In a world increasingly driven by data, the importance of quantitative analysis cannot be overstated. From the financial markets to public health, the ability to decipher complex datasets and extract meaningful information is a critical skill for decision-making. This blog post delves into the essence of quantitative analysis, providing an in-depth exploration of its fundamentals, methodologies, applications, and the challenges and opportunities it presents.
I remember my first encounter with quantitative analysis during my undergraduate studies. As a psychology major, I was initially intimidated by the prospect of working with numbers and statistics. However, as I delved deeper into the subject, I began to appreciate the power of quantitative methods in uncovering patterns and trends that would otherwise remain hidden.
The Basics of Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis refers to a methodological approach whereby data is collected and analyzed numerically. At its core, it is the process of turning observations into numbers and processing these numbers to reach conclusions. Used across various sectors, this method provides a systematic empirical investigation of observable phenomena via computational, statistical, and mathematical tools.
Differentiating Quantitative from Qualitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis often contrasts with qualitative analysis, which emphasizes understanding phenomena through a more descriptive and subjective lens. While qualitative research explores the 'why' and 'how' of decision processes, quantitative analysis seeks to answer questions of 'how many' or 'how much.' This distinction is crucial as it aligns the type of analysis with the nature of the problem at hand.
In my own research, I've found that a combination of both quantitative and qualitative methods often yields the most comprehensive understanding of a given phenomenon. While quantitative data provides the objective backbone, qualitative insights add depth and context to the numbers.
Real-life Applications of Quantitative Analysis
The applicability of quantitative analysis is extensive. It aids businesses in understanding market trends, enables economists to forecast economic shifts, and assists scientists in testing theoretical models. In healthcare, it can be employed to evaluate treatment outcomes or understand the prevalence of diseases within a population. These examples only scratch the surface of how deeply ingrained this analytical approach is in contemporary data analysis practices.
I've personally witnessed the impact of quantitative analysis in the field of education. By analyzing student performance data, educators can identify areas where students are struggling and develop targeted interventions to improve learning outcomes. This data-driven approach has revolutionized the way we think about teaching and learning.
The Impact of Quantitative Analysis in Decision-making
Quantitative analysis significantly impacts decision-making processes as it provides objective evidence that can be used to make informed decisions. It removes much of the guesswork that often accompanies decision-making, replacing subjective judgment with data-driven insights. This approach can improve efficiency, accuracy, and consistency in decisions across all levels of an organization or research enterprise.
In my experience working with businesses, I've seen how quantitative analysis can be a game-changer in strategic planning. By analyzing market trends, customer behavior, and financial data, companies can make more informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and resource allocation.
How Quantitative Analysis Works
The process of quantitative analysis involves several stages, each with its unique set of challenges and requirements. From the initial hypothesis formation to the final interpretation of results, every step must be carefully considered to ensure the integrity and validity of the analysis.
Key Steps in Quantitative Analysis
Key steps in quantitative analysis begin with defining the question or hypothesis. From there, relevant data is collected, prepared, and then analyzed using various statistical methods. The results are then interpreted, often requiring a deep understanding of both the analytical methods used and the domain to which the data pertains.
As someone who has taught quantitative methods to graduate students, I cannot stress enough the importance of a solid foundation in these key steps. Without a clear understanding of the research process, it's easy to fall into the trap of drawing erroneous conclusions from data.
Primary and Secondary Data in Quantitative Analysis
Data collection is a pivotal element in quantitative analysis. Primary data collection involves gathering new data directly through experiments or surveys. Secondary data, on the other hand, refers to the use of existing data sourced from previous studies, institutional records, or large databases. Each type has its advantages and challenges, from the control and specificity of primary data to the breadth and accessibility of secondary data.
In my own research, I often rely on a combination of primary and secondary data. While primary data allows me to tailor my data collection to my specific research questions, secondary data provides a wealth of information that would be impossible to gather on my own.
The Use and Importance of Statistical Tools
Statistical tools are the workhorses of quantitative analysis, enabling researchers to sift through data and extract patterns and correlations. Tools such as regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and variance analysis transform raw data into actionable insights. The mastery of these tools is vital, as they can uncover relationships within data that would otherwise remain obscure.
