In today's fast-paced and complex world, problems are an inevitable part of life. Whether it's in our personal lives or professional endeavors, we are constantly faced with challenges that require effective problem-solving skills. However, merely addressing the symptoms of a problem is akin to putting a band-aid on a deep wound. To truly resolve issues and prevent their recurrence, we must dig deeper and identify the root causes. This is where the art and science of root cause identification comes into play.
As someone who has worked in various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare, I have witnessed firsthand the transformative power of root cause analysis. It's not just a buzzword or a trendy management technique; it's a fundamental philosophy that underpins effective decision-making and problem-solving. When I was working as a quality assurance manager at a pharmaceutical company, we were faced with a perplexing issue of product contamination. Despite our best efforts to maintain stringent hygiene protocols and quality checks, we kept encountering instances of contamination at various stages of the production process.
Initially, we were tempted to blame individual employees or specific machines, but through a systematic root cause identification process, we discovered that the real culprit was a design flaw in our air filtration system. By identifying and addressing this root cause, we not only eliminated the contamination issue but also improved the overall efficiency and reliability of our production line. This experience taught me that investing time and resources into root cause analysis is not a luxury, but a necessity for long-term success.
Defining the Problem
Importance of Clearly Defining the Problem
Proper problem identification is the first critical step in root cause analysis. Accurately articulating the problem at hand is imperative as it sets the direction of the entire analytics process. A misidentified problem can lead to wasted efforts, misdirected resources, and ultimately, ineffective solutions.
Techniques and Tools for Problem Definition
Several techniques are employed to articulate the problem correctly, such as the 5 Whys, Fishbone diagrams, and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). These methods foster a rigorous examination of the problem statement, ensuring that subsequent steps are built upon a foundation of clarity and precision.
Data Collection
Steps for Effective Data Collection
Root cause analysis is inherently data-driven. Gathering accurate, relevant, and sufficient data is essential to discerning the real issues behind a problem. This involves collecting historical data, physical evidence, and expert insights, which then need to be meticulously reviewed to ensure reliability.
Role of Data in Root Cause Identification
Data serves as the bedrock of root cause identification. It informs the decision-making process and supports in hypothesizing potential causes. Analysts rely on this data to draw correlations and identify trends that may pinpoint underlying issues.
Cause Analysis
Tools and Methodologies for Cause Analysis
Several analytical tools are available to dissect and examine the problem from different angles. Root cause analysts might use the Pareto Chart to identify the most common causes of a problem, or process mapping to visualize a process and detect inefficiencies or bottlenecks.
Identifying Potential Root Causes
Through these methodologies, practitioners compile a list of probable causes that merit further investigation. It is an iterative process that requires discernment and patience to filter out the noise from the substantial links to the problem.
Root Cause Identification
Evaluating Potential Root Causes
With a list of potential root causes, the task of evaluating and testing each one to confirm their validity begins. This evaluation is meticulous and can involve simulations, further data analysis, or trial-and-error methods to ascertain which root causes are more than mere correlations but truly causal factors.
Verifying the Root Cause
Verification of the root cause is finalized through a series of systematic checks and validations. Only when a cause is irrefutably linked to the problem can it be confirmed as the root cause. This is a crucial step before strategizing solutions to ensure that interventions address the correct issues.
Developing and Implementing Solutions
Creating an Action Plan Based on Root Cause Identification
Identified root causes are then used to sculpt an actionable and targeted solution. This plan must be detailed, with clear timelines, responsibilities, and expected outcomes.
Monitoring and Adjusting the Implemented Solution
No solution is foolproof, and hence, the implemented plan must be continuously monitored to measure its efficacy. Real-time adjustments based on feedback loops ensure that the solution remains effective and can yield sustainable results.
Common Mistakes in Identifying Root Causes
Misidentifying Symptoms as Causes
A common mistake is confusing symptoms of the problem with its actual causes. It can result from a lack of in-depth analysis and can lead to solutions that provide only a temporary remedy without addressing the fundamental issues.
