Sensitivity Analysis in Logistics Management: Navigating Complexities for Optimal Decision-Making
I still remember the first time I was tasked with choosing a mode of transportation for a large shipment when I was working in logistics management. It felt a bit like standing at a crossroads, each path leading to a different destination, with its own set of challenges and rewards. This decision wasn't just about picking the fastest route or the cheapest carrier; it was about analyzing the myriad variables that could impact the entire supply chain. That's where sensitivity analysis came into play, and let me tell you, it was a game-changer for me.
Introduction
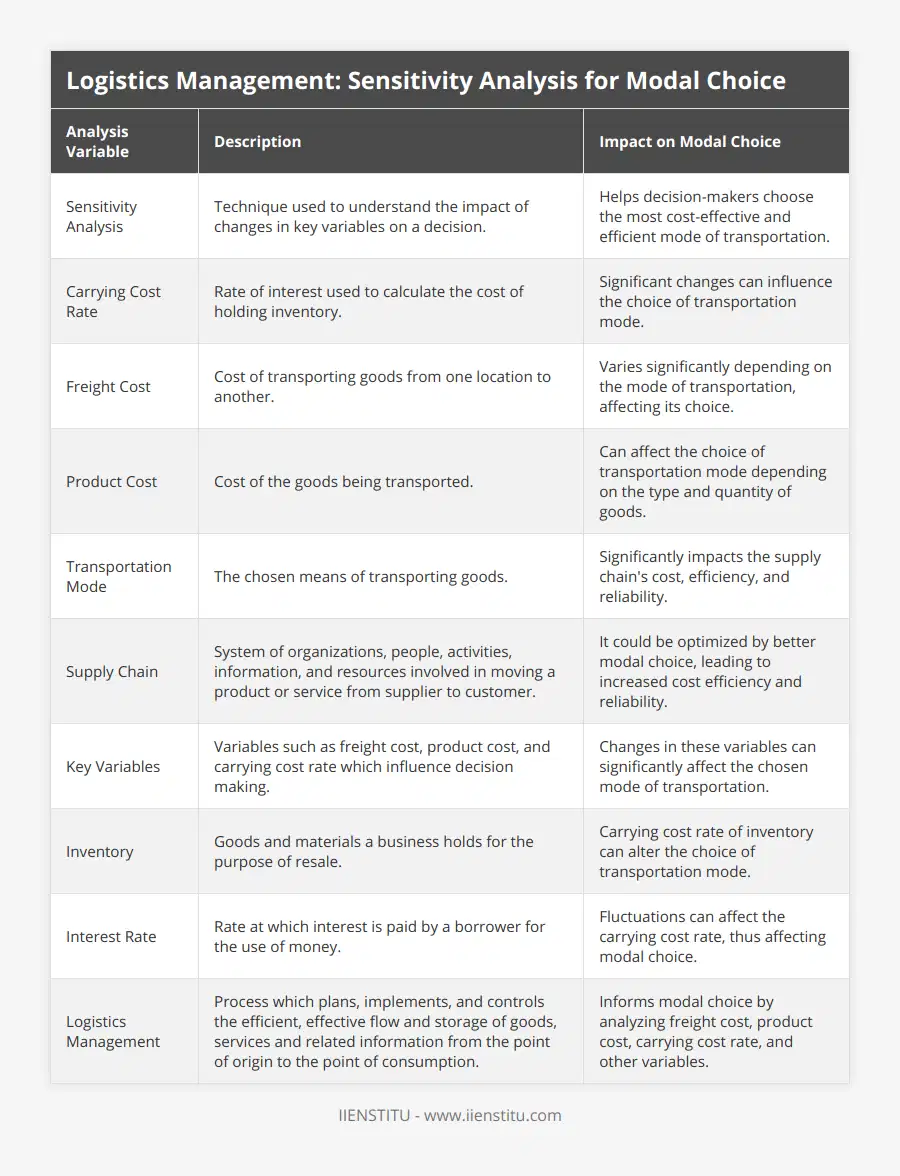
Sensitivity Analysis: A Key Component of Modal Choice
Variables for Sensitivity Analysis
Carrying Cost Rate
Freight Cost
Product Cost
Conclusion
Introduction
In the world of logistics, making informed decisions is crucial. Sensitivity analysis is a powerful tool that helps professionals evaluate the impact of changes in critical variables on their choices. By understanding how fluctuations in factors such as carrying cost rate, freight cost, and product cost influence outcomes, we can make more resilient plans that optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, And Replenishment Benefits İn Supply Chain Management
Distribution Requirements Planning İmplementation Strategies
The Importance of Sensitivity Analysis
Navigating the Science of Batch Order Picking in Supply Chain Operations
Maximizing Inbound Logistics: Benefits, Challenges & Strategies
Diving Deep into the Concept of Vendor Rating and Evaluation
I once worked on a project where we had to ship high-value electronics across continents. Initially, air freight seemed like the obvious choice due to its speed. However, when we conducted a sensitivity analysis, we found that slight changes in freight costs and carrying cost rates significantly impacted the overall expense. This led us to reevaluate our options and consider sea freight, which had lower freight costs but higher carrying costs due to longer transit times. By finding the right balance, we were able to optimize our expenses and ensure the success of the project.
Sensitivity analysis allows us to:
Identify the most influential variables in our decisions
Understand potential risks associated with fluctuations
Make plans that can withstand market changes
İmproving Customer Service With Product Substitutes İn Logistics Management
Most Searched Keyword About The Key İmplications Of The Bill Of Lading İn Business Transactions
Key Variables in Sensitivity Analysis
To effectively conduct sensitivity analysis in logistics management, it's essential to understand the key variables involved. Let's dive into each of these factors:
1. Carrying Cost Rate
The carrying cost rate refers to the expenses associated with holding inventory over time, including storage, insurance, depreciation, and opportunity costs. Changes in this rate can significantly impact modal choice decisions, especially when weighing faster, more expensive transportation options against slower, cheaper ones.
For example, if the carrying cost rate is high, it might be more economical to choose a faster mode of transportation to reduce the time inventory is held, even if the freight cost is higher.
2. Freight Cost
Freight cost is the price paid to transport goods from one point to another. This cost can vary based on factors such as:
Mode of transportation
Distance
Fuel prices
Market demand
Sudden changes in these factors, like a spike in fuel prices, can make certain modes less cost-effective. I recall a time during a peak oil price period when many companies had to shift from road to rail transport to mitigate high fuel surcharges. Sensitivity analysis helps predict how such changes in freight costs can impact the overall logistics strategy.
3. Product Cost
Product cost encompasses all expenses up to the point of sale, not just the manufacturing cost. When dealing with high-value goods, the risk associated with transportation becomes a significant factor. Expensive products might necessitate faster or more secure transportation modes, even if the freight cost is higher.
In one of my roles, we were transporting luxury goods. The high product cost meant that any delays or damages would be extremely costly. Sensitivity analysis helped us justify the higher freight costs for premium transportation services by highlighting the risks and potential losses associated with cheaper options.
The key to successful logistics management lies in the sensitivity analysis of modal choice.
The Interplay of Variables in Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management (SCM), decisions are rarely made in isolation. Changes in one variable can create a ripple effect throughout the entire chain, impacting everything from procurement to customer satisfaction. Let's consider an example to illustrate this interplay.
Balancing Act: A Perishable Goods Scenario
Imagine a company that produces perishable goods. The product cost includes not just the raw materials but also the potential loss if the goods spoil before reaching the market. Here's how sensitivity analysis can guide the modal choice:
1- Freight Cost: Air freight is more expensive than sea freight.
2- Carrying Cost Rate: Longer transit times increase the carrying cost due to refrigeration and risk of spoilage.
3- Product Cost: High if goods spoil, leading to potential loss of sales and waste.
By analyzing these factors, the company might conclude that despite the higher freight cost, air freight minimizes carrying costs and reduces the risk associated with product cost, leading to a better overall outcome.
Practical Tips for Implementing Sensitivity Analysis
Incorporating sensitivity analysis into your decision-making process can seem daunting at first, but with practice, it becomes an invaluable tool. Here are some practical tips to help you get started:
Start Small: Begin by focusing on the key variables that have the most significant impact on your decisions.
Gather Accurate Data: Ensure you have reliable and up-to-date information on freight costs, carrying costs, product costs, and other relevant factors.
Use Scenario Planning: Explore different "what-if" scenarios to understand how changes in variables affect outcomes.
Collaborate with Stakeholders: Involve relevant parties, such as finance, procurement, and operations teams, to gain comprehensive insights.
Leverage Technology: Utilize transport management systems (TMS) and other software tools to streamline data analysis and scenario modeling.
The Role of Technology in Sensitivity Analysis
Advanced transport management systems (TMS) have revolutionized the way we conduct sensitivity analysis in logistics management. These integrated platforms offer:
Real-time data on freight costs and market conditions
Simulation capabilities for quick scenario testing
Seamless integration with other supply chain management systems
By leveraging these tools, professionals can enhance their strategies, ensuring they remain competitive in an ever-changing market.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of sensitivity analysis are clear, it's important to be aware of potential challenges:
Data Quality: Inaccurate or outdated data can lead to misleading conclusions.
