This article discussed the importance of analyzing data to understand gender inequality, the work-family narrative and its implications for gender inequality, and strategies for addressing gender inequality. Organizations can use data to identify areas of vulnerability regarding gender inequality and develop strategies for addressing this issue, such as implementing policies and practices that promote gender equality and creating a culture of inclusivity.
Introduction
Analyzing Data to Understand Gender Inequality
The Work-Family Narrative
Strategies for Addressing Gender Inequality
Conclusion
Introduction: Gender inequality is a pervasive issue in many workplaces, and organizations need to take a data-driven approach to address and address this issue. By analyzing data about the gender makeup of the workforce, organizations can gain insight into the current state of gender inequality, identify areas of vulnerability, and develop strategies for addressing gender inequality. This article will discuss the importance of analyzing data to understand gender inequality, the work-family narrative and its implications for gender inequality, and strategies for addressing gender inequality.
Analyzing Data to Understand Gender Inequality
Data analysis is an essential tool for understanding gender inequality in the workplace. By gathering data about the gender makeup of the workforce, organizations can gain insight into the current state of gender inequality, identify areas of vulnerability, and develop strategies for addressing gender inequality.
For example, data can be used to determine the percentage of women in senior roles versus those in lower-level positions and the number of women employed at the company. This data can then identify areas where gender inequality may be particularly prevalent, such as the lack of women in senior roles or the lack of women in specific departments.
The Work-Family Narrative
The work-family narrative is essential when analyzing data to understand gender inequality. This narrative refers to the idea that women are more likely to take on family responsibilities than men, which can lead to a lack of career advancement for women. This narrative is often reinforced by workplace culture prioritizing men's needs over women's, such as offering more flexible work arrangements for men than for women.
As a result, women may be more likely to leave the workforce or take on less prestigious and fewer remunerative roles than their male counterparts. This narrative can be further reinforced by the lack of equitable family leave policies, making it difficult for women to balance their work and family responsibilities.
Strategies for Addressing Gender Inequality
Once organizations have identified areas of vulnerability regarding gender inequality, they can develop strategies for addressing this issue. These strategies can include implementing policies and practices that promote gender equality, such as offering flexible work arrangements that accommodate both men and women, providing equitable family leave policies, and creating mentorship and sponsorship programs to support women's career advancement.
Additionally, organizations can develop a culture of inclusivity by encouraging open and honest dialogue about gender inequality and creating an environment where everyone feels safe and respected.
Conclusion:
Gender inequality is a pervasive issue in the workplace, and organizations need to take a data-driven approach to understand and address this issue. By analyzing data about the gender makeup of the workforce, organizations can gain insight into the current state of gender inequality, identify areas of vulnerability, and develop strategies for addressing gender inequality.
Additionally, organizations should consider the work-family narrative and its implications for gender inequality and create a culture of inclusivity by encouraging open and honest dialogue about gender inequality and creating an environment where everyone feels safe and respected. By taking a data-driven approach to understanding and addressing gender inequality, organizations can create a more equitable and inclusive workplace.
Inclusion is the key to unlocking gender inequality in the workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What strategies can HR departments use to address gender inequality in the workplace?
Gender inequality in the workplace has been an ongoing issue for many years. However, despite the efforts of organizations and governments to promote gender equality, progress has been slow. This is mainly due to a lack of awareness and understanding of the issues and a lack of effective strategies to address them. As such, Human Resources (HR) departments need to develop and implement effective strategies to address gender inequality in the workplace.
One of the most effective strategies for HR departments to address gender inequality is to increase awareness and understanding of the issue. This can be done by implementing policies and educating employees on the subject. This includes providing training on gender equality and awareness and developing policies that promote gender equality in the workplace. Additionally, HR departments should ensure that these policies are being implemented and enforced and that employees are held accountable for any breaches.
Another strategy that HR departments can use to address gender inequality is to ensure that the recruitment and promotion process is fair and equitable. This means ensuring that all candidates have equal access to the recruitment and promotion process and that decisions are based on qualifications and merit rather than gender. Additionally, HR departments should ensure that any pay gaps are addressed and that employees are compensated fairly and equitably.
Finally, HR departments should ensure that any complaints of gender inequality are taken seriously and addressed appropriately. This includes ensuring that there is a straightforward procedure for investigating and addressing such complaints and creating an environment where employees feel comfortable raising such issues. Additionally, HR departments should ensure that any action taken is fair and equitable and that employees are not subjected to discrimination or harassment.
By implementing these strategies, HR departments can ensure that gender equality is promoted and maintained in the workplace. This will create an environment where individuals of all genders can thrive and contribute to the organization's success. It will also help create a workplace where employees feel safe, respected, and valued.