Overlooking Underlying Issues
Sometimes, the immediate causes seem so apparent that deeper issues are neglected. Underlying issues are often systemic and require a more profound, sometimes uncomfortable, questioning of the status quo.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges
Implementing a Systematic Approach
A disciplined, methodical approach can mitigate the risks of such mistakes. It demands a detachment from biases and a commitment to following through with the chosen analytical methodologies.
Remaining Open to Multiple Potential Causes
In complex systems, multiple root causes can contribute to a single problem. Analysts must, therefore, remain open to the possibility of several factors and investigate each with due diligence.
So, what exactly is root cause identification, and why is it so important? At its core, root cause identification is a systematic approach to understanding the underlying factors that contribute to a problem's manifestation. It goes beyond the surface-level symptoms and delves into the deeper, often hidden, issues that are the true drivers of the problem. By addressing these root causes, we can develop long-lasting solutions that prevent problems from recurring, rather than merely treating the symptoms.
Examples of Successful Root Cause Identification
Case Study 1: Take, for instance, a manufacturing defect that recurrently halts production. Through methodical root cause identification, analysts might uncover a design flaw that, once corrected, not only resolves the production delays but enhances the overall product quality.
Case Study 2: In a different scenario, a healthcare facility struggling with patient readmissions may find that through comprehensive cause analysis, the issue stems from inadequate patient education prior to discharge, not the clinical treatment itself. Addressing the educational process could lead to a decrease in readmissions, benefiting both patients and the healthcare system.
Lessons Learned from Noted Case Studies
The importance of effective root cause identification cannot be overstated. According to a study published in the Journal of Quality Technology, organizations that consistently employ root cause analysis techniques experience significant improvements in product quality, process efficiency, and overall customer satisfaction (Suri & Pradhan, 2015). Moreover, a survey conducted by the American Society for Quality revealed that 92% of organizations that implemented formal root cause analysis programs reported significant cost savings and operational improvements (ASQ, 2018).
But how exactly does one go about identifying root causes? The process of root cause identification involves several key steps, each of which requires a systematic and disciplined approach. Let's explore these steps in detail:
1. Defining the Problem
The first and arguably most critical step in root cause identification is accurately defining the problem at hand. As the famous philosopher John Dewey once said, "A well-defined problem is half solved." Without a clear and precise understanding of the issue, all subsequent efforts will be misguided and ineffective.
To define the problem effectively, practitioners often employ techniques such as the 5 Whys, which involves repeatedly asking "why" to drill down to the core of the issue (Serrat, 2017). Another powerful tool is the Fishbone diagram, also known as the Ishikawa diagram, which helps in visualizing the potential causes of a problem in a structured manner (Bose, 2012). These techniques ensure that the problem is articulated in a specific, measurable, and actionable way, setting the stage for a focused and effective root cause analysis.
2. Data Collection
Once the problem is clearly defined, the next step is to gather relevant data. Root cause identification is a data-driven process, and the quality of the data collected directly impacts the accuracy of the analysis. This involves collecting historical records, performance metrics, and any other pertinent information related to the problem at hand.
During my time as a manufacturing engineer, I learned the importance of meticulous data collection. We were troubleshooting a persistent issue with equipment breakdowns, and initially, we relied on anecdotal evidence and gut feelings to guide our analysis. However, it wasn't until we started collecting detailed maintenance logs, machine performance data, and operator feedback that we were able to identify patterns and correlations that pointed us towards the root cause.
3. Cause Analysis
Armed with data, the next phase involves analyzing the information to identify potential causes. This is where various analytical tools and methodologies come into play. One of the most commonly used tools is the Pareto Chart, which helps in identifying the most significant contributors to a problem (Talib et al., 2010). By visualizing the data in a Pareto Chart, analysts can quickly identify the "vital few" causes that account for the majority of the problem's impact.
