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainable practices?
Understanding Environmental Impact in Logistics
To optimize logistics processes and minimize their environmental impact, it is crucial to first comprehend the carbon footprint generated by transportation, warehousing, and packaging operations. Equipped with this knowledge, businesses can identify areas with the potential for improvement and adopt targeted sustainable measures.
Strategies for Sustainable Transportation
Shortening the transportation route is a fundamental step towards reducing fuel consumption and emissions. This can be achieved by consolidating shipments, opting for intermodal transport solutions, and utilizing route optimization software. Additionally, companies can transition to greener fleets, such as electric vehicles, biofuel-powered vehicles, or newer models with improved fuel efficiency.
Implementing Eco-friendly Warehousing Technologies
Incorporating energy-efficient technology in warehouses and distribution centers presents opportunities to reduce energy consumption and emissions. This may include installing solar panels, utilizing energy-efficient lighting, and implementing intelligent heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. Additionally, embracing technologies like automation and robotics can improve warehouse management and minimize energy wastage.
Rethinking Packaging and Materials
Adopting eco-friendly packaging materials and solutions, such as biodegradable or recycled materials, can significantly decrease waste and contribute to sustainable practices. Analyzing and optimizing packaging designs can reduce the use of excess materials, which in turn minimizes waste and lowers the overall weight of transported goods.
Promoting Collaboration and Information Sharing
Collaborating with suppliers, customers, and logistics partners allows companies to share knowledge and best practices, leading to improved sustainability throughout the entire supply chain. Implementing information systems that facilitate real-time communication and data exchange can aid in better decision-making and support greener practices.
Tracking and Measuring Sustainability Performance
Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and setting targets is essential for measuring and monitoring sustainability progress. This enables companies to evaluate the effectiveness of implemented solutions, as well as identify and address areas for further improvement.
In summary, achieving a reduced environmental impact in logistics requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses sustainable transportation strategies, eco-friendly warehousing technologies, optimized packaging solutions, collaboration and information sharing, and continuous performance tracking. By adopting these practices, companies can improve their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
What role does effective communication play in improving the efficiency and effectiveness of logistics processes?
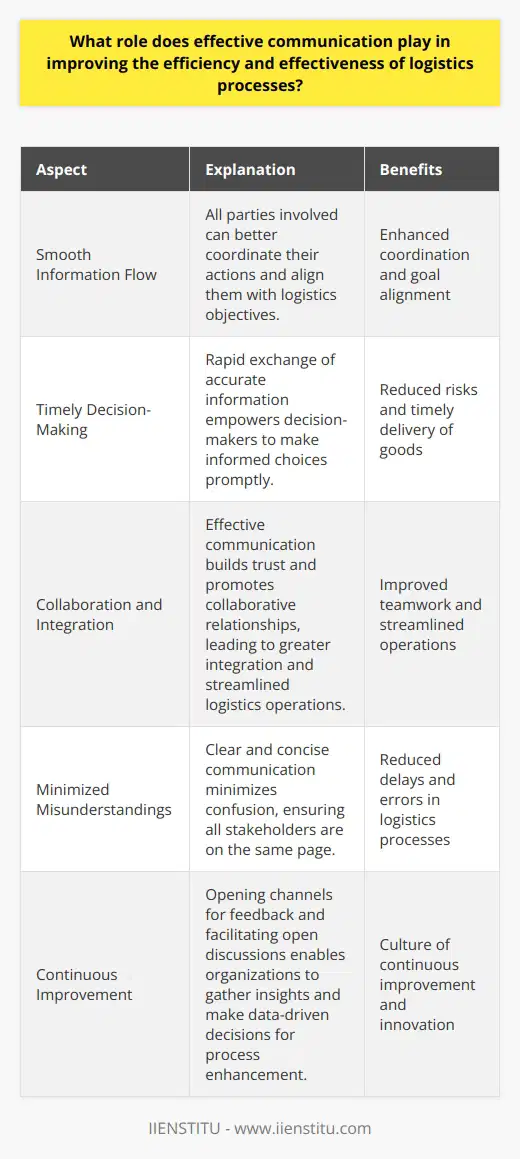
Significance of Effective Communication in Logistics
Effective communication plays a critical role in improving the efficiency and effectiveness of logistics processes. By fostering smooth information flow, communication allows all parties involved to better coordinate their actions, aligning them with the overall logistics objectives.