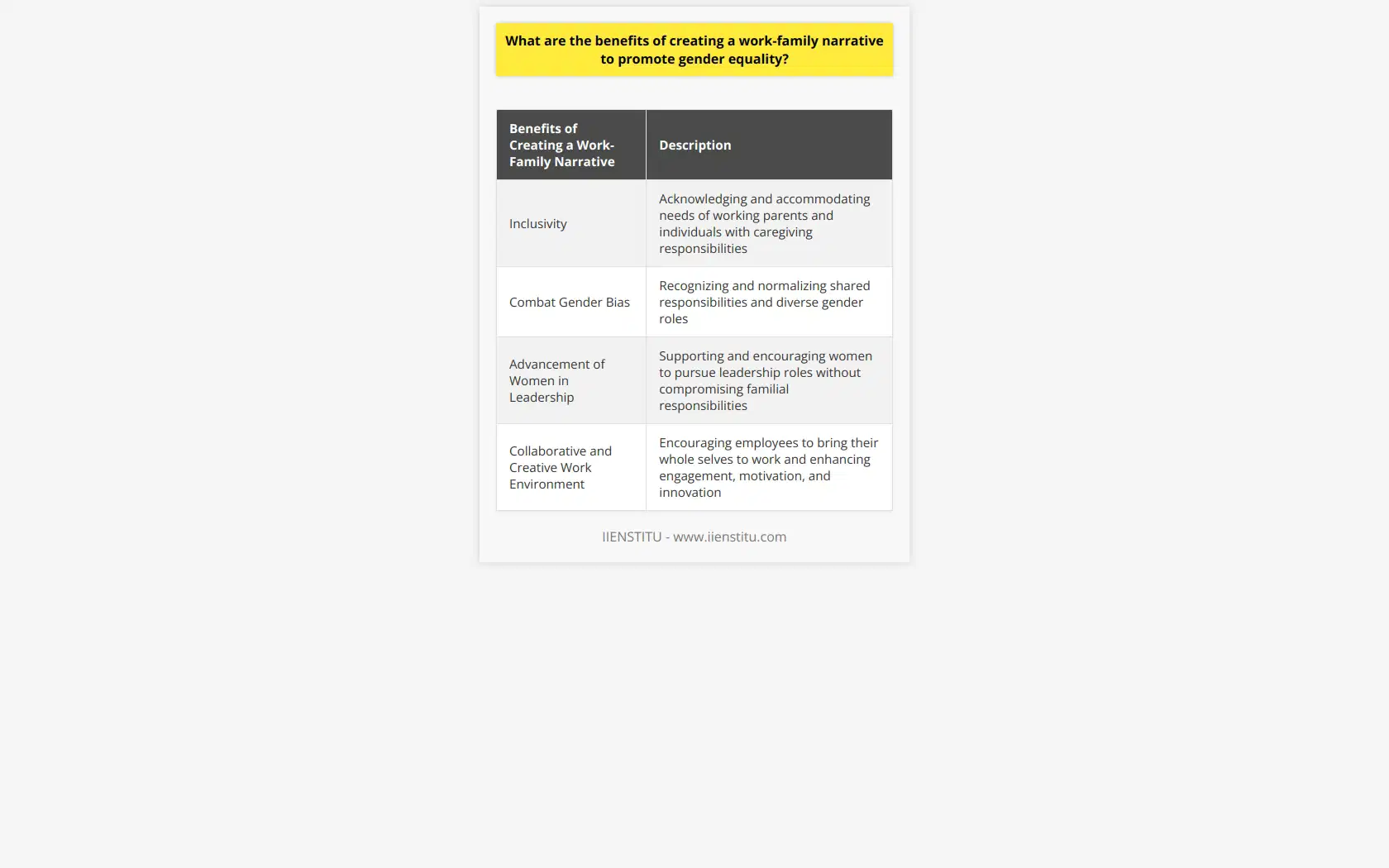
How can data be used to better understand gender inequality in the workplace?
Gender inequality in the workplace is a pervasive issue that affects women and members of marginalized communities worldwide. While the ongoing struggle for workplace equality has progressed in recent years, there is still a long way to go. Data analysis is a powerful tool that can better understand the root causes of workplace gender inequality and provide insights into how to address it.
One way data can be used to understand gender inequality in the workplace better is to analyze employment and wage data. This type of analysis can provide insights into discrepancies between men and women in terms of access to opportunities, as well as in terms of wages. This analysis can also shed light on the prevalence of glass ceilings and gender pay gaps in specific industries.
In addition to analyzing employment and wage data, data can be used to track the representation of women in leadership positions. This type of analysis can provide insights into the prevalence of gender bias in the hiring process and the prevalence of glass ceilings in specific industries or organizations.
Data can also be used to track workplace policies and benefits related to gender equality. This analysis can provide insights into which organizations are most promoting gender equality and which approaches are most effective in achieving this goal.
