The Logistical Packaging Process
Optimizing the Process
Product distribution is one of the most important aspects of modern Supply Chain Management. It involves deploying a product from its production point to its final destination, ensuring that it reaches the right people in the right quantities and in a timely and efficient manner. Logistical packaging is a vital part of this process, as it helps to ensure that products are properly stored and transported. This blog post will examine the process of logistical packaging, discuss how it can be optimized and improved, and provide some valuable resources for further information.
The Logistical Packaging Process
Logistical packaging is securing, protecting, and packaging products for storage, transport, and delivery. This process starts at the point of production, where items need to be collated and consolidated. Once the products have been grouped, they are either shrinkwrapped or placed in boxes or sacks, depending on their size and weight. Ideally, the packaging should be strong enough to resist shock, moisture, and other external conditions so that the products remain in their original state throughout their journey.
There are several benefits to the logistical packaging process:
First, it helps reduce the potential for damage while the products are stored and transported.
It allows for more accessible organization, allowing teams to quickly and accurately identify and count items.
It reduces the labor costs associated with product distribution.
Businesses can pack larger volumes in fewer containers, reducing packing and transportation costs.
Optimizing the Proces
It is possible to make several suggested improvements to the process of logistical packaging. Firstly, businesses should consider how their packaging can reduce product waste. They should ensure that the materials used to package the items are free of toxins, non-toxic and biodegradable, and use minimal resources. They should also ensure that the packaging is designed to be reused, recycled, or composted after use.
Secondly, businesses should focus on optimizing their container selection. Using a variety of sizes and shapes can reduce deficiencies, overruns, and damages in the supply chain. Companies should also consider using RFID tags, which allow for better tracking and inventory management of their products.
Finally, businesses should focus on the optimization of their transportation methods. They should use a combination of air, ground, and sea transportation to reduce their transport costs and pay close attention to the regulations of each country they are shipping to. They should also consider using digital asset tracking software, enabling real-time visibility across the entire logistical network.
Challenges of Implementation
There are several challenges that businesses need to consider when it comes to implementing the suggested improvements. Firstly, companies need to ensure that they have sufficient resources to implement the proposed improvement measures. This may mean investing in additional storage facilities and recruiting more staff to manage the process. Secondly, businesses must ensure their teams are properly equipped to handle data. For example, introducing RFID tags and digital tracking software will require increased data handling and analysis. Finally, companies must be aware of the regulations surrounding their transportation methods, which can vary from country to country.
Conclusion: Logistical packaging plays a vital role in product distribution, helping to reduce damage, wastage, and labor costs. However, businesses can further improve their packaging process to optimize their Supply Chain Management. Suggested improvements include reducing product waste through eco-friendly packaging, optimizing container selection, and optimizing transportation methods. While these measures can bring various benefits, businesses must also consider the resources, data handling, and regulatory requirements involved in their implementation.
Adequate logistical packaging can help ensure smoother product distribution.
Frequently Asked Questions
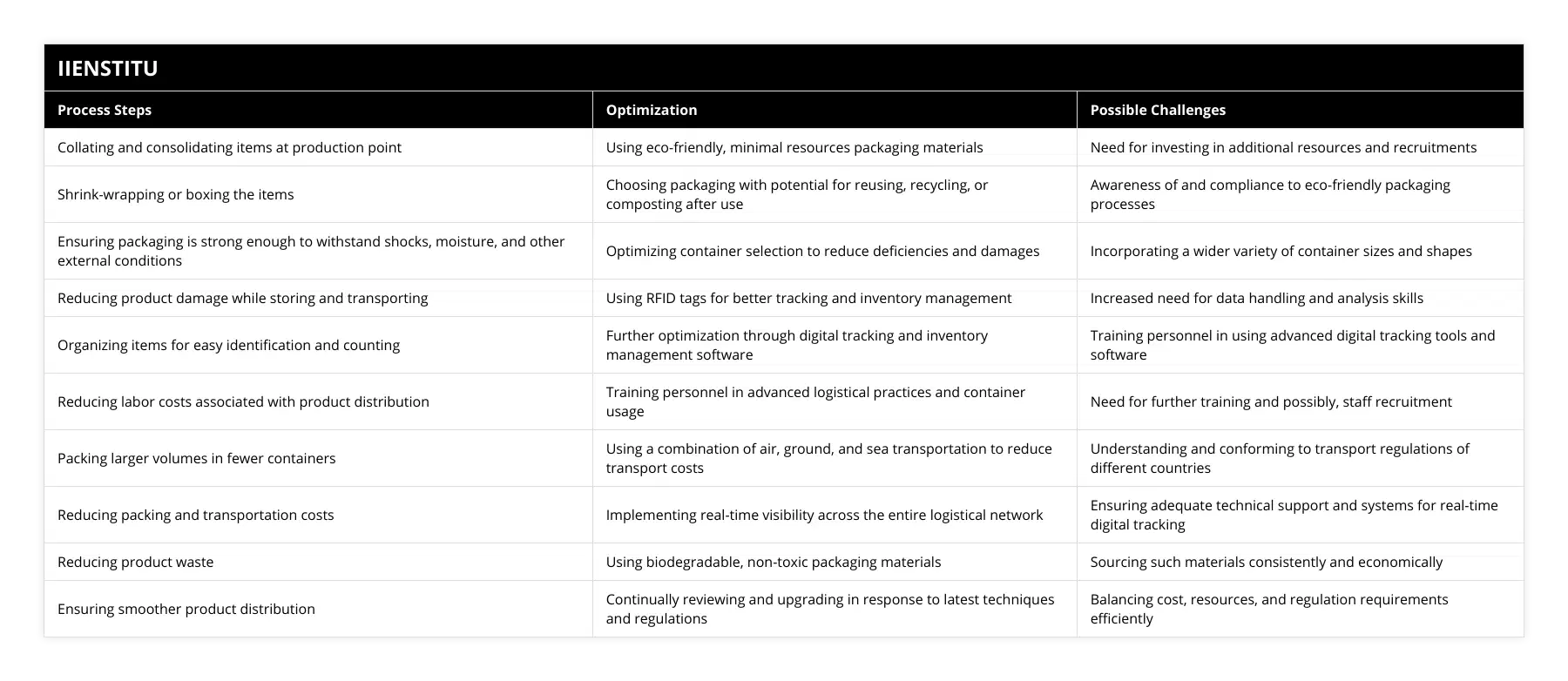
What criteria should be used when considering different packaging materials for logistical product distribution?
Logistical product distribution is a complex and essential process to the success of numerous businesses. One key element of this process is the packaging material used to distribute the products. When considering different packaging materials, there are several criteria to consider.
In terms of cost, the purchase price of the material needs to be considered to determine which packaging material is the most cost-effective. The package's overall weight should also be considered, as this can affect shipping costs.
The material's durability and longevity must be considered in terms of practicality. In addition, the material must protect the product for its intended purpose, ensuring it arrives in perfect condition. Furthermore, the choice of packaging material must consider the industry standards for packing requirements for the product.
When it comes to environmental considerations, it is essential to consider the recyclability of the chosen material. The packaging material should be biodegradable, compostable, and recyclable. In addition, the material should not require excessive resources, such as water and energy, to produce and distribute.
Finally, the chosen packaging material should consider the product's aesthetic value. The packaging should appeal to customers, communicate the brand image and stand out from other packaging materials.
When considering different packaging materials for logistical product distribution, cost, practicality, environmental considerations, and the product's aesthetic value should all be considered. Doing so will result in the most effective packaging materials being chosen for distribution.
