When I first stepped into the world of management, I vividly remember feeling both excited and overwhelmed. The sheer responsibility of guiding a team toward a common goal was daunting. Over the years, through trial and error, I discovered that understanding and mastering the managerial functions is essential for any leader aiming to make a meaningful impact. These functions are not just theoretical concepts taught in business schools; they're the pillars that hold up every successful organization.
The Essence of Managerial Functions
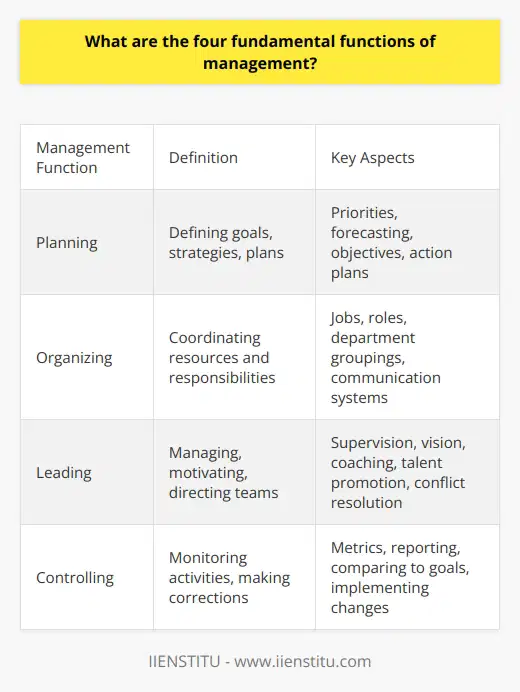
At the heart of every thriving business lies effective management. Managerial functions are the actions and responsibilities that managers undertake to ensure that an organization runs smoothly. They encompass planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Each function plays a critical role in achieving organizational objectives and in fostering an environment where both the company and its employees can flourish.
Planning: Charting the Course
Planning is often considered the cornerstone of management. It's akin to setting out on a journey without a map—without proper planning, you might end up lost. I recall a time when our company faced a significant market shift. Competitors were quickly adapting, and we risked falling behind. By dedicating time to strategic planning, we identified our strengths, anticipated market trends, and developed a roadmap that not only kept us afloat but propelled us ahead.
Key aspects of effective planning include:
1- Setting Clear Goals: Defining what the organization aims to achieve in the short and long term.
2- Developing Strategies: Outlining the methods to reach these goals.
3- Anticipating Challenges: Considering potential obstacles and how to overcome them.
4- Allocating Resources: Determining where to best invest time, money, and personnel.
5- Monitoring Progress: Regularly reviewing plans to adjust as necessary.
As Peter Drucker once said, "Plans are only good intentions unless they immediately degenerate into hard work." Planning sets the stage, but action brings plans to life.
Organizing: Building the Framework
Once a plan is in place, organizing becomes crucial. This function involves structuring the organization in a way that resources are optimally utilized. Think of it as constructing a building—you need a solid framework to support everything else.
During my tenure at a manufacturing firm, we faced inefficiencies in our supply chain. By reorganizing the process and implementing optimize supply chain management process tips, we reduced delays and cut costs significantly. This not only improved our bottom line but also enhanced customer satisfaction.
Workforce planning: Assessing the organization's current and future staffing needs and developing strategies to meet these requirements.
Organizational development: Ensuring the organization's structure, culture, and processes support its objectives and facilitate effective human resource management.
Employee engagement: Developing and implementing strategies to promote employee satisfaction, commitment, and motivation.
Performance management: Establishing performance standards, monitoring employee performance, and providing feedback to facilitate continuous improvement.
Compliance management: Ensuring the organization adheres to relevant employment laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
Business planning: Developing a comprehensive business plan that outlines the company's goals, strategies, and action plans.
Resource management: Allocating financial, human, and material resources effectively to support the growth and success of the business.
Team development: Building and managing a talented and motivated team to achieve the company's objectives.
Risk management: Identifying and addressing potential risks and challenges that may impact the business's success.
