
Have you ever walked into a new workplace and sensed that the person calling the shots wasn't necessarily the one with the fanciest title? I remember my first job right out of college. I was brimming with enthusiasm, ready to make a difference, and keen to impress the company's CEO. But it didn't take long for me to realize that the organizational chart hanging on the wall was more of a formality than a reflection of how things actually got done. Understanding who truly held the power was like trying to navigate a maze without a map.
Introduction
The Real Org Chart: Who Has the Power?
Identifying the Key Stakeholders
Understanding the Dynamics of Power
Conclusion
So, how do we uncover this "real org chart," and why does it matter? Let's dive into the fascinating world of organizational power dynamics and explore how recognizing the true power structures can make all the difference in achieving our goals and fostering stakeholder satisfaction.
The Hidden Layers of Organizational Power
In every organization, there's the official structure—the one neatly laid out in flowcharts and directories. Then there's the unofficial, yet very real, network of relationships and influences that actually drive decision-making. This is what's often referred to as the "real org chart."
Most Searched Keyword: Principles Of Management And Organizational Behavior For Effective Leadership
Principles Of Management Key Features For Effective Leadership
The Official vs. The Real Org Chart
On paper, roles and responsibilities are clearly defined. The CEO sits at the top, followed by senior managers, team leaders, and so on. But does this hierarchy always reflect who has the real influence? Not necessarily. Sometimes, a long-time employee without a fancy title might wield more sway than a newly appointed manager.
For example, in my previous job at a manufacturing firm, there was a receptionist named Linda. She'd been with the company for over 20 years and knew everyone—from the janitors to the board members. Linda wasn't just a receptionist; she was the glue that held the place together. If you needed something done swiftly, Linda was your go-to person. She had the ear of the top executives and could make things happen with a simple phone call.
Factors That Influence Real Power Dynamics
Several elements contribute to these hidden power structures:
1- History with the Company: Long-standing employees often accumulate informal power.
2- Personal Relationships: Friendships and alliances can override formal hierarchies.
3- Specialized Knowledge: Employees with unique expertise gain influence.
4- Access to Resources: Control over budgets, information, or key contacts elevates one's power.
5- Personality and Charisma: Natural leaders can inspire and direct others regardless of their title.
Understanding these factors is crucial. Why? Because they affect how decisions are made and how effectively an organization operates.
Identifying the Key Stakeholders
So, how do we spot these influencers within an organization? It's akin to being a detective, keenly observing and gathering clues.
Asking the Right Questions
To identify who holds real power, consider the following:
Who do people go to for advice or approval?
Who has the final say during meetings, even if they're not the highest-ranking person there?
Revealing the actual power structure of leadership is essential to understanding the dynamics of an organization.
Who brings teams together and facilitates collaboration?
Who controls critical resources or information?
Who has strong relationships across different departments?
By answering these questions, you can start to map out the informal networks that exist within the company.
Building Relationships with Influencers
Once you've identified key stakeholders, it's beneficial to build genuine relationships with them. Here are some steps to consider:
1- Engage in Active Listening: Show genuine interest in their perspectives.
2- Offer Support: Find ways to assist them in their initiatives.
3- Seek Mentorship: Learn from their experiences and wisdom.
4- Communicate Effectively: Be clear and respectful in all interactions.
5- Demonstrate Reliability: Build trust by following through on commitments.
By fostering these connections, you not only gain insights into the organization's dynamics but also enhance your own influence.
Understanding the Dynamics of Power
Power in an organization isn't just about position; it's about influence and the ability to effect change. Let's explore the different types of power at play.
Types of Organizational Power
1- Legitimate Power: Derived from a formal position or rank within the organization.
2- Expert Power: Based on knowledge, skills, and expertise.
3- Reward Power: The ability to grant benefits or rewards.
4- Coercive Power: The capacity to impose sanctions or punishments.
5- Referent Power: Coming from being respected, admired, or liked.
Understanding these power types helps us navigate the complex web of organizational relationships.
The Role of Influence and Persuasion
Influence often outweighs formal authority. According to Dr. Robert Cialdini's principles of persuasion, factors like reciprocity, commitment, social proof, authority, liking, and scarcity play significant roles in how we sway others [^1].
Consider a project manager who lacks formal authority over team members from other departments. By leveraging expert power and building referent power through strong relationships, they can effectively lead and coordinate the team.
Navigating the Real Org Chart
Now that we've uncovered who holds the power and understand the dynamics at play, how do we effectively operate within this framework?
Strategies for Success
Map Out Influencer Networks: Create a visual representation of key players and their relationships.