Another powerful methodology is the Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), which involves systematically examining a process or product to identify potential failure points and their consequences (Carlson, 2012). FMEA enables practitioners to prioritize risks and focus their efforts on the most critical potential causes.
In my experience, cause analysis often requires a collaborative effort, bringing together individuals with diverse expertise and perspectives. When I was part of a cross-functional team tasked with reducing patient wait times in a hospital emergency department, we employed a combination of process mapping and brainstorming sessions to identify potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies. By leveraging the collective knowledge and experience of the team, we were able to uncover insights that would have been difficult for any individual to discern.
4. Root Cause Identification
With a list of potential causes identified, the next step is to evaluate each one to determine which are the true root causes. This involves a process of hypothesis testing and validation, where each potential cause is systematically investigated to confirm its causal relationship with the problem.
One effective technique for root cause validation is the "Five-Why Analysis," which involves repeatedly asking "why" until the underlying cause is uncovered (Seidl & Graven, 2009). This iterative questioning helps in peeling back the layers of symptoms to reveal the true root causes.
During a project to improve the quality of a software product, my team employed the Five-Why Analysis to investigate a recurring issue with system crashes. By repeatedly asking "why," we traced the problem back to a flawed architectural decision made early in the development process. Had we stopped at the initial symptom of system crashes, we would have merely treated the surface-level issue without addressing the fundamental design flaw.
5. Developing and Implementing Solutions
Once the root causes have been identified and validated, the focus shifts to developing targeted solutions. This involves creating a detailed action plan that addresses each root cause, with clear timelines, responsibilities, and expected outcomes.
However, it's important to recognize that implementing solutions is not a one-and-done endeavor. Any solution, no matter how well-designed, requires continuous monitoring and adjustment based on real-world feedback. This iterative approach ensures that the solutions remain effective and sustainable over time.
In one memorable case, our team had identified the root cause of a quality issue in a manufacturing process and implemented a solution that involved modifying the equipment settings. While the initial results were promising, we soon realized that the operators were struggling to adapt to the new settings, leading to inconsistent results. By actively seeking feedback and making necessary adjustments, we were able to refine the solution and achieve the desired outcomes.
Challenges and Mistakes in Root Cause Identification
Despite the structured nature of root cause identification, the process is not immune to challenges and mistakes. One of the most common pitfalls is misidentifying symptoms as causes. This often stems from a lack of in-depth analysis and can lead to solutions that merely provide temporary relief without addressing the underlying issues.
Another challenge is the tendency to overlook underlying systemic issues in favor of more obvious, surface-level causes. This is particularly prevalent in complex systems where multiple factors interact in intricate ways. In such cases, a myopic focus on immediate causes can lead to a failure to recognize the deeper, more fundamental issues at play.
To overcome these challenges, it's crucial to adopt a systematic and disciplined approach to root cause identification. This involves following a structured methodology, such as the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework, which provides a step-by-step guide to problem-solving (Gupta, 2013). By adhering to a rigorous process, practitioners can minimize the risk of biases and ensure a comprehensive analysis.
Additionally, it's important to cultivate an open-minded and curious mindset, one that is willing to question assumptions and explore multiple potential causes. As the renowned physicist Richard Feynman once said, "The first principle is that you must not fool yourself—and you are the easiest person to fool." By remaining intellectually honest and open to alternative perspectives, practitioners can avoid the pitfalls of confirmation bias and groupthink.
