
In business, many different aspects must be managed for a company to succeed. While some people may think that management is simply about telling other employees what to do, the management field is much more complex than that. In this blog post, we will explore the management theory and discuss some of the key concepts essential to understanding it.
We will also look at how the idea of management has evolved and examine some of the criticisms that have been leveled against it. By the end of this post, you should better understand the theory of management and why it is so essential for businesses.
What is the theory of management, and what are its key components?
The management theory is a body of ideas that helps explain how managers work. It has three major components: goal setting, planning, and coordinating. The view of management also has two subcomponents: control and decision-making. The goal-setting component helps managers identify what needs to be done to improve performance.
The planning component helps managers develop a plan of action to achieve goals. The coordinating part helps managers coordinate the activities of the workers. The control component helps managers monitor and evaluate the performance of the workers.
Finally, the decision-making component helps managers decide what actions to take to improve performance. Control and decision-making are essential subcomponents of the management theory because they help managers ensure that the goals are achieved and that the workers perform at their best.
How did the theory of management develop over time, and who were some key contributors?
The theory of management has evolved significantly over time, and several vital contributors have shaped its development. One of the earliest theorists was Henri Fayol. He proposed five critical functions of management: planning, organizing, staffing, leading, and controlling. He also suggested that managers should have a clear hierarchy to be effective.
Another early contributor was Frederick Taylor, who is often considered the father of scientific management. He argued that work should be structured in a way that maximized efficiency and productivity. Later theorists such as Elton Mayo and Chester Barnard would build on these ideas and develop new theories about human behavior and motivation in the workplace.
As the field of management has continued to evolve, so too has the approach upon which it is based. Theories about management are constantly being refined and expanded as our understanding of what it takes to manage people and resources continues to grow effectively.
Most Searched Keyword: Principles Of Management And Organizational Behavior For Effective Leadership
What are some criticisms of the theory of management, and how might it be improved upon?
One of the most prominent criticisms of the theory of management is that it relies too heavily on formal rules and procedures. This can create an environment that is impersonal and inflexible, and it can stifle creativity and innovation.
Additionally, the theory has been accused of downplaying the importance of human factors, such as emotion and motivation. Another criticism is that the approach fails to address environmental factors, such as global economic conditions, adequately. Finally, some scholars have argued that the theory places too much emphasis on efficiency and productivity and needs to be more on other objectives, such as social responsibility.
While there is undoubtedly some validity to these criticisms, it is essential to remember that management is an evolving field, and new approaches are constantly being developed in response to these critiques. As such, it is likely to continue to evolikely live in order to address these concerns.
What are some future directions for the theory of management research and practice?
There is no one answer to this question, as the future of management research and practice will be shaped by a number of factors. However, some possible future directions for management theory include a greater focus on ethical leadership, sustainable workplace practices, and workplace diversity.
Related Course: Leadership Development Course
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, there is also likely to be a greater emphasis on global perspective-taking in management research and practice. Additionally, as technology continues to evolve, there will likely be a need for management theory to keep pace in order to provide relevant guidance for managers.
Ultimately, the future of management research and practice will be determined by the changing needs of organizations and society.
The theory of management is a critical framework for understanding how organizations function and how to optimize their performance. While the idea has evolved over time, its key components remain central to our understanding of how businesses operate. Despite its criticisms, the theory of management provides an essential foundation for effective organizational practice. If you're interested in learning more about the idea of management, join our fundamentals of management course today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the theory of management?
The theory of management is a set of principles and practices that guide how organizations are structured, managed, and operated in order to achieve their goals. It incorporates elements from multiple disciplines, such as economics, sociology, psychology, and political science. The theory includes concepts such as organizing and planning.
What are some key contributors to the theory of management?
Key contributors to the theory of management include early pioneers such as Henri Fayol, Mary Parker Follett, and Elton Mayo. More modern thinkers such as Abraham Maslow, Frederick Herzberg, Douglas McGregor, and Chester Barnard have also made significant contributions to the field. Each of these individuals has helped shape our understanding of how organizations function and the best ways to optimize their performance. As a result, the theory of management has become increasingly sophisticated over time, with new sources emerging as its command, coordination, control, and motivation. The idea of management is used to analyze how organizations operate in order to identify areas for improvement or efficiency gains. It also provides guidance on how to effectively lead and manage teams in order to maximize organizational performance.

What are some criticisms of the theory of management?
The theory of management has been subject to criticism from multiple angles. One common critique is that it oversimplifies the complexities of human behavior, and foundations continue to be explored. As a result, the theory of management has become a valuable tool for managers and leaders in today's organizations.
Some other criticisms include that it ignores the dynamics of power within an organization, fails to account for changing external contexts, relies too heavily on positivism, and lacks cultural sensitivity. These criticisms point to the need for a more nuanced, sophisticated approach to management theory that is attuned to the complexities of organizations and their diverse stakeholders.
How does the theory of management help improve business operations?
The theory of management helps improve business operations by providing a framework for understanding and improving how an organization is run. It helps managers and business owners make better decisions, develop strategies and plans for the future, and identify problems before they become too large to manage. It also helps organizations measure their performance and identify areas for improvement. By using the principles of management, companies can create efficient processes, better use resources, and create a competitive advantage.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using the theory of management?
Advantages:
Provides a framework for understanding and analyzing complex management issues.
Allows for better decision-making by offering a systematic approach for evaluating options.
Helps managers develop more efficient and effective management practices.
Increases the likelihood of success by providing a structure for understanding and implementing change.
Disadvantages:
May not be applicable to all situations, leading to the development of ineffective solutions.
Can be too rigid and inflexible, making it difficult to adjust to changing circumstances.
Can lead to over-reliance on the theory, leading to a lack of creativity and innovation.
Can become outdated due to the rapid pace of change in the business environment.
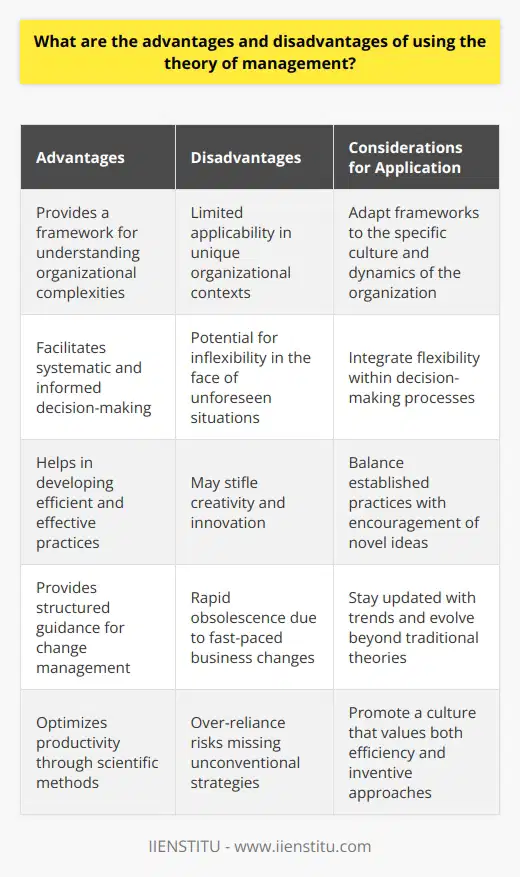
How can the theory of management be applied to different types of organizations?
The theory of management can be applied to different types of organizations in a variety of ways. The most fundamental application of management theory is to understand the process of management, which includes planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. This can be applied to any type of organization, such as a small business, a large corporation, a government agency, or a non-profit organization. By understanding the principles and processes of management, organizations can better develop strategies, motivate employees, and make decisions that will help them achieve their goals. Additionally, management theory can be used to improve human resources management, operations management, and financial management. For example, management theory can be used to guide organizational decision-making and to develop effective strategies for managing organizational resources. In sum, the theory of management can be applied to different types of organizations in order to help them achieve success.
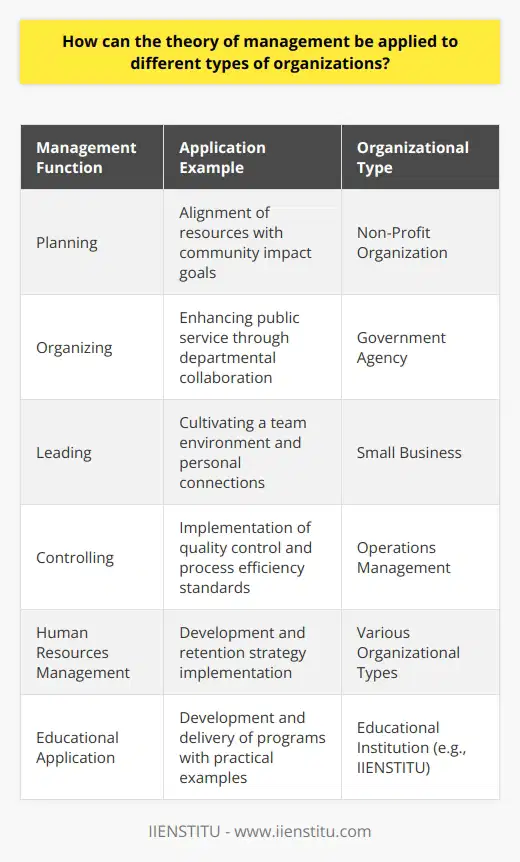
What is the significance of management theories in organizational success?