Communicate Across Levels: Don't limit interactions to your immediate team or superiors.
Showcase Your Value: Demonstrate how your contributions align with organizational goals.
Be Adaptable: Stay open to change and be willing to adjust your approach.
Practice Emotional Intelligence: Recognize and manage your emotions and those of others.
By implementing these strategies, you position yourself to work more effectively within the true power structures of your organization.
The Importance of Systematic Logistics in Organizational Success
In industries like supply chain and logistics, understanding power dynamics is crucial. The systematic logistics packaging transport safety procedures are vital for operational efficiency and safety compliance. But who oversees these procedures? It's often a combination of formal leaders and informal influencers who ensure protocols are followed and optimized.
For example, a logistics coordinator might have the legitimate power to enforce safety procedures, but a veteran warehouse worker with years of experience and the team's respect might be the key to ensuring everyone actually follows them.
The Impact on Organizational Goals and Stakeholder Satisfaction
Recognizing and navigating the real org chart isn't just about personal success—it's about contributing to the organization's overall effectiveness.
Achieving Organizational Goals
When we understand who makes things happen, we can:
Align initiatives with those who can champion them.
Anticipate challenges and mitigate risks.
Foster collaboration across departments.
This alignment leads to more efficient processes and better outcomes.
Enhancing Stakeholder Satisfaction
Stakeholders—be they employees, customers, or investors—are more satisfied when:
Communication is transparent and effective.
Their needs and concerns are addressed promptly.
They see progress towards shared goals.
By leveraging the real org chart, we ensure that stakeholder interests are acknowledged and prioritized.
Conclusion
Understanding the real org chart is like uncovering the hidden engine that powers an organization. It's not always visible, but it's essential to the journey. By identifying key stakeholders, comprehending the dynamics of power, and navigating these waters carefully, we can contribute more meaningfully to our organizations and achieve both personal and collective success.
I still think back to my early days in the workforce, grateful for the lessons learned about the subtle currents of influence that exist in every company. It's not just about climbing the ladder; it's about knowing which walls the ladder is leaning against.
[^1]: Cialdini, R. B. (2006). Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion. Harper Business.
References
Handy, C. (1993). Understanding Organizations. Oxford University Press.
Pfeffer, J. (1992). Managing with Power: Politics and Influence in Organizations. Harvard Business School Press.
French, J. R. P., & Raven, B. (1959). "The Bases of Social Power" in Studies in Social Power. University of Michigan.
Kotter, J. P. (1985). Power and Influence: Beyond Formal Authority. The Free Press.
Cialdini, R. B. (2006). Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion. Harper Business.
Remember, the next time you're trying to get a project off the ground or seeking approval for a new initiative, take a moment to consider the real org chart. Who holds the keys to the castle? By understanding and respecting the true power dynamics, you'll find doors opening that you didn't even know existed.
And who knows? You might just become one of those influential players who make things happen, not through title or position, but through understanding, relationships, and strategic action.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key stakeholders in uncovering the real org chart?
Organizational charts are an essential tool for understanding the structure and roles of an organization and for communicating that structure to members of the organization. However, in many cases, an organization's network and parts may not be accurately reflected in the official org chart. This can lead to confusion, misunderstandings, and inefficiencies. Therefore, it is essential to identify and involve the critical stakeholders in uncovering the actual org chart.
The organization's members are the first key stakeholder in uncovering the actual org chart. These individuals are likely to accurately understand the roles, responsibilities, and relationships within the organization. In some cases, they may even be aware of unofficial roles and relationships that are not included in the official org chart. Therefore, uncovering the org chart is essential, as their insights can provide valuable information about the organization's structure.
External stakeholders, such as customers, vendors, and partners, are the second key in uncovering the org chart. These individuals may have different perspectives on the organization's structure and roles. They may also be able to provide valuable insights into the organization's relationships with other organizations. Therefore, involving these stakeholders in uncovering the org chart is essential, as their senses can provide helpful information about the organization's relationships with external entities.
The organization's leadership is the third key stakeholder in uncovering the actual org chart. Leaders have the power to shape the organization's structure and roles and therefore have a unique perspective on the organization. Consequently, it is essential to involve the organization's leadership in uncovering the actual org chart, as their insights can provide valuable information about the organization's structure and roles.
In conclusion, uncovering the actual org chart is a complex process requiring several vital stakeholders' involvement. These stakeholders include the organization's members, external stakeholders, and leadership. Involving these stakeholders in uncovering the actual org chart can provide valuable insights into the organization's structure and roles and help ensure that the official org chart accurately reflects the organization's reality.

