In the complex ecosystem of quality management, Quality Function Deployment (QFD) stands as a strategic tool, influential in steering product development toward excellence. The significance of QFD transcends the mere translation of customer requirements; it enhances the synergy between market demands and technical design choices, ultimately manifesting as superior products and services. As we embark on a deeper exploration of QFD's seminal role in the realm of quality management, this blog post aims to provide a comprehensive dissection for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Through the examination of its historical roots, procedural nuances, and application in modern technology, readers will leave with a fortified understanding of its application and relevance in the current industrial landscape.
History and Evolution of QFD
Origin of QFD – articulation and attribution
QFD's genesis can be traced back to Japan in the late 1960s when it was developed at the shipbuilding company Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Originally conceptualized to improve the design quality and reliability of products, QFD's principle of starting with comprehensive customer insights shifted the paradigm from a production-focused approach to a customer-centric one.
As an outcome of collaborative hard work and profound insight, QFD introduced a more systematic method to the intricate process of product design and development.
Evolution and advancements in the QFD process
From its origins in Japan, QFD crossed international waters, impressing and being adopted by Western industries in the 1980s. Evolving from the basic models used in the 1960s, contemporary QFD has expanded into a sophisticated tool that incorporates multiple matrices and analytical strategies to better serve complex production and design needs. Moreover, the flexibility and adaptability of QFD have allowed its principles to be applied to services, software development, and even healthcare and education sectors.
Current trends and issues in QFD
In today's fast-paced and innovation-driven market, QFD is facing fresh challenges and discussions. The increasing complexity of products, the dynamic nature of customer preferences, and the speed at which technology changes demand a more agile and responsive QFD framework. The ongoing discourse now revolves around the integration of QFD with agile methodologies, design thinking, and sustainability concerns to ensure that it remains a relevant and powerful tool in the delivery of quality.
Understanding the QFD Process
Basic elements in QFD – Voice of the Customer (VOC), the Quality House, Competitive Analysis, and Prioritization
At its foundation, QFD hinges on the 'Voice of the Customer' (VOC), a term that encapsulates customer needs, wants, and expectations. It involves in-depth market research, feedback collection, and customer interaction to accurately interpret and fulfill customer demands. The Quality House, or House of Quality, is another pivotal element in QFD; it is a structured planning matrix that translates VOC into design requirements. Competitive Analysis complements these elements by benchmarking against competitors, while Prioritization ensures that resource allocation aligns with the highest-impact aspects of customer satisfaction.
The four phases of QFD
QFD unfurls over four distinct phases, starting with Product Planning, which is actualized in the House of Quality matrix. This initial stage emphatically scrutinizes customer demands alongside technical capabilities and market competition. It is succeeded by Part Deployment, fleshing out the specific parts or systems to meet the established design requirements. Process Planning comes next, delineating the production processes, and lastly, Production Process, which scrutinizes the actual manufacturing procedures to ensure they align with the planned quality attributes.
Detailed look into the four phases, explaining each phase with an practical example
Breaking the QFD framework further, let's apply it to designing a high-tech wearable, for instance. Phase one involves defining the vital needs of users, such as battery life or user interface, and comparing these against competitors. In phase two, the R&D team determines the battery technology or screen type needed to fulfill the set requirements. The third phase plans the assembly process, assessing what technology or manual skill is required for manufacturing. The final phase then fine-tunes the production process, ensuring the wearables fabricated meet the stringent quality demands initially set forth.
The Role of QFD in Risk Management and Customer Satisfaction
The correlation between QFD and risk management – highlighting the preemptive nature of QFD
The proactive nature of QFD inherently intertwines it with risk management. By bringing potential issues to light in the early stages of product design, QFD helps managers anticipate risks and implement mitigative strategies before substantial costs or delays occur.
This forward-thinking approach allows for smoother transitions throughout the product development cycle and averts the possibility of large-scale redesign after production has commenced.
The impact of QFD on customer satisfaction – illustrating how QFD aligns product specifications with customer needs
The key to achieving high degrees of customer satisfaction lies in the competent alignment of product specifications with customer requirements. QFD aids in this by acting as a bridge between the customer's voice and the technical solutions provided by the company.
It systematically ensures that every product feature is scrutinized through the lens of customer value, which not only leads to higher satisfaction post-purchase but also fosters brand loyalty and market competitiveness.
