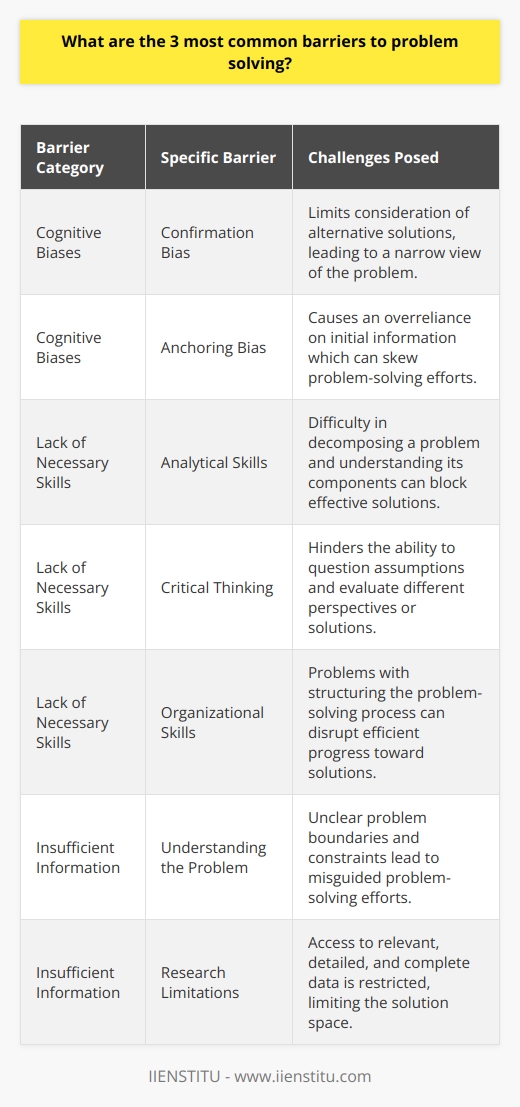
This article explores the characteristics of poor problem solvers, the benefits of strengthening problem-solving skills, and steps to avoid guessing. Poor problem solvers often lack the belief that persistent analysis is an effective way to work through academic reasoning problems, are careless in their work, and cannot see patterns or make connections between different parts of a problem.
Strengthening problem-solving skills can help to reduce the number of errors made, improve the speed and accuracy of problem solving, and increase the problem-solvers ability to apply the same problem solving skills to other areas of life.
Steps to avoid guessing include taking the time to read through a problem carefully, breaking a problem down into smaller parts, checking each step of the problem solving process, and keeping track of the progress of the problem solving process.
Introduction
Characteristics of Poor Problem Solvers
Benefits of Strengthening Problem-Solving Skills
Steps to Avoid Guessing
Conclusion
Introduction: Problem-solving abilities are critical to success, yet many people fail to develop them to their fullest potential. Poor problem solvers often make mistakes because they jump to conclusions and guess answers without going through all the steps needed to ensure that the answers are accurate. Good problem solvers, on the other hand, work problems from beginning to end in small, careful steps. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of poor problem solvers, the benefits of strengthening problem solving skills, and measures to avoid guessing.
Characteristics of Poor Problem Solvers
Poor problem solvers have several common characteristics that can lead to errors in their problem-solving. First, they often lack the belief that persistent analysis is an effective way to work through academic reasoning problems. This lack of motivation to work on an entire issue precisely and thoroughly can lead to mistakes. Second, poor problem solvers tend to be careless in their work, often skipping steps or making assumptions without checking to see whether they are correct. Finally, poor problem solvers cannot usually see patterns or make connections between different parts of a problem, which can lead to errors.
Comprehensive Guide To Regression Analysis For Quantitative Forecasting
Benefits of Strengthening Problem-Solving Skills
Strengthening problem solving skills can be beneficial in a variety of ways. First, it can help to reduce the number of errors made when working through issues. Second, it can help improve the speed and accuracy of problem solving and the confidence of the problem-solver. Finally, it can help to increase the problem solver’s ability to apply the same problem solving skills to other areas of life.
Steps to Avoid Guessing
Guessing can often lead to problem-solving errors, so avoiding it is essential. First, it is necessary to take the time to read through a problem carefully and make sure that all the information is understood. Second, it is required to break a problem into smaller parts and work through each piece in detail. Third, checking each step of the problem-solving process is essential to ensure it is correct. Finally, it is necessary to keep track of the progress of the problem-solving process and ensure that it is on its way.
Conclusion: Problem solving skills are an essential part of life, yet many people fail to develop them to their fullest potential. Poor problem solvers often make mistakes because they jump to conclusions and guess answers without going through all the steps needed to ensure that the answers are accurate. Strengthening problem-solving skills can be beneficial in various ways, and taking steps to avoid guessing is essential. By following these steps, it is possible to increase the accuracy and speed of problem solving and the confidence of the problem-solver.
When solving a problem, never guess - seek knowledge instead.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of strengthening problem solving skills?
Problem-solving skills are essential for success in both academic and professional life. Developing problem-solving skills can help students and professionals gain a competitive advantage in the workplace. They are also critical for making decisions, managing projects, and developing strategies.
Strengthening problem-solving skills can help individuals become better decision-makers, think more critically, and develop problem-solving strategies. They can also help individuals become more creative, as well as develop better communication, research, and planning skills.
One of the significant benefits of improving problem-solving skills is increased productivity. Individuals with strong problem-solving skills are more likely to come up with creative solutions and make better decisions, leading to increased productivity and better performance in the workplace.
Another benefit of improving problem-solving skills is increased self-confidence. Individuals who can solve problems quickly and effectively are more likely to feel confident in their abilities, which can help them to manage their workload better and make better decisions.
Finally, strengthening problem-solving skills can help individuals better understand complex issues. By creating their problem-solving skills, individuals can learn how to break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable pieces, which can help them come up with better solutions.
In conclusion, developing problem-solving skills can provide individuals with various benefits, including increased productivity, self-confidence, and a better understanding of complex issues. In addition, improving problem-solving skills can lead to tremendous success in both academic and professional life.