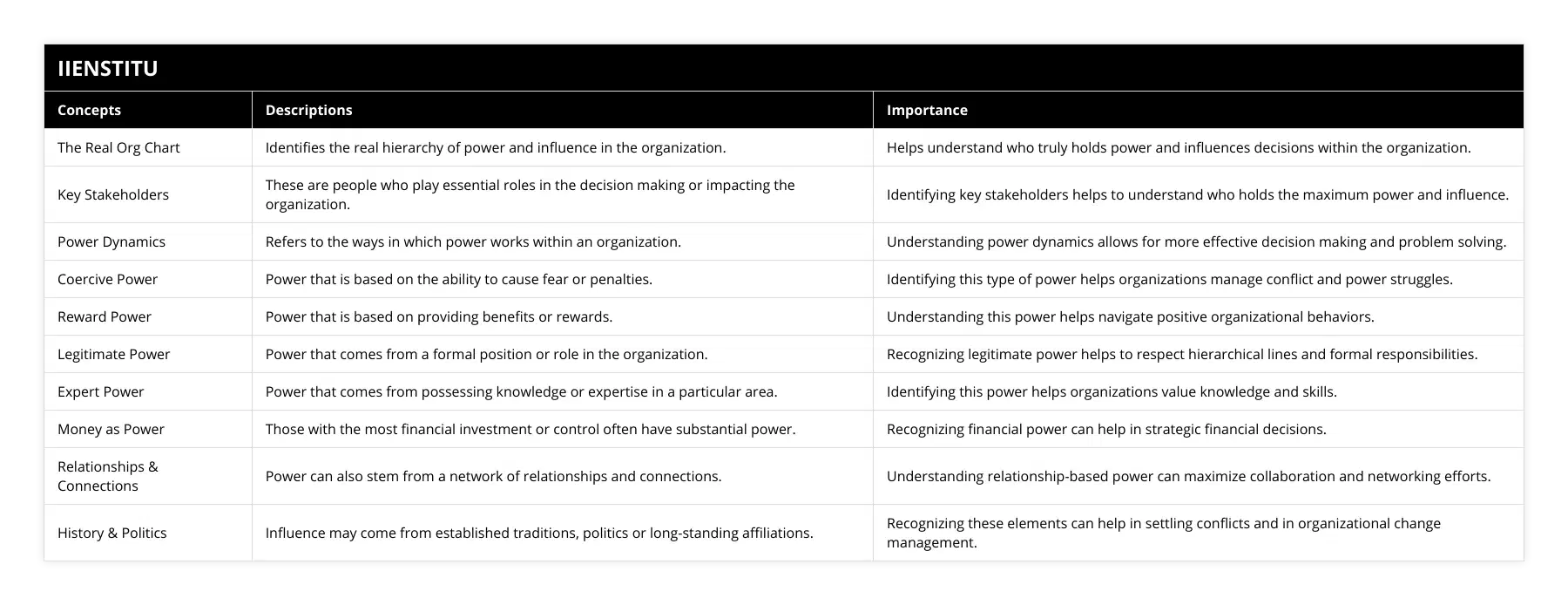
How can understanding the dynamics of power help to identify who has the power in leadership?
When looking at power dynamics in leadership, it is essential to understand how power is distributed and used to identify who has the power in a given context. Power is a complex concept defined in various ways depending on the context. Generally speaking, power is the ability to influence or affect people and their behavior.
In leadership, power can be seen as the ability to make decisions and have authority. It is often used to motivate and inspire others to work towards a common goal. However, power can also control and manipulate people and create a sense of loyalty and commitment.
Power dynamics can be examined through several different lenses. First, power can be divided into two categories: formal and informal. Standard power is derived from a person's position in an organization or an institution. In other words, it is the power given to someone due to their position in the organization. Examples of formal power include the CEO of a company or the President of a country.
In contrast, informal power is derived from a person's relationships, knowledge, and influence. This type of power is often seen in personal relationships, such as mentorship or friendship. Examples of informal power include a mentor-mentee relationship or a friendship between two people.
Second, power can be divided into three types: coercive, reward, and legitimate. Coercive power is the power to control or manipulate people through threats or punishments. Reward power is the power to motivate and inspire people through rewards. Finally, legitimate power is influencing people through authority or respect.
Finally, power can be divided into four levels: individual, group, organizational, and societal. Individual power is the power that a person has over themselves. Group power is a group of people's power over each other. Executive power is the power that an organization has over its members. Finally, societal power is a society's power over its members.