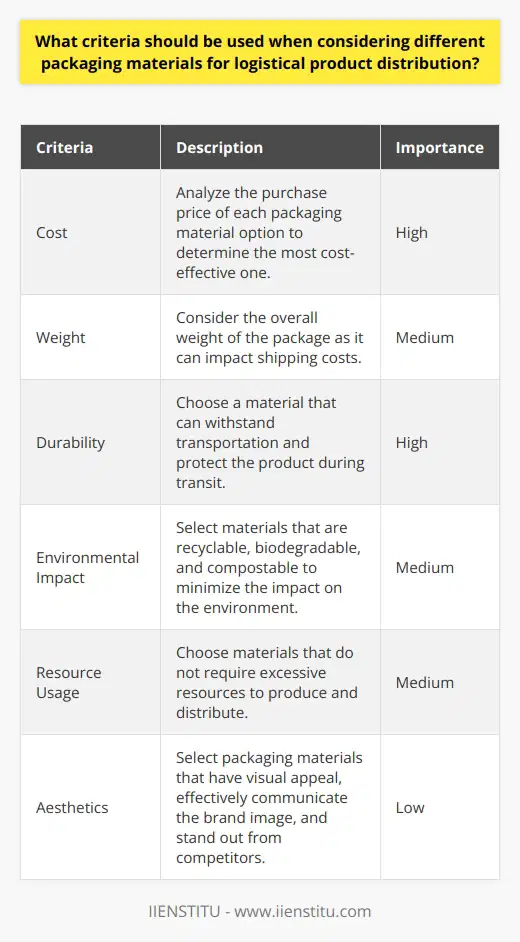
What are the advantages and disadvantages of single-trip packaging compared to multi-trip packaging for product distribution?
Single-trip and multi-trip packaging are two common approaches for product distribution. In single-trip packaging, products are packed in a single offering and shipped for delivery, usually without repackaging. In the case of multi-trip packaging, products are packed and sent in multiple bulk shipments from the vendor to a reseller or customer. Both packaging methods have advantages and disadvantages that should be considered before deciding.
One of the critical advantages of single-trip packaging is cost, time, and labor efficiency. Since the entire shipment is delivered simultaneously, manufacturers save on transportation costs and eliminate the need to repack shipments, thus saving time and labor. Additionally, single-trip packaging is environmentally friendly since there is often no need for additional packaging materials.
However, single-trip packaging also has some drawbacks. For instance, if an end-user returns a packaged product, it may be challenging to produce it in its original state or resale it, as it has already been packed. Furthermore, single-trip packing may be less cost-effective for large-quantity orders since there is usually a minimum quantity order requirement for specific products.
On the other hand, multi-trip packaging often offers more flexibility for product distribution. For example, it allows for smaller shipments of products to be sent to multiple locations, thus reducing the need for large-quantity orders. Furthermore, suppose an accident occurs, or a customer returns a product. In that case, repackaging and reselling the effect is much easier than single-trip packaging. Finally, multi-trip packaging offers greater control over shipments since they can be segmented and tracked more easily than single-trip packaging.
On the downside, multi-trip packaging is less efficient than single-trip packaging as it incurs additional labor costs due to the need to package and repack shipments. Additionally, the need to transport multiple loads can also increase transportation costs. Finally, since various shipments may be sent, there can be an increased risk of product damage, particularly if individual packages need to be packed correctly.
Overall, single-trip and multi-trip packaging offer advantages and disadvantages when deciding which approach is best for product distribution. Single-trip packaging is generally more cost-effective but requires large-quantity orders. In contrast, multi-trip packaging offers more flexibility but is less efficient. Ultimately, manufacturers must weigh the pros and cons of both approaches to determine which method is most suitable for their product distribution needs.
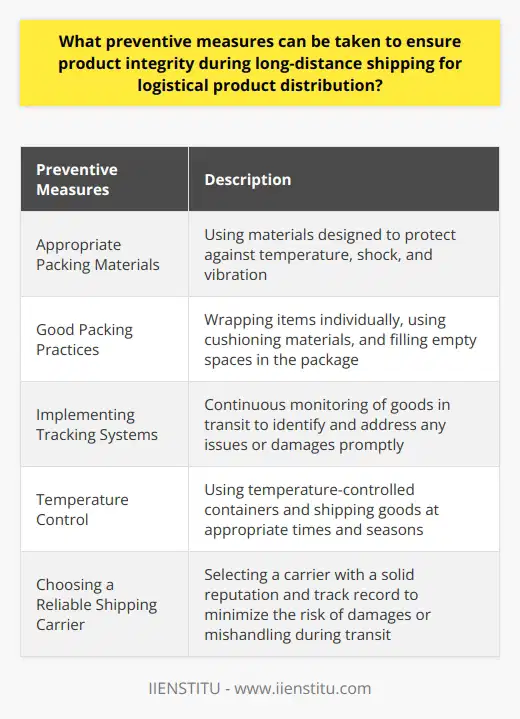
What preventive measures can be taken to ensure product integrity during long-distance shipping for logistical product distribution?
Product integrity is a priority in the logistic product distribution process. Maintaining product integrity during long-distance shipping is essential to ensure that goods reach their destination in the same condition as when shipped. Several preventive measures can be taken to address this challenge to ensure that product integrity is maintained during long-distance shipping for logistical product distribution.
An essential step in ensuring product integrity is using appropriate packing materials. The quality of the materials used to package goods can directly affect the integrity of the goods. Using packaging materials designed to protect the interests from external factors such as temperature, shock, and vibration can help maintain the goods in their original state during long-distance shipping. Additionally, good packing practices should be adopted, such as wrapping items individually, using cushioning materials, and filling empty spaces in the package.
In addition to using appropriate packing materials, tracking systems can ensure product integrity during long-distance shipping. Tracking techniques allow goods to be monitored while in transit and allow any issues with the goods to be identified and addressed early. This helps to ensure that goods arrive at their destination in the same condition they were shipped in.
Temperature control is another crucial factor in ensuring product integrity. Many goods, such as food and medical products, require temperature-controlled environments to maintain their product quality. For goods that require temperature control, temperature-controlled containers should be used. These containers can provide insulation and temperature regulation to keep goods at the correct temperatures during transit. Also, goods should be shipped at the correct times and seasons to maintain the right temperature.
Finally, selecting a reliable shipping carrier ensures product integrity during long-distance shipping. Choosing a reputable shipping carrier with a good track record can help to ensure that goods arrive at their destination safely and in the same condition they were shipped.
In conclusion, following these preventive measures can ensure product integrity during long-distance shipping for logistical product distribution. Product integrity is essential to ensure that goods arrive at their destination intact and as expected. Using appropriate packing materials, tracking systems, temperature-controlled containers, and selecting a reliable shipping carrier can help maintain product integrity during long-distance shipping.
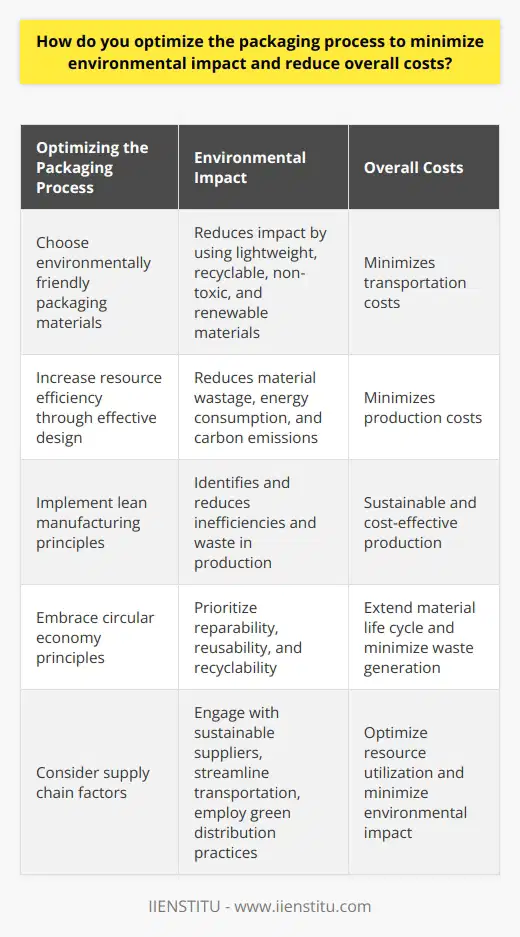
How do you optimize the packaging process to minimize environmental impact and reduce overall costs?