Finally, data can be used to analyze the impact of gender inequality on employee morale and productivity. This type of analysis can provide insights into how gender inequality affects employee engagement, job satisfaction, and the overall well-being of employees.
In conclusion, data analysis is a powerful tool that can be used better to understand the root causes of workplace gender inequality and provide insights into how to address it. By analyzing employment and wage data, representation of women in leadership positions, workplace policies and benefits, and the impact of gender inequality on employee morale and productivity, organizations can gain valuable insights into how to promote gender equality in the workplace.
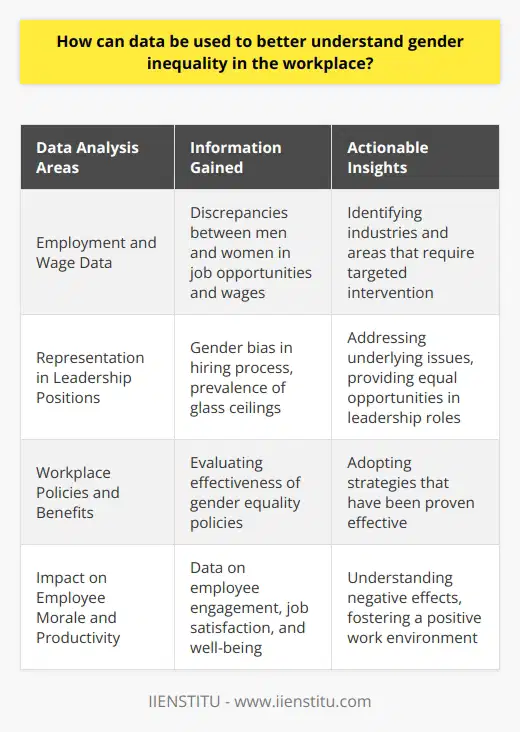
What are the benefits of creating a work-family narrative to promote gender equality?
Recent studies have shown that creating a work-family narrative for the workplace can be a powerful tool for promoting gender equality. A work-family history is a set of stories, beliefs, and shared values that recognize and support work and family life integration. It is a way to shift the focus from the traditional view of work as a primary source of identity and meaning to a more inclusive view of work, family, and community.
The traditional view of workplace gender dynamics is that men are seen as the primary providers and women as the primary carers. This view has become increasingly outdated as more and more women are entering the workforce and men are assuming a more significant role in family life. A work-family narrative allows organizations to recognize and support the changing dynamics of gender roles in the workplace.
One of the main benefits of creating a work-family narrative is that it can create a more inclusive workplace. By recognizing and supporting the integration of work and family, organizations can create a more accommodating work environment for working parents and those with other caregiving responsibilities. This can increase job satisfaction, productivity, and employee loyalty.
Another benefit of creating a work-family narrative is that it can help to reduce gender bias in the workplace. By recognizing the roles and responsibilities of both men and women in the workplace, organizations can reduce the gender gap in wages and other areas of employment. Additionally, by creating a narrative that values and supports the integration of work and family, organizations can make a workplace culture more supportive of women in leadership positions.
Finally, creating a work-family narrative can help to foster a more collaborative and creative workplace. Organizations can promote collaboration and creativity by recognizing the importance of family and other caregiving responsibilities. This can lead to more innovative ideas and more productive workplaces.
In conclusion, creating a work-family narrative can be a powerful tool for promoting gender equality in the workplace. By recognizing and supporting the integration of work and family, organizations can create a more inclusive workplace, reduce gender bias, and foster a more collaborative and creative workplace. In doing so, organizations can create a workplace environment more supportive of gender equality.
How can organizations implement effective mentorship programs to foster gender inclusion in the workplace?
Developing a Comprehensive Framework
To implement effective mentorship programs cultivating gender inclusion in workplaces, organizations should begin by developing a comprehensive framework. This framework must encompass clear objectives, policies, and procedures to support its effective functioning. For instance, targeting professional growth, skill enhancement, and better decision-making abilities among both male and female employees.
Selection of Mentors and Mentees
The next step is to carefully select mentors and mentees based on their qualifications, interests, and career aspirations. Organizations should ensure that potential mentors possess relevant expertise, effective communication skills, and a genuine commitment to promoting gender inclusivity. Similarly, potential mentees must exhibit enthusiasm and readiness to learn from the program. This cultivated environment can encourage positive and fruitful interactions between both parties, accelerating the process of knowledge and experience transfer.
Mentee-centered Approach
To foster gender inclusion, the program must adopt a mentee-centered approach. This implies that mentors provide guidance tailored to the individual needs, strengths, and aspirations of their mentees. By focusing on the unique journey of each participant, mentors can nurture a sense of belonging and empowerment that is fundamental to increasing workplace inclusivity.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring and evaluation are crucial components for improving mentorship programs over time. Regular assessments, supported by both qualitative and quantitative data, can inform decision-makers about the effectiveness of their initiatives in fostering gender inclusivity. Feedback from mentors, mentees, and other stakeholders must be taken into account, allowing organizations to refine and adapt their programs to better serve the intended purpose.