I remember the first time I used SPSS, a popular statistical software package, to analyze a large dataset. It was like a whole new world opened up before me. Suddenly, I could see patterns and relationships that were invisible to the naked eye.
Different Methods of Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis encompasses a range of methods, each suited to specific types of data and research questions. Surveys, observations, experiments, and various data analysis methods offer analysts a rich toolkit to approach their data.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Surveys
Surveys are a popular method for collecting data directly from respondents. They are versatile, capable of reaching large audiences, and can be executed relatively quickly. However, surveys also present challenges such as response bias and limitations in the depth of information that can be obtained.
I've conducted numerous surveys in my research, and I've learned that the key to a successful survey is in the design. Careful consideration of question wording, order, and format can make a big difference in the quality of the data collected.
Value and Limitations of Observations & Experiments
Observations and experiments are fundamental for collecting primary data. Observations offer the opportunity to gather data in natural settings, while experiments provide controlled environments to test specific hypotheses. Nevertheless, these methods require meticulous planning to avoid confounding variables and to ensure the reliability of outcomes.
In my field work, I've conducted both observations and experiments. While observations provide a rich, real-world context, experiments allow for a level of control and precision that is essential for testing specific hypotheses.
The Power and Pitfalls of Data Analysis Methods
The power of data analysis methods lies in their ability to simplify and clarify complex data. Techniques like factor analysis, cluster analysis, and time series analysis can reveal the underlying structure of datasets. However, a critical eye is necessary to avoid misinterpretations that could result from the misuse of these advanced techniques. Expertise is essential to navigate both the power and the pitfalls inherent in these methods.
I once spent weeks analyzing a dataset using advanced statistical methods, only to realize that I had made a critical error in my assumptions. It was a humbling experience, but it taught me the importance of double-checking my work and seeking feedback from colleagues.
Challenges and Opportunities in Quantitative Analysis
The evolving landscape of data and technology presents both obstacles and openings for quantitative analysis. Anticipating and preparing for these dynamics is a decisive factor in maintaining the efficacy of this analytical practice.
Overcoming Challenges in Quantitative Analysis
Current challenges include concerns around data privacy, the complexity of 'big data,' and the need for advanced computational resources. To overcome these challenges, analysts must be equipped with not only robust statistical know-how but also a nuanced understanding of ethical considerations and technological advancements.
In my work with sensitive health data, I've had to navigate complex ethical and legal considerations around data privacy. It's a constant balancing act between the need for data and the imperative to protect individual privacy.
The Future of Quantitative Analysis
Future opportunities in quantitative analysis are boundless, with ongoing innovations in areas such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies have the potential to automate and enhance existing quantitative methods, leading to faster and potentially more accurate analyses.
I'm excited about the potential of machine learning to revolutionize quantitative analysis. By training algorithms on vast datasets, we can uncover patterns and insights that would be impossible for a human analyst to detect.
Conclusion
Throughout this discussion, it has become clear that quantitative analysis is an indispensable element in data-driven decision-making. Its application permeates countless domains, providing a methodological framework for transforming raw data into digestible and actionable insights.
The importance of understanding and using quantitative analysis remains paramount in an era defined by information uncertainty and complexity. As the data landscape continues to expand and shift, proficiency in this area will be synonymous with both professional and academic success.
Reflecting on my own journey with quantitative analysis, from my initial trepidation to my current passion, I am struck by the incredible power of this approach. It has transformed the way I think about the world and has given me tools to make a real impact in my field.
To those embarking on their own quantitative journey, I offer this advice:
Don't be afraid of numbers. Quantitative analysis is not about being a math whiz, it's about learning to think critically and systematically about data.
Start with the basics. Before diving into advanced methods, make sure you have a solid foundation in basic statistical concepts and research design.
Practice, practice, practice. The best way to learn quantitative analysis is by doing it. Seek out opportunities to work with data, whether through coursework, research projects, or professional experiences.