Case Study: QFD in Practice
Detailed case study analyzing the application of QFD process in a real-world product development cycle
To manifest the practical utility of QFD, consider a tech company developing a new smartphone. By implementing QFD, it starts by gathering extensive customer feedback to identify attributes such as camera quality, battery life, and usability as decisive for customer satisfaction. Subsequently, through multiple House of Quality matrices, these attributes are broken down into engineering characteristics and part specifications.
Over the course of the development, the company maintains vigilant surveillance over how well the evolving product adheres to these customer-derived attributes, enabling targeted development that culminates in a product highly resonant with customer expectations.
Challenges and Limitations of QFD
Common challenges encountered in implementing QFD
The application of QFD, while highly beneficial, is not without its challenges. Companies often struggle with the scale and complexity of QFD matrices, leading to potential oversights or misinterpretation of customer data. The success of QFD also hinges on effective interdepartmental communication and consistent commitment from all levels of the organization, which can be difficult to sustain in larger corporations.
Understanding the limitations and criticisms of QFD
Critics of QFD argue that it can become cumbersome and rigid if not carefully implemented, potentially stifling creativity or sidelining non-quantifiable aspects of product design that may appeal to customers. There is also the danger of becoming too insular within the QFD process, relying heavily on existing customer data and failing to anticipate future market shifts or emergent customer desires.
QFD and Modern Technology
Integration of QFD with digital technologies for more efficient product development
The integration of QFD with modern digital technologies has ushered in a new era of efficiency and accuracy in product development. Tools such as simulation software, digital prototyping, and data analytics enable more precise assessments of customer desires and faster iteration of design matrices. This technological symbiosis enhances the dynamism and responsiveness of QFD, allowing it to flourish further in today’s digital landscape.
Future implications of technological advancements in QFD
As technology progresses, the potential of AI and machine learning to transform QFD is substantial. Predictive analytics, for instance, can refine the understanding of customer preferences, adapting product development proactively rather than reactively. Moreover, technological advancements may foster a more nuanced and widespread adoption of QFD, ensuring that its principles underpin even more innovative and customer-centric products.
Recap of the key points discussed in the blog
We have navigated the role of QFD in quality management from its historical conception to its contemporary applications. Throughout its phase-based process, we have seen QFD's vital function in aligning product development with the Voice of the Customer, preemptively managing risks, and securing customer satisfaction. Additionally, we have discussed its current challenges and the promising horizon that modern technology brings to QFD's effectiveness.