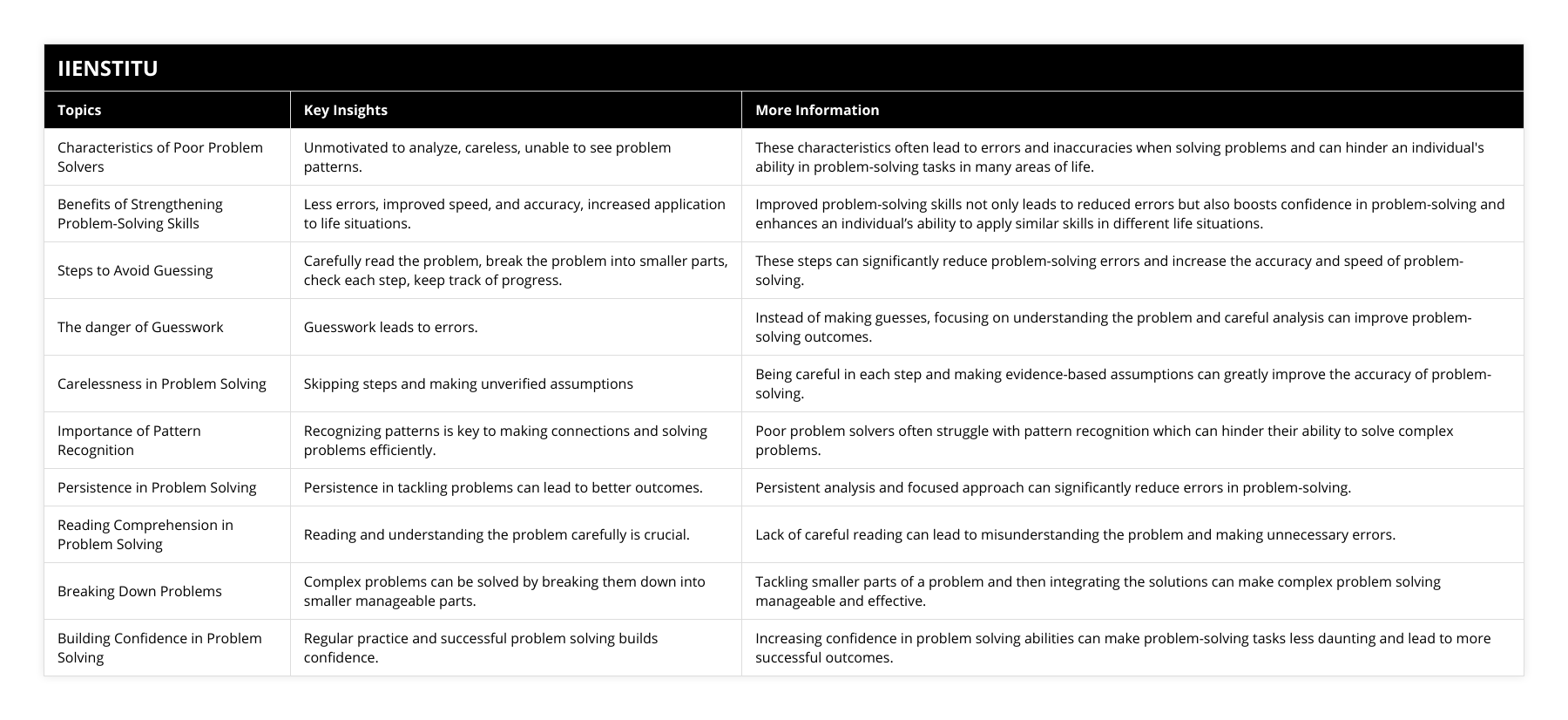
What are the characteristics of poor problem solvers?
Poor problem solvers often lack the skills and knowledge to effectively identify and address a problem. In addition, poor problem solvers tend to be overly narrow-minded and often overlook the bigger picture, resulting in an inability to make well-informed decisions. They may also be excessively reliant on trial and error, leading to inefficient solutions that lack creativity. Finally, poor problem solvers may also lack the ability to plan, leading to ineffective problem-solving strategies.
Poor problem solvers often cannot think abstractly, leading to a lack of creative solutions. They may also be unable to identify patterns or trends, making it difficult to anticipate how a problem may evolve. Furthermore, poor problem solvers may be unable to think logically, leading to misjudging the impact of different solutions.
Poor problem solvers are often unable to recognize the consequences of their actions, which can lead to ineffective solutions. Additionally, they may be unable to think critically and analyze problems unbiasedly, leading to flawed decision-making. Finally, they may also be unable to recognize the importance of collaboration, leading to inefficient solutions.
Poor problem solvers are often unaware of the resources available, making it challenging to find suitable solutions. They may also have difficulty understanding their decisions' implications, which can lead to ineffective solutions. Additionally, they may be unable to break down tasks into manageable steps, hindering progress.
Poor problem solvers often lack the necessary skills and knowledge to address a problem effectively. They may be overly narrow-minded and overlook the bigger picture, leading to ineffective solutions. Additionally, they may be unable to think abstractly or logically, leading to flawed decision-making. Furthermore, they may be unable to recognize the consequences of their actions or the importance of collaboration, which can hinder progress. Finally, they may be unaware of the resources available, making it challenging to find suitable solutions.
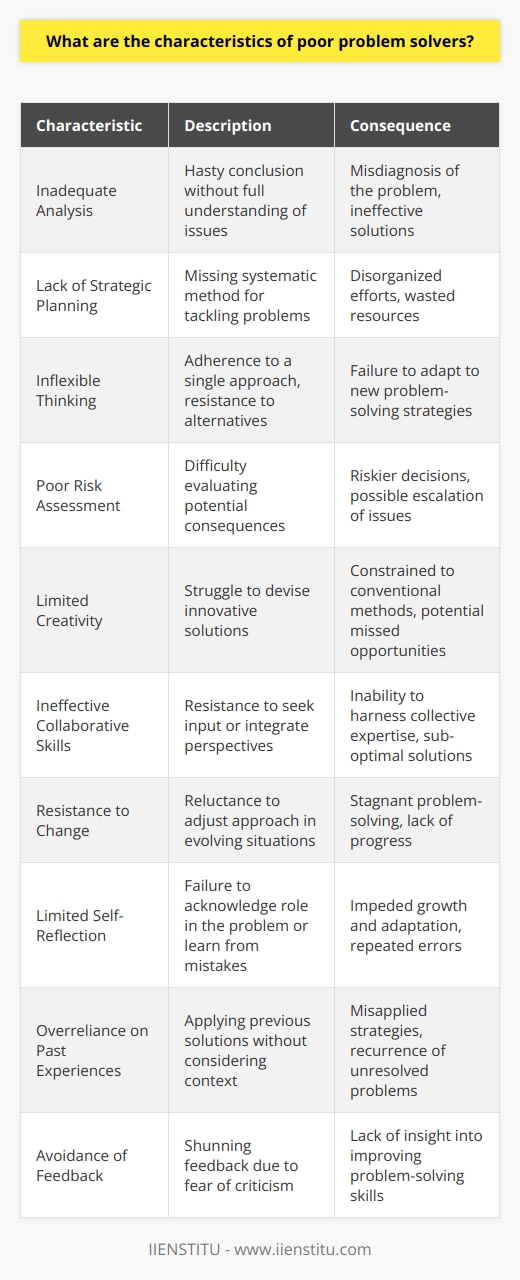
What are the steps to avoid guessing when problem solving?
