In today's fast-paced and technology-driven world, identifying and assessing potential failures within systems, products, or processes is crucial. Failure Mode Analysis (FMA), a methodology deeply rooted in industrial practices, serves as a powerful tool for understanding vulnerabilities and mitigating risks before they lead to costly or dangerous consequences. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of FMA, covering its definition, types, processes, and the value it brings to various industries.
As someone who has worked in the manufacturing industry for over a decade, I have witnessed firsthand the transformative power of FMA. In one particular instance, our team was tasked with optimizing the production process for a critical component used in automotive safety systems. By conducting a thorough PFMEA (Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis), we identified several potential failure points that could have led to defective parts and compromised vehicle safety. Armed with this knowledge, we implemented targeted solutions, such as adding redundancy checks and improving operator training, which significantly reduced the risk of failures and enhanced the overall quality of our products.
The importance of FMA cannot be overstated, especially in sectors where safety, effectiveness, and quality are of utmost importance. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and manufacturing rely on FMA to proactively address potential failure points, safeguarding their operations and reputations. By implementing this analytical framework, businesses can not only identify risks but also build resilient operational models.
Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA): DFMEA focuses on analyzing product designs before they move into production. It identifies possible failure points, assesses their potential impacts and causes, and allows engineers and designers to make modifications that proactively address potential flaws.
Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA): PFMEA, on the other hand, concentrates on manufacturing and assembly processes. It identifies weaknesses that could lead to product defects or hazards, ensuring that every aspect of the production line is optimized to minimize the risk of errors that could compromise quality or safety.
Understanding Failure Mode Analysis
What is FMA?
At its core, FMA is a systematic, step-by-step approach used to identify potential failure modes within a system and evaluate the impact of those failures on product performance or user safety. It is a proactive method that aims to quantify and mitigate risk by thoroughly examining potential weaknesses in design or process before they result in malfunctions. This preventive approach is essential for ensuring reliability and quality, acting as a safeguard against unforeseen issues.
Enhanced safety standards
Improved product quality
Increased customer satisfaction
Reduced costs associated with failures
According to Smith and Mobley (2011), FMA is "a systematic method of identifying potential failure modes in a system, product, or manufacturing process and providing a means for ranking the severity of the failure modes" (p. 3). By breaking down complex systems into their constituent parts and analyzing each component's potential for failure, FMA enables organizations to develop targeted strategies for risk mitigation.
Types of FMA
There are two main types of FMA:
1- Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA): DFMEA focuses on analyzing product designs before they move into production. It identifies possible failure points, assesses their potential impacts and causes, and allows engineers and designers to make modifications that proactively address potential flaws.
2- Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA): PFMEA, on the other hand, concentrates on manufacturing and assembly processes. It identifies weaknesses that could lead to product defects or hazards, ensuring that every aspect of the production line is optimized to minimize the risk of errors that could compromise quality or safety.
While both DFMEA and PFMEA share the common goal of identifying and mitigating risks, they differ in their focus and timing within the product development lifecycle. DFMEA is typically conducted during the design phase, while PFMEA is performed during the process planning and manufacturing stages (Stamatis, 2003).
Resistance to change
Data collection complexities
Difficulties in fostering cross-departmental collaboration
The FMA Process
Conducting an FMA involves a cross-functional team that maps out the process or product and brainstorms every possible failure mode. After identifying these risks, the team assesses their severity, frequency, and detectability, prioritizing them accordingly. This forms the basis for developing targeted strategies to reduce risks.
The FMA process typically follows these steps:
1- Define the scope and objectives of the analysis
2- Assemble a cross-functional team
3- Identify potential failure modes
4- Assess the severity, occurrence, and detection of each failure mode
5- Calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN) for each failure mode
6- Develop and implement corrective actions
7- Reassess the RPN after implementing corrective actions
8- Document the results and maintain records for future reference
By adhering to this structured approach, organizations can systematically identify and address potential failures, leading to improved product quality, enhanced safety, and reduced costs associated with failures.
Benefits of Conducting FMA
Implementing FMA offers numerous benefits, including:
Enhanced safety standards: By proactively identifying and mitigating potential failure modes, FMA helps organizations improve the safety of their products and processes, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Improved product quality: FMA enables organizations to identify and address potential quality issues early in the product development lifecycle, leading to higher-quality products and increased customer satisfaction.