Collaborate with others. Quantitative analysis is a team sport. Seek out collaborators with different skills and perspectives to enhance your own work.
Stay curious. The field of quantitative analysis is constantly evolving. Stay up to date with new methods and technologies, and never stop learning.
By embracing these principles, anyone can develop the skills and mindset needed to succeed in the exciting world of quantitative analysis. The data is out there, waiting to be understood. All it takes is a curious mind and a willingness to dive in.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of quantitative analysis in supporting data-driven decision-making processes in organizations?
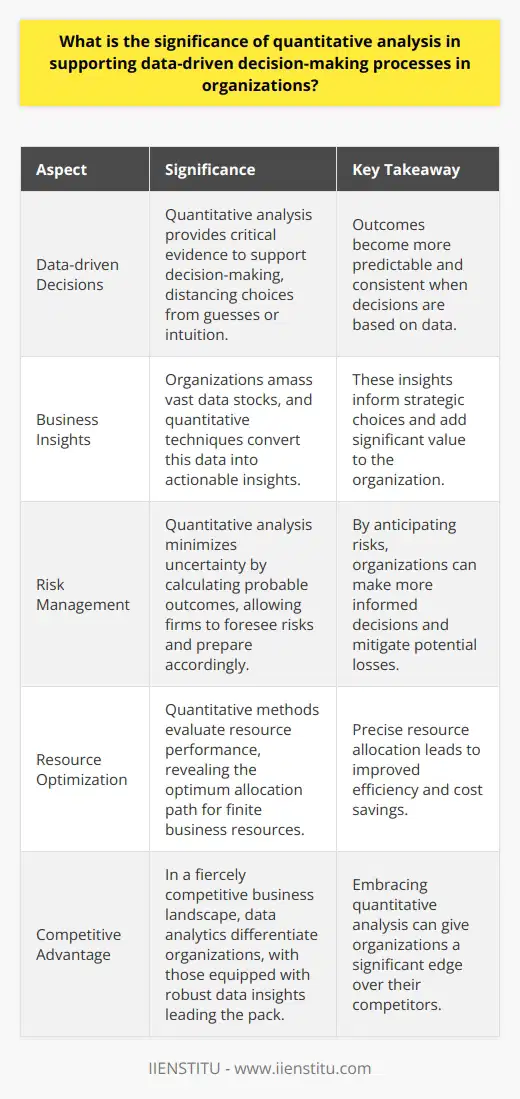
Quantitative Analysis Defined
Quantitative analysis harnesses mathematical and statistical methods. It assesses numerical data. This approach aids in measuring, comparing, and projecting organizational performance.
Its Role in Decision-Making
Data-driven decisions rely on evidence. Quantitative analysis provides this critical evidence. It distances decisions from guesses or intuition. Outcomes become predictable and consistent.
Enhancing Business Insights
Organizations amass vast data stocks. Without analysis, this bounty adds little value. Quantitative techniques convert data into insights. These insights inform strategic choices.
Risk Management
Risk accompanies business decisions. Quantitative analysis minimizes uncertainty. It calculates probable outcomes. Firms foresee risks, prepare accordingly.
Resource Optimization
Resources in business are finite. Allocating these demands precision. Quantitative methods evaluate resource performance, revealing the optimum allocation path.
Performance Measurement
Firms need to track success. Metrics arise from quantitative analysis. These performance indicators guide day-to-day operations and long-term strategies.
Competitive Advantage
The business landscape is fiercely competitive. Data analytics differentiate organizations. Those equipped with robust data insights lead the pack.
Continuous Improvement
Stagnancy spells decline in business. Quantitative analysis identifies growth areas. Continuous improvement becomes ingrained in the organizational culture.
In Summary
Quantitative analysis sits at the heart of modern decision-making. It strengthens strategy with structured, numerical support. Firms embrace data-driven guidance. They achieve improved operational efficiency and strategic foresight. Quantitative analysis is not merely relevant. It is indispensable.
How can the application of quantitative analysis techniques assist in predicting and modelling future business trends?