Problem-solving is an essential skill necessary for success in professional and personal contexts. However, when tackling a complex problem, relying on guesswork can often be tempting. Unfortunately, this can lead to incorrect conclusions and missed opportunities. Fortunately, some steps can be taken to avoid guessing when problem-solving.
The first step is to identify the root cause of the problem. This involves breaking down the problem into its parts and understanding the underlying principles that are causing the issue. This can be achieved through a process of critical thinking, which can help to identify potential causes and solutions.
The second step is to gather evidence. This can involve collecting information from various sources, such as interviews, surveys, and experiments. This evidence can then be used to support or refute potential solutions.
The third step is to test potential solutions. This can involve running experiments or simulations to determine the effectiveness of the proposed solution. This can help to eliminate guesswork and ensure that the best solution is chosen.
The fourth step is to evaluate the results of the tests. This can involve analyzing the data to determine what worked and what did not. This can help to refine the solution and ensure it is the best possible solution to the problem.
Finally, the fifth step is to implement the solution. This can involve developing a plan to implement the solution and ensuring all necessary steps are taken. This can help to ensure that the answer is implemented correctly and efficiently.
By following these steps, it is possible to avoid guesswork when problem-solving and ensure that the best solution is chosen. This can help to improve the success rate of problem-solving and ensure that the best solution is chosen every time.
What are the four tactics for improving your problem-solving abilities?
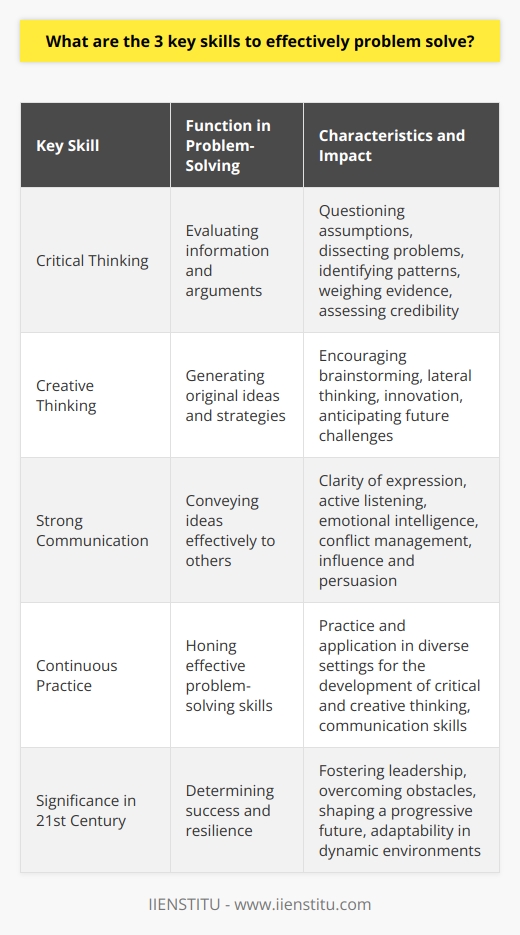
**Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills**
Developing strong problem-solving abilities is essential for success in various aspects of life, from personal to professional. There are four primary tactics that one can employ to improve problem-solving skills: critical thinking, brainstorming, the application of the scientific method, and collaboration with others.
**Critical Thinking**
One of the most effective ways to tackle problems is by employing critical thinking. This involves using logic, reasoning, and reflection to systematically analyze a situation, generate potential solutions, and evaluate their effectiveness. By honing critical thinking skills, individuals can become more adept at finding creative and efficient ways to solve problems.
**Brainstorming**
Another potent strategy for improving problem-solving abilities is brainstorming. This tactic entails rapidly generating a wide array of ideas to find unique, innovative solutions to the problem at hand. Brainstorming allows individuals to think outside conventional frameworks and explore various possibilities before settling on a course of action, thereby increasing their problem-solving efficacy.
**Scientific Method**
Applying the scientific method can also be a valuable tactic in enhancing problem-solving skills. This process involves observing a problem, formulating a hypothesis regarding its cause and potential solutions, and testing this hypothesis through experiments or analysis. By approaching problems scientifically, individuals can objectively evaluate different strategies and more accurately identify the most effective solution, gaining a deeper understanding and ability to address similar problems in the future.
**Collaboration**
Lastly, collaboration with others is an excellent way to strengthen problem-solving abilities. By working in a team or seeking input from different perspectives, individuals can benefit from the diverse knowledge, experience, and critical thinking skills of others. Collaborating effectively requires communication, listening, and adaptability, which are crucial aspects to develop in order to become a proficient problem-solver.
In conclusion, improving problem-solving abilities requires focused effort and the regular practice of various tactics. By engaging in critical thinking, brainstorming, applying the scientific method, and collaborating with others, individuals can refine their skills and better face the challenges that life presents. Ultimately, possessing strong problem-solving skills is integral in navigating the complexities and accomplishing goals in both personal and professional spheres.
What are the 3 characteristics of a strong problem solver?
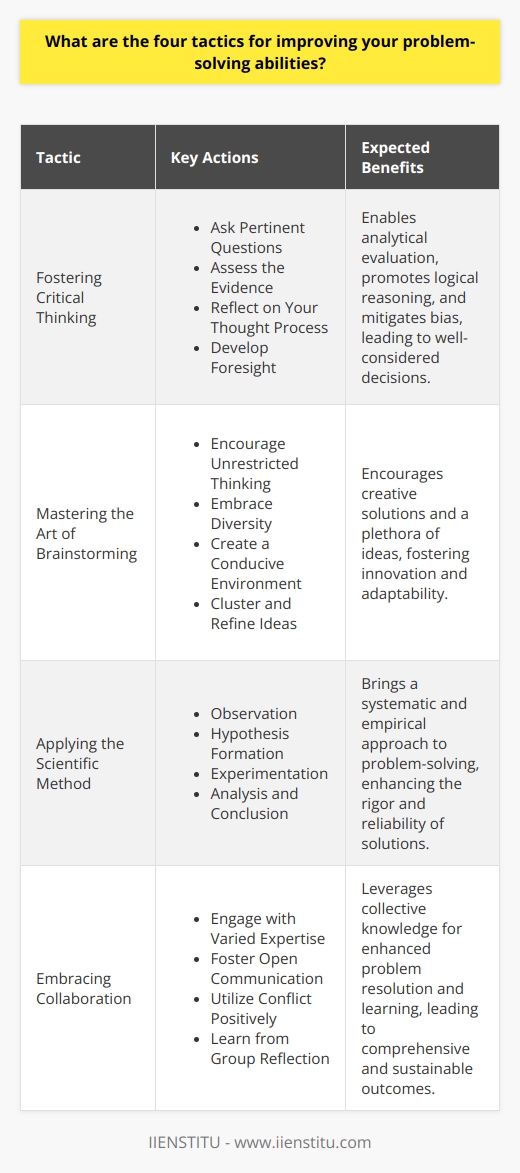
Analytical Skills
One key characteristic of a strong problem solver is their analytical skills. Analytical skills refer to the ability to understand complex information, identify patterns, and develop logical solutions. In order to solve problems effectively, a person must be able to objectively collect and analyze data, make informed decisions based on that data, and effectively communicate their findings to others.