Optimizing Material Selection
In order to optimize the packaging process, the first step is choosing environmentally friendly packaging materials. These materials should be lightweight to reduce transportation costs, easily recyclable or reusable, non-toxic, and sourced from renewable resources. Utilizing biodegradable or plant-based packaging materials can help lessen the environmental impact and contribute to a circular economy.
Increasing Resource Efficiency
Effective packaging design can significantly reduce overall costs while minimizing environmental impact. Implementing a minimalistic design reduces material wastage, energy consumption during production, and carbon emissions during transportation. Applying design techniques such as modular packaging, product concentration, and right-sizing enables the efficient use of space and resources, while still providing product protection and consumer convenience.
Implementing Production Techniques
Environmentally friendly production techniques can help in optimizing the packaging process. Lean manufacturing principles applied to the packaging industry can identify and reduce inefficiencies and waste. Utilizing automated equipment and systems can increase production speed while minimizing resource consumption, ensuring sustainable and cost-effective production.
Embracing Circular Economy Principles
Adopting circular economy principles in the packaging process aids in reducing environmental impact and costs. By prioritizing reparability, reusability, and recyclability, businesses can extend the life cycle of packaging materials and minimize waste generation. Also, engaging in reverse logistics practices, such as collection and recycling programs, can help redirect waste away from landfills towards material recovery processes.
Consideration of Supply Chain Factors
The supply chain plays a significant role in the overall sustainability and cost-effectiveness of packaging. Engaging with sustainable suppliers, streamlining transportation, and employing green distribution practices can have a positive impact on both cost and the environment. Implementing packaging waste reduction strategies along the supply chain can lead to optimized resource utilization and minimized environmental impact.
Through the adoption of sustainable materials, effective design, production techniques, circular economy principles, and consideration of supply chain factors, businesses can optimize the packaging process, thereby reducing their overall environmental impact and costs.
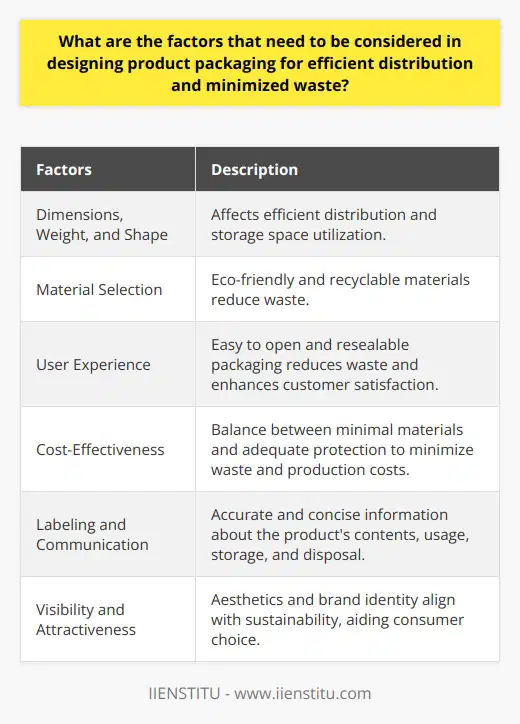
What are the factors that need to be considered in designing product packaging for efficient distribution and minimized waste?
Factors to Consider in Packaging Design
Efficient Distribution
A primary factor to consider in product packaging design is efficient distribution. This encompasses the package's dimensions, weight, and shape, which impact transportation costs and storage space. To minimize costs, it is essential to design packages that optimize space management and reduce unnecessary material usage.
Material Selection
Another crucial aspect is material selection. Using eco-friendly and recyclable materials is vital for sustainability and waste reduction. It is also essential to choose materials that provide adequate protection, ensuring that the product remains undamaged during transportation and storage.
User Experience
Designing packaging with the end-user in mind is crucial for effective functionality and minimizing waste. This includes easy-to-open and resealable packaging options that prolong the product's life and reduce the likelihood of spoilage or damage, further contributing to waste reduction.
Cost-Effectiveness
Reducing packaging costs is essential for efficient distribution. This necessitates a balance between using minimal material and ensuring product protection. By incorporating cost-effective and sustainable materials, businesses can create packages that minimize both production costs and waste.
Labeling and Communication
Accurate and concise labeling is critical to inform consumers about contents, proper usage, storage, and disposal. Clear communication of the product's sustainability efforts can help to reduce waste and encourage environmentally responsible behavior from the consumer.
Visibility and Attractiveness
Lastly, aesthetic appeal and brand identity should align with sustainability values. Attractive, easy-to-identify packaging can facilitate consumer decision-making and increase the likelihood of them choosing an environmentally-friendly product.
In conclusion, designing product packaging for efficient distribution and minimized waste requires considering factors such as efficient distribution, material selection, user experience, cost-effectiveness, labeling and communication, and visibility and attractiveness. By addressing these factors, businesses can adapt to the growing consumer demand for sustainable products while reducing their ecological impact.
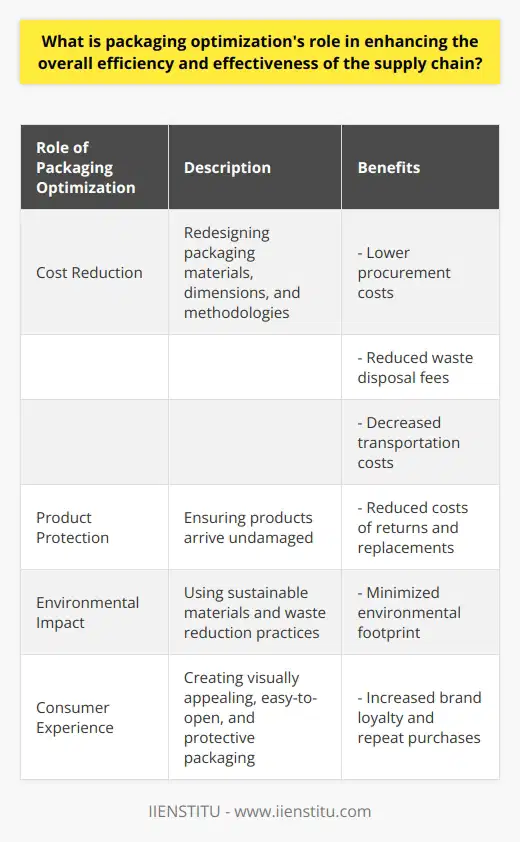
What is packaging optimization's role in enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain?
Role of Packaging Optimization
Packaging optimization plays a crucial role in enhancing supply chain efficiency and effectiveness. This process involves the redesign and improvement of packaging materials, dimensions, and methodologies to reduce waste, minimize transportation costs, and improve product protection. In turn, this contributes to an improved overall supply chain performance.
Cost Reduction
One of the primary benefits of packaging optimization is cost reduction. By minimizing the materials required for packaging, businesses can save on procurement costs as well as reduce waste disposal fees. Furthermore, optimized packaging can also decrease transportation costs, as it enables more products to be transported within a given space, thus increasing shipment efficiency.
Enhanced Product Protection
Optimized packaging also improves product protection, resulting in reduced product damages and associated costs. By utilizing effective packaging materials and designs, companies can ensure their products arrive at their destination undamaged, thereby reducing the costs associated with returns and replacements.
Environmental Impact Reduction
By using optimized packaging methods, companies can minimize their environmental footprint while also improving supply chain performance. By utilizing sustainable materials and incorporating waste reduction practices, businesses demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility, which may resonate positively with environmentally conscious customers.
Consumer Experience Improvement
Finally, optimized packaging can contribute to an enhanced customer experience. Packaging that is visually appealing, easily opened, and adequately protective can create a positive impression on the consumer, which may translate to increased brand loyalty and repeat purchases.
