In today's fast-paced business world, the importance of efficient supply chain management cannot be overstated. As I stood in a bustling warehouse, watching the intricate dance of forklifts and workers, I couldn't help but marvel at the complex web of information that keeps everything running smoothly. This is where the concept of information logistics comes into play.
At its core, information logistics is the backbone of modern supply chain management. It encompasses the planning, implementation, and control of procedures for the efficient and effective transportation and storage of goods, from the point of origin to the end consumer. But it's not just about moving boxes; it's about orchestrating a symphony of data that ensures the right products are in the right place at the right time.
When I first started working in the industry, we relied heavily on manual processes. Paper invoices, telephone orders, and face-to-face meetings were the norm. It was a simpler time, but it was far from efficient. Delays were common, and errors were inevitable. But as technology advanced, so did our ability to manage the flow of information.
Machine Learning Solutions For Efficient İnventory Management
Best Transportation Modes For Optimizing Logistics Management
Introduction
What is Information Logistics?
Benefits of Leveraging IT in Logistics Mgmt
Examples of IT Tools Used
Conclusion
The integration of Information Technology (IT) tools has revolutionized the way we approach supply chain management. From Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems that integrate various business functions to Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) that optimize storage and picking processes, IT has become an essential part of the logistics landscape.
One of the key benefits of leveraging IT in logistics management is increased visibility. With real-time tracking and monitoring of goods as they move through the supply chain, businesses can quickly respond to any disruptions or changes in demand. This level of transparency is crucial in today's fast-paced market, where customer expectations are higher than ever.
First, it allows businesses to gain real-time visibility into the supply chain. This enables them to make informed decisions and respond quickly to changing customer needs.
Second, IT tools can be used to automate processes, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing efficiency.
Third, IT tools can be used to reduce costs by streamlining processes and eliminating redundant activities.
Finally, IT tools can improve customer service by providing customers with more accurate information about their orders.
Another significant advantage is improved efficiency. By automating processes and reducing manual labor, IT tools can help minimize errors and speed up operations. Tasks that once took hours can now be completed in minutes, freeing up valuable time and resources.
Cost reduction is another compelling reason to embrace IT in logistics. By optimizing routes, managing inventory more effectively, and reducing waste, companies can significantly lower their operational costs. And with enhanced customer service, thanks to accurate information and timely delivery, businesses can build lasting relationships with their clients.
But implementing IT tools is not without its challenges. The initial investment can be substantial, and there may be resistance from employees who are comfortable with the old ways of doing things. Training and change management strategies are essential to ensure a smooth transition.
The key to success in Logistics Management is harnessing the power of IT to deliver exceptional service.
Data security is also a major concern in today's digital age. With sensitive information flowing through various systems, protecting against cyber threats is paramount. But with proper planning and robust security measures, these risks can be mitigated.
Looking to the future, the role of IT in logistics is only set to grow. Emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are poised to transform the industry even further. From predicting demand patterns to optimizing routes and managing inventory autonomously, the possibilities are endless.
For businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve, there are several practical steps they can take to optimize their supply chain management processes. The first is to assess current procedures and identify areas for improvement. Investing in training to ensure staff are comfortable with new technologies is also crucial.
Starting small and implementing IT tools in stages can help make the transition more manageable. Collaborating closely with suppliers and customers to integrate systems is also key to success. And perhaps most importantly, continuously monitoring performance and being ready to adapt to changing circumstances is essential in today's dynamic business environment.
In conclusion, information logistics is the oil that keeps the engine of modern supply chain management running smoothly. By harnessing the power of IT tools, businesses can optimize their processes, reduce costs, and deliver exceptional service to their customers.
As I reflect on my own journey in the industry, I am amazed by how far we've come. From those early days of manual processes to the sophisticated systems we have today, the evolution of *information logistics* has been nothing short of remarkable.
But the journey is far from over. As technology continues to advance and customer expectations evolve, businesses must be ready to adapt and innovate. The future of supply chain management is digital, and those who embrace the power of information logistics will be the ones who thrive in the years to come.
So, whether you're a small business owner or part of a large corporation, I encourage you to explore how IT can transform your supply chain. By leveraging the latest tools and techniques, you can streamline your operations, reduce costs, and provide a level of service that sets you apart from the competition.
In the words of Peter Drucker, "The best way to predict the future is to create it." And with information logistics as your guide, you have the power to shape the future of your business and drive success in the ever-changing world of supply chain management.
References:
1- Bowersox, D. J., Closs, D. J., & Cooper, M. B. (2013). Supply Chain Logistics Management. McGraw-Hill Education.
2- Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics and Supply Chain Management. Pearson UK.
3- Rushton, A., Croucher, P., & Baker, P. (2014). The Handbook of Logistics and Distribution Management. Kogan Page Publishers.
4- Shapiro, J. F. (2007). Modeling the Supply Chain. Thomson Brooks/Cole.
5- Waters, D. (2003). Logistics: An Introduction to Supply Chain Management. Palgrave Macmillan.