Creativity
Another crucial characteristic of a strong problem solver is creativity. Creative thinking allows individuals to approach problems from different perspectives, identify novel solutions, and think outside the box. This skill is particularly important when faced with unique or unconventional challenges, as it enables problem solvers to develop innovative approaches rather than relying solely on traditional or common strategies.
Persistence
Finally, persistence is an essential quality for successful problem solving. Problem solvers who are persistent maintain a positive attitude and are highly motivated to find a solution, even when faced with obstacles or setbacks. They demonstrate resilience and determination, continuously seeking new approaches until they find one that works. A persistent problem solver is willing to learn from their mistakes, reflecting on their experiences to improve their skills and apply their knowledge to future challenges.
In conclusion, strong problem solvers possess a combination of analytical skills, creativity, and persistence. These characteristics enable them to effectively dissect complex information, develop innovative solutions, and persevere in their quest for a solution. By cultivating these skills, individuals can significantly enhance their problem-solving abilities, leading to greater success in both their professional and personal lives.
What are the 5 problem-solving techniques?
Problem-Solving Techniques Overview
The process of problem-solving is essential in various aspects of life, whether personal, professional, or academic. This article explores five problem-solving techniques that can help individuals enhance their ability to tackle and resolve issues more effectively.
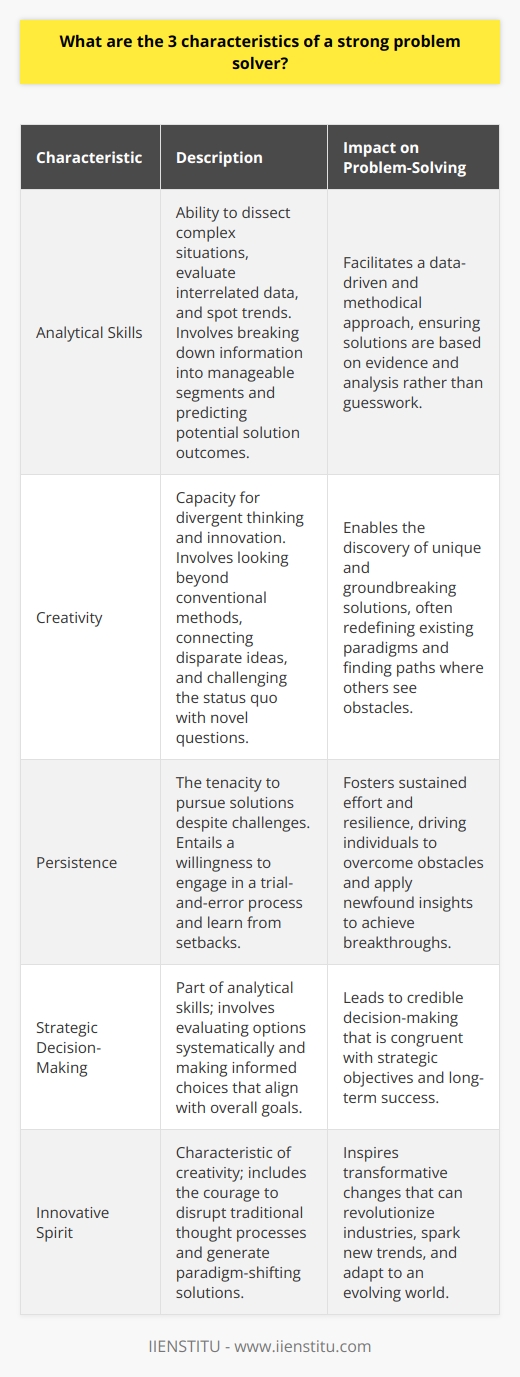
Brainstorming Session
The first technique involves brainstorming, a creative process that encourages individuals to generate ideas, no matter how unusual or impractical they may initially seem. By prioritizing quantity over quality, brainstorming allows for the identification of various possible solutions and stimulates creative thinking.
Root Cause Analysis
The second problem-solving technique focuses on identifying the root cause of the issue. By systematically analyzing and understanding the underlying factors contributing to a problem, individuals can target causative elements, thereby making it possible to develop long-term solutions rather than merely addressing immediate symptoms.
The Five Whys
The third technique, known as the Five Whys, involves asking 'why' repeatedly until the central issue is uncovered. This method aids in simplifying complex problems, gradually breaking them down into smaller, manageable components. The Five Whys can also help identify areas for improvement and formulate actionable strategies to prevent similar issues from arising in the future.
SWOT Analysis
The fourth technique, SWOT analysis, refers to the examination of the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to a problem. By evaluating internal and external factors, this method enables individuals to position themselves advantageously and optimize resources, resulting in improved problem-solving capabilities.
Collaborative Approach
Finally, the fifth technique involves a collaborative approach towards problem-solving. Encouraging input and cooperation from different individuals or teams allows for the pooling of diverse perspectives, knowledge, and experiences, fostering the identification of innovative solutions and reducing the likelihood of overlooking essential factors.
In conclusion, exploring various problem-solving techniques enables individuals to address issues more effectively by fostering creativity, targeting root causes, simplifying and breaking down complex problems, evaluating strengths and weaknesses, and promoting collaboration. Incorporating these methods into one's problem-solving toolkit can greatly enhance the ability to tackle and resolve a wide range of problems.
What are the 4 effective problem-solving strategies?
#### Identifying the Problem
Effectively solving problems begins with accurately identifying the issue at hand. This involves clearly defining the problem, gathering relevant information, and determining the scope and impact of the issue. By understanding the problem's complexity, you can create a solid foundation for outlining potential solutions.
