In the realm of systematic problem-solving, Problem Tree Analysis stands as a superior tool for dissecting Complex Issues into comprehensible segments. At its core, the concept involves a structural breakdown of problems to their root causes and subsequent effects, presenting a visual and analytical framework to address multifaceted challenges. Tracing its lineage to strategic planning methods and monitoring approaches, the Problem Tree Analysis has gained prominence within various professional fields for its methodical precision. The importance of such an approach lies in its ability to render clarity to otherwise convoluted predicaments, enabling stakeholders to undertake informed decision-making with enhanced precision.
The breadth of Problem Tree Analysis cannot be overstated in its capability to provide insights into the interconnections that govern dynamic issues. Its adoption is widely considered indispensable for public sector strategists, business analysts, and key decision-makers. This academic exposition delves deep into the methodology, practical applications, strengths, and limitations of Problem Tree Analysis, equipping readers with an expert roadmap to harness its benefits effectively.
Revisiting the evolution of this technique necessitates an acknowledgment of the nuanced evolution of Complex Issues themselves. As challenges burgeon in complexity, so too must the tools employed to dissect and resolve them. Historically, the development of Problem Tree Analysis mirrors the rising intricacies of social, political, and environmental issues, offering a structured lens to scrutinize obstacles that impede progress across various domains.
Understanding Complex Issues through Problem Tree Analysis
The Essence of Complex Problems
Complex issues in contemporary society transcend simple cause-and-effect relationships, often involving multiple stakeholders, intersecting policies, and contradictory objectives. These issues demand a problem-solving approach that can navigate the intricate layers and broader implications of each decision. By define, complex issues manifest in numerous sectors, including climate change initiatives, healthcare reforms, and economic development strategies, each presenting its unique set of challenges and requiring bespoke solutions.
Foundations of Problem Tree Analysis
The canvas of Problem Tree Analysis is painted with three essential elements: the core problem, its root causes, and the resulting effects. These components interact within a problem-oriented framework, often linked to the Logical Framework Approach, a strategic planning instrument. The interplay between Problem Tree Analysis and the Logical Framework Approach is a testament to their complementary nature, the former serving to untangle the web of causality, while the latter facilitates the crafting of goal-oriented action plans.
The conceptual scaffolding of Problem Tree Analysis is built upon this tripartite structure, enabling practitioners to distill Complex Issues into manageable elements. In doing so, it permits a granular examination of the multifaceted factors contributing to a central dilemma. Through a layer-by-layer analysis, stakeholders can systematically navigate through the thicket of interdependencies, paving the way for effective remediation strategies.
Methodology of Problem Tree Analysis
Step-by-Step Guide to Constructing a Problem Tree
Commencing with identifying the core problem is the foundational step in constructing a Problem Tree. A thorough and nuanced understanding of the central issue is essential before one can delineate its causes and effects. Subsequently, mapping out these factors progresses in a hierarchal manner, with primary, secondary, and even tertiary layers of influences demarcated in a structured diagram. This visual representation transforms abstract Complex Issues into a tangible framework, yielding clarity and direction in the pursuit of solutions.
Analytical Methods Complementing Problem Tree Analysis
Problem Tree Analysis does not operate in isolation; rather, it is part of a suite of Analytical Methods and Decision-making Tools that facilitate comprehensive problem-solving. Its integration with other methodologies, such as SWOT analysis or Cost-Benefit Analysis, enhances the robustness of the conclusions drawn. Through this synergy, a multi-dimensional perspective on challenges emerges, empowering stakeholders to devise strategies that are both innovative and grounded in empirical rigor.
Therefore, a problem solving course or an online mba course often integrates Problem Tree Analysis within its curriculum to cultivate a holistic analytical acumen among participants. Learners are taught to harmonize Problem Tree Analysis with other Analytical Methods, crafting a sophisticated blueprint for navigating business and policy decisions.
Applications of Problem Tree Analysis in Decision Making
Case Studies: Problem Tree Analysis in Action
The practical utility of Problem Tree Analysis is underscored through numerous case studies across different sectors. For example, environmental agencies may employ this tool to dissect the multifarious causes behind habitat degradation, while international development organizations use it to identify barriers to education in underprivileged communities. These real-world scenarios serve as powerful testimonies to the effectiveness of the Problem Tree in making sense of complex, high-stakes issues.
