I still remember the days when I first started working at my uncle's small manufacturing company. Back then, I didn't fully grasp the importance of logistics. All I knew was that sometimes our products reached the customers on time, and sometimes they didn't, and that seemed to affect our business more than anything else. As I dove deeper into understanding the workings of the company, I realized that logistics is not just about moving goods from point A to point B. It's an intricate dance of planning, execution, and management that ensures everything runs smoothly. And let me tell you, when logistics is managed well, it's like watching a well-rehearsed orchestra play a symphony.
Introduction
Definition of Logistics
System Approach for Logistics
Inventory Control
Conclusion
Understanding Logistics: More Than Just Transportation
So, what exactly is logistics? Logistics meaning goes beyond mere transportation. It involves the planning, execution, and control of goods, services, and information from their point of origin to their point of consumption. It's about ensuring that the right products reach the right place at the right time, and in the right condition.
When we think about how products get to us, we often overlook the complex processes behind it. There's a whole world of supply chain management that works tirelessly to make this happen. Supply and chain management, or SCM, is the backbone of any successful business operation. It encompasses everything from procurement, production, distribution, to even the after-sales services.
The System Approach in Logistics
One day, while sipping coffee with my uncle, he mentioned something that stuck with me: "You can't just look at one part of the process; you have to see how everything fits together." This is essentially the system approach for logistics. Instead of viewing each component in isolation, this approach integrates all aspects of the supply chain.
Procurement of Goods and Services: This is where it all begins. Acquiring raw materials or products requires careful planning and supplier relationships.
Analyzing the Implications and Benefits of Asset Tracking in Business Operations
Unlocking Benefits from CPFR: A Collaborative Planning Journey
Production and Distribution: Once we have the materials, producing and distributing them efficiently is crucial.
Customer Service Management: At the end of the day, it's all about the customer. Ensuring they are satisfied can make or break a business.
By adopting a system approach, businesses can optimize their supply chain activities and improve overall efficiency. This holistic view helps in identifying bottlenecks and provides solutions that benefit the entire chain.
Inventory Control: The Balancing Act
Inventory control is like walking a tightrope. On one hand, you don't want to have too much stock sitting idle, tying up capital and storage space. On the other, you definitely don't want to run out of products when customers are knocking on your door. I recall an instance when we had a massive order come in unexpectedly. Due to poor inventory management, we couldn't fulfill it on time, leading to a lost opportunity and an unhappy customer.
An effective inventory control system involves:
1- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): This system helps in planning the amount of materials needed for production, ensuring that nothing goes to waste.
2- Inventory Level Decisions: Setting the right levels to meet customer service objectives without overstocking.
3- Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory: A strategy where materials are ordered and received just in time for production, reducing holding costs.
4- Safety Stock Management: Keeping an extra buffer of inventory to prevent stockouts during unexpected demand surges.
5- ABC Analysis: Categorizing inventory based on importance to prioritize management efforts.
A systematic approach to inventory control is the key to successful logistics management.
Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance supply chain mgmt. It ensures that goods are available when needed, improving customer satisfaction and reducing costs.
The Importance of Efficient Supply Chain Management
In today's fast-paced world, businesses cannot afford delays. Efficient chain of supply management is essential. It not only improves operational efficiency but also gives a competitive edge. Here's why:
Cost Reduction: By optimizing logistics, businesses can reduce transportation and storage costs.
Improved Customer Satisfaction: Timely delivery and product availability enhance customer loyalty.
Risk Mitigation: Identifying potential disruptions in the supply chain can prevent future issues.
Market Expansion: Efficient logistics enable businesses to reach new markets globally.
Sustainability: Streamlined supply chains can reduce environmental impact through efficient resource use.
I remember reading in Logistics & Supply Chain Management by Martin Christopher that supply chains compete, not companies (Christopher, 2016). This resonated with me, emphasizing the critical role of logistics in overall business success.
Negative SEO Tactics and Penalties in Logistics
You might wonder, what does negative SEO tactics and penalties have to do with logistics? Well, in the digital age, logistics companies rely heavily on online presence for marketing and customer engagement. Negative SEO tactics can harm a company's online reputation, leading to penalties from search engines.
Poor Content Management: Not updating or managing content effectively can reduce visibility.
Backlink Issues: Unnatural links can lead to penalties, affecting how customers find your services.
Duplicate Content: Having the same content across multiple pages or sites can hurt rankings.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures that customers can find your company easily, enhancing your supply and chain management efforts.
The Human Element in Logistics
Behind all the systems and processes, it's people who make logistics happen. From the truck drivers navigating long distances to the warehouse workers ensuring products are safely stored, every individual plays a vital role.
Communication: Effective communication ensures that everyone is on the same page.
Training and Development: Investing in employee skills leads to better performance.
Safety Measures: Ensuring the safety of workers is paramount.
Team Collaboration: Encouraging teamwork enhances efficiency and problem-solving.
I recall a time when our warehouse manager suggested a new method for stacking products, which reduced damage and improved efficiency. It reminded me that sometimes the best ideas come from those on the front lines.
Technological Advances in Logistics
Technology has revolutionized the way we approach logistics. I recall when we first implemented a logistics software system at our company. At first, some of us were skeptical, but soon we realized how it streamlined our operations.
Automation: Automated systems reduce human error and increase efficiency.
Data Analytics: By analyzing data, companies can predict trends and adjust accordingly.
GPS and Tracking: Real-time tracking of shipments improves transparency.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Software that optimizes warehouse operations.
These advancements not only improve supply chain operations but also enhance customer satisfaction. When customers can track their orders in real-time, it builds trust and reliability.
Challenges in Supply Chain Management
Despite the benefits, there are challenges that companies face in supply and chain management.
1- Globalization: Operating on a global scale introduces complexities like different regulations and cultural differences.
2- Environmental Concerns: There's increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices.
3- Risk Management: Natural disasters, political instability, and pandemics can disrupt the supply chain.
4- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to various laws and regulations across different regions.
5- Technological Integration: Implementing new technology can be costly and requires training.
Addressing these challenges requires flexibility and innovation. For instance, after the recent global events, many companies had to rethink their chain of supply management to mitigate risks.
The Role of E-Commerce in Logistics
With the rise of e-commerce, logistics has become even more critical. Companies like Amazon have set high standards for delivery times and customer service. This has forced other businesses to up their game.
Faster Delivery Times: Customers now expect next-day or even same-day delivery.
Return Policies: Easy returns require efficient reverse logistics processes.
Inventory Management: Online sales data helps in predicting demand and managing stock levels.
Personalization: Tailoring services to individual customer preferences.
Embracing e-commerce strategies can enhance management chain supply, making businesses more competitive.
Sustainability in Logistics
Sustainability isn't just a buzzword; it's becoming a necessity. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of their purchases.
Green Transportation: Using fuel-efficient vehicles or alternative energy sources.
Eco-Friendly Packaging: Reducing waste by using recyclable materials.
Optimizing Routes: Reducing fuel consumption by planning efficient delivery routes.
Sustainable Procurement: Sourcing materials from environmentally responsible suppliers.
Implementing sustainable practices can not only reduce costs but also improve brand image.
Career Opportunities in Logistics
For those interested in a career in logistics, the field offers numerous opportunities.
Logistics Coordinator: Overseeing the movement of goods.
Supply Chain Analyst: Analyzing data to improve operations.
Inventory Manager: Managing stock levels and storage.
Procurement Specialist: Handling supplier relationships and purchasing.
Transportation Manager: Coordinating the movement of goods domestically and internationally.
With the growth of global trade, expertise in supply chain management management is in high demand.
Final Thoughts
Looking back, my journey in understanding logistics has been eye-opening. From the early days at my uncle's company to now, I've seen firsthand how vital logistics is to business success. It's a field that combines strategic thinking with practical execution.
For anyone involved in business or considering a career in this area, I encourage you to dive in. There's always something new to learn, and the impact you can have is significant.
References
Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & Supply Chain Management. Pearson Education.
Ballou, R. H. (2004). Business Logistics/Supply Chain Management. Pearson Prentice Hall.
Chopra, S., & Meindl, P. (2015). Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation. Pearson.
Grant, D. B., & Trautrims, A. (2013). Sustainable Logistics and Supply Chain Management. Kogan Page.
Simchi-Levi, D., Kaminsky, P., & Simchi-Levi, E. (2008). Designing and Managing the Supply Chain. McGraw-Hill.