Decision-making: Making informed and strategic decisions to guide the company toward its goals.
Organizing involves:
Creating a Structure: Establishing departments, teams, and hierarchies.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities: Ensuring everyone knows their duties.
Allocating Resources: Distributing assets where they're most needed.
Entrepreneurial role: Identifying new opportunities, initiating projects, and fostering innovation within the organization.
Disturbance handler: Addressing and resolving conflicts, crises, or unforeseen problems that may arise in the organization.
Resource allocator: Distributing resources, such as finances, personnel, and time, effectively to support organizational goals.
Negotiator: Negotiating with stakeholders, such as employees, suppliers, customers, and partners, to reach mutually beneficial agreements.
Coordinating Activities: Aligning efforts across different parts of the organization.
Establishing Communication Channels: Facilitating information flow.
An effectively organized company can respond swiftly to changes, a vital trait in today's fast-paced business environment.
Figurehead: Representing the organization in formal and ceremonial activities and acting as its public face.
Leader: Guiding, motivating, and supporting employees to achieve their full potential and contribute to the organization's success.
Liaison: Establishing and maintaining connections with external stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, and industry partners, to promote collaboration and information exchange.
Leading: Inspiring Towards Success
Leadership is more than just supervising—it's about inspiring and motivating. I remember a manager who, despite having brilliant plans, couldn't rally the team behind them. It wasn't until a new leader took charge, one who genuinely listened and engaged with us, that we saw real progress.
Guiding and supervising employees in the execution of their tasks,
Providing feedback and support, and
We ensure they have the necessary resources and information to perform effectively.
Effective leading entails:
Communication: Clearly conveying vision and expectations.
Motivation: Encouraging employees to perform at their best.
Influence: Guiding team behavior toward achieving goals.
Support: Providing the necessary tools and assistance.
Adaptability: Changing leadership styles to meet team needs.
According to Daniel Goleman's work on emotional intelligence, understanding and managing emotions play a significant role in leadership effectiveness. Leaders who connect on a personal level can harness the collective energy of their teams.
Controlling: Ensuring the Path is Followed
Controlling doesn't mean micromanaging; it's about ensuring that the organization's activities align with the established plans. It involves setting performance standards, monitoring outputs, and making adjustments as needed.
Key steps in the controlling function include:
