In the ever-evolving landscape of academia, the ability to think creatively has become an indispensable skill. It goes beyond simply acquiring knowledge; it enables individuals to generate novel ideas and solutions. Creative thinking is not an innate talent but a skill that can be cultivated and refined through deliberate practice and techniques. In this blog post, we will explore various creative thinking methodologies and how they can be harnessed to foster innovation in the academic realm.
Introduction to Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is the intersection of imagination and critical analysis. It involves breaking away from conventional thought patterns and embracing original and divergent thinking. It is the ability to generate innovative ideas by combining existing knowledge in unique ways or discovering entirely new solutions to problems. The importance of creative thinking lies in its transformative power, which drives progress across various fields of study and industries.
The Significance of Creative Thinking in Academia
In an academic context, developing creative thinking skills provides a distinct advantage. It allows students and scholars to approach complex problems with fresh perspectives and produce work that is both original and insightful. As a result, there is a growing emphasis on problem-solving training courses and educational resources that enhance these cognitive abilities.
Differentiating Creative Thinking from Critical Thinking
It is crucial to understand the difference between creative thinking and critical thinking. Creative thinking involves divergent thinking, which seeks multiple possible answers. On the other hand, critical thinking employs convergent thinking, aimed at reaching a single, correct solution. The interplay between the two is essential in academic endeavors, where a balance is often needed to produce rigorous yet inventive work.
Overview of Creative Thinking Techniques
There is a wide range of creative thinking techniques, each serving a specific purpose and catering to different contexts. These methodologies act as tools to break down the cognitive barriers that hinder innovative thought, fostering an environment conducive to idea generation and creative exploration.
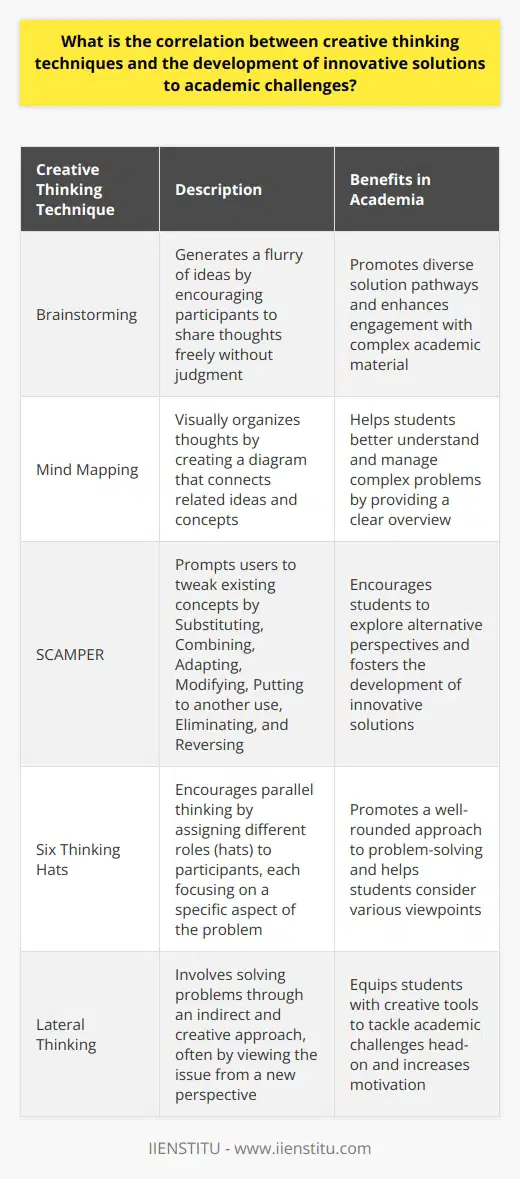
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a widely recognized technique for generating a large number of ideas within a limited timeframe. It encourages free-thinking and minimizes judgment during the initial stages to stimulate creativity within a group setting. Effective brainstorming sessions require a skilled facilitator to guide the process, ensuring the participation of all members and harnessing the collective intellectual capacity of the group.
The Principle of Deferring Judgment
One of the key principles of successful brainstorming is deferring judgment. This principle creates a safe space for the wildest ideas to surface without the fear of immediate dismissal. A real-world application of this can be observed in design think tanks, where brainstorming has led to breakthrough innovations by embracing the unexpected and often unconventional suggestions of team members.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual representation of thought processes. It begins with a central concept, from which related ideas branch out in a non-linear manner. This visual approach breaks free from the constraints of linear thinking and allows for connections between disparate concepts to become more apparent.