Frequently Asked Questions
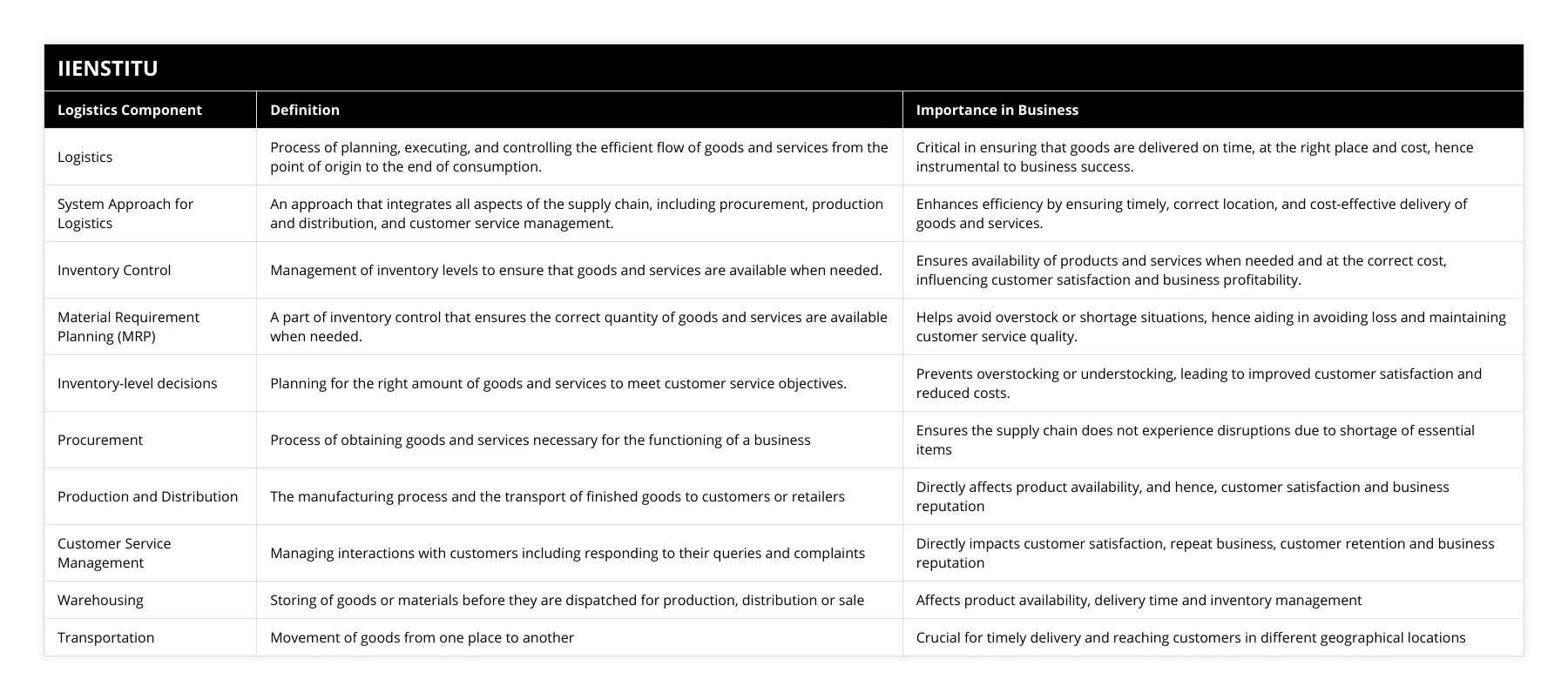
What are the advantages of using a system approach for inventory control in logistics management?
Inventory control is a crucial element of logistics management, as it allows companies to maintain adequate stock levels and reduce costs. A system approach to inventory control offers several advantages and can benefit a company's logistics operations.
The first advantage of a system approach to inventory control is that it provides a comprehensive view of all supply chain elements. This enables companies to track and monitor their inventory levels in real time, which allows for better decision-making and improved efficiency. Furthermore, this approach helps identify potential areas for improvement and allows for better forecasting of inventory needs.
A system approach to inventory control also helps to reduce costs. By using this approach, companies can optimize their inventory levels and reduce the amount of overstocking. This means that the company cannot carry extra inventory and can avoid unnecessary costs. Additionally, companies can use this approach to implement Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory systems, allowing them to order supplies as needed and further reduce costs.
Another advantage of a system approach to inventory control is that it can help to improve customer service. By keeping accurate inventory records, companies can ensure they have the right stock when customers need it. This helps to reduce customer wait times and can lead to improved customer satisfaction. Additionally, this approach helps ensure that all customer orders can be fulfilled in a timely manner, contributing to better customer service.
In conclusion, a system approach to inventory control offers several advantages for logistics management. This approach helps to reduce costs, improve customer service, and provide a comprehensive view of the supply chain. As such, companies should consider implementing this approach to maximize their logistics operations' efficiency.
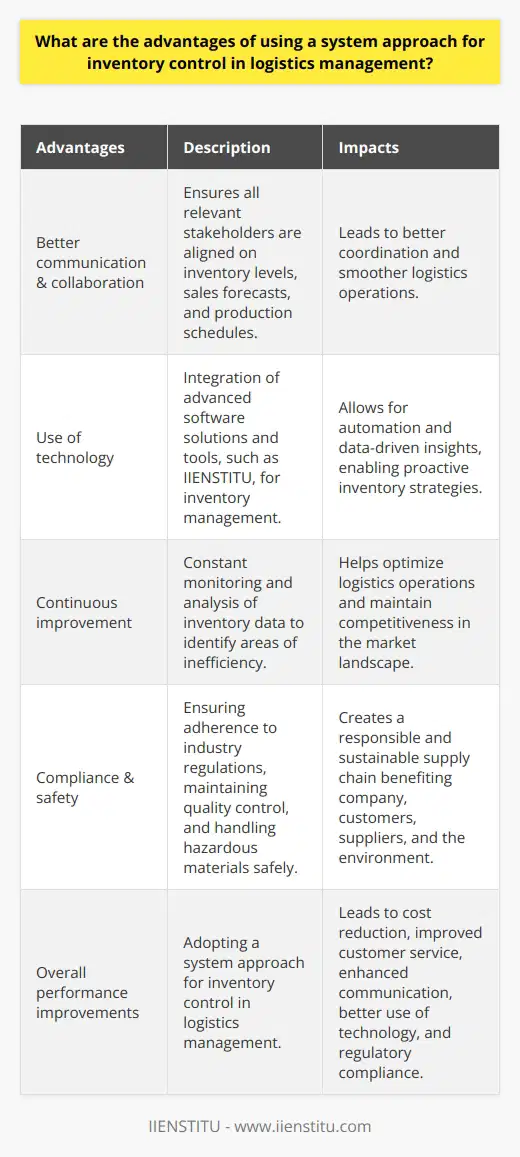
How does the system approach for inventory control help to improve the efficiency of logistics management?
In recent years, the system approach has been increasingly adopted by logistics managers to improve inventory control efficiency. The system approach consists of three components; the first is identifying all factors likely to affect the inventory control process. The second is developing an integrated system to monitor and control the inventory. Finally, the third element is implementing a plan to ensure an efficient and effective inventory control process.
The first step in the system approach is identifying all factors that can impact the inventory control process. This includes customer demand, supplier availability, inventory levels, and other external factors. Once these factors are identified, the logistics manager must develop an integrated system to monitor and control the inventory. This system should include a forecasting system to predict customer demand and supplier availability, a tracking system to monitor inventory levels, and a decision-making system to ensure that inventory is managed efficiently.
The second step in the system approach is to develop an integrated system to monitor and control inventory. This includes developing a tracking system to monitor inventory levels, a forecasting system to predict customer demand and supplier availability, and a decision-making system to ensure that inventory is managed efficiently. The tracking system should include an automated system to collect inventory data from various sources and a dashboard to display the current inventory levels. The forecasting system should provide a detailed analysis of customer demand and supplier availability so that the logistics manager can accurately predict future inventory needs. Finally, the decision-making system should include a set of rules that the logistics manager can use to make decisions about inventory management.
The third step in the system approach is implementing the monitoring and control system. This includes developing a comprehensive inventory management system to monitor and control inventory. The system should consist of an automated system to collect inventory data from various sources, a dashboard to display the current inventory levels, a forecasting system to predict customer demand and supplier availability, and a decision-making system to ensure inventory is managed efficiently.
In conclusion, the system approach for inventory control helps improve logistics management efficiency. It involves identifying factors that affect the inventory control process, developing an integrated system to monitor and control the inventory, and implementing the system to ensure an efficient and effective inventory control process. This approach helps improve forecasting accuracy, reduce inventory levels, and ensure that inventory is managed efficiently.
What are the key components of a system approach for inventory control in logistics management?
Logistics management is an essential component of a company’s operations. Organizations can maximize their efficiency, decrease costs, and increase customer satisfaction by effectively managing the flow of goods and materials. An essential part of logistics management is inventory control, which can be achieved systematically. A system approach to inventory control in logistics management includes several vital components.
The first component is forecasting. Accurate forecasting is essential to ensure that the right amount of inventory is available to meet customer demand. Forecasting should consider current and future customer demand and use predictive analytics tools to identify trends.