In conclusion, packaging optimization is a vital aspect of supply chain management that offers several benefits, including reduced costs, improved product protection, minimized environmental impact, and enhanced consumer experience. By addressing these aspects, businesses can positively contribute to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of their supply chain operations.
What are the key components of a successful packaging optimization strategy for improving distribution efficiency?
Components of a Packaging Optimization Strategy
Efficient Material Selection
A successful packaging optimization strategy starts with selecting the right materials, such as lightweight and sustainable materials that can reduce shipping costs and the environmental impact of distribution. Moreover, employing durable materials can also minimize product damage during transportation.
Size and Shape Optimization
Optimizing the size and shape of packages is vital. The utilization of a minimalistic design approach and adapting packages according to product dimensions can help reduce materials used and maximize space within transportation vehicles. This results in fewer shipments and lower transportation costs, thus leading to enhanced distribution efficiency.
Standardization and Modularization
Creating standardized and modular packaging designs is another key component. By using similar structural elements and interchangeable parts, the packages can be easily assembled, disassembled, or reused. This harmonization of packaging elements simplifies the production process and allows for cost savings.
Smart Packaging Technologies
Implementing smart packaging technologies, such as radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags, sensors, or QR codes, can contribute to efficient distribution. These technologies enable real-time tracking and tracing of products, facilitating inventory management, reducing errors, and speeding up the supply chain process.
Reducing Negative Environmental Impact
Finally, minimizing the environmental footprint of distribution operations is crucial for a sustainable packaging optimization strategy. Companies should employ eco-friendly materials, such as biodegradable or recycled materials, and ensure that packages are easily recyclable or reusable. Reducing waste, conserving resources, and decreasing carbon emissions contribute to a positive brand image and better long-term sustainability.
In conclusion, a successful packaging optimization strategy encompasses efficient material selection, size and shape optimization, standardization of design, integration of smart packaging technologies, and a focus on reducing environmental impact. These key components, when combined, lead to improved distribution efficiency, cost savings, and overall sustainability in the supply chain process.
How can advancements in packaging technology and materials contribute to optimizing the packaging process for distribution?
Enhancing Efficiency in Distribution
Advancements in packaging technology and materials significantly contribute to optimizing the packaging process for distribution. By introducing innovative techniques and eco-friendly substances, manufacturers can improve efficiency, save on resources, and decrease the overall environmental impact.
Utilizing Smarter Materials
Firstly, by employing smart materials with properties such as temperature responsivity or built-in sensors, manufacturers can ensure product safety throughout transportation. For example, smart packaging that changes color to indicate potential spoilage or damage can help distributors identify and address issues more efficiently.
Reducing Packaging Weight
Secondly, modern lightweight materials help to optimize the distribution process by reducing packaging weight. As a result, transportation becomes more cost-effective, as lower weights translate into lower fuel consumption and reduced shipping costs. Also, a decrease in packaging waste benefits the environment, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Incorporating Cost-effective Solutions
Next, advancements in packaging technology allow manufacturers to adopt more cost-effective packaging solutions. These solutions, such as vacuum or aseptic packaging, can be more affordable and efficient compared to traditional methods. In turn, this helps companies save on material and labor costs during the distribution process.
Automation and Robotics
The integration of automation and robotics in the packaging process also plays a crucial role in optimization for distribution. Automated packaging systems significantly reduce the time and labor-intensive manual tasks, leading to increased productivity and decreased human errors. Additionally, robotic systems can handle fragile or delicate products more precisely, ensuring their safety during the distribution process.
Improving Sustainability
Lastly, modern packaging technologies and materials focus on environmentally-friendly practices, which are crucial for fulfilling corporate sustainability commitments. Biodegradable and recyclable packaging options, such as bio-based polymers or paper-based alternatives, serve to reduce the amount of waste generated throughout the distribution process while minimizing the depletion of natural resources.
In conclusion, advancements in packaging technology and materials offer several opportunities to optimize the packaging process for more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable distribution. By adapting to these innovative solutions, companies can considerably enhance their packaging strategies, ultimately benefiting not only their businesses but also the global environment.
What role does consumer behavior and preferences play in the development and optimization of product packaging for effective distribution?
Consumer Behavior and Product Packaging
One crucial aspect driving the development and optimization of product packaging is consumers' behavior and preferences. Analyzing these factors ensures that packaging not only serves its purpose of safeguarding a product but also influences potential buyers. By examining trends and customer feedback, companies can create and adjust a product's packaging to align with market demands, thereby enhancing its distribution success.
Market Research to Understand Preferences
Conducting thorough market research on target consumers helps determine their preferences and purchase behaviors. By understanding what appeals to the audience, manufacturers can create innovative packaging designs catering to unique requirements. This process establishes brand differentiation and elevates customers' emotional connection to the product.
Environmental Consciousness in Packaging
One significant trend shaping consumer preferences is a heightened collective environmental consciousness. Numerous buyers now prioritize environmentally friendly packaging that promotes sustainability and better waste management. Companies can respond to this demand by using renewable materials and reducing excessive packaging, thereby positively impacting purchase decisions and product distribution.
Influencing Decisions Through Color and Functionality
The choice of colors and functional features also plays a pivotal role in improving packaging effectiveness. Different colors evoke diverse psychological responses, aiding in conveying the product's identity and attracting attention. Moreover, functional elements such as easy-to-open and resealable packaging can enhance customer satisfaction, resulting in increased market share.
Digital Integration and Personalization
Consumers continually embrace tech-savvy solutions, and incorporating digital elements into packaging can impact preferences. For example, adding QR codes for easy access to product information or augmented reality experiences can improve engagement and generate interest. Additionally, offering personalized packaging options can heighten a customer's emotional attachment to the product, increasing the likelihood of repeat purchases.
In conclusion, acknowledging and understanding consumer behavior and preferences is vital for companies to develop or optimize product packaging effectively. By aligning packaging strategies with market trends, manufacturers can enhance customers' experiences and, in turn, optimize distribution within the competitive marketplace. With the ever-evolving nature of consumers' preferences, continued adaptations and innovations remain essential.
How do you optimize the packaging process to achieve both sustainability goals and cost reduction in logistics activities?
Optimizing Packaging Design
To optimize the packaging process for achieving sustainability goals and cost reduction in logistics activities, it is essential to begin with innovative packaging design. Implementing eco-friendly materials, such as recyclable or biodegradable elements, can significantly reduce the environmental impact. Additionally, optimizing size and shape not only minimizes waste but also reduces transportation costs by maximizing space utilization in storage and transit.
Utilizing Efficient Packing Techniques
Efficient packing techniques ensure that packaging materials are used optimally, reducing the number of resources needed for production. Automated packing systems, for instance, can improve process speed, accuracy, and consistency, leading to reduced labor costs, minimized waste, and improved environmental outcomes. Furthermore, training employees on sustainable packaging practices can increase awareness of environmental issues, fostering a culture that prioritizes sustainability while reducing costs.
Adopting Reusable Packaging Solutions
Reusable packaging solutions, such as returnable transportation items (pallets, crates, and containers), contribute significantly to sustainability goals and cost reduction. Reusable products minimize materials consumption, lower waste generation, and often provide higher durability compared to single-use alternatives. In addition, collaborating with suppliers and customers to establish reverse logistics systems incentivizes the return of reusable items, which reduces the need for new packaging and related costs.
Minimizing Packaging Layers
Reducing the layers of packaging used for products can result in a smaller environmental footprint and decreased costs by minimizing the amount of materials needed. This approach focuses on eliminating excessive packaging or utilizing alternatives, such as multipurpose packaging that serves as both protection and promotion for the product. Moreover, streamlined packaging typically results in lighter shipments, reducing fuel consumption and the associated costs in transportation.