Creating a Mind Map
To create a mind map, start by identifying a central theme and then explore associated subtopics, keywords, and ideas, organizing them into interconnected branches. An example of its effectiveness can be seen in project planning within academic research, where mind maps can clarify the scope and interrelation of multiple components of the study.
SCAMPER
The SCAMPER technique provides a structured approach to creative transformation by prompting users to ask questions from different perspectives: Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. This methodological approach to idea evolution can be applied across various scenarios, from product development to curriculum design.
Applying SCAMPER in Education
For instance, an educational institution may apply SCAMPER to reimagine a traditional curriculum. By substituting certain textbooks with interactive media, combining classroom lessons with real-world experiences, or eliminating outdated assessment methods, they can revitalize the learning experience for their students.
Developing a Creative Thinking Mindset
Nurturing a creative mindset is essential to fostering a culture of innovation. It requires creating environments that encourage risk-taking, support diverse thought, and celebrate unconventional solutions. This mindset is particularly crucial in the academic domain, where the freedom to explore and the capacity to think differently often leads to significant breakthroughs and successes.
Value Engineering Guide To Optimize Design And Cost Efficiency
Operational Risk Assessment Guide For Efficient Business Operations
Cultivating an Open Mind
Having an open mind means being receptive to new experiences and alternative perspectives. It expands the horizon for potential creative insights and breakthroughs. Open-mindedness can be fostered by regularly exposing oneself to different disciplines, cultures, and intellectual debates, thus enriching one's cognitive palette.
Reducing Preconceived Notions and Biases
Encouraging open-mindedness often coincides with the reduction of preconceived notions and biases, which can stifle inventiveness. Educational strategies, such as interdisciplinary courses or international exchange programs, can significantly promote this expansive way of thinking.
Embracing Risk and Failure
Embracing risk and learning from failure are integral components of a robust creative mindset. They enable individuals and organizations to step out of their comfort zones and challenge the status quo. This attitude toward risk and failure is not about seeking failure but about understanding that some degree of risk is essential for innovation.
Case Studies of Embracing Risk and Failure
There are numerous case studies illustrating that many successful entities have embraced this ethos. For example, technology companies often celebrate 'failing fast' as a means to quickly iterate and refine groundbreaking products or services.
Practical Exercises for Enhancing Creative Thinking
Just as muscles require regular exercise to grow stronger, the mind also needs consistent practice to improve its ability for creative thinking. There are several exercises that one can engage in to sharpen their creative faculties and enhance their cognitive flexibility.
Solitude and Creative Thinking
Solitude can provide the quiet needed for introspective thought and the fostering of deep concentration, both of which are conducive to creativity. An exercise one might practice is setting aside dedicated time for solitary reflection, free from external distractions, to engage in deep work that could lead to creative insights.
Creative Thinking and Collaboration
While solitude has its place, collaboration can also be a powerful stimulant for creativity. Engaging in group activities, such as collective problem-solving or collaborative storytelling exercises, taps into the collective creativity of the group, enabling a cross-pollination of ideas.
Personal Experience and Insights
As someone who has actively pursued creative thinking in my academic and professional life, I can attest to the transformative power of these techniques. I recall a particular instance during my graduate studies where I was faced with a complex research problem. By employing mind mapping and brainstorming techniques, I was able to break down the problem into manageable components and generate novel solutions that I had not previously considered.
Moreover, I have found that cultivating an open mind and embracing risk have been instrumental in my personal growth and development. Attending interdisciplinary seminars and engaging in intellectual discussions with individuals from diverse backgrounds have expanded my perspective and sparked new ideas. I have also learned to view failure as an opportunity for learning and growth, rather than a setback.
Conclusion
The pursuit of creative thinking is more than an academic exercise; it is an essential skill set for innovation and problem-solving in virtually every field. By understanding and employing the techniques outlined in this blog post, individuals can significantly enhance their ability to think creatively and apply these skills toward academic and professional achievements.
I encourage readers to explore online certificate courses in creative thinking, integrate the recommended exercises into their daily routines, and share their experiences and insights. As we nurture innovation within ourselves and the institutions we are a part of, the horizon of what we can achieve expands boundlessly.
Remember, creative thinking is a journey, not a destination. It requires consistent practice, an open mind, and a willingness to embrace the unknown. By cultivating these qualities and employing the techniques discussed, we can unlock our creative potential and make significant contributions to our fields of study and beyond.