Problem Tree Analysis in Strategic Planning and Policy Formulation
In strategic planning and policy-making arenas, Problem Tree Analysis has proven itself to be an invaluable asset. It guides the formulation of policies and strategies that are both target-specific and resilient to unforeseen variables. Organizations leverage the clarity it provides to decide where to allocate resources, how to engage with stakeholders, and the means to measure the impact of their initiatives. The structuring and visualizing capabilities of the Problem Tree contribute significantly to the strategic planning process, delivering insights that inspire confidence among decision-makers.
The strategic worth of Problem Tree Analysis is evident in the way it empowers planners to forecast potential pitfalls and preemptively address them. By linking cause and effect, it advances the policy development process, ensuring the robustness and efficacy of decisions made. Whether in public administration or corporate strategy, this tool aids in aligning objectives with actions, ushering in a future of informed and impactful governance.
Advantages and Limitations of Problem Tree Analysis
The Strengths of Using Problem Tree Analysis
Problem Tree Analysis excels in rendering opaque dilemmas into clear, manageable components. Users benefit from a systematic approach that promotes focus and coherence when addressing Complex Issues. Given its structured format, it adeptly facilitates team discussions, consensus-building, and the dissemination of findings among stakeholders. The visual nature of the tree diagram serves as an effective communication tool, ensuring that all participants have a shared understanding of the problem and its intricacies.
Recognizing the Constraints of Problem Tree Analysis
Despite its many advantages, Problem Tree Analysis is not without constraints. One potential limitation is the oversimplification of Complex Issues, possibly leading to neglect of subtle nuances or the underestimation of certain causes and effects. Additionally, the participatory nature of the analysis may give rise to conflicts or biases if not carefully managed. Thus, it is crucial to utilize a balanced approach when applying Problem Tree Analysis and consider supplemental research and consultation to enrich the insights it offers.
The tool necessitates a clear-headed acknowledgement of its limitations and a conscientious effort to mitigate the risks associated with its use. By doing so, practitioners can maximize the potential of Problem Tree Analysis, ensuring a comprehensive and unbiased evaluation of Complex Issues.
Conclusion and Summary
As we navigate towards the close of this exploration, the indelible significance of Problem Tree Analysis in tackling modern-day conundrums stands reaffirmed. It has emerged as an indispensable tool that augments our capacity to dissect and address multifaceted problems. This article has charted the course from the foundational principles of Problem Tree Analysis to its potential for strategic decision-making and policy formulation, asserting the methodology's transformative impact.
In conclusion, this examination posits Problem Tree Analysis not merely as a technical instrument, but as a conceptual compass guiding stakeholders through the labyrinth of complex challenges. Its adaptability across numerous contexts, paired with the ability to integrate with other problem-solving frameworks, denotes a bright and promising trajectory for its future application.
Frequently Asked Questions
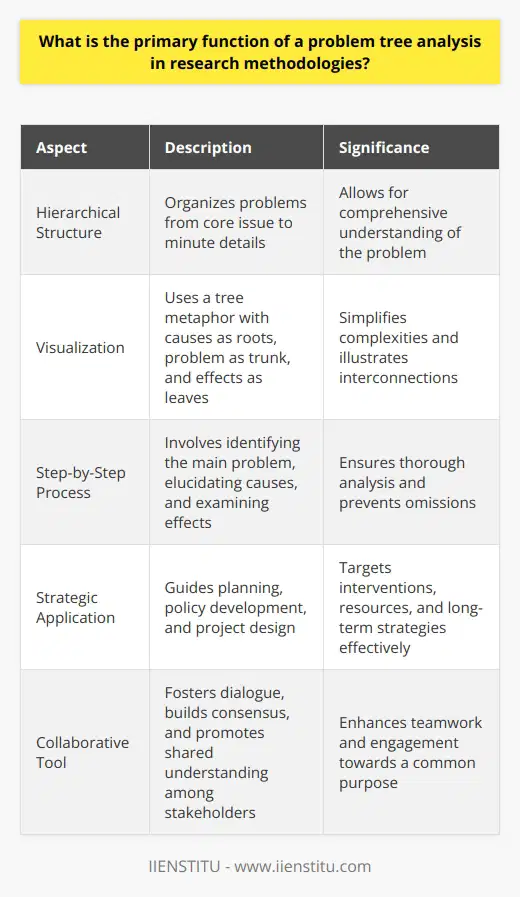
What is the primary function of a problem tree analysis in research methodologies?
Understanding Problem Tree Analysis
In research methodologies, problem tree analysis stands out. It serves as a pivotal tool. Researchers dissect complex problems with it. They identify root causes. They also explore effects. It is vital for solution crafting.
The Core Aim
The primary function is crystal clear. This technique structures problems hierarchically. From core issue to minute details, it digs deep. It visualizes elements interlinked within an issue. This allows for comprehensive problem understanding.