Significance of Management Theories
Understanding the importance of management theories is crucial as they play a vital role in organizational success. These theories serve as a foundation for managers to build effective strategies and create a conducive environment that encourages growth, innovation, and performance.
Principles of Management Theories
Acting as a roadmap, management theories help managers identify problems, analyze possible solutions, and implement effective approaches. These theories serve as guidelines for executing key functions, such as planning, organizing, directing, and controlling.
Role of Management Theories in Decision-making
By providing managers with a structured approach, management theories facilitate informed decision-making. By applying relevant theories, managers examine the organization's objectives and gather critical information to make well-informed decisions that have long-term implications on overall success.
Boosting Organizational Efficiency
Management theories contribute to increased organizational efficiency by streamlining processes and workflow. By applying these theories, managers can identify potential bottlenecks, allocate resources effectively, and maintain a balance between stability and change, ensuring optimal performance.
Fostering Employee Engagement
The application of management theories improves employee engagement and team cohesion. Managers who incorporate these theories in their approach promote a positive work culture and provide a sense of direction and purpose for employees, leading to greater job satisfaction, motivation, and productivity.
Adapting to Change and Innovation
Furthermore, management theories are crucial for organizations to adapt to change and foster innovation. By utilizing these theories, managers can anticipate shifts in the business environment and adopt innovative practices, technologies, and processes to maintain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, management theories hold significant value in organizational success as they provide managers with the necessary tools and guidance to navigate various challenges and drive the organization towards growth, innovation, and efficiency. By instilling a systematic approach, management theories ensure an organization’s objectives are met while continuously adapting to the dynamic business landscape.
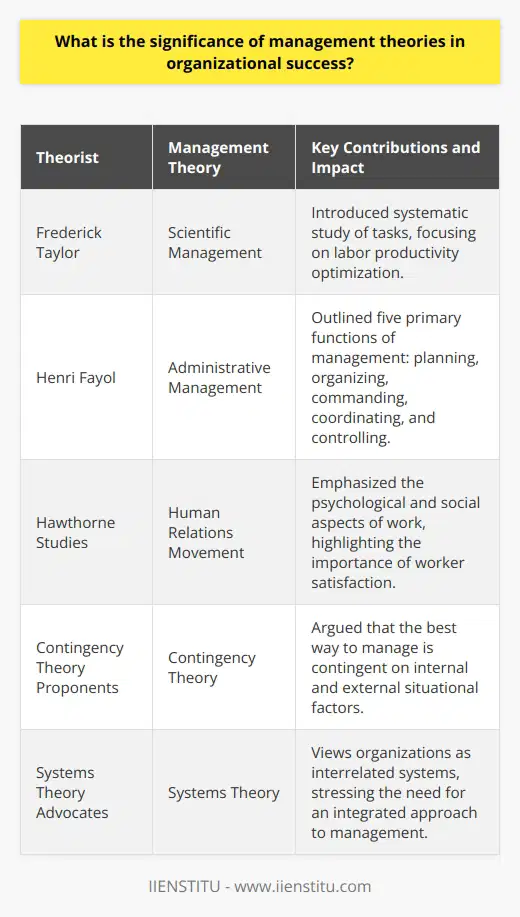
How have management theories evolved over time, and what are the primary factors influencing their development?
Evolution of Management Theories
In the course of history, management theories have evolved substantially. Initially, management theories focused on organizational structure and efficiency. These early theories, such as Frederick Taylor's Scientific Management and Henri Fayol's Administrative Theory, aimed to increase productivity and streamline operations.
Influence of Globalization
Over time, the forces shaping management theories have shifted as well. A notable change occurred due to globalization, which emphasized the importance of adapting to diverse environments and cultures. This shift led to the development of new management theories such as Geert Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions and the Contingency Model. These approaches focused on finding effective management practices that suited distinct business contexts, considering factors such as cultural values, environmental uncertainty, and organizational complexity.
Role of Behavioral Sciences
Another key driver in the evolution of management theories is the increasing influence of behavioral sciences. The incorporation of human psychology and social aspects in management theories has contributed to the development of enriched organizational cultures and employee engagement. The Human Relations Movement, spearheaded by Elton Mayo and Abraham Maslow, paved the way for considering the intrinsic needs and motivations of employees in management practices. Additionally, Douglas McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y provided insights into the significance of adapting leadership styles to the needs and expectations of employees.
Technological Advancements
In recent decades, technological advancements have played a significant role in shaping management theories. The advent of Information Technology and its integration into business operations has given rise to theories that emphasize the importance of innovation, flexibility, and adaptability. Notable among these are the Knowledge-based Theory and the Learning Organization, which focus on leveraging organizational knowledge and learning as essential competitive advantages.
Impact of Sustainability
More recently, societal concerns about environmental sustainability and social responsibility have also influenced the development of management theories. It has now become vital for organizations to incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their strategies to maintain their competitiveness and ensure long-term success. This shift has led to the emergence of sustainable and ethical management theories such as the Triple Bottom Line Approach and Stakeholder Theory.
In summary, the evolution of management theories can be primarily attributed to shifting societal expectations, globalization, advancements in technology, and an increased understanding of human psychology. These factors have successively enriched organizational practices, transforming management approaches from solely focusing on productivity and efficiency to incorporating elements such as cultural adaptability, employee motivation, innovation, sustainability, and social responsibility.
In what ways do various management theories complement or contradict one another in addressing contemporary organizational challenges?
Complementarity Among Management Theories
Various management theories have been proposed to address contemporary organizational challenges effectively. One way that these theories complement one another is through their application within different organizational contexts. For instance, classical management theories, such as scientific management and bureaucratic management, emphasize standardization and efficiency, making them suitable for large, well-established organizations. In contrast, contemporary theories, such as contingency theory and systems theory, focus on adaptability and interconnectedness, making them suitable for smaller organizations and those operating in rapidly changing environments. By addressing specific organizational needs and contexts, each management theory can contribute valuable insights to enhance organizational performance.
Contradictions Between Management Theories
Notwithstanding these complementarities, some management theories contradict one another regarding the nature of human behavior and the most effective ways to manage it. For example, classical theories like scientific management view employees as primarily motivated by economic incentives and consider their interests separate from those of the organization. In contrast, human relations theories acknowledge that social and psychological factors play a significant role in employee motivation and emphasize the importance of maintaining a positive organizational culture. These contrasting perspectives on employee motivation lead to different prescriptions for management strategies, thereby contradicting one another.
Bridging Conflicting Management Approaches
To reconcile these contradictions and capitalize on the strengths of each theory, managers may choose to employ a situational approach. By recognizing that no single management theory can address every challenge a contemporary organization might face, situational management accounts for the benefits and limitations of various theories and tailors them to particular circumstances. In doing so, it encourages managers to apply a flexible, context-sensitive approach to address the diverse needs of their organizations.
In conclusion, while some management theories may complement one another in addressing contemporary organizational challenges, others can offer contradictory perspectives that need to be reconciled. In each case, the effectiveness of the theory depends on its relevance and application within specific organizational contexts. By adopting a situational approach, managers can tap into the insights of various management theories, combining their strengths and overcoming their limitations, to address the complex challenges that modern organizations face.
What is management theory and why is it important?
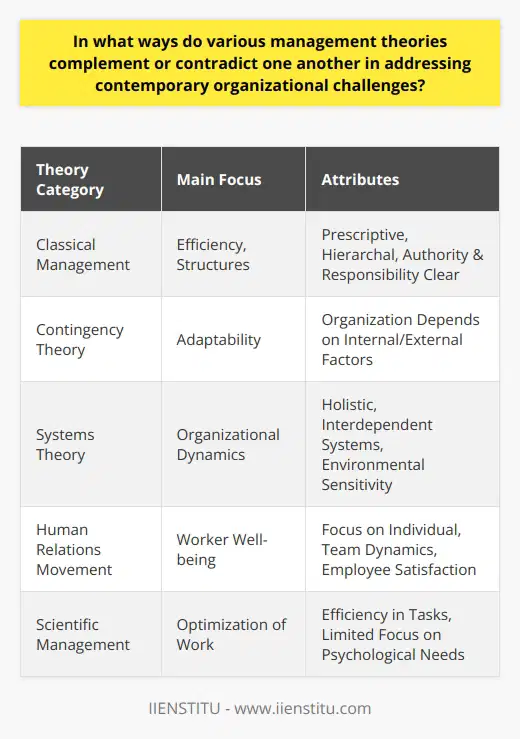
Understanding Management Theory
Management theory is a collection of ideas and concepts that focus on understanding how organizations function and how individuals within them interact to achieve organizational objectives. These theories have evolved over time to provide a comprehensive understanding of organizational behavior, leadership, decision-making, and employee motivation.