I hope this blog post has provided valuable insights and practical strategies for nurturing creative thinking in the academic realm. I invite you to share your own experiences and thoughts in the comments section below. Let us continue to learn from one another and foster a community of creative thinkers who are passionate about driving innovation and making a positive impact in the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some proven techniques that can help to enhance creative thinking for academic success?
Enhancing Creative Thinking for Academic Success
Creativity stands as a cornerstone in the realm of academics. It fuels innovation, problem-solving, and a deeper understanding of complex concepts. Researchers and educators alike stress the significant role that creativity plays in academic achievement.
Cultivate a Growth Mindset
Developing a growth mindset proves paramount. This mindset supports the notion that abilities can improve through dedication and hard work. It encourages resilience and a willingness to learn from failures. Students with a growth mindset often exhibit greater creative thinking capabilities.
Engage in Diverse Learning Experiences
Exposure to diverse learning experiences also enhances creativity. This includes:
- Interdisciplinary studies
- Cultural exchanges
- Varied problem-solving tasks
These activities broaden perspectives, fostering an environment where creative thought thrives.
Embrace Curiosity and Questioning
Students should embrace curiosity. Asking questions kickstarts the critical thinking process. This nurtures an inquisitive mind, laying the groundwork for innovative ideas.
Allocate Time for Reflection
Reflection time aids in consolidating learning. It allows students to make connections between disparate pieces of information. These connections often spark creative insights.
Pursue Collaborative Projects
Participation in collaborative projects endows students with alternative viewpoints. It instills an appreciation for the creative process as a collective endeavor.
Practice Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation techniques provide clarity of thought. They remove mental clutter, making space for creative ideas. Regular practice fosters a calm, focused mind conducive to creativity.
Take Intellectual Risks
Encouraging students to take intellectual risks can lead to breakthroughs. This involves:
- Exploring unknown topics
- Challenging existing ideas
- Attempting novel approaches
Risks like these push the boundaries of conventional thought.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Physical activity bolsters brain function. It stimulates neuronal growth, enhancing cognitive capabilities, including creativity. Regular exercise can break mental blocks and generate new ideas.
Establish a Structured Routine
Surprisingly, a structured routine can support creative thinking. Deadlines and organized work habits create a sense of urgency. This can prompt innovative solutions to emerge under pressure.
Foster a Positive Learning Environment
A positive learning environment remains crucial. Support from peers and educators encourages creative risk-taking. This positive reinforcement builds a safety net for exploring creative ideas.
Learning from Creativity Pioneers
Studying the lives and works of creativity pioneers can inspire. Insight into their thought processes and habits offers invaluable lessons.
Use Analogies and Metaphors
Analogies and metaphors aid in understanding complex topics. They enable students to visualize concepts and discover novel insights.
Journaling and Free Writing
Journaling and free writing exercises can unblock the flow of ideas. They provide a judgment-free space for exploring thoughts.
Brainstorming Sessions
Structured brainstorming sessions hold the potential to generate diverse ideas. They encourage rapid idea generation without immediate criticism.
Exposure to Art and Nature
Art and nature serve as powerful stimuli for creativity. They evoke emotional responses and create neural connections that can spark original thought.
Each of these techniques requires commitment and persistence. Educators should integrate them into teaching strategies. Students should practice them regularly. Through consistent effort, these proven techniques will progressively enhance creative thinking. This will foster academic success in a multitude of disciplines.

How does innovation play a significant role in fostering academic accomplishment?
Innovation's Impact on Academic Success
In today's dynamic world, innovation remains crucial. It drives progress. Academia is no exception. Innovative teaching tools and methods transform educational landscapes. They create engaging learning environments. They cater to diverse learning profiles.