Case Studies: Effective Root Cause Identification
To illustrate the power of effective root cause identification, let's consider a few real-world examples:
Case Study 1: Manufacturing Defect
In a manufacturing facility producing electronic components, a recurring defect was causing significant production delays and customer complaints. The initial assumption was that the issue stemmed from operator error or equipment malfunction. However, through a systematic root cause analysis, the team discovered that the real culprit was a design flaw in the product itself. By identifying and addressing this root cause, the company not only resolved the production delays but also improved the overall product quality, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Case Study 2: Healthcare Readmissions
A healthcare facility was grappling with a high rate of patient readmissions, which was not only costly but also indicative of suboptimal patient care. The initial focus was on improving the clinical treatment protocols, but a comprehensive root cause analysis revealed that the underlying issue was inadequate patient education and discharge planning. By addressing these root causes through enhanced patient education programs and more robust discharge processes, the facility was able to significantly reduce readmission rates, improve patient outcomes, and optimize resource utilization.
These case studies underscore the importance of a holistic and unbiased approach to root cause identification. They also highlight the need for a culture that values and supports in-depth problem-solving, rather than settling for quick fixes or surface-level solutions.
The Future of Root Cause Identification
As we look towards the future, it's clear that the field of root cause identification is poised for significant advancements. With the rapid pace of technological progress, new tools and techniques are emerging that can greatly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of the root cause analysis process.
One notable trend is the growing application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in root cause identification. AI and ML algorithms can sift through vast amounts of data, identifying patterns and correlations that may be difficult for human analysts to discern. For example, researchers have developed AI-based systems that can analyze historical maintenance data to predict equipment failures and identify potential root causes (Diez-Olivan et al., 2019). Such technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way we approach problem-solving, enabling faster and more accurate identification of root causes.
Another emerging trend is the increasing adoption of systems thinking in root cause analysis. Systems thinking is a holistic approach that recognizes the interconnectedness of various elements within a system (Arnold & Wade, 2015). By viewing problems through a systems lens, practitioners can better understand the complex web of cause-and-effect relationships that underlie most real-world issues. This approach is particularly relevant in today's interconnected and globalized business environment, where seemingly isolated problems can have far-reaching and unintended consequences.
In conclusion, root cause identification is a critical skill that separates effective problem-solvers from those who merely treat symptoms. By investing in the intellectual and technological resources necessary to master this skill, individuals and organizations can position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly complex and dynamic world.
As we navigate the challenges of the 21st century, the ability to identify and address root causes will be a key differentiator. Whether it's in the realm of business, healthcare, education, or beyond, those who can effectively diagnose and solve problems at their source will be the ones who shape the future.
References:
Arnold, R., & Wade, J. (2015). A Definition of Systems Thinking: A Systems Approach. Procedia Computer Science, 44, 669-678.
ASQ (2018). Root Cause Analysis: A Survey of Quality Professionals. American Society for Quality.
Bose, T. K. (2012). Application of Fishbone Analysis for Evaluating Supply Chain and Business Process-A Case Study on the St James Hospital. International Journal of Managing Value and Supply Chains, 3(2), 17-24.
Carlson, C. (2012). Effective FMEAs: Achieving Safe, Reliable, and Economical Products and Processes Using Failure Mode and Effects Analysis. John Wiley & Sons.
Diez-Olivan, A., Del Ser, J., Galar, D., & Sierra, B. (2019). Data fusion and machine learning for industrial prognosis: Trends and perspectives towards Industry 4.0. Information Fusion, 50, 92-111.
Gupta, P. (2013). Six Sigma Business Scorecard: Ensuring Performance for Profit. McGraw-Hill Education.
Seidl, B., & Graven, P. (2009). The Five Why Analysis: Minimize Problem Solving Time. Quality Progress, 42(3), 60-61.
Serrat, O. (2017). The Five Whys Technique. Knowledge Solutions, 307-310.
Suri, R., & Pradhan, S. (2015). Effective Use of Root Cause Analysis for Quality Improvement: A Study of Manufacturing Organizations. Journal of Quality Technology, 47(1), 74-89.
Talib, F., Rahman, Z., & Qureshi, M. N. (2010). Pareto analysis of total quality management factors critical to success for service industries. International Journal of Quality Research, 4(2), 155-168.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the process of root cause identification contribute to more effective decision making?
