Human resource management (HRM) recruits, hires and manages employees. HRM includes various activities, from recruitment and selection to employee training and development, to compensation and benefits.
Related Course: Hr Training
The goal of HRM is to help organizations achieve their strategic objectives by attracting, developing, and retaining a high-performing workforce. HR can play a crucial role in achieving organizational success by aligning HRM activities with the organization's business strategy.
The field of HRM is constantly evolving, and the challenges faced by HR professionals are constantly changing. To stay ahead of the curve, it is essential to keep up with the latest trends and developments.
There are many different resources that professionals in the HR field can use to stay informed and up-to-date, including industry publications and professional associations. Additionally, organizations increasingly use social media to share HR news and information. Many firms also offer internal training programs for employees interested in learning more about human resource management.
If you are interested in pursuing a career in HRM, many different Educational options are available, including associate's degrees, bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, and PhDs. There is also a wide range of certifications available to help you specialize in specific aspects of human resource management.
Regardless of what type of position you seek or the level of education you have achieved, working in HRM can be challenging and rewarding. If you are interested in helping organizations achieve their goals by managing and developing their most important asset - their people - then a career in HRM may be the right choice.
HR management and business administration relationship
The field of business administration is a broad one that encompasses many different specialties. Human resource management is just one of the many areas of business administration that can be studied. While human resources management deals specifically with employee recruitment, selection, and training, business administration covers a much more comprehensive range of topics. For example, business administration programs typically include courses in accounting, finance, Marketing, and organizational behavior. As a result, business administration students develop a well-rounded understanding of how businesses operate. In addition, the skills learned in a business administration program can be applied to a wide variety of careers, including human resources management. Consequently, business administration and human resources management are closely related fields with many commonalities.
Strategic human resource management
In business, strategic human resource management is a crucial consideration. This is because HR management plays a vital role in supporting organizational goals and helping to facilitate growth and success. This involves strategic hiring, retention, compensation, training, and development decisions. These areas are intrinsically tied to business administration and require careful strategic planning to be successful.
Companies can foster a strong sense of teamwork and collaboration among employees through effective HR management practices. Furthermore, strategic human resource management helps organizations identify potential talent within their existing workforce, allowing them to invest in their employees' professional development and better prepare for future challenges. Overall, it is clear that there is a strong connection between HR management and business administration, making strategic human resource management an essential consideration for any successful organization.
Definitions
HR department: HR is a team that helps find, train and keep employees. They do this by recruiting new talent for your company or organization's needs and helping existing staff members grow in their careers with feedback from managers about how they can become even better at what they do best!
HR manager: HR managers are tasked with managing staff members' hiring, firing, and promotion. They are responsible for creating an efficient work environment that allows employees to excel in their positions while maximizing productivity within company guidelines set by law or policy.
Human resource executive: A human resources executive is responsible for managing an organization's human resources department. This includes overseeing recruitment, interviewing, hiring employees, administering employee benefits and compensation programs, and ensuring that all HR policies and procedures comply with applicable laws. Some HR executives may also be responsible for developing and implementing employee training programs, conducting exit interviews, and maintaining employee records. The HR executive may report to a senior manager or the CEO in larger organizations.
The importance of human resources management in the modern workplace
An HR manager's role involves:
Recruiting and retaining excellent employees.
Supporting collaboration and managing conflicts.
Even keeping the Leadership in setting business goals.
Related Course: Online Leadership Course
HR Managers provide practical value to organizations through the ability to mentor and coach people. They also offer professional services and manage benefits and ensure a healthy lifestyle. Human resource management means supporting employees through each stage of employment. Tell me about the role of HR Managers?
The role of HR Managers has changed dramatically over the years. In the past, they were often referred to as Personnel managers, and their primary responsibility was to manage the recruitment, selection, and hiring of employees. Today, HR Managers are expected to do much more than that. They are responsible for all aspects of employee management, from recruitment and selection to training and development, to compensation and benefits. Additionally, HR Managers must also align their activities with the organization's business strategy to help achieve organizational goals.
What are some of the challenges faced by HR professionals?
One of the biggest challenges HR professionals faces is staying up-to-date with the latest trends and developments in the field. With the ever-changing workplace landscape, HR professionals must constantly adapt their practices to stay ahead of the curve. Additionally, another challenge faced by HR professionals is managing the increasing amount of available data and information. With the advent of big data, HR professionals must now contend with vast amounts of data when making decisions about employee management.
What are some of the resources that HR professionals can use to stay informed?
There are many different resources that HR professionals can use to stay informed and up-to-date, including industry publications, professional associations, and social media. Additionally, many organizations offer internal training programs for employees interested in learning more about human resource management.
How can someone interested in pursuing a career in HRM get started?
There are many different educational options available for those interested in pursuing a career in human resource management, including associate's degrees, bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, and PhDs. Additionally, there are many certifications available that can help you specialize in specific aspects of human resource management.
Human resource management is a critical function in any organization. It's responsible for ensuring that the organization has the right people with the right skills in the right jobs. Additionally, human resource management is responsible for managing the employee lifecycle, from recruitment and selection to training and development to compensation and benefits. If you're interested in pursuing a career in human resource management, many different educational options are available, including associate's degrees, bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, and PhDs. There is also a wide range of certifications available to help you specialize in specific aspects of human resource management.
Functions of human resource management in an organization
The human resource management approach has developed over time. It emerged in the 20th century due to globalization and advances in technology, as well as increased competitiveness. When HR began to link with business, it focused on the employment and benefits of its personnel. Over time, more enterprises recognized that alignment was required for continued development and efficient operations. HR departments tend to function as an essential component of company growth in modern workplaces. Here are the main HRM activities in an organization:
Employee recruitment and selection
Employee training and development
Employee compensation and benefits
Employee performance management
Organizational development
Talent management
Compliance with labor laws and regulations
Employee retention and engagement
While each of these functions is critical to the success of an organization, many HR professionals also face several challenges in their roles. These may include keeping up with changing trends and technologies, managing large amounts of data and information, and navigating shifting organizational priorities. To stay informed and up-to-date in the field, HR professionals can utilize various resources such as industry publications, professional associations, and social media platforms. Additionally, many companies offer internal training programs for employees interested in learning more about human resource management. If you are interested in pursuing a career in HRM, many different educational options are available at the undergraduate or graduate level. You can also pursue specialized certifications that will help you focus on specific aspects of the field.
Human resource management is a critical function in any organization. Those working in the field play a vital role in ensuring that the organization has the right people with the right skills in the right jobs. Additionally, human resource management is responsible for managing the employee lifecycle, from recruitment and selection to training and development to compensation and benefits. If you're interested in pursuing a career in human resource management, many different educational options are available, including associate's degrees, bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, and PhDs. There is also a wide range of certifications available to help you specialize in specific aspects of human resource management.
What are some common challenges faced by HR professionals?
Challenges faced by HR professionals typically include keeping up with changing trends and technologies, managing large amounts of data and information, and navigating shifting organizational priorities. To stay informed and up-to-date in the field, HR professionals can utilize various resources such as industry publications, professional associations, and social media platforms. Additionally, many companies offer internal training programs for employees interested in learning more about human resource management. If you are interested in pursuing a career in HRM, many different educational options are available at the undergraduate or graduate level. You can also pursue specialized certifications that will help you focus on specific aspects of the field. Some common challenges HR professionals may include recruitment and retention issues due to an increasingly competitive labor market, compliance with evolving laws and regulations, and managing employee data and analytics.
What are some everyday HRM activities in an organization?
Everyday HRM activities in an organization may include:
Employee recruitment and selection.
Employee training and development.
Employee compensation and benefits.
Employee performance management.
Organizational development.
Talent management.
Compliance with labor laws and regulations.
Employee retention and engagement.
While each of these functions is critical to the success of an organization, many HR professionals also face several challenges in their roles.
These may include keeping up with changing trends and technologies, managing large amounts of data and information, and navigating shifting organizational priorities. To stay informed and up-to-date in the field, HR professionals can utilize various resources such as industry publications, professional associations, and social media platforms.
Additionally, many companies offer internal training programs for employees interested in learning more about human resource management. If you are interested in pursuing a career in HRM, many different educational options are available at the undergraduate or graduate level. You can also pursue specialized certifications that will help you focus on specific aspects of the field. Some common challenges HR professionals may include recruitment and retention issues due to an increasingly competitive labor market, compliance with evolving laws and regulations, and managing employee data and analytics.