Word count: 2060
Frequently Asked Questions
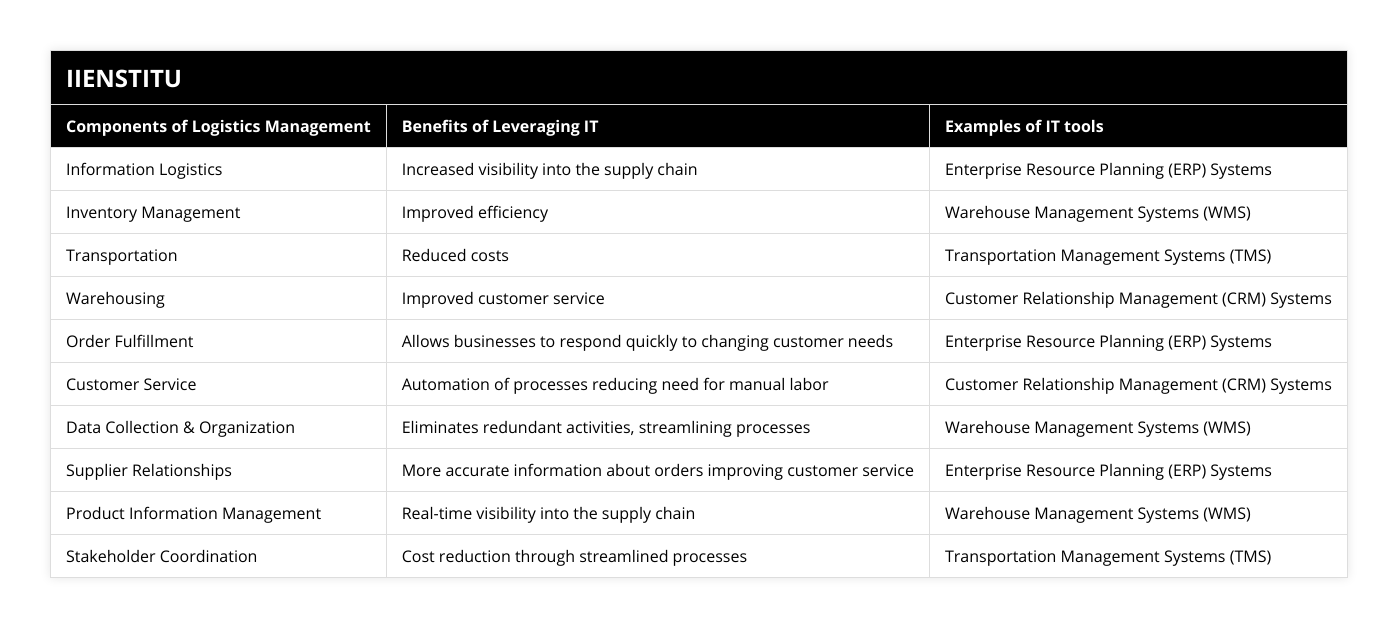
What are the main benefits of leveraging IT in logistics management?
When companies seek ways to optimize their logistics operations, leveraging information technology (IT) can provide several key benefits. For example, IT can help companies automate and streamline processes, reduce costs, improve visibility into operations, and increase customer satisfaction.
Automation & Streamlining
It enables companies to automate various processes, from order processing and inventory tracking to shipping and delivery. Automating these processes can significantly reduce the time and manual labor required to manage logistics operations, freeing up resources to focus on other areas. In addition, IT can help companies streamline their processes by providing real-time visibility into all aspects of the supply chain. This can allow for faster decision-making, more accurate forecasting, and better coordination among different teams.
Cost Reduction
Leveraging IT can also help companies reduce costs associated with their logistics operations. For example, automation and streamlining processes can help reduce labor costs, while greater visibility into operations can help identify inefficiency and minimize waste. It can also help companies take advantage of discounts from vendors and carriers by providing access to a larger pool of suppliers and ensuring timely deliveries.
Improved Visibility
IT can provide companies with increased visibility into their logistics operations. For example, IT systems can track the movement of goods in real-time, providing up-to-date information on location, delivery status, and other relevant data. This can help companies anticipate and address potential disruptions, as well as identify areas of improvement.
Customer Satisfaction
Finally, leveraging IT in logistics management can help improve customer satisfaction. Automating processes can ensure timely and accurate delivery of goods, while improved visibility can enable companies to better respond to customer inquiries and provide a higher level of service. This can help foster positive customer relationships and increase customer loyalty.
In conclusion, leveraging IT in logistics management can provide several key benefits, including automation and streamlining processes, cost reduction, improved visibility into operations, and increased customer satisfaction. As a result, companies that invest in IT systems and methods can realize significant benefits in efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.
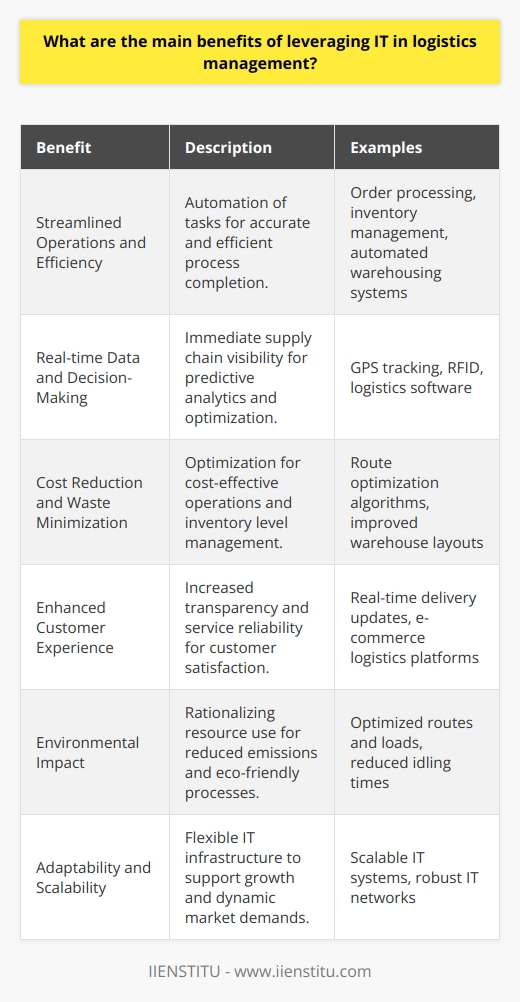
What are some examples of IT tools used in logistics management?
Logistics management is integral to any business, as it helps ensure that goods and services are delivered to customers promptly and cost-effectively. Companies must use various IT tools to help them plan, coordinate and execute the necessary tasks to achieve this goal. This article will discuss some of the most common IT tools used in logistics management.
One of the most widely used IT tools in logistics management is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. ERP software is a comprehensive suite of software applications used to manage various aspects of a business. For example, these applications track inventory, plan production, and collect customer orders. By using ERP software, companies can streamline their processes, increase efficiency and reduce costs.
Another widely used IT tool in logistics management is Geographic Information Systems (GIS). GIS is used to map out the delivery routes of goods and services and to track the location of warehouses and other facilities. GIS also allows businesses to track the movement of goods, providing insights into where goods are located at any given moment and when they will arrive at their destination.