Understanding the dynamics of power and how it is distributed and used in leadership makes it possible to identify who has the power in a given context. This can be done by examining the different types of energy and the different levels of ability. Analyzing the power dynamics in a given situation makes it possible to identify who has the power and how it is used. This understanding can be used to create more effective leadership and ensure that power is used positively and equitably.
What are the implications of uncovering the real org chart for organizational success?
Organizational success is primarily determined by the effectiveness of the organizational Chart (Org Chart), which outlines the chain of command and delineates the roles and responsibilities of each member of the organization. Therefore, uncovering the actual structure of an organization’s Org Chart can lead to significant implications for organizational success.
One of the implications of uncovering the absolute Org Chart is the potential for improved employee engagement and job satisfaction. When employees understand their roles, responsibilities, and reporting structure, they can better focus on their job duties and be more productive. Additionally, employees are more likely to feel respected, valued, and motivated when they understand their place in the organization, leading to improved job satisfaction.
Another implication of uncovering the accurate Org Chart is the potential for improved communication and collaboration within the organization. When there is an understanding of the roles and responsibilities of each team member, they can be more easily held accountable for their work. Furthermore, when the reporting structure is delineated, employees can better collaborate and coordinate efforts to maximize team productivity.
A third implication of uncovering the absolute Org Chart is improved customer service. When employees understand their roles and responsibilities within the organization, they can better respond to customer inquiries, resolve customer complaints, and address customer needs. Additionally, when there is a clear understanding of reporting structures, customer service teams can quickly identify the appropriate resources and personnel to handle customer issues.
In conclusion, uncovering the actual structure of an organization’s Org Chart can lead to significant implications for organizational success. Improved employee engagement, job satisfaction, communication and collaboration, and customer service are just a few of the potential benefits of uncovering the actual structure of an organization’s Org Chart.

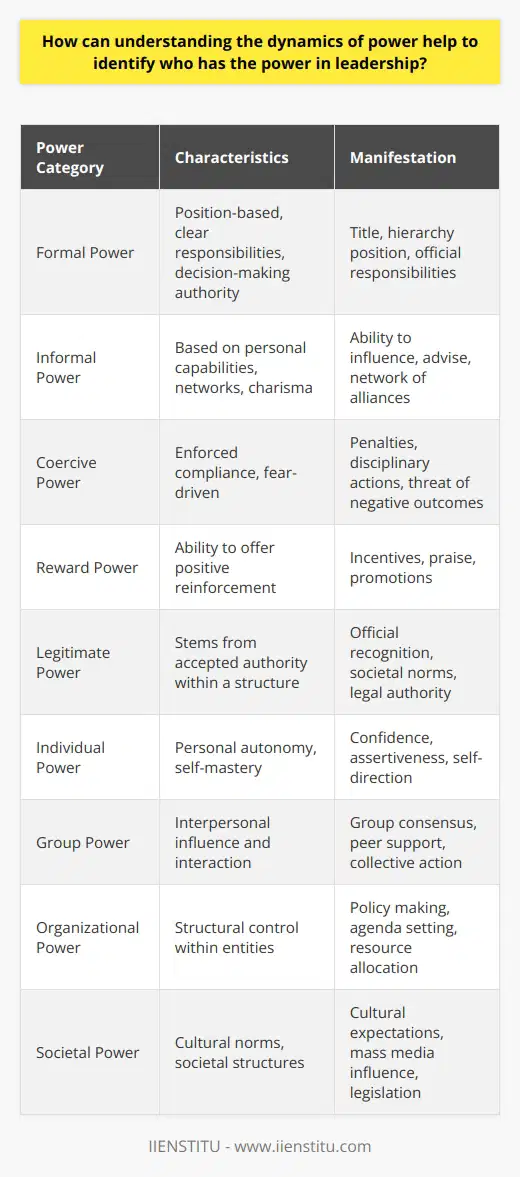
What is the influence of an organizational chart in understanding an organization's power dynamics?
Organizational Chart's Role in Power Dynamics
An organizational chart presents a visual representation of the hierarchy and structure within an organization, which has a significant influence on understanding its power dynamics. By outlining the various positions, departments, and reporting relationships, this essential tool enables individuals to comprehend how authority and responsibilities are distributed among the organization's members.
Visibility of Decision-Making Authority
One key aspect of power dynamics within an organization is the decision-making authority, which is often directly related to the level of hierarchy. As organizational charts display the different levels of management, from top executives to entry-level employees, they provide critical insights into who holds the decision-making power at each level. This visibility enables individuals to recognize their own authority and the chain of command for communication and decision-making purposes.