Facilitation of Timely Decision Making
One key aspect of effective communication in logistics is the rapid exchange of accurate information. This empowers decision-makers to act promptly and make informed choices in response to changing circumstances. Consequently, it helps in mitigating potential risks and ensuring the timely delivery of goods.
Enhancing Collaboration and Integration
In a complex supply chain, numerous stakeholders, including suppliers, transporters, and customers, need to work together harmoniously. Effective communication helps in building trust and promoting collaborative relationships, which in turn result in greater integration and streamlined logistics operations.
Reducing Misunderstandings and Delays
Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings, resulting in costly delays and inefficiencies. On the other hand, clear and concise communication minimizes confusion, ensuring that everyone is on the same page. This increases the overall efficiency of logistics processes by enabling seamless execution of tasks and reducing the likelihood of errors.
Supporting Continuous Improvement
Effective communication also plays a vital role in identifying areas for improvement within the logistics processes. By opening channels for feedback and facilitating open discussions, organizations can gather valuable insights and make data-driven decisions to enhance their operations. Moreover, transparent communication fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation in the logistics sector.
In conclusion, effective communication is an indispensable element in enhancing logistics efficiency and effectiveness. By facilitating timely decision-making, fostering collaboration, reducing misunderstandings, and supporting continuous improvement, it contributes to the successful execution of logistics processes and ensures a seamless supply chain.
How can performance measurement and benchmarking contribute to the optimization of logistics processes within a production chain?
Role of Performance Measurement
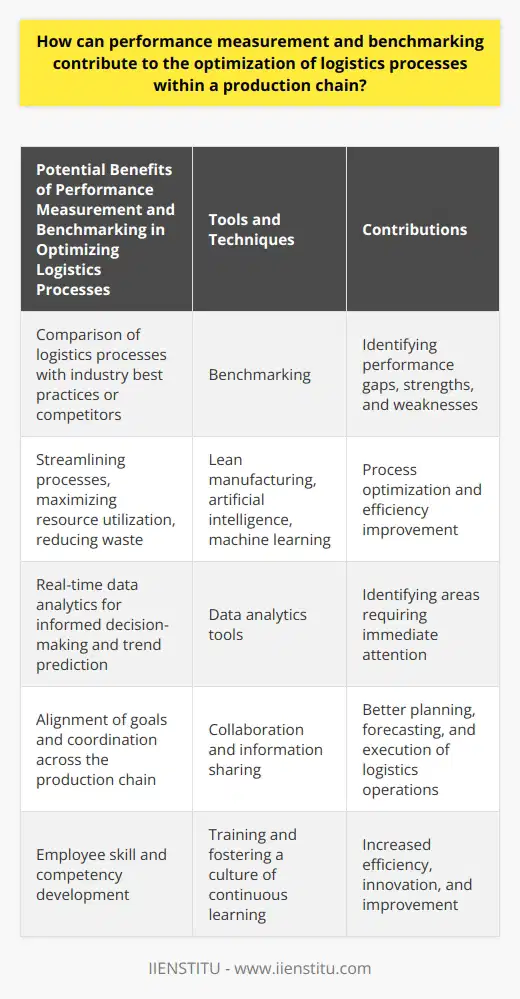
Performance measurement plays a significant role in the optimization of logistics processes within a production chain. It involves setting pre-defined standards and goals, monitoring progress, identifying areas of improvement, and taking necessary actions to eliminate inefficiencies. By systematically evaluating the performance of various logistics operations, companies can identify bottlenecks and optimize the overall process to meet customer demands while minimizing costs.
Benefits of Benchmarking
Benchmarking complements performance measurement by allowing businesses to compare their logistics processes with industry best practices or competitors. Analyzing performance gaps helps identify strengths and weaknesses in the existing processes and develop specific improvement strategies. This competitive intelligence enables companies to stay ahead of the market by continuously improving and adopting innovative practices in their logistics operations.
Process Optimization Techniques
Implementing process optimization techniques can have a considerable impact on logistics process improvements. Techniques such as lean manufacturing and the use of advanced technologies, like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), can streamline processes, maximize resource utilization, and cut down waste. Additionally, real-time data analytics tools can allow for more informed decision-making, predicting trends, and identifying areas that need immediate attention.