Importance of Management Theory
The significance of management theory lies in its ability to address a range of issues impacting organizations and their stakeholders. By providing practical solutions to these challenges, these theories enable managers to develop effective strategies for achieving organizational success.
Enhancing Organizational Performance
By understanding various management theories, leaders can learn how to successfully navigate complex organizational environments. This knowledge enables them to identify potential areas of improvement and implement the necessary changes to enhance overall organizational performance.
Guiding Leadership Styles
Different leadership styles may be more effective in particular situations. Management theory provides insights into these styles, allowing leaders to adapt their approach depending on the context, ultimately leading to better decision-making and increased productivity.
Empowering Employees
Management theories, such as those focusing on employee motivation and job satisfaction, highlight the relationships between employees and their work environments. Managers can enhance the well-being of their workforce by being aware of these relationships and taking actions to promote a positive work environment.
Effective Decision-Making
One of the essential aspects of running a successful organization is making effective decisions. Through the study of management theory, leaders gain a better understanding of the factors impacting decision-making processes, enabling them to make informed decisions that benefit their organizations.
Innovation and Adaptation
The dynamic nature of the business world demands that organizations continuously adapt to stay competitive. Management theory helps leaders understand emerging trends, equipping them with the tools to drive innovation and respond to changes in the market effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, management theory provides a foundation for understanding various aspects of organizational behavior, leadership, and decision-making. By applying the concepts and insights derived from these theories, leaders are better prepared to navigate the complexities of the business world, empowering them to achieve sustained organizational success.
What are the 3 main theories of management?
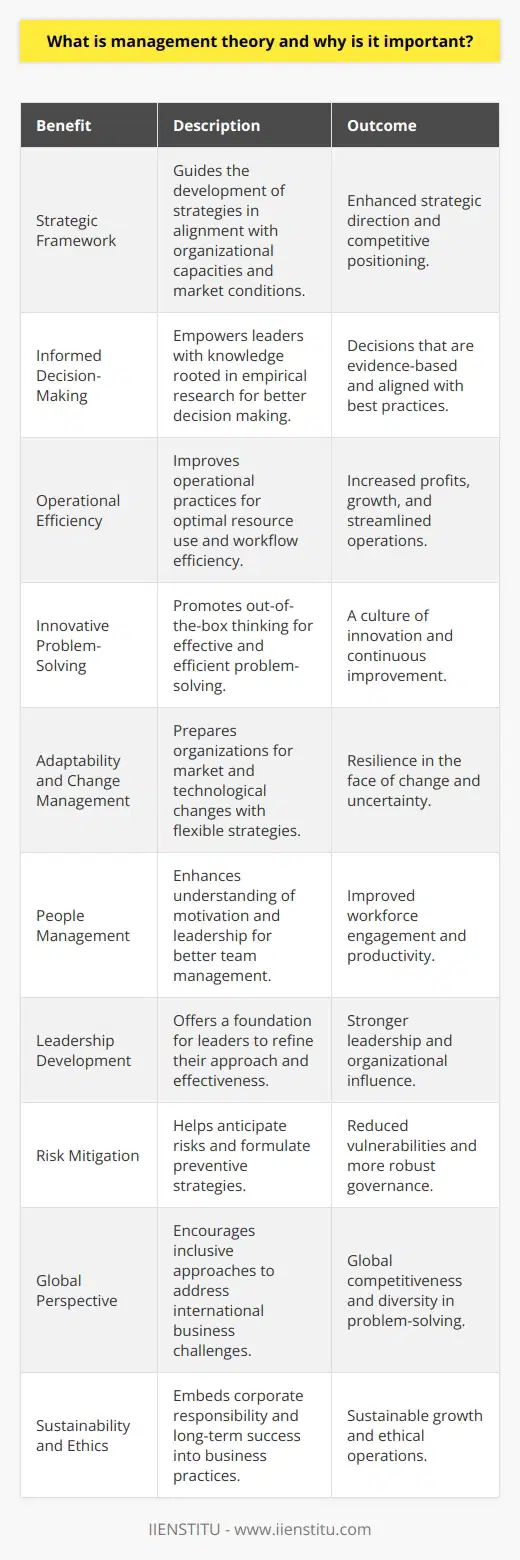
Scientific Management Theory
One of the main theories of management is the Scientific Management Theory, proposed by Frederick Winslow Taylor in the early 20th century. According to this theory, organizations can achieve maximum efficiency by breaking down work into simplified tasks and optimizing the performance of each task. Taylor also emphasized the importance of selecting and training workers to perform these tasks most effectively.
Human Relations Theory
Another dominant theory in the field of management is the Human Relations Theory, primarily advanced by Elton Mayo and his colleagues through the famous Hawthorne Studies conducted in the late 1920s and early 1930s. This theory postulates that employees' motivation, satisfaction, and productivity are affected by their social environment, personal relationships, and job rewards. Therefore, management must foster a supportive work atmosphere and recognize employees' individual needs through communication, feedback, and positive reinforcement.
Contingency Theory
Lastly, Contingency Theory is a fundamental theory of management that suggests there is no one-size-fits-all approach to running an organization. Developed by researchers such as Joan Woodward and Paul Lawrence, this theory contends that the most effective management style depends on numerous factors, including organizational size, structure, culture, resources, and external environment. By assessing these factors, managers can tailor their strategies to achieve maximum efficiency, effectiveness, and adaptability.
In conclusion, the three primary theories of management—Scientific Management Theory, Human Relations Theory, and Contingency Theory—each offer unique perspectives on the diverse factors that contribute to the success of an organization. By understanding these theories, managers can employ the most suitable management strategies for their specific situations to optimize their organizations' performance.
What are the 5 theories of management?
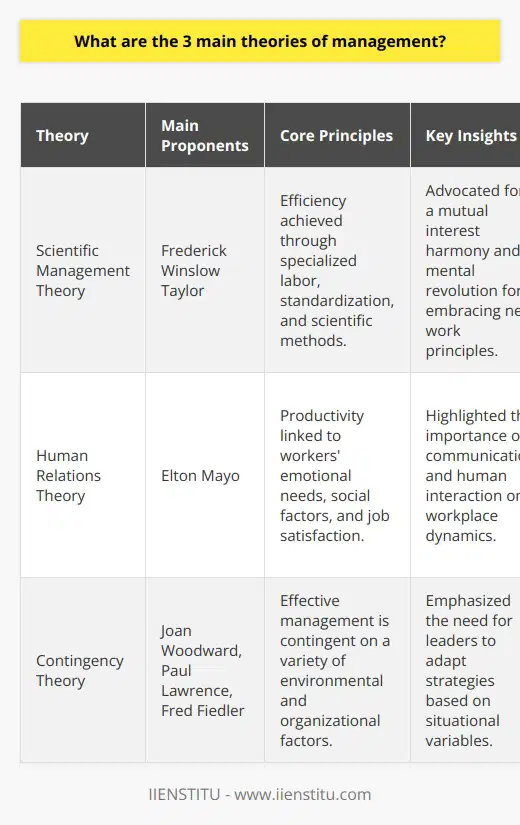
Scientific Management Theory
The Scientific Management Theory, founded by Frederick Taylor, revolves around the concept of maximizing efficiency within an organization. Taylor believed that the implementation of workflow processes and standardized practices could improve productivity, and that management could use time and motion studies to optimize work.
Bureaucratic Management Theory
Max Weber's Bureaucratic Management Theory emphasizes the establishment of a hierarchical structure to maintain order and ensure clear separation of responsibilities. Weber considered organizational consistency and adherence to rules as essential for efficiency, thus advocating for a centralized authority that disciplines and values meritocracy.
Human Relations Theory
In contrast, the Human Relations Theory, introduced by Elton Mayo, prioritizes the social aspects of management. Mayo argued that employees are motivated by more than just financial incentives, and that fostering positive interpersonal relationships within the workplace can enhance employee satisfaction and productivity levels.
Systems Theory
The Systems Theory of management examines organizations as complex, interconnected systems. Developed by Ludwig von Bertalanffy, this approach emphasizes the importance of understanding the relationships between various components of a business, such as processes, goals, and functions, to achieve organizational equilibrium and effectiveness.
Contingency Theory
Based on Fiedler's Contingency Theory, management effectiveness depends on matching the leadership style and situational context. According to this theory, there is no universally applicable approach to management; instead, leaders should adapt their strategies based on specific environmental factors such as employee competence, organizational culture, and external constraints.