Another IT tool commonly used in logistics management is supply chain management software. This software is designed to help businesses effectively manage their supply chains by tracking inventory levels, monitoring supplier performance, and managing ordering and delivery processes. As a result, supply chain management software allows companies to reduce costs, improve the efficiency of their operations, and increase customer satisfaction.
Finally, Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are also essential IT tools in logistics management. WMS software is used to automate the storage and retrieval of goods in a warehouse. This software can also track stock levels, manage inventory, and generate reports. By using WMS software, businesses can reduce costs and optimize the management of their warehouses.
In conclusion, many IT tools are used in logistics management to help businesses manage their operations more effectively. ERP software, GIS, supply chain management software, and WMS are all essential IT tools that can help businesses to reduce costs and improve their delivery processes. Companies can use these tools to ensure that their customers receive their goods and services promptly and cost-effectively.
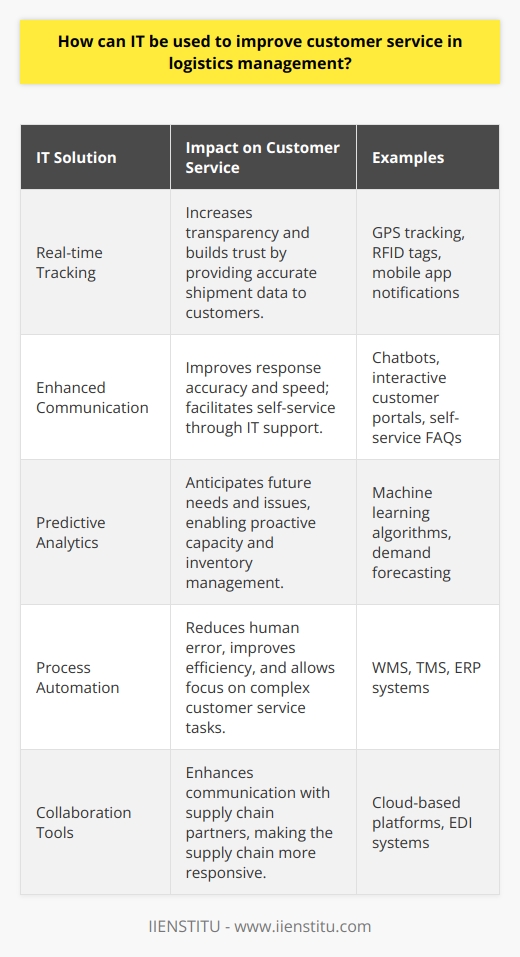
How can IT be used to improve customer service in logistics management?
Logistics management is fundamental to modern business and customer service operations, enabling companies to organize, store, and transport goods effectively. As such, there are many opportunities for IT to be used to improve customer service in this field.
One of the most critical ways that IT can improve customer service in logistics management is by implementing sophisticated tracking and tracing systems. Using advanced IT systems makes it possible to track goods from their source to their destination, ensuring that customers are kept informed of their order status and allowing for any potential issues to be quickly addressed and resolved. Furthermore, IT can enable companies to quickly identify and respond to customer queries and provide customers with a more efficient way to communicate with the company.
In addition to tracking and tracing, IT can also improve customer service in logistics management through predictive analytics. By leveraging data collected from customer orders, it is possible to create models that can accurately predict customer behavior and anticipate customer needs. This information can then be used to plan for and provide better customer service, as well as to identify opportunities to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
Finally, IT can also improve customer service in logistics management by automating specific processes. For example, IT systems allow it to automate order management, inventory tracking, and delivery schedules, thus reducing the time and resources required to manage customer orders. This can result in a faster and more efficient delivery process, as well as improved customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, IT can be a powerful tool for improving customer service in logistics management. By leveraging IT systems, companies can track and trace goods, predict customer needs, and automate critical processes, thus ensuring that customers receive the best possible service.
What is the role of IT in logistics management?
Role of IT in Logistics Management
Efficiency and Accuracy Enhancement
Information technology (IT) plays a crucial role in logistics management by enhancing efficiency and accuracy in the supply chain process. IT systems such as Transport Management Systems (TMS) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) streamline operations, automate repetitive tasks, and simplify complex processes, leading to improved productivity and cost reduction.
Real-time Tracking and Visibility
IT also enables real-time tracking and visibility of products throughout the supply chain. Advanced tools like GPS tracking, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), and barcode scanners provide real-time data on the location, status, and condition of goods. This information allows decision-makers to make informed choices and respond promptly to potential disruptions, ensuring timely delivery and customer satisfaction.
Data-driven Decision Making
Data analysis and visualization offered by IT greatly impact logistics management. Advanced analytics tools enable managers to identify patterns and trends in the supply chain, allowing for more strategic decision-making. Data-driven insights can be used to optimize inventory levels, improve forecasting accuracy, identify potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies, and ultimately drive performance improvements.
Integration and Collaboration
IT facilitates integration and collaboration among various stakeholders within the logistics industry. The use of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allows seamless communication and data exchange among different organizations, promoting a more collaborative approach to logistics management. This integration fosters better coordination among supply chain partners, reducing errors and inefficiencies while improving overall performance.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Lastly, the adoption of IT in logistics management has significant implications for sustainability and environmental concerns. Through the use of advanced algorithms and predictive analytics, businesses can optimize transportation routes, reduce fuel consumption, and minimize greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, IT solutions can also help companies implement waste reduction initiatives, monitor resource usage, and measure the environmental impact of their logistics operations.
In conclusion, IT plays an indispensable role in logistics management by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and visibility across the supply chain. Through the use of advanced technologies and data analysis, IT supports data-driven decision-making, encourages collaboration, and mitigates the environmental impact of logistics operations. As IT continues to evolve, it is vital for logistics professionals to adapt and embrace these technological advancements to remain competitive and drive meaningful improvements in the industry.