Final thoughts and reflections on the importance and applications of QFD in product design and development
As organizations strive to stand out in competitive markets, the importance of methodologies such as QFD cannot be overstated. When adeptly executed, QFD remains a compelling practice capable of guiding companies toward fulfilling the most paramount goal of all – delivering products that not only meet but surpass customer expectations, thereby yielding undeniable success.
Frequently Asked Questions
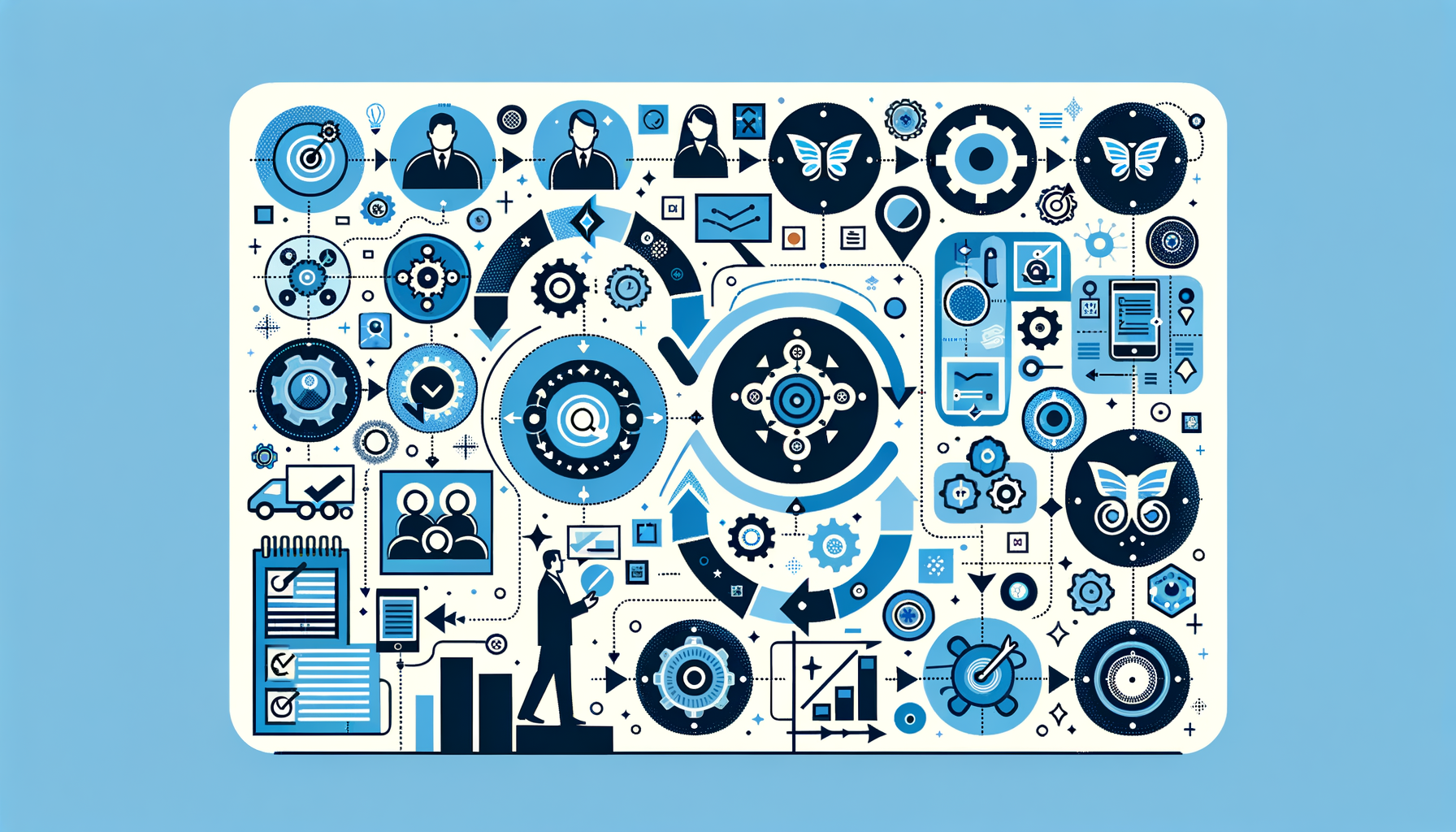
What is the relationship between QFD (Quality Function Deployment) and overall quality management strategies in organizations?
Quality Function Deployment in Quality Management
QFD: A Definition
QFD stands for Quality Function Deployment. It is a structured method. It captures customer requirements. It converts these requirements into engineering specifications. These specifications guide product development.
Link to Overall Quality Management
Quality management strategies encompass various tools. QFD is one such tool. It aligns products with customer expectations. This alignment leads to higher customer satisfaction. It also translates into better product quality.
QFD’s Role in Quality Improvement
QFD helps teams focus on customer needs. It encourages cross-functional collaboration. It also aids in prioritizing product features. Through clear communication, it reduces errors and rework. This approach aligns with Total Quality Management (TQM) principles.
Enhancing Competitiveness
Organizations that implement QFD can gain a competitive edge. They understand customer needs better. They deliver products that meet these needs effectively. This approach can create a reputation for quality.
Process Integration Aspect
In quality management, integration is key. QFD integrates with other organizational processes. It does this through its matrix, often called the House of Quality. The matrix maps customer requirements to operational steps.
Customer-Centric Approach
QFD requires deep customer understanding. It starts with the Voice of the Customer (VOC). Organizations gather customer insights. They translate these insights into actionable product features.
Feedback Loops and Continuous Improvement
QFD provides a framework for feedback. It allows for continuous product improvement. Users' feedback becomes integral. Product refinements follow. This cycle perpetuates quality enhancements.
Risk Reduction in Development
QFD mitigates risks in product development. It identifies potential failure modes. It fosters proactive issue resolution. It thus aligns with risk management approaches within quality strategies.
Supporting Documentation
QFD creates detailed documentation. This documentation tracks the development process. It justifies decisions. It is vital for ISO quality standards and other certifications.