Ultimately, the success of any HR function depends heavily on effective communication within the organization and strong collaboration with other stakeholders such as senior leaders, managers, and individual employees. Additionally, to be successful in this field, it is essential to have a solid understanding of HR best practices and the ability to adapt to the ever-changing needs of an organization.
Tell me about the role of human resources?
Human resources, or HR, is a multifaceted field that plays an integral role in supporting the success of organizations through strategic planning, talent management, and employee development. At the core of this role is the need to effectively manage people and relationships within the organization by ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations, onboarding new employees, providing training and coaching opportunities, and resolving issues related to recruitment and retention. Other key responsibilities may include:
Designing organizational structures.
Setting performance goals for individuals and teams.
Developing compensation strategies.
Analyzing workforce data to identify trends and patterns.
Managing employee relations issues such as conflict or harassment claims.
To be successful in human resources, it is essential to have strong interpersonal skills and a solid understanding of industry best practices. Additionally, HR professionals must be able to adapt to the ever-changing needs of an organization and its workforce.
Definition & examples of Human Resource Management?
Human Resource Management is the organizational function whose tasks involve managing the people of an enterprise. This includes compensation, hiring, recruitment, performance management, organization development, security, wellness benefits, employee motivation, communication, policies, administration, and training & support. First, tell me the basics about implementing human resource management. Human Resource Management (HRM) is managing people within an organization. It includes a wide range of activities, such as recruiting and selecting employees, providing training and development opportunities, managing employee benefits and compensation, and handling employee relations issues. HRM is a critical function in any organization as it plays a vital role in supporting the business's success.
Some everyday HRM activities in an organization may include employee recruitment and selection, employee training and development, employee compensation and benefits, employee performance management, organizational development, talent management, compliance with labor laws and regulations, and employee retention and engagement. While each of these functions is critical to the success of an organization, many HR professionals also face several challenges in their roles. These may include managing a diverse workforce, dealing with employee relations issues, and complying with evolving laws and regulations. Additionally, HR professionals must adapt to the ever-changing needs of an organization to be successful in their roles.
The seven HR essential functions
The Human Resources Management field focuses on a wide range of areas that require an effective HRM policy. It'd help if you're interested and have a good idea of handling a stumbling block. are:
Recruiting and selecting employees
This involves sourcing and identifying new candidates for available job openings, evaluating applicants based on selection criteria, and making hiring decisions.
Training and development
This typically involves assessing the training needs of an organization, designing appropriate training programs to address those needs, delivering or facilitating those programs, evaluating their effectiveness, and making adjustments as necessary.
Performance management
This involves setting performance goals for individuals and teams, monitoring employee performance against these goals, identifying areas of improvement or areas requiring additional support, providing feedback and coaching opportunities as needed, and developing incentive/reward systems when appropriate.
Compensation and benefits
This includes developing compensation packages that align with organizational objectives while also being competitive in the marketplace, administering employee benefits programs, and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Employee relations
This encompasses various activities, such as managing conflict resolution, handling employee discipline issues, investigating harassment claims, and developing policies and procedures to ensure a positive and productive work environment.
Organizational development
This refers to assessing an organization's current state, identifying areas in need of improvement or change, developing plans to address those needs, and implementing those plans to achieve the desired results.
Talent management
This encompasses all activities related to attracting, retaining, and developing top talent within an organization. These may include recruiting high-potential employees, providing development opportunities, succession planning, and more.
While each of these human resource management functions is important in its own right, they must also be integrated to be genuinely effective. A well-run organization will have a human resource management plan that outlines the specific roles and responsibilities of the HR team, as well as the strategies and tactics that will be used to support the overall business goals. Additionally, the HR team should always be working closely with other departments to ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards common objectives.
When done correctly, human resource management can be a significant driver of business success. By attracting, developing, and retaining top talent, optimizing organizational performance, and complying with relevant laws and regulations, HR teams can help to ensure the long-term Sustainability and growth of their organizations. Thus, if you are interested in pursuing a career in human resource management, it is essential that you have a solid understanding of these core competencies and are equipped with the skills needed to navigate the various complexities of this field.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the meaning of Human Resource Management?
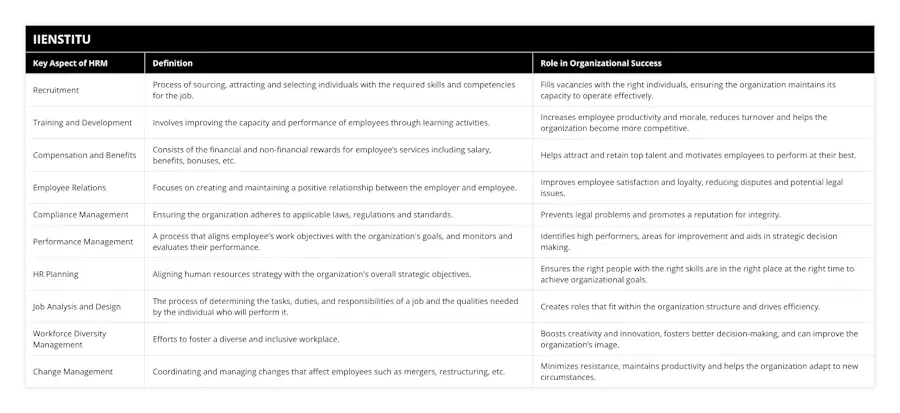
Understanding Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a multifaceted approach to managing the people within an organization. It encompasses various aspects that are crucial to the success and sustainability of a business, including recruitment, development, and retention of talent.
Key Objectives
The primary goal of HRM is to facilitate the efficient utilization of human resources to achieve organizational objectives. In this context, HRM involves planning, organizing, directing, and controlling human resources to support the organization's strategic goals.
Recruitment and Selection
Integral to HRM is the process of recruitment and selection, which ensures that organizations hire suitable individuals with the necessary skills and qualifications. This function involves advertising job opportunities, screening candidates, conducting interviews, and making final hiring decisions.
Training and Development
HRM also focuses on the training and development of employees, with the aim of enhancing their knowledge, skills, and abilities. This process enables employees to perform at their best and contributes to the overall success of the organization. Training and development programs may include job-specific training, skill development workshops, or leadership and management courses.
Performance Management
Another crucial aspect of HRM is performance management, which involves setting performance expectations, evaluating employee performance, and providing feedback to motivate and improve performance. Ensuring that employees are assessed fairly and systematically helps organizations identify high-performers who can potentially advance into leadership positions in the future.
Employee Relations
HRM also addresses employee relations, fostering a positive work environment through effective communication, conflict resolution, and employee engagement strategies. HRM practitioners strive to establish a company culture that nurtures trust, collaboration, and teamwork, promoting employee satisfaction and organizational loyalty.
Compensation and Benefits
Moreover, HRM is responsible for developing competitive compensation and benefits packages that attract, retain, and motivate a talented workforce. This function involves determining salary structures, benefits offerings, and incentive programs based on industry benchmarks, organizational objectives, and budget constraints.
Legal Compliance
Lastly, HRM ensures that organizations comply with relevant laws and regulations governing employment, labor relations, and workplace safety. Failure to adhere to these laws can result in substantial financial penalties, reputational damage, and employee dissatisfaction.
In conclusion, Human Resource Management is an essential function that focuses on the recruitment, development, and retention of a talented workforce necessary for organizations' success. As such, HRM contributes to a company's competitive advantage by optimizing the utilization of human resources and fostering a positive work environment.
What is the role of HR in an organization?