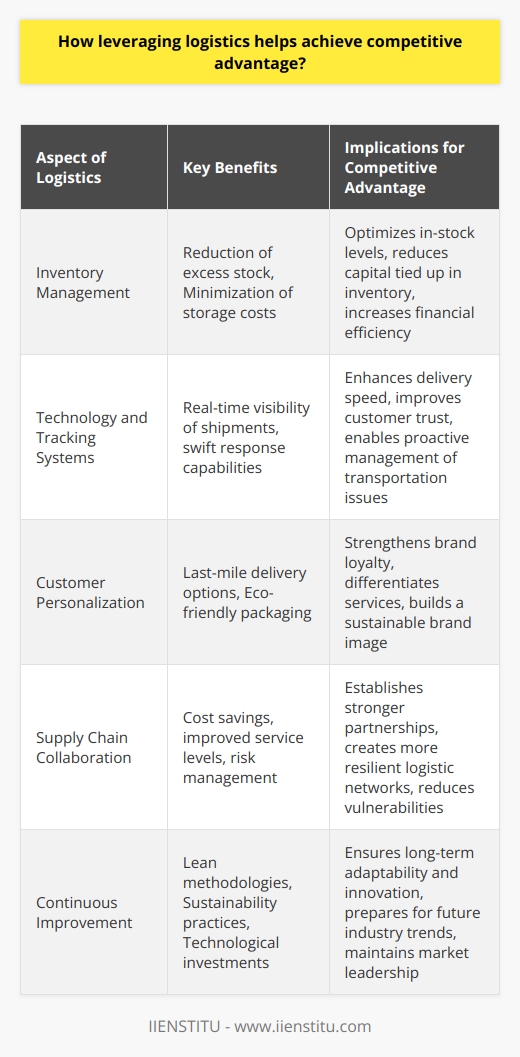
How leveraging logistics helps achieve competitive advantage?
Leveraging Logistics for Competitive Advantage
Strategic Role of Logistics
To achieve a competitive advantage, businesses must effectively leverage logistics by utilizing strategic planning and efficient supply chain management. This involves integrating their logistics operations into core business strategies and aligning them with the company's goals and objectives. The process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, cost-effective flow of raw materials, in-process inventory, and finished goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption is essential for maintaining the company's high standards of quality and service.
Operational Efficiency and Differentiation
Logistics play a crucial role in operational efficiency, which is a key determinant of competitive advantage. Efficient logistics management can lead to improvements in areas such as inventory control, warehouse management, and transportation management. By implementing effective and efficient logistics practices, companies can reduce their overall costs, increase operational efficiency, and provide quick delivery to their customers. This helps to set them apart from their competitors and attract more potential customers.
Moreover, leveraging logistics enables businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors by providing value-added services, such as customized packaging and personalized delivery options. These additional services enhance their overall customer experience and create a unique selling proposition for the company.
Speed and Flexibility in Response
The ability to react quickly and adapt to changes in market demands and competition is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in today's fast-paced business environment. Effective logistics management helps companies become more agile and responsive to these changes by providing the necessary infrastructure, processes, and resources to deliver products and services to customers more quickly and efficiently than their competitors. This flexibility allows them to quickly identify and capitalize on new market opportunities, giving them an advantage in the highly competitive market landscape.
Collaborative Partnerships
Fostering strong relationships with suppliers, distributors, and customers is essential for logistics-related success. By engaging in collaborative partnerships, businesses can optimize their logistics operations through the sharing of information, best practices, and resources. This collaborative approach enables the companies involved to streamline their supply chains, reduce risk, and improve their overall performance. These strategic partnerships ultimately contribute to the creation of shared value and contribute to a sustainable competitive advantage.
In conclusion, leveraging logistics is an instrumental part of achieving competitive advantage for any business. By focusing on operational efficiency, differentiation, quick response, and collaboration, companies can create a logistics system that is an integral part of their overall business strategy, allowing them to thrive and stay ahead of the competition in the ever-evolving global marketplace.
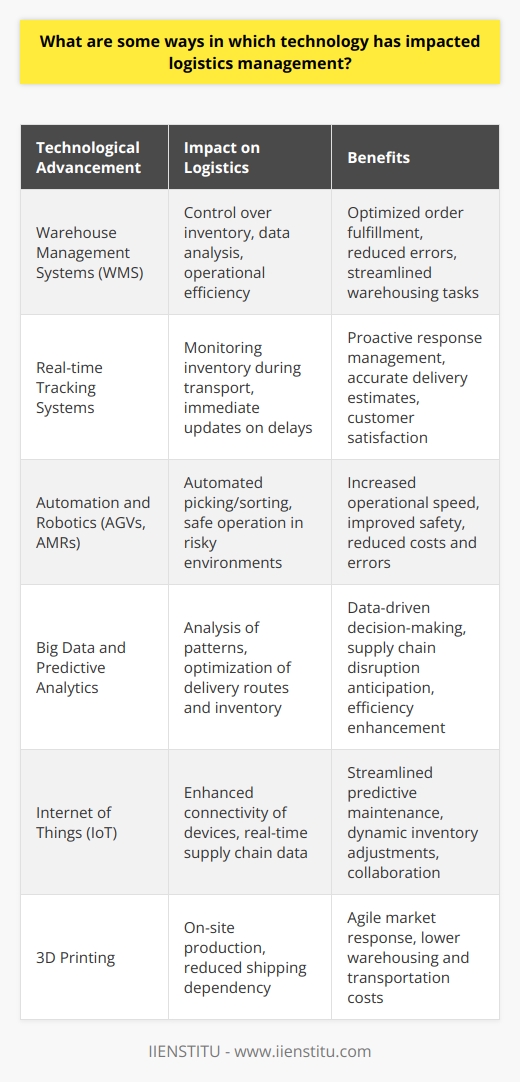
What are some ways in which technology has impacted logistics management?
**Technology's Role in Logistics Management**
One significant way technology has impacted logistics management is through the implementation of warehouse management systems (WMS). These software applications enhance efficiency by automating storage and retrieval processes, managing inventory control, and streamlining order fulfillment.
**Real-time Tracking and Visibility**
Another transformative technology in logistics management is real-time tracking systems, which provide a precise and up-to-date view of the location and status of shipments. Employing GPS technology and other advanced sensors, these systems allow managers to proactively address potential issues and optimize routing to minimize delays and reduce costs.
**Automation and Robotics in Warehouses**
The use of automation and robotics in warehouses has drastically improved the speed and accuracy of various tasks, such as picking and packing, thus increasing overall productivity. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) not only reduce the need for manual labor but also minimize errors and improve workplace safety.