1- Establishing Standards: Defining what success looks like.
2- Measuring Performance: Collecting data on outputs and outcomes.
3- Comparing Against Standards: Assessing whether goals are met.
4- Taking Corrective Action: Implementing changes to address deviations.
5- Feedback Loop: Using insights to inform future planning.
During a project rollout, we noticed that customer feedback wasn't as positive as anticipated. By closely monitoring performance metrics and being open to adjustments, we were able to refine our approach, ultimately leading to a successful outcome.
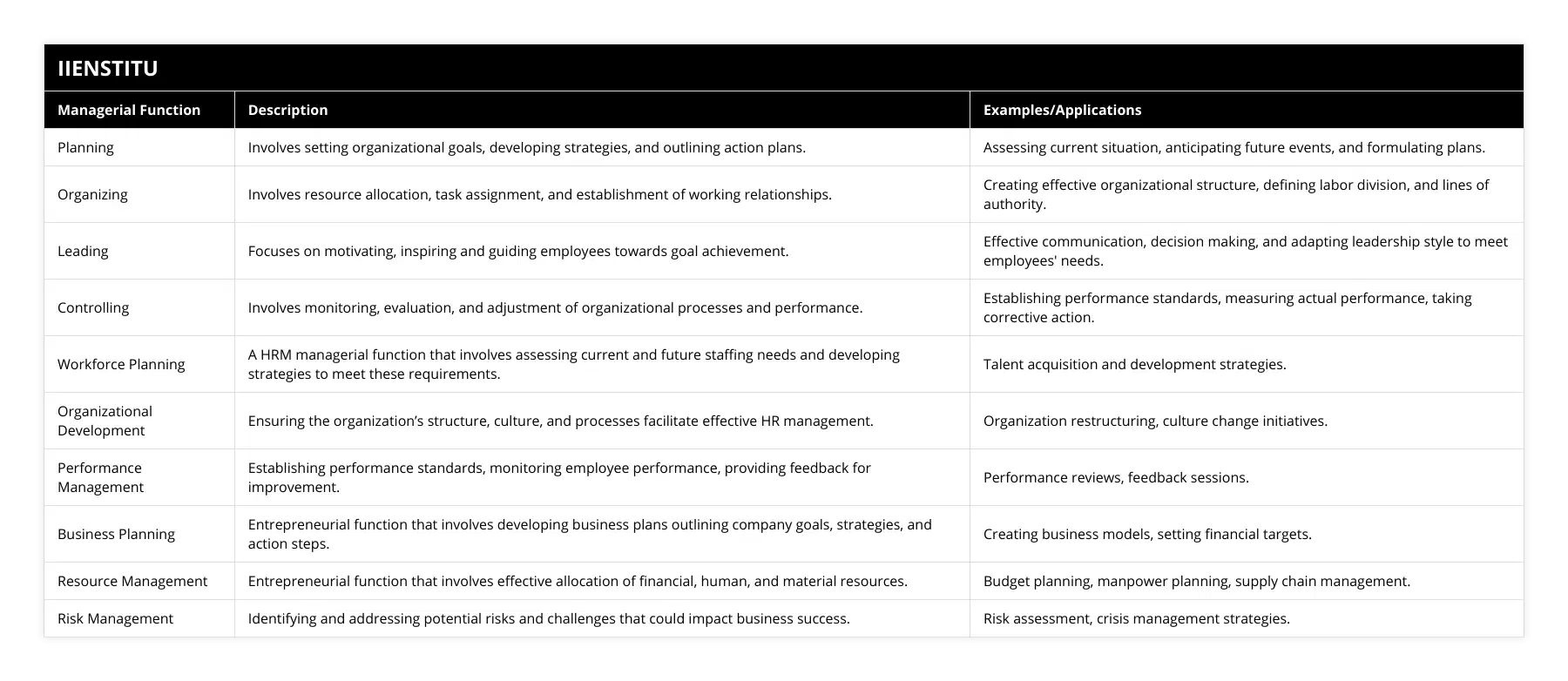
Managerial Functions in Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) is the backbone of any organization. It's not just about hiring and firing; it's about nurturing talent and fostering a positive work environment.
Managerial and Operative Functions of HRM
HRM encompasses both managerial functions—planning, organizing, leading, and controlling—and operative functions like recruitment, training, and development.
Managerial functions in HRM involve:
Workforce Planning: Anticipating future staffing needs.
Organizational Development: Shaping the company culture and structure.
Performance Management: Evaluating and enhancing employee performance.
Compliance Management: Ensuring adherence to laws and regulations.
Operative functions include:
Recruitment and Selection
Training and Development
Employee Relations
Compensation and Benefits
By integrating managerial functions with operative tasks, HR can strategically contribute to organizational success.
Personal Experience with HRM Functions
I recall implementing a new training program aimed at developing leadership skills among junior staff. By investing in employee development, we not only improved individual performance but also bolstered overall team morale. It was a testament to how effective leadership skills for managers can emerge from proactive HR practices.
Managerial Functions in Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurs often juggle multiple roles, making managerial functions even more critical in startups and small businesses.
Applying Managerial Functions to Startups
For entrepreneurs:
Business Planning: Crafting a comprehensive business plan is vital. It serves as a roadmap and a tool for attracting investors.
Resource Management: With limited resources, efficient allocation is essential.
Team Development: Building a cohesive team can make or break a startup.
Risk Management: Identifying potential pitfalls early can save the business.
Decision-Making: Swift and informed decisions drive momentum.
An entrepreneur friend once told me, "In the early days, you're not just the captain of the ship; you're also the crew." Understanding managerial functions helps in navigating the turbulent waters of new business ventures.
Decisional and Interpersonal Roles of Managers
Beyond the core functions, managers perform various roles that impact both the organization and its stakeholders.