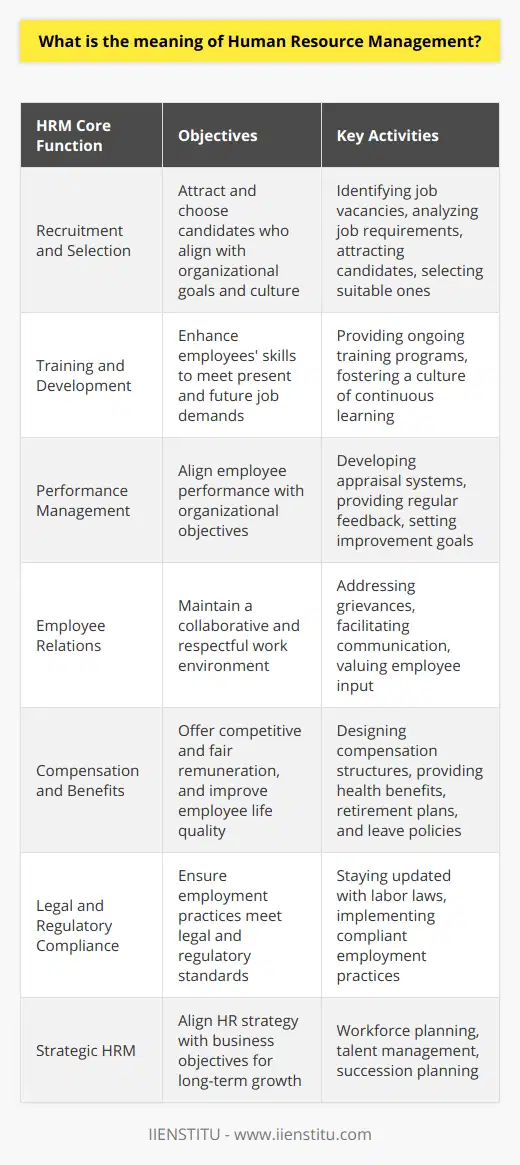
Role of HR in Recruitment and Selection Process
Human resource departments play a crucial role in the recruitment and selection of employees within an organization. HR is responsible for advertising job openings, shortlisting and interviewing potential candidates, and making offers to the top contenders based on qualifications, experience, and suitability for the role. The process is vital to ensuring that organizations have the right talent and skills needed for optimal performance and future growth.
Employee Training and Development
Another critical function of HR is employee training and development. HR professionals identify gaps in employees' knowledge and skills, and then design and implement training programs to fill these gaps. This development process ensures that employees are equipped with the necessary tools to perform their roles effectively and efficiently. Moreover, HR plays a role in creating career advancement opportunities to retain and motivate the workforce.
Performance Management and Appraisal
Human resource departments also focus on employee performance management and appraisal. HR teams actively monitor and evaluate employees' performance, thereby setting measurable objectives and key performance indicators. This system enables organizations to identify high-potential employees, provide adequate feedback to improve productivity, and make informed decisions about promotions or terminations, ensuring that only the best constitute the workforce.
Employee Relations and Conflict Resolution
Promoting a positive working environment is crucial for employee satisfaction and retention. HR professionals strive to create an inclusive workplace culture that fosters collaboration, communication, and respect among employees. They also act as mediators in conflicts or disagreements between employees and management, ensuring that both parties reach a fair resolution. This function helps to maintain a harmonious work environment, leading to increased employee satisfaction and performance.
Legal Compliance and Risk Management
Organizations must comply with various labor laws and regulations to avoid legal issues and financial penalties. HR professionals ensure that the organization's policies and practices adhere to relevant employment and labor laws, such as anti-discrimination legislation, minimum wage requirements, and occupational health and safety standards. This risk management function safeguards the organization by reducing the chances of penalties and potential damage to its reputation.
Employee Compensation and Benefits
Last but not least, HR plays a central role in designing and implementing competitive compensation and benefits packages to attract, retain, and reward top talent. These packages may include salary, bonuses, health insurance, retirement plans, and other non-monetary benefits tailored to employees' needs and preferences. HR teams consistently research market trends and benchmark company compensation to ensure parity and fairness among employees, thus maintaining the organization's reputation as an attractive employer.
In conclusion, the human resource department is fundamental to an organization's overall success. They oversee key aspects such as recruitment, employee development, performance management, conflict resolution, legal compliance, and compensation. By fostering a positive working environment, ensuring legal compliance, and attracting and retaining top talent, HR professionals ultimately contribute to the organization's growth and profitability.
What is HR in simple terms?
Understanding Human Resources
In simple terms, HR, or Human Resources, refers to the management of an organization's most important asset: its people. In essence, it involves the recruitment, training, development, compensation, and motivation of employees to effectively drive the success of the organization.
Functions of Human Resources
The primary functions of HR can be broadly categorized into four areas: talent acquisition, employee relations, performance management, and compensation and benefits.
Talent Acquisition
This involves the process of recruiting, selecting, and onboarding new hires that possess the necessary skills and aptitude to drive an organization's goals. HR professionals play a pivotal role in creating job descriptions, attracting candidates, and conducting interviews to ensure the best fit.
Employee Relations
One of HR's key responsibilities is facilitating strong and productive relationships between employees and management. This includes designing policies and procedures to ensure fair treatment, addressing grievances, managing disciplinary actions, and fostering a positive organizational culture.
Performance Management
HR monitors and evaluates employee performance to identify gaps, develop relevant training programs, and provide resources for improvement. By setting performance goals and providing feedback, HR helps employees grow professionally and make valuable contributions to the organization.
Compensation and Benefits
To attract and retain top talent, HR develops competitive compensation packages and benefits programs. They analyze market trends, determine job value, and design appealing programs that include elements such as salary, bonuses, vacation time, insurance, and retirement plans.
In conclusion, HR is a multifaceted discipline focused on managing an organization's human capital. Through effective talent acquisition, employee relations, performance management, and compensation and benefits, HR professionals contribute to the overall success of the organization by supporting and developing its most valuable resource – its people.
What does HR actually do?
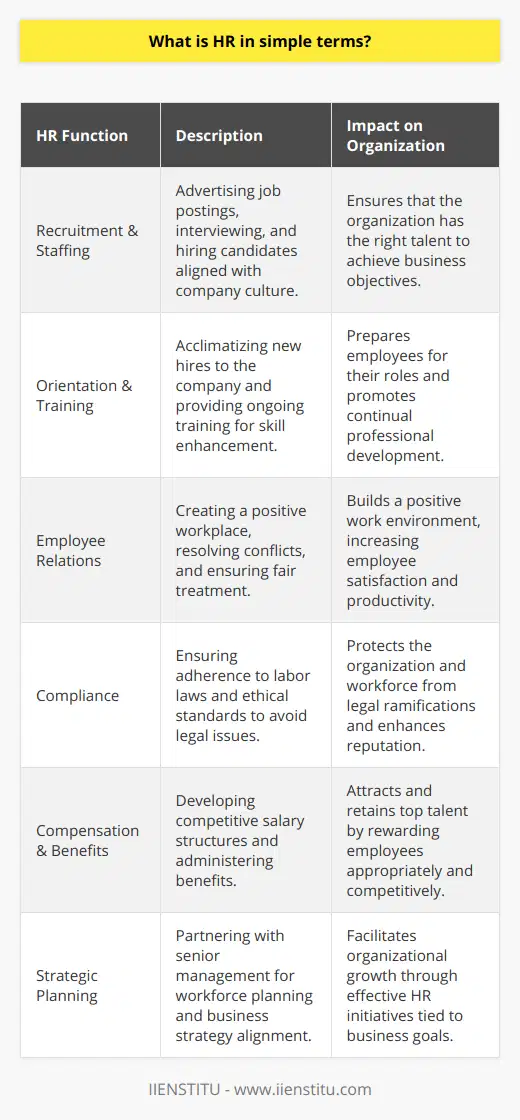
Functions of Human Resources
In the contemporary business world, Human Resources (HR) plays a crucial role in an organization's overall success. The primary function of HR lies in managing an organization's most valuable asset - its employees. This revolves around four key responsibilities: recruitment, employee retention and development, administrative tasks, and maintaining legal and regulatory compliance.
Recruitment and Selection
The HR department is responsible for finding and attracting talented individuals to join the organization, which includes advertising job vacancies, reviewing applications, conducting interviews, and ultimately selecting the most qualified candidates for the respective roles. This process ensures that the organization is staffed with competent employees, contributing to a thriving and sustainable competitive advantage.
Employee Retention and Development
Another essential HR function is to create a supportive working environment that ensures employee satisfaction and fosters professional growth. HR professionals are responsible for implementing employee engagement initiatives, providing resources for professional development, and enabling a healthy work-life balance. Additionally, they manage performance appraisals, promotions, and compensation adjustments that reward and recognize employee contributions to the organization.