The Power of Quantitative Analysis in Forecasting Business Trends
Quantitative analysis stands as a stronghold in today's fast-paced business environment. It harnesses mathematical and statistical tools. These tools transform raw data into insights. Insights become the basis for strategic decisions. By using quantitative analysis, businesses may anticipate market shifts. They refine their strategies accordingly. Moreover, it equips them to model future business trends reliably.
Quantitative Techniques in Business Modeling
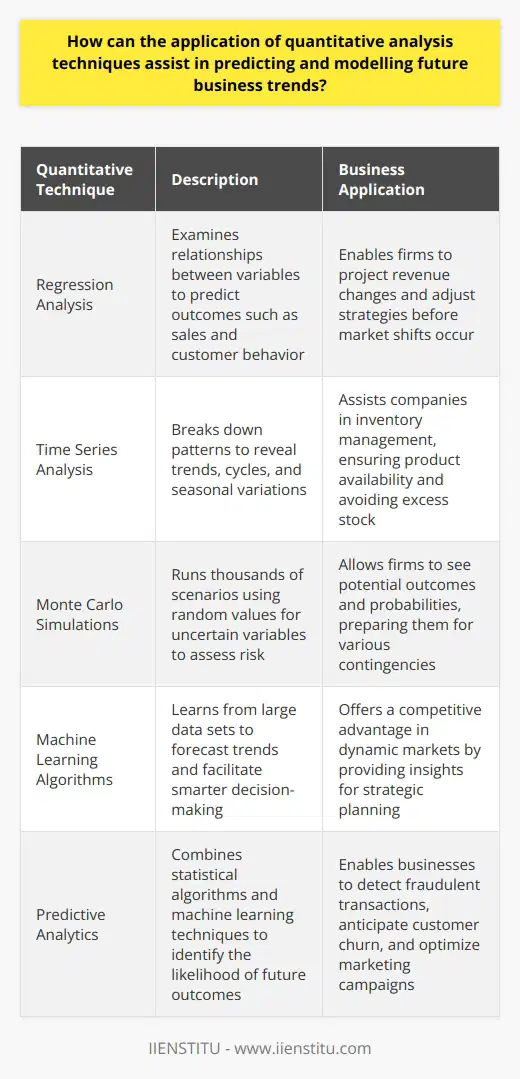
Regression analysis predicts variables. It examines relationships between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. This analysis foretells outcomes. These include sales and customer behavior. Firms can project revenue changes. They can adjust their strategies before shifts occur.
Time series analysis breaks down patterns. It reveals trends, cycles, and seasonal variations. Companies use it for inventory management. They ensure product availability. They avoid excess stock.
Monte Carlo simulations allow risk assessment. They run thousands of scenarios. Each scenario uses random values for uncertain variables. Firms see potential outcomes and probabilities. They prepare for various contingencies.
Machine learning algorithms forecast trends. They learn from large data sets. These insights facilitate smarter decision-making. They offer a competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Advantages of Applying Quantitative Techniques
Quantitative methods enhance strategic forecasting. They offer numerous advantages:
- Objective insight cuts through bias. Decisions rely on data, not intuition.
- Improved precision in forecasts. Better accuracy guides better decisions.
- Risk management identifies potential pitfalls. Companies strategize proactively.
- Resource optimization allows focused investments. Resources go where most impactful.
Business Applications
Industries across the board benefit from quantitative analysis. Consider these applications:
- Retail sectors predict inventory needs. They maximize sales while minimizing waste.
- Financial institutions assess credit risks. They tailor their loan offerings.
- Manufacturing sectors optimize production schedules. They meet demand efficiently.
Quantitative techniques are indispensable. They enhance an organization's predictive capabilities. They inform strategic planning. They allow companies to adapt swiftly. They push the boundaries of what businesses can anticipate about their future.
In conclusion, quantitative analysis paves the way. It clears the fog from the crystal ball of business foresight. It equips decision-makers. They act not on hunches, but on hard evidence. In an era of big data, it is the beacon. It lights the path toward successful futures for businesses that dare to follow its lead.
What are some challenges faced when implementing quantitative analysis methods in the decision-making process and how can they be surmounted?
