In the dynamic landscape of modern business, the art of demand planning has emerged as a critical competency, akin to a lighthouse guiding ships through the tempestuous seas of market volatility. As a quintessential component of supply chain management, demand planning transcends mere number-crunching and statistical analysis; it is a strategic endeavor that weaves together data, insights, and foresight to create a tapestry of informed decisions and optimized operations.
The significance of demand planning cannot be overstated, for it is the cornerstone upon which the edifice of supply chain efficiency is built. It is the compass that directs businesses towards the north star of customer satisfaction and profitability. In a world where the winds of change blow incessantly, and the tides of consumer preferences shift unexpectedly, demand planning emerges as the steadfast anchor that keeps businesses grounded and prepared.
At its core, demand planning is a proactive approach to forecasting customer demand and aligning it seamlessly with the cogs of production and supply chain operations. It is a disciplined process that involves the meticulous collection and analysis of historical sales data, market trends, and customer insights. However, it is not merely a retrospective exercise; it is a forward-looking endeavor that takes into account a myriad of external factors such as economic indicators, competitive landscape, and technological advancements.
The importance of demand planning for businesses cannot be emphasized enough. It is the key that unlocks the door to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. By accurately predicting future demand, businesses can optimize their inventory levels, reducing the burden of carrying excess stock while simultaneously mitigating the risk of stockouts. This delicate balance between supply and demand is the hallmark of a well-oiled supply chain, and it is achieved through the rigorous application of demand planning principles.
Moreover, demand planning serves as a strategic compass, guiding businesses in their decision-making processes. It provides valuable insights that inform product development, market expansion, and resource allocation strategies. By understanding the pulse of the market and anticipating customer needs, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and seize opportunities for growth and innovation.
The process of demand planning is a complex and multi-faceted one, involving several critical steps. It begins with the collection of data from various sources, including sales history, customer feedback, and market research. This data forms the foundation upon which the edifice of demand planning is built. As the renowned statistician W. Edwards Deming once said, "Without data, you're just another person with an opinion" (Deming, 2000, p. 37). The importance of data collection cannot be overstated, for it is the bedrock of accurate forecasting.
Once the data is collected, the next step is data analysis. This is where the magic happens, where raw data is transformed into meaningful insights. It involves the application of statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and domain expertise to identify patterns, trends, and correlations. The goal is to uncover the hidden stories within the data, the nuggets of wisdom that can inform strategic decisions. As the renowned economist Peter Drucker once said, "What gets measured gets managed" (Drucker, 1954, p. 103). Data analysis is the key to unlocking the potential of demand planning.
The third step in the demand planning process is forecasting. This is where the insights gleaned from data analysis are translated into tangible predictions about future demand. It is a delicate balance between art and science, requiring a combination of statistical rigor and intuitive judgment. The goal is to create a forecast that is accurate, reliable, and actionable. As the famous mathematician John von Neumann once said, "Prediction is very difficult, especially if it's about the future" (von Neumann, 1955, p. 271). Forecasting is a challenging endeavor, but it is one that is essential for effective demand planning.
The final step in the demand planning process is review and adjustment. This is where the rubber meets the road, where the forecast is put to the test against real-world data. It involves the continuous monitoring of actual demand and the adjustment of the forecast based on new information and insights. This iterative process ensures that the demand plan remains relevant and accurate, adapting to the ever-changing market conditions. As the famous physicist Niels Bohr once said, "Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future" (Bohr, 1958, p. 125). Review and adjustment is the key to ensuring that the demand plan remains a living, breathing document that evolves with the business.
The benefits of effective demand planning are manifold and far-reaching. Perhaps the most significant benefit is improved inventory management. By accurately predicting future demand, businesses can optimize their inventory levels, reducing the carrying costs associated with excess stock while simultaneously ensuring that they have sufficient stock to meet customer needs. This leads to improved cash flow, reduced waste, and enhanced profitability. As the renowned management consultant Peter Drucker once said, "Inventory is the graveyard of business" (Drucker, 1963, p. 89). Effective demand planning is the key to avoiding this graveyard.