Evaluating Packaging Life Cycle
Assessing the life cycle of packaging materials is crucial in identifying opportunities for improvement in sustainability and cost reduction. Companies can conduct life cycle assessments (LCAs) to evaluate the environmental impacts of their packaging choices, from raw material extraction to disposal or recycling. By analyzing data gathered during the LCA, organizations can make informed decisions about potential changes, like switching to biodegradable materials or enhancing reusability, to improve their overall sustainability and cost-efficiency.
What are the main challenges and obstacles faced when implementing packaging optimization strategies in a complex distribution system?
Main Challenges of Packaging Optimization
In a complex distribution system, implementing packaging optimization strategies presents several challenges and obstacles. These can be broadly classified into operational, technological, and financial categories.
Operational Challenges
The first set of challenges arises from the need to balance competing demands within the supply chain processes. For instance, efficient space utilization may lead to compromises in the protection and preservation of products. Additionally, the varying lead times and batch sizes across different distribution channels can complicate the optimization process. Moreover, changes in the distribution networks can impact the effectiveness of packaging optimization strategies, making constant refinements necessary.
Technological Limitations
The second category of challenges lies in the technological limitations associated with packaging optimization. A successful implementation of these strategies often requires sophisticated computer simulations and advanced analytics to derive valuable insights. The availability, adaptability, and compatibility of these tools can be difficult to manage in a complex distribution system. Also, the lack of standardized data formats and the need to integrate multiple data sources can hinder the effective use of these technologies.
Financial Constraints
Lastly, implementing packaging optimization strategies might involve considerable upfront investments in infrastructure, equipment, and training. Budgetary constraints and the need to prioritize other business initiatives can often hinder these investments. Furthermore, the long-term benefits of packaging optimization may not be immediately evident, causing decision-makers to question the feasibility and profitability of implementing these strategies. In such circumstances, securing internal and external funding for packaging optimization initiatives can be a considerable obstacle.
In conclusion, operational challenges, technological limitations, and financial constraints are the main obstacles faced when implementing packaging optimization strategies in a complex distribution system. Overcoming these challenges requires a collaborative approach among stakeholders, as well as investments in training, technology, and infrastructure.
How can companies monitor and measure the success of their packaging optimization efforts throughout the supply chain?
Monitoring Packaging Optimization Success
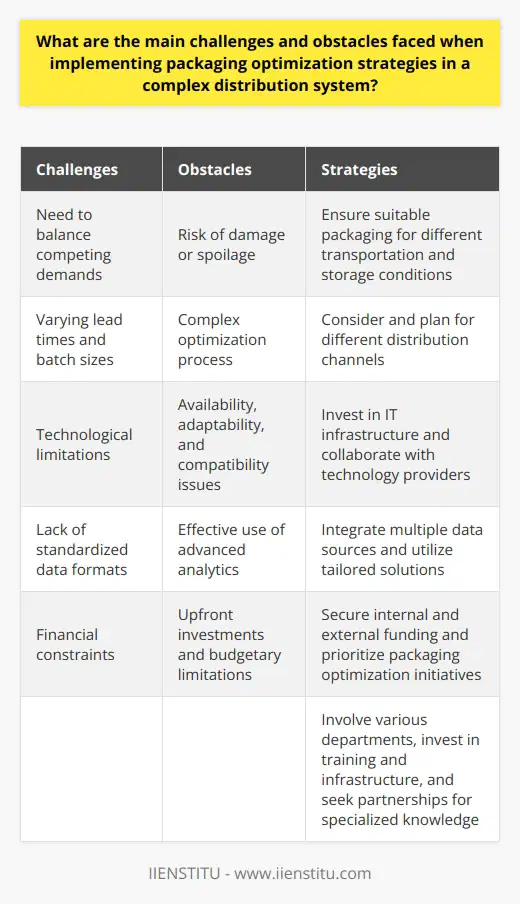
To evaluate the efficacy of their packaging optimization initiatives, companies can adopt several measurement and monitoring techniques across the supply chain. Firstly, they should quantify cost savings by comparing the monetary expenses of previous packaging systems with the optimized solutions. This includes analyzing the differences in materials, labor, and storage expenses.
Assessing Environmental Impact
An essential aspect of packaging optimization is the reduction of environmental impact. Companies can determine their success in this area by calculating the decrease in waste generated and the utilization of sustainable materials in the optimized packaging. This data can then be compared to the waste levels and material utilization rates of the previous packaging to gauge improvement.
Product Damage Reduction
One of the primary goals of packaging optimization is to minimize the damage to products throughout the supply chain. To measure the success of optimization efforts, companies can track the number of damaged products pre and post implementation. A lower percentage of damaged products indicates that this goal has been successfully achieved.
Customer Satisfaction Analysis
It is crucial to ensure that packaging optimization efforts do not negatively impact customer satisfaction. To measure the customer's perception, companies should gather and analyze feedback through surveys, reviews, and social media interactions. Positive customer feedback is indicative of successful packaging optimization.
Improvement in Workflow Efficiency
Optimized packaging solutions should lead to an overall improvement in the efficiency of the supply chain processes. Companies can analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) such as time taken for packaging, loading, and transportation to ensure that optimization efforts yield the desired results.
Comparative Benchmarking
By comparing their packaging optimization performance with industry standards, companies can understand their position in the competitive landscape. This comparative analysis, also known as benchmarking, helps companies identify areas of improvement and adopt best practices, thereby continuing to refine their packaging optimization initiatives.
In conclusion, monitoring packaging optimization success can be achieved through the analysis of cost savings, environmental impact, product damage reduction, customer satisfaction, workflow efficiency, and benchmarking against industry standards. A multi-pronged approach to evaluating optimization efforts will provide companies with valuable insights while ensuring the desired outcomes across the supply chain.
How do you optimize packaging for the integration of automation and robotics in the logistical process?
Optimizing Packaging Design
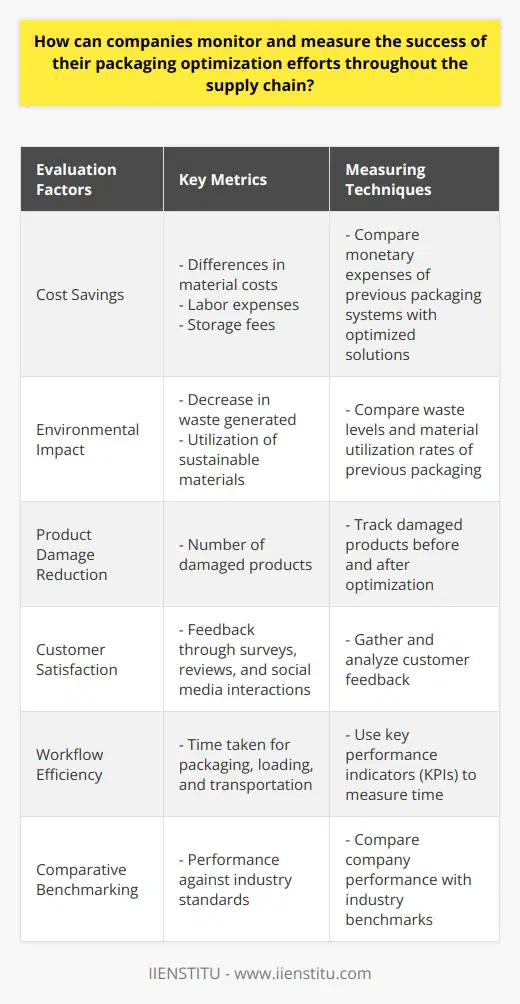
To optimize packaging for the seamless integration of automation and robotics in the logistical process, it is essential to consider the relevant factors that affect their functioning. This involves analyzing the design, materials used, and compatibility with robotic handling systems.
Design Accommodating Automation
First, it is crucial to develop packaging designs that cater to the needs of robotic systems. This can include incorporating features like handles, grasping points, and compatible shapes that enable robots to easily pick up, manipulate, and transport the packages. Additionally, consistency in features across various package sizes can further improve robotics' efficiency in handling different products.