Continuous Training and Support
Lastly, organizations should invest in ongoing training and support mechanisms for mentors, mentees, and other employees involved in the program. By addressing challenges and fostering continuous learning, organizations can ensure that the mentorship program remains a dynamic and engaging platform for driving gender inclusion in the workplace.
In conclusion, organizations can implement effective mentorship programs to promote gender inclusivity through developing a comprehensive framework, careful selection of participants, adoption of a mentee-centered approach, data-driven monitoring and evaluation, and continuous training and support. By doing so, they can foster an inclusive workplace environment, contributing to the overall growth and success of the organization.
What role do unconscious biases play in perpetuating gender inequality and how can we address them?
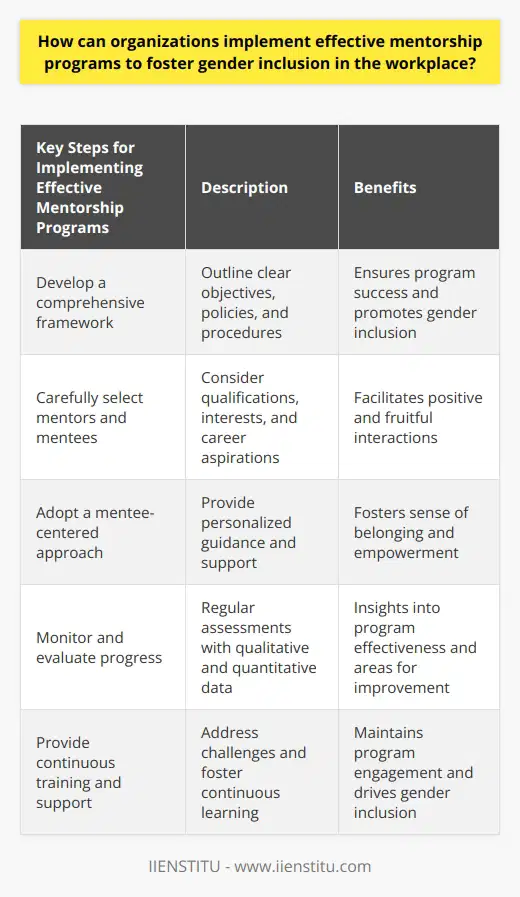
Unconscious Biases and Gender Inequality
Unconscious biases contribute significantly to perpetuating gender inequality in various aspects of society. These biases arise from deep-seated beliefs, stereotypes, and social norms that we have internalized over time, leading to discriminatory behavior, unequal opportunities, and unfair treatment based on gender.
Impact on Career Advancement
In the workplace, unconscious biases create barriers to women's career advancement by influencing recruitment, promotion, and salary decisions. This perpetuates the well-documented gender pay gap and reinforces the proverbial 'glass ceiling' that prevents women from reaching leadership positions in many organizations.
Perpetuation of Harmful Gender Stereotypes
The media and advertising industries may also unwittingly reinforce gender inequality by continuing to promote harmful stereotypes. For instance, women are often portrayed as emotional or submissive, while men are depicted as strong and dominant. These depictions contribute to the belief that certain jobs or positions are more suitable for a particular gender, thus further exacerbating the issue.
Effects on Mental Health
Unconscious biases impact mental health by engendering feelings of inadequacy, diminished self-confidence, and reduced motivation among those affected. This emotional toll can have negative consequences for one's well-being, ambition, and overall quality of life, perpetuating a vicious cycle of self-doubt and missed opportunities.
Addressing Unconscious Biases
To tackle the problem of unconscious biases, it is crucial to raise widespread awareness about their existence, impact, and potential consequences. This can be achieved through comprehensive educational campaigns, targeted corporate training, and open discussions on the topic, aimed at fostering understanding and empathy.
Encouraging Diversity
Promoting diversity and inclusion in all areas of society is another vital step in addressing unconscious biases. Employers should prioritize fair recruitment and promotion practices, emphasizing diversity as a valuable source of creativity, innovation, and resilience. Simultaneously, media and advertisers should challenge gender stereotypes by depicting individuals of all genders in various roles and activities, breaking the mold of traditional narratives.
Ultimately, addressing unconscious biases in a meaningful manner requires a concerted effort from individuals, organizations, and society at large. By cultivating awareness, embracing diversity, and fostering an environment of equity and equality, we can take significant strides towards overcoming the detrimental effects of these biases and achieving true gender equality.
How can performance evaluations and promotions be structured to reduce gender disparities within a company?