Complexity: As supply chains grow more intricate, the number of variables to consider can become overwhelming.
Assumptions: The analysis is based on certain assumptions that may not hold true in all situations.
To mitigate these challenges:
1- Invest in reliable data sources and regularly update information.
2- Break down complex analyses into smaller, manageable components.
3- Clearly document assumptions and regularly reassess their validity.
The Future of Sensitivity Analysis in Logistics
As global supply chains become more interconnected and vulnerable to disruptions, the importance of sensitivity analysis will only continue to grow. Events like trade wars, pandemics, and natural disasters have highlighted the need for robust risk assessment and contingency planning.
I believe that professionals who master sensitivity analysis will be well-positioned to lead the field of supply chain management. They will have the skills to navigate uncertainty, drive efficiency, and create resilient logistics strategies that can withstand the test of time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sensitivity analysis is a powerful tool that every logistics professional should have in their arsenal. By understanding how changes in key variables impact supply chain decisions, we can make more informed choices that optimize costs, mitigate risks, and ultimately, drive success.
Whether you're a seasoned logistics manager or just starting in the field, I encourage you to embrace sensitivity analysis. Explore resources, attend workshops, and most importantly, apply it in your daily work. You'll be amazed at the insights it can reveal and the confidence it can bring to your decision-making process.
The road ahead in logistics is full of challenges and opportunities. But with sensitivity analysis as your guide, you'll be well-equipped to navigate even the most complex supply chain landscapes. So, take that first step, and unlock the power of this invaluable tool. Your future self will thank you.
References:
1- Coyle, J. J., Langley, C. J., Novack, R. A., & Gibson, B. J. (2016). Supply Chain Management: A Logistics Perspective (10th ed.). Cengage Learning.
2- Rushton, A., Croucher, P., & Baker, P. (2017). The Handbook of Logistics and Distribution Management: Understanding the Supply Chain (6th ed.). Kogan Page.
3- Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & Supply Chain Management (5th ed.). Pearson Education Limited.
Frequently Asked Questions
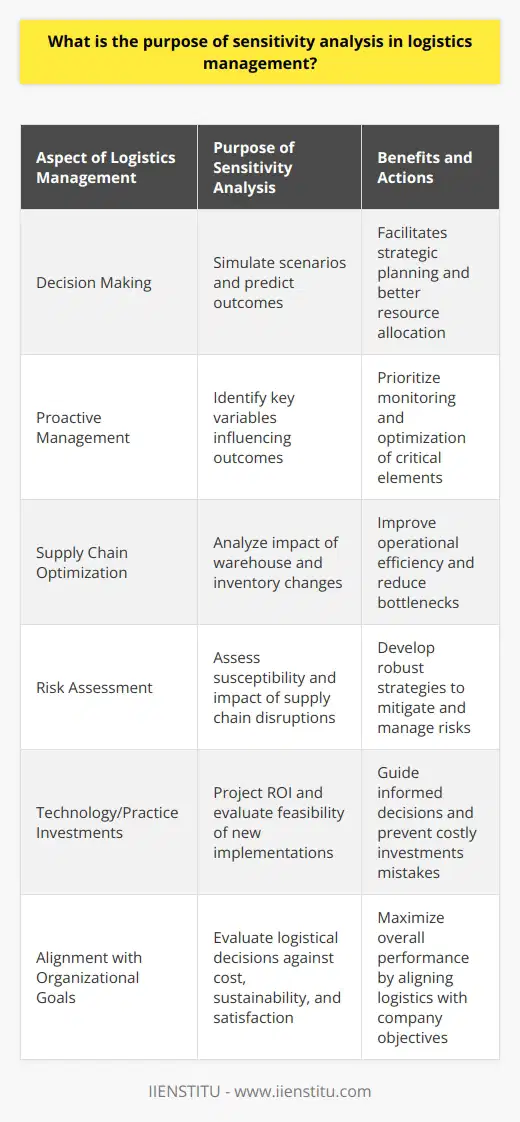
What is the purpose of sensitivity analysis in logistics management?
Sensitivity analysis is an essential tool for logistics managers. It measures the impact of input variable changes on a system's output or outcome.
The purpose of sensitivity analysis in logistics management is to identify the key factors and parameters that affect the performance of a logistics system and to evaluate the effects of changes in these factors and parameters on the system’s performance.
Logistics management is a complex task that requires careful planning and monitoring of resources, costs, and operations.
Sensitivity analysis helps logistics managers identify the key variables that affect the performance of a logistics system. It can be used to identify which factors should be monitored more closely and to determine the impact of changes in the variables on the system’s performance.
Sensitivity analysis can also identify areas where improvements can be made. For example, it can be used to determine the cost of implementing a new technology or process. It can also identify areas where there are opportunities for reducing costs or increasing efficiency.
Sensitivity analysis can also be used to evaluate the impact of changes in the system on the performance of the logistics system. This is important for assessing the impact of changes in the system on the overall organization's performance.
For example, if a new technology is implemented, it may cause changes in the system that could result in increased costs or decreased efficiency.
In conclusion, sensitivity analysis is a valuable tool for logistics managers. It can be used to identify the key factors and parameters that affect the performance of a logistics system and to evaluate the effects of changes in these factors and parameters on the system’s performance.
Sensitivity analysis is also helpful in evaluating the impact of changes in the system on the overall organization's performance, the cost of implementing new technologies or processes, and customer satisfaction.
How does the carrying cost rate affect modal choice?
The carrying cost rate has been seen to directly impact the modal choice, which is the selection of the most efficient and economical mode of transportation for the movement of goods. The carrying cost rate measures the total cost of storing, handling, and insuring goods over time.
This cost is usually expressed as a percentage of the value of the goods being stored. As the carrying cost rate increases, the cost of storing goods becomes more expensive, thus making it more expensive to use a particular mode of transportation.
The higher carrying cost rates can affect modal choice in various ways. For example, a higher carrying cost rate can discourage using shorter-distance transportation modes, such as trucks, due to the higher cost associated with storing the goods. This may lead to long-distance modes, such as rail and air, as they may be more cost-effective in the long run.
Similarly, suppose the carrying cost rate is too low. In that case, it may lead to the selection of a mode of transportation that is more expensive than necessary, resulting in an overall higher cost for transportation.
The carrying cost rate also affects the choice of container size when transporting goods. Generally, the cost of transportation increases with increasing container size, as larger containers tend to require more fuel and crew costs. However, if the carrying cost rate is high, selecting larger containers may be more cost-effective, as the cost savings may outweigh the cost of storage in transportation.
In conclusion, the carrying cost rate is vital in the modal choice. It can affect the selection of the most economical mode of transporting goods and the choice of container size. Thus, it is essential to consider the carrying cost rate when selecting the most appropriate mode of transportation.

What variables should be considered when conducting a sensitivity analysis for modal choice?
Several variables need to be considered when conducting a sensitivity analysis for modal choice.
Firstly, the characteristics of the transport system being analyzed must be considered. This includes the characteristics of each transport mode, such as its speed, capacity, cost, and schedule.
Secondly, the preferences of travelers need to be considered. This includes their perception of the mode, attitude, and willingness to use it. Thirdly, the availability of information on each mode needs to be considered. This includes the availability of route information, timetables, and real-time data for each mode.
Finally, the external factors that may influence mode choice must be considered. These include land-use patterns, socioeconomic characteristics, the availability of parking, and the availability of alternative modes.
A range of data collection techniques can be used to measure the sensitivity of modal choice to these variables accurately. These include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and stated preference techniques.
Surveys can collect information on traveler preferences and attitudes toward the various transport modes. Interviews can be used to collect detailed information on traveler behavior and the factors influencing their decision-making.
Focus groups can be used to understand travelers' collective behavior and preferences for different transport modes.
Stated preference techniques can measure travelers' willingness to change their mode of transport in response to changes in the environment or other factors.
In conclusion, various variables must be considered when conducting a sensitivity analysis for modal choice. These include the transport system's characteristics, travelers' preferences, information availability, and external factors. Data collection techniques such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and stated preference techniques can be used to measure the sensitivity of modal choice to these variables accurately.
What is the role of sensitivity analysis in evaluating transportation alternatives?
