As digital disruptions forge their path into various industrial sectors and procure conspicuous changes, it's no surprise that logistic executives are left pondering over the concept of "Logistics future in 5-10 years."
Employers ask this particular question during an interview to gauge both the candidate's understanding of the ongoing industry trends and their ability to predict and adapt to potential shifts in the ecosystem.
The Purpose of the Question about Logistics Future in 5-10 Years
Now you may be wondering why such a futuristic question gets space in an interview setting. Interviewers aim to understand your vision and strategy for the future.
They are also interested in your ability to stay updated with current industry trends, anticipate changes, and prepare strategically for the transformations ahead.
With the sheer velocity at which technology is progressing, the logistics sector is expected to undergo profound transformation, and the company would want to ensure they are bringing somebody on board who is equipped to surf the tide of change, not get swept away by it.
At what interview level is it asked?
The question, "Logistics future in 5-10 years," is most likely to surface in mid-level to senior executive interviews, mainly in the operations, logistics management, or supply chain verticals.
Related Course: Logistics Certificate Programs
Interview Question: How Has Time Management Impacted Your Personal Growth?
Interview Question: How Did You Improve a Digital Marketing ROI?
This is because these roles require a comprehensive understanding, foresight, strategic thinking, and the ability to adapt to market trends and technological advancements.
Not only is this question likely in job interviews, it may also arise in project pitches, strategy sessions, and stakeholder meetings.
What Kind of Answer is Expected from the Candidate?
The best responses to this question should showcase your sharp insight into the ongoing trends in the logistics sector, coupled with well-reasoned predictions rooted in logic and evidence.
The response should reflect the comprehension of various dimensions - technology, regulation, human resource, environment, and competition.
Remember, there is no "right" answer. The interviewer is not looking for crystal-ball gazing but an analytical and thoughtful answer, fostering animated discussion around the topic.
Possible Answers to Consider
So, how would a sterling response to "Logistics future in 5-10 years" look like? Here's a glimpse:
"In my perspective, the logistics sector in the next 5-10 years bears the possibility of revolutionized by technology. Real-time tracking, autonomous vehicles, drone delivery, and AI-enhanced operational efficiency will gain more ground.
We can anticipate a shift towards an integrated eco-system, leveraging Internet of Things, big data, and blockchain technology. These changes would render the logistics sector more transparent, efficient, and customer-focused. However, these developments will bring their unique challenges such as data security and stringent regulations."
When Considering Your Response
When deliberating your response to "Logistics future in 5-10 years," drive your focus towards current trends and their potential escalation, based on technological advancements, economic landscape, environmental concerns, and changing customer demands.
Position your response aligning with the company's vision, but don't shy away from talking about challenges and the actions needed to counter them.
In conclusion, when confronted with the question, "Logistics future in 5-10 years," it's your opportunity to Marco Polo your way into the future of logistics - navigate with insight, curiosity, and analytical thinking, and you are bound to leave an indelible mark.
Remember, the industry's future is not just about science fiction-style tech but also about people, policies, and practices. Figures and stats might forget, but they'll remember how you made them think - so steer the wheel and ride into the future.
Technology Innovations Impacting Future of Logistics
Predicted Trends in Global Supply Chain Management
Potential Challenges and Solutions in Logistics for the Next Decade
Similar interview questions:
What will the landscape of logistics look like in the next 5-10 years?
How do you envision the future of logistics in the next decade?
What advancements could the logistics industry experience in the next 5-10 years?
Can you predict any major changes in the logistics sector in the forthcoming decade?
How will logistics evolve in the next 5-10 years?
What innovations might take place in the logistics industry in the next 5-10 years?
How may the logistics field change in the course of the next five to ten years?
What transformations do you anticipate in the logistics sector moving forward the next 5-10 years?
What might be different about logistics in 5-10 years as compared to now?
In your opinion, how might the logistics industry reshape itself in the next 5 to 10 years?
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key trends or technologies likely to shape the logistics future in 5-10 years?