In conclusion, understanding these distinct management theories can provide invaluable insights for organizations seeking to enhance their overall effectiveness. By considering various approaches tailored to different contexts, organizations can select and implement optimal management strategies to suit their unique needs and achieve their objectives.
What are the 4 major management theories?
Four Major Management Theories
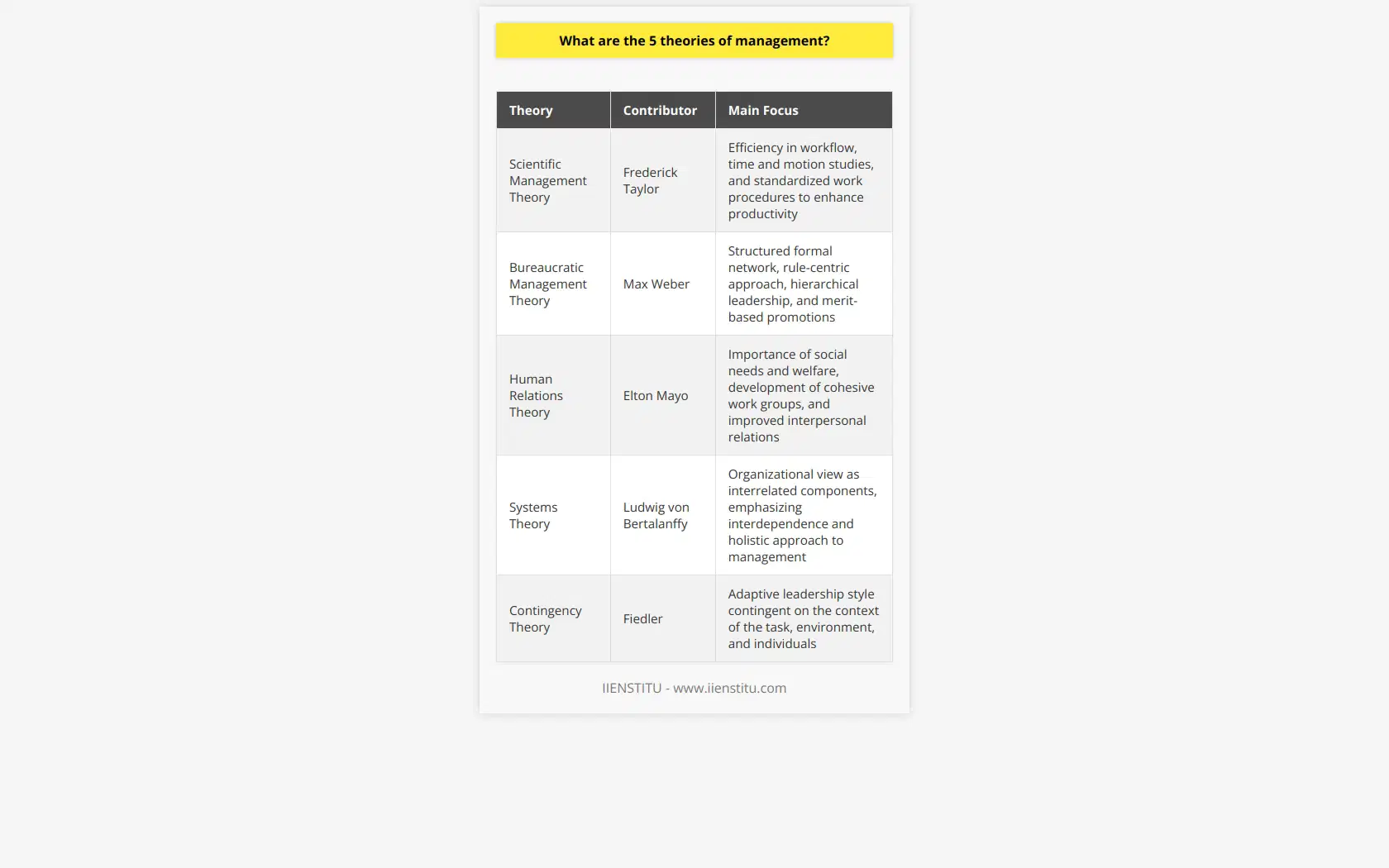
Classical Theory of Management
The first major management theory is the Classical Theory of Management, which originates from the early 19th century. It comprises three subprocesses: Scientific Management, Administrative Management, and Bureaucratic Management. This theory emphasizes efficiency and productivity, relying on task specialization, authority, and centralization in decision-making processes.
Human Relations Theory of Management
The Human Relations Theory, which emerged in the 1920s and 1930s, focuses on employee motivation and job satisfaction to improve the effectiveness of a company. This approach underscores the importance of interpersonal skills, informal work relationships, and communication to maintain a positive work environment. Management responsiveness is vital as workers invest emotionally in their jobs.
Contingency Theory of Management
Developed in the 1950s and 1960s, Contingency Theory of Management recognizes that different management styles suit various types of organizations, depending on factors such as size, technology, and environment. This theory stresses the adaptability of leadership as managers are encouraged to assess and tailor their approach to fit each unique situation effectively.
Systems Theory of Management
The Systems Theory, originating in the 1970s, considers the organization as a whole, focusing on interdependencies among different components or subsystems. It highlights the importance of understanding the complex interactions and relationships within the organization, as well as the external environment affecting it. Thus, effective operation and adaptability to change are crucial to an organization's success.
In conclusion, the four major management theories – Classical, Human Relations, Contingency, and Systems Theory – offer distinct approaches to management based on factors such as productivity, workforce motivation, adaptability, and interconnectivity. Successful organizations can benefit from understanding and applying these diverse theories to navigate complex and ever-changing business environments.
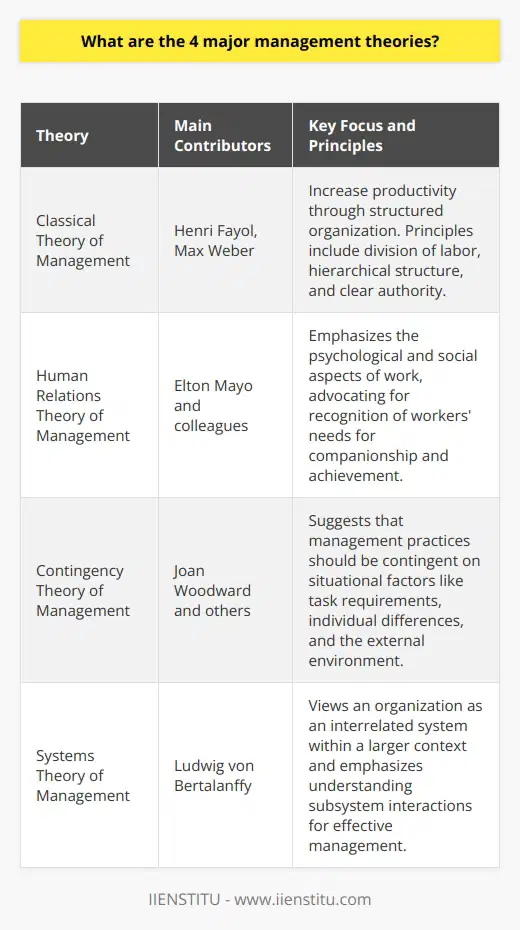
How do management theories contribute to decision-making processes and problem-solving techniques within organizations?
Management Theories and Decision-making Processes
Management theories play a crucial role in organizations' decision-making processes and problem-solving techniques. By providing conceptual frameworks and practical guidelines, these theories enable managers to tackle complex issues and make informed decisions.
Classical Approach and Rational Decisions
The classical management approach focuses on rational and systematic decision-making. It argues that by analyzing all available information, weighing alternatives, and identifying the most efficient course of action, managers can optimize their decisions and solve problems effectively. This approach emphasizes planning, forecasting, and quantitative analysis as essential tools for managers to navigate uncertainties and achieve desired outcomes.
Human Relations and Social Factors
Human relations theories emphasize the importance of social factors and interpersonal relationships in decision-making processes. They postulate that through effective communication, collaboration, and motivation, managers can create harmonious work environments and improve organizational performance. By addressing employees' psychological and emotional needs, managers can foster trust and commitment, encouraging problem-solving abilities and enhancing collective decision-making capacity.
Contingency Theory and Adaptable Strategies
The contingency theory posits that there is no single best way to make decisions or solve problems, instead stressing the importance of adapting strategies to specific situations, contexts, and environmental factors. This perspective encourages managers to consider various alternatives and adopt flexible approaches based on the nature of the problem, the needs of the organization, and the skills of the available personnel.
Systems Thinking and Holistic Perspectives
Systems thinking emphasizes the interconnectedness and interdependencies of various elements in an organization. This approach calls for a comprehensive understanding of the organization as a whole, recognizing the consequences of decisions and problem-solving efforts across different departments and operations. By considering the organization as a system, managers can envisage the broader impact of their decisions and prioritize actions that not only address immediate concerns but also support long-term objectives.