Another significant benefit of demand planning is improved customer satisfaction. By anticipating customer needs and ensuring that the right products are available at the right time, businesses can enhance the customer experience and build brand loyalty. This is particularly important in today's hyper-competitive market, where customers have a plethora of choices and are increasingly demanding. As the famous marketer Seth Godin once said, "The best way to build a brand is to be remarkable" (Godin, 2003, p. 57). Effective demand planning is a remarkable way to build a brand that customers love and trust.
Demand planning also enables businesses to improve their supply chain efficiency. By aligning supply with demand, businesses can reduce lead times, minimize stockouts, and optimize their production schedules. This leads to reduced costs, improved productivity, and enhanced competitiveness. As the renowned management consultant Peter Drucker once said, "The only way to control costs is to prevent them" (Drucker, 1963, p. 117). Effective demand planning is a powerful tool for preventing costs and optimizing supply chain efficiency.
Furthermore, demand planning enables businesses to make informed strategic decisions. By providing insights into market trends, customer preferences, and competitive dynamics, demand planning enables businesses to make data-driven decisions about product development, market expansion, and resource allocation. This leads to improved agility, responsiveness, and competitiveness. As the famous economist John Maynard Keynes once said, "The importance of money flows from it being a link between the present and the future" (Keynes, 1936, p. 293). Effective demand planning is a link between the present and the future, enabling businesses to make informed decisions that shape their destiny.
However, demand planning is not without its challenges. One of the biggest challenges is the complexity of the process. Demand planning involves the integration of multiple data sources, the application of sophisticated statistical models, and the coordination of various stakeholders across the organization. This complexity can be overwhelming, particularly for businesses that are new to the process. As the renowned physicist Albert Einstein once said, "The hardest thing to understand in the world is the income tax" (Einstein, 1963, p. 18). Demand planning can be equally hard to understand, but it is a challenge that businesses must embrace if they want to succeed in today's market.
Another challenge of demand planning is the need for accurate and timely data. Demand planning is only as good as the data that feeds it. If the data is incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated, the demand plan will be flawed. This is particularly challenging in today's fast-paced market, where data is generated at an unprecedented rate and from a variety of sources. As the famous statistician W. Edwards Deming once said, "In God we trust, all others must bring data" (Deming, 2000, p. 37). Businesses must invest in robust data collection and management systems if they want to reap the benefits of demand planning.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of demand planning far outweigh the costs. In today's market, businesses that fail to plan for demand are planning to fail. As the renowned management consultant Peter Drucker once said, "The best way to predict the future is to create it" (Drucker, 1985, p. 97). Effective demand planning is a powerful tool for creating the future that businesses want to see.
To illustrate the power of demand planning, consider the example of Walmart, the world's largest retailer. Walmart has long been a pioneer in the field of demand planning, investing heavily in data collection, analysis, and forecasting. By accurately predicting customer demand and optimizing its inventory levels, Walmart has been able to reduce its inventory carrying costs by billions of dollars while simultaneously improving its customer service levels. As the famous investor Warren Buffett once said, "Price is what you pay, value is what you get" (Buffett, 2008, p. 53). Walmart's investment in demand planning has paid off in spades, delivering immense value to the company and its customers.
Another example of the power of demand planning is Apple, the world's most valuable company. Apple is renowned for its ability to predict customer demand and align its supply chain accordingly. By accurately forecasting demand for its products, Apple has been able to minimize stockouts and excess inventory, while simultaneously delivering products that customers love. As the famous entrepreneur Steve Jobs once said, "Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower" (Jobs, 2011, p. 147). Apple's innovation in demand planning has made it a leader in the technology industry.
