Decision-making in complex systems often requires an in-depth analysis of underlying issues that contribute to a problem's manifestation. The root cause tree diagram stands as a powerful visual and analytical tool, aiding in the identification and exploration of these foundational issues. Within the realms of quality control, process improvement, and incident investigation, the root cause tree diagram allows individuals and organizations to visually dissect a problem, learn problem solving strategies, and methodically address the root causes rather than merely mitigating symptoms.
This article endeavors to elucidate the theoretical underpinnings, pragmatic constructions, and practical applications of the root cause tree diagram, underscoring its vital role in informed and effective decision-making.
Understanding the Fundamentals of the Root Cause Tree Diagram
Basics Components of the Root Cause Tree Diagram: The root cause tree diagram is typically comprised of three essential components: primary roots, secondary roots, and leaves. The primary roots signify the fundamental underlying issues that prevail as the core contributors to the problem at hand. These are the problems that, if addressed properly, could prevent the undesirable event from recurring. Secondary roots branch off from the primary ones, representing subsequent, more specific causes that stem from these larger issues. Lastly, leaves on the tree symbolize the visible symptoms or outcomes that the organization notices and experiences. The interrelationship among these components forms a hierarchical blueprint for analyzing problems.
Overview of the Structural Design of a Root Cause Tree Diagram: A root cause tree diagram is articulated through a structure that mirrors that of a biological tree, presenting a clear and orderly way to visually navigate through a problem's complexity. At its base lies the effect or problem that prompted the analysis, ascending to the trunk where the immediate causes are identified. Branching out from these causes are the finer details of contributing factors, the secondary roots, which provide further granularity into the issue. This architecture not only enables ease of understanding but also ensures that all relevant aspects are examined.
Importance of the Sequential Representation in the Diagram: Sequential representation within the root cause tree diagram is crucial. It offers a pathway that practitioners can follow to ensure a logical flow of investigation from the general to the specific. The intent is to facilitate systematic exploration of the problem, fostering a clear view of the relationships and dependencies among causes and their effects. This structured approach not only supports meticulous analysis but also makes it easier to communicate the problem and its origins to stakeholders with varying levels of expertise.
Step by Step Procedure to Create a Root Cause Tree Diagram
Identifying the Problem: The initial step in developing a root cause tree diagram is the clear and concise articulation of the problem. This problem statement acts as the focal point from which the entirety of the root cause analysis branches off. It must be defined with enough specificity to be actionable yet broad enough to encapsulate all relevant issues.
Tracing Back the Primary Causes (Roots): Once the problem is identified, the next step is to work backward to trace the primary causes. This often involves asking a series of "why" questions to move from the effect to the origins of the issue. By repeatedly inquiring about the cause behind each identified factor, a chain leading to the primary causes is revealed.
Identifying Secondary Causes: Secondary causes are traced in the same manner as primary ones. These are often the specific actions, omissions, or failures that lead directly to the primary causes. Identifying these secondary causes is critical in understanding the full complexity of the problem and ensuring that more targeted solutions are developed.
Practical Applications of the Root Cause Tree Diagram
Use in Incident Investigation: The root cause tree diagram is extensively applied in incident investigation scenarios, such as in the aftermath of workplace accidents or system failures. In these instances, it is crucial to dissect the sequence of events and the network of causation, preventing similar events in the future. The visual representation aids in unraveling the intricate web of causes behind an incident, providing a roadmap for developing preventive measures.
Application in Business Process Improvement: Business process improvement projects often benefit from the application of root cause tree diagrams. By applying this tool, organizations can delve deeply into process inefficiencies and dysfunctions, identifying areas where enhancements are both needed and can be most effectively implemented. The clarity provided by the diagram allows for targeted interventions, resulting in more efficient and effective processes.
Role in Quality Control and Monitoring: Quality control and monitoring systems utilize the root cause tree diagram to pinpoint the origins of quality lapses. By tracing quality issues back to the root causes, organizations can implement improvements that ensure sustained quality enhancements rather than short-term fixes. The methodical nature of the diagram assists teams in keeping track of complex quality issues and the measures taken to address them.
Advantages and Limitations of Root Cause Tree Diagram
Key Advantages: The root cause tree diagram offers numerous advantages, chief among them being the facilitation of a better understanding of the problem. By visually mapping out the problem, stakeholders can quickly comprehend the intricacies involved. Additionally, the tool aids in identifying hidden or overlooked causes that might not be obvious at first glance. Implementing this tool within an organization also promotes a proactive approach to online certificate courses and other educational resources, ensuring that personnel is equipped with the necessary analytical skills.
Possible Limitations: However, this tool has its limitations. The root cause tree diagram can sometimes lead to an oversimplification of complex issues, potentially overlooking the multi-faceted nature of some problems. Furthermore, it might not be as effective when applied to convoluted scenarios with multiple adjacent problems requiring concurrent resolution.