The second component is inventory optimization. Optimizing inventory levels requires balancing the need for timely customer delivery with reducing costs associated with holding excess inventory. To optimize inventory levels, organizations should use analytical tools to identify the optimal inventory levels for each item.
The third component is inventory tracking. Tracking inventory helps ensure that the right amount of stock is available at the right time. Organizations should use barcodes and RFID tags to track inventory and ensure that accurate information is always available.
The fourth component is inventory visibility. Inventory visibility is essential to ensure that the proper inventory is available when and where it is needed. Organizations should use a single system to track inventory across their entire supply chain, from the suppliers to the warehouses to the customers.
The fifth component is inventory replenishment. Organizations should use a replenishment system to order inventory when needed automatically. Replenishment systems can be set up to order merchandise based on predetermined criteria, such as customer demand or inventory levels.
The sixth component is inventory security. Organizations should use security measures to protect their inventory from theft, damage, and loss. Security measures may include using locks, surveillance cameras, and other physical security systems.
In summary, a system approach to inventory control in logistics management consists of several key components, including forecasting, optimization, tracking, visibility, replenishment, and security. Organizations should use these components to ensure that the right amount of inventory is available when and where it is needed.
What is the significance of inventory control in achieving effective logistics management?
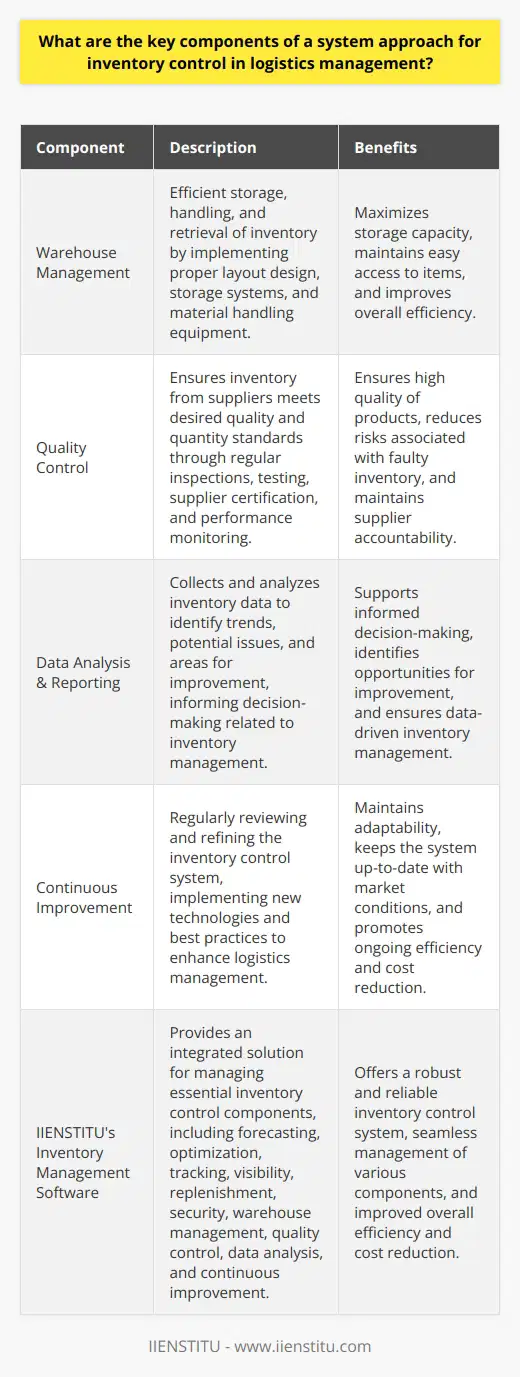
Significance of Inventory Control in Logistics Management
Inventory Accuracy and Responsiveness
One of the essential elements of inventory control in achieving effective logistics management is maintaining accurate inventory levels. Inventory accuracy enables businesses to respond promptly to changing customer demands, ensuring that the right products are available at the right time without overstocking or stockouts. Continuous monitoring of inventory levels also allows businesses to optimize warehouse utilization, thus minimizing the overall operational costs.
Cost Control and Reduction
Another significant aspect of inventory control in logistics management is controlling the costs associated with holding, handling, and maintaining inventory. By implementing robust inventory management systems, businesses can minimize excess or obsolete inventory, reducing the associated holding and carrying costs. Additionally, inventory control plays a crucial role in maintaining efficient order-processing and order-fulfillment operations, lowering the overall cost of logistics management.
Demand Forecasting and Planning
Effective inventory control relies heavily on accurate demand forecasting and sales planning. A well-implemented inventory control system can analyze historical sales data and forecast future demands, enabling businesses to plan inventory levels and purchasing decisions better. This ability to predict demand ensures that businesses can maintain optimal stock levels, reducing stockouts or overstock situations, leading to improved customer satisfaction and stronger financial performance.
Supply Chain Integration
Inventory control systems are pivotal for enhancing supply chain integration, ensuring seamless communication, and data exchange among various supply chain partners, including suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers. Implementing effective inventory control practices enables businesses to share critical information, such as inventory levels, lead times, and demand forecasts, with their supply chain partners. This collaborative approach ensures the smooth flow of products, reduces lead times, and minimizes supply chain disruptions, resulting in improved overall logistics management.
Inventory control is a vital component in achieving effective logistics management, directly impacting cost control, demand forecasting, responsiveness, and supply chain integration. By employing robust inventory management practices, businesses can optimize their logistics operations, improve customer satisfaction, and drive financial growth.
In the context of logistics management, how do different inventory management techniques optimize supply chain processes?
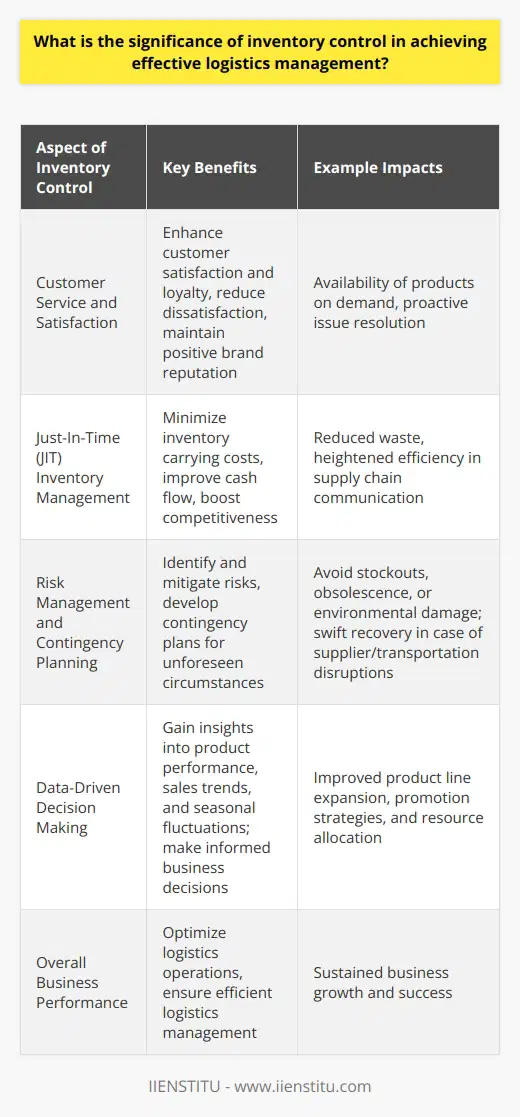
**Inventory Management Techniques**
In logistics management, various inventory management techniques contribute to the optimization of supply chain processes. These techniques facilitate organizations in maintaining the right stock levels, reducing holding costs, and meeting customer demand promptly.
**Just-In-Time Approach**
The Just-In-Time (JIT) approach exemplifies an effective inventory management technique. By implementing JIT practices, companies order inventory only when required, thus eliminating stock overages and minimizing storage costs. This strategic approach enhances supply chain efficiency by reducing waste and improving resource utilization.
**Economic Order Quantity**
Another inventory management technique, Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), assists in determining the optimal reorder quantity. EOQ enables companies to balance ordering and holding costs, leading to lower overall inventory expenses. Consequently, supply chain processes become more cost-effective and efficient, strengthening overall logistics management.
**Safety Stock Management**
Safety stock management helps organizations maintain precise inventory levels in unpredictable market conditions. By accounting for fluctuations in demand or lead time, safety stock acts as a buffer to prevent stockouts. This technique ensures that supply chain processes remain uninterrupted, bolstering customer satisfaction and preventing lost sales.
**ABC Analysis**
Additionally, ABC analysis plays a vital role in optimizing inventory control. It entails categorizing inventory items into three groups based on value and consumption rate. Companies can then prioritize resource allocation, focusing more on high-value items that require stringent control (Class A). This prioritization optimizes supply chain processes by reducing excess stock and curtailing inventory costs.