Role of Sensitivity Analysis
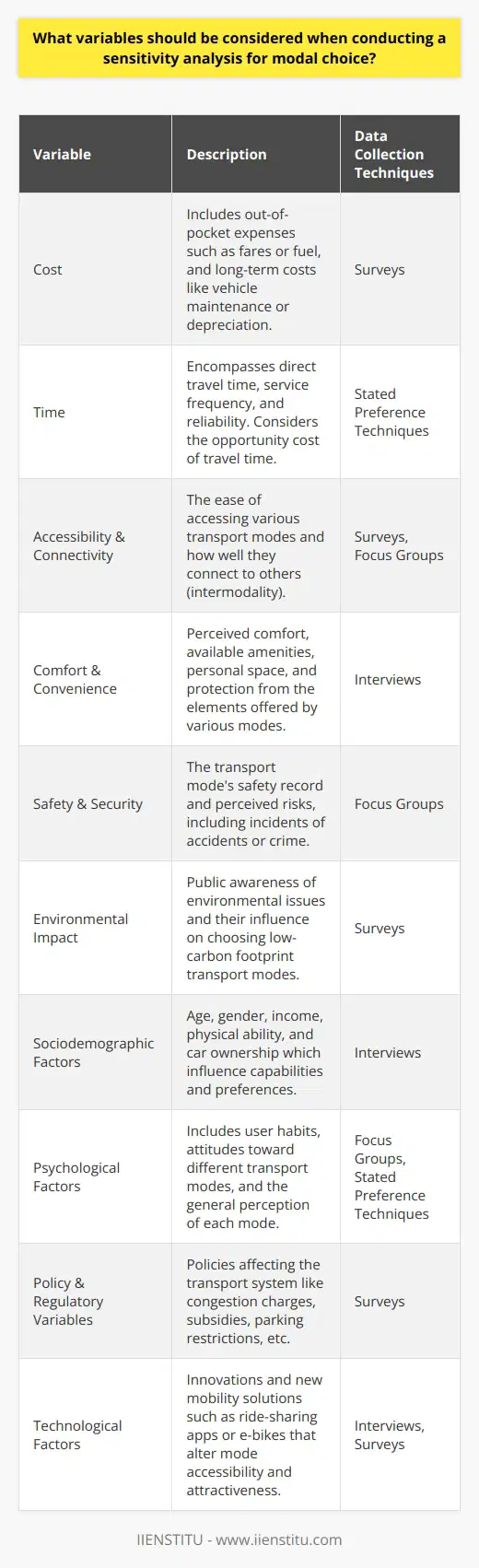
Sensitivity analysis plays an essential role in evaluating transportation alternatives by assessing the robustness of results and identifying critical parameters. As decision-making processes in transportation planning are often characterized by ambiguity and uncertainty, sensitivity analysis provides valuable insights into the potential impacts of changes in underlying assumptions and input data.
Assessing Robustness of Results
In the context of evaluating transportation alternatives, sensitivity analysis helps to determine the reliability and stability of results generated by models or simulations. By systematically examining the impact of variations in input parameters on the outcome, a decision-maker can gauge the robustness of a preferred alternative under different scenarios. This information can then help in choosing a transportation solution that performs well even when the uncertainties materialize.
Identifying Critical Parameters
Furthermore, sensitivity analysis aids in identifying parameters that are critical to the performance of transportation alternatives. Understanding the most influential factors allows decision-makers to focus their resources, attention and data collection efforts on these parameters. It also supports the fine-tuning of decision models and improves the overall quality of decision-making by highlighting areas that warrant further investigation or monitoring.
Enhancing Decision-making Transparency
Lastly, sensitivity analysis enhances transparency in decision-making processes. By explicitly addressing uncertainties and demonstrating how they affect the evaluation of transportation alternatives, sensitivity analysis makes decision-making more defensible and supports communication with stakeholders. This increased transparency ultimately leads to more robust decisions, grounded in a solid understanding of the system's behavior under various conditions.
In conclusion, sensitivity analysis contributes significantly to the evaluation of transportation alternatives by assessing the robustness of results, identifying critical parameters, and enhancing decision-making transparency. By incorporating sensitivity analysis in transportation planning processes, decision-makers can make more informed choices that account for uncertainties and foster robust and resilient transportation systems.
How do the different logistics management models impact supply chain efficiency?
Logistics Management Models and Supply Chain Efficiency
Understanding Logistics Management Models
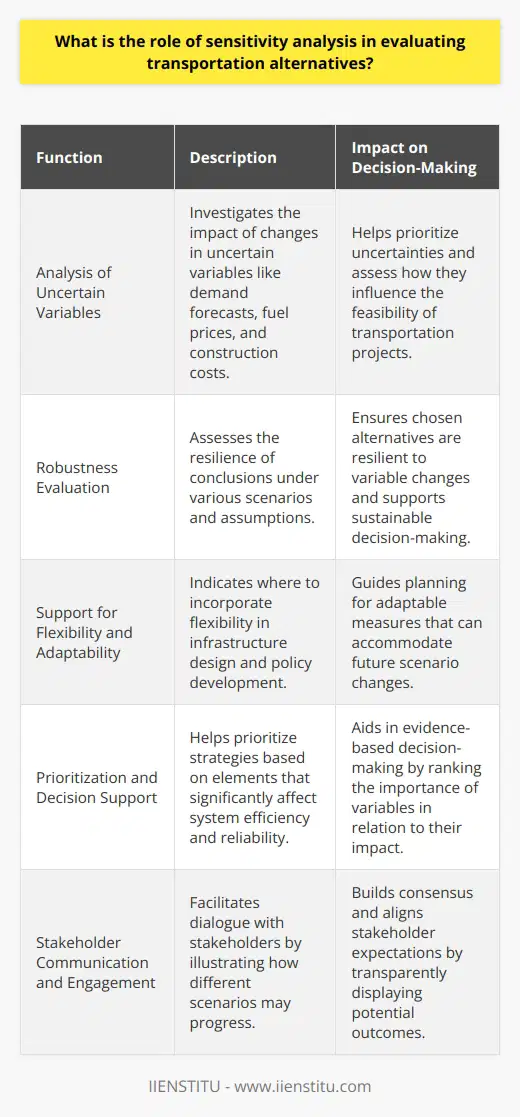
Logistics management models are essential for designing, implementing and controlling the efficient flow and storage of goods, services, and related information in a supply chain. The objective is to meet customer requirements while minimizing costs. Different logistics management models impact supply chain efficiency in various ways, as discussed below.
Traditional Logistics Model
The traditional logistics model focuses on product-centric planning, warehousing, and transportation activities. With this model, supply chain efficiency may be compromised due to the lack of visibility, collaboration, and real-time data. As a result, companies following the traditional model may experience inefficiencies such as stockouts, overstocking, and difficulties in meeting customer demand.
Just-in-Time Logistics Model
The Just-in-Time (JIT) logistics model promotes the efficient delivery of products to customers, minimizing inventory levels and associated costs. By relying on accurate demand forecasting and supplier collaboration, this model can prevent supply chain inefficiencies. However, JIT may also face risks related to supply disruptions, leading to stockouts or increased lead times.
Agile Logistics Model
The agile logistics model emphasizes flexibility and responsiveness to changing market conditions. This model enables supply chains to adapt to disruptions, fluctuating customer demand, and supply uncertainties. However, the increased focus on adaptability may lead to higher operational costs and potential inefficiencies in the absence of proper information sharing and coordination among supply chain partners.
Lean Logistics Model
The lean logistics model is based on the principles of lean manufacturing, which seeks to eliminate waste and maximize efficiency. By applying these principles to supply chain management, this model drives continuous improvement, process standardization, and cost reduction. However, a strict focus on minimizing waste may limit flexibility and hinder responsiveness to dynamic market conditions.
Conclusions
The choice of logistics management model has significant implications for supply chain efficiency. Companies must carefully evaluate their specific requirements, market conditions, and desired performance metrics before selecting a model. By adopting the most suitable logistics model, organizations can enhance supply chain efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall competitiveness.
In what ways are logistics management decisions influenced by external factors such as politics, regulations, and environmental concerns?
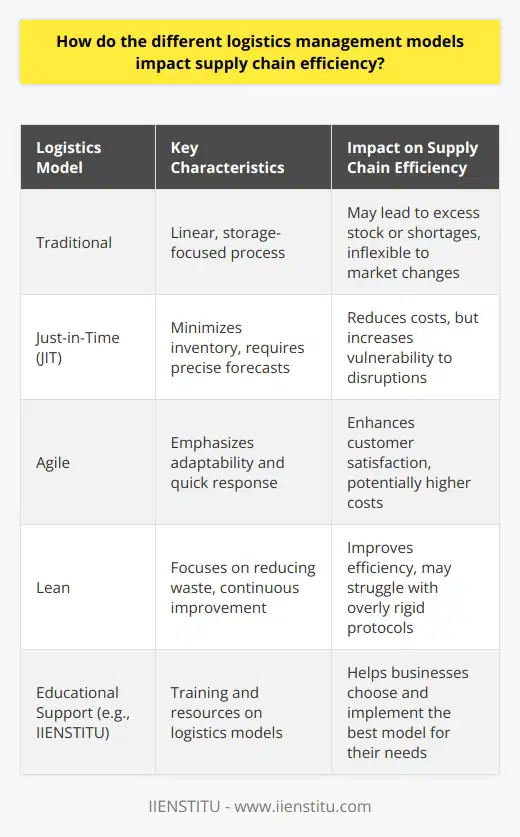
Impact of Politics on Logistics Management Decisions
In the realm of logistics management, political factors play a significant role in influencing decisions. Governments can impose trade restrictions or tariffs that will directly affect the movement of goods and services across international borders. Additionally, the stability of a country's political landscape, such as civil unrest, can prompt companies to reconsider their supply chain strategies to ensure business continuity.