Interdepartmental Relationships
In addition to illustrating the distribution of power through hierarchy, an organizational chart also demonstrates the relationships between various departments and teams. By showcasing the connections and dependencies between different units, it becomes apparent where collaboration and communication are central to the accomplishment of organizational goals. Thus, the chart influences power dynamics by highlighting the avenues through which cooperation and coordination are essential for achieving success.
Centers of Influence and Decision-Makers
Organizational charts often reveal positions that hold significant influence within the organization, even if they may not be at the highest level of hierarchy. For instance, certain management positions, such as project managers or department heads, might hold considerable power within their designated areas. By identifying these influential positions on the chart, employees can better understand the distribution of power and the key decision-makers within the organization.
Overall, an organizational chart plays a crucial role in understanding an organization's power dynamics by visually representing the hierarchy, decision-making authority, and interdepartmental relationships. Through this information, individuals can identify not only the formal structure of power but also the subtleties of influence within the organization. As a result, organizational charts facilitate effective communication, collaboration, and decision-making processes to support the organization in achieving its objectives.
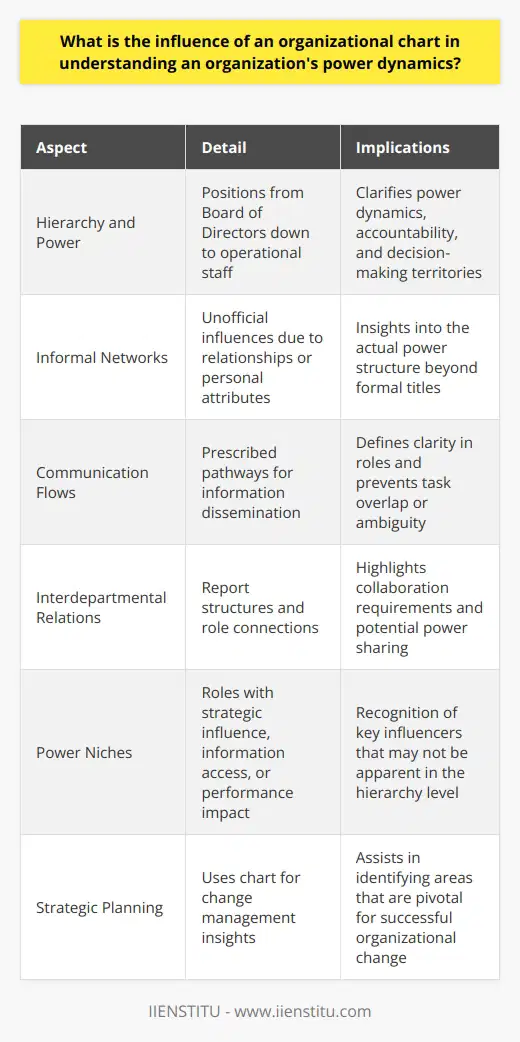
How is the chain of command depicted in an organizational chart, and how does it illustrate reporting relationships?
Organizational Chart Structure
A chain of command is represented in an organizational chart, demonstrating the hierarchical structure of a company or institution. The chart typically comprises boxes or nodes representing different positions, connected by lines to indicate the relationships and flow of communication within the organization. The structure may take on a variety of shapes, such as a vertical hierarchy, matrix, or flat design, depending on the complexity and nature of the organization.
Hierarchy and Reporting Relationships
In a hierarchical organizational chart, the top-most box signifies the highest-ranking position, such as the CEO or president, followed by subsequent tiers that contain a decreasing level of authority. Each box in the chart represents an individual role or a department, with lines connecting them to show the reporting relationships, from supervisors and subordinates to support staff. Thus, the chart serves as a visual illustration of each employee's position within the organization and their reporting responsibilities to their superiors.
Importance of Clear Reporting Structure
An effective organizational chart enables an organization to function efficiently by clarifying reporting lines, responsibilities, and communication channels. Managers and team members can quickly understand the decision-making process, chains of accountability, and delegation of tasks, which streamlines workflow and fosters collaboration across teams. Moreover, a well-designed organizational chart encourages transparency, as it allows employees to comprehend the company's overall structure and sets expectations for the chain of command. This clarity minimizes misunderstandings, facilitates swift conflict resolution, and fosters a positive work environment.
In summary, an organizational chart is a critical tool for illustrating a company's chain of command and reporting relationships. By offering a visual representation of hierarchies, the chart enables employees to better understand their roles, their supervisors, and their subordinates, promoting effective communication and collaboration. Ultimately, an easily discernible organizational chart contributes to a smoothly functioning organization, aligning all parties toward common goals and maintaining transparency throughout the workplace.
In what way does organizational structure impact leadership roles and decision-making processes within an organization?