Collaboration and Information Sharing
Promoting collaboration and information sharing across the production chain is fundamental to optimizing logistics processes. Aligning the goals of various stakeholders such as manufacturers, suppliers, and third-party logistics providers can lead to better coordination and synergies. With the help of integrated technology platforms like an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, real-time information can be shared between partners to facilitate better planning, forecasting, and execution of logistics operations.
Employee Skill and Competency Development
Finally, investing in employee skill and competency development is essential for optimizing logistics processes. This includes training in new technological tools and fostering a culture of continuous learning and problem-solving. An educated and skilled workforce not only accomplishes tasks more efficiently but also contributes to long-term company growth by driving innovation and improvement.
In conclusion, performance measurement and benchmarking play a crucial role in logistics process optimization within a production chain. By implementing these strategies, businesses can enhance their competitive advantage, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve sustainable growth.
What are the main components and objectives of optimizing logistics processes in the manufacturing industry?
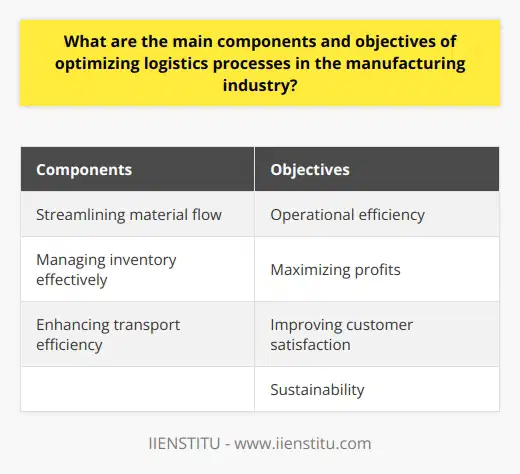
Optimization in Logistics Processes
In the manufacturing industry, optimizing logistics processes primarily involves three main components. Firstly, streamlining material flow is crucial. It ensures uninterrupted production, preventing delays and inefficiencies. Secondly, managing inventory effectively is vital. This entails maintaining an optimal stock level, balancing the costs of holding inventory against the risk of stockouts. Thirdly, enhancing transport efficiency plays a significant role. It focuses on reducing costs, time and environmental impact of transporting goods.
Objectives of Logistics Optimization
The key objectives of logistics process optimization in manufacturing fall into four main categories. Operational efficiency is one of the most crucial objectives. The aim is to minimize time, cost, and resource consumption, while ensuring seamless operations.
Maximizing profits is another main target. By reducing unnecessary costs throughout the logistics process, there can be a substantial improvement in the bottom line. Improving customer satisfaction also forms an integral part of the objectives. Ensuring timely delivery and keeping products in optimal condition enhance the overall customer experience.
Last but not least, sustainability should always be an objective in modern-day manufacturing. Reducing the carbon footprint of logistics activities and promoting ethical practices ensures the manufacturing operations are environmentally and socially responsible.
In conclusion, optimizing logistics processes in the manufacturing industry is a complex task that involves multiple components and aims to achieve numerous objectives. Nevertheless, with careful planning and implementation, it can lead to significant benefits to the business, customers and the environment.
How does the integration of various supply chain functions contribute to overall optimization of the logistics processes?
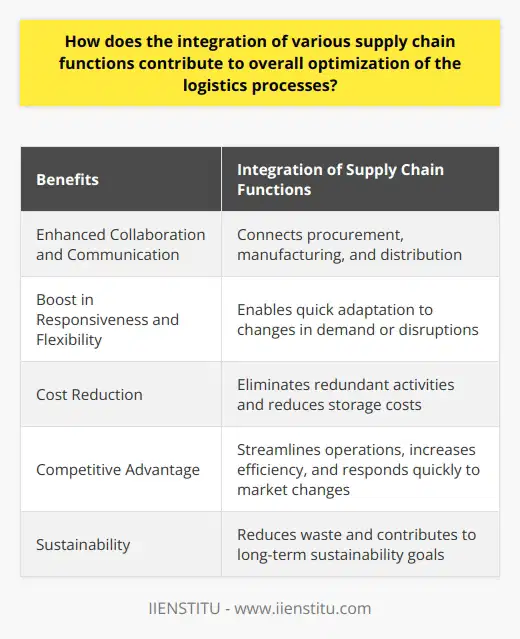
Enhancing Efficiency with Integrated Supply Chain Functions
The integration of various supply chain functions heightens logistics processes optimization. When companies integrate processes such as procurement, manufacturing, and distribution operations, they create an interconnected business model. This model strengthens interdepartmental collaboration and communication, making it easier to identify and mitigate potential inefficiencies.