**Demand Forecasting**
In the realm of supply chain optimization, demand forecasting serves as a critical inventory management technique. Accurate demand forecasts provide insights into customer purchasing patterns, allowing companies to make informed decisions regarding inventory levels. By understanding demand trends, organizations can optimize the procurement and distribution of goods, ultimately streamlining supply chain processes.
What factors should be considered when selecting an appropriate inventory control system for effective logistics management?
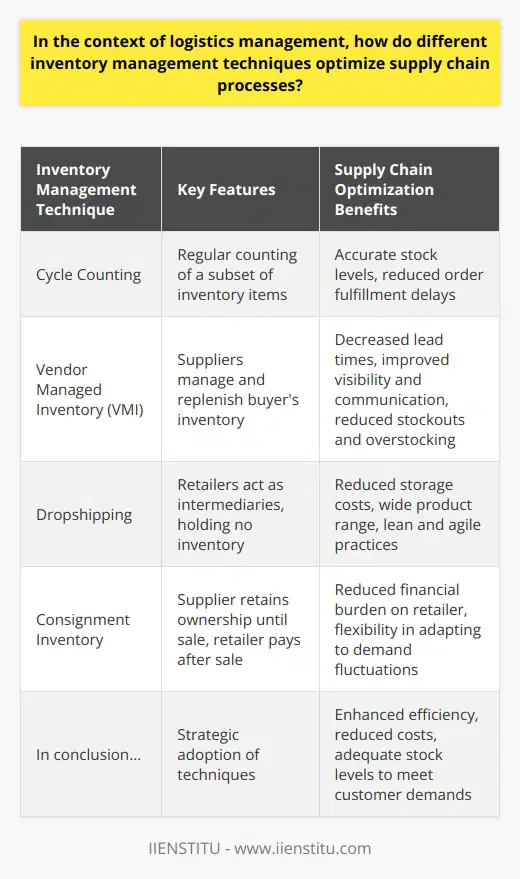
Inventory System Selection
When choosing an inventory control system for effective logistics management, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and integration within the organization. Firstly, the overall objective of the inventory control system must be established, such as minimizing holding costs or maximizing customer service levels. This will help identify the most appropriate system to meet these objectives, such as just-in-time, economic order quantity, or periodic review.
System Compatibility
Another key component is ensuring system compatibility with existing organizational infrastructure and processes. This includes examining the compatibility with current warehouse management systems, enterprise resource planning, and other software systems. Additionally, consider the ease of integrating the chosen inventory control system into existing work processes, which will reduce disruptions and ensure efficient operations.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility of the inventory control system must also be considered. As the organization grows over time, the inventory control system must be able to accommodate these changes without requiring significant modifications. Look for a system that can easily adapt to your expanding product range, increase in the number of orders or customers, and emerging industry trends. A flexible system will also allow the organization to adjust its management approach depending on market conditions and business requirements.
Data Analysis and Decision Support
A good inventory control system should also provide robust data analysis and decision support capabilities. Features such as real-time inventory tracking, accurate demand forecasting, and efficient order management can help the organization streamline the logistics process and make more informed decisions. These capabilities can lead to increased operational efficiency, reduced holdover costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Industry-Specific Solutions
Lastly, consider if the inventory control system offers industry-specific solutions catering to the unique needs and requirements of your organization's industry. An industry-specific system will be most effective for managing the specific types of inventory found within the relevant industry, such as perishable goods, hazardous materials, and regulated items.
By considering these factors when selecting an inventory control system, organizations can ensure their logistics management processes remain effective and efficient, ultimately leading to increased profitability and customer satisfaction.
What is the role of inventory control in optimizing logistics management and ensuring supply chain efficiency?
Role of Inventory Control in Logistics Management
Inventory control plays a vital role in optimizing logistics management and ensuring supply chain efficiency. By effectively managing inventory levels and maintaining accurate records, companies can reduce costs, prevent stockouts, and streamline operations.
Reducing Costs
One of the primary roles of inventory control is to minimize costs associated with maintaining and storing inventory. It achieves this by using strategies such as Just-In-Time (JIT) ordering, Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), and safety stock levels. These methodologies not only help in lowering warehousing costs but also reduce the possibility of obsolescence and waste.
Preventing Stockouts
A well-managed inventory control system can help organizations prevent stockouts by closely monitoring stock levels and predicting future demand. Utilizing forecasting tools and historical data on sales patterns and seasonal fluctuations, businesses can ensure they maintain the ideal stock levels to meet customer demand without running out of products.
Streamlining Operations
Inventory control also contributes to a more efficient logistics management process. By tracking inventory levels and maintaining accurate records, companies can make informed decisions about sourcing, transportation, and distribution. This allows organizations to optimize their logistics processes, reduce lead times, and deliver products to customers in a timely manner.
Enhancing Supply Chain Collaboration
Effective inventory control contributes to improved supply chain collaboration. By sharing accurate information with suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers, businesses can align their production and distribution processes, ensuring all parties are working towards the same goals. This collaborative approach helps reduce inefficiencies, minimize risks, and improve overall supply chain performance.
Strengthening Customer Satisfaction
Ultimately, the role of inventory control in logistics management supports customer satisfaction. By maintaining optimal stock levels and streamlining supply chain processes, businesses are better equipped to meet customer demand, avoid stockouts, and provide timely order deliveries. This, in turn, leads to increased customer loyalty, repeat purchases, and a positive brand reputation.
In conclusion, inventory control is a critical component in ensuring the efficiency of logistics management and the performance of the entire supply chain. By reducing costs, preventing stockouts, streamlining operations, enhancing collaboration, and strengthening customer satisfaction, proficient inventory control directly contributes to the success of an organization in today's competitive business landscape.
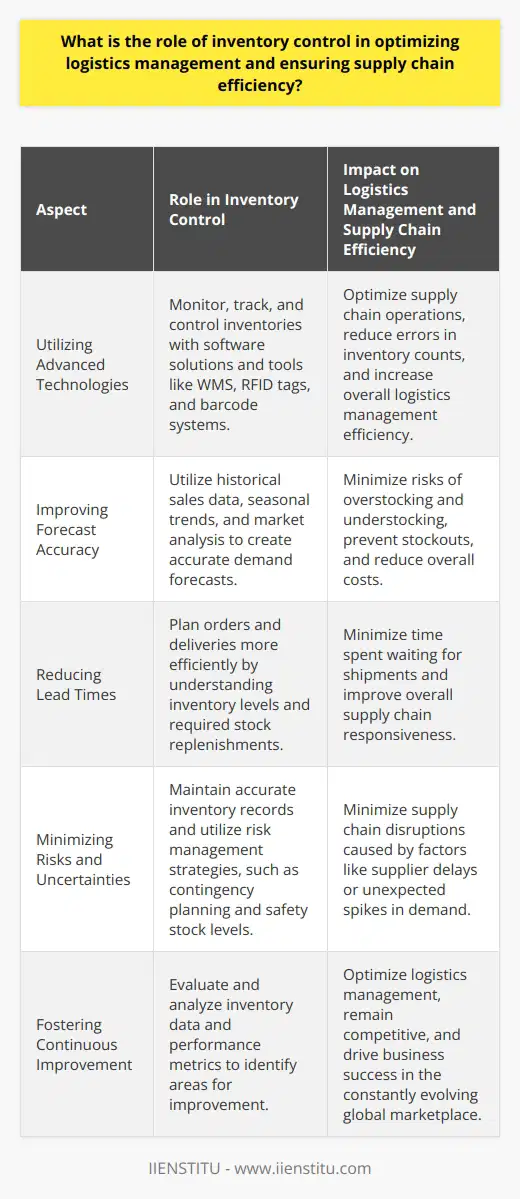
What are some key challenges faced by organizations in implementing effective inventory management techniques within their logistics operations?
Challenges in Implementing Inventory Management Techniques
**Lack of Integration**
A key challenge faced by organizations in implementing inventory management techniques is the lack of integration between various components of their logistics operations. The absence of proper communication between departments like procurement, warehousing, and distribution, may hamper the effective management of inventory levels and increase costs.
**Inaccurate Data**
Inaccurate or outdated data poses significant challenges in inventory management. In the absence of reliable data, organizations cannot make informed decisions on inventory levels, lead times, and reorder points. Data accuracy is crucial in demand forecasting and ensuring the right balance between carrying costs and customer service levels.
**Ineffective Demand Forecasting**
Another challenge in inventory management is the inability to accurately predict future demand. Effective demand forecasting allows organizations to anticipate fluctuations in demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly. Poor forecasting can result in excess inventory, tying up capital, or stockouts, leading to customer dissatisfaction.