Material Selection
Another critical aspect of optimizing packaging for automation and robotics is selecting appropriate materials that are both lightweight and strong. This reduces the energy consumed in moving packages while ensuring they can withstand the rigors of automated handling. Moreover, the chosen material should be easy to grip for robotic systems, presenting minimum challenges for their functioning.
Compatibility with Robotic Systems
Lastly, ensuring that the packaging is compatible with the types of robots used in the logistical process is vital for a proper optimization. This may require making adjustments in the packaging design to suit the specifications and limitations of different robotic systems. For instance, some robots may have weight limitations, while others could require specific attachment points to hold the packages securely.
In conclusion, the optimization of packaging for the integration of automation and robotics in the logistical process involves a careful evaluation of design, material selection, and compatibility with robotic handling systems. By attending to these aspects, companies can effectively streamline their logistical processes and reduce overall costs, while maximizing the potential of automation and robotics in their supply chains.
What are the key principles for designing packaging systems that facilitate efficient handling, storage, and transportation in logistics activities?
Key Principles for Effective Packaging Design
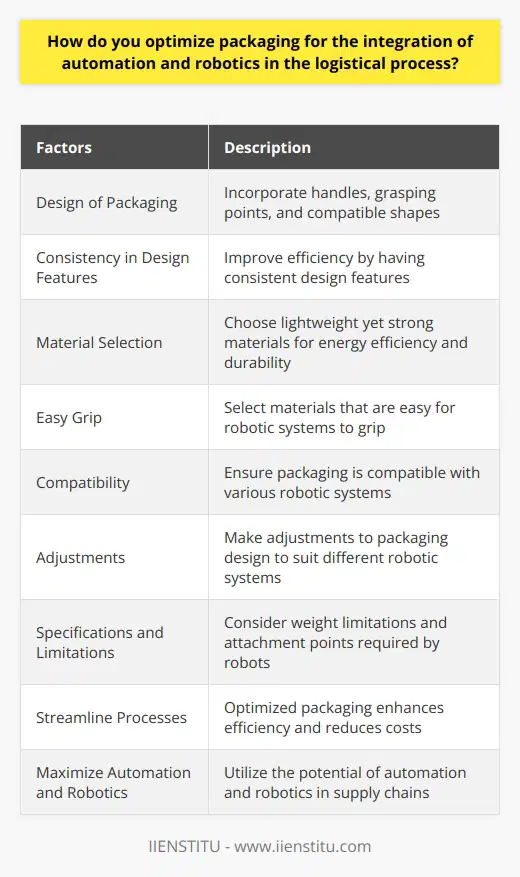
Material Selection for Optimal Protection
One key principle in designing packaging systems is selecting appropriate materials for optimal protection against potential damages during handling, storage, and transportation. Material choice should consider the product's characteristics, such as weight, fragility, and sensitivity to environmental factors, ensuring the chosen materials provide adequate support and protection.
Maximizing Space Utilization
Efficient space utilization is another essential principle for packaging design. Creating streamlined packaging shapes and sizes that conform well to transportation and storage systems not only reduces waste in terms of materials but also allows for easier stacking and positioning. To maximize space utilization, packaging designers must consider the size and shape of storage and transportation containers when designing their packages.
Containment and Accessibility
In logistics activities, personnel need to easily access the products within the packaging for tasks such as inspections or inventory management. Therefore, another key principle is designing packaging systems that prioritize containment and accessibility. Packaging designs should prevent accidental product spills or losses while still enabling ease of access for required tasks in logistics activities.
Standardization for Interoperability
Standardization of packaging dimensions, labeling, and handling procedures is crucial for creating a seamless and efficient logistics process. By ensuring packaging designs adhere to universal standards, packages are more likely to be compatible with a wider range of handling equipment, storage, and transportation systems. This eliminates potential delays or issues arising from mismatched or incompatible packaging elements.
Information and Identification System
A robust information and identification system is a vital feature in modern packaging designs. Easy-to-read labels that adhere to standardized labeling guidelines, as well as the integration of technology, such as barcodes or Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) chips, enable quick, accurate tracking and management of products throughout the supply chain. This improves overall efficiency and minimizes potential errors in logistics activities.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Lastly, with increasing focus on environmental sustainability and waste reduction, innovative packaging designs must incorporate eco-friendly materials and packaging waste minimization strategies. To achieve this, packaging designers should consider the lifecycle of packaging materials, from production to disposal, and explore opportunities for reusability, recyclability, or biodegradability in their designs.
In conclusion, effective packaging system designs should prioritize protection, space utilization, containment, accessibility, standardization, information systems, and sustainability. By adhering to these principles, companies can create packaging systems that support efficient handling, storage, and transportation processes in logistics activities.
How can data analytics and predictive modeling be utilized to optimize packaging and support decision-making in logistics operations?
Utilizing Data Analytics
Data analytics can be invaluable in optimizing packaging and decision-making in logistics operations. By analyzing large sets of historical data, managers can identify trends and patterns to make better-informed decisions. For instance, analyzing past packaging data can reveal the most effective materials and designs to reduce costs, minimize environmental impact, and maximize product protection.
Predictive Modeling for Packaging
Predictive modeling goes a step further by forecasting future outcomes based on historical data. In logistics operations, predictive models can estimate the demand for specific packaging materials, predict failures, and optimize packaging configurations. By applying machine learning algorithms to observed data, decision-makers can gain insights into the best packaging options to meet customer needs, reduce waste, and increase efficiency.
Supporting Decision-Making
The insights derived from data analytics and predictive modeling act as crucial support for decision-making in logistics operations. By identifying patterns, trends, and future outcomes, logistics managers can make informed decisions on packaging materials, determine optimal designs, and engage in more accurate demand planning. This information can lead to cost savings, reduced lead times, and enhanced overall operational efficiency.
Optimizing Packaging Performance
To optimize packaging performance, data analytics and predictive modeling can provide crucial information on package durability, storage conditions, and transportation factors. By identifying potential weaknesses, managers can redesign or modify packaging to meet functional requirements and minimize damage to products. When implementing sustainable packaging solutions, the data-driven approach can ensure that ecological goals are achieved without compromising on performance.
Enhancing Logistic Operations
Lastly, data analytics and predictive modeling can enhance the overall efficiency of logistic operations. For example, by identifying trends in shipment data, managers can make informed decisions on route optimization, carrier selection, and transport mode choice, resulting in reduced costs and improved service levels. Moreover, actionable insights from data analysis can drive continuous improvements in logistics operations, leading to a long-lasting competitive advantage.
In conclusion, data analytics and predictive modeling serve as vital tools for optimizing packaging and driving informed decision-making in logistics operations. Their utilization allows managers to make data-driven decisions, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
How do you optimize packaging to better align with evolving consumer preferences and sustainability trends?
Understanding Consumer Preferences
To optimize packaging in alignment with evolving consumer preferences and sustainability trends, it is imperative to first understand the specific concerns and desires of the target audience. Surveys, focus groups, and market research can help identify key factors that consumers consider important, such as recyclability, reusability, or biodegradability.
Eco-friendly Materials Selection
Next, selecting appropriate materials is crucial for ensuring both the desired packaging functionality and its environmental impact. Materials like recycled paper, cardboard, bioplastics, and plant-based alternatives can be used to create packaging that still meets the demands of consumers while minimizing its ecological footprint.
Innovative Packaging Designs
Utilizing innovative designs can help optimize packaging by reducing the overall amount of material used and simplifying the packaging process. Striving for minimalism and incorporating features like easy-to-open systems or collapsible structures can significantly decrease materials wastage while still maintaining consumer satisfaction.