#### Generating Alternative Solutions
Once the problem has been identified, brainstorming potential solutions is essential. This process should involve generating various ideas without evaluating or filtering them initially. Encouraging creativity and innovative thinking can lead to the discovery of new and effective strategies to address the problem. It is also helpful to consider the potential risks, unintended consequences, and benefits of each solution during this phase.
#### Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
After generating alternative solutions, the next step in problem-solving is to evaluate and select the best option. This process includes comparing the pros and cons of each solution, considering factors such as feasibility, resource availability, and potential impact. It is necessary to prioritize solutions that best address the problem while also mitigating risks and promoting benefit maximization. Involving stakeholders and subject matter experts in this phase can reinforce the credibility and viability of the selected solution.
#### Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Once a solution has been chosen, it must be properly implemented and monitored for effectiveness. This involves the full execution of the selected strategy and regular assessment of its impact on the problem. Monitoring allows for adjustments and improvements to be made as needed, ensuring that the solution stays on course and achieves its intended goals.
In summary, effective problem-solving relies on accurately identifying the problem, generating alternative solutions, evaluating and selecting the best option, and implementing and monitoring the chosen strategy. By following these practical steps, individuals, teams, and organizations can navigate complex challenges and achieve success in their endeavors.

What are the 3 key skills to effectively problem solve?
**Effective Problem-Solving Skills**
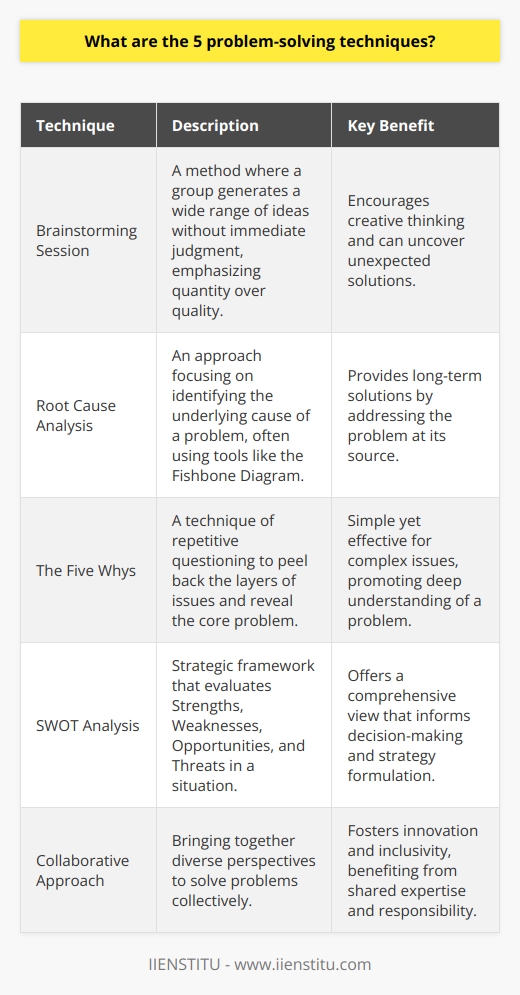
In order to effectively problem-solve, individuals must possess three key skills: critical thinking, creative thinking, and strong communication. These skills play a crucial role in enabling individuals to analyze, evaluate, and devise suitable solutions to various issues and challenges across a wide range of contexts.
**Critical Thinking**
Critical thinking involves the ability to approach problems logically, systematically, and objectively. This means being able to break down complex issues into manageable components, identify underlying assumptions and biases, and evaluate the reliability and validity of relevant information. By employing critical thinking, individuals are better equipped to make well-informed decisions and develop practical solutions to problems.
**Creative Thinking**
Creative thinking is the ability to view problems and issues from new perspectives or different angles, and generate novel ideas for resolution. This skill requires individuals to think outside of conventional boundaries and seek innovative ways to approach problems. For instance, brainstorming is a technique used in creative thinking to stimulate the free flow of ideas, which may lead to unique and innovative solutions. By cultivating creativity, individuals can adapt to changing contexts, overcome obstacles, and discover unconventional strategies to effectively address issues.
**Strong Communication**
Finally, strong communication skills are essential in problem-solving, as they enable individuals to understand others’ needs and perspectives, and express their own ideas and beliefs effectively. To foster strong communication, individuals must be active listeners, empathize with others' viewpoints, and convey their message efficiently both verbally and nonverbally. Furthermore, it involves the ability to negotiate and persuade, which is especially important in reaching consensual resolutions to disagreements or conflicts. In summary, good communication skills contribute not only to the process of problem-solving, but also to the successful implementation of solutions across various contexts.
In conclusion, problem-solving necessitates the integration of critical thinking, creative thinking, and strong communication skills. By mastering these skills, individuals can navigate complex situations and develop effective solutions to problems, thereby contributing to personal growth, academic success, and professional excellence.
What are the four fundamental stages to effective problem-solving?
## Identifying the Problem
The first stage in effective problem-solving involves accurately identifying the issue at hand. This stage requires a clear understanding of the situation and a comprehensive analysis of the problem's components. Determining the root cause of the problem helps guide future decision-making and sets a solid foundation for finding a solution.
## Generating Potential Solutions
Once the problem is identified, the second stage involves generating various potential solutions. During this stage, the individual should draw on their prior knowledge, experience, and creativity to brainstorm as many ideas as possible, regardless of their initial feasibility. This process allows for a wide range of solutions to be considered before narrowing down to the most viable option.
## Evaluating and Selecting a Solution
The third stage in problem-solving involves critically evaluating and selecting the most appropriate solution from the list of potential options generated during the brainstorming stage. This process requires the consideration of numerous factors, such as the time and resources required to implement the solution, the potential risks and benefits of each option, and the likelihood of success. Once a solution has been chosen, the individual can proceed to the final stage.
## Implementing and Assessing the Solution
The fourth and final stage in problem-solving involves implementing the chosen solution and assessing its effectiveness in addressing the initial problem. This stage requires careful planning and monitoring to ensure that the solution is carried out as intended, and adjusting the approach if necessary based on real-time feedback. Once the solution has been implemented, the individual should evaluate its success in solving the problem and, if needed, revisit earlier stages to generate and select alternative solutions.
What are the 3 skills to solve problems effectively?