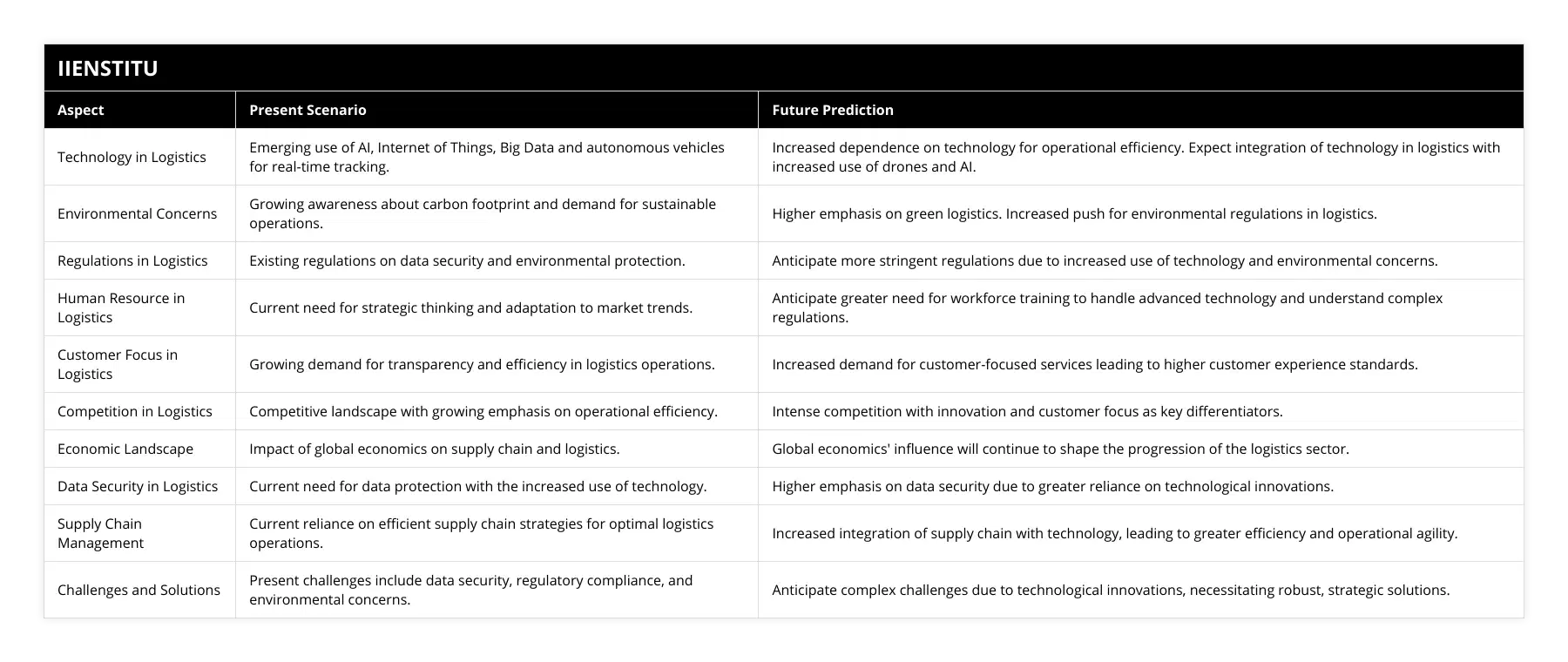
Logistics will transform through several key trends. First, Robotics and Automation will shape the future significantly. There will be extensive use of robots in warehouses for the management of goods. This will reduce human effort, ensure precision, and decrease errors.
Second, the adoption of the ‘Blockchain.’ It will improve transparency and decrease fraud in supply chains. It will enable tracking goods from their points of origin to destinations.
Third trend is Big Data and Predictive Analytics. This technology will allow businesses to predict future outcomes. They can cut costs, improve efficiencies, and drive customer satisfaction.
Fourth, the Internet of Things (IoT). It is a growing technology that uses network sensors to collect data. This enables real-time tracking, monitoring, and optimization of logistics processes.
Fifth, AI and Machine Learning will become increasingly vital. These technologies can optimize routes, reduce fuel costs, and improve delivery times.
Sixth, Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) can also transform logistics. AR can assist in navigation while delivering goods, and VR can be useful in training staff.
Seventh, Green Logistics is another trend. This includes environmentally-friendly and sustainable practices. It is pertinent due to increasing environmental concerns.
Finally, Drone Delivery and Autonomous Vehicles are emerging trends. Drones are useful for prompt delivery in congestive areas. Autonomous vehicles can transport goods without human intervention.
All these trends will make logistics faster, more efficient, and more cost-effective in the next 5-10 years.