Organizational Structure's Influence on Leadership Roles
An organization's structure affects leadership roles in several ways, notably by determining how decision-making responsibilities are allocated among the hierarchy. In a centralized structure, leaders at the upper echelon wield more power, while in decentralized structures, authority is more dispersed, with leaders at various levels enabled to make crucial decisions autonomously.
Hierarchy-Decision-Making Relationship
The organizational structure dictates the decision-making processes within an organization, and as such, it impacts the extent of cooperation and collaboration among leaders. In a tall hierarchical structure, there is a clear chain of command, and decisions often flow from the top, reflecting the predetermined direction of the organization's mission and goals. On the other hand, a flat structure promotes open communication, allowing leaders of different departments to collaborate on decision-making and contribute their expertise more extensively.
Authority and Empowerment of Leaders
Organizational structure also shapes the roles of leaders by influencing their level of authority and ability to empower subordinates. In a rigid hierarchy, employees are less likely to feel empowered; however, this can be mitigated by adopting a flexible leadership style that encourages feedback and employee input. Conversely, a more flexible, more collaborative organizational structure offers leaders an opportunity to empower their teams, fostering higher engagement and performance levels.
Leadership Style and Organizational Culture
The impact of organizational structure on leadership roles extends to the organization's culture. Leaders in hierarchical organizations often adopt more autocratic and directive leadership styles, leading to a top-down culture, while organic structures inspire more democratic and participative decision-making. A leader's adaptability and openness to fostering a dynamic work environment are essential in creating an organizational culture that embraces change and innovation, allowing the organization to thrive amid evolving market conditions.
In conclusion, organizational structure significantly impacts leadership roles and decision-making processes within an organization. Understanding these implications is crucial in determining the most effective structure for an organization, as well as shaping the leadership style and culture that best promotes the organization's success.
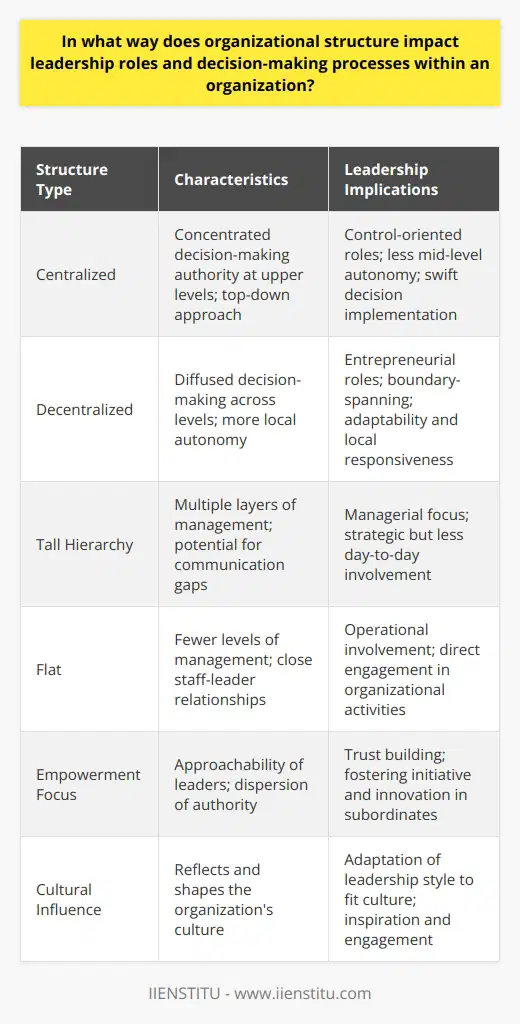
Which kind of chart indicates who has authority over whom within an organization?
Organizational Hierarchies and Charts
An Overview of Hierarchical Charts
A critical aspect of understanding an organization's structure and functioning is determining the relationships and lines of authority among its members. The kind of chart that effectively demonstrates who has authority over whom within an organization is called an organizational chart or an org chart.
Characteristics of Organizational Charts
Typically, org charts use a hierarchical structure to showcase different layers of management and employee positions. They display relationships in the form of easy-to-read flowcharts, which help visualize distinct roles and reporting relationships within the organization.
Types of Organizational Charts
Various organizational charts exist to serve specific needs of an organization. The most commonly used types include the following:
Hierarchical Organizational Chart: This chart showcases the traditional top-down structure with a CEO at the top level followed by other senior executives, department heads and employees further down the hierarchy.
Matrix Organizational Chart: This type of chart is used in matrix organizations, where employees may report to multiple managers. It illustrates the complex reporting relationships across departments, highlighting cross-functional collaborations.