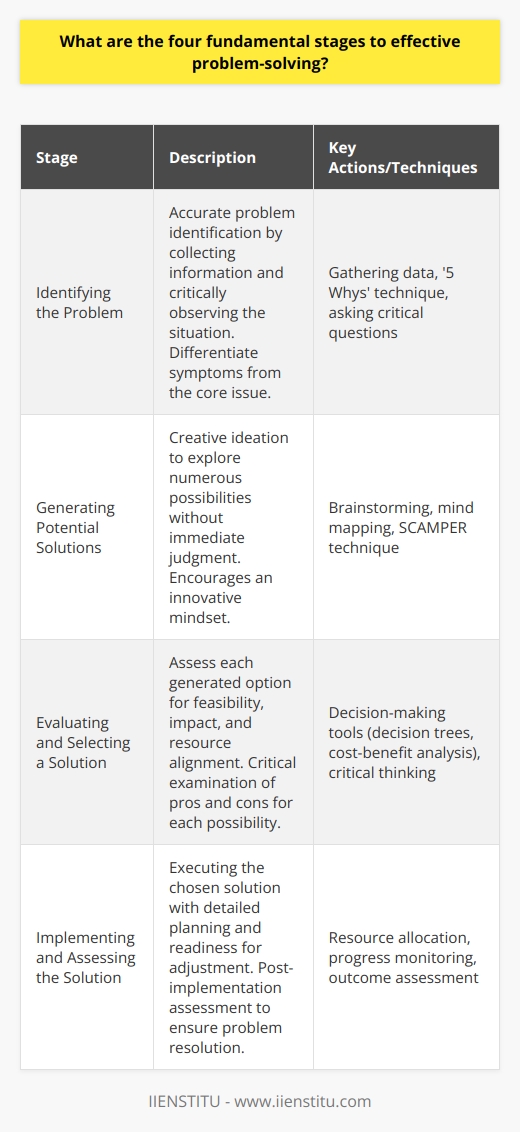
**Critical Thinking**
One essential skill for effective problem-solving is critical thinking. This involves structured, purposeful exploration of multiple potential solutions, a deep understanding of a problem’s complexities, and an ability to use logic and reasoning to identify optimal solutions. Integrating rigorous analytical methods with creative thinking, individuals who possess strong critical thinking skills can approach a wide range of problems, employing various perspectives and techniques to generate well-informed, nuanced responses.
**Communication and Collaboration**
Another crucial skill in problem-solving is effective communication and collaboration. When solutions require the input and expertise of multiple individuals, it is necessary for someone to facilitate the discussion, negotiation, and information sharing among team members. This skill requires both receptive and expressive communication abilities, as well as an understanding of group dynamics, which involve the coordination of diverse perspectives and the management of potential conflicts. Through open and respectful exchanges, team members can collectively explore different approaches and synthesize novel, innovative ideas to address challenges.
**Adaptability and Resilience**
Lastly, adaptability and resilience are integral to successful problem-solving. As situations and contexts often evolve unpredictably, it is crucial for individuals to demonstrate flexibility and adapt their strategies to changing circumstances. In some cases, initial solutions may be insufficient or even exacerbate issues, necessitating timely revisions or adjustments. Additionally, failures are common in problem-solving processes, and the ability to learn from them, maintain a resilient mindset, and persist in the face of adversity are essential for ultimately achieving one's goals. Consequently, fostering adaptability and resilience can significantly enhance the efficacy of one's problem-solving efforts.
What are the 4 types of problem-solving strategies?
Types of Problem-Solving Strategies
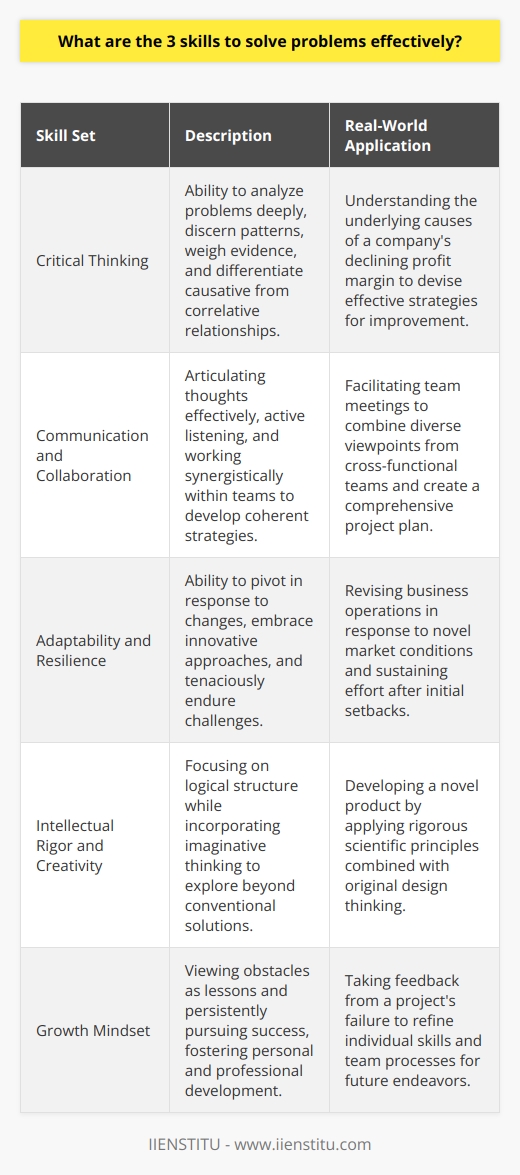
Identifying the Four Major Types
Problem-solving strategies are essential skills for individuals to navigate their daily lives and work effectively with others. Four distinct types of strategies are commonly employed, including trial and error, algorithm, heuristic, and insight.
Trial and Error Approach
The trial and error strategy involves testing different solutions until finding one that works. This approach is commonly used when dealing with simple problems that have a limited number of potential solutions. While trial and error can be time-consuming and inefficient, it is a useful method for solving problems when other strategies are not applicable.
Algorithm Strategy
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that can be followed to arrive at a definite solution to a problem. This strategy is often utilized in mathematical problems and computer programming. Algorithms are effective in guaranteeing a solution, provided that the steps are correctly followed. However, they can be time-consuming and complex, making them less suitable for problems that require quick decision-making.
Heuristic Strategy
Heuristics are mental shortcuts that help individuals find solutions to problems more quickly. These strategies are generally more efficient than algorithms, though they do not guarantee an accurate solution. Heuristics can be useful for complex problems that have no clearly defined solution and involve large amounts of uncertainty. For example, when making decisions based on limited information or time, using heuristics can increase the chances of finding a satisfactory solution.
Insight Strategy
Insight is a problem-solving strategy that involves a sudden realization of the solution to a problem, often referred to as an 'aha' moment. This strategy relies on creativity and intuition, and it can help individuals solve problems for which other more systematic approaches may not be effective. However, insight cannot be relied upon consistently, as it is dependent on individual cognitive abilities and the specific problem at hand.