Administrative Tasks
HR professionals are also responsible for completing various administrative tasks, such as maintaining personnel files, coordinating employee benefits, and administering payroll processing. These tasks ensure the smooth functioning of the organization and contribute to the overall employee experience. Moreover, HR professionals manage communication between employees and the administration, addressing employee concerns, and facilitating conflict resolution when necessary.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Lastly, HR plays a pivotal role in maintaining legal and regulatory compliance within the organization. HR professionals must continually stay up-to-date on employment laws and regulations, ensuring that organizational practices and policies comply with these legal requirements. This helps to protect the organization from any potential liabilities and maintain its reputation as an ethical and law-abiding corporate entity.
In summary, the HR department contributes significantly to an organization's success by diligently managing its workforce. Through their expertise in recruitment, employee retention and development, administrative tasks, and maintaining legal and regulatory compliance, HR professionals help create an engaged, competent, and satisfied workforce that drives organizational growth and sustainability.
What is the role of a human resource manager?
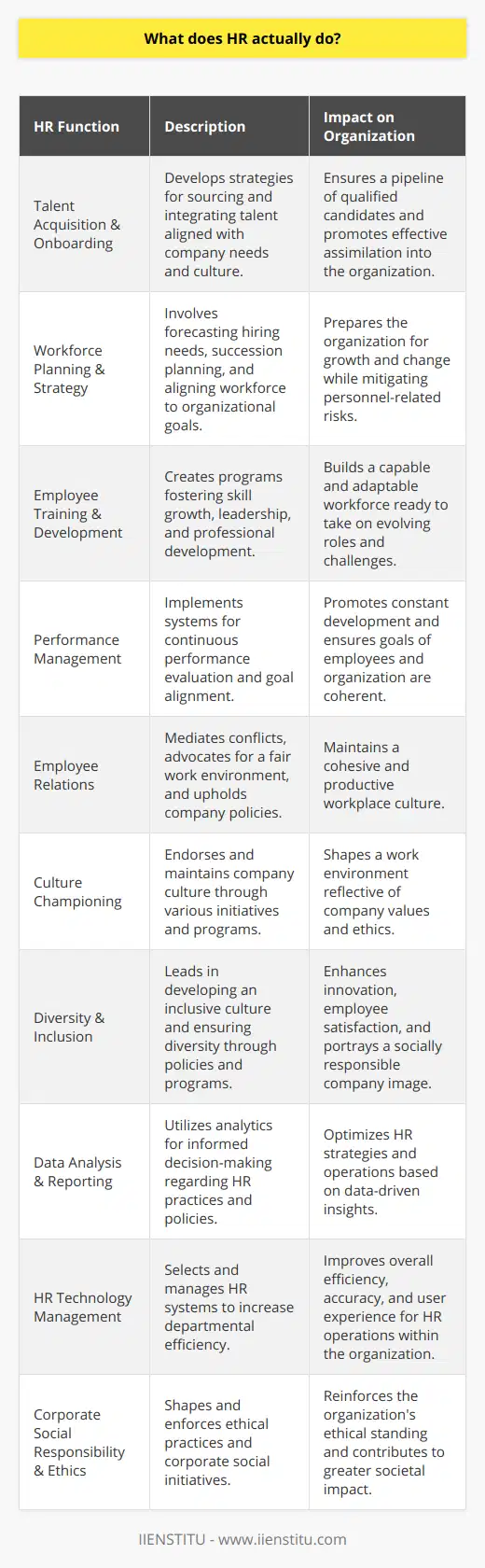
Role of a Human Resource Manager
Recruitment and Selection
Human resource managers play a crucial role in the recruitment and selection of employees for an organization. They are responsible for identifying potential candidates, conducting interviews, and making hiring decisions based on the company's needs and organizational fit. By ensuring that the organization hires the best talent, human resource managers contribute to the overall success and growth of the company.
Training and Development
Another key responsibility of a human resource manager is overseeing the training and development of employees. They identify the skills gaps within the organization and develop appropriate training programs to address them. This enables employees to improve their skills, which in turn leads to increased productivity and a higher level of job satisfaction. Human resource managers also work on succession planning to ensure that the organization is prepared for future leadership changes.
Employee Relations
Maintaining positive employee relations is critical for any organization, as it directly affects employee morale and job satisfaction. Human resource managers are in charge of addressing employee concerns and resolving any disputes that may arise. This includes conducting performance evaluations, addressing disciplinary issues, and managing workplace policies to ensure that they are in line with the organization's values and objectives.
Legal Compliance
Human resource managers are responsible for ensuring that the organization complies with all relevant labor laws and regulations. This encompasses a wide range of issues such as employee benefits, health and safety regulations, and equal employment opportunity laws. By staying up-to-date on changes in legislation and ensuring that their organization is compliant, human resource managers help to minimize potential legal liabilities and maintain a positive workplace environment.
Conclusion
In sum, the role of a human resource manager is critical for the success of any organization. They help with the recruitment and selection of employees, oversee their training and development, manage employee relations, and ensure legal compliance. By effectively executing these responsibilities, human resource managers contribute to the growth and prosperity of their organization, ultimately leading to a more satisfied and productive workforce.
How does human resource management contribute to an organization's success?
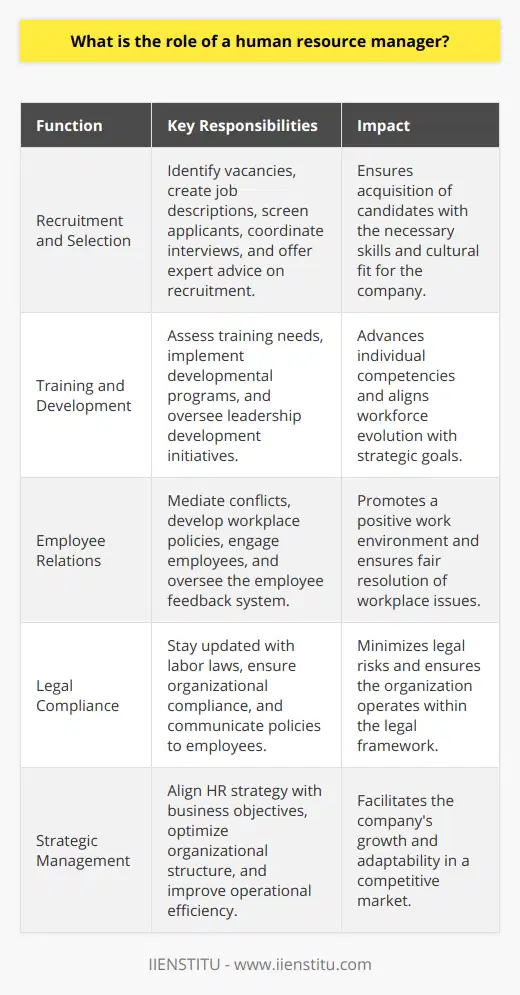
**Role in Achieving Organizational Goals**
Human resource management (HRM) plays a crucial role in an organization's success by aligning individual and group efforts with organizational goals. Effective HRM practices lead to higher employee engagement, resulting in improved productivity, innovation, and ultimately, better business performance.
**Staff Recruitment and Retention**
Recruiting the right talent is essential for organizational success. HRM professionals focus on attracting qualified candidates and selecting the best fit for the company. By implementing rigorous recruitment and selection processes, HRM helps organizations build a skilled and competent workforce. In addition, strategic retention initiatives reduce employee turnover, preserving valuable organizational knowledge and increasing workforce stability.
**Training and Development**
Employee training and development foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement within an organization. HRM designs and implements various employee development programs, enhancing overall workforce competence and empowering individuals to excel in their roles. As employees grow and adapt to new technologies, changing market dynamics, and shifting customer expectations, organizations benefit from increased efficiency and competitiveness.
**Performance Management**
Effective performance management systems enable HRM to assess employee performance, identify gaps, and provide feedback to support continuous improvement. By setting clear performance expectations and ensuring regular monitoring, organizations can maintain a high-performance culture, driving individual and collective success. HRM also helps design and administer reward and recognition programs, motivating employees to achieve their fullest potential.