In conclusion, demand planning is a critical competency for businesses that want to succeed in today's fast-paced and ever-changing market. By accurately predicting customer demand and aligning supply chain operations accordingly, businesses can optimize their inventory levels, improve customer satisfaction, and make informed strategic decisions. While the process of demand planning can be complex and challenging, the benefits far outweigh the costs. As the famous inventor Thomas Edison once said, "The value of an idea lies in the using of it" (Edison, 1929, p. 63). The value of demand planning lies in its use, and businesses that embrace it will be well-positioned for success in the years to come.
References:
Bohr, N. (1958). Atomic Physics and Human Knowledge. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Buffett, W. (2008). The Essays of Warren Buffett: Lessons for Corporate America. Carolina Academic Press.
Deming, W. E. (2000). The New Economics for Industry, Government, Education. MIT Press.
Drucker, P. F. (1954). The Practice of Management. New York: Harper & Row.
Drucker, P. F. (1963). Managing for Results. New York: HarperCollins.
Drucker, P. F. (1985). Innovation and Entrepreneurship. New York: HarperCollins.
Edison, T. A. (1929). The Diary and Sundry Observations of Thomas Alva Edison. New York: Philosophical Library.
Einstein, A. (1963). Relativity: The Special and the General Theory. New York: Crown Publishers.
Godin, S. (2003). Purple Cow: Transform Your Business by Being Remarkable. New York: Portfolio.
Jobs, S. (2011). Steve Jobs. New York: Simon & Schuster.
Keynes, J. M. (1936). The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money. London: Macmillan.
von Neumann, J. (1955). Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Mechanics. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Frequently Asked Questions
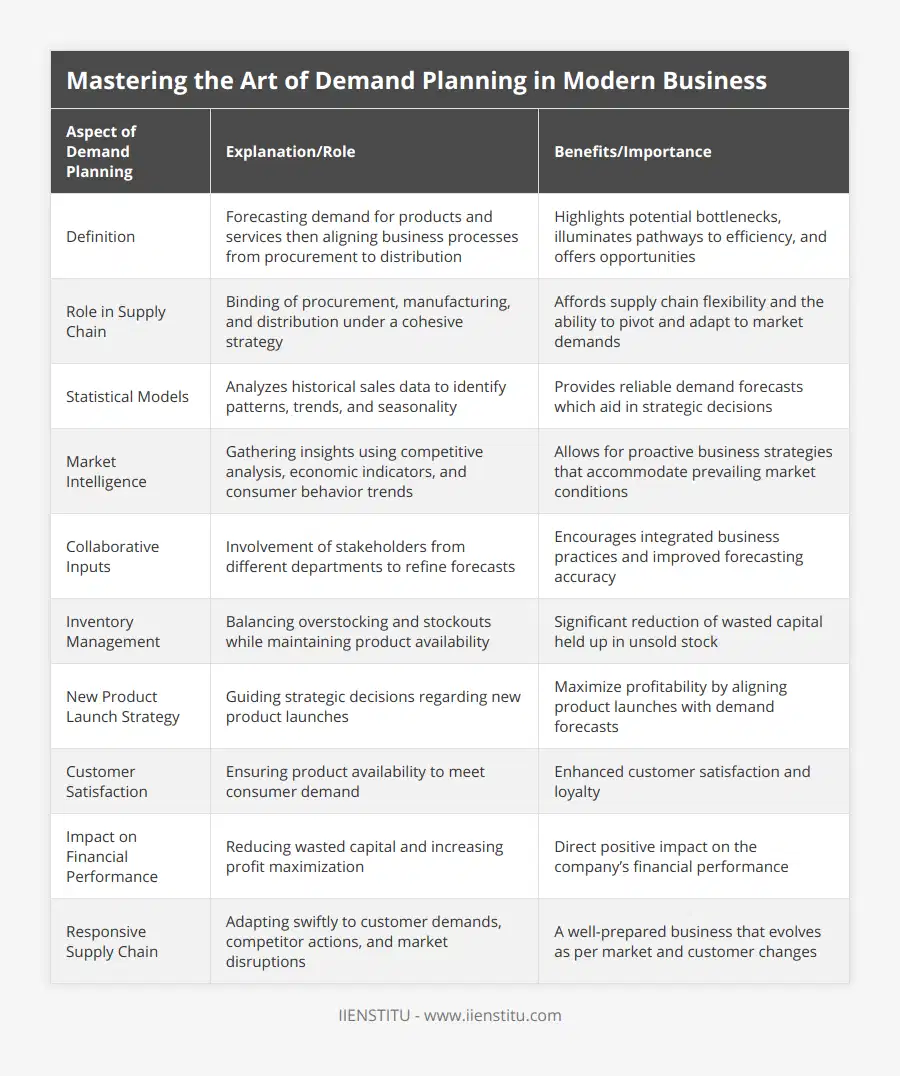
What are the key elements to consider in mastering the art of demand planning in modern business?