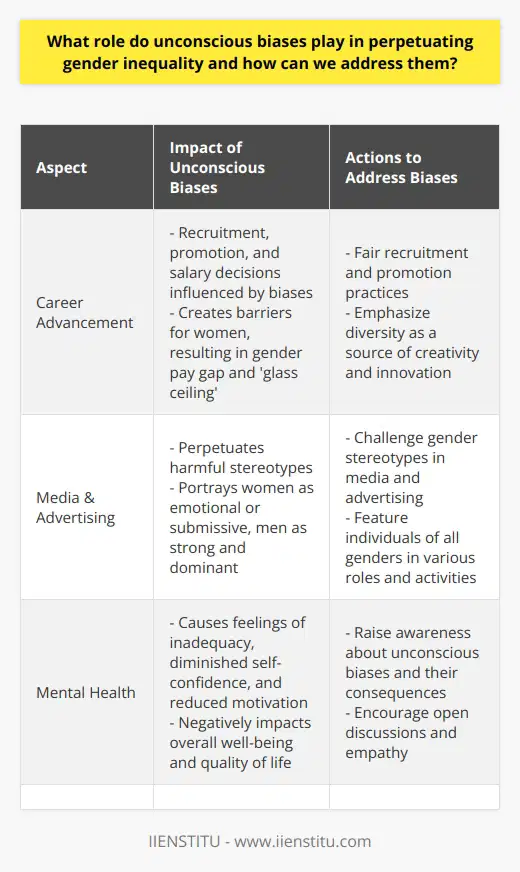
**Creating Fair Performance Evaluations**
Companies can reduce gender disparities in performance evaluations and promotions by implementing fair and comprehensive assessment methods. Objective performance metrics should be prioritized, focusing on quantifiable achievements and productivity measures. This minimizes the impact of gender stereotypes and unconscious biases in subjective evaluations.
**Mitigating Unconscious Bias**
To address unconscious biases, managers should be adequately trained on gender-sensitive decision-making. This includes understanding common stereotypes that may affect evaluations and being aware of personal beliefs that may alter judgments. Additionally, workplace policies should be in place to ensure gender-neutral language and behaviors during evaluations and promotions.
**Inclusive Growth Opportunities**
Open communication about available paths for promotions can encourage equal growth opportunities. All employees should be informed of potential advancement options and the requirements for each. Management should encourage all team members, regardless of gender, to pursue career development opportunities, such as attending workshops or pursuing relevant certifications.
**Structured Promotion Process**
A well-defined promotion process may alleviate gender disparities within a company. The process should include clear and measurable criteria for each promotion level, which will help prevent discrimination based on gender. Furthermore, decisions should be made by a diverse committee, consisting of members from various backgrounds, genders, and positions within the company.
**Regular Monitoring and Analysis**
Continual assessment of performance evaluations and promotions should be conducted, with special attention to gender-related disparities. Companies can utilize external audits, employee surveys, and internal statistical analyses to identify potential biases and rectify them promptly. By doing so, organizations can ensure an inclusive and equitable work environment for all employees.
In conclusion, companies can reduce gender disparities in performance evaluations and promotions by incorporating objective metrics, addressing unconscious biases, communicating growth opportunities, having a clear promotion process, and conducting regular monitoring and analysis. These strategies contribute to creating a fair and inclusive workplace, fostering diversity and equal opportunities for all employees.
How can organizations create and maintain a diverse talent pipeline to support gender equality in the workplace?
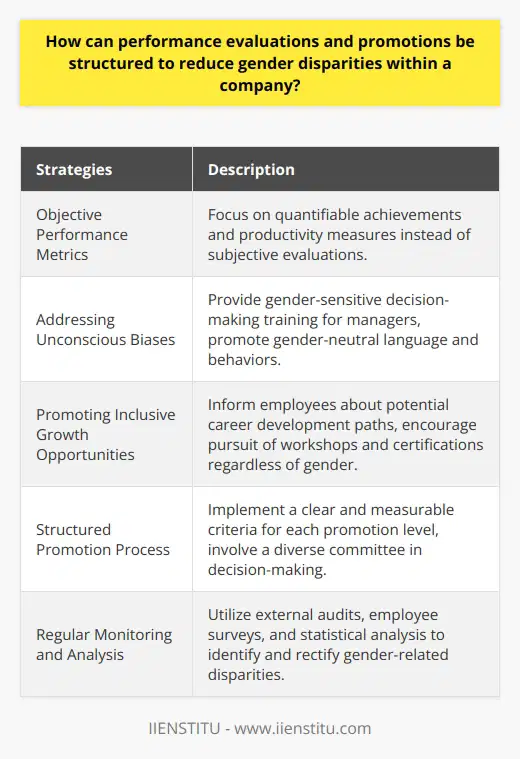
### Fostering Inclusive Recruitment Practices
To create and maintain a diverse talent pipeline that supports gender equality in the workplace, organizations can begin by implementing inclusive recruitment practices. These policies ensure that job advertisements are neutral and incorporate gender-inclusive language. Thus, attracting a diverse pool of applicants.