**Maintaining a Positive Work Environment**
A positive work environment is crucial to employee satisfaction and productivity. HRM contributes to fostering a culture of trust, collaboration, and open communication by developing and enforcing policies related to workplace ethics, diversity, and inclusion. Ensuring employee well-being through measures like flexible working conditions, stress management initiatives, and health and safety guidelines further contributes to organizational success.
**Strategic HR Planning**
HRM plays a pivotal role in aligning human resource strategies with the overall business strategy. Through strategic HR planning, organizations identify current and projected workforce gaps, devise initiatives to attract and retain the required talent, and ensure continuous growth and development. This proactive approach supports the organization's long-term objectives and helps adapt to fluctuating market conditions.
In summary, human resource management significantly contributes to an organization's success by effectively recruiting, developing, and managing talent. HRM's focus on creating a positive work environment, fostering employee engagement, and aligning HR strategies with business objectives ensures that the company remains competitive, efficient, and agile in an ever-changing market landscape.
What are the core functions of human resource management?
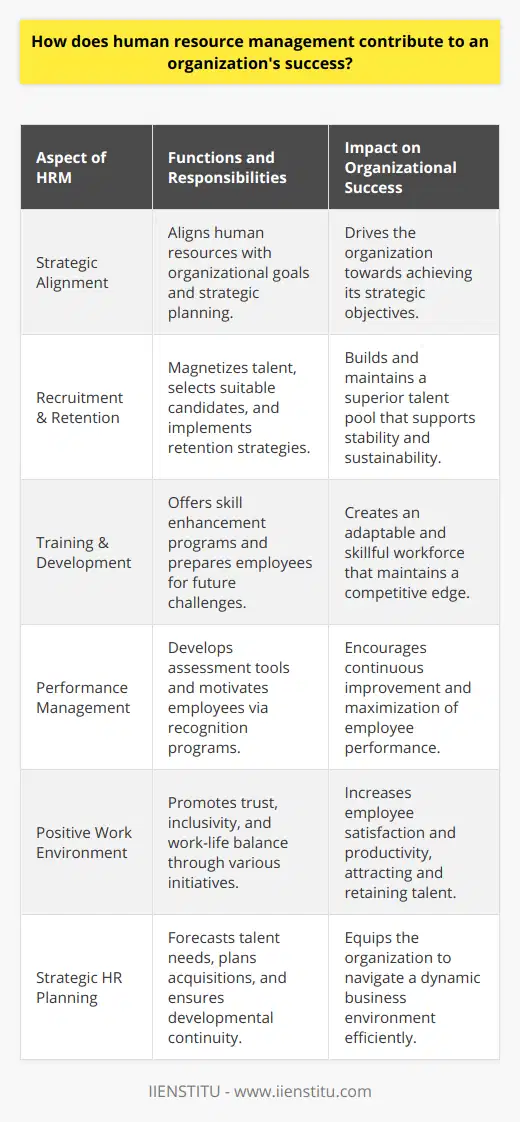
Core Functions of human resource management
Staffing and Recruitment
A primary responsibility of human resource management (HRM) is to ensure the organization has a skilled and qualified workforce. HRM accomplishes this through the processes of recruitment and selection, ensuring that the right candidates are well-matched to the job requirements and organizational culture.
Training and Development
Effective HRM actively develops the potential of employees. This process includes assessing employees' skills and identifying their strengths and areas requiring improvement. HRM creates and implements training programs that enhance employee performance, improve their skillset and support career development.
Performance Management
HRM is responsible for evaluating and monitoring employee performance. This process may involve setting performance goals, conducting periodic performance appraisals, and providing regular feedback. This supports both employee growth and overall organizational success by enabling the identification of high-performing employees and addressing performance-related challenges proactively.
Compensation and Benefits
Fair and competitive compensation is a necessary component of HRM. It involves designing and administering employee pay structures, including salaries, wages, incentives, and bonuses. Moreover, HRM is responsible for providing employee benefits, such as insurance, retirement plans, and vacation time, that contribute to job satisfaction and employee retention.
Employee Relations
To foster a positive working environment, HRM is tasked with managing employee relations. This function includes conflict resolution, enforcing company policies, and addressing employee concerns or grievances. HRM also supports and encourages open communication between employees and their supervisors, ensuring that all parties feel heard and respected.
Legal Compliance
HRM must ensure that the organization complies with all relevant employment laws and regulations. This responsibility entails staying informed about current legislation, developing policies and practices accordingly, and advising managers and employees on legal matters. Legal compliance helps avoid costly fines, litigation, and damage to the organization's reputation.
In conclusion, human resource management plays a vital role in the success of an organization through the recruitment and selection of skilled employees, ongoing development and training, performance management, and the administration of fair compensation and benefits. Furthermore, effective HRM fosters positive employee relations, promoting a healthy work environment, and ensuring legal compliance for the organization.
How does HR support the strategic goals of an organization?
HR Alignment with Organizational Strategy
Human resource (HR) departments play an essential role in supporting the strategic goals of an organization by ensuring the right talent is in place and fostering a supportive work environment. One way HR achieves this is through the recruitment and selection process, targeting individuals with appropriate skills, experiences, and cultural fit to contribute to the organization's objectives. This enables the company to build a capable workforce that can drive growth, innovation, and performance.
Talent Development and Retention
Another critical responsibility of HR is talent development and retention, nurturing employee growth to meet the evolving needs of the organization. By focusing on employee development programs and performance management systems, HR helps personnel grow professionally and align their objectives with organizational goals. This commitment to growth not only builds a more skilled workforce but also enhances employee satisfaction and retention, ensuring continuity of operations and preservation of organizational knowledge.
Workplace Culture and Employee Engagement
Moreover, HR supports strategic goals by fostering a positive workplace culture and driving employee engagement. Through the development of policies and procedures that promote diversity, inclusion, and work-life balance, human resources helps to create a supportive environment that encourages employee commitment and productivity. Additionally, HR professionals facilitate employee communication, mediate conflicts, and maintain feedback channels, which are essential for ensuring employees remain informed, motivated, and focused on the organization's objectives.
Legal Compliance and Risk Management
Finally, HR contributes to organizational strategy by managing legal compliance and risk management. As the landscape of labor regulations evolves, human resources must protect the organization from potential legal and financial issues by ensuring adherence to relevant laws and regulations. This includes matters such as managing health and safety policies, monitoring employee benefits, and overseeing contract negotiations. By proactively addressing potential risks, the HR department safeguards the organization's reputation and fosters stability, ensuring its long-term viability to pursuing strategic goals.
In conclusion, the HR department is crucial in supporting an organization's strategic goals by attracting and retaining key talent, nurturing employee development, fostering a positive workplace culture, and managing legal compliance and risk. By aligning HR initiatives with the organization's objectives, the department serves as a cornerstone for the company's success, enabling it to achieve sustainable growth and competitive advantage.

What are the ethical considerations and responsibilities in HR management?
Ethical Considerations in HR Management
One critical aspect in human resource (HR) management is the ethical considerations surrounding the practices and policies. These considerations ensure that employees are treated fairly, with dignity, and that their rights are protected. For HR professionals, understanding and adhering to these ethical principles and responsibilities is the key to promoting a positive work culture and ultimately enhancing organizational effectiveness.
Employee Privacy and Confidentiality
HR managers are responsible for maintaining employee privacy by ensuring the protection of their personal information. This includes keeping sensitive data confidential and secure, as well as limiting access only to authorized personnel. HR managers should also be transparent about the purpose for collecting and storing employee information and fully respect individuals' privacy rights.
Fair Employment Practices
Ensuring a fair and equal recruitment process is another ethical responsibility for HR management. Discrimination prevention in hiring, promotions, compensation, and employee development presents an essential value that shapes a company’s corporate citizenship. HR managers should develop recruitment strategies and criteria that promote equal opportunity employment and ensure policies and procedures are in place to prevent bias and discrimination.
Employee Relations and Communication
Promoting open communication between employees and management is crucial in establishing trust and transparency. HR professionals should encourage feedback and foster an environment conducive to addressing grievances while adhering to company policies and legal requirements. This ongoing interaction will enhance employees' job satisfaction and organizational commitment while allowing for continuous improvement.