Understanding Demand Planning
Demand planning forms the cornerstone. It is crucial in modern business. Companies strive to master it. Accurate planning ensures efficiency. It avoids overproduction. It prevents stockouts. Demand planning balances supply and demand.
Data Quality and Analysis
Data is king. Accurate demand planning starts here. Data must be high-quality. It informs all predictions. It forms the planning basis.
Consider data sources critically. Use point-of-sale data. Include promotional histories. Analyze past trends.
Data analysis technology is vital. Harness machine learning. Apply statistical models. Forecast demand accurately.
Integration and Collaboration
Collaboration is necessary across departments. Marketing informs demand planning. Sales provides frontline insights. Operations bring capacity constraints. Integration aligns all players. Everyone must understand the goals. Supply chain partners need inclusion too.
Market Understanding
Know your market well. Understand customer behavior. Stay current with trends. Anticipate changes in demand. Consider seasonality. Recognize product life cycles.
Technology and Tools
Choose the right tools. Consider scalability. Ensure ease of use. Tools must provide actionable insights. They should facilitate collaboration.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is useful. So are Advanced Planning Systems (APS). They ensure information sharing.
Forecasting Techniques
Diverse forecasting methods exist. They range from simple to complex. Use quantitative techniques. Apply qualitative insights. Combine several methods. Test and refine forecasts.
Inventory Management
Inventory affects demand planning. Too much is costly. Too little disappoints customers. Embrace Just in Time (JIT) inventory. Implement Economic Order Quantity (EOQ). These methods optimize inventory. They support demand planning.
Continuous Improvement
Demand planning is not static. It evolves. Regularly assess performance. Learn from mistakes. Adjust strategies. Seek continuous improvement always.
Feedback Loops
Incorporate feedback. This aids adjustment. It allows for agility. Seek feedback from all channels. Use it to refine planning.
Conclusion
Demand planning is multifaceted. Grasp the key elements. Ensure data quality. Collaborate and integrate. Understand your market. Use technology wisely. Manage inventory effectively. Aim for continuous improvement. Establish feedback loops. Mastering these leads to success in demand planning.
How does technology and data analytics impact demand planning in today's business environment?