### Offering Bias-Free Assessments
During the interview process, organizations can apply structured interviewing techniques to reduce unconscious biases. This strategy involves using a standard set of questions, focusing on job-related capabilities, and maintaining a diverse panel of interviewers to ensure fairness in candidate evaluation.
### Encouraging Mentorship and Sponsorship Programs
Mentorship and sponsorship programs can be effective in retaining and promoting gender diversity within organizations. By providing guidance, support, and advocacy, these initiatives enable female employees to overcome potential barriers to career advancement, enhancing their representation in leadership roles.
### Providing Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
Workplace policies that support flexibility and work-life balance can foster gender equality by allowing all employees, particularly parents and caregivers, the opportunity to excel in their careers. Examples of such policies include flexible working hours, telecommuting, and generous parental leave provisions.
### Ensuring Comprehensive Diversity Training
Organizations committed to gender equality need to provide comprehensive diversity and inclusion training to all employees. This training should address unconscious biases, stereotypes, and microaggressions, fostering a culture of understanding, empathy, and inclusivity.
### Establishing Pay Equity
In the pursuit of gender equality, organizations must commit to eliminating pay discrepancies based on gender. A regular audit of compensation structures should be conducted to identify and rectify any disparities, ensuring equal pay for equal work.
### Enhancing Visibility and Empowerment
Finally, organizations can encourage gender equality by highlighting the achievements of female employees and leaders. Showcasing diverse role models can inspire and empower all employees, demonstrating the organization's commitment to an inclusive culture where everyone thrives.
In conclusion, organizations can create and maintain a diverse talent pipeline that drives gender equality by actively revising hiring practices, nurturing employee growth, and instilling a culture of inclusivity. These collective efforts will propel organizations toward a more equitable and diverse workforce, rewarding both employees and companies with innovation, creativity, and success.
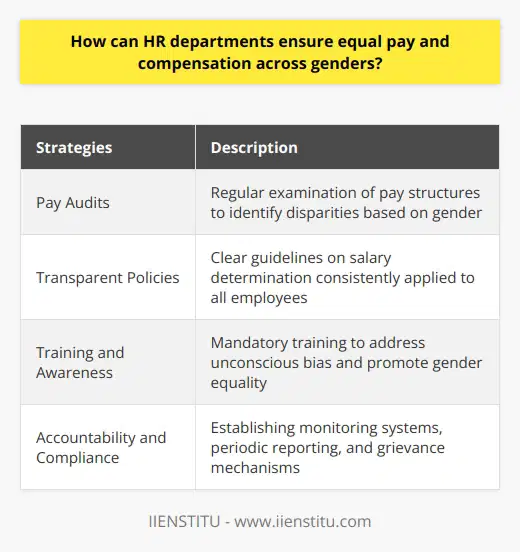
What are the most effective approaches for engaging men as allies in the fight for gender equality and inclusivity at work?
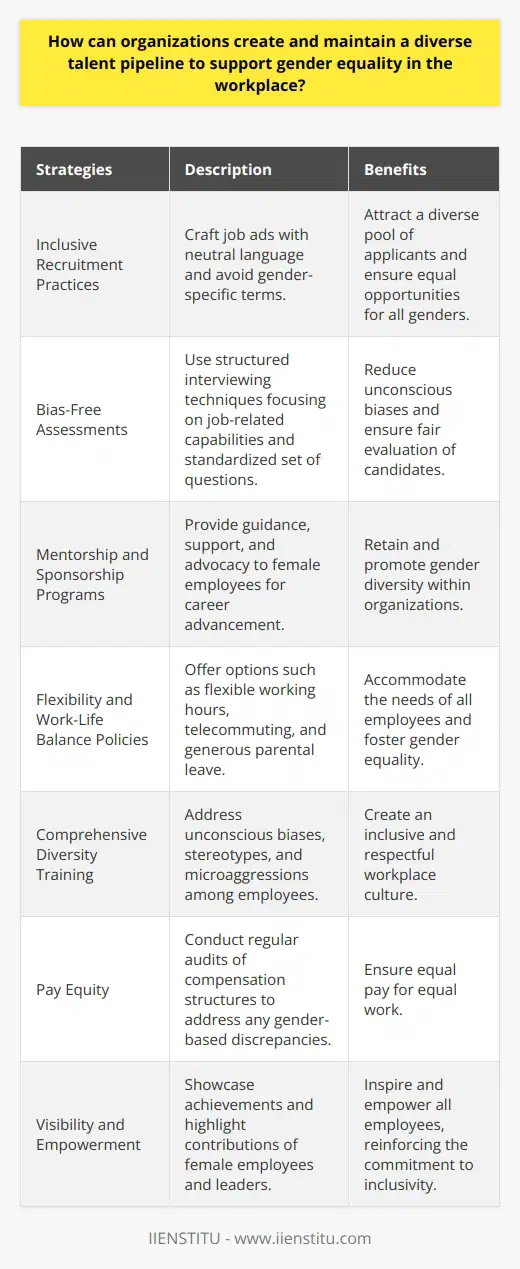
Identifying Common Goals
Effective approaches for engaging men as allies in the pursuit of gender equality and inclusivity at work often involve identifying common goals. By emphasizing the benefits of diversity and inclusion in the workplace, individuals can recognize the advantages of collaborating to create more equitable environments.