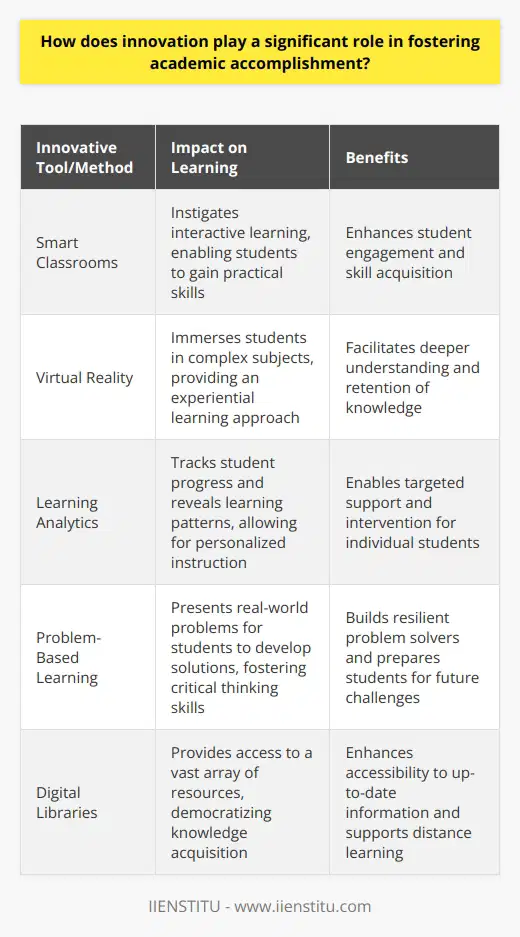
Evolving Educational Technologies
Consider smart classrooms. Such technologies instigate interactive learning. Students gain practical skills. Virtual reality is a prime example. It immerses students in complex subjects. Interactive whiteboards are another. They facilitate collaborative problem-solving.
Tailored Learning Experiences
Innovation begets personalized education. Learning analytics come into play here. They track student progress. They reveal learning patterns. Teachers then tweak instruction methods. Support flows more effectively to where it's needed.
Encouraging Critical Thinking
Innovation often demands critical thinking. Problem-based learning embodies this approach. Students face real-world problems. They develop solutions. Thus, they learn by doing. Such experiences build resilient problem solvers.
Collaborative Opportunities
Innovation fosters collaboration. It breaks down traditional classroom walls. Students interact globally. They engage in cross-cultural projects. They learn from global perspectives. Social media platforms can amplify this. They provide forums for discussion. They encourage knowledge exchange.
Enhanced Accessibility
Digital libraries epitomize increased accessibility. Knowledge becomes more democratic. Students anywhere can access resources. E-books and online journals multiply rapidly. They provide up-to-date information. Distance learning emerges as a significant benefit. It offers flexibility. It supports diverse lifestyles.
Continuous Feedback
Feedback is vital for learning. Innovation streamlines this process. Digital platforms offer real-time feedback. They highlight areas for improvement immediately. This enhances the learning process. It enables timely interventions.
Preparing for the Future
Finally, innovation prepares students for the future. Technological fluency is fundamental. Students must navigate digital tools. They engage with artificial intelligence. Robotics becomes familiar. These skills are crucial. They are relevant to future job markets.
In conclusion, innovation lies at academia's heart. It propels students toward academic accomplishment. It equips them with vital skills. It ensures education keeps pace. The world evolves rapidly. Education must match this pace. Innovation makes this achievable. It shapes future leaders. It sculpts informed citizens. Therefore, embracing innovation transcends mere adaptation. It ensures academic institutions continue to thrive.
What is the correlation between creative thinking techniques and the development of innovative solutions to academic challenges?
Creative Thinking in Academia
Defining Creative Thinking
Creative thinking embodies the ability to forge novel connections. It necessitates openness to unorthodox ideas. Creative thinkers often challenge conventional wisdom. This mindset is not confined to arts or literature. It thrives across all domains, including academia.
Techniques Enhance Innovation
Various techniques stimulate creative thinking. Brainstorming generates a flurry of ideas. Mind mapping visually organizes thoughts. The SCAMPER method prompts users to tweak existing concepts. These tools, among others, prime the brain for innovation.
Application to Academic Challenges
Academic problems often require novel approaches. Creative techniques facilitate these approaches. Educators and students alike benefit from their use. These methodologies promote diverse solution pathways. They enhance engagement with complex academic material.
Results in Academic Settings
Incorporation of these techniques can yield substantial outcomes. They encourage students to explore alternative perspectives. Complex problems often become more manageable. Students equipped with creative tools often exhibit higher motivation. They are better positioned to meet academic challenges head-on.
Case Studies and Research
Empirical studies support the correlation between creativity and innovation. Institutions that champion creative methods report enhanced problem-solving success. Students who embrace these techniques often experience increased academic achievement.
Conclusion
In sum, creative thinking techniques are crucial. They foster the development of innovative solutions. They directly correlate with academic success. Adoption of these practices can transform academic challenges into opportunities.