Reusability and Multi-functionality
Promoting reusability and multi-functionality in packaging can lead to a significant reduction in the environmental impact while enhancing customer satisfaction. By offering packaging that can be reused or repurposed, companies can cater to eco-conscious consumers and encourage sustainable practices.
Biodegradable and Compostable Alternatives
Incorporating biodegradable and compostable alternatives when creating packaging can provide a more sustainable option for waste disposal, reducing the negative impact of single-use packaging. This approach not only reduces the environmental footprint but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly products.
Clear Communication and Labelling
Finally, improved communication and labelling are essential in optimizing packaging in line with consumer preferences and sustainability trends. By providing transparent information on the environmental impact of the packaging, its recyclability, or usage instructions, companies can empower their customers to make informed decisions and contribute to a more sustainable future.
In conclusion, optimizing packaging to better align with consumer preferences and sustainability trends requires a multifaceted approach that combines understanding consumer preferences, material selection, design innovation, reusability, biodegradability, and clear communication. By adopting these strategies, businesses can contribute to a greener environment and attract eco-conscious customers.
What role does interdisciplinary collaboration play in the development and implementation of optimized packaging strategies for logistical processes?
Interdisciplinary Collaboration in Packaging Strategies
One key aspect of developing optimized packaging strategies for logistical processes is interdisciplinary collaboration. This approach involves leveraging expertise from various fields to create innovative solutions tailored to specific industry needs. It enhances efficiency, sustainability, and overall effectiveness of the packaging process.
Design and Material Selection
Designers and materials scientists work together to create packaging that meets both functional and aesthetic demands. Engineers may evaluate material properties for strength, durability, or environmental impact, while designers ensure aesthetics and functionality. This collaboration results in packaging solutions that protect goods during transportation and storage while minimizing resource consumption and environmental impact.
Technological Integration
Collaborating with information technology specialists allows for the integration of advanced tools, such as data analytics and automated systems, in the development of packaging strategies. These technologies enable better tracking, efficiency, and decision-making throughout supply chains. A seamless flow of information between various stakeholders becomes possible, enhancing overall logistical effectiveness.
Supply Chain Optimization
The involvement of supply chain experts in developing packaging strategies ensures that solutions are aligned with industry best practices and standards. This collaboration allows for the identification of potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies within the supply chain, enabling targeted improvements. Additionally, understanding regulatory requirements and compliance ensures that packaging solutions remain compliant with regional and international regulations.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental scientists play a crucial role in interdisciplinary collaboration for packaging optimization. Their expertise helps identify the environmental impact of materials, processes, and disposal methods associated with packaging. This holistic view enables the development of sustainable packaging strategies, taking into account factors such as recyclability, renewability, and overall life cycle management.
In conclusion, interdisciplinary collaboration plays a pivotal role in the development and implementation of optimized packaging strategies for logistical processes. By encompassing expertise from design, materials science, technology, supply chain management, and environmental science, this approach leads to innovative and sustainable solutions that ultimately enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact in the world of logistics.
How can a circular economy framework be incorporated into packaging optimization efforts to create sustainable and efficient distribution systems?
Adopting a Circular Approach
A circular economy framework involves designing packaging systems that minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency, thereby promoting sustainable distribution systems. To incorporate this framework into packaging optimization efforts, businesses need to focus on three essential aspects: material selection, design innovation, and end-of-life recovery.
Choosing Sustainable Materials
Sustainable material selection is crucial for circular packaging optimization. By utilizing materials that are renewable, biodegradable, and recyclable, businesses can significantly reduce the environmental impact of their packaging. Examples of more sustainable materials include bioplastics made from plant-based sources and paperboard made from responsibly-sourced wood fibers. These materials can be recycled or composted, enabling them to reenter the circular economy and reduce reliance on finite resources.
Implementing Design Innovations
Design innovation is another critical aspect of integrating a circular economy framework. By adopting eco-friendly designs that minimize unnecessary material usage, manufacturers can optimize packaging to be lighter, more durable, and less resource-intensive. Examples of design innovations include the elimination of single-use plastic components, the utilization of tray-less packaging, and the creation of more modular shapes. These design elements not only ensure the longevity of the packaging itself but also add value to the contents within, ultimately improving the overall sustainability and efficiency of the distribution system.
Facilitating End-of-Life Recovery
End-of-life recovery is the final step in incorporating a circular economy framework in packaging optimization. Effective end-of-life management options, such as recycling or composting, must be considered when developing packaging materials and designs. Businesses should provide clear instructions on proper disposal, and work to develop partnerships with waste management organizations to ensure packaging materials are channeled into the circular economy. This initiative further contributes to environmental conservation by promoting recycling and reducing waste in landfill sites.
By focusing on material selection, design innovation, and end-of-life recovery, businesses can incorporate a circular economy framework into their packaging optimization efforts. This approach fosters the creation of sustainable and efficient distribution systems that reduce environmental impact, conserve resources, and foster a healthier economy for both present and future generations.
How do you optimize packaging to ensure product safety and security while minimizing damage and loss during transportation in logistics activities?
Product Packaging Optimization
Adopting optimal packaging strategies is a critical element in ensuring product safety and minimizing damage during transportation.
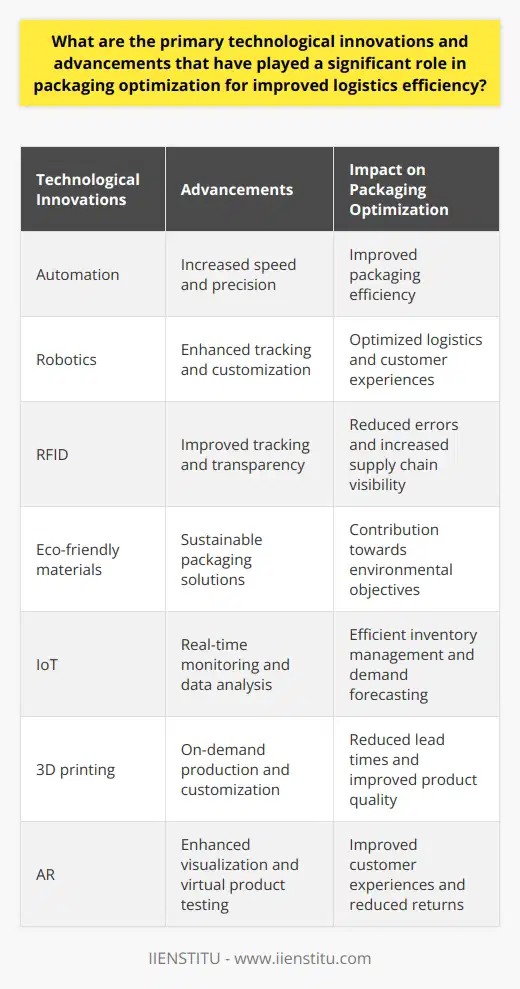
Application of Cushioning Materials
Including cushioning materials in product packaging can drastically reduce breakage during transport. Materials like bubble wrap, packing peanuts, and foam pads can absorb shock and vibration, protecting the product inside.
Utilizing Durable Packaging Materials
Investing in sturdy and durable packaging materials further ensures product safety. The use of waterproof, tear-resistant materials protects your goods against environmental factors like temperature changes, moisture, and physical impact, thus reducing potential damage.
Effective Labeling
Proper labeling is another critical strategy. Labels containing handling instructions like 'fragile' or 'this side up' can direct handlers on how to appropriately handle and stack your product, minimizing damage and loss.
Integrating Tamper-Evident Packaging
To enhance security and discourage theft, integrating tamper-evident packaging in your logistics process can be fruitful. Such packaging is hard to open without leaving visible signs of tampering, providing an additional layer of security.
Review and Analysis
Lastly, regularly reviewing and analyzing your packaging strategy offers insights into areas of improvement. Collaborate with your logistics provider, evaluating any damages or losses on delivery, and make appropriate changes to your packaging.