In conclusion, the four major types of problem-solving strategies include trial and error, algorithm, heuristic, and insight. Each strategy has its unique advantages and disadvantages and may be more or less effective depending on the nature of the problem being addressed. By understanding the characteristics of each strategy and applying the appropriate one to the problem at hand, individuals can improve their problem-solving skills and enhance their overall effectiveness in a variety of settings.
What are the 3 most common barriers to effective problem-solving?
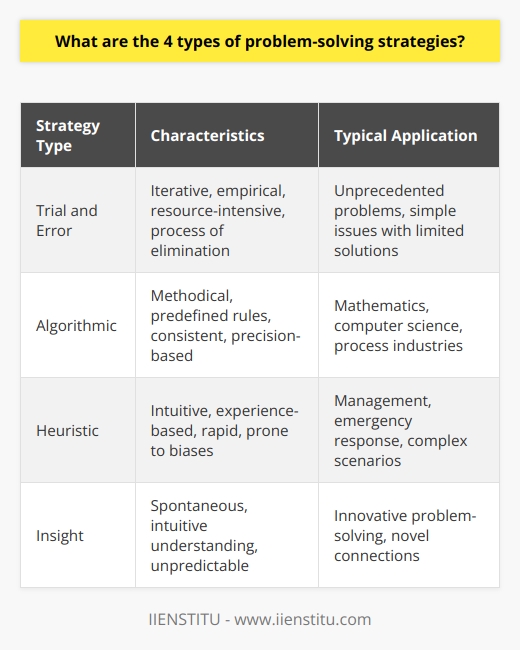
Cognitive Biases
One common barrier to effective problem-solving is the presence of cognitive biases. These are systematic errors in thought processes that can lead to irrational judgments or decisions, deviating from logical reasoning. Cognitive biases, such as confirmation bias, anchoring effect, and overconfidence, can hinder an individual's ability to accurately perceive a problem and identify the most relevant solutions. For instance, confirmation bias can cause someone to favor information that reaffirms their pre-existing beliefs and ignore conflicting evidence, thus limiting their ability to perceive the problem objectively.
Insufficient Information
A second barrier to effective problem-solving is the lack of adequate information. Solving a problem typically requires having accurate data and relevant knowledge at one's disposal. However, individuals often face the challenge of gathering and processing information when encountering a new or complex problem. Even when enough information is available, people may struggle to discern which pieces of data are most pertinent to the problem at hand. Moreover, cognitive overload can occur when the volume of available information is overwhelming, resulting in reduced ability to effectively process and analyze the data required for problem-solving.
Poor Communication and Collaboration
Finally, poor communication and collaboration among team members can significantly hinder effective problem-solving. Inadequate communication can lead to misunderstandings, resulting in either duplicated efforts or a lack of action altogether. A lack of collaboration and trust within a team might also result in team members withholding important information or ideas, further impeding the problem-solving process. Additionally, ineffective group dynamics and workplace politics can contribute to the formation of unproductive cliques that obstruct open communication and hinder efficient problem-solving processes. To overcome these challenges, fostering an environment of clear communication, trust, and respect among team members is crucial for effective problem-solving efforts.
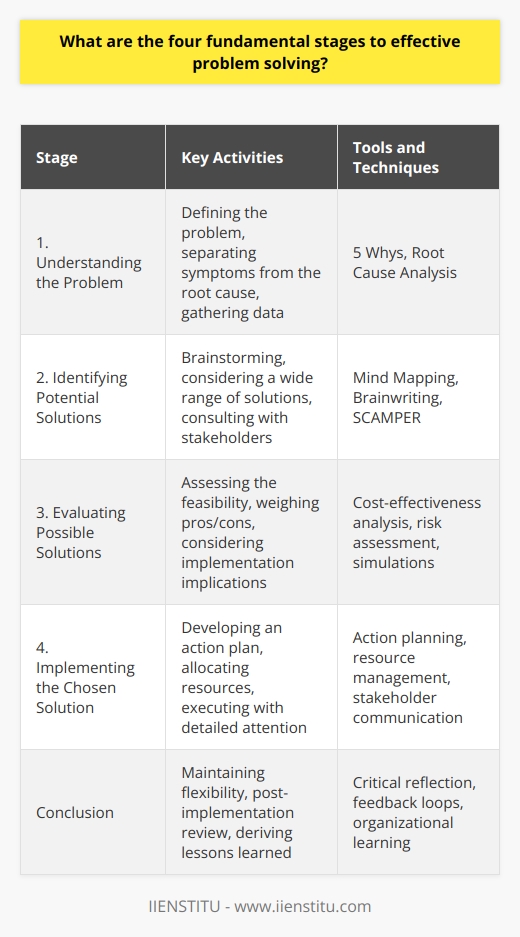
What are the four fundamental stages to effective problem solving?
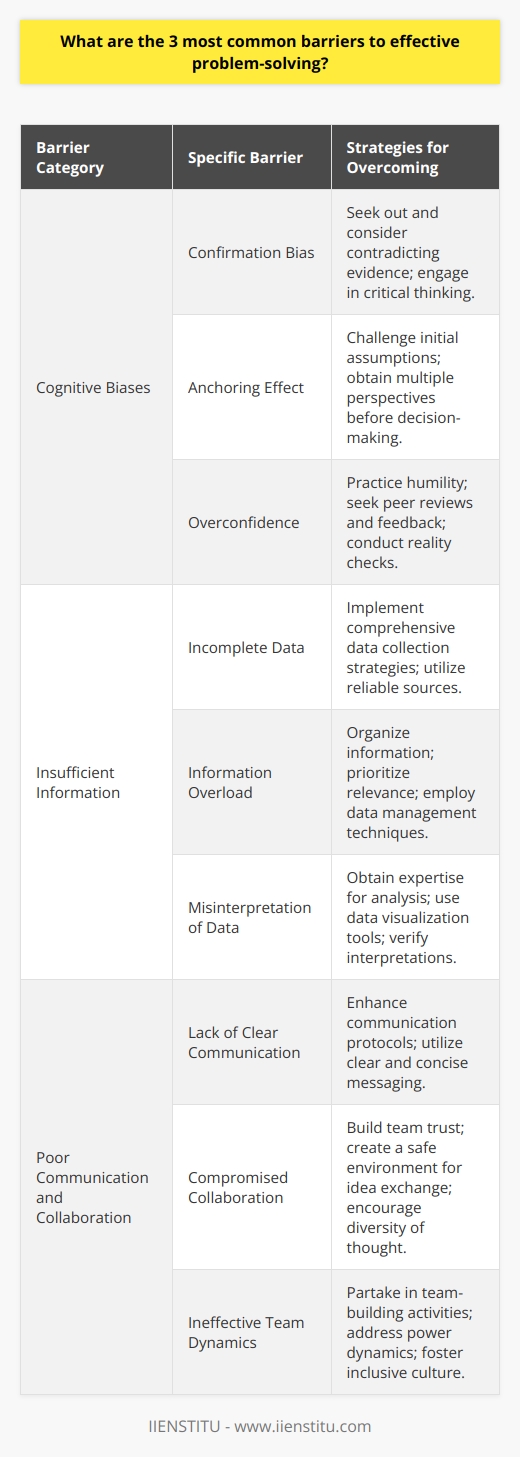
Understanding the Problem
The initial stage in effective problem solving involves understanding the problem. It requires defining the problem in clear and concise terms, allowing for a practical approach.