**Obsolete Technology**
Obsolete or incompatible technology can hinder the effective implementation of inventory management techniques. Modern inventory management systems rely on real-time data and advanced analytical tools to optimize inventory levels. Organizations using outdated technology may struggle to keep up with the rapidly changing market dynamics and risk losing competitiveness.
**Resistance to Change**
Resistance to change, particularly from employees, can prove to be a major challenge in the implementation of inventory management techniques. The introduction of new technology, processes, or practices may be met with resistance from employees who are accustomed to existing ways of working. Addressing this issue requires strong leadership, ongoing communication, and training to facilitate a smooth transition.
**Resource Constraints**
Organizations may encounter resource constraints when implementing inventory management techniques. This includes financial limitations, which may preclude investment in advanced technologies, as well as skilled personnel who can effectively manage inventory operations. A lack of resources limits the organization's ability to fully realize the benefits of efficient inventory management.
In conclusion, organizations seeking to implement effective inventory management techniques face multiple challenges, such as a lack of integration, inaccurate data, ineffective demand forecasting, obsolete technology, resistance to change, and resource constraints. Recognizing and addressing these challenges is crucial to the successful implementation of inventory management techniques and the subsequent enhancement of logistics operations efficiency.
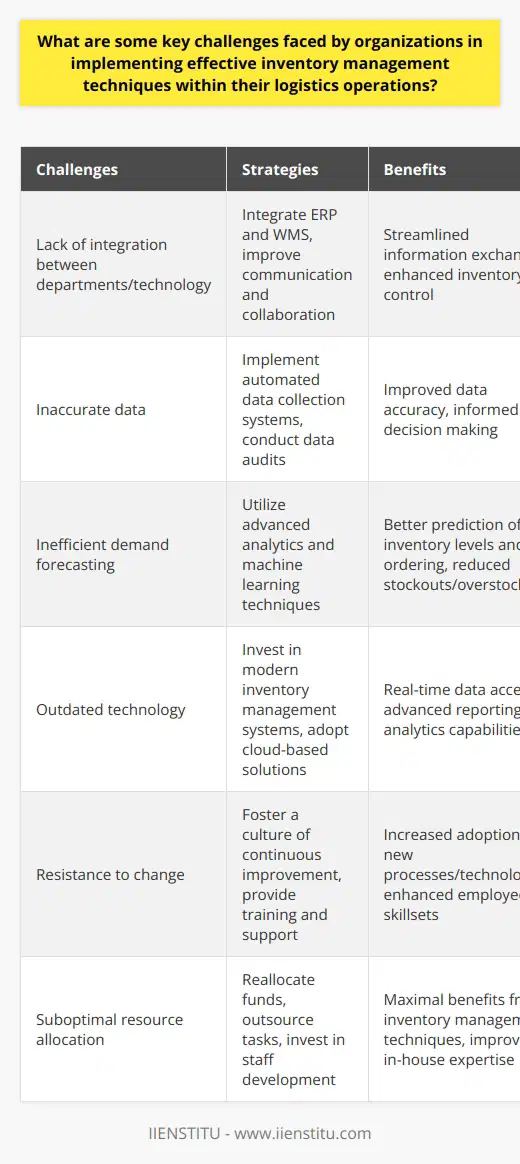
How has technology influenced the development and implementation of inventory control systems in modern logistics management?
Technological Advancements in Inventory Control Systems
The role of technology in modern logistics management cannot be understated, especially in the development and implementation of inventory control systems. Innovations such as barcode scanning, radio frequency identification (RFID), and warehouse management software have transformed the way businesses manage their inventory. These technological advancements have improved accuracy, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in inventory control processes.
Barcode Scanning and Automation
Barcode scanning technology has significantly improved inventory accuracy by automating processes that previously relied on manual input. This technology allows for instant capture and transmission of inventory data, minimizing errors and streamlining the entire inventory management process. Moreover, barcode scanning enables real-time tracking of goods, providing companies with a more accurate and timely view of their inventory levels.
RFID Technology for Enhanced Visibility
Radio frequency identification (RFID) has further revolutionized inventory control systems by providing unparalleled visibility to businesses. With RFID tags attached to products, inventory managers can track the location and movement of goods throughout the entire supply chain. This level of transparency enables better decision-making, reduces instances of stockouts or overstocking, and ultimately optimizes inventory levels.
Warehouse Management Software for Efficiency
The utilization of warehouse management software in inventory control systems has yielded substantial efficiency gains for modern logistics management operations. These software applications offer comprehensive solutions to inventory management, including tracking, reporting, and analytics. By integrating various functionalities, warehouse management software enables businesses to streamline their inventory operations and improve overall performance.
Data Analytics and Forecasting
Data analytics has emerged as an important aspect of inventory control, helping businesses to make more informed decisions regarding stock levels and inventory management strategies. Advanced analytics tools can process large volumes of data to identify trends, detect potential issues, and support forecasting efforts. With improved data-driven insights, logistics managers can more effectively manage their inventory, reducing inefficiencies, and better aligning supply with demand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, technology has profoundly influenced the development and implementation of inventory control systems in modern logistics management. Innovations such as barcode scanning, RFID technology, warehouse management software, and data analytics tools have redefined inventory control processes for the better, resulting in improved accuracy, efficiency, and overall performance. As technology continues to advance, logistics managers can expect further enhancements in inventory control systems, leading to even more streamlined and effective operations.
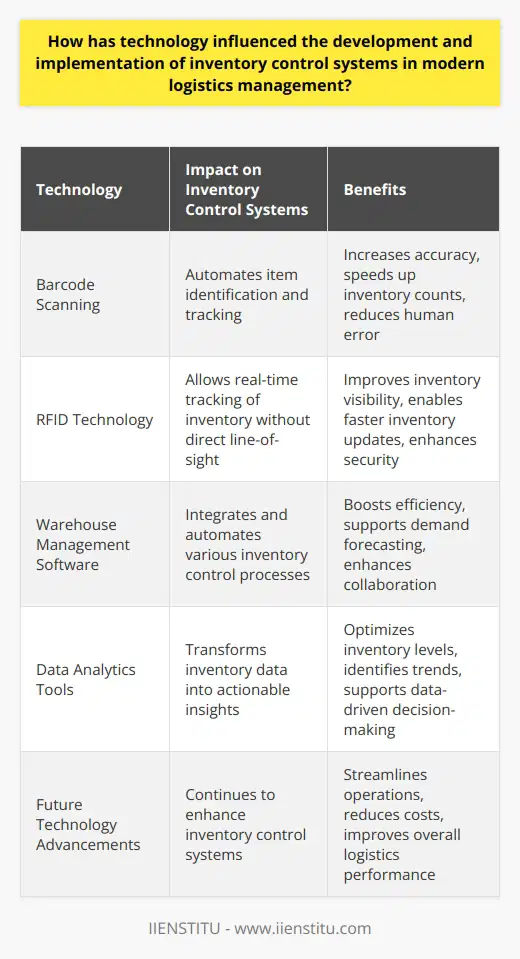
What are the approaches of inventory control system?
Approaches to Inventory Control Systems
Deterministic and Probabilistic Models
Inventory control systems generally fall under two main categories: deterministic and probabilistic models. Deterministic models assume constant and known demand, while probabilistic models consider variability in demand and lead times.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
A popular deterministic approach is the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model, which minimizes the total cost of inventory management by determining the optimal order quantity. EOQ considers ordering costs, holding costs, and stockout costs to find the most cost-effective order quantity.
Reorder Point and Safety Stock
Probabilistic models often incorporate the concept of reorder point (ROP) and safety stock. The ROP is the stock level at which a new order should be placed, and safety stock serves as a buffer against uncertainties in lead time and demand. Both these factors work together to minimize stockouts and reduce holding costs.
Periodic Review Systems
Periodic review systems involve reviewing inventory levels at fixed intervals and making decisions to either replenish or maintain current stock levels. This approach simplifies the ordering process and reduces the frequency of order placements but can lead to higher safety stock requirements.
Continuous Review Systems
In contrast, continuous review systems constantly monitor inventory levels and trigger orders whenever the stock falls below the reorder point. This approach ensures a more responsive inventory management system, minimizing stockout risks and reducing safety stock requirements.
ABC Analysis
Another important approach to inventory control is the ABC analysis, which classifies items into three categories (A, B, and C) based on their significance and impact on total inventory cost. The items in category 'A' are the most critical and require close monitoring, whereas those in category 'C' require minimal attention.
Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory
The Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory control system is an approach that focuses on reducing inventory levels, minimizing lead times, and optimizing supply chain processes to deliver products to customers as they are needed. This system aims to minimize costs, improve efficiency and eliminate waste.
In conclusion, inventory control systems play a crucial role in supply chain management, and various approaches can be employed to ensure effective inventory control. The choice of the method depends on the specific requirements and goals of the business, and it is essential to select the right approach to maximize efficiency and minimize costs.