Root cause tree diagrams are indubitably powerful tools in the pantheon of problem-solving methods. They afford an intricate yet accessible means of visualizing the origins of problems and guiding corrective action. By laying out a step-by-step guide to creating these diagrams and detailing their vast applications and potential limitations, we hope to have reinforced their value. Embracing the root cause tree diagram across various fields could significantly uplift an organization's capability to address issues at their core, thereby promoting systemic improvements and fostering a culture of continual learning and development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of a Root Cause Tree Diagram in the decision-making process?
The Root Cause Tree Diagram and Decision-Making
Understanding the Tool
The Root Cause Tree Diagram serves as a visual tool. It helps to unpack complex problems. Users identify primary and secondary causes of issues.
Dissecting Problems
The diagram acts as a map. It guides users through layers of causation. At the top sits the observed problem. Branching out are contributing factors.
Promoting Analytical Thinking
Its structure fosters systematic exploration. Users follow paths to underlying reasons. This promotes analytical thinking. It curbs the rush to judgment.
Highlighting Interconnections
The diagram shows how causes interlink. Users see how one factor can influence another. Understanding these connections is crucial for informed decisions.
Prioritizing Actions
By identifying root causes, the diagram aids in prioritizing. It steers focus to the most impactful solutions. This ensures effective use of resources.
Facilitating Communication
One uses it to explain complex problems simply. Teams can thus discuss solutions with clarity. This shared understanding is vital in decision-making.
Mitigating Risk
Foreseeing potential risks becomes easier through the diagram. One can anticipate the effects of certain decisions. This risk mitigation is key to any strategy.
Enabling Continuous Improvement
The tool is not just for immediate decision-making. It aids in learning from past choices. This ensures that continuous improvement is part of the process.
In summary, the Root Cause Tree Diagram is a powerful ally. It sharpens focus, enhances communication, and promotes effective solutions. Its use is a testament to the importance of structured problem-solving in decision-making.
How does the Root Cause Tree Diagram enhance the effectiveness of organizational problem-solving efforts?
Understanding the Root Cause Tree Diagram
Organizations constantly battle problems of varying complexities. A popular method to tackle these issues is the Root Cause Tree Diagram. It represents a structured approach to identify and analyze root causes. Here, we explore how this tool enhances the effectiveness of problem-solving efforts.
Breaking Down the Diagram’s Influence
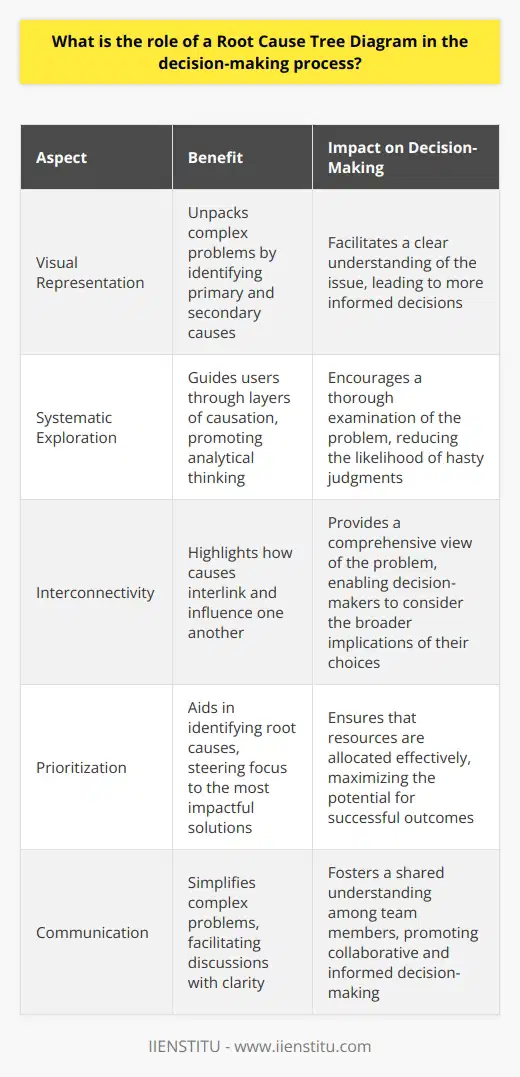
Enhanced Focus
Organizations often grapple with surface-level symptoms. The Root Cause Tree Diagram redirects attention. It leads teams to underlying issues. This concentrated focus prevents energy wastage on mere symptoms.
Promotes Thorough Analysis
Quick fixes seldom offer long-term solutions. This diagram encourages deep analysis. Teams must dissect layers of potential causes. Through this rigorous examination, lasting solutions likely surface.
Encourages a Systematic Process
Problem-solving can become chaotic. The tree diagram provides a methodical framework. Each step leads to the next. This systematic progression streamlines the resolution process.