**Advanced Analytics for Decision-making**
Big data and advanced analytics have enabled logistics managers to make more informed decisions about optimizing resources, identifying areas for improvement, and predicting future trends. Predictive analytics, in particular, can forecast potential bottlenecks and risks, allowing managers to enact preemptive measures and maintain smooth operations.
**Integration of Internet of Things (IoT)**
IoT integration has led to a more connected logistics infrastructure. Smart devices equipped with IoT capabilities generate large volumes of data, enabling logistics companies to monitor equipment performance, enhance asset utilization, and reduce maintenance costs. This real-time data exchange also supports collaboration and coordination among different logistics stakeholders.
**3D Printing and Its Applications**
3D printing technology has revolutionized the manufacturing process, offering the possibility of producing spare parts and customized products on-demand. The adoption of 3D printing in logistics reduces shipping distances, storage requirements, and reliance on large-scale production facilities, ultimately lowering transportation costs and lead times.
In conclusion, technology has profoundly impacted logistics management by introducing innovative systems, automation, and real-time tracking capabilities. These advancements optimize resources, enhance decision-making, and promote efficiency, ultimately supporting the growth and competitiveness of the logistics industry.
What is the role of IT in improving supply chain visibility?
Role of IT in Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility
Information Integration
The role of Information Technology (IT) in improving supply chain visibility lies in its ability to seamlessly integrate information across the entire supply chain network. By centralizing and standardizing data, IT enables faster and more accurate communication between suppliers, manufacturers, retailers, and customers, ultimately strengthening collaboration and reducing uncertainties.
Real-Time Access
IT also enables real-time access to critical information, meaning that stakeholders can immediately identify and address potential bottlenecks, disruptions, or quality issues. As a result, organizations can proactively manage demand and supply imbalances, make data-driven decisions, and optimize the overall supply chain performance.
Advanced Analytics
The use of advanced analytics tools and techniques is another key aspect of IT's role in supply chain visibility. Solutions such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, and predictive analytics help organizations uncover hidden patterns, trends, and insights from large datasets. By leveraging these insights, businesses can identify opportunities for process improvements, cost reductions, and better risk management.
Tracking and Monitoring
IT also plays a critical role in tracking and monitoring various supply chain components, including raw materials, production processes, inventory levels, and transportation. Modern technologies like RFID, GPS, and IoT devices provide granulated real-time data, which can be used to enhance visibility and ensure the smooth flow of goods from suppliers to end customers.
Enhanced Collaboration
Improved supply chain visibility is also achieved by enhancing collaboration among different stakeholders through IT platforms. For instance, cloud-based solutions and collaborative platforms ensure real-time information sharing and communication, enabling organizations to work more efficiently, reduce redundancy, and minimize errors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of IT in improving supply chain visibility is multifaceted and essential for maintaining a competitive edge. By fostering information integration, enabling real-time access to data, employing advanced analytics, facilitating tracking and monitoring, and enhancing collaboration, IT helps organizations overcome supply chain challenges and optimize their operations. As technology continues to evolve rapidly, it is vital for businesses to adopt and leverage IT solutions to ensure supply chain resilience and maintain an advantage in the marketplace.

How does leveraging logistics contribute to the sustainability of business operations?
Leveraging Logistics for Sustainability
Logistic optimization not only drives cost efficiency but also plays an essential role in enhancing sustainable practices within business operations. By leveraging logistics, businesses can mitigate their environmental impact, foster societal development, and maintain economic viability, thus contributing to overall sustainability.
Environmental Impact Reduction
One way to achieve sustainability through logistics is by minimizing businesses' carbon footprints through the efficient use of transportation and distribution. Optimizing routes, consolidating shipments, and selecting environmentally friendly modes of transport all contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, waste generation, and fossil fuel consumption. Furthermore, implementing cleaner technologies and energy-efficient equipment in warehouses and distribution centers enhances sustainability.
Societal Development Support
Sustainable logistics fosters positive relationships with local communities by promoting fair labor practices, health and safety measures, and employee skills development. Moreover, sustainable logistics management involves collaborating with suppliers to adopt responsible sourcing and promoting similar practices throughout the supply chain. By aligning their logistics with ethical standards and principles, businesses can improve their reputations and promote societal development.
Economic Viability Maintenance
Financial stability is a core component of sustainability, and leveraging logistics contributes to it by reducing operational costs and risks. Adopting lean logistics methodologies helps businesses eliminate waste, minimize stockholding and warehouse costs, and streamline supply chain processes, leading to improved cash flow and profitability. Additionally, businesses with a focus on sustainable logistics can tap into green market opportunities and cater to the increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and practices.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Leveraging logistics for sustainability encourages businesses to continuously seek innovative ways to optimize their operations and practices. By investing in research and development, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement, implement new technologies, and stay ahead of industry trends. In this manner, companies remain competitive while fostering an environment that values sustainability.
In conclusion, leveraging logistics significantly contributes to the sustainability of business operations by reducing environmental impact, promoting societal development, and ensuring economic viability. Embracing sustainable practices within logistics promotes continuous improvement, innovation, and a beneficial alignment with ethical standards and principles.

What are the key challenges faced by organizations in implementing IT solutions for logistics management?
Challenges in IT Implementation for Logistics Management
Choosing the Right Technology
A significant challenge faced by organizations while implementing IT solutions for logistics management is selecting suitable technologies. Various tools offer diverse functionalities that can affect operability or compatibility within the organization's existing system. Companies must ensure the chosen solution aligns with organizational needs and can seamlessly integrate, preferably with limited disruption.
Data Security and Privacy
Implementing IT solutions for logistics management requires a considerable amount of data sharing and storage. Consequently, data security and privacy become critical concerns for organizations. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, companies must prioritize safeguarding their systems while using IT solutions, ensuring they comply with regulations such as GDPR.
Skillset and Training Requirements
The implementation of IT solutions for logistics management often necessitates specialized skillsets and trainings for personnel. Limited knowledge or inadequate training can result in mismanaged systems, ineffective use of resources, and infrastructure failures. Organizations must invest in training programs to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge, which can be both time-consuming and costly.