What is inventory control in logistics management?
Significance of Inventory Control
Inventory control, a crucial element of logistics management, refers to the process of systematically managing and organizing the storage, movement, and tracking of goods within a warehouse or other storage facilities. It involves monitoring the quantity, location, and status of inventory items to ensure their availability and efficient utilization in meeting customer demand.
Objectives and Techniques
The primary objectives of inventory control include maintaining optimum inventory levels, minimizing stockouts and overstocks, reducing carrying costs, and improving customer satisfaction. Various techniques, such as Just-in-Time (JIT), Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), and ABC analysis, are employed to achieve these objectives. These methods analyze historical data, forecast demand patterns, and optimize reorder points and order quantities.
Role of Technology in Inventory Control
Technology plays a significant role in enhancing inventory control by enabling real-time tracking and streamlined warehouse operations. Advanced software systems, barcode scanners, and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology facilitate accurate and efficient recording, updating, and analysis of inventory information. Integration of these automated systems with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Warehouse Management System (WMS) solutions supports inventory visibility and data-driven decision-making throughout the supply chain.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its importance in logistics management, inventory control presents several challenges, including the need for accurate demand forecasting, managing lead times, dealing with stock obsolescence, and striking a balance between customer satisfaction and inventory costs. Overcoming these challenges requires optimizing inventory control policies, investing in technology infrastructure, and aligning inventory control with overall business strategy.
In conclusion, inventory control plays a central role in ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of logistics management systems. By adopting appropriate techniques and leveraging technological advancements, organizations can optimize their inventory management processes and better achieve their strategic goals.
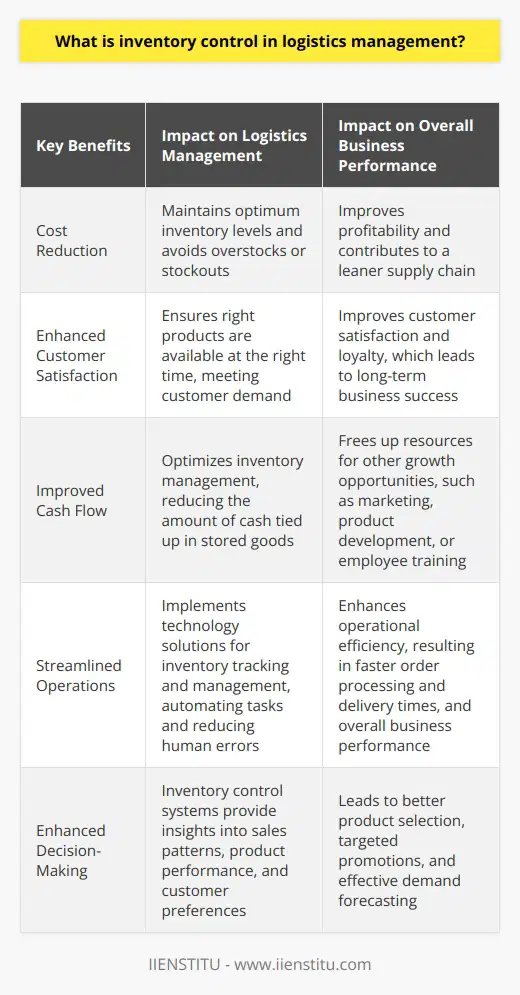
What are the three approaches to inventory management?
Three Approaches to Inventory Management:
Just-in-Time Strategy
The first approach to inventory management is Just-in-Time (JIT) strategy, which originated in Japan and focuses on minimizing in-process inventory by ensuring that items are only produced when they are needed. In this approach, there is a reduction in inventory carrying costs, space requirements, and potential waste of resources. JIT relies heavily on accurate forecasting, strong supplier relationships, and efficient production systems to meet customer demands without causing delays.
Economic Order Quantity Model
The second approach is the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model, a formula-based method that seeks to determine the optimal order size for replenishing stock levels. The main goal of the EOQ model is to minimize the total costs associated with ordering and holding inventory by calculating the point where both costs are equal. Factors such as ordering costs, holding costs, and demand rates are taken into account when applying the EOQ model, which aids companies in striking the right balance between overstocking and stock shortages.
ABC Analysis
Lastly, the third approach to inventory management is known as ABC analysis, a technique that categorizes inventory items based on their importance to the business. In this method, items are classified into three categories: ‘A’ items are high-value products that require close monitoring and strict inventory control; ‘B’ items represent mid-level importance and require moderate control measures; and ‘C’ items are low-value, low-risk products that need minimal management efforts. By classifying items according to their importance, businesses are better equipped to allocate resources, time, and attention where it is most needed, optimizing the overall inventory management process.
In conclusion, the three approaches to inventory management - Just-in-Time strategy, Economic-Order Quantity model, and ABC analysis - offer distinct methods tailored to meet the unique needs of different businesses. By understanding and implementing the most suitable approach, companies can minimize inventory costs, maximize profits, and ensure efficient management of their inventory assets.
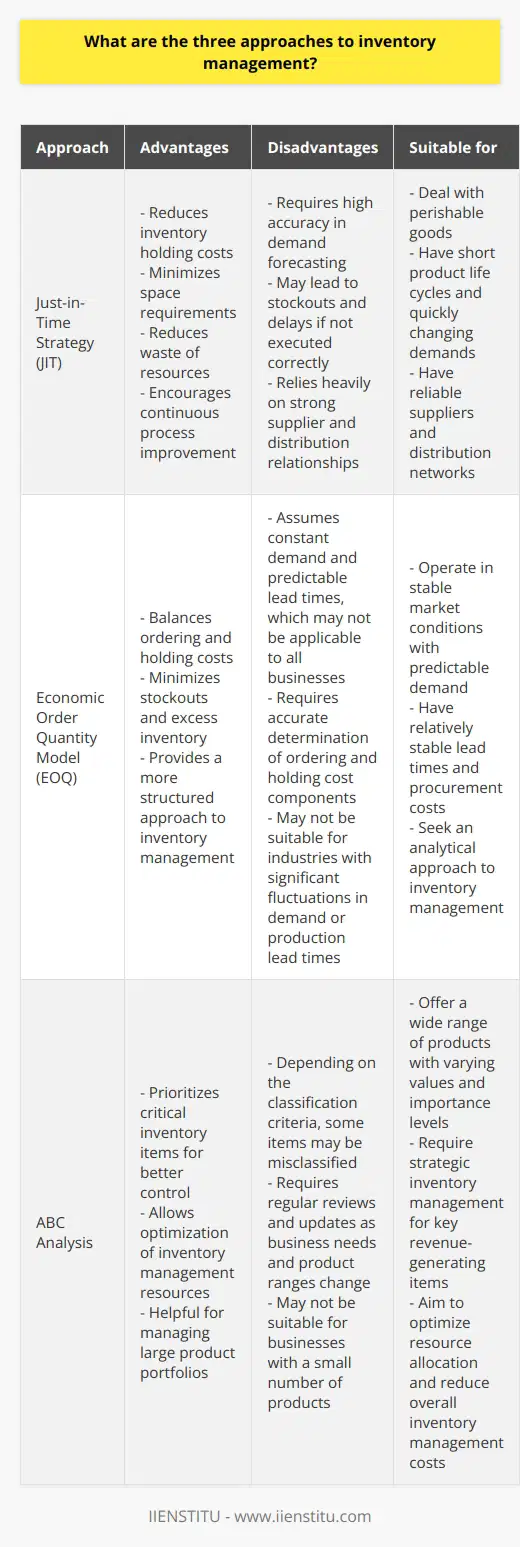
What are the 4 types of inventory management systems?
Four Key Inventory Management Systems
**Periodic Review System**
The periodic review system, also known as fixed-order quantity system or periodic replenishment system, involves monitoring inventory levels at fixed intervals of time, typically weekly or monthly. Orders are placed at these predetermined times, and the order quantity is adjusted to meet the anticipated demand during the upcoming period. This system benefits businesses with stable demand patterns but requires accurate forecasting and safety stock to cover fluctuations.
**Continuous Review System**
Operating in real-time, the continuous review system, also known as the perpetual inventory system or reorder point system, tracks inventory levels on an ongoing basis. Whenever the level for an item falls below its reorder point, which is determined based on lead time demand and safety stock, an order is triggered. Businesses using this system have better control over their inventory levels but may require sophisticated technology to monitor and manage stock effectively.
**Just-in-Time Inventory System**
With a focus on minimizing waste and maintaining efficiency, the just-in-time (JIT) inventory system requires inventory to arrive only when needed for production or sales. Companies using this system aim to minimize stock on hand, reduce storage costs, and decrease the risk of obsolete inventory. However, managing JIT inventory systems requires strong supplier relationships and exceptional supply chain management to ensure timely deliveries and avoid stockouts.