Promoting a Safe and Healthy Work Environment
HR managers must ensure the implementation of health and safety policies to protect employees from hazards and ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations. Developing safety programs, offering training sessions, and cultivating a safety-first culture helps maintain a productive work environment while minimizing risk and liability for the organization.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Organizations need to consider the ethical implications of their business practices and make a positive impact on their employees, clients, and the local community. HR management plays a vital role in integrating corporate social responsibility (CSR) into organizational culture and practices, fostering a commitment to ethical values both internally and externally.
Ensuring Compliance with Laws and Regulations
Adherence to relevant employment laws and regulations is an ethical responsibility for HR managers. Ensuring compliance with applicable legislation not only avoids legal issues but also demonstrates the organization's commitment to fair and ethical treatment of their employees.
In conclusion, ethical considerations in HR management encompass a wide range of responsibilities that contribute to building a positive work culture and maintaining the organization's reputation. Upholding these ethical principles encourages trust, loyalty, and commitment among employees, ultimately leading to improved organizational effectiveness.
What is Human Resource Management in simple terms?
Defining Human Resource Management
In simple terms, Human Resource Management (HRM) refers to the comprehensive process of managing people within an organization. It ultimately aims to optimize the performance and productivity of employees by implementing various strategies, policies, and practices. HRM is a multidimensional function that encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, including recruitment, training, and development, as well as ensuring a safe and positive work environment.
Main Components of HRM
Recruitment and Hiring
One of the primary responsibilities of Human Resource Management is to attract and select the most qualified candidates for job positions within the organization. This involves the identification of job requirements, advertising vacancies, screening applicants, conducting interviews, and making appropriate employment offers.
Training and Development
HRM also focuses on training and development, which is essential for providing employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their roles effectively. This process includes designing and implementing training programs, evaluating performance, and providing feedback to employees. Furthermore, HRM facilitates continuous professional development through organizing seminars, workshops, and other learning opportunities.
Performance Management
Another critical aspect of HRM is monitoring and evaluating employee performance. HR professionals establish performance standards and goals aligned to the organization's objectives, conduct periodic performance reviews, and provide feedback to employees. By doing so, HRM helps to maximize productivity, identify areas for improvement, and reward excellent performance.
Compensation and Benefits
In order to attract and retain a talented workforce, HRM is responsible for devising and implementing competitive compensation and benefits packages. This process involves the development of salary structures, administering employee benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, and establishing policies around promotions, bonuses, and other incentives.
Employee Relations and Conflict Resolution
HRM plays an essential role in maintaining positive employee relations and fostering a harmonious work environment. This includes addressing and resolving workplace conflicts, mediating disputes or grievances, and managing issues related to disciplinary action or performance. Moreover, HRM ensures adherence to relevant labor laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
Health, Safety, and Well-being
Prioritizing employee health, safety, and well-being is a fundamental aspect of HRM. To achieve this, HR professionals develop and enforce policies and procedures concerning workplace safety, ergonomics, and occupational health. They also promote mental health and well-being initiatives, such as employee assistance programs and stress management resources.
In conclusion, Human Resource Management is an essential organizational function that strives to manage and develop a high-performing, motivated workforce to achieve the organization's strategic goals. Through various components, HRM addresses all aspects of the employee life cycle, from recruitment to career growth, ensuring efficient and effective management of human resources.
What is HR and its purpose?
Human Resource Management: Overview
Human Resource (HR) refers to the strategic and coherent approach to managing an organization's most valuable asset: its employees. The main purpose of HR is to maximize employee performance and productivity in order to achieve the goals and objectives of the organization.
Roles and Functions
HR involves several key roles and functions, such as recruitment, employee development, performance management, and compensation. By handling these tasks effectively, HR professionals contribute to the overall success of the organization and ensure that the employees are engaged and motivated to perform at their best.
Recruitment and Selection
The process of finding and hiring the right people for the organization is one of the most critical tasks of HR professionals. This includes understanding the job requirements, attracting suitable candidates, evaluating their qualifications, and making a final selection to ensure a good fit with the company's culture and objectives.
Training and Development
Once employees are hired, it is essential to provide them with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their roles effectively. Through various training and development programs, HR professionals support employees in their continuous growth and encourage them to improve their performance constantly.
Performance Management
HR also focuses on monitoring and managing employee performance. This involves setting clear goals and expectations, providing regular feedback, and conducting performance appraisals. Through these processes, HR professionals foster a culture of high-performance in the organization.
Compensation and Benefits
To attract and retain the best talent, HR is responsible for designing and administering competitive compensation and benefits packages. These include salaries, bonuses, health insurance, and other perks, ensuring fair and equitable treatment of employees according to their performance and contribution to the organization.
Employee Relations
HR plays a crucial role in navigating and resolving issues related to the workplace environment, employee relations, and organizational policies. They act as mediators between employees and management, addressing grievances, and promoting a positive and inclusive work culture.
Compliance with Laws and Regulations
Finally, HR professionals must ensure that the organization complies with all relevant labor laws and regulations, including occupational health and safety standards, equal employment opportunity, and anti-discrimination policies. By doing so, they help prevent potential legal problems and maintain a positive reputation for the organization.
In conclusion, HR is a vital function in any organization, as it helps to manage and develop the workforce effectively, ensuring optimal performance and alignment with the company's goals.
How do HR policies and practices align with an organization's overall mission and objectives?
Alignment of HR Policies and Practices
Organizational Mission and Objectives
HR policies and practices play a vital role in aligning with an organization's overall mission and objectives. Through the establishment of clear guidelines and expectations, these policies ensure that employees understand and work towards achieving the organizational goals. This alignment leads to a cohesive and productive work environment conducive to success.
Role of HR in Strategy Development
HR professionals are involved in the development of an organization's strategic plan, working closely with top management to identify key organizational objectives. Their role includes translating these objectives into actionable HR policies and practices that support the overall mission. By ensuring a strong connection between HR strategies and organizational aims, HR professionals contribute to creating a competitive advantage for their organization.
Employee Training and Development
One critical aspect of aligning HR policies and practices with organizational objectives is employee training and development. By offering training programs that enhance employees' skills and competencies, HR helps build a talented and knowledgeable workforce. This workforce is crucial for achieving organizational goals and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Performance Management and Evaluation
Employing effective performance management and evaluation systems is another way through which HR policies align with organizational objectives. By setting clear performance expectations, HR ensures that employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities in achieving organizational goals. Moreover, performance evaluations provide valuable feedback and enable HR to make informed decisions regarding employee development, promotions, or disciplinary actions.
Culture and Employee Engagement
A strong organizational culture is key to achieving strategic objectives. Therefore, HR policies and practices must promote a culture that aligns with the organization's mission and values. Fostering a positive work environment, encouraging open communication, and recognizing employee achievements can boost employee engagement, leading to increased commitment and better performance.
Inclusion and Diversity
A diverse and inclusive workforce is an essential component of an organization's success. HR policies that promote diversity and inclusion support the organizational mission by attracting and retaining top talent with various perspectives and experiences. This diversity drives innovation and helps organizations stay competitive in today's global market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HR policies and practices play a significant role in aligning with an organization's overall mission and objectives. These policies contribute to the development of a skilled workforce, effective performance management, a strong organizational culture, and a diverse and inclusive work environment. By ensuring that HR strategies support and enhance the organization's goals, HR professionals can drive organizational success and competitiveness on a global scale.
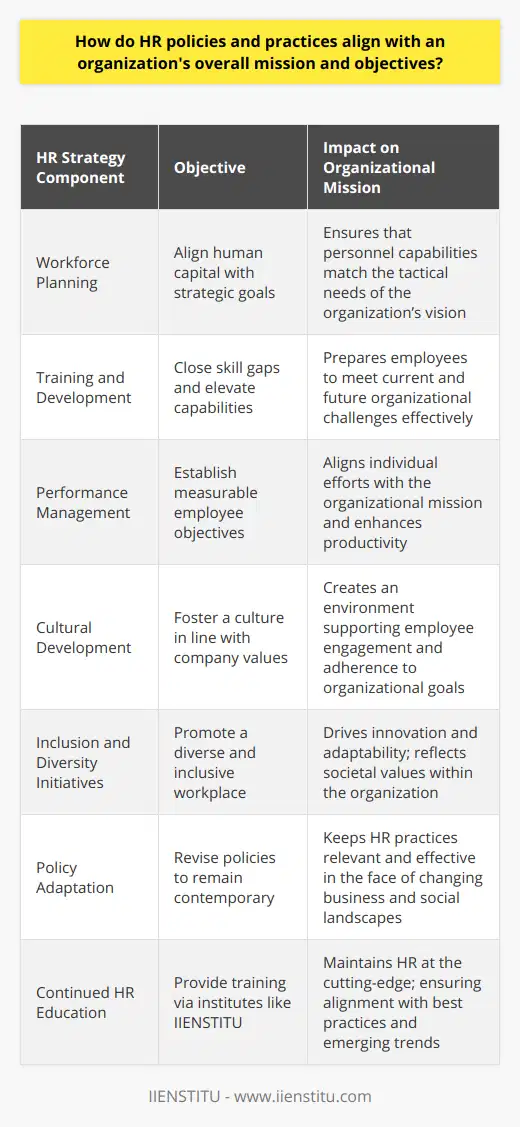
What is Human Resource Management in simple terms?