Mentorship and Sponsorship
Another successful strategy involves promoting mentorship and sponsorship programs that encourage men to actively support women's careers. This shared responsibility helps create a culture of accountability and fosters open communication, ultimately contributing to gender equality.
Training and Education
Comprehensive training and education can also drive meaningful change. Diversity and inclusion workshops foster awareness and understanding of unconscious biases, addressing the root causes of gender inequalities. By actively engaging both men and women in these learning experiences, we can facilitate impactful discussions and promote allyship.
Active Listening and Empathy
Fostering an environment of active listening and empathy is essential for engaging men as allies. Providing a safe space for open and non-judgmental conversations encourages men to share their experiences, ask for guidance, and learn from others.
Inclusive Language and Policies
Workplace language and policies also play a crucial role in establishing an inclusive environment. Companies should review and revise any potentially discriminatory language, ensuring that policies promote and support both men and women equally. Additionally, organizations must communicate the implementation and enforcement of such policies clearly to all employees to foster accountability.
Role Models and Representation
Finally, showcasing positive examples of male allies can inspire and motivate others to take action. Highlighting the achievements of men who champion diversity and inclusivity sends a powerful message that allyship is both valued and encouraged.
In summary, engaging men as allies in the fight for gender equality and inclusivity at work involves a multi-faceted approach that includes identifying common goals, mentorship and sponsorship, training and education, active listening and empathy, inclusive language and policies, and celebrating role models. By incorporating these strategies, companies can create a culture where all individuals feel empowered to contribute to and benefit from a more diverse and inclusive workplace.
How can flexible work policies be designed to ensure both gender-neutral access and benefits for all employees?
Assessing Employee Needs
Flexible work policies can be designed to ensure gender-neutral access and benefits for all employees by considering the specific needs and preferences of diverse staff members. Conducting surveys and focus groups can provide valuable insights into various requirements, work-life balance issues, and potential impediments.
Inclusivity in Policy Design
An inclusive approach to drafting flexible work policies is crucial to avoid perpetuating gender stereotypes or unintentionally disadvantaging particular groups. Employers should incorporate feedback from employees across different genders, roles, and life stages to ensure that diverse perspectives are represented. This will enable the creation of a policy that accommodates various needs and promotes equitable opportunities for all.
Communication and Transparency
Clear and consistent communication plays a significant role in the successful promotion of gender-neutral, flexible work policies. By providing comprehensive information on the range of available options and eligibility criteria, employers can minimize biases in decision-making and prevent any misunderstandings that may perpetuate inequalities. Regularly reviewing and updating communication strategies will further solidify the culture of transparency and inclusivity.
Managerial Support and Training
Ensuring that managerial staff understand and support the principles underlying a gender-neutral, flexible work policy is essential for promoting equitable access and benefits for all employees. Providing training on unconscious biases, prioritizing employee well-being, and addressing any concerns raised by staff is crucial to foster a culture that accommodates diverse work preferences and promotes equal opportunities.
Periodic Policy Review
Establishing periodic reviews of flexible work policies allows for continuous improvement and the identification of any unintended gaps that may be reducing the policy's efficacy. Employers should actively encourage employee feedback to ensure they are aware of any emerging trends, challenges or inequalities. By iterating on the flexible work policy to address these concerns, employers can ensure that the policy remains inclusive, gender-neutral, and effectively meets the needs of all staff.