Influence of Regulations on Decision-Making
Logistics management is also strongly affected by regulatory factors established by local, national, and international authorities. Regulations vary between countries, resulting in supply chain managers needing to adapt their strategies to adhere to those specific requirements. Examples of these regulations include safety standards, import and export restrictions, and labor laws. Companies need to comply with these regulations to avoid potential financial penalties or legal consequences.
Environmental Considerations in Logistics Management
Finally, several environmental concerns have influenced logistics management decisions in recent years. Companies have started to prioritize sustainable practices in response to growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and services. This includes minimizing waste and packaging, optimizing transport routes to reduce fuel consumption and emissions, and implementing energy-efficient warehouse operations. Furthermore, environmental disasters, such as earthquakes and floods, can affect logistics management decisions by disrupting supply chains and necessitating contingency planning to maintain smooth operations.
In conclusion, logistics management decisions are significantly impacted by external factors such as politics, regulations, and environmental concerns. Addressing these factors requires businesses to develop agile and flexible strategies, ensuring the resilience and sustainability of their supply chains, while remaining competitive in an ever-changing environment.
What is the significance of incorporating sensitivity analysis in the decision-making process of logistics management?
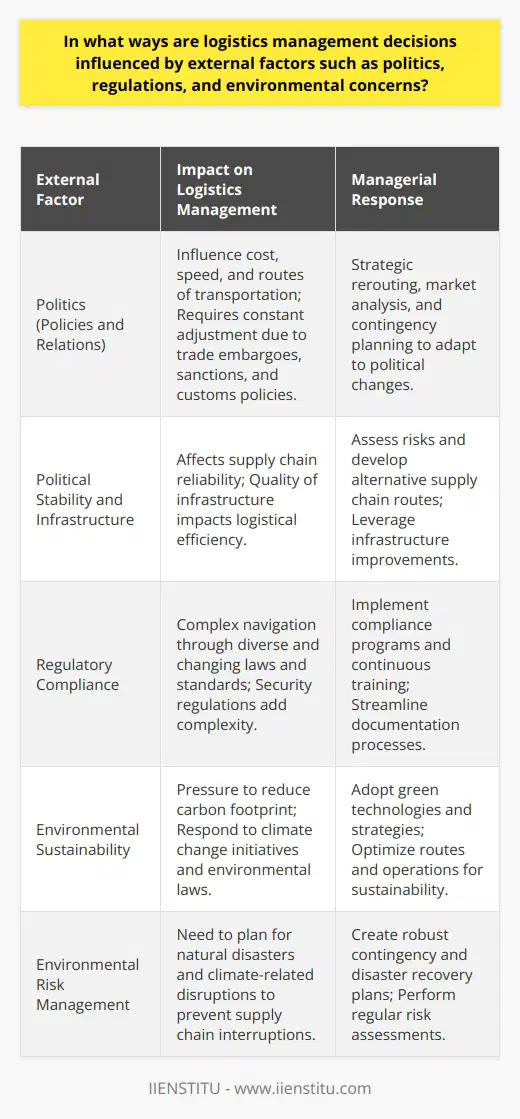
**Significance of Sensitivity Analysis in Logistics Management Decision-Making**
Incorporating sensitivity analysis in the decision-making process of logistics management holds significant importance. Sensitivity analysis enables managers to understand the impact of various parameters on the overall outcome of a decision. Consequently, this analytical approach helps identify risks, uncertainties, and the potential consequences of different decisions, leading to better-informed choices.
**Uncovering Risks and Uncertainties**
Logistics management can be a complex undertaking, with various factors influencing the efficiency and reliability of the supply chain. Sensitivity analysis assists in quantifying the extent of the influence that individual parameters exert. By performing this analysis, logistics managers can pinpoint critical factors that could cause disruptions in the supply chain or lead to increased costs if they are not properly addressed. This critical information guides managers in developing contingency plans, optimizing resources, and allocating budget to address potential bottlenecks and risks accordingly.
**Guiding Resource Optimization**
Resource optimization is crucial in logistics management since it directly impacts the cost and effectiveness of the supply chain. Sensitivity analysis can aid in identifying the most cost-efficient distribution of resources across different elements of the supply chain. With this information, logistics managers can make data-driven decisions that minimize transportation expenses, reduce stockpiling costs, and enhance overall productivity.
**Informing Decision-Making Processes**
Decision-making in logistics management carries significant consequences, impacting long-term success and profitability. Sensitivity analysis offers insights that can aid managers in making informed decisions rooted in quantitative evidence. This analytical tool considers the interplay between various factors, such as demand fluctuations, transportation costs, and lead times, to present a comprehensive view of potential outcomes. Ultimately, this informed approach facilitates the selection of optimal strategic and operational decisions, ensuring efficiency and effectiveness in logistics management.
In conclusion, the significance of incorporating sensitivity analysis in the decision-making process of logistics management lies in its ability to comprehensively assess the impact of various factors on logistics outcomes. This valuable information assists in uncovering risks and uncertainties, guiding resource optimization, and informing data-driven decision-making processes, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain.
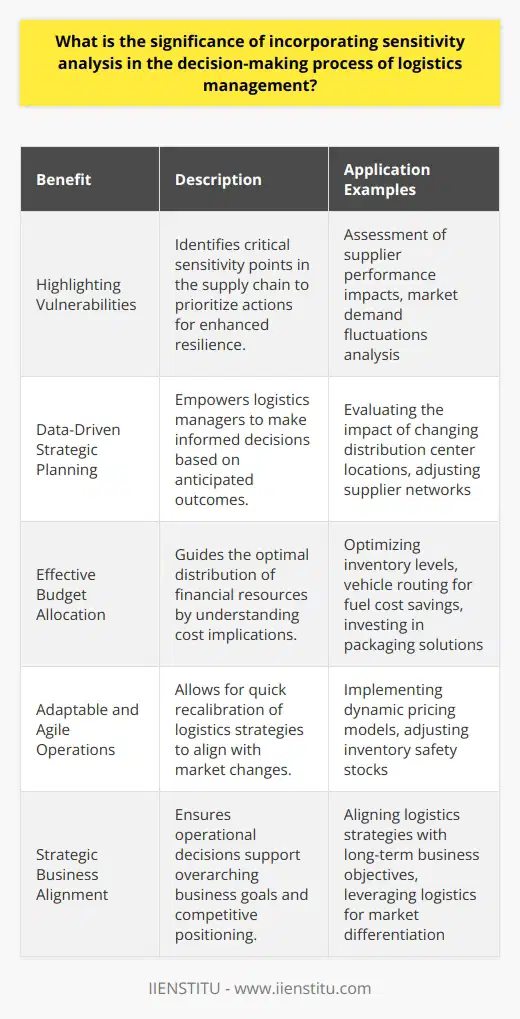
How do various factors, such as cost, time, and reliability, influence the selection of transportation modes in logistics management?
Factors Influencing Transportation Mode Selection
Cost Considerations
In logistics management, cost stands as a significant factor in the selection of transportation modes. Organizations must weigh the overall expenses involved in using various transportation options, including freight charges, handling costs, and insurance premiums. Lower cost modes will be more appealing, especially when transporting items with lower profit margins or in cost-sensitive industries.
Time Sensitivity
The time required for transportation is crucial in industries where products have a short shelf life or with customers who demand quick delivery. Fast transportation modes, such as air, become necessary when the time factor is of high importance. On the contrary, in cases where time is not a pressing issue, slower and usually more cost-effective modes like maritime or rail transportation can be selected.
Reliability Factors
Reliability is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction, ensuring consistent delivery times, and avoiding disruptions in the supply chain. Transportation modes with a proven track record of timely delivery, limited instances of damage or loss, and predictable transit times generally gain preference in logistics management.
Capacity and Flexibility
Transportation capacity is another critical factor influencing mode selection. The volume, weight, and size of the cargo determine the type of transportation mode required. Modes with large capacities, such as ships or trains, are more suitable for accommodating heavy or voluminous shipments, whereas smaller-capacity options like trucks may need to be chosen for more modest freight sizes. Additionally, transportation modes that can accommodate sudden changes in shipment size or frequency, such as road transport, can offer a higher degree of flexibility.
Geographical Coverage
Finally, the geographical reach of each transportation mode impacts the selection process, with companies considering the availability and accessibility of specific options for their logistical needs. For example, landlocked countries may rely more on road and rail transportation, whereas those with extensive coastlines might favor maritime shipping options.
In conclusion, a multitude of factors, including cost, time, reliability, capacity flexibility, and geographical coverage, significantly influence the selection of transportation modes in logistics management. Each factor plays an essential role in ensuring that organizations make informed decisions when choosing the most suitable and efficient means of transportation for their specific needs.