Understanding Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) can be understood as the strategic and coherent approach to managing an organization's most valuable assets: its people. In simple terms, HRM refers to the activities and practices involved in acquiring, developing, motivating, and retaining employees. This encompasses a range of functions such as recruitment, selection, training, performance management, compensation and benefits, employee relations, and workforce planning.
Recruitment and Selection
A key aspect of HRM is the recruitment and selection process, which refers to the process of attracting, screening, and selecting suitable candidates for a job. This involves designing job advertisements, conducting interviews, and choosing the most suitable candidate based on their skills, experience, and personality fit with the organization.
Training and Development
Another important function of HRM is providing training and development opportunities to employees. This involves identifying skill gaps, delivering training programs, and supporting career progression to improve overall employee performance and job satisfaction. It helps to ensure that employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to fulfill their roles effectively.
Performance Management
Performance management is a critical component of HRM, focusing on the assessment and improvement of employee performance. This involves setting performance expectations, monitoring progress, providing feedback, and implementing performance improvement plans as needed. The main purpose of performance management systems is to ensure that employees are working towards organizational goals and functioning at their highest potential.
Compensation and Benefits
HRM also involves determining appropriate compensation and benefits packages for employees. This includes salary, bonuses, incentives, and other non-monetary rewards such as healthcare and retirement benefits. The aim is to strike a balance between offering competitive compensation packages that attract and retain top talent, while maintaining the financial stability of the organization.
Employee Relations
Maintaining positive employee relations is another crucial aspect of HRM. This involves fostering a supportive work environment that allows employees to voice their concerns and be treated fairly and respectfully. HRM professionals may handle issues such as conflict resolution, mediation, and grievance procedures to ensure the well-being and satisfaction of employees, ultimately reducing turnover and increasing productivity.
Workforce Planning
Finally, HRM plays a pivotal role in workforce planning, which entails forecasting the organization's future staffing needs and developing strategies to meet these requirements. This can involve activities such as succession planning, talent management, and workforce optimization, ensuring that the organization has a skilled, motivated, and engaged workforce to achieve its strategic goals.
In conclusion, HRM is a multifaceted discipline that involves managing the entire employee lifecycle, from recruitment and selection to training, performance management, compensation, and beyond. Its primary goal is to ensure that organizations make the most of their human capital, driving both individual and organizational success.
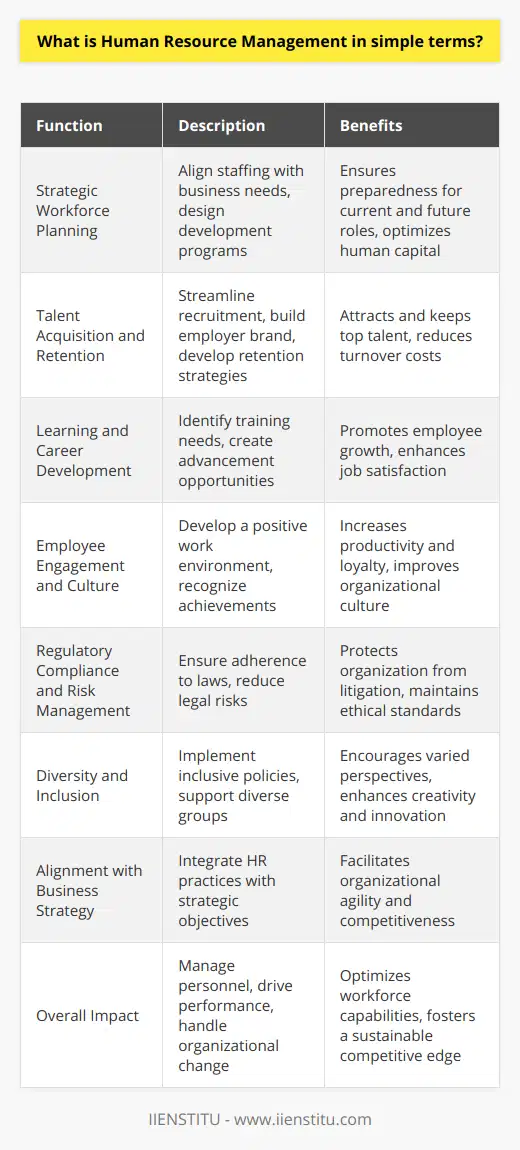
What do Human Resource Management professionals do?
Role of HRM Professionals
Human Resource Management (HRM) professionals play a critical role in the success of an organization by developing and executing strategies focused on leveraging human capital. They are responsible for multiple aspects of workforce management, such as recruitment, training, compensation, employee relations, and compliance with labor laws.
Recruitment and Selection
A primary responsibility is the recruitment and selection of employees. HRM professionals create job postings, review resumes, and conduct interviews to identify candidates who possess the necessary skills, knowledge, and attitudes to contribute positively to the organization's goals and objectives.
Employee Training and Development
Another essential aspect is the design and implementation of employee training and development programs. HRM professionals assess the organization's needs and develop targeted learning opportunities to build the skills and competencies of employees, enhancing their performance and driving overall organizational success.
Compensation and Benefits Management
HRM professionals also develop and manage competitive compensation and benefits packages to attract and retain talent. They ensure fair pay practices, design employee incentive programs, and monitor market trends to offer competitive benefits that align with the organization's objectives and values.
Employee Relations and Workplace Culture
Promoting a positive workplace culture and managing employee relations is another vital area of focus. HRM professionals address employee issues and grievances, facilitate clear communication between employees and management, and help maintain a productive, safe, and supportive work environment.
Legal Compliance and Risk Management
A significant aspect of HRM professionals' work revolves around ensuring the organization's compliance with labor laws and regulations. They stay informed of changes in workplace legislation and develop policies to minimize legal risks, such as discrimination, harassment, and wage violations.
Performance Management and Talent Retention
Lastly, HRM professionals develop methods to measure employee performance and create strategies to address underperformance, as well as manage talent retention initiatives. They provide feedback to employees, work with managers to set performance objectives, and create development plans to help employees grow in their roles.
In conclusion, HRM professionals play a vital role in organizations by managing and supporting employees, driving the organization's growth and success. They recruit and retain talent, develop the workforce, maintain compliance with regulations, and foster a positive workplace culture, making them an indispensable asset to any organization.
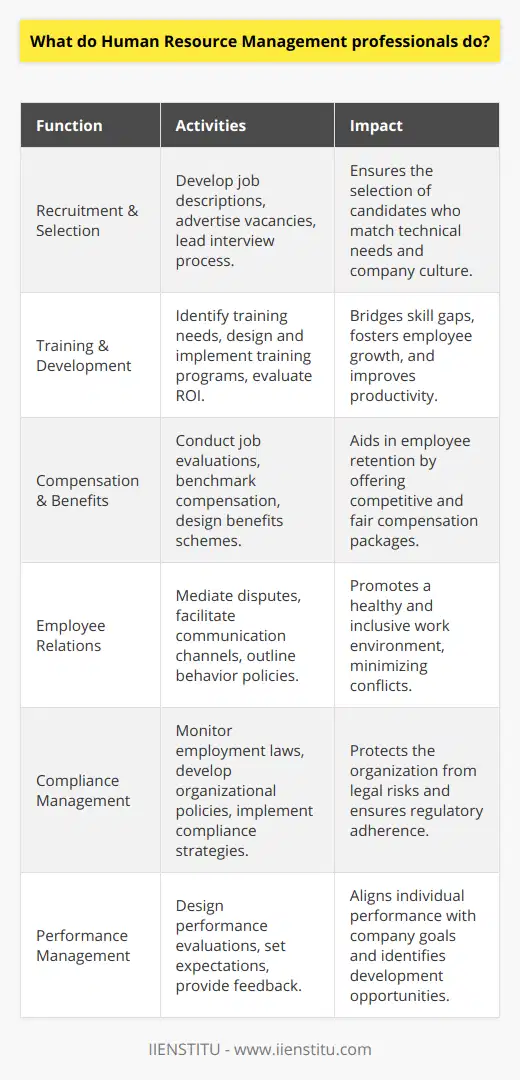
What are the 4 types of human resources?