In conclusion, optimizing your packaging involves investing in robust materials and effective cushioning, using clear labels, and employing tamper-evident solutions. Repeated review and amendments to your strategy also contribute towards the safety and security of your product during transport.
What are the primary technological innovations and advancements that have played a significant role in packaging optimization for improved logistics efficiency?
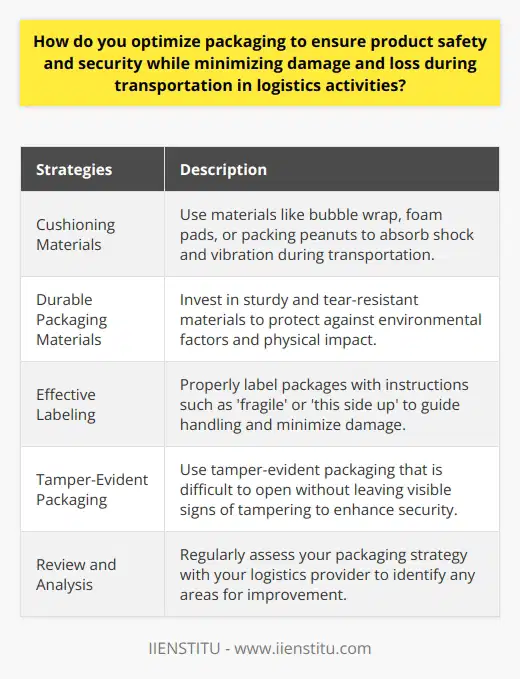
Technological Advancements in Packaging
The first noteworthy technology in packaging optimization is automation. Companies extensively use automation in packaging processes. Automated machines offer faster, error-free packaging operations.
Robotics in Packaging
Robotics is another significant innovation. Robotic technologies tackle complicated packing tasks. They also ensure precision and improvements in packaging speed.
Significance of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
The use of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has transformed logistics. RFID-tagged packages help track products throughout the supply chain. This increases transparency and reduces errors.
Eco-friendly Packaging Materials
A shift towards eco-friendly packaging materials is also a significant advancement. Technological innovation has led to the creation of recyclable, biodegradable materials. These materials are reducing carbon footprints and offering sustainable packaging solutions.
Impact of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is also playing a role in packaging optimization. IoT technologies aid in real-time tracking and monitoring of packages. This ensures safety and enhances the overall efficiency of logistics.
3D Printing Technology
3D printing technology has opened up new possibilities in packaging design. Companies can create customized, cost-effective, and efficient packaging solutions. Now, they can tailor packaging according to product requirements.
Augmented Reality (AR) in Packaging
Lastly, Augmented Reality (AR) is revolutionizing the way of packaging products. AR applications can enhance customer experiences. With AR, customers can interact digitally with the product before purchase.
In conclusion, these technological advancements have significantly impacted logistics efficiency. They have played a considerable role in optimizing packaging processes.
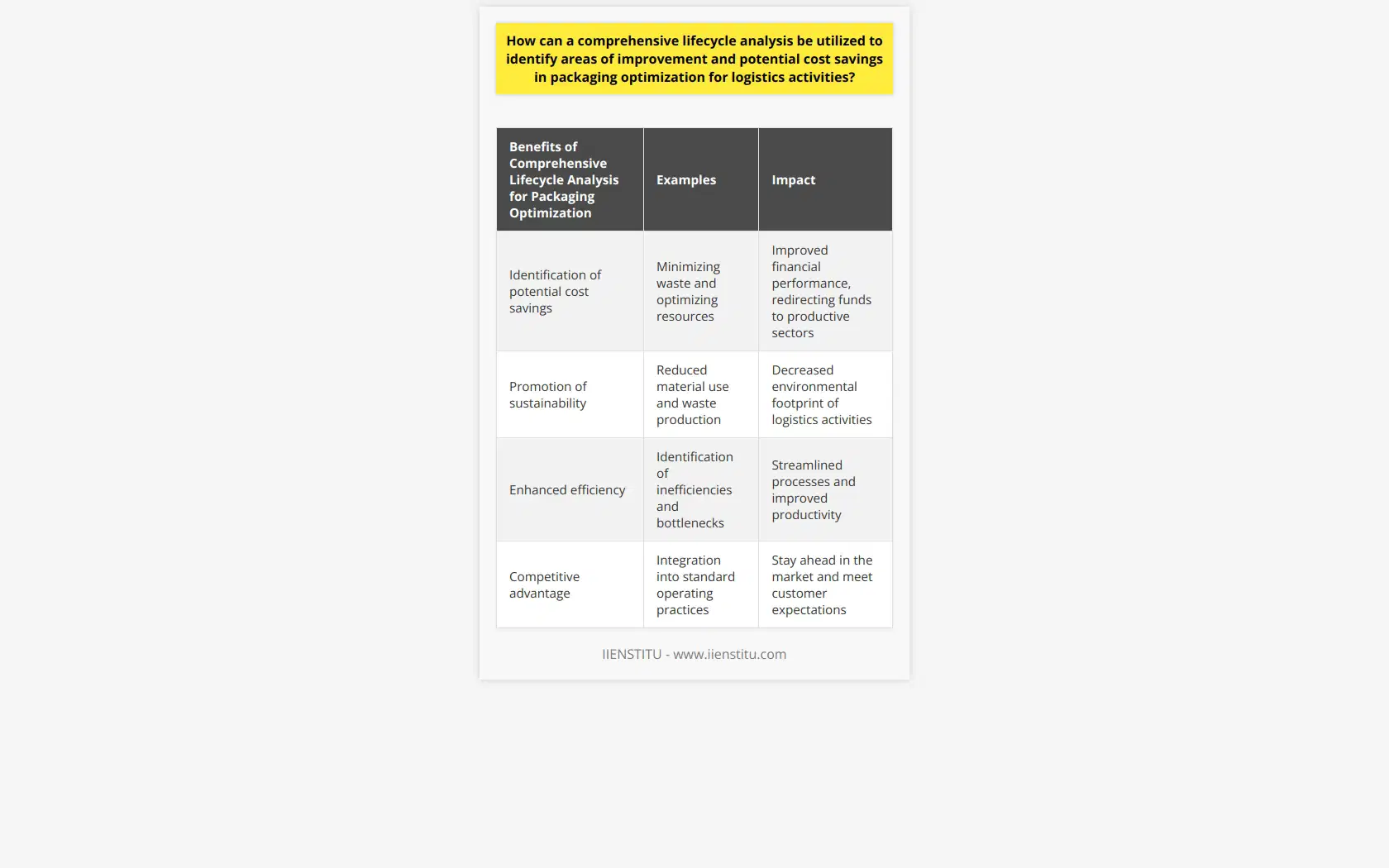
How can a comprehensive lifecycle analysis be utilized to identify areas of improvement and potential cost savings in packaging optimization for logistics activities?
Understanding Lifecycle Analysis Impact
A comprehensive lifecycle analysis, in the context of packaging optimization for logistics activities, plays a crucial role. It contributes by providing valuable insight into all stages of a product’s lifecycle.
Identifying Improvement Areas
Such an analysis systematically reviews the stages of a product's life. From raw material extraction, manufacturing, and distribution, to use and final disposal. This approach uncovers critical areas of improvement. It spots inefficiencies, unnecessary waste, and potential bottlenecks in the overall process.
Potential for Cost Saving
Through this analysis, potential cost savings are identified. This results from the optimization of resources and minimization of waste. Funds otherwise spent on unnecessary material or inefficient processes can be channeled toward other productive sectors.
Leveraging Sustainability
Lifecycle analysis not merely highlights financial savings. It opens avenues for environmental sustainability as well. By reducing material use and waste production, the overall environmental footprint significantly decreases.
Conclusion
In essence, a comprehensive lifecycle analysis serves as an essential tool for logistics activities. It helps in enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and promoting sustainability. Hence, organizations should integrate this into their standard operating practices to fully maximize their operations.