Identifying Potential Solutions
The next crucial stage involves the identification of potential solutions. One should explore all possible strategies, ideas, or actions that could potentially solve the problem identified.
Evaluating Possible Solutions
Once various solutions are in place, the third stage is to evaluate these possibilities. This stage involves analyzing each option critically, in terms of its feasibility, potential efficiency, and the resources it might require.
Implementing the Chosen Solution
Finally, the fourth stage is implementing the selected solution. After choosing the most suitable solution, it entails putting it into action, carefully monitoring the process, and adjusting the solution as necessary. This stage requires a well-structured plan for successful implementation.
Every stage in this problem-solving process is equally important, building upon the previous one to lead towards effective problem-resolution. A thorough understanding and execution of these four fundamental stages are imperative to effectively solve any problem.
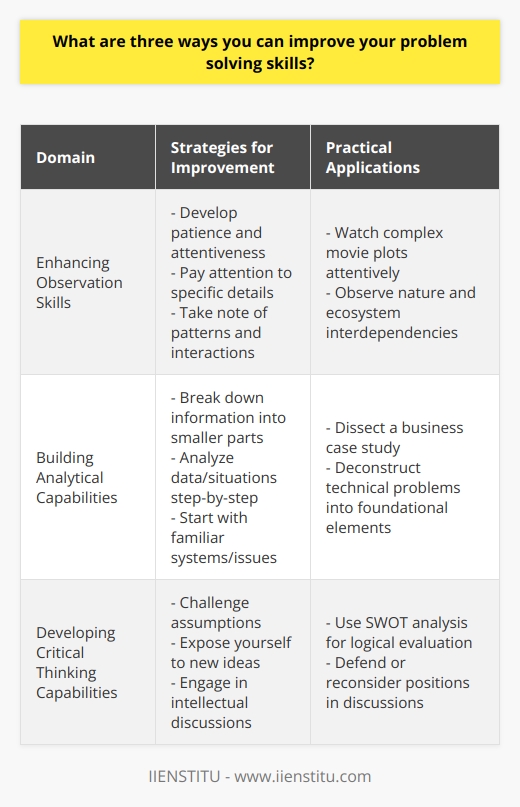
What are three ways you can improve your problem solving skills?
Strengthening About Observation Skills
The first step to improve problem-solving skills revolves around enhancing observation skills. Observing a situation meticulously allows us to understand the problem deeply. This is a key element in determining a plausible solution. Correspondingly, observers should make a conscious effort to absorb information actively, fostering a deeper understanding of the problem.
Building Analytical Capacities
Secondly, improving analytical skills helps in improving problem-solving skills. It involves dissecting a situation or problem into smaller, manageable parts to understand it better. This approach facilitates identifying root causes, aids hypothesis generation and consequently, problem-solving. Routinely engaging in puzzles, brain teasers and logical reasoning activities can sharpen these skills, impacting problem-solving abilities positively.
Developing Critical Thinking capabilities
Lastly, nurturing critical thinking capacities positions us better for problem-solving. It equips us with the ability to comprehensively evaluate options and make informed decisions. This involves questioning assumptions, recognizing patterns and integrating various pieces of information effectively. Continuous self-education and a quest for knowledge foster critical thinking, aiding in effective problem-solving.
In conclusion, honing observation skills, analytical capacities, and critical thinking abilities are three feasible approaches to enhance problem-solving skills. Systematic and consistent efforts towards these strategies can equip us with an improved capacity for problem-solving – a skill of immeasurable value in diverse professional scenarios.
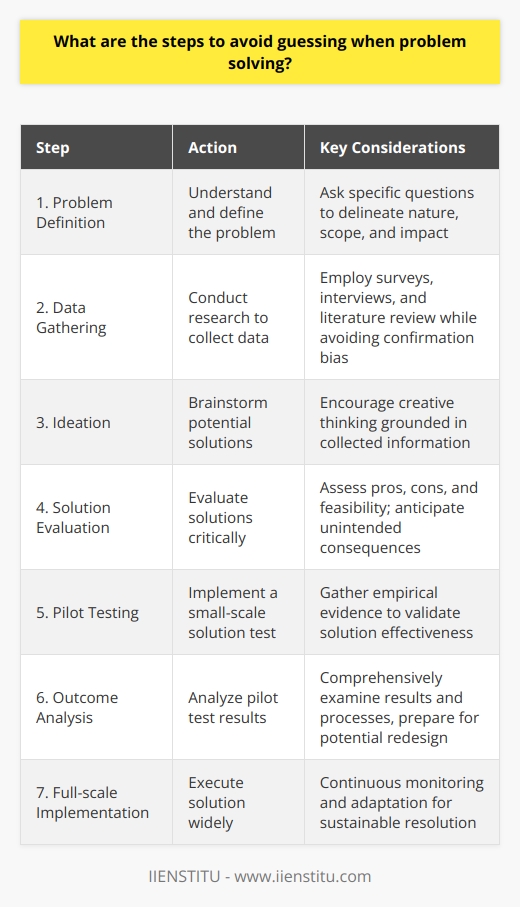
What are the 3 most common barriers to problem solving?
Cognitive Biases
Cognitive biases hinder effective problem-solving by distorting our perception of reality. Unconscious biases, such as confirmation bias and anchoring bias, skew our logic and impede objective thinking.
Lack of Necessary Skills
The absence of critical problem-solving skills forms another common barrier. The ability to analyse, evaluate, organise and communicate crucial data varies among people. Without these essential skills, an individual may find problem-solving an uphill task.
Insufficient Information
Insufficient or inadequate information also challenges problem-solving efforts. When we don't understand a problem fully, arriving at a workable solution becomes difficult. Lack of relevant data might lead to incorrect conclusions and ineffective solutions.
In summary, cognitive biases, the lack of necessary skills, and insufficient information represent the three most common barriers to problem-solving. These challenges can seriously hamper effective problem-solving. By being aware of these barriers, individuals and organisations can take steps to overcome them and improve their problem-solving capabilities.