Change Management
Change resistance among stakeholders is a recurring challenge for organizations implementing IT solutions for logistics management. Efficiently managing the change process is crucial to ensure successful implementation and user adoption. This requires open communication, participation, management buy-in, and addressing stakeholder concerns directly to create a seamless transition.
Cost and Resource Allocation
Another challenge faced by organizations is the cost and resource allocation associated with implementing IT solutions for logistics management. Such implementations usually involve upfront investments, integration costs, training, and ongoing maintenance. Organizations must strike a balance between allocating resources effectively and ensuring a continuous return on investment within budgetary constraints.
In conclusion, organizations face numerous challenges in implementing IT solutions for logistics management, including choosing the right technology, data security and privacy concerns, skillset and training requirements, change management, and cost and resource allocation. Overcoming these barriers necessitates strategic planning, efficient problem-solving, and a commitment to investing in innovative solutions or improvements in logistics management, further enhancing overall operations.

What is leveraging of logistics?
Understanding Leveraging of Logistics
Leveraging of logistics refers to the strategic utilization of an organization's logistical capabilities to gain a competitive advantage. This involves optimizing various logistics processes, such as transportation, warehousing, and inventory management, to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Role of Technology
The use of digital solutions and new technologies plays a crucial role in leveraging logistics. For instance, implementing advanced software solutions for warehouse management, transportation management, and supply chain management helps businesses analyze and optimize their logistical operations.
Partnering with Other Organizations
Collaborations and partnerships with other logistics companies or experts can also contribute to the leveraging of logistics. By engaging in partnerships, organizations can combine their respective resources and expertise, resulting in increased efficiency and a broader range of services.
Embracing Sustainability
In the modern business world, sustainability is a key factor in gaining a competitive edge. By incorporating sustainable practices in their logistics operations, companies can reduce their environmental impact, improve their brand image, and attract environmentally conscious customers.
Customer-Centric Approach
Adopting a customer-centric approach in logistics is crucial to enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering loyalty. This entails understanding customers' needs and preferences, and then tailoring logistical operations to meet those expectations.
Benefits of Leveraging Logistics
Effective leveraging of logistics can yield numerous benefits for an organization. These include reduced operational costs, improved customer satisfaction, and increased business growth. Furthermore, engaging in sustainable practices and embracing new technologies in logistics can enhance a company's reputation and help attract new customers.
In conclusion, leveraging of logistics represents a strategic approach employed by businesses to optimize their logistics operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive advantage in the market. With the rapid advancements in technology and increasing focus on sustainability, leveraging logistics has become essential for organizations to succeed in the modern business landscape.

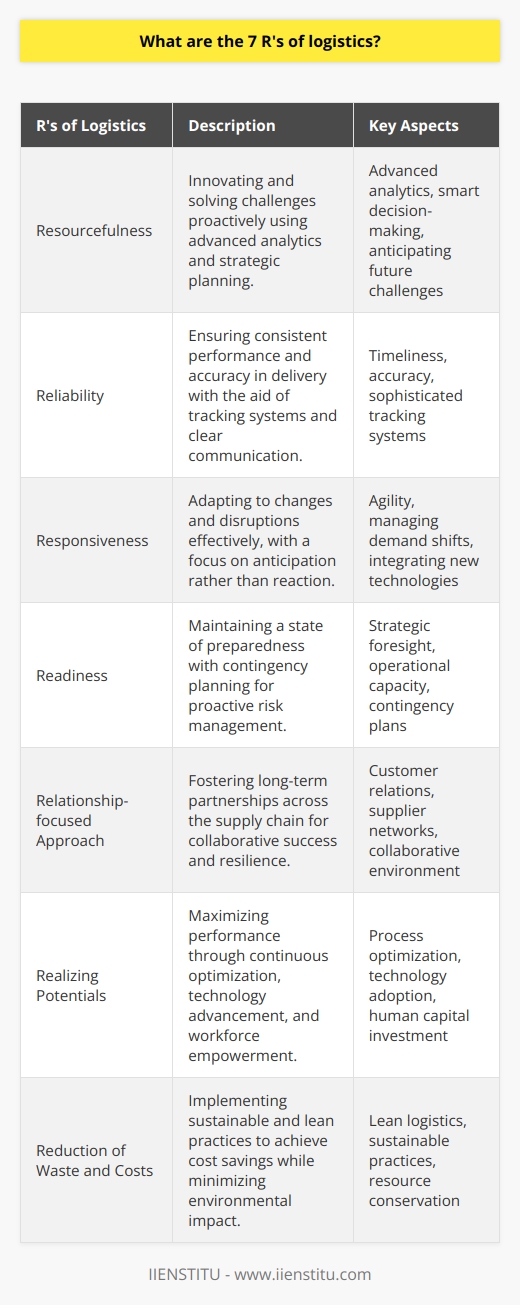
What are the 7 R's of logistics?
Seven Key Components of Logistics
**Resourcefulness**
Resourcefulness in logistics means finding innovative solutions to meet the unique demands of different industries. This involves devising cost-effective strategies to cater to the customers' requirements without compromising on the quality of service.
**Reliability**
Reliability is crucial in logistics management, as it ensures that the supply chain partners can depend on each other. The ability to consistently deliver goods and services on time and in the desired condition is instrumental in maintaining strong relationships between all stakeholders involved.
**Responsiveness**
In the context of logistics, responsiveness refers to the ability of a supply chain to adapt quickly to changes in market dynamics. This includes fluctuations in demand, shifts in customer preferences, and unforeseen disruptions in the supply chain. A responsive logistics system is agile and flexible, enabling it to easily adapt to new circumstances.
**Readiness**
Readiness in logistics means being prepared for any situation, whether it be a sudden spike in demand or an unexpected disruption in the supply chain. This involves having contingency plans in place and ensuring that adequate resources are available to address unforeseen challenges.
**Relationship-focused Approach**
A relationship-focused approach in logistics prioritizes effective communication and collaboration among all parties involved in the supply chain. Establishing strong relationships with customers, suppliers, and other supply chain stakeholders fosters trust, promoting a more efficient and effective logistics system.