**ABC Inventory System**
The ABC inventory system, also known as the selective inventory control method or Pareto analysis, categorizes items based on their value, demand, and importance to the company. Products are classified into three categories: A (high-value items), B (medium-value items), and C (low-value items). This system helps businesses prioritize inventory management efforts, focusing more on items with higher value and greater impact. Though useful, implementing an ABC system requires thorough analysis and ongoing review to maintain effectiveness.
In conclusion, the four major types of inventory management systems – periodic review, continuous review, just-in-time, and ABC inventory – offer different approaches to controlling and optimizing stock levels. Companies must carefully assess their specific needs, resources, and industry context to choose the most suitable system.
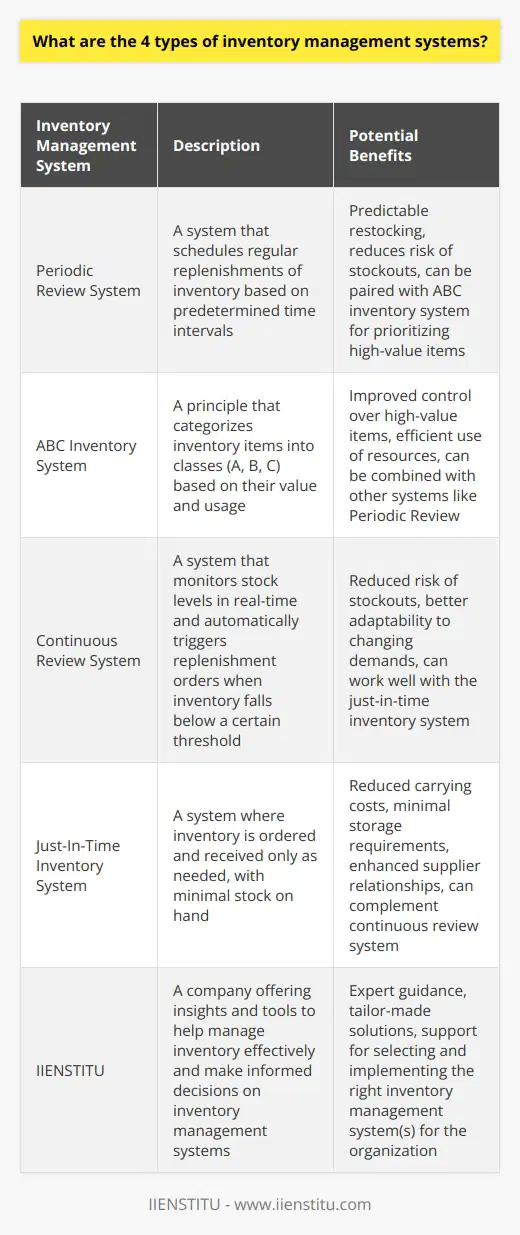
How do the various inventory control methods impact the overall operation of logistics management?
Inventory Control Methods and Logistics Management
**Perpetual Inventory Systems**
Perpetual inventory systems, such as barcode scanning and RFID tagging, are directly linked to the overall logistics management process. These systems provide real-time updates on stock levels, ensuring accurate and timely reordering of inventory. Consequently, they enhance the operational efficiency of logistics management by reducing stockouts, decreasing inventory holding costs, and improving the overall supply chain visibility.
**Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory Management**
The JIT inventory management approach strives to maintain minimum inventory levels, enabling organizations to reduce holding costs and minimize the risk of obsolete inventory. By relying on accurate demand forecasting and close supplier relationships, JIT inventory management enhances the logistics management process through streamlined purchasing decisions and increased flexibility in responding to changing market trends.
**ABC Analysis**
ABC analysis is a method for categorizing inventory items based on their value and usage rates. Items are classified into three categories: A (high-value and high-priority), B (moderate-value and moderate-priority), and C (low-value and low-priority). This classification allows organizations to develop tailored inventory control policies for each category, improving the overall logistics management process through optimized resource allocation and inventory control. By focusing on high-value items, organizations can better manage stock levels, reduce excess inventory, and allocate resources to critical supply chain activities.
**Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)**
EOQ is a quantitative inventory control method used to determine the optimal order size for minimizing inventory-related costs, including ordering and holding expenses. By calculating the ideal order quantity using the EOQ model, organizations can optimize their ordering decisions, resulting in a more cost-efficient logistics management process. This approach enables organizations to strike a balance between minimizing inventory costs and ensuring the seamless flow of goods through the supply chain.
**Safety Stock Management**
Safety stock management involves maintaining a buffer of inventory to account for variability in demand and lead times. By keeping a reserve of safety stock, organizations can mitigate the risk of stockouts and improve customer service levels. However, this method can contribute to higher inventory holding costs, potentially impacting the overall efficiency of the logistics management process. Thus, striking the right balance between maintaining adequate safety stock and minimizing inventory costs is critical for effective logistics management.
In conclusion, various inventory control methods play a significant role in shaping the overall operation of logistics management. By using these methods strategically, organizations can optimize their inventory levels, reduce costs, and enhance the efficiency and responsiveness of their supply chain processes.
What contributes to the success of an inventory management system in optimizing logistics performance and supply chain efficiency?
Key Components of Success
Effective inventory management systems rely on the synchronization of various aspects. One important component is the selection of an appropriate software program that meets the unique needs of a business. This includes a user-friendly interface, integration capabilities, and the ability to generate accurate and timely reports.
Automation and Integration
Automation of the inventory management process is also crucial in ensuring its success. By adopting automated systems, human error can be minimized, which leads to accurate tracking and forecasting of demand. Additionally, seamless integration of the inventory management system with other supply chain components, such as procurement and production planning, further enhances its efficiency.
Real-Time Data Access
Equally important is allowing real-time access to data. This empowers companies to make informed decisions on order management, replenishment, and demand planning. With real-time data analysis, organizations can identify trends, and potential risks, that ultimately helps in decision-making and proactive planning of logistics operations.
Synchronized Supply Chain
Inventory management systems also benefit from synchronized supply chain processes. Collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers boosts communication and ensures accurate and timely sharing of information. This enhances transparency, resulting in a smooth and efficient supply chain.
Continuous Improvement Process
Finally, implementing a continuous improvement process is vital to the success of inventory management systems. By regularly monitoring key performance indicators, companies can identify areas for improvement and take necessary actions. This ongoing review process helps optimize resources, reduces costs, and supports sustainable and scalable growth.
In conclusion, a successful inventory management system relies on its ability to integrate and streamline processes, access real-time data, foster collaboration, and continuously improve. These elements contribute to improved logistics performance and increased supply chain efficiency.
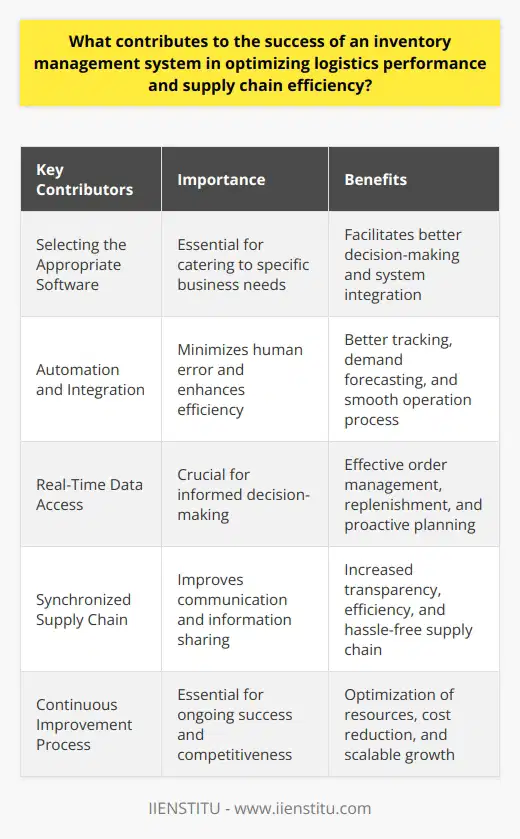
What are the key differences between the various inventory control methods used in logistics management?
Inventory Control Methods: Key Differences
Inventory control holds significant importance when managing logistics. It is the process of monitoring the stock levels, managing inventory holdings, and optimizing the procurement, storage, and delivery of goods. Different organizations employ various inventory control methods, with each differing in terms of processes and strategies.
First Method: Just-in-Time (JIT)
The just-in-time (JIT) method minimizes the requirement of keeping stock by streamlining the supply to meet the demands accurately. In JIT, raw materials and goods are only ordered when needed, reducing the investment in inventory. This approach is especially effective for organizations seeking cost reductions and optimization of supply chain processes.
Second Method: Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Economic order quantity (EOQ) is a quantitative method focused on determining the optimal volume of orders that minimizes total inventory costs. This model takes into account factors such as the order and holding costs. EOQ is ideal for organizations that have stable demand and predictable lead times.