Problem tree analysis springs from one central problem. It branches out into causes and effects. The approach is systematic. Causes form the roots. The problem itself forms the trunk. Effects become the leaves. This visual metaphor simplifies complexities.
Breaking Down the Process
A step-by-step process defines problem tree analysis. Initially, one must identify the main problem. Researchers must remain specific. Vagueness diminishes the tool's effectiveness.
Following identification, causes undergo elucidation. Researchers look for contributing factors. They delve deep into underlying issues. Identifying every possible cause is crucial. Omissions can lead to incomplete analysis.
Once roots are established, the focus shifts. Effects come under the microscope. What does this problem lead to? What ripples across the system? Each effect ties back to the central problem. Interconnections become apparent. This lays bare the issue's true scope.
Utilizing the Output
Why go through this process? The answer lies in application. The problem tree guides strategic planning. It informs policy development. It shapes project design.
- Program interventions draw from root causes.
- Resources target the most impactful points.
- Long-term strategies hinge on understanding effects.
Enhancing Collaboration
Problem tree analysis fosters collaborative dialogue. It serves as a communication tool. Stakeholders gain shared problem awareness. It builds consensus. It forms a cohesive understanding. Team members engage with shared purpose.
The Academic and Practical Crossover
Within academia, the methodology holds high value. It promotes critical thinking. It enhances academic discourse. Yet, practitioners also gain. Development professionals, policymakers, and strategists employ it. It aids in navigating complex societal challenges.
In conclusion, problem tree analysis is foundational. It structures thought. It defines problems. It clarifies causes and effects. The tool is robust. It is flexible. It aids researchers and practitioners alike. From simple endeavours to global issues, its function stands central. It is about understanding today. It is about shaping tomorrow.
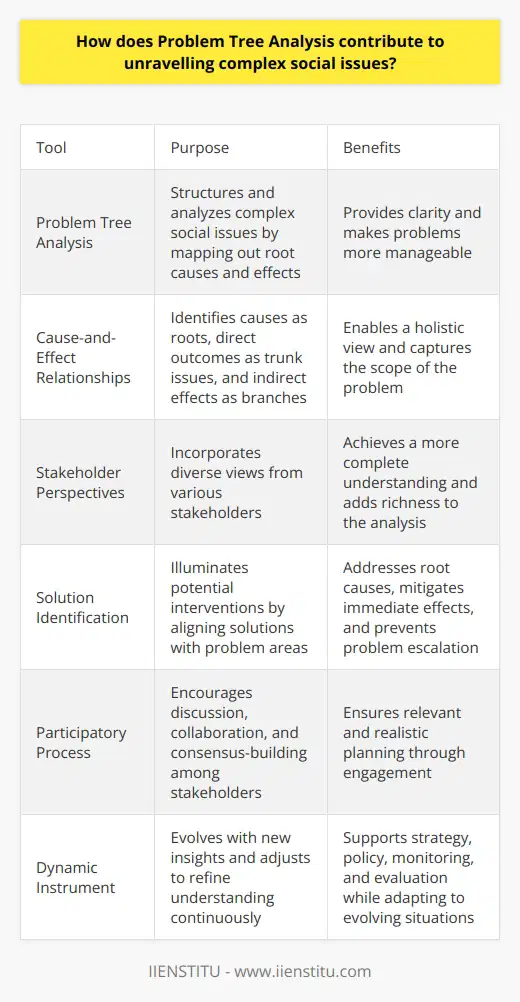
How does Problem Tree Analysis contribute to unravelling complex social issues?
Problem Tree Analysis Defined
Problem tree analysis stands as a tool. It aids in structuring and analyzing issues. Particularly, it dissects complex social dilemmas. Analysts use it to map out root causes and effects. They clarify the anatomy of problems this way. Complex social issues thus become more manageable.
Breaking Down Complexity
Social issues often intertwine like a knotted web. Layers of causes and consequences exist. Problem tree analysis untangles these. It starts with the identification of a core problem. Surrounding issues branch out like tree limbs. Thus, a visual representation emerges. It is akin to a map of problems.
Causes and Consequences
The analysis recognizes cause-and-effect relationships. Causes anchor the roots of the tree. Direct outcomes rise as trunk issues. Indirect effects spread like branches. This enables a holistic view. It captures the scope of the problem.
Stakeholder Perspectives
Various stakeholders carry unique insights. Problem tree analysis includes these diverse views. It thus achieves a more complete understanding. Stakeholders contribute to root identification. They also help clarify broader implications. Each voice adds to the analysis. Hence, a richer picture forms.