**Realizing Potentials**
Realizing potentials in logistics requires optimizing the supply chain to operate at its full capacity. This involves continual improvement of processes, embracing new technologies, and developing the skills and capabilities of the workforce.
**Reduction of Waste and Costs**
The ultimate goal of an efficient logistics system is minimizing waste and costs while maximizing profits. This can be achieved through streamlined processes, better inventory management, and a focus on sustainability. Identifying and eliminating inefficiencies in the supply chain contributes to reducing operational costs, ultimately benefiting both the company and its customers.
How logistics management creates competitive advantage?
Logistics as a Source of Competitive Advantage
Logistics management plays a pivotal role in creating a competitive advantage for businesses in today's global market. By orchestrating the efficient and timely movement of goods and resources, logistics management enables companies to meet customer demands, reduce operational costs, and ultimately achieve higher profit margins.
Efficiency in Operations
Efficient operations are crucial for businesses to maintain a competitive edge. Logistics management helps companies optimize their supply chains by streamlining transportation, warehousing, and inventory management. This enables businesses to reduce lead times, improve product availability, and increase order accuracy, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction and fostering brand loyalty.
Cost Reduction
Effective logistics management leads to significant cost reductions, which contribute to a company's competitive advantage. By strategically sourcing and consolidating shipments, optimizing warehouse layouts, and implementing advanced technologies such as automated picking systems and real-time inventory tracking, businesses can minimize operational expenses. Reduced costs allow companies to price their products more competitively, increasing market share and profitability.
Flexibility and Adaptability
In a rapidly changing business landscape, the ability to adapt quickly to market fluctuations is essential. Logistics management enables companies to respond to sudden changes in demand, supply chain disruptions, and emerging market trends by reallocating resources and modifying transportation routes as needed. This adaptability ensures companies maintain a competitive advantage amid shifting customer preferences and global economic conditions.
Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility
Environmental and social responsibility efforts have become increasingly important in differentiating businesses in today's market. Logistics management plays a critical role in implementing sustainable practices such as reducing emissions from transportation, minimizing packaging waste, and using energy-efficient warehousing solutions. By integrating environmentally friendly and socially responsible initiatives into their logistics operations, businesses can not only improve their public image but also take advantage of cost savings associated with sustainable practices.
In conclusion, effective logistics management drives competitive advantage by increasing operational efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing flexibility and adaptability, and incorporating sustainable practices. By continuously improving and optimizing logistics processes, companies can strengthen their market position and achieve long-term success in the global marketplace.

What is the role of logistics management in enhancing supply chain resilience?
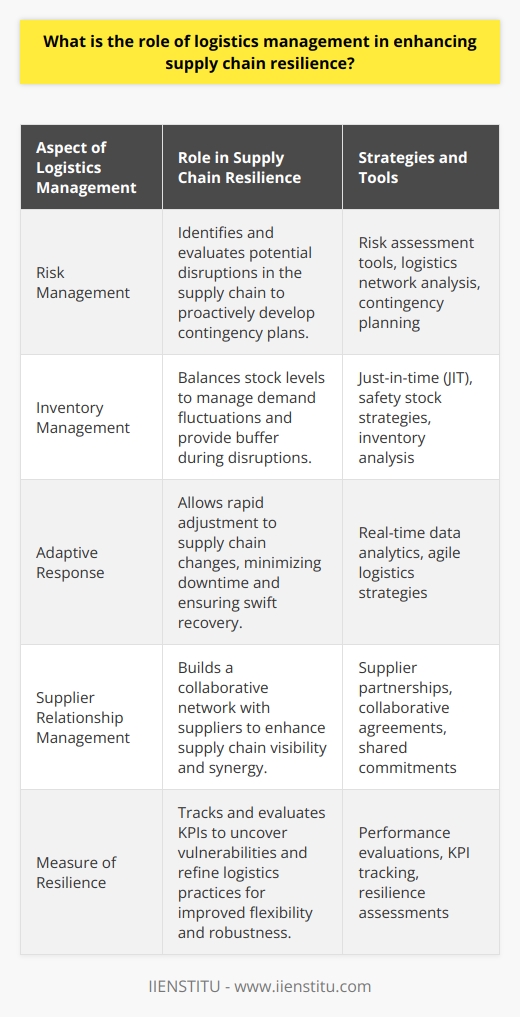
Supply Chain Resilience Enhancement
Logistics management plays a crucial role in enhancing supply chain resilience. At its core, it bolsters companies' abilities to perpetually supply goods and services, even during a disruption. It achieves this through a variety of strategies and methods.
Risk Management
One way logistics management enhances resilience is by identifying, assessing and mitigating supply chain risks. By mapping all steps involved in a process, potential vulnerabilities can be identified and guarded against.
Inventory Management Technique
Additionally, efficient inventory management is key to resilience. This includes having appropriate stock levels to meet demand, while avoiding excess inventory to minimize cost and waste. Also, by introducing safety stocks and backup suppliers, organizations can maintain operations in case of a disruption.
Adaptive Response Mechanism
Logistics management functions also ensure that organizations respond adaptively to changes. Using advanced technology, real-time data can be obtained and used to make prompt decisions, reducing potential damage during a crisis.
Supplier Relationship
Furthermore, building solid relationships with suppliers enhances resilience. Cooperating closely with suppliers ensures continuous goods delivery and minimizes risk.
Measure of Resilience
Lastly, logistics management provides a measure of resilience. By monitoring and evaluating performance indicators, organizations can identify weak points, change strategies, and strive for continuous improvement.
In summary, logistics management significantly contributes to supply chain resilience. From risk and inventory management techniques, adaptive response mechanisms, supplier relationship management to providing measures of resilience, logistics management is a vital aspect of resilient supply chains. As such, companies should invest significantly in this function to help foster robust, adaptable businesses.
How does effective logistics management contribute to the overall sustainability of a business?