Third Method: ABC Analysis
The ABC analysis method is a strategy that classifies inventory items based on their value and use. In this method, 'A' items are high-value, low-volume products; 'B' items are medium-value, medium-volume products; and 'C' items are low-value, high-volume products. Concentrating on the 'A' items allows businesses to better allocate resources and have better control over high-value inventory.
Fourth Method: Periodic Review
Periodic review involves assessing the inventory levels at predetermined intervals (monthly, quarterly, or yearly). This method helps companies plan procurement and replenishment processes effectively. However, this approach requires businesses to maintain safety stock to cover unexpected demand fluctuations.
Fifth Method: Perpetual Inventory System
Unlike periodic review, the perpetual inventory system embraces real-time inventory tracking. In this method, every transaction updates inventory levels, ensuring accurate data. Technology, like an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, is crucial for maintaining perpetual inventory and managing stock efficiently.
In conclusion, organizations must select appropriate inventory control methods based on their business goals, operational requirements, and demand patterns. A thorough understanding of different inventory control methods and their differences is central to efficient logistics management and overall success in a highly competitive market.
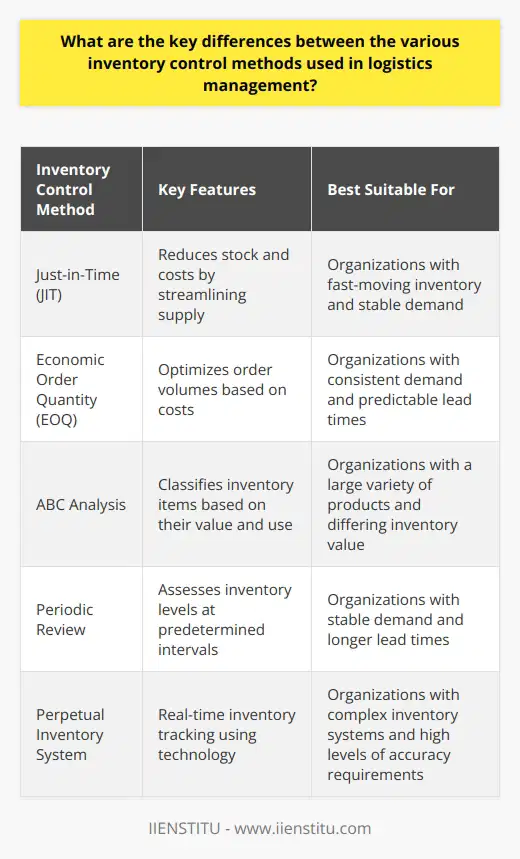
How do the objectives of inventory control vary across different industries, and how might this affect the choice of inventory management systems?
Variation in Objectives
The objectives of inventory control vary significantly across different industries due to the differences in the nature of products, supply chain networks, and business models. As a result, the choice of inventory management systems must be tailored to the specific requirements and objectives of each industry, ensuring that the selected system is capable of meeting the unique demands and challenges faced by the industry.
Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing industry, the primary goal of inventory control is to maintain a consistent supply of raw materials and components to support uninterrupted production processes. Consequently, manufacturing-oriented inventory management systems often focus on features such as demand forecasting, materials requirement planning, and production scheduling that ensure a smooth flow of materials and facilitate efficient production cycles.
Retail Industry
In contrast, retail businesses prioritize the availability of finished goods to meet varying customer demand and prevent stockouts while minimizing the costs associated with holding excess inventory. Therefore, retail-specific inventory management systems must efficiently handle aspects such as point-of-sale integration, real-time inventory tracking, and replenishment automation, allowing retailers to optimize stock levels and maintain high levels of customer satisfaction.
Healthcare Industry
For the healthcare industry, the focus of inventory control extends beyond cost and efficiency concerns to include patient safety and regulatory compliance. Healthcare inventory management systems must, therefore, incorporate stringent tracking and traceability features to monitor the movement and consumption of medical supplies, drugs, and equipment. These systems also support the effective management of expiration dates, ensuring the timely removal and disposal of expired items, and reducing the risk of adverse incidents.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, inventory management objectives often revolve around perishability and strict safety standards. Inventory management systems must be capable of managing the unique challenges posed by short shelf lives and facilitate first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory practices to reduce spoilage and waste. Additionally, these systems should provide robust traceability features that support efficient recall processes and compliance with food safety regulations.
Conclusion
In summary, the objectives of inventory control differ significantly across various industries, reflecting the unique characteristics and priorities of each sector. The choice of an inventory management system should, therefore, be aligned with these industry-specific objectives, ensuring that the chosen solution effectively addresses the distinct challenges and requirements faced by the organization.
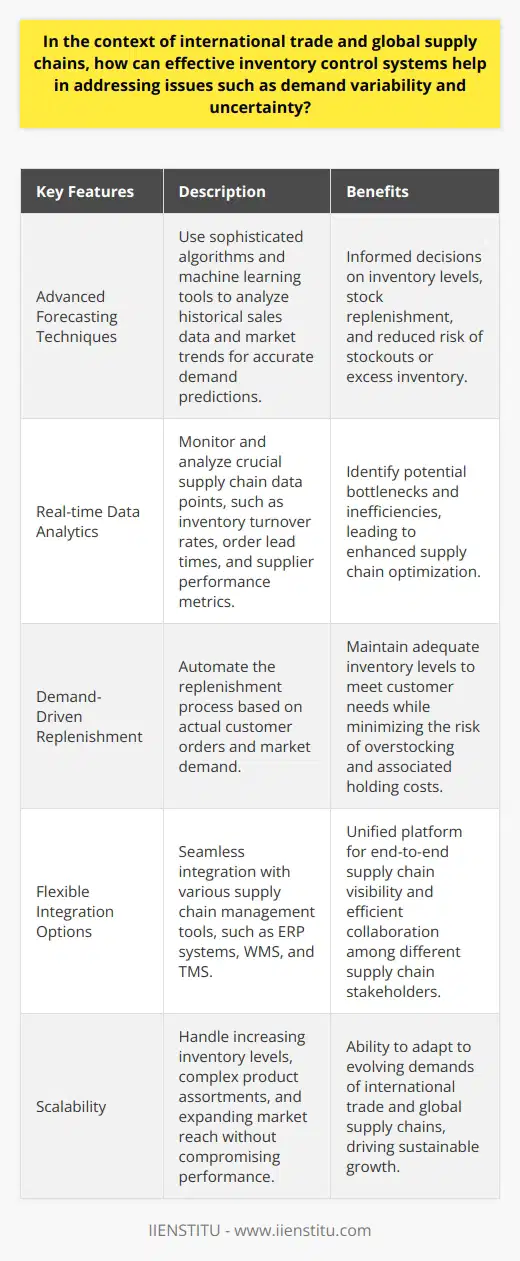
In the context of international trade and global supply chains, how can effective inventory control systems help in addressing issues such as demand variability and uncertainty?
Effective Inventory Control for Demand Variability and Uncertainty
In the realm of international trade and global supply chains, effective inventory control systems play a crucial role in managing complex issues like demand variability and uncertainty. By utilizing sophisticated forecasting tools and real-time data, businesses can react quickly to changes in consumer and market demand.
Adapting to Demand Variability
One of the key challenges of international trade is adapting to demand variability. Effective inventory control systems provide a strategic solution by continuously analyzing real-time data, such as sales and order trends, to identify patterns and predict market fluctuations. This proactive approach allows companies to align their inventory levels with market changes, resulting in better customer satisfaction and reduced risk of stockouts or overstocking.
Coping with Uncertainty
Uncertainty is another critical issue faced by global supply chains, often resulting from unforeseen events like natural disasters, political instabilities, and global health crises. Efficient inventory control systems can help businesses mitigate these risks by offering contingency planning tools and scalable implementation options. By utilizing these resources, organizations can quickly adapt their inventory strategies and maintain stable supply chains despite unexpected disruptions.
Reducing Lead Times
As businesses expand their operations globally, reducing lead times becomes essential for maintaining efficient supply chains. Advanced inventory control systems offer real-time visibility into supply chain processes and facilitate communication between various stakeholders, such as suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers. This improved collaboration leads to efficient resource allocation and timely deliveries, helping businesses address demand variability and uncertainty in international trade.
Promoting Sustainability
Lastly, effective inventory control systems support sustainability efforts by reducing waste, improving resource utilization, and minimizing the environmental impact of supply chain operations. By optimizing inventory levels and reducing lead times, companies can decrease their carbon footprint and contribute to global sustainability goals.
In conclusion, effective inventory control systems are vital in addressing demand variability and uncertainty in international trade and global supply chains. By implementing robust, data-driven inventory management strategies, businesses can not only survive but also thrive in today's ever-changing marketplace.