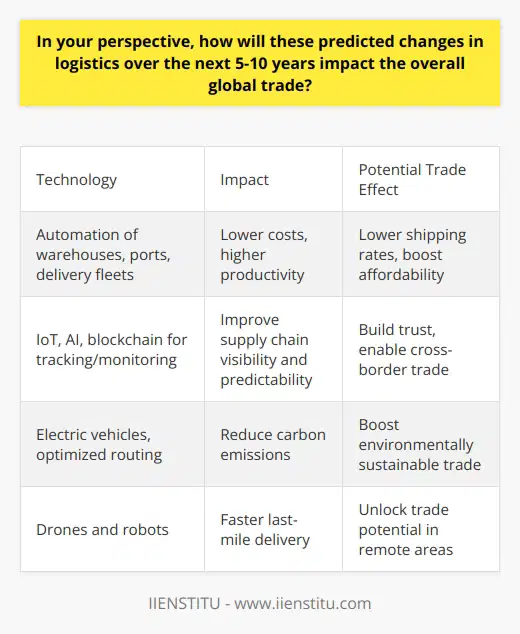
In your perspective, how will these predicted changes in logistics over the next 5-10 years impact the overall global trade?
Advancements in logistics will reshape global trade. The infusion of advanced technologies will make transport more efficient and effective. Increased automation will lower labor costs significantly. This will disrupt traditional pricing structures. Enhanced tracking capabilities will improve reliability. This will foster customer trust, boosting trade volume.
The adoption of green logistics can lower carbon emissions substantially. This has immense potential to promote sustainable trade practices. It can also boost trade in eco-friendly goods. Drones and robots will aid in faster delivery. This can unlock new trade prospects in remote areas.
Blockchain in logistics will enable enhanced transparency. It can curb illegal trade practices improving overall trade health. Greater use of predictive analytics will foster precise strategic planning. This will reduce trade risks and enhance profitability. Hyperlocal delivery can revolutionize local trade dynamics.
3D printing in logistics will redirect trade routes. It can promote localized production mitigating trade barriers. Increased use of artificial intelligence will reshape customer experiences. Personalized experiences can drive customer loyalty, enhancing trade. In essence, these changes may potentially redefine rules of global trade in the foreseeable future.
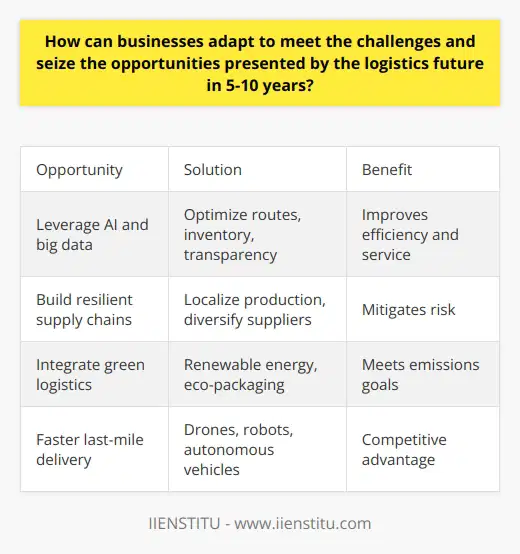
How can businesses adapt to meet the challenges and seize the opportunities presented by the logistics future in 5-10 years?
Businesses must make key adjustments to thrive in an evolving logistics future. Embracing digital tools is the initial step they can take. These tools range from artificial intelligence to blockchain technologies. Their potential to streamline operations is immense.
Companies also need to foster resiliency in their supply chains. Changing market forces necessitate this. Shifting geopolitical landscapes and extreme weather events can disrupt logistics. A resilient supply chain can withstand such challenges.
Integration of green logistics is another essential change. Customers increasingly prefer environmentally-friendly companies. Modern businesses need to meet this demand. Carbon offsetting, using eco-friendly materials, and optimizing delivery routes can contribute to this.
Investing in advanced technologies is crucial too. The growth of e-commerce necessitates rapid and accurate deliveries. Drones and autonomous vehicles can cater to this need. They enhance delivery speed while reducing human error.
Data analytics can transform decision-making in logistics. It provides insights into market trends, customer behaviour, and operational bottlenecks. Companies can leverage this information to optimize their logistics.
A shift towards local sourcing can also benefit businesses. Global supply chains can be unpredictable or disrupted by external factors. Local sourcing reduces such risk and can also enhance brand reputation.
Training and development of employees is essential. Future logistics will have technological nuances. A workforce adept with high-tech tools can give companies a competitive edge.
Lastly, businesses must develop agile business models. Agility allows adapting quickly to changing market dynamics. Incorporating flexibility in logistics operation can offer a strategic advantage.
In conclusion, these measures can aid businesses in navigating the logistics future. Adapting proactively will fuel their competitiveness and growth.