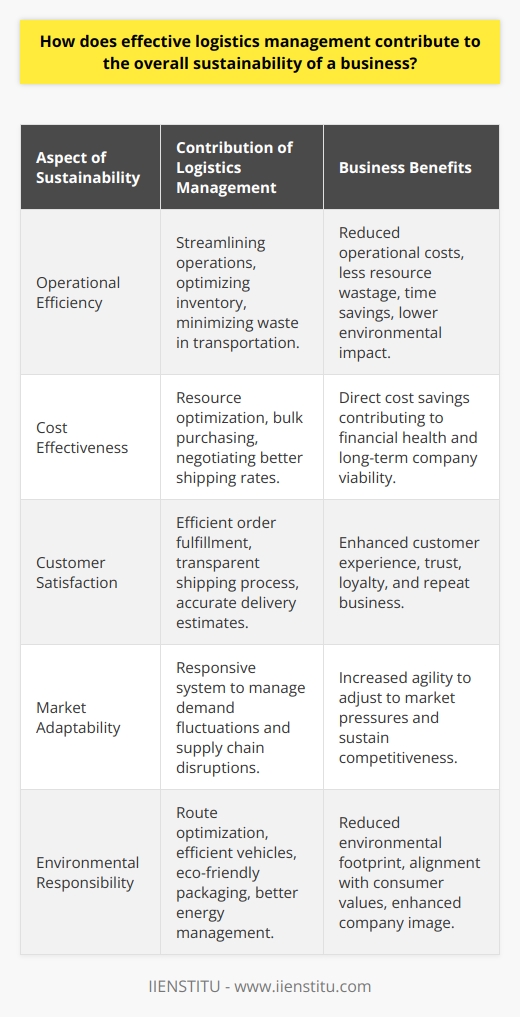
Efficiency in Operations
Effective logistics management greatly enhances a business's sustainability through operational efficiency. Logistics management streamers the flow of goods, services, and information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. It helps in reducing redundant processes, minimizing wastage, and leveraging cost-saving opportunities.
Savings Amidst Costly Operations
Apart from improving efficiency, robust logistics management can also result in cost savings that enhance a business’s financial sustainability. By harnessing economies of scale and optimizing distribution networks, businesses can substantially reduce their operational expenses. Such cost reductions directly contribute to better margins and an improved bottom line.
Increased Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is crucial to a business's long-term sustainability. Effective logistics management ensures timely delivery of products and services, enhancing a customer’s experience. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat buyers, ensuring a steady revenue stream for the business.
Adaptability to Change
In an ever-changing business environment, adaptability is key to sustainability. A strong logistics management framework enables a business to seamlessly adapt to changes. It offers the flexibility to navigate through supply chain disruptions, fluctuating demand, and other unforeseen challenges.
Sustainability Through Eco-Friendly Practices
Finally, effective logistics management can enhance a business's environmental sustainability. By optimizing routes, reducing packaging, and consolidating shipments, businesses can minimize their carbon footprint. This not only contributes to global sustainability efforts but also attracts eco-conscious consumers, improving the overall business prospects.
In conclusion, effective logistics management significantly contributes to a business's sustainability in multiple ways, including operational efficiency, cost savings, customer satisfaction, business adaptability, and eco-friendly practices.
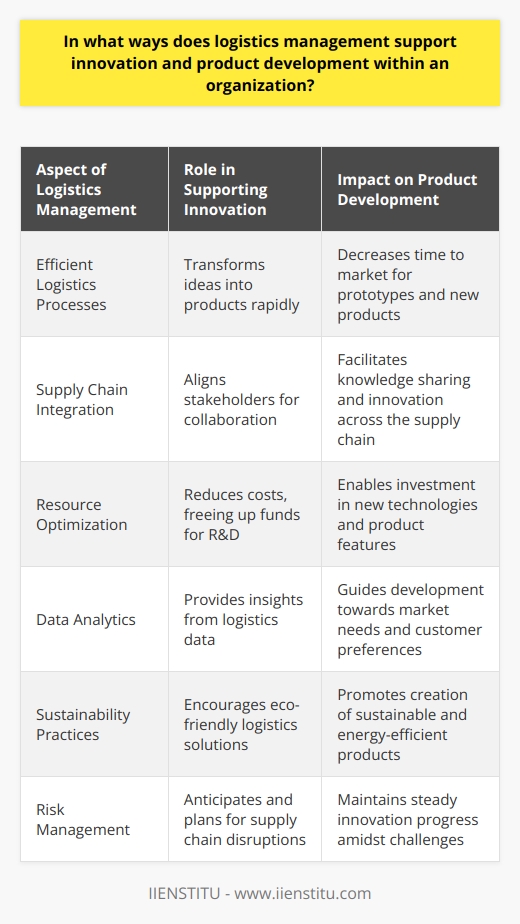
In what ways does logistics management support innovation and product development within an organization?
Promoting Innovation Through Streamlined Processes
Logistics management aids innovation and product development by enhancing processes. Effective logistics strategies reduce time-waste, hence aiding quicker turnaround of ideas into physical products. They ensure seamless handling, storage and transportation of goods, which minimizes production delays.
Improving Supplier-Customer Relationship
Logistics management facilitates stronger relationships with suppliers and consumers. Procuring materials on time, effective inventory control, and timely delivery, supports continuous product development. Such fine-tuned operations also attract customers, driving innovation efforts.
Cost Management and Resource Optimization
Effective logistics management aids cost-efficiency - a crucial factor in innovation and product development. By optimizing resource usage, minimizing production costs and reducing waste, organizations can reallocate funds to innovation.
Supporting Market Research
Logistics management supports market research initiatives. It provides vital consumer data like buying patterns, preferences and feedback, informing product development trends.
Incorporating Sustainable Practices
Logistics also plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainable innovation. Using eco-friendly transportation and packaging methods encourages the development of sustainable products. This not only meets increasing consumer demands for 'green' products but also paves the way for a sustainable future.
Risk Management in Logistics
Finally, logistics management aids in risk mitigation. Accurate demand forecasting, contingency planning, and robust supply chains minimize disruptions, contributing to smoother execution of innovation strategies.
In conclusion, logistics management acts as the backbone for innovation and product development within an organization. By streamlining processes, building relationships, supporting research initiatives, and endorsing sustainability, it cultivates an environment conducive to keen innovation.