Types of Human Resources
Organizations rely on diverse human resources to achieve their objectives and drive success. Four key types of human resources can be identified within business environments: operational, managerial, strategic, and administrative.
Operational Human Resources
Operational human resources exist at the entry and intermediate levels of an organization, encompassing roles such as customer service representatives, salespeople, and technical support specialists. These individuals contribute to the organization by completing daily tasks and directly impacting customers' or clients' experiences. As frontline employees, they play a vital role in generating revenue, maintaining quality standards, and delivering products or services effectively.
Managerial Human Resources
Managerial human resources comprise middle and upper-management roles within an organization, such as team leaders, supervisors, and department heads. These individuals are responsible for overseeing operational staff, setting goals and objectives, monitoring performance, and providing guidance and support. Managerial human resources work to ensure that the operational functions align with the organization's broader strategic vision, promoting efficiency and effectiveness.
Strategic Human Resources
Strategic human resources comprise the top-level management, including executive leadership such as CEOs, CFOs, and directors. These individuals are responsible for setting an organization's overall direction, shaping its long-term vision, and making key decisions about growth, sustainability, and competitive advantage. They develop and implement policies to guide managerial and operational staff and achieve desired organizational outcomes. Strategic human resources play a critical role in ensuring that the organization remains adaptable, innovative, and capable of navigating complex business environments.
Administrative Human Resources
Administrative human resources, commonly known as the Human Resources Department, focus on managing and supporting an organization's workforce. These professionals work in areas such as recruitment, training and development, compensation and benefits, employee relations, and performance management. This type of human resource helps ensure that the organization maintains a skilled, motivated, and engaged workforce, capable of driving success and achieving organizational goals.
In conclusion, the four types of human resources - operational, managerial, strategic, and administrative - each play an essential role in the overall functioning and success of an organization. By understanding the different types of human resources, organizations can effectively structure their workforce to promote growth, efficiency, and competitiveness in today's dynamic business landscape.
What is HRM and why is it important?
Understanding Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a vital field oriented toward managing people within an organization. Conceptually, it encompasses the strategies, practices, and policies used to attract, manage, develop, and retain an organization's human capital. The core functions of HRM include recruitment, performance management, learning and development, compensation, and talent management.
Significance of HRM
The importance of HRM in an organization cannot be overstated. It is a critical tool for fostering a work culture that enhances both individual and team performance. Effective HRM can motivate employees, foster better workplace relationships, and create a positive work environment. It also helps in compliance with labor laws, which protects an organization from potentially costly litigation.
HRM in Recruitment
In recruitment, HRM plays a crucial role in attracting and selecting potential candidates. It ensures that hired individuals possess the necessary skills and competencies to deliver on their tasks, contributing to overall business success.
HRM and Employee Performance
HRM also plays a significant role in managing and improving employee performance. This involves setting performance standards, providing feedback, and investing in training and development programs to upskill employees.
Role of HRM in Employee Retention
Employee retention is another area where HRM plays a significant role. Through fair compensation, benefits, and a healthy work environment, HRM can help retain qualified and experienced staff. It creates a culture that values employees, which can lead to increased job satisfaction and reduced turnover.
In conclusion, HRM does not only manage the workforce, but also contributes to an organization's competitive advantage. An effective HRM strategy can lead to enhanced productivity, efficiency, and overall business success. Therefore, understanding and implementing effective HRM practices should be a core aspect of every organization's strategy.

What are the primary objectives of human resource management?
Understanding Objectives
The key aim of human resource management (HRM) is staff acquisition, development, and retention. HRM focuses on recruiting the right person for the right job. This includes making job descriptions, posting ads, and managing the recruitment process.
Employee Acquisition
Once a hire happens, HRM's role shifts to onboarding and training. Training is crucial for equipping employees with necessary skills. Ongoing training ensures these skills remain up-to-date. In turn, this enables businesses to stay competitive.
Employee Development
Another fundamental objective HRM has is employee performance management. Performance reviews assess an employee’s skill and productivity. Feedback from this process helps employees grow and improve. It also aids managers in making decisions about promotions or terminations.
Performance Management
Retention of employees is another primary HRM objective. High employee turnover can cost a business greatly. Therefore, it's HRM's role to ensure positive work environments and competitive compensation packages. This will motivate employees to stay within the company.
Staff Retention
Lastly, HRM must ensure legal compliance. From hiring practices to terminations, every process must adhere to local employment laws. This is crucial to avoiding legal complications. It also aids in maintaining a fair and just workplace.
Compliance with Laws
In summary, HRM is pivotal in acquiring, developing, and retaining employees. It also ensures legal compliance. By achieving these objectives, HRM plays a crucial role in enhancing organizational productivity and growth.

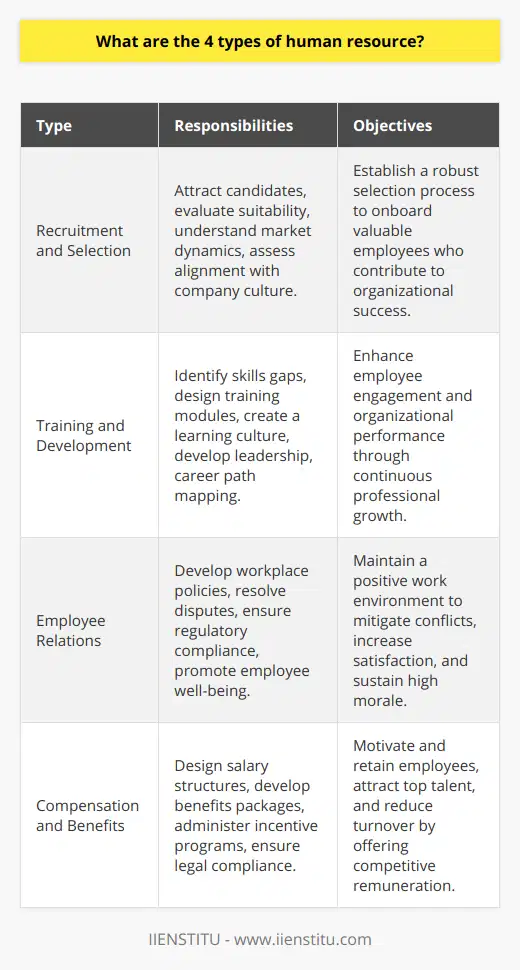
What are the 4 types of human resource?
Recruitment and Selection
The first type of human resource is recruitment and selection. This involves the process of identifying, attracting, and selecting skilled individuals who can fulfill organizational goals. It requires a keen understanding of an organization's strategic objectives, the specific job requirements, and the ability to assess and select candidates effectively.
Training and Development
Secondly, training and development is an integral aspect of human resource. It is vital in enhancing the capabilities of the staff and aligning them with the organization's strategy. Training empowers employees, improves their performance and productivity, increases job satisfaction, and reduces turnover.
Employee Relations
Thirdly, employee relations is an area that focuses on building and maintaining a positive and productive relationship between employers and employees. By ensuring proper communication, conflict resolution, and a healthy work environment, organizations can boost morale, foster loyalty, and increase worker retention.
Compensation and Benefits
Lastly, compensation and benefits involve designing and managing a company's reward system. This involves drafting the right compensation, benefits, and incentive plans for employees. An effective reward system encourages employees to perform optimally, increasing overall organizational productivity.
In summary, the four types of human resource - recruitment and selection, training and development, employee relations, and compensation and benefits - are all critical to an organization's success. When implemented effectively, they can contribute to improved employee performance, job satisfaction, and organizational productivity.