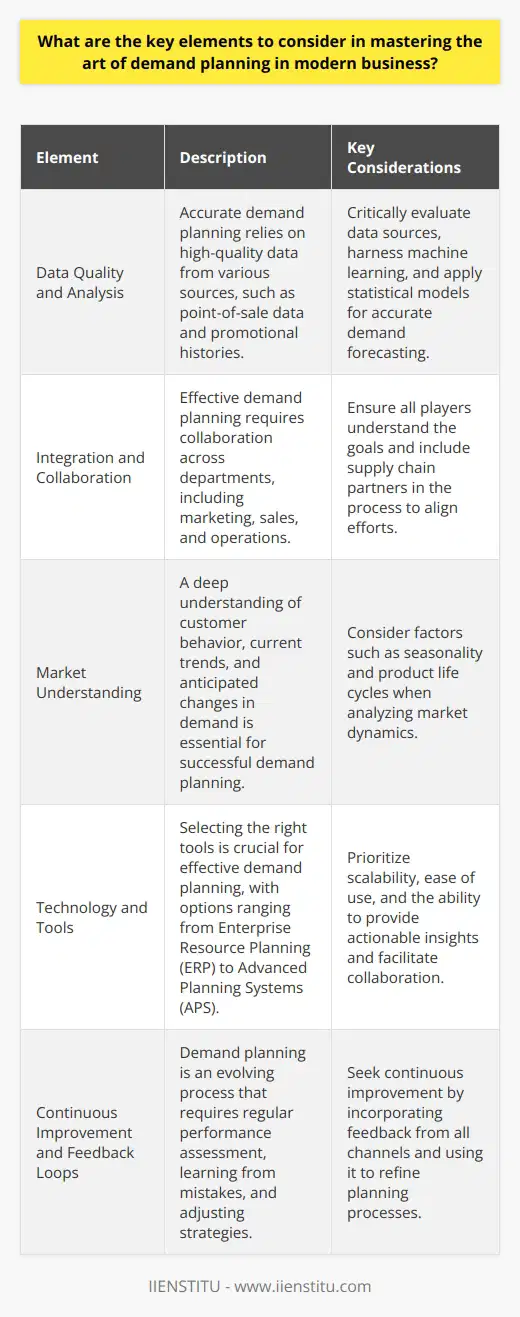
Technology Shapes Demand Planning
In the realm of business, technology reigns supreme. It refines demand planning processes. Automation now rules repetitive tasks. Sophisticated algorithms predict demand nuances. Systems integrate data in real time. This fusion enables unparalleled efficiency.
Data Analytics as a Pillar
Data analytics spearhead informed decision-making. They uncover patterns from vast data oceans. Businesses harness these insights daily. Predictive analytics craft future demand pictures. They rely on historical and real-time data. Machine learning algorithms learn from this data. They provide forward-looking forecasts with enhanced accuracy.
Impact on Forecast Accuracy
Forecast accuracy has seen remarkable improvements. Advanced analytics applications reduce human error. They also allow for faster recalibration. This nimbleness adapts to market shifts quickly. Demand signals trigger algorithms to adjust predictions. Traditional approaches can't match this responsiveness.
Inventory Management Transformation
Inventory management experiences a seismic shift. Excess stock represents sunk costs. Stockouts equal missed sales opportunities. Data-driven demand planning balances these extremes. It helps maintain optimal inventory levels. Predictive models gauge replenishment cycles. They prevent inventory glut or scarcity.
Real-Time Data Integration
Firms embrace real-time data integration. It enriches demand planning outcomes. Retailers track purchases as they occur. Supply chains monitor deliveries the minute they happen. This information feeds back into planning platforms. It ensures strategies reflect current market states.
Holistic View Across Channels
Multichannel sales complicate demand planning. Each channel exhibits unique demand patterns. Analytics merge these disparate streams. They present a cohesive demand viewpoint. Strategies align with this comprehensive understanding. Channel-specific plans benefit too. Tailored stock plans emerge for various outlets.
Enhanced Collaboration
Collaboration sees marked improvements. Internal teams share data effortlessly. External partners join this data ecosystem. Shared analytics platforms facilitate this. They foster synergy among stakeholders. Decisions reflect input from diverse sources. Cooperation supplants siloed planning.
Optimizing the Supply Chain
Supply chains now operate with agility. Technology eradicates bottlenecks. Data analytics forecast disruptions early. Preemptive action minimizes negative impacts. Information flows seamlessly from supplier to consumer. The supply chain becomes less reactive. It leans towards anticipatory management.