Training and Culture
Effective QFD use requires proper training. It also demands a quality-centric culture. Staff must understand customer focus ideals. Quality must permeate all levels of an organization.
Strategic Planning
QFD aligns with strategic planning. It helps define clear goals. It guides resource allocation. It ensures efforts concentrate on quality outcomes.
Conclusion
In sum, QFD is integral to quality management. It acts as a bridge. It connects customer needs to operational excellence. It drives continuous improvement. It enhances an organization's quality reputation. Deploying QFD can lead to robust and customer-focused products. It enhances the potential success of overall quality management strategies.
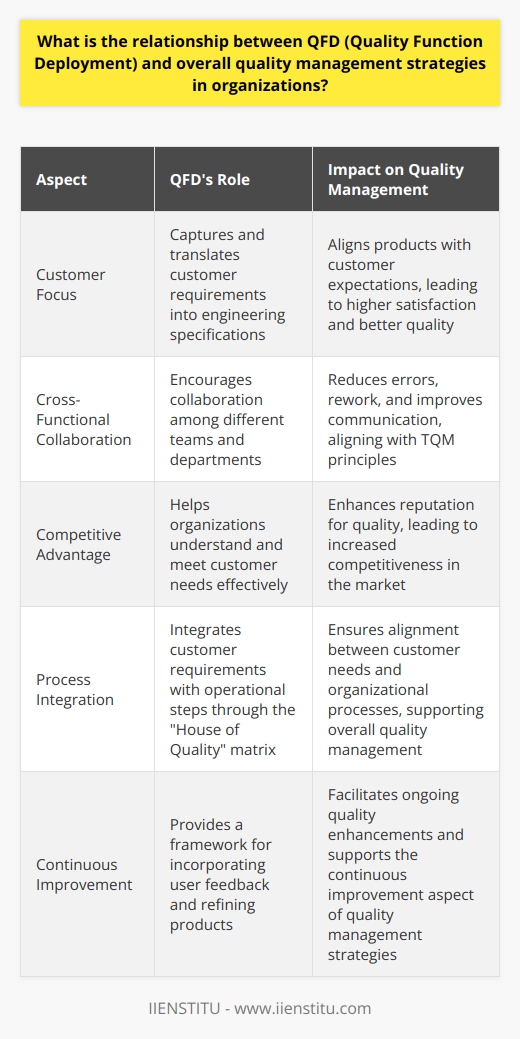
How does QFD help in translating customer needs into specific product or service requirements?
Understanding QFD
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) begins with the customer. This method recognizes their importance. It focuses on their needs. It helps in designing quality products. It does this systematically.
From Voice to Value
QFD translates the voice of the customer. It turns their needs into explicit specifications. This ensures that the design meets expectations. It focuses on what the customer values.
The House of Quality
The House of Quality stands central in QFD. It is the primary tool used. It represents customer desires. It relates these to concrete product attributes. It helps in understanding the relationships.
A Structured Approach
QFD uses a structured matrix. This matrix links customer needs to design requirements. It brings clarity. It guides decision-making.
- Listen: Identify what the customer wants.
- Translate: Convert needs into product features.
- Analyze: Evaluate how well features meet needs.
- Optimize: Balance trade-offs to maximize satisfaction.
Benefits of QFD
QFD offers several benefits. It prioritizes customer needs effectively. It aligns product development with these needs. It reduces time to market. It accomplishes this by eliminating misunderstandings early. It results in higher quality products. It also enhances cross-functional collaboration.
Case by Case
QFD is not one size fits all. It adapts to different products and industries. It considers the uniqueness of each situation. It moulds to a particular development process.
Conclusion
QFD is a powerful tool. It bridges customer desires to tangible products. It requires thoughtful implementation. It leads to better products. This pleases customers. It benefits businesses. It ensures that customer needs shape the products we use.