Flat Organizational Chart: Flat or horizontal charts depict organizations with minimal or no levels of middle management. This structure emphasizes a collaborative and decentralized approach to decision-making.
Applying Organizational Charts in Practice
Organizational charts remain crucial tools for staff, stakeholders, and regulators to grasp the nature and function of a business setup. They use symbols and shapes to represent specific titles, positions, and departments, making it simpler for observers to understand the decision-making hierarchy and effective routes of communication in organizations. While org charts are dynamic and may change as the organization evolves, their fundamental purpose remains consistent: to provide a clear roadmap of authority and accountability within an organization.
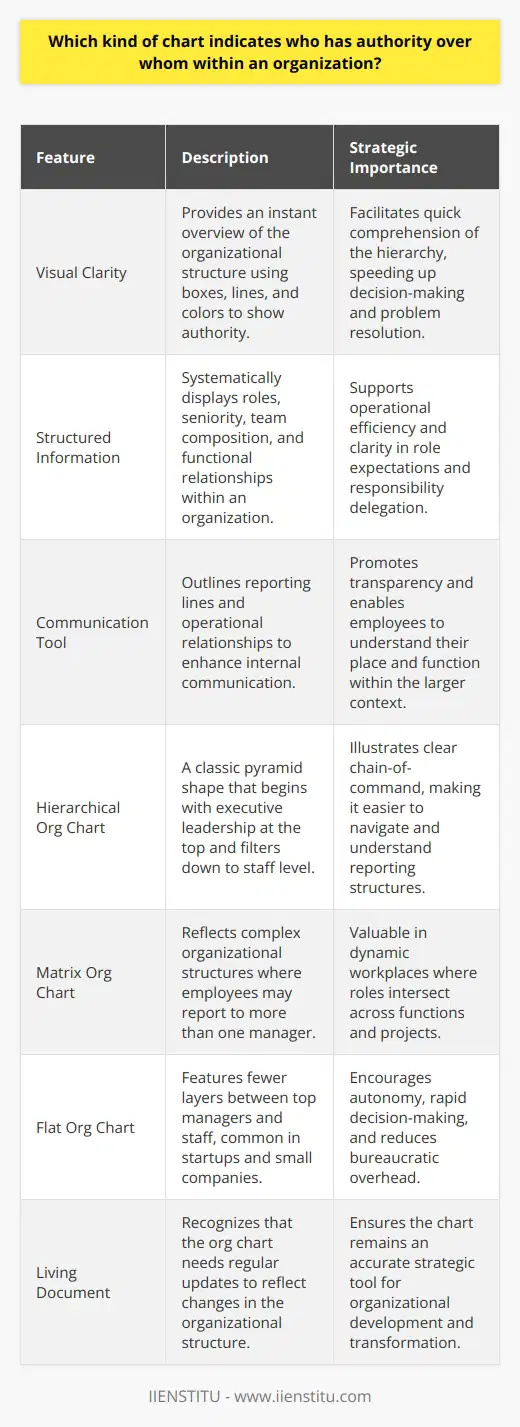
What is the role of organizational structure on leadership?
Organizational Structure's Impact on Leadership
A significant aspect of effective leadership involves understanding and employing the right organizational structure. Organizational structure can be defined as the framework in which an organization's roles, responsibilities, and communication systems are arranged to achieve its goals. In essence, the structure determines how leadership is exercised and how authority and decision-making are distributed within the organization.
Leadership Styles and Organizational Structures
There are various organizational structures such as hierarchical, flat, matrix, and network structures, each influencing leadership styles differently. For instance, a hierarchical structure, which is characterized by a top-down approach, requires a more authoritative and directive leadership style. Conversely, a flat structure, which promotes equality and collaboration among employees, calls for a more participatory and empowering leadership approach.
Adaptability and Flexibility in Leadership
The organizational structure's role in leadership extends beyond determining the appropriate leadership style; it also impacts the leader's ability to adapt and be flexible. In dynamic environments that require quick and innovative responses, a leader must be able to adapt to new circumstances and adopt different styles of leadership, depending on the situation at hand. This adaptability and flexibility are facilitated by the organizational structure that enables leaders to make decisions and respond to changes effectively.
Communication and Information Flow
Moreover, an organization's structure has a direct impact on the flow of communication and information within the organization. Efficient communication within an organization is crucial for effective leadership, as it provides feedback, ensures coordination, and prevents misunderstandings. A well-designed organizational structure encourages open communication channels for sharing information, addressing concerns, and fostering collaboration, ultimately contributing to sustainable leadership.