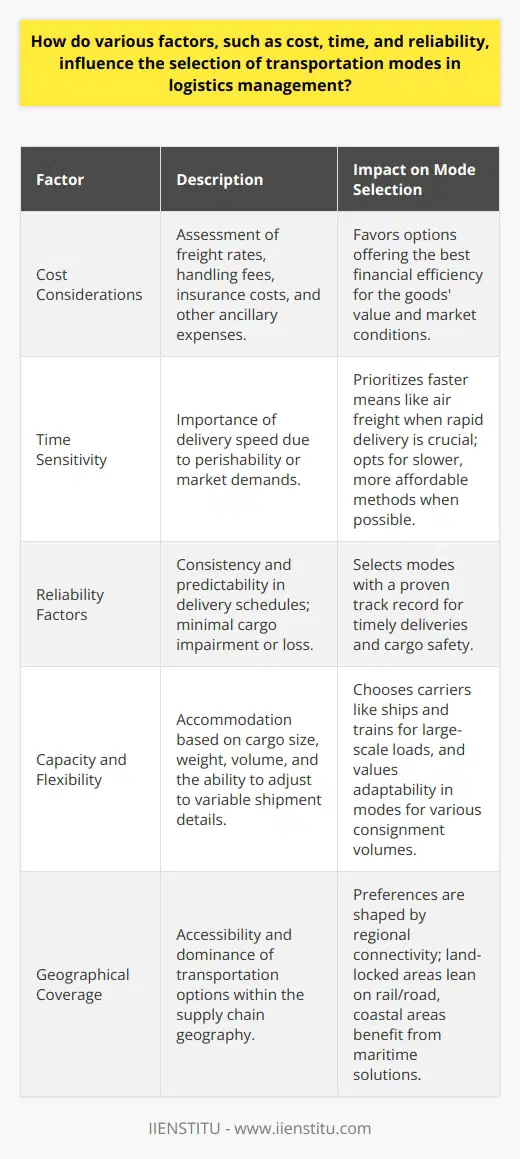
What role do external variables, such as economic conditions, technological advancements, and infrastructure, play in shaping logistics management models and strategies?
Impact of Economic Conditions
Economic conditions significantly influence logistics management models and strategies. In periods of economic growth, companies often expand their distribution networks and invest in technology to improve efficiency. During economic downturns, however, organizations may prioritize cost reductions, potentially outsourcing logistics operations or consolidating distribution centers to minimize expenses.
Role of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements shape logistics management by introducing innovative solutions and tools. Modern information systems enable better visibility and control over supply chains, fostering data-driven decision-making. Warehouse automation technologies, such as robotics and inventory management systems, optimize order fulfillment processes and reduce the need for manual labor. Furthermore, advancements in transportation solutions, including electric and autonomous vehicles, have the potential to dramatically improve efficiency and sustainability in logistics.
Importance of Infrastructure
Infrastructure plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of logistics management strategies. Efficient transportation networks, such as roads, railways, and ports, facilitate the swift movement of goods and reduce transportation costs. Moreover, reliable energy supplies and communication infrastructure are vital for supporting digital technologies and advanced equipment within logistics operations. Investments in infrastructure development can, therefore, contribute to improved logistics performance and competitive advantage for businesses.
In conclusion, logistics management models and strategies are heavily influenced by external variables, such as economic conditions, technological advancements, and infrastructure. Organizations must constantly adapt to these changing factors to maximize operational efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
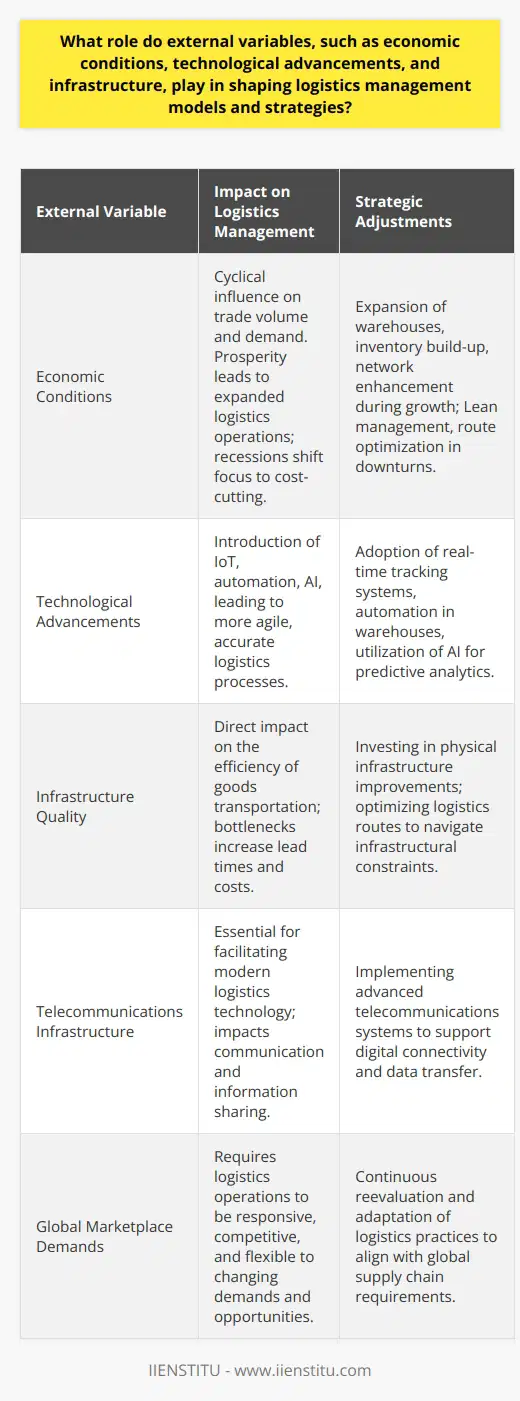
What is the relationship between sensitivity analysis and risk assessment in logistics management?
Relationship Overview
Sensitivity analysis and risk assessment are two essential components of logistics management. They are interrelated processes that help organizations make informed decisions by evaluating potential uncertainties and their impact on business operations.
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis is the examination of various factors that influence logistics management outcomes, such as demand, costs, and lead times. It aims to quantify how changes in input variables and assumptions can affect the decision-making process. Understanding the sensitivity of these factors is vital for organizations to prioritize resources and take corrective actions when needed.
Risk Assessment
On the other hand, risk assessment is the systematic identification and evaluation of potential risks associated with logistics processes. This involves measuring the likelihood and severity of adverse events that can disrupt supply chains, leading to financial losses, customer dissatisfaction, or operational inefficiencies. Mitigating these risks is central to maintaining an efficient logistics network and achieving organizational objectives.
Interdependence of Both Processes
The relationship between sensitivity analysis and risk assessment lies in their complementary role in identifying vulnerabilities that may arise in logistics management. Sensitivity analysis provides a foundation for assessing the potential consequences of changes in critical parameters, allowing organizations to recognize potential risks associated with these fluctuations. Risk assessment, in turn, uses this information to prioritize mitigation measures, enabling businesses to proactively manage and minimize uncertainties.
Collaborative Decision-Making
By employing sensitivity analysis and risk assessment in a coordinated manner, logistics managers can evaluate the performance of different strategies and identify opportunities for improvements. This collaborative decision-making approach ensures that decisions are supported by rigorous analysis, enhancing the resilience of logistics operations and reducing exposure to unexpected disruptions.
Conclusion
In summary, sensitivity analysis and risk assessment are intertwined aspects of logistics management that contribute to more robust decision-making processes. Sensitivity analysis reveals areas where potential risks may emerge, while risk assessment evaluates their severity and likelihood. By understanding and addressing these vulnerabilities, logistics managers can improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of their supply chain operations.