Understanding Root Cause Identification
Identifying the root cause is a critical step. It concerns finding the original issue. This issue is responsible for a given problem. Decision making relies on understanding problems thoroughly. Effective decision making needs deep, accurate insights.
Role of Root Cause Analysis in Decision Making
Root cause analysis ensures decision makers focus accurately. They must address the true problem at its source. Not just the symptoms. Today, various methods exist to identify root causes. Examples include the Five Whys and Fishbone Diagram. These tools help peel back layers of symptoms. They reveal the underlying issues.
Precise Focus Leads to Effective Solutions
Effective decision making requires precision. Root cause identification narrows down focus areas. This precision targets resources and efforts where needed. It prevents misuse of time and funds.
Avoiding Recurrence and Creating Long-Term Value
Solving root causes can help avoid problem recurrence. This builds more sustainable solutions. Decisions made with root causes in mind create long-term value. They address the issue at the systemic level.
Advantages of Root Cause Identification in Decision Making
Increased Efficiency: Decisions focus on the true issue.
Cost-effectiveness: Solutions address the root, preventing waste.
Enhanced Problem-Solving: Solutions become more creative and systemic.
Risk Mitigation: Understanding root causes can prevent future issues.
Improved Stakeholder Trust: Decisions demonstrate a thorough understanding.
Root cause identification guides effective decision making. It grounds decisions in a factual basis. It promotes solution-oriented thinking. When decision makers identify root causes, their actions become more impactful. They build resilient systems that endure and adapt. Identifying root causes is not just problem solving. It is about creating frameworks for ongoing success. It forms the backbone of strategic, informed decision making.
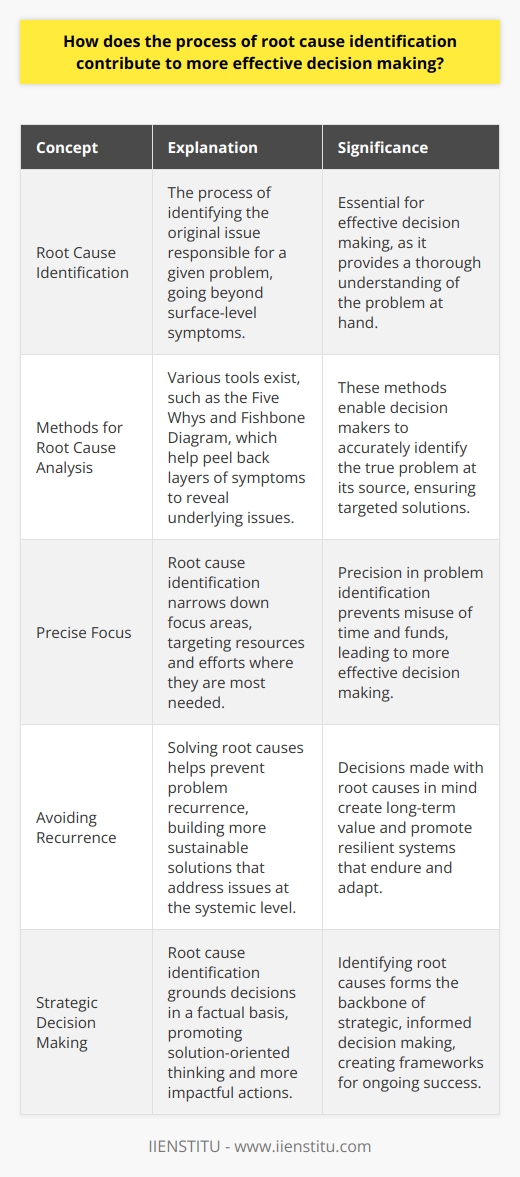
What techniques and methodologies are typically utilized in root cause identification?