Sustainability Driven by Data
Sustainability gains prominence in demand planning. Businesses seek to reduce waste. Data analytics inform eco-friendly decisions. They enhance resource utilization. Products meet demand without excess.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, technology and data analytics redefine demand planning. They instill accuracy, speed, and efficiency. Businesses navigate the volatile market better. They deliver value sustainably. Data-driven strategies no longer suggest a competitive edge. They constitute a business imperative.
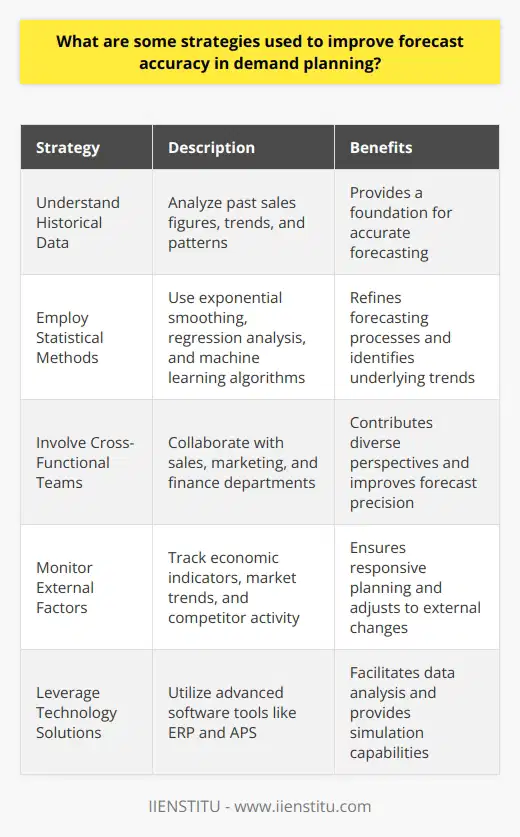
What are some strategies used to improve forecast accuracy in demand planning?
Strategies to Enhance Forecast Accuracy
Understand Historical Data
Accurate forecasts begin with historical data. Analysts dissect past sales figures. They look for trends and patterns. This process requires meticulous data management. Clean, organized data is essential.
Employ Statistical Methods
Statistical methods refine forecasting processes. They include exponential smoothing, regression analysis, and machine learning algorithms. These methods interpret historical data. They find underlying trends that simple observations might miss.
Involve Cross-Functional Teams
Demand planning thrives on collaboration. It combines insights from sales, marketing, and finance. Cross-functional teams contribute diverse perspectives. Such engagement improves forecast precision.
Monitor External Factors
Factors outside an organization affect demand. These include economic indicators, market trends, and competitor activity. Analysts must track these continuously. Responsive planning adjusts to external changes.
Utilize Market Intelligence
Market intelligence pertains to customer preferences. It also includes competitor positioning. It provides context for interpreting data. Such intelligence comes from market research and feedback analysis.
Embrace Integrated Business Planning
Integrated business planning aligns strategic, financial, and operational goals. It ensures all departments work towards a common forecast. Alignment reduces silos. It enhances forecast accuracy.
Leverage Technology Solutions
Technology plays a key role. Advanced software tools aid demand forecasting. They facilitate data analysis. They provide simulation and what-if capabilities. Tools like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Advanced Planning Systems (APS) are examples.
Continuously Refine Processes
Demand planning is not static. It requires constant refinement. Analysts should assess forecast performance regularly. They must adjust models as needed. Continuous improvement is crucial.
Conduct Demand Sensing
Demand sensing involves short-term forecasting. It uses real-time data to predict immediate demand. It responds quickly to market changes. It makes forecasting more agile.
Foster a Forecasting Culture
A culture that values forecasting benefits an organization. It encourages data-driven decision-making. It supports transparency in planning. A forecasting culture minimizes bias and error.
Demand planning is complex. It involves various strategies. Accuracy is paramount. Consistent effort and adaptation improve outcomes. Success depends on both human expertise and technological support.