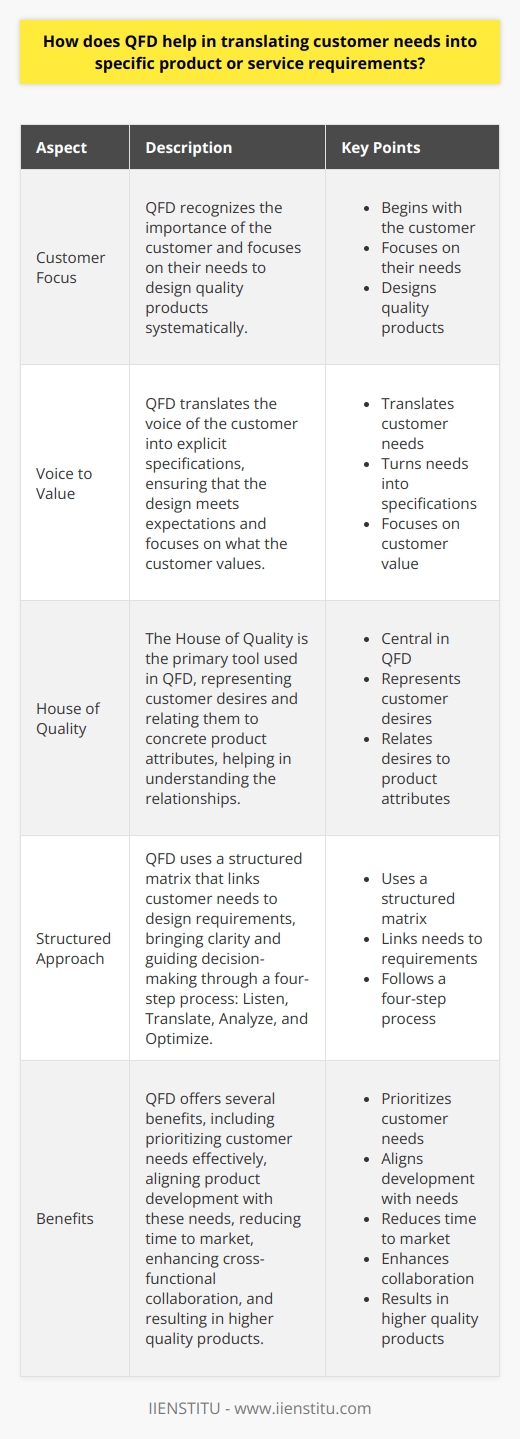
How do the principles of QFD interact with and impact other aspects of operational management such as product development and process improvement?
Understanding QFD and Its Place in Operational Management
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is a unique approach. It prioritizes customer satisfaction in product and service design. Organizations that embrace QFD aim to meet or even exceed customer expectations. They integrate QFD principles into every stage of their operational management.
The Interplay Between QFD and Product Development
QFD Shapes Customer-Centric Product Design
In product development, customer needs guide the design process. QFD begins with the "voice of the customer". It translates these needs into design requirements. This ensures that the final product aligns with customer expectations.
Enhancing Cross-Functional Collaboration
Product development relies on teamwork. QFD fosters cross-functional collaboration. It brings together sales, marketing, engineering, and manufacturing. This integrated approach leads to more innovative and customer-focused products.
Fostering Agile Prototyping and Testing
With QFD, teams develop prototypes and run tests early on. They do this to gather feedback quickly. This loop of rapid prototyping and testing fine-tunes products. It ensures that they serve the intended purpose efficiently.
QFD's Role in Process Improvement
Driving Continuous Improvement
Process improvement is crucial for operational efficiency. QFD aids in identifying areas that need enhancement. It provides a structured methodology for continuous improvement.
Addressing Real Customer Pain Points
QFD directs process improvement by spotlighting customer pain points. It leads to processes that are not just efficient but also effective in delivering value.
Reducing Waste and Increasing Quality
The QFD approach minimizes waste. It does so by ensuring that every process step adds value from a customer's perspective. This streamlining results in higher-quality outcomes.
The Ripple Effects of QFD Throughout Operations
Cultivating a Quality Culture
QFD instills a quality-centered ethos in an organization. It emphasizes that every employee plays a part in delivering quality. This mind-set can revitalize an organization's culture.
Making Data-Driven Decisions
QFD involves quantitative and qualitative data about customers' needs. This data guides decision-making throughout all operational aspects.
Aligning Strategic Objectives with Execution
Strategies often fall short during execution. QFD ensures that operational practices support strategic objectives. It closes the gap between strategy formulation and its practical application.
In closing, QFD marks a transformative tool. It touches all corners of operational management. It bridges the gap between customer desires and the delivered finished product. QFD fosters continuous process improvement. It aligns operational practices with strategic goals. It melds customer demands with product design and development. By doing so, it secures a competitive edge and long-term success.