Boosting Responsiveness and Flexibility
Integrated supply chains are more responsive and flexible. They can quickly adapt to changes in demand, supplier issues, or other interruptions. Robust connectivity allows instant data sharing, reducing lead times and promoting efficient inventory management. A responsive supply chain better accommodates customer needs and manages risk, resulting in fewer disruptions and higher satisfaction levels.
Reducing Costs and Enhancing Customer Satisfaction
Integration also reduces logistics costs. By linking all steps, redundant activities are eliminated, increasing the speed of goods to the market. Companies can cut down on storage costs and reduce financial risks associated with holding excess inventory. Improved efficiency therefore translates into improved customer satisfaction from faster delivery times.
Driving Competitive Advantage and Sustainability
Lastly, integrating supply chain functions can yield a competitive advantage. Companies that streamline their operations, increase performance efficiency, and respond quickly to changes, gain an edge over competitors. Furthermore, an efficient supply chain reduces waste in the form of time, effort, and resources, contributing to the sustainability goals of the company.
In conclusion, integrating supply chain functions optimizes logistics processes by enhancing efficiency, responsiveness, and flexibility, reducing costs, and driving competitive advantages. It indeed serves as a strategic tool to streamline operations, thereby improving overall business performance and sustainability.
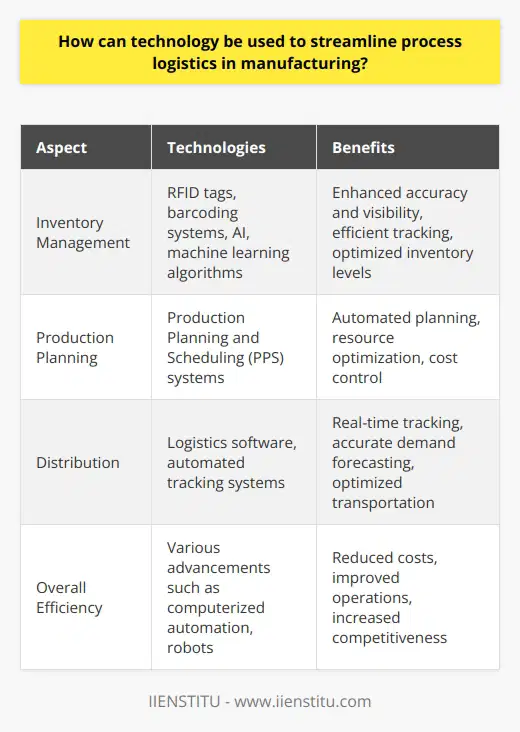
What are some best practices and principles in optimizing the logistics processes to ensure competitive advantage for manufacturing organizations?
Optimizing Logistics for Competitive Advantage
Streamlining Supply Chain Management
To enhance the efficiency of manufacturing establishments, they should pay great attention to the supply chain. One tip is integrating suppliers into the organization’s operations. Logistical integration with suppliers allows for improved visibility, less inventory, and reduced lead time.
Inventory Management Practices
Efficient inventory management is vital. They should aim at reducing the carrying cost. Practice like Just-In-Time inventory offers an optimal balance between stock availability and cost.
Logistic Process Optimization
Process optimization is key. Reducing non-value-adding activities within the processes enhances efficiency. For instance, simple changes like reducing distance covered in warehouses can make a big difference.
Harnessing Technology
Technology can aid in optimizing every process. Tools like Warehouse Management Systems can help on managing inventory effectively. RFID tags can provide real-time visibility of shipments.
Outsourcing Logistical Functions
Outsourcing non-core functions like transportation can enhance focus on core operations. Contracting third-party logistics players with specialization and scalability will ensure better results.
Benchmarking Performance
It is crucial to compare one’s performance with industry best practices. Benchmarking with other companies will highlight areas for improvement.
In summary, optimizing logistics process should be a continuous process. Regular review and updates will ensure that manufacturing organizations stay ahead of competition. Continuous optimization guarantees maximum productivity in the shortest time possible.