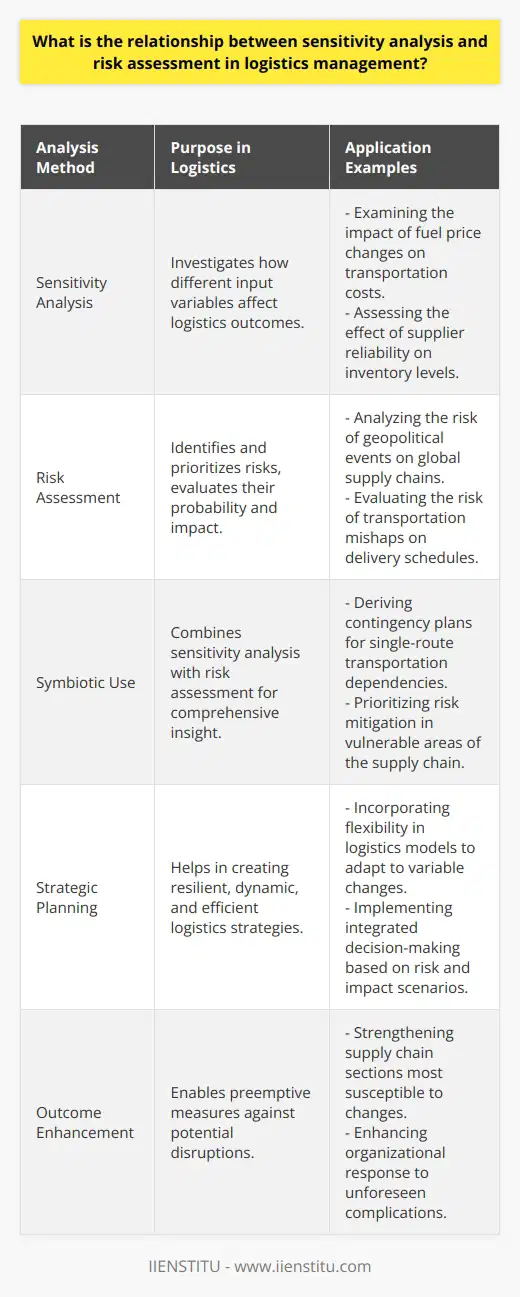
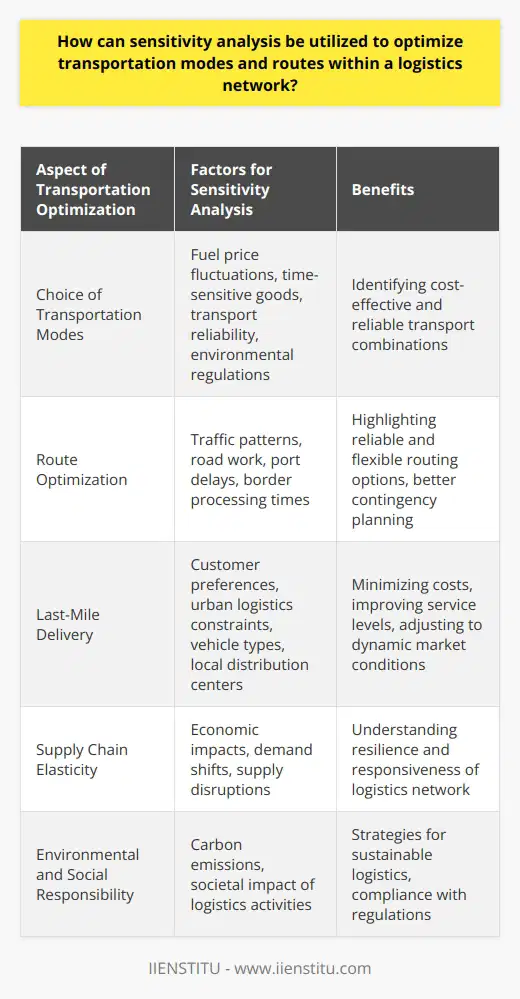
How can sensitivity analysis be utilized to optimize transportation modes and routes within a logistics network?
Sensitivity Analysis for Logistics Network Optimization
Understanding Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis is a useful method of determining how various factors can impact the efficiency of a logistics network by studying the effect of changes in inputs. In the context of transportation modes and routes, sensitivity analysis can help in finding the optimal solution by considering different scenarios and their potential outcomes. It assists in making informed decisions, while also ensuring resilience and flexibility to accommodate changes in external conditions, such as disruptions or unforeseen events.
Application in Transportation Modes
For optimizing transportation modes, sensitivity analysis can be used to predict the optimal mix of various modes — such as air, rail, road, and sea — for delivering goods within a logistics network. By analyzing different factors, such as cost, time, service quality, and environmental impact, decision-makers can find the most efficient combination that minimizes costs and maximizes customer satisfaction. Sensitivity analysis enables a better understanding of the trade-offs involved in selecting specific transportation modes, helping organizations achieve their operational and sustainability goals.
Optimizing Routes through Sensitivity Analysis
Besides transportation modes, sensitivity analysis can also be employed to optimize transportation routes within a logistics network. By considering factors such as travel time, distance, traffic congestion, infrastructure, and stakeholder requirements, sensitivity analysis can enable logistics managers to devise efficient routing schemes. The analysis can help identify the most cost-effective and time-saving routes, ensuring timely delivery and improved customer satisfaction. Moreover, this analysis can support companies in exploring alternative routes in case of disruptions or varying seasonal demands, offering better adaptability and resilience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sensitivity analysis serves as a valuable tool for optimizing transportation modes and routes within a logistics network. By considering various factors and exploring different scenarios, sensitivity analysis helps decision-makers to find the optimal combination of transportation modes and routes that maximize efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. Furthermore, it instills flexibility and resilience in logistics networks, enabling organizations to stay prepared for unforeseen disruptions and changing market conditions.
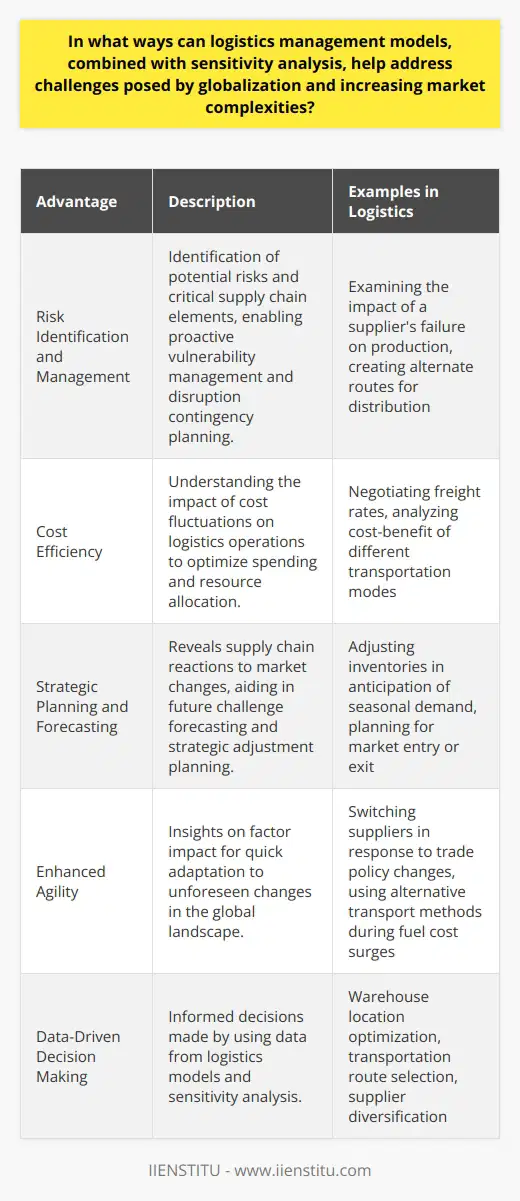
In what ways can logistics management models, combined with sensitivity analysis, help address challenges posed by globalization and increasing market complexities?
Addressing Globalization Challenges
Logistics management models are effective tools in addressing the challenges posed by globalization and market complexities. These models focus on streamlining distribution channels and ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services across borders, thus enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. By employing these models, businesses can tackle the bottlenecks, delays, and uncertainties that globalization entails.
Incorporating Sensitivity Analysis
Furthermore, integrating sensitivity analysis into logistics management models augments their adaptability to market fluctuations. Sensitivity analysis evaluates the impact of various factors, such as changes in demand, transportation costs, and exchange rates, on the overall supply chain performance. This information aids businesses in better understanding and forecasting future global market trends, enabling them to anticipate and adapt to disruptions efficiently.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
One significant advantage of combining logistics management models and sensitivity analysis is the enhancement of supply chain resilience. This process involves identifying vulnerabilities and devising strategies to counteract potential disruptions. By examining different scenarios, organizations can identify and prioritize risks accordingly, strengthening their capacity to navigate complex markets and recover from unforeseen challenges.
Optimizing Resource Allocation
Efficient resource allocation is another benefit derived from the fusion of logistics management models and sensitivity analysis. Organizations can allocate resources across different logistics functions more effectively, considering the diverse priorities and opportunities within the supply chain. Consequently, this optimizes cost, lead time, and flexibility in alignment with their business objectives and overall market conditions.
Enabling Strategic Decision Making
Lastly, the amalgamation of logistics management and sensitivity analysis assists organizations in making well-informed strategic decisions. The comprehensive understanding of market dynamics and supply chain vulnerabilities enables managers to devise proactive strategies and make smarter choices when facing trade-offs. For instance, decisions on sourcing, production, distribution, and supplier relations can be based on a solid foundation of data-driven insights.
In conclusion, logistics management models combined with sensitivity analysis play a vital role in helping organizations navigate the challenges posed by globalization and increasing market complexities. By evaluating the impact of various factors, providing valuable insights, and guiding decision-making, these tools empower businesses to achieve a competitive edge and thrive in unpredictable global markets.
What is sensitivity analysis of a model and how does it aid in understanding the impact of input variable fluctuations on output predictions?
**Concept of Sensitivity Analysis**
Sensitivity analysis of a model refers to the systematic examination of how varying input variables can affect output predictions. In essence, it seeks to quantify the dependence of the model's outcomes on changes in input values and helps in determining the robustness of a model.
**Role in Understanding Input-Output Relationships**
By conducting sensitivity analysis, researchers can gain insights into the impact of input variable fluctuations on output predictions. It enables them to identify critical input parameters, which have the most influence on the model's outcomes. In turn, this knowledge helps in refining the model, focusing resources on crucial parameters, and improving the quality of predictions.
**Assessing Model Robustness**
One primary objective of sensitivity analysis is to assess the robustness of a model. A robust model maintains its predictive capabilities despite fluctuations in input variables. In practice, this means that the model's performance remains consistent even when uncertainties in the input data are introduced. Therefore, a model with low sensitivity to changes in input data is considered more robust.