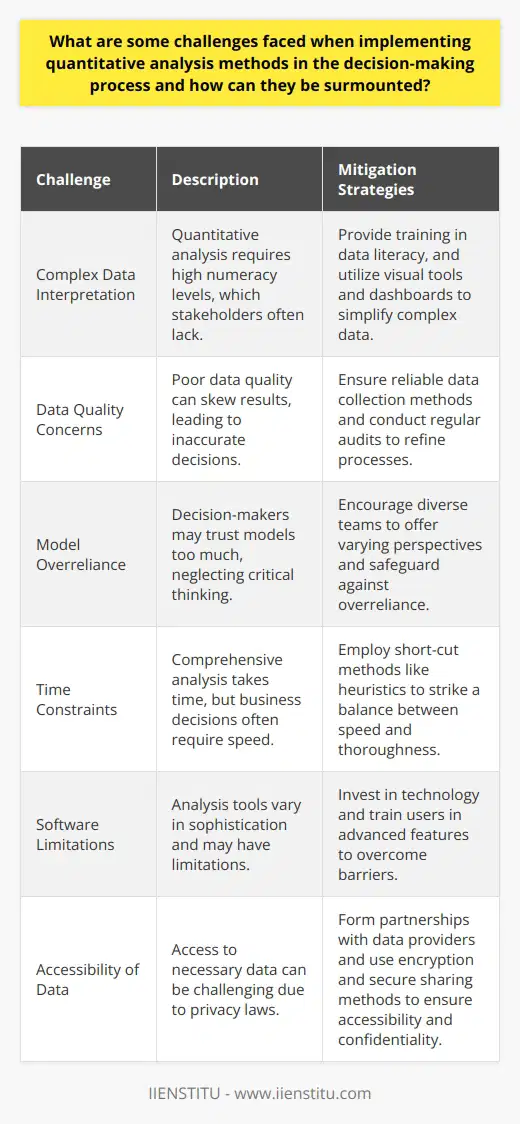
Quantitative Analysis in Decision-Making
Complex Data Interpretation
Quantitative analysis demands high numeracy levels. Stakeholders often lack these skills. Training in data literacy can bridge this gap. Visual tools and dashboards also simplify complex data. They make interpretation less daunting.
Data Quality Concerns
Accurate decisions need good data. Poor quality skews results. Institutions must ensure reliable data collection methods. Regular audits refine these processes.
Model Overreliance
Decision-makers sometimes trust models too much. Critical thinking must supplement quantitative findings. Diverse teams offer varying perspectives. They safeguard against overreliance.
Time Constraints
Speed often drives business decisions. Comprehensive analysis takes time. Short-cut methods like heuristics can assist. They strike a balance between speed and thoroughness.
Software Limitations
Analysis tools are imperfect. They range widely in sophistication. Continuous investment in technology overcomes such barriers. Training users in advanced features is also essential.
Accessibility of Data
Access to necessary data can prove challenging. Privacy laws often restrict data use. Partnerships with data providers can ensure accessibility. Encryption and secure sharing methods protect confidentiality.
Cost of Implementation
Financial investment deters quantitative methods use. Cost-benefit analysis demonstrates long-term gains. These gains often outweigh initial costs.
Communication of Results
The presentation of results impacts their acceptance. Communicate findings clearly. Use language stakeholders understand. Successful communication ensures results drive the desired action.
Resistance to Change
Inertia impedes new methods' adoption. Engagement with all users encourages buy-in. Focus on improvement over replacement. Such framing reduces resistance.
Skewed Interpretations
Bias affects interpretation. Training in unbiased data analysis is crucial. It enhances the integrity of results.
Evaluation of Outcomes
Quantitative analysis requires outcome evaluation. Monitor decisions to assess their effectiveness. Feedback refines future analysis. It informs better decision-making practices.
To conclude, challenges in implementing quantitative analysis are manifold. Each presents a unique barrier to data-driven decision-making. Yet, with targeted strategies, organizations can overcome these hurdles. In doing so, they enhance decision quality and operational success.