In conclusion, management theories provide organizations with valuable insights and methods for improving their decision-making processes and problem-solving techniques. By drawing upon classical approaches, human relations, contingency theory, and systems thinking, organizations can cultivate a diverse range of strategies that address their unique situations and contribute to their overall success.
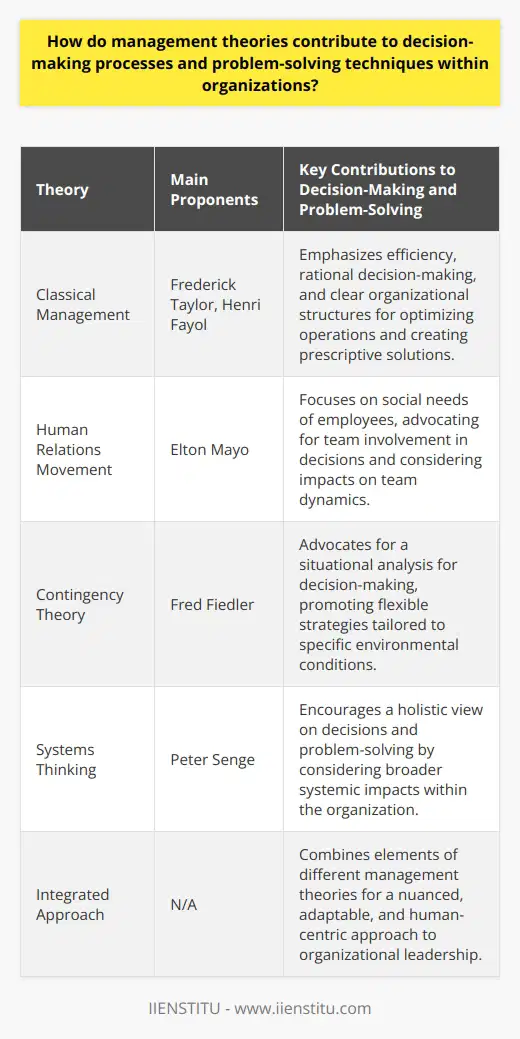
What is the relationship between management theories and leadership styles in enhancing organizational performance?
Management Theories and Leadership Styles
The relationship between management theories and leadership styles is a vital factor in enhancing organizational performance. Management theories provide a foundation for understanding how managers operate, while leadership styles dictate the manner in which leaders guide their teams. Together, these two aspects contribute significantly to the effectiveness and success of an organization.
Foundational Management Concepts
Management theories, such as scientific management, human relations theory, and contingency theory, present various principles that guide managers in their roles. These theories focus on topics like work efficiency, employee motivation, and adapting to different situations. By following the principles derived from these theories, managers can make better decisions, optimize resource utilization, and ultimately improve organizational performance.
Diverse Leadership Approaches
Leadership styles, on the other hand, encompass the diverse approaches that leaders take when directing their teams. Some common leadership styles include autocratic, democratic, transformational, and transactional styles. These styles impact how leaders communicate, motivate, and shape the culture within their organizations. By adopting a suitable leadership style, leaders can enhance team dynamics, boost morale, and foster an environment that drives success.
Matching Theory and Style for Optimal Results
To maximize organizational performance, it is crucial to recognize the connection between management theories and leadership styles. The choice of leadership style should complement the principles established by management theories relevant to the organization. For instance, a company that prioritizes employee motivation might benefit from a transformational leader who can inspire team members and align them with the company's vision.
Adapting to Change and Evolving Conditions
Furthermore, it is important for managers and leaders to adapt their approach based on the evolving needs of the organization. This may involve adjusting their leadership style or adopting new elements from various management theories. The ability to adapt and align with the changing priorities of the company can further enhance the organization's performance.
In conclusion, the relationship between management theories and leadership styles plays a significant role in enhancing organizational performance. By understanding the management principles and adopting suitable leadership styles, managers and leaders can create an environment that fosters success and drives the organization towards achieving its goals.
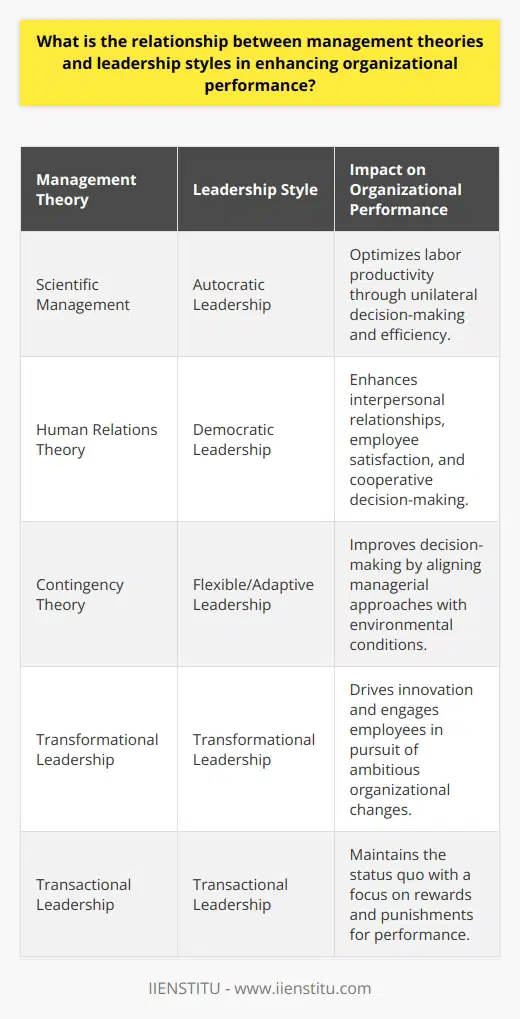
What is the role of management theories in fostering innovation and adaptability among organizations?
Role of Management Theories in Innovation
Management theories play a crucial role in fostering innovation and adaptability among organizations by providing frameworks and guidelines for decision-making and strategy formulation. These theories, such as Scientific Management, Human Relations, and Contingency theories, shape the managerial mindset, enabling leaders to recognize what is needed for change and growth within the organization.
Scientific Management Theory and Innovation
Scientific Management Theory emphasizes the significance of research, experimentation, and evidence-based practices. It supports organizations in developing systematic approaches to problem-solving and process improvements, which promote efficiency and cost-saving. By utilizing this theory, organizations can effectively identify gaps, optimize processes, and foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
Human Relations Theory and Adaptability
The Human Relations Theory places importance on the psychological and emotional aspects of human resources within the organization. This theory encourages managers to create a healthy work environment by focusing on employee morale, motivation, and job satisfaction. By nurturing these elements, organizations can effectively develop a more adaptable workforce, enabling them to respond quickly to changes in their business environment and retain a competitive advantage.
Contingency Theory and Responsive Strategy
Contingency Theory asserts that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing an organization. This theory suggests that organizations should adapt their management style based on situational factors, such as the complexity of tasks, the external environment, and organizational structure. Adopting a flexible management approach enables organizations to navigate the uncertainty and complexities of the business landscape while proactively embracing opportunities for innovation and adaptability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, management theories provide a foundation for organizations to leverage innovation and adaptability. By integrating principles from these theories, organizations can create the conditions necessary for fostering a culture of change, encouraging employees to embrace new ideas, and adapting to the evolving business environment. As a result, organizations will be able to sustain their competitive advantage, achieve long-term success, and be responsive to the demands of a dynamic global market.
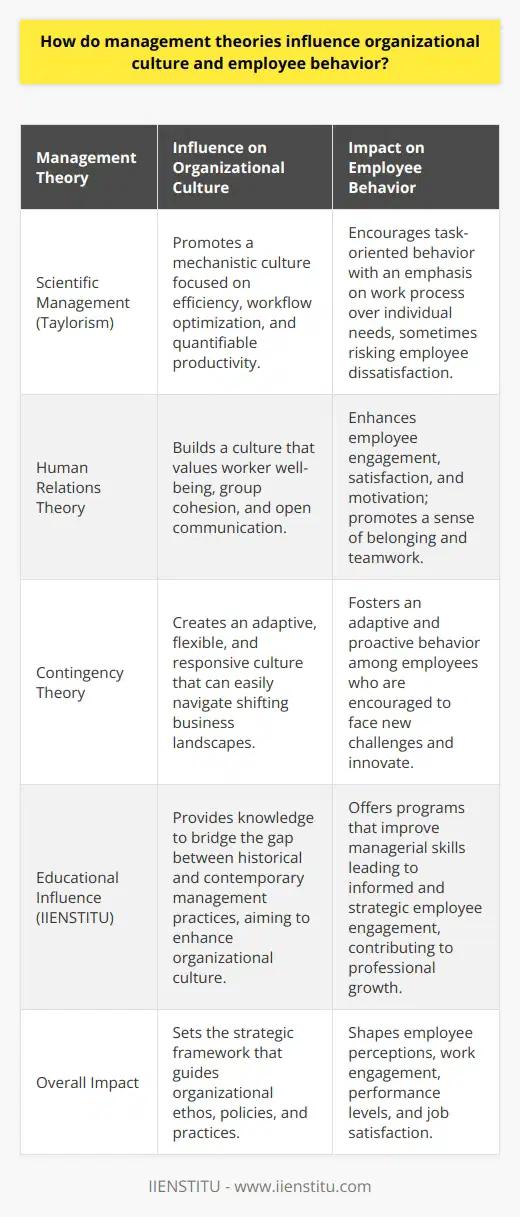
How do management theories influence organizational culture and employee behavior?