Facilitates Team Collaboration
Problems are hardly one-dimensional. The tree diagram gathers diverse perspectives. It invites contributions from various team members. This collaboration fosters more comprehensive solutions.
Involves Evidence-based Decision Making
Guesswork can derail organizational efforts. The tree diagram demands factual backing. Each cause links to evidence. Therefore, decisions rest on solid, empirical ground.
Highlights Multiple Cause-and-effect Relationships
Complex issues rarely stem from single causes. The diagram maps out multiple cause-and-effect pathways. Understanding these relationships is crucial. It aids in addressing all contributing factors.
In conclusion, the Root Cause Tree Diagram empowers organizations. It turns problem-solving into a targeted, team-oriented, evidence-based activity. With it, entities can better navigate the intricate web of workplace challenges.
Can you explain the structure and function of a typical Root Cause Tree Diagram in a decision-making context?
Root Cause Tree Diagram: A Decision-Making Tool
A Root Cause Tree Diagram represents a methodical approach. It aims to identify the primary cause of problems. Managers often use it in various industries to improve decision-making processes. The structure of this diagram resembles a tree. This design provides visual mapping of root causes stemming from a central issue.
Understanding the Structure
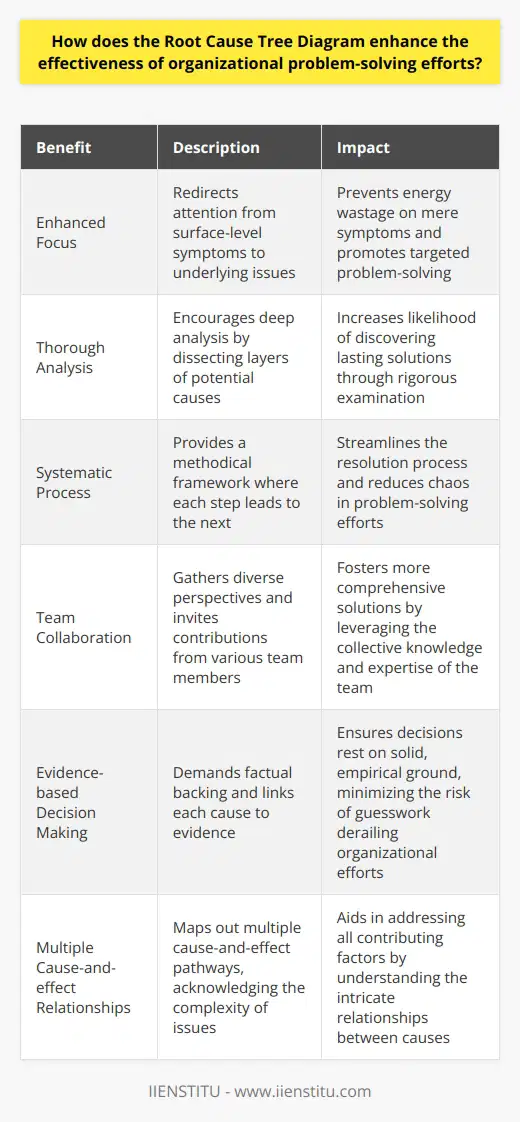
The top node represents the detected problem. This is the starting point of the diagram. From this node, branches extend to represent potential causes. At this level, these are known as "symptoms" or "effects" of the primary problem. Each branch may further subdivide into smaller branches. These smaller branches indicate more specific causes, delving deeper into the issue.
As the diagram progresses downward, the user reaches the "leaves." These "leaves" symbolize the root causes. Unlike higher-level symptoms, root causes are actionable. They offer insights into how to solve the core problem.
Functionality in Decision Making
Root Cause Tree Diagrams provide clarity. They serve to untangle complex issues. By presenting a structured breakdown, they make it easier to see where problems originate.
In decision-making, these diagrams guide critical thinking. They promote a systematic exploration of contributing factors. Their purpose is to avoid recurrence of the problem by addressing its origin.
In use, teams brainstorm potential causes and place them on the diagram. They assess each potential cause through further analysis. This typically involves asking "why" until no further reasoning is possible. This method gets labeled "the 5 Whys technique".
Once the root causes emerge, they become targets for corrective action. Decision-makers thus receive a prioritized list of interventions. These focus on the highest-impact issues.
Applications and Benefits
Complexity Reduction: Breaks down complicated problems
Improved Focus: Helps concentrate on underlying issues
Accountability: Makes it clear who should address each cause
Resource Allocation: Guides where to best assign resources
Preventive Action: Enables the development of strategies to prevent future problems
Overall, the Root Cause Tree Diagram is a powerful device. It takes the guesswork out of problem-solving. It lays the groundwork for informed and effective decisions. As such, it proves indispensable in continual improvement initiatives across diverse fields.