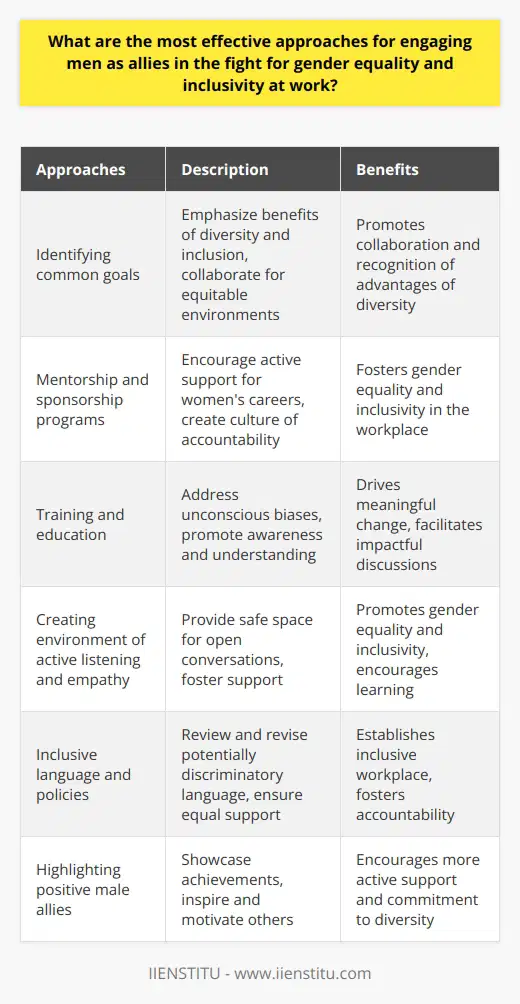
How can HR promote gender equality through equitable recruitment and selection processes?
Establishing Equitable Recruitment and Selection Policies
One of the crucial steps HR can take to promote gender equality in organizations is by developing fair recruitment and selection processes. By utilizing systematic approaches that reduce or eliminate biases, HR professionals can provide equal opportunities for all candidates, regardless of their gender.
Crafting Gender-Neutral Job Advertisements
The first stage of addressing gender inequality in recruitment starts with designing job advertisements free of gender-specific language. This ensures that potential applicants do not feel discouraged from applying due to gender-related perceptions. Phrases such as 'he or she' should be replaced with neutral alternatives like 'the candidate,' and job requirements must focus on essential skills and qualifications.
Utilizing Blind Recruitment Practices
Blind recruitment practices, in which personal information such as names, genders, and other demographic identifiers are removed from resumes and applications, can be effective in minimizing potential biases during the screening process. This allows HR departments to focus on the candidates' qualifications and experiences, rather than making assumptions based on stereotypes or preconceptions related to gender.
Conducting Standardized Interviews
To further reduce biases, HR professionals should embrace standardized interviews using structured questions that evaluate the candidate's competencies and skills relevant to the role. This also reduces the influence of personal opinions and impressions arising from factors unrelated to job performance, such as the candidate's gender.
Ensuring Diversity in Selection Panels
Another crucial aspect of equitable recruitment processes is ensuring diversity within the selection panels involved in hiring decisions. By promoting diversity among interviewers, HR can counteract potential gender biases and foster a more inclusive decision-making process.
Enforcing Equal Pay Policies
HR departments should also develop and enforce equal pay policies to guarantee that all employees receive equal remuneration regardless of their gender. Regular audits should be conducted to identify and rectify any pay disparities between employees of different genders performing the same roles.
Providing Training on Implicit Biases
Lastly, HR should provide regular and comprehensive training to employees involved in recruitment and selection processes to make them aware of their implicit biases. Such training can help them recognize and address any unconscious stereotypes that may impact their evaluation of candidates, contributing to a more equitable and gender-neutral hiring process.
In conclusion, HR professionals can promote gender equality by ensuring equitable and unbiased recruitment and selection processes through methods such as crafting gender-neutral job advertisements, utilizing blind recruitment practices, conducting standardized interviews, ensuring diversity in selection panels, enforcing equal pay policies, and providing training on implicit biases. By adopting these strategies, organizations can foster a diverse and inclusive workforce where all employees have equal opportunities for success.
What strategies can be employed to make workplace culture more inclusive, fostering a sense of belonging for employees of all genders?
Active Engagement in Diversity and Inclusion Programs
One effective strategy to create a more inclusive workplace culture for all genders is the active engagement in diversity and inclusion programs. Companies should establish and regularly provide training sessions focusing on eliminating biases, promoting empathy, and celebrating differences. This approach actively educates employees and encourages them to work collaboratively, fostering a sense of belonging in all team members.
Promote Open Communication
Another essential element in building an inclusive workplace culture is promoting open communication. Companies can implement various communication strategies, such as anonymous feedback channels, regular town hall meetings, and employee forums, to welcome diverse opinions and ideas. By creating an environment where employees feel comfortable expressing themselves, businesses can empower workers of all genders, allowing for a more inclusive and collaborative environment.
Flexible Work Arrangements
Adopting flexible work arrangements is another strategy that can contribute to a more inclusive workplace culture. By allowing for remote work options or modifying traditional work schedules, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to accommodating the diverse needs of employees of all genders. Moreover, these measures can enhance work-life balance, leading to improved job satisfaction, increased loyalty, and ultimately, a