Increased customer satisfaction: By delivering products that are reliable, safe, and free from defects, organizations can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to increased market share and profitability.
Reduced costs associated with failures: FMA helps organizations avoid the costs associated with product recalls, warranty claims, and legal liabilities by identifying and addressing potential failures before they occur.
Montgomery (2019) emphasizes the importance of FMA in achieving operational excellence, stating that "organizations that embrace FMA as a core part of their quality management system are better positioned to deliver high-quality products and services, while minimizing the risk of costly failures" (p. 27).
By integrating FMA into organizational practices, businesses not only protect themselves against immediate risks but also position themselves strategically for long-term industry leadership.
FMA in Action: Case Studies
To better understand the practical application of FMA, let's explore two case studies from different industries.
Case Study 1: FMA in the Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, FMA is crucial for ensuring performance and safety. The analysis targets both the design and manufacturing stages, meticulously searching for vulnerabilities that could lead to systemic failures or pose risks to consumers.
Historically, analyses in this sector have led to significant design revisions and process improvements. For example, the introduction of certain safety features in vehicles often stems from FMA, which details the possible failure modes during emergency situations, marking substantial progress toward accident prevention.
Stamatis (2003) highlights a case study involving a major automotive manufacturer that used DFMEA to identify potential failure modes in the design of a new steering system. By conducting a thorough analysis, the team identified several potential issues, such as the risk of steering column collapse during a collision. Based on these findings, the design was modified to include a collapsible steering column, which significantly improved the vehicle's safety performance.
Case Study 2: FMA in the Manufacturing Industry
Manufacturing companies heavily rely on PFMEA to optimize their operations. This analysis is particularly critical in high-stakes production environments where the tolerance for error is minimal, and the cost of failure can be substantial.
In cases where PFMEA has been thoroughly conducted, factories have experienced improved process reliability, reduced defective products, and enhanced overall operational efficiency. This has reinforced the industry's emphasis on continuous improvement and quality control.
Smith and Mobley (2011) describe a case study involving a manufacturing company that used PFMEA to improve the reliability of its production process for a critical component. By identifying and addressing potential failure modes, such as improper machine calibration and inadequate operator training, the company was able to reduce the defect rate by 80% and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by 15%.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing FMA
While FMA offers significant benefits, its implementation can face various challenges, such as:
Resistance to change: Implementing FMA often requires organizations to change their existing processes and practices, which can be met with resistance from employees who are comfortable with the status quo.
Data collection complexities: Conducting an effective FMA requires accurate and comprehensive data on potential failure modes, which can be challenging to collect and analyze, especially in large and complex systems.
Difficulties in fostering cross-departmental collaboration: FMA requires collaboration and communication across different departments and functions, which can be challenging in organizations with siloed structures and conflicting priorities.
To fully realize the potential of FMA, these obstacles must be addressed head-on. Organizations must foster a culture of continuous improvement, provide training and support for employees, and establish clear communication channels and protocols to facilitate cross-functional collaboration.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced FMA
Advancements in technology and data analytics can greatly enhance the effectiveness of FMA. Automation and predictive modeling, for instance, have transformed how risks are identified and assessed, leading to a more dynamic and evolved approach to problem-solving.
For example, the use of machine learning algorithms can help organizations analyze vast amounts of data on potential failure modes, identifying patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent to human analysts. This can lead to more accurate and comprehensive risk assessments, enabling organizations to develop more effective mitigation strategies.
Similarly, the adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies can enable real-time monitoring and analysis of systems and processes, providing organizations with a continuous stream of data on potential failure modes. This can help organizations identify and address potential issues before they escalate into full-blown failures, reducing the risk of costly downtime and accidents.
Nandagopal and Ramamurthy (2017) discuss the potential of blockchain technology in enhancing the security and integrity of FMA data, stating that "blockchain can provide a tamper-proof and transparent record of FMA data, enabling organizations to collaborate more effectively and share information securely" (p. 1247).
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of FMA, highlighting its fundamental role across various industries. Through its proactive nature and structured approach, FMA helps organizations prevent failures and strengthen their operational resilience. We have explored specific methodologies, analyzed case studies, and discussed the ongoing challenges faced in implementing such analytical protocols.