Understanding Root Cause Identification
Root cause identification forms the crux of problem-solving. Experts analyze it through various lenses. Many techniques assist in this critical process. They lend structure to investigative efforts. These methodologies also enhance solution effectiveness. Below we discuss prevalent approaches.
The Five Whys Technique
The Five Whys represents simplicity itself. One asks "Why?" repeatedly. The goal stands clear: uncover the problem's essence. The technique encourages deep questioning. Analysts often use it to trace problem origins. It seeks the underlying issues outright. Many consider it an insightful, straightforward method.
The Fishbone Diagram
Also known as Ishikawa or Cause and Effect, the diagram visualizes causes. It categorizes potential reasons for problems. This brainstorming tool engenders collaborative analysis. It effectively clusters ideas. Users find it aids in hypothesis generation. The method promotes comprehensive investigation.
The Pareto Analysis
Pareto Analysis emphasizes the "vital few" causes. It arises from the Pareto principle. The concept suggests that a minority causes most problems. Analysts use it to prioritize issues. It involves data collection and statistical analysis. Decision-making gains clarity. Resources allocate better with its guidance.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
FMEA is proactive. Experts identify potential failure points here. They assess associated risks. The method ranks potential failures by significance. It factors in occurrence likelihood and detection ease. Prioritization is the result. Thus, preemptive actions can take place.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
RCA is comprehensive. It considers multiple angles. Analysts collect data. They review processes and systems. They examine evidence thoroughly. RCA methodologies vary. They may include Events and Causal Factor Analysis. Here, chronologies shed light. Barrier Analysis is another. It inspects control systems. Change Analysis reviews deviations from norms.
The Kepner-Tregoe Method
Decision-making expertise defines the Kepner-Tregoe method. Analysts clarify problems here. They identify desired outcomes first. Subsequently, they prioritize alternatives. Assessment of risks follows. The method's systematic nature commands respect. Structured problem-solving becomes attainable.
Identifying root causes necessitates a robust toolkit. Practitioners leverage these techniques. They suit different scenarios and issues. Mastery of these methodologies enhances efficacy. Problem-solvers thus can identify, analyze, and address core issues systematically.
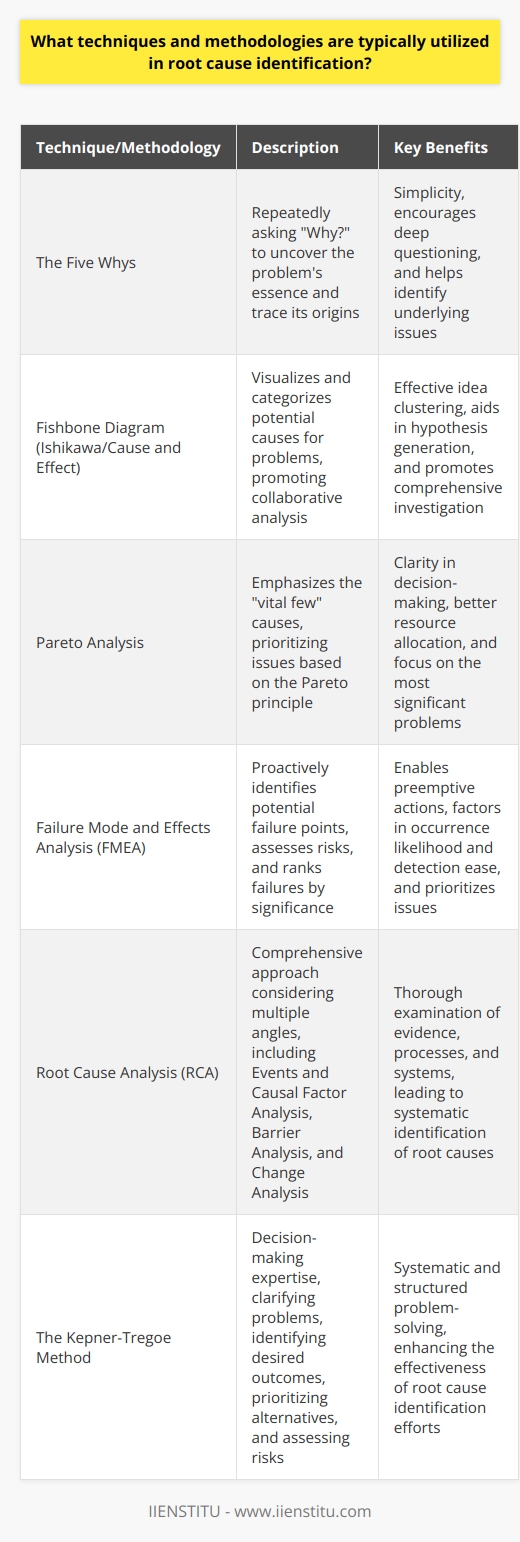
What challenges are most frequently faced in the implementation of root cause identification in decision-making processes?