Advancing Solutions
The analysis not only unravels problems. It also illuminates potential interventions. Cause branches suggest entry points for action. Addressing root causes could prevent problem escalation. Mitigating immediate effects may offer relief. Solutions thus align with problem areas.
Participatory Process
The process builds consensus among stakeholders. It encourages a participatory approach. Discussion and collaboration are central. Stakeholders align on the problem and its nature. They collectively explore and agree on solutions. Engagement ensures relevant and realistic planning.
A Dynamic Instrument
The problem tree is not static. It evolves with new insights. Adjustments refine the understanding continuously. Continuous use informs strategy and policy. It supports monitoring and evaluation too. The methodology adapts as situations evolve.
Conclusion
Problem tree analysis simplifies complicated social issues. It provides clarity in the midst of complexity. Stakeholder participation strengthens its application. As a dynamic tool, it revises with ongoing learning. It, therefore, contributes to turning entangled social challenges into organized, actionable plans.
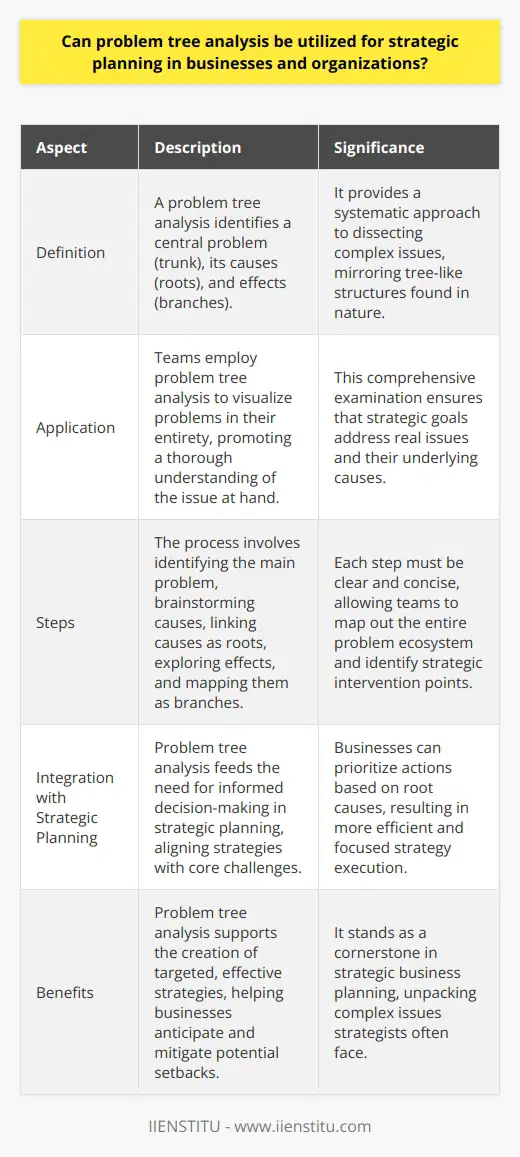
Can problem tree analysis be utilized for strategic planning in businesses and organizations?
Problem Tree Analysis in Strategic Planning
Strategic planning anchors on understanding challenges. It involves setting goals and devising methods. Problem tree analysis aids this process significantly. It allows organizations to dissect complex issues systematically.
Definition and Application
A problem tree analysis starts with identifying a central problem. This serves as the tree's trunk. Causes branch off as roots. Effects extend as branches. It mirrors tree-like structures found in nature. Teams employ it to visualize problems in their entirety.
Advantages for Businesses
Businesses benefit from this methodology. It encourages comprehensive examination. It ensures that strategic goals address real issues. The process promotes a thorough understanding of underlying causes.
Steps in Conducting Problem Tree Analysis
The process exhibits simplicity and order.
- Identify the main problem
- Discuss and brainstorm causes
- Link causes as roots
- Explore immediate and long-term effects
- Map these effects as branches
Each step must be clear and concise. Teams map out the entire problem ecosystem. This granularity helps identify strategic intervention points.
Integration with Strategic Planning
Strategic planning pivots on informed decision-making. Problem tree analysis feeds this need. It aids in aligning strategies with core challenges. Businesses can prioritize actions based on root causes. This results in more efficient and focused strategy execution.
Conclusion
In essence, problem tree analysis dovetails neatly with strategic planning. It unpacks complex issues strategists often face. It supports the creation of targeted, effective strategies. Businesses leverage it to anticipate and mitigate potential setbacks. It truly stands as a cornerstone in strategic business planning.