Looking ahead, the evolution of FMA will be closely tied to technological advancements and continuous refinement of methodologies. The growing popularity of FMA in risk management underscores the recognition of FMA's critical importance in an increasingly interconnected and complex global economy. FMA remains an invaluable tool in the fight against risk, driving the relentless pursuit of excellence across diverse industrial landscapes.
As organizations continue to embrace FMA as a core part of their quality management systems, they will be better positioned to deliver high-quality products and services, while minimizing the risk of costly failures. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and leveraging the power of technology, organizations can unlock the full potential of FMA, driving innovation, enhancing safety, and ultimately, achieving long-term success in an ever-changing business environment.
References
Montgomery, D. C. (2019). Introduction to statistical quality control (8th ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
Nandagopal, M. S. G., & Ramamurthy, P. (2017). Blockchain for improved traceability and transparency in manufacturing. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 93(1-4), 1247-1254.
Smith, D. J., & Mobley, R. K. (2011). Rules of thumb for maintenance and reliability engineers. Butterworth-Heinemann.
Stamatis, D. H. (2003). Failure mode and effect analysis: FMEA from theory to execution. ASQ Quality Press.
Frequently Asked Questions
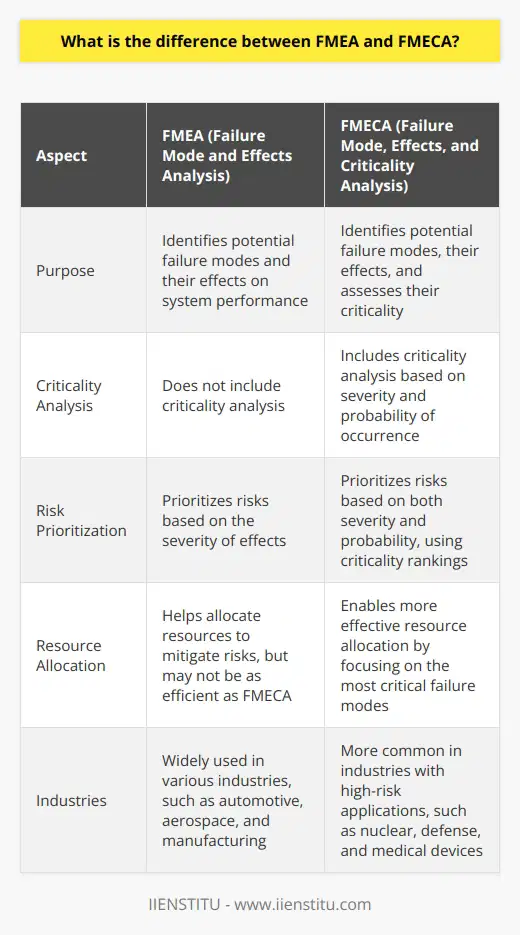
What is the difference between FMEA and FMECA?
FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) and FMECA (Failure Mode, Effects, and Criticality Analysis) are closely related techniques used for risk assessment and mitigation. The main difference lies in the additional step of criticality analysis in FMECA. While FMEA focuses on identifying potential failure modes and their effects, FMECA takes it a step further by assessing the criticality of each failure mode based on its severity and probability of occurrence. This criticality analysis helps prioritize risks and allocate resources more effectively.
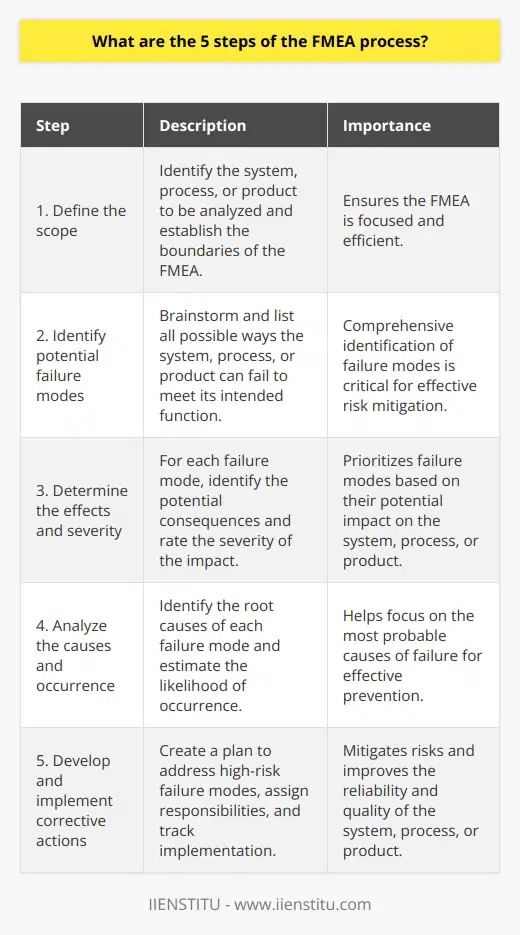
What are the 5 steps of the FMEA process?
