The intricate fabric of contemporary business practices is woven with various threads of ethical deliberation, particularly within the domain of Human Resource (HR) management. HR Ethics refers to the moral principles that govern the conduct of individuals within the HR profession and their application to the decision-making processes affecting employees and the organization. This field's gravity lies in its power to shape the workplace environment and influence organizational culture profoundly.
By emphasizing ethical behavior and decision-making, HR professionals can foster a climate of trust and respect, thus reinforcing the organization's social responsibility. In this blog post, we will delve into the role of HR in upholding organizational ethics, discuss key ethical principles, explore the challenges faced and the importance of maintaining such standards in the contemporary workplace, providing a comprehensive insight into corporate morality.
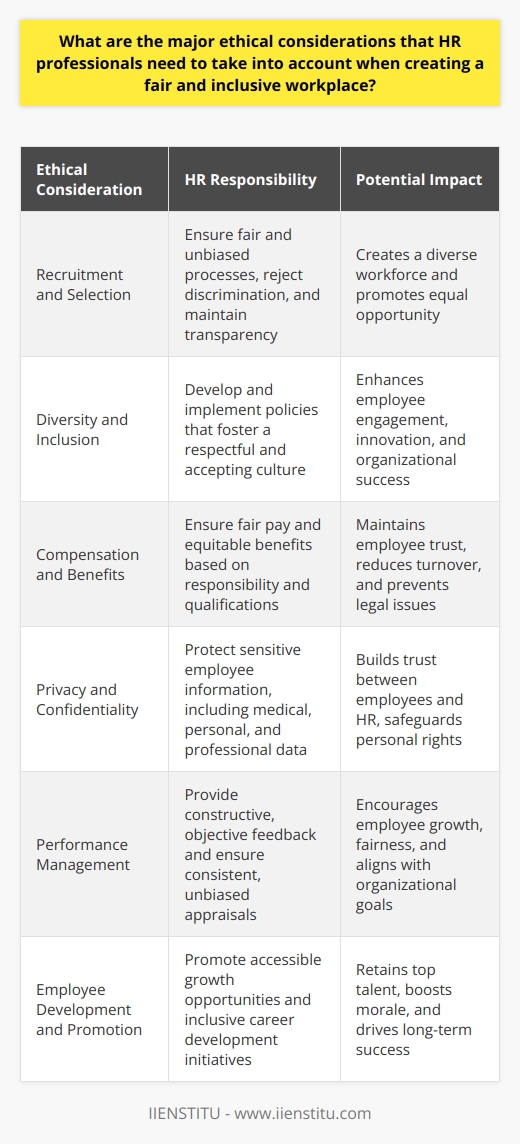
The Role of HR in Upholding Organizational Ethics
HR as a Gatekeeper of Ethical Conduct
HR professionals serve as the custodians of ethical conduct within organizations, tasked with the responsibility of crafting and safeguarding a work environment that adheres to ethical standards. This includes monitoring workplace behavior and ensuring it aligns with the organization's core values.
They are instrumental in setting the tone for what is acceptable by explicitly communicating ethical expectations to all staff levels. Through their disciplinary mechanisms, they ensure consequences for infractions and consistently uphold the standards set forth. An effective human resources course could adequately train HR personnel in identifying and handling ethical issues, subsequently ensuring they are well-equipped to serve as ethical gatekeepers within their organizations.
HR’s Responsibility in Developing an Ethical Climate
To cultivate an ethical workplace, HR departments must ensure that the importance of ethical behavior is underscored through ongoing training and development programs. These initiatives should span from onboarding processes to executive training, casting focus on ethical decision-making, and reinforcing the organization's core ethical values.
Moreover, HR is responsible for crafting and implementing a comprehensive code of conduct along with other organizational policies that delineate expectations and prescribed behaviors. This acts not only as a guideline for employees but also as a protective measure for the organization, reducing potential legal and reputational risks.
HR's Role in Resolving Ethical Dilemmas
HR professionals frequently encounter ethical dilemmas where competing interests and values necessitate nuanced solutions. By systematically analysing the issue, consulting relevant policies, and weighing the outcomes, HR can approach ethical challenges judiciously. The resolution of such dilemmas often involves delicate communication and negotiation, yet through experience and adherence to a strong ethical frame, HR can navigate these complexities. Regarded case studies of HR professionals confronted with ethical dilemmas exemplify this balancing act and serve to provide insightful lessons for those in the field.
Key Ethical Principles in Human Resource Management
Confidentiality
The principle of confidentiality within HR cannot be overstated; it forms the bedrock of trust between employees and the organization. HR is entrusted with sensitive employee information that must be safeguarded with the utmost integrity. The breach of this confidential information can lead to significant trust erosion and legal consequences which can severely damage an organization’s credibility.
Fairness and Justice
Respect for Individual Rights
Respecting individual rights is vital in promoting a diverse and inclusive workplace. This respect is demonstrated by HR through the maintenance of equitable hiring practices, respect for work-life balance, and the strict adherence to anti-discrimination laws. Instances of rights violation can serve as sobering reminders of the importance of this principle, underscoring the need for a vigilant and proactive HR department.
Challenges in Upholding HR Ethics and Ways to Overcome Them
Pressure to Compromise on Ethical Behavior
At times, HR professionals may face situations where there is pressure to compromise on ethical behavior, be it to meet business objectives or align with management's interests. These instances of ethical stress require resilience and a clear commitment to ethical standards. By developing a sense of moral courage and leveraging support networks within the profession, HR professionals can develop the capacity to resist such pressures. Staying abreast of legal requirements and following certificate courses online on ethical practices can further empower HR professionals to stand firm in their principles.
Dealing with Unethical Corporate Culture
Changing an organizational culture steeped in unethical practices is a significant challenge for HR. It requires identifying the root causes of such practices, fostering open communication channels, and incrementally implementing changes that promote ethical behavior. HR can leverage its strategic position to influence leadership and incrementally shift the overarching organizational culture towards more ethical practices, as illustrated by success stories in the industry.
Importance of HR Ethics in the Modern Workplace
Impact of HR Ethics on Employee Satisfaction and Retention
The integrity of HR ethics directly correlates with employee satisfaction and retention rates. Several research studies have illuminated the positive relationship between ethical HR practices and employees' likelihood to remain with their employer. Such findings emphasize the importance of HR's ethical conduct for the long-term health and stability of the workforce.
Influence on Corporate Reputation
The reputation of a corporation can be significantly enhanced or detrimentally impacted by the ethical nature of its HR practices. Companies that abide by high ethical standards often see a positive reflection on their brand image, attracting talent and customers who value such integrity. Conversely, a lapse in these practices can lead to negative media attention and a tarnished brand image, emphasizing the need for HR to ensure ethical adherence in all its functions.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration, we have underscored the pivotal role that ethics plays within HR practices. From the gatekeeping of ethical conduct to the promotion of fairness, justice, and individual rights, HR ethics lie at the heart of a well-functioning organization. As we contend with modern complexities, the call for enhancing ethical practice among HR professionals becomes ever clearer. While challenges abound, there is a clear pathway towards improvement, bolstered by the development of strong ethical frameworks and the cultivation of moral resilience. As we look ahead, we remain hopeful for the advancement of ethical HR practices, recognizing their significance in shaping a conscientious and sustainable corporate world.