Root Cause Identification: Key Challenges in Decision-Making
Complex Systems Pose Analytical Difficulties
Organizations must navigate complex systems. These systems often obscure root causes. Problems seldom arise in isolation. Interconnectivity creates obscurity, hindering straightforward analysis. Decision-makers struggle with such entangled systems. They work to identify singular causal factors. However, multiple variables usually contribute. Complexity also breeds uncertainty. It fosters ambiguous relationships between cause and effect.
Data Overload Clouds Judgment
Modern organizations drown in data. More data doesn't always mean better insights. Decision-makers face data inundation. Sifting through massive datasets proves challenging. Relevant information gets buried. Non-essential data distracts. Analysts need skills in data discernment. Big data requires careful management. Without it, identifying root causes becomes daunting.
Cognitive Biases Skew Perspectives
Humans exhibit cognitive biases. These biases impact decision-making. Individuals make judgments based on preconceived notions. They often ignore contrary evidence. Confirmation bias is particularly prevalent. People seek information confirming their beliefs. This undermines objective analysis. Decision-makers must guard against such biases. It requires continuous vigilance.
Time Constraints Limit In-depth Analysis
Decisions often need swift action. Time constraints become pressing. They limit the analysis depth. Superficial investigation bypasses root cause identification. Short-term solutions gain preference. This can lead to recurring issues. Organizations must balance speed with rigor. Otherwise, they risk implementing ineffective solutions.
Poor Cross-Functional Collaboration
Departments work in silos. This impedes information flow. Different functions possess unique insights. Without collaboration, a full picture remains unseen. Cross-functional teams must unite. They should share data and perspectives. Integrated efforts aid in uncovering root causes. Siloed functions frustrate comprehensive analysis.
Inadequate Problem-Solving Methodologies
Organizations often lack structured methodologies. Structured approaches guide root cause analysis. Without them, analyses prove erratic. Consistency becomes crucial for reliable identification. Decision-makers benefit from a systematic process. It aids in examining all potential causes. Ad hoc methods fall short. They fail to deliver repeatable results.
Resistance to Change and Uncertainty
Change elicits resistance. Decision-makers may avoid unsettling discoveries. Root cause identification can reveal uncomfortable truths. It can challenge existing practices. Employees might oppose changes necessary for resolution. To embrace change, organizations need leadership. Leadership must foster an open culture. An open culture permits vulnerability. It also encourages constructive feedback.
Skills and Knowledge Gaps
Expertise is essential for complex problem-solving. Organizations sometimes lack this expertise. They might not have access to knowledgeable analysts. Training becomes vital. Decision-makers must understand root cause analysis. They need skills in critical thinking. Without these, efforts to identify root causes flounder.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Root cause identification is not straightforward. Yet, it remains an indispensable facet of informed decision-making. Overcoming its challenges requires dedication. It demands robust systems, openness, and collaboration. Organizations can then turn obstacles into stepping stones. These steps guide towards solutions that are both effective and enduring.