Management Theories Impact on Organizational Culture
Management theories provide a framework for understanding and influencing organizational culture and employee behavior. These theories offer insights into how managers can create an environment that promotes productivity, employee satisfaction, and organizational success. By implementing practices derived from various management theories, organizations can develop a culture that aligns with their objectives and values.
Taylorism and its Efficiency Focus
Among the earliest management theories is Taylorism, also referred to as Scientific Management. Developed by Frederick Taylor, this theory emphasizes efficiency and productivity in the workplace through rationalization and standardization of tasks. Taylorism has influenced organizational culture by instilling the importance of precision and time-management in employees, which may improve overall performance. However, excessive focus on efficiency can lead to employee burnout and disengagement, reducing the positive impact on organizational culture.
Human Relations Theory and Employee Satisfaction
The Human Relations Theory, developed by Elton Mayo, emerged as a response to the shortcomings of Taylorism. This theory highlights the social aspects of work, emphasizing the importance of employee satisfaction, communication, and teamwork. By implementing practices inspired by Human Relations Theory, managers can foster a positive and supportive work environment, which can lead to increased employee motivation, loyalty, and collaboration. This approach can contribute to a more resilient and sustainable organizational culture.
Contingency Theory and Adaptive Management
Contingency Theory posits that there is no one-size-fits-all management approach; instead, it suggests that the best management style depends on the specific situation and organizational context. By employing Contingency Theory, managers can adopt a more flexible and adaptive approach to decision-making, considering the unique circumstances and requirements of each scenario. This adaptability can promote a culture of innovation, creativity, and continuous learning, which can enhance employee behavior and overall organizational success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, management theories significantly influence organizational culture and employee behavior. By exploring different theories and their implications, organizations can develop strategies and practices that promote a positive work environment, sustainable performance, and competitive advantage in the market. However, managers must remain vigilant and adaptive, adjusting their approach as needed to respond effectively to the ever-changing landscape of modern businesses.
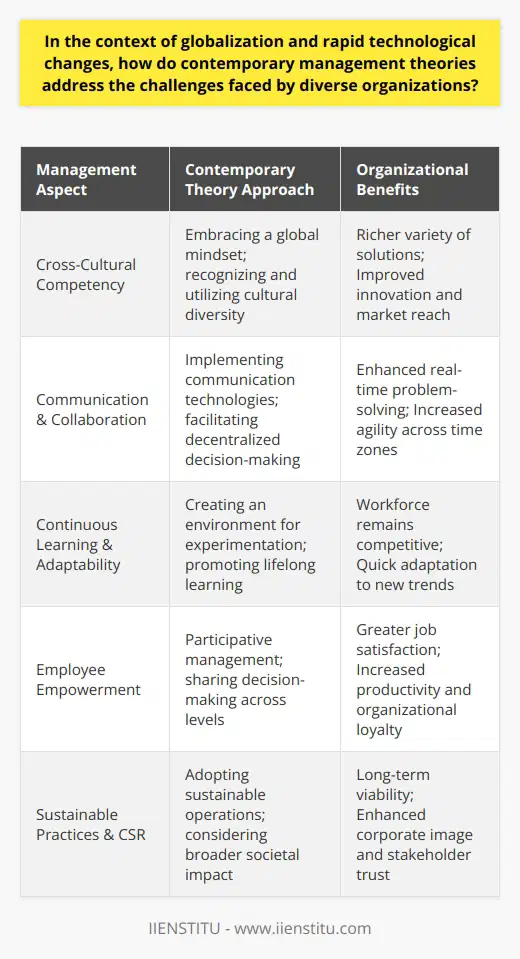
In the context of globalization and rapid technological changes, how do contemporary management theories address the challenges faced by diverse organizations?
Contemporary Management Theories
In response to the challenges posed by globalization and rapid technological advancements, contemporary management theories have evolved to address the complexities faced by diverse organizations. These modern paradigms provide guidance for managing diverse teams, leveraging new technologies and adapting to the dynamic environment of today's business world.
Diversity and Inclusivity
One of the prominent ways contemporary management theories address diversity is by advocating for inclusive work environments. Managers implement policies and practices that encourage open communication, knowledge sharing, and mutual respect among employees with different backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives. Inclusivity fosters innovation and creativity, as it allows organizations to harness the potential of their diverse workforce.
Emphasis on Communication and Collaboration
As organizations operate across borders, effective communication and collaboration have become essential in overcoming cultural, language, and time-zone barriers. Contemporary management theories highlight the role of active listening, feedback, and interpersonal skills as vital components in bridging gaps among team members. By fostering a supportive and communicative work culture, managers can maximize their teams' collective intelligence and improve decision-making.
Adaptability and Continuous Learning
Modern management theories emphasize the need for adaptability and continuous learning in response to technological shifts and global market fluctuations. Organizations must develop a culture of learning, in which employees are encouraged to adapt to changing environments and acquire new skills. Managers must be proactive in identifying opportunities for innovation and creating platforms for employees to exchange ideas and best practices.
Empowerment and Employee Engagement
Contemporary theories also focus on empowering employees and fostering engagement, as this results in higher job satisfaction and better overall performance. Managers should provide autonomy to employees, enabling them to take ownership of their tasks and have greater control over their work. By creating an environment of trust and open communication, organizations can improve employee commitment and reduce turnover.
In conclusion, contemporary management theories have adapted to tackle the challenges faced by diverse organizations in an era of globalization and rapid technological advancements. They stress the importance of embracing diversity and inclusivity, enhancing communication and collaboration, promoting adaptability and continuous learning, and empowering employees in order to stay relevant and thrive in the modern business landscape.
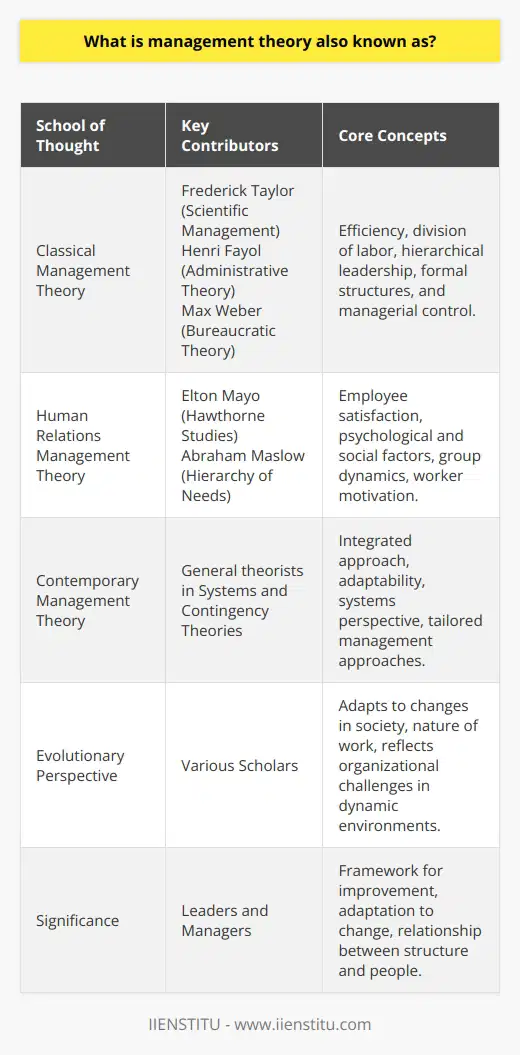
What is management theory also known as?
Overview of Management Theory
Management theory, also known as organizational theory or administrative theory, encompasses a range of principles and frameworks aimed at optimizing an organization's overall operations and performance. It focuses on understanding the interactions between various organizational components and explores different approaches to addressing challenges and achieving goals within an organization.
Evolution of Management Theory
Throughout history, theorists have proposed multiple models and frameworks that form the foundation of modern management theory. These theories can be broadly categorized into classical, human relations, and contemporary management theories, each with unique characteristics and emphases on various aspects of organizational management.