Developing Future Leaders
Another important role of organizational structure in leadership is developing and nurturing future leaders. A clear and transparent structure provides opportunities for potential leaders within the organization to grow, learn, and take on new responsibilities. This development of future leaders is critical for the long-term success and sustainability of an organization.
In conclusion, the role of organizational structure on leadership is multifaceted and substantial. It influences leadership styles, adaptability, communication, and the overall effectiveness of an organization's leaders. By selecting and implementing the appropriate organizational structure, an organization can shape its leadership to better achieve its objectives and excel in today's ever-changing business landscape.
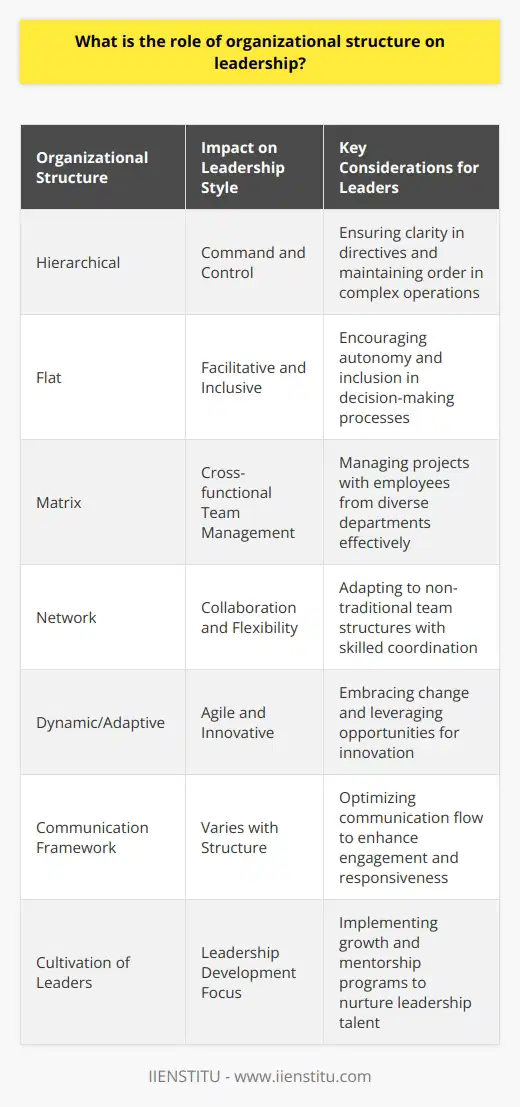
What is the power structure of an organization?
Organizational Power Structure
The power structure of an organization refers to the distribution of authority, influence, and control within that entity. In essence, it dictates the ways decisions are made, resources allocated, and performances assessed. Various factors contribute to shaping the power structure of an organization, including its size, industry, and corporate governance. By understanding the power structure, leaders, employees, and stakeholders can better navigate the organization to achieve desired outcomes.
Formal Hierarchies
One key aspect of an organization's power structure is its formal hierarchy. This system outlines the levels of authority and reporting relationships among staff members, typically displayed in an organizational chart. There are usually three organizational levels: top-level management, middle-level management, and lower-level management. As employees move up the hierarchy, their decision-making power, authority, and responsibilities increase.
Centralized and Decentralized Structures
Depending on the organization, the degree of centralization or decentralization of power can significantly influence decision-making processes. Centralized structures concentrate decision-making authority at the top level, such as in a CEO or a small group of executives. In contrast, decentralized structures distribute decision-making responsibilities among different levels and departments, empowering middle and lower-level managers to make decisions more autonomously.
Functional and Divisional Structures
In addition to hierarchies, the way organizations group their activities can impact power dynamics. A functional structure organizes employees by their functions or skills, such as marketing, finance, or human resources. The power is often centralized in the functional executives, who oversee their respective departments. Meanwhile, a divisional structure groups employees based on products, services, or regions, with each division having its own management system. This setup allows for more decentralized control and decision-making.
Informal Networks and Social Capital
Beyond formal structures, the power dynamics in organizations can be strongly influenced by informal networks and social capital. These refer to the relationships, trust, and shared norms among employees, which can foster collaboration, access to resources, and influence within the organization. Employees who have strong social capital and are part of extensive networks can have greater informal power, regardless of their position in the formal hierarchy.
In conclusion, the power structure of an organization comprises various components, such as formal hierarchies, centralization, and functional or divisional categorization. It also encompasses informal networks and social capital, which can significantly affect influence and decision-making. Understanding the power dynamics can aid employees, managers, and stakeholders in strategic planning, conflict resolution, and overall success in their organizational roles.