The five key steps of the FMEA process are:
Define the scope: Clearly identify the system, product, or process to be analyzed and establish the boundaries of the analysis.
Identify potential failure modes: Brainstorm and list all possible ways in which the system, product, or process could fail to meet its intended function or performance requirements.
Assess the effects: For each identified failure mode, determine the potential consequences and impacts on the system, end-users, or customers.
Assign severity, occurrence, and detection ratings: Evaluate each failure mode based on its severity (impact of the failure), occurrence (likelihood of the failure happening), and detection (ability to detect the failure before it reaches the end-user).
Prioritize and take action: Calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN) by multiplying the severity, occurrence, and detection ratings. Use the RPN to prioritize failure modes and develop action plans to mitigate or eliminate the highest-priority risks.
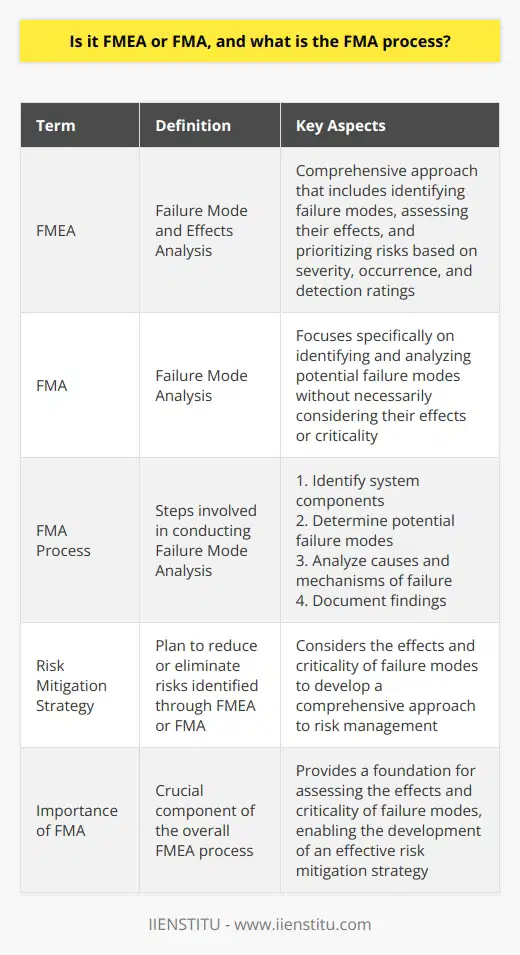
Is it FMEA or FMA, and what is the FMA process?
FMEA and FMA are often used interchangeably, but they refer to slightly different aspects of the risk assessment process. FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a more comprehensive approach that includes identifying failure modes, assessing their effects, and prioritizing risks based on severity, occurrence, and detection ratings. On the other hand, FMA (Failure Mode Analysis) focuses specifically on identifying and analyzing potential failure modes without necessarily considering their effects or criticality. The FMA process typically involves the following steps:
Define the system: Clearly identify the system, product, or process to be analyzed.
Identify failure modes: Brainstorm and list all possible ways in which the system, product, or process could fail.
Analyze failure modes: Examine each identified failure mode to understand its causes, mechanisms, and potential consequences.
Document the results: Record the findings of the analysis, including the identified failure modes, their causes, and any recommendations for improvement.
While FMA is a crucial component of the overall FMEA process, it is essential to consider the effects and criticality of failure modes to develop a comprehensive risk mitigation strategy.