**Influence on Decision-Making**
Sensitivity analysis plays a crucial role in supporting decision-making processes. It aids stakeholders in understanding the potential range of outcomes resulting from various assumptions or uncertainties in input data. By providing a better understanding of the model's performance in different scenarios, it empowers decision-makers to make informed choices and select the most appropriate course of action.
**Enhancing Model Development Process**
Lastly, sensitivity analysis contributes to the continuous improvement of the model development process. By identifying which input variables significantly impact output predictions, model developers can prioritize refining those variables to optimize their model's performance. Furthermore, it encourages model developers to incorporate relevant factors and interactions within the model, leading to a more realistic representation of the studied system.
In conclusion, sensitivity analysis plays a critical role in understanding the impact of input variable fluctuations on output predictions within a model. It assists in evaluating the model's robustness, informing decision-making processes, and enhancing the model development process. Ultimately, sensitivity analysis is essential for delivering more accurate and reliable predictions to support various applications and decisions.

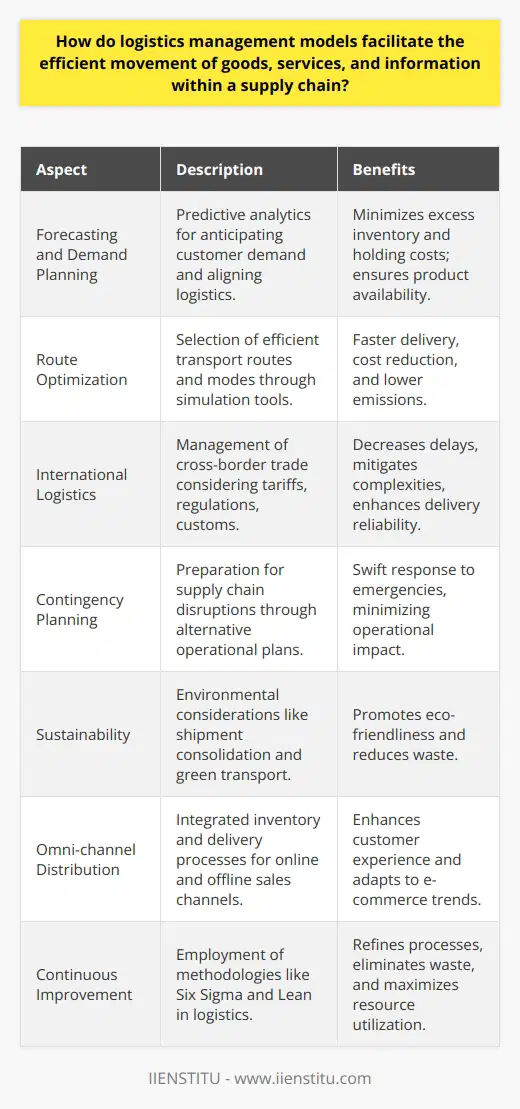
How do logistics management models facilitate the efficient movement of goods, services, and information within a supply chain?
Logistics Management Models
Logistics management models play a crucial role in ensuring the successful delivery of goods, services, and information within a supply chain. By utilizing these models, organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall supply chain performance.
Process Standardization and Streamlining
One key aspect of logistics management models is the standardization and streamlining of supply chain processes. Standardizing processes minimizes variations, which lowers the likelihood of errors and inefficiencies. Streamlining, on the other hand, identifies and eliminates unnecessary steps in the supply chain, thus improving productivity and reducing operating costs.
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is another essential element of logistics management models. It involves maintaining an optimal level of inventory to meet customer demands while keeping storage and carrying costs low. Implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory management strategies or leveraging advanced inventory management software helps organizations efficiently manage their inventory levels while minimizing waste and costs.
Technology Integration
The integration of technology within logistics management models facilitates the efficient movement of goods, services, and information. Faster and more accurate data transmission through technological advancements like Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) allows for real-time visibility into a supply chain. This visibility enables organizations to make better-informed decisions, optimize routing, and improve transportation efficiency.
Collaboration and Coordination
Logistics management models also encourage collaboration and coordination among various supply chain partners. By promoting communication and information sharing across organizations, these models foster coordinated efforts to meet customer demands. Such synergies strengthen the entire supply chain, boosting its overall resilience and efficiency.
Performance Measurement
Lastly, logistics management models emphasize the importance of performance measurement to gauge the efficiency of a supply chain. By setting specific key performance indicators (KPIs) and continually monitoring them, organizations can identify areas in need of improvement. Regular evaluations drive continuous performance improvement, ensuring the supply chain remains resilient and competitive in an ever-changing business landscape.
In conclusion, logistics management models are vital in facilitating the efficient movement of goods, services, and information within a supply chain. They help organizations standardize and streamline processes, manage inventory effectively, integrate technology, encourage collaboration, and measure performance. Implementing these models leads to optimized operations, cost reductions, and improved supply chain performance.
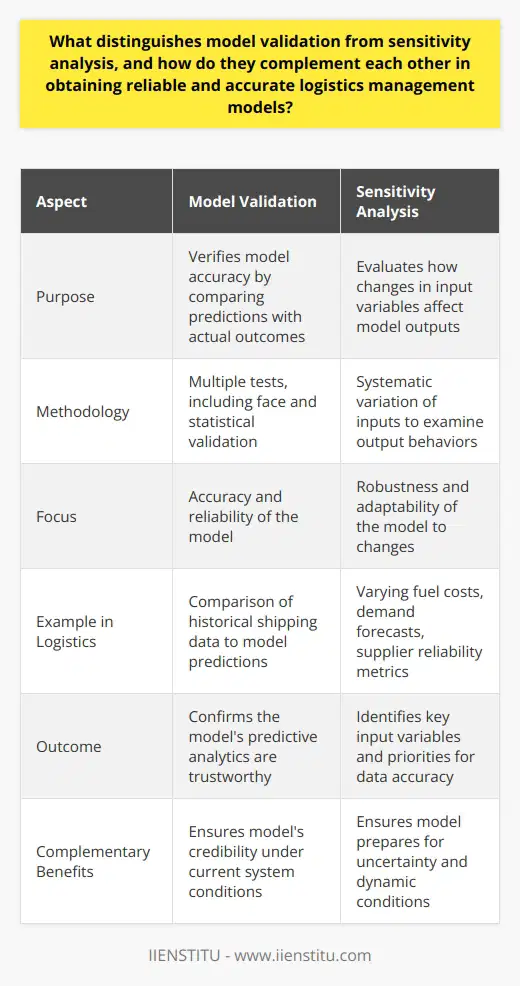
What distinguishes model validation from sensitivity analysis, and how do they complement each other in obtaining reliable and accurate logistics management models?
Model Validation: Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability
Model validation focuses on assessing the accuracy and reliability of logistics management models by comparing their predictions with actual observed data. This process involves testing a model's performance using historical or real-world data to ensure its robustness and applicability in diverse scenarios. Model validation is essential to determine if a logistics management model can be practically applied and trusted for decision-making.
Sensitivity Analysis: Evaluating Model Responses
On the other hand, sensitivity analysis evaluates the responsiveness of a logistics management model to changes in its input parameters. It examines how variations in model inputs, such as demand and transportation costs, affect the outputs and performance of the model. Sensitivity analysis helps identify critical parameters influencing the model outcomes and guides researchers to refine and improve the model by addressing these significant variables.
Complementary Roles in Model Development
Model validation and sensitivity analysis play complementary roles in obtaining reliable and accurate logistics management models. Model validation ensures that the model accurately reflects reality and can be trusted to make decisions in practical applications. Sensitivity analysis, in contrast, provides insights into the model's performance under different conditions and helps identify areas of improvement.
Combining these two approaches, researchers can develop robust logistics management models that closely represent real-world scenarios and respond appropriately to variations in input parameters. This combination increases model reliability, accuracy, and applicability in diverse situations and supports informed decision-making in logistics management.
In conclusion, model validation and sensitivity analysis are distinct yet complementary techniques for obtaining reliable and accurate logistics management models. By combining these approaches, researchers can ensure that the developed models are robust, accurate, and responsive to real-world conditions, thereby improving their practical applicability and supporting informed decision-making in logistics management.