Classical Management Theory
The classical management theory comprises concepts such as scientific management, bureaucratic management, and administrative management, which mainly focus on optimizing productivity and efficiency. For instance, scientific management emphasized the importance of breaking down tasks into their simplest components to streamline processes, whereas bureaucratic and administrative management focused on creating clearly defined hierarchies, divisions of labor, and standardized procedures.
Human Relations Management Theory
The human relations approach to management theory emerged as a counterpoint to the classical theorists, emphasizing the role of interpersonal relationships and the human element in organizational success. It maintains that factors such as employee motivation, collaboration, and job satisfaction can greatly impact productivity and overall performance. The Hawthorne Studies and Maslow's hierarchy of needs are considered foundational works in this field, highlighting the importance of understanding the psychological and sociological aspects of work-related behaviors.
Contemporary Management Theory
Contemporary management theories integrate insights from classical and human relations approaches to create more holistic and flexible frameworks for managing organizations. Systems theory, for example, considers organizations as complex, interdependent systems and explores how each component works together to achieve common goals. Additionally, contingency theory emphasizes the importance of adapting management styles and strategies to suit varying internal and external factors, such as market conditions, organizational culture, and employee skillsets. The implementation of these modern theories helps organizations to navigate the challenges of today's highly competitive and constantly changing business landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, management theory, also known as organizational or administrative theory, is a critical field of study that aims to enhance organizational performance by understanding and addressing the various components and processes within businesses. By evaluating and implementing relevant principles, organizations can constantly optimize their operations and adapt to new challenges on their journey towards success.
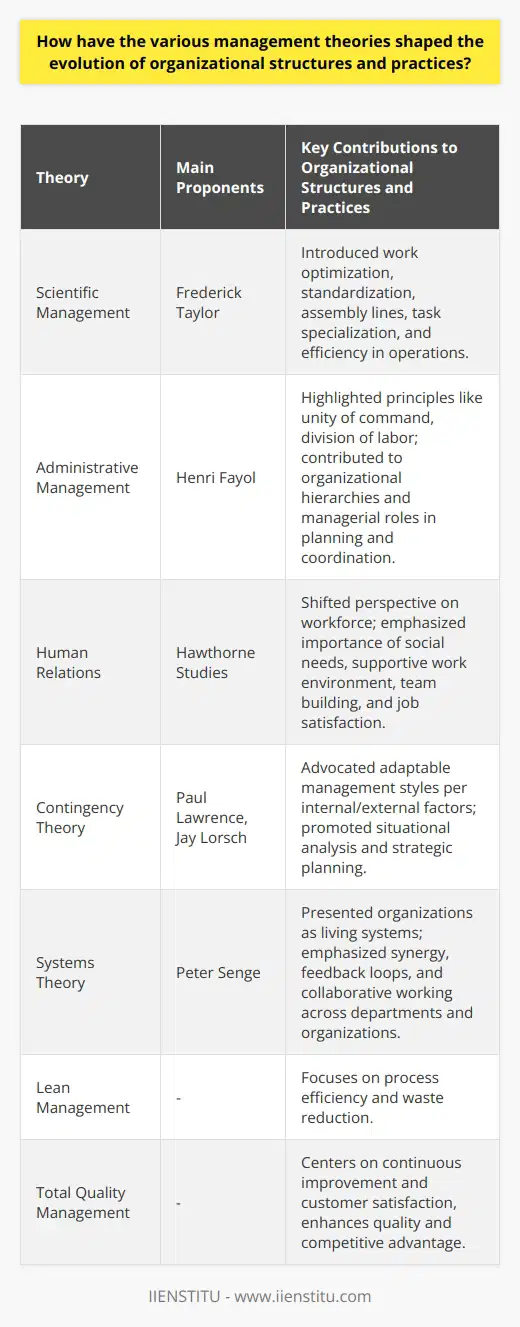
How have the various management theories shaped the evolution of organizational structures and practices?
Management Theories and Organizational Evolution
Classic Theories' Influence
The development of organizational structures and practices has been significantly impacted by various management theories. The classical theories such as Scientific Management, developed by Frederick Taylor, and Administrative Management, proposed by Henri Fayol, laid the foundation for modern organizational structures. These theories emphasized specialization, division of labor, and hierarchical structures which increased efficiency and productivity.
Human Relations Approach
The Human Relations approach, pioneered by the Hawthorne Studies and Elton Mayo, shifted the focus from task efficiency to employee satisfaction. This new perspective regarded human behavior, motivation, and social interactions as crucial components in organizational success. Consequently, organizations began to prioritize employee well-being, better supervision, and improved communication in their practices.
Contingency Theory and Adaptability
The Contingency Theory, developed in the 1960s by Paul Lawrence and Jay Lorsch, highlighted the importance of flexibility in organizations. It acknowledged that different methods of management would be effective under different circumstances. This theory promoted adaptable and responsive organizational structures, leading to the emergence of matrix, network, and team-based organizations.
Systems Theory and Collaboration
The Systems Theory, exemplified in works by Peter Senge and others, conceptualized organizations as a collection of interrelated components working together to achieve a common goal. This holistic approach fostered collaboration, cross-functional teams, and the integration of complex networks beyond traditional organizational boundaries.
Contemporary Management Approaches
More recently, globalization, technological advancements, and increased competition have led to the emergence of various contemporary management approaches. These include Lean Management, Total Quality Management, and Knowledge Management. Altogether, these theories have nurtured a culture of innovation, process improvement, and knowledge sharing among organizations.
In conclusion, the evolution of organizational structures and practices can be traced back to the influence of several management theories. These theories have offered unique insights and brought about significant changes in the way organizations operate and function. By understanding the impact of these theories, organizations can develop more effective management practices and strategies tailored to their unique circumstances and environmental demands.
What contextual factors and external forces have influenced the development and transformation of management theories over time?
Historical Context and Societal Changes
The transformation of management theories has been a product of the dynamic historical context and societal changes. The industrial revolution, for instance, saw the emergence of classical management theories such as scientific management, administrative principles, and bureaucratic management. These theories aimed to improve productivity through specialization, control, and hierarchical structures in response to the growing demand for mass production and expansion of organizations.
Technological Advancements
Moreover, the continuous technological advancements, such as the rise of automation and digital solutions, have shaped the understanding of management practices. These developments demand constant adaptation, innovation, and learning to remain competitive. As a result, modern management theories, like knowledge management, emphasize creativity, intellectual capital, and the significance of innovation in driving organizational success.
Cultural and Demographic Shifts
Cultural and demographic shifts in the workforce have also played a crucial role in the development of management theories. The increasing cross-cultural interactions and diversification of the workforce necessitate more effective communication and understanding of different cultural perspectives. Consequently, contemporary models like the multi-cultural management theory, focused on building cultural awareness and responsiveness, have evolved.
Globalization and Economic Factors
Similarly, globalization and economic factors have also markedly influenced management theories. The global marketplace creates fierce competition and necessitates a strategic approach to management. Hence, strategic management theories, such as the resource-based view and competitive advantage theory, have gained traction to ensure long-term survival and success in the global market.
Regulatory and Legal Framework
The regulatory and legal framework within which organizations operate significantly affect management practices. Compliance with laws, policies, and guidelines, such as labor laws, environmental regulations, and corporate governance guidelines, has informed the development of theories like corporate social responsibility and sustainable management.
In conclusion, an array of contextual factors and external forces have contributed to the continuous evolution of management theories. As we navigate through the ever-changing business environment, it is vital to remain aware of these influences and adapt accordingly to ensure success in management practices.

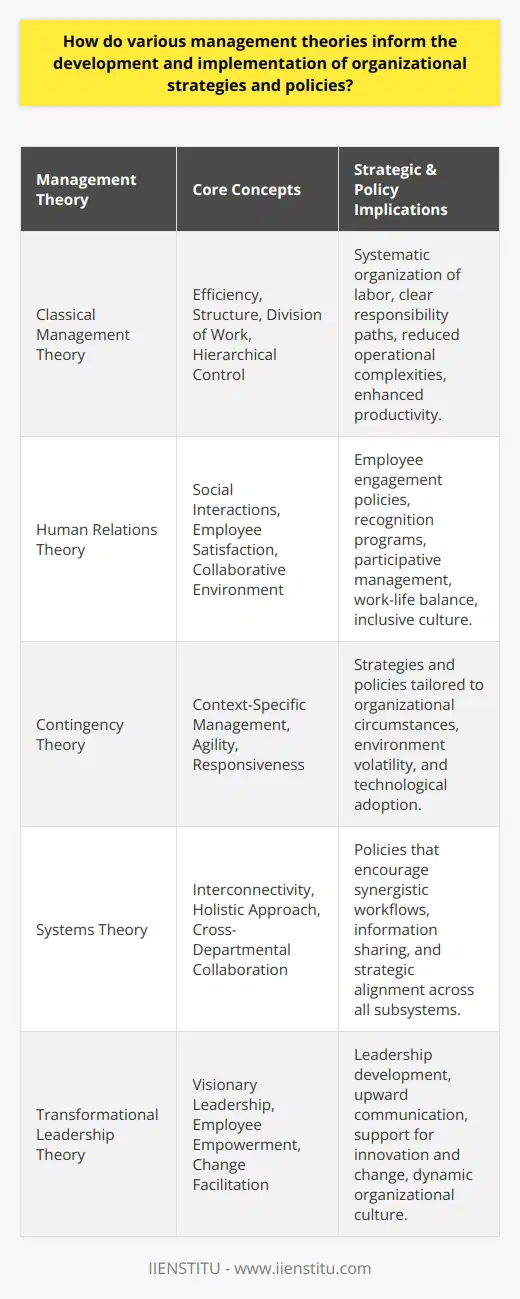
What is the relationship between the evolution of management theories and corresponding changes in the nature of work and the workforce?