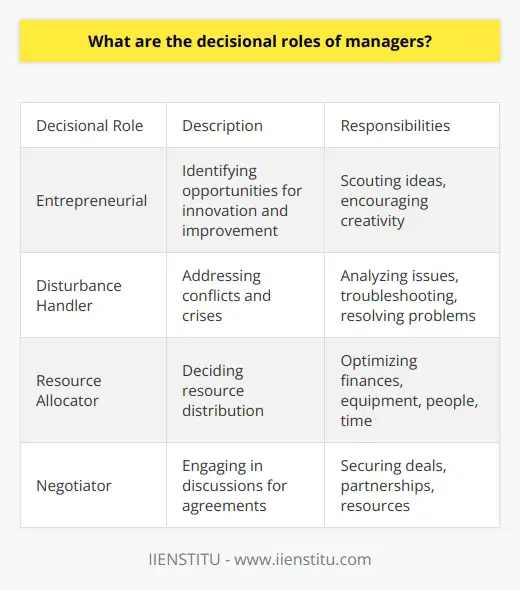
Decisional Roles
Managers are constantly making decisions that affect the company. These roles include:
1- Entrepreneur: Initiating change and innovation.
2- Disturbance Handler: Addressing unexpected challenges.
3- Resource Allocator: Determining where to apply resources.
4- Negotiator: Representing the organization in negotiations.
Interpersonal Roles
Building relationships is key to management success:
Figurehead: Symbolizing the organization's mission and values.
Leader: Directing and motivating the team.
Liaison: Networking within and outside the organization.
Henry Mintzberg's studies highlight these roles as integral to a manager's daily activities. Balancing these can enhance both personal effectiveness and organizational performance.
Directing and Controlling: The Dynamic Duo
Directing and controlling work hand in hand. While directing focuses on guiding employees, controlling ensures that activities align with goals.
The Art of Directing
Directing involves:
Providing Clear Instructions
Motivating Employees
Communicating Effectively
Leading by Example
A mentor once advised me, "You can't expect others to go the extra mile if you're not willing to walk it yourself." This resonated deeply and influenced my approach to leadership.
The Science of Controlling
Controlling ensures that deviations from the plan are corrected. This involves:
Setting Performance Metrics
Monitoring Outputs
Implementing Feedback Mechanisms
By embracing both directing and controlling, managers can create a responsive and agile organization.
Conclusion: Embracing Managerial Functions for Success
The journey through the managerial functions—from planning to controlling—reveals a comprehensive framework for effective management. These functions are interrelated and together form the foundation upon which successful organizations are built.
In my own career, embracing these functions has made all the difference. Whether it's organizing resources efficiently or applying successful entrepreneurship strategies, understanding and applying these principles can lead to significant improvements.
For anyone stepping into a managerial role, I encourage you to delve deep into these functions. Learn from others, but also be willing to adapt and find what works best for your unique situation. After all, management is as much an art as it is a science.
References
Drucker, P. F. (1954). The Practice of Management. Harper & Row Publishers.
Goleman, D. (1995). Emotional Intelligence. Bantam Books.
Mintzberg, H. (1973). The Nature of Managerial Work. Harper & Row.
Robbins, S. P., & Coulter, M. (2018). Management (14th ed.). Pearson Education.
Fayol, H. (1949). General and Industrial Management. Pitman Publishing.
By understanding and implementing these managerial functions, we not only enhance our own capabilities but also contribute to the growth and success of our organizations. So, here's to leading with purpose and making a positive impact in the world of business!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the four fundamental functions of management?
The four fundamental functions of management are planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.
How do managerial functions contribute to effective human resource management?
Managerial functions in HRM, such as workforce planning, organizational development, employee engagement, performance management, and compliance management, help develop and implement HR strategies that align with the organization's objectives and contribute to its success.
What are the decisional roles of managers?
Decisional roles of managers include the entrepreneurial role (identifying new opportunities and fostering innovation), disturbance handler (addressing and resolving conflicts or crises), resource allocator (distributing resources effectively), and negotiator (engaging in negotiations with stakeholders).