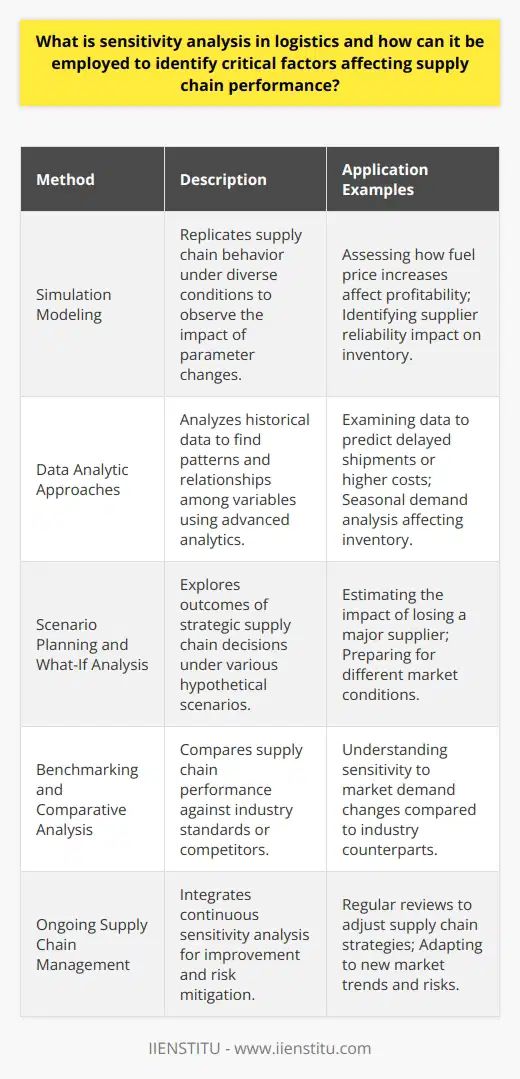
What is sensitivity analysis in logistics and how can it be employed to identify critical factors affecting supply chain performance?
Understanding Sensitivity Analysis in Logistics
Sensitivity analysis in logistics is a crucial quantitative tool that allows supply chain professionals to understand the impact of various factors on the overall performance of the supply chain. It facilitates the identification of critical factors affecting supply chain performance by analyzing the potential changes in various parameters, such as inventory levels, transportation costs, and lead times. Sensitivity analysis helps in predicting how changes in these parameters would affect the overall performance of the supply chain.
Employing Sensitivity Analysis for Identifying Critical Factors
Sensitivity analysis can be employed in several ways to identify critical factors affecting supply chain performance. Some key approaches include:
Simulation Techniques: By using simulation models, supply chain professionals can analyze various scenarios for different factors and their interactions within the supply chain. This method enables them to identify which variables have the most significant impact on overall performance and make informed decisions to optimize their supply chain management.
Data-Driven Analysis: Analyzing historical data and performance metrics can help supply chain professionals recognize trends and correlations between various factors, such as demand fluctuations, lead times, and transportation issues. This insight allows them to prioritize critical factors and make necessary adjustments to improve supply chain performance.
What-If Scenarios: Conducting what-if scenarios is another effective way to employ sensitivity analysis. This approach allows supply chain managers to examine how changes in specific factors would affect overall performance, enabling them to prepare for potential challenges and develop contingency plans accordingly.
Benchmarking and Comparative Analysis: By comparing their supply chain performance against industry best practices and competitor performance, professionals can identify areas of improvement and potential challenges that need to be addressed. Sensitivity analysis supports this process by highlighting the impact of critical factors on supply chain performance.
In conclusion, sensitivity analysis in logistics provides supply chain professionals with valuable insights into the critical factors that heavily impact their performance. By employing sensitivity analysis using various approaches, they can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to optimize and strengthen their supply chain resilience and efficiency.
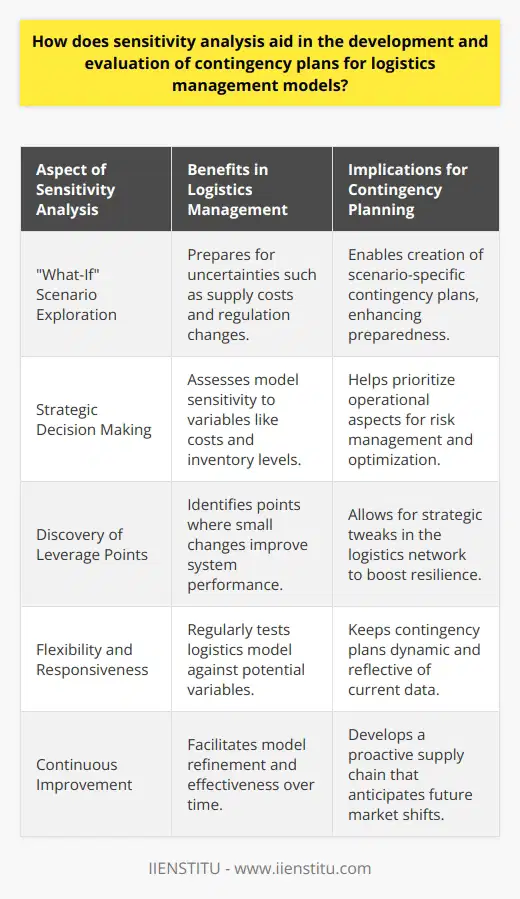
How does sensitivity analysis aid in the development and evaluation of contingency plans for logistics management models?
Sensitivity Analysis in Logistics Models
Sensitivity analysis plays a crucial role in developing and evaluating contingency plans for logistics management models. By examining different scenarios and understanding the variability of inputs and outputs, logistics managers are better prepared to address potential issues and mitigate risks within their supply chains.
Identifying Key Variables and Uncertainties
A key component of sensitivity analysis involves identifying the critical variables and uncertainties affecting logistics management models. These variables may include factors such as demand fluctuations, supply chain disruptions, or transportation delays. By evaluating the impact of these uncertainties, logistics managers can develop robust contingency plans and make informed decisions throughout the entire supply process.
Evaluating Potential Outcomes
Sensitivity analysis enables logistics managers to quantify the possible outcomes of various scenarios. By running simulations or conducting a thorough analysis of historical data, managers can evaluate the potential effects of different decision-making strategies on their supply chain processes. This promotes flexibility and adaptability, which are essential in today's rapidly evolving global supply chains.
Sensitivity analysis not only identifies vulnerabilities and areas for improvement in logistics management models but also supports informed decision-making and problem-solving. Despite the inherent uncertainty in logistics operations, incorporating sensitivity analysis in the planning stages can significantly increase the likelihood of success and overall performance.
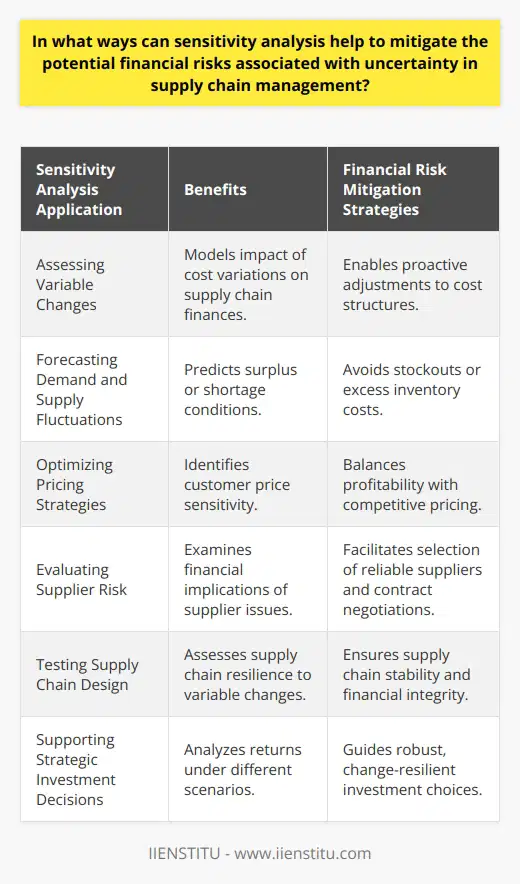
In what ways can sensitivity analysis help to mitigate the potential financial risks associated with uncertainty in supply chain management?
**Sensitivity Analysis in Financial Mitigation**
Sensitivity analysis serves as an essential tool in mitigating financial risks related to uncertainty in supply chain management. In particular, it helps managers evaluate the impact of different input parameters on the final outcome, leading to a more informed decision-making process.
**Simulating Multiple Scenarios**
Firstly, the method allows companies to simulate multiple scenarios by varying crucial input variables such as demand forecasts, lead times, and supplier reliability. This examination of changes empowers businesses to anticipate potential disruptions in the supply chain and to develop contingency measures in response.
**Identifying Key Parameters**
Secondly, sensitivity analysis aids practitioners in identifying the most critical variables affecting the supply chain. By pinpointing these crucial elements, managers focus on optimizing and monitoring them to increase the overall resilience and stability of the supply chain.
**Cost-Benefit Analysis Enhancement**
Thirdly, sensitivity analysis improves the quality of cost-benefit analyses by highlighting the impact of uncertainties on expected outcomes. As a result, companies can effectively allocate resources and prioritize proposed investments to mitigate the effects of supply chain disruptions.
**Preparing for External Factors**
Lastly, sensitivity analysis permits supply chain managers to explore and prepare for the influence of external factors such as economic downturns, policy changes, and fluctuations in exchange rates. By taking these factors into account, organizations build more adaptable and resilient supply chains to protect against unfavorable market conditions.
In conclusion, sensitivity analysis offers multiple benefits, enabling supply chain professionals to navigate through uncertainty and minimize financial risks. By simulating scenarios, identifying key parameters, enhancing cost-benefit analyses, and preparing for external factors, companies can better manage their supply chains and ensure the long-term stability of their operations.