Evolution of Management Theories and Workforce Changes
The relationship between the evolution of management theories and corresponding changes in the nature of work and the workforce is interconnected and influential. As work environments and employee needs have shifted over time, management theories have evolved to address and adapt to these changes, helping organizations remain competitive and efficient.
Classical Management Approaches
During the Industrial Revolution, organizations prioritized efficiency and productivity, leading to the development of classic management theories, such as Taylor's Scientific Management and Fayol's Administrative Theory. These theories emphasized specialization, hierarchy, and bureaucratic structures in the workplace. These approaches recognized the dominance of manual labor and focused on optimizing performance through standardized tasks and strict supervision.
Human Relations Movement
As the demand for white-collar jobs grew in the 20th century, the nature of work shifted from manual labor to knowledge-based tasks. This shift highlighted the importance of employee satisfaction and motivation, leading to the emergence of the Human Relations Movement. Theories like Elton Mayo's Hawthorne Studies and Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs emphasized the significance of positive work environments, interpersonal relationships, and employee recognition as factors impacting productivity.
Contingency Theory
With increasing globalization and diversification, the workforce became more complex and heterogeneous. Contingency Theory emerged as an adaptive approach, positing that no single management style is universally applicable. Instead, this theory contends that effective management depends on the alignment between an organization's structure, leadership style, and the internal and external factors affecting work processes. This approach recognizes the importance of adaptability and flexibility in addressing diverse workforce needs and evolving work conditions.
Knowledge Management Era
In the information age, the nature of work has continued to shift more significantly toward knowledge-based tasks and intellectual capital management. Theories like Nonaka's knowledge creation process and Senge's learning organization emphasize the importance of continuous learning, innovation, and information sharing across the organization. These theories recognize the need for organizations to harness the collective intelligence and creative potential of their workforce to remain competitive in a rapidly changing environment.
Conclusion
In summary, the evolution of management theories is closely linked to the consequential changes in the nature of work and the workforce. Over time, management approaches have moved from a focus on specialization and hierarchy to an emphasis on adaptability, employee satisfaction, and continuous learning. As organizations continue to face complex challenges and environments, management theories must continue to evolve to address the dynamic needs of the workforce and promote organizational growth and success.
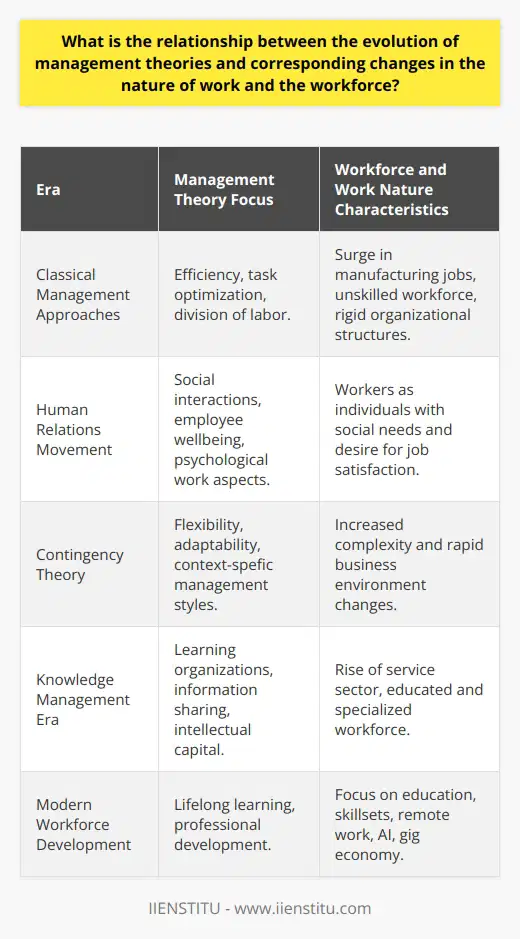
How do various management theories inform the development and implementation of organizational strategies and policies?
Management Theories and Organizational Strategies
Understanding Management Theories
Various management theories play a crucial role in shaping organizational strategies and policies. These theories provide frameworks for managers to analyze and implement effective decision-making processes. They assist in streamlining the allocation of resources, enhancing organizational structure, developing employee motivation schemes, and facilitating communication within the organization.
Classical Management Theory
The classical management theory, which emerged during the Industrial Revolution, focuses on improving the efficiency of work processes and organizational structures. By adopting principles of scientific management, managers can optimize productivity and reduce waste. This theory informs the development of strategies that emphasize efficient division of labor, standardization of tasks, and hierarchical decision-making.
Human Relations Theory
The human relations theory, initiated by the Hawthorne Studies in the 1920s, underscores the importance of interpersonal relationships and employee satisfaction in the workplace. This approach suggests that motivated and fulfilled employees contribute to a more productive and efficient organization. Application of this theory informs strategies that prioritize employee welfare, open communication, and the establishment of a positive work environment.
Contingency Theory
The contingency theory, which gained popularity in the 1960s, posits that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to management. Instead, the effectiveness of a management style depends on the specific situation and context. By considering various internal and external factors, this theory helps managers adopt a flexible and adaptable approach in developing organizational strategies and policies.
Systems Theory
The systems perspective on management, which emerged during the mid-20th century, views organizations as complex and adaptive systems. According to this theory, organizations consist of interrelated and interdependent components that function in harmony to achieve common goals. Systems theory informs organizational strategies by emphasizing the importance of coordination, integration, and communication between various departments and units.
Transformational Leadership Theory
The transformational leadership theory, which has gained prominence in recent decades, focuses on the role of leaders in inspiring and motivating employees to achieve extraordinary results and exceed expectations. This theory guides the development of strategies and policies that encourage vision-driven leadership, employee empowerment, and continuous learning and innovation.
Conclusion
In summary, various management theories inform the development and implementation of organizational strategies and policies. By understanding these theories, managers can design effective systems, structures, and processes that adapt to dynamic conditions and promote organizational growth and success. Each theory offers valuable insights that contribute to an organization's ability to make informed decisions, maximize resources, and foster a positive work environment.
In light of emerging trends such as remote work and environmental sustainability, how are management theories adapting to address the evolving needs and priorities of organizations?
Adapting Management Theories for Remote Work
As remote work becomes increasingly prevalent, management theories are adapting to address the evolving needs of organizations. One such adaptation involves a shift from traditional hierarchical structures to more decentralized models, promoting increased autonomy and self-management among employees. This approach enables organizations to leverage the skills and competencies of their workforce effectively, as employees have more agency and flexibility in how they work.
Incorporating Technological Advancements
In addition to promoting decentralization, technology plays a significant role in the evolution of management theories. With advancements in communication tools and data analytics, managers can better facilitate collaboration and feedback among remote employees, ensuring alignment and coherence within the organization. These methods help managers not only track key performance indicators but also gain insights into employee well-being and engagement, fostering a supportive and inclusive work environment.
Embracing Environmental Sustainability
Another emerging trend that challenges traditional management theories is the growing emphasis on environmental sustainability. Organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of adopting responsible business practices that minimize negative environmental impacts. As such, management theories are evolving to accommodate sustainability by integrating it into performance management systems, strategic decision-making, and employee training. This incorporation enables organizations to align their goals with the broader global social and environmental context, ultimately promoting shared value creation.
Holistic Approaches to Employee Well-being
Finally, in response to the shifting workplace dynamics, management theories are increasingly integrating a holistic approach to employee well-being. These approaches consider the physical, mental, and emotional aspects of the work environment and prioritize employee satisfaction, engagement, and health. By creating supportive and flexible work environments, managers can better address the unique challenges posed by remote work arrangements and foster a culture that promotes long-term organizational success.
In conclusion, management theories are evolving to address the emerging trends of remote work, environmental sustainability, and employee well-being by fostering a culture of flexibility, accountability, and support. These adaptations enable organizations to meet the complex and dynamic challenges of an ever-changing business landscape effectively. As a result, successful leaders must remain agile and forward-thinking, continuously adapting their management approaches to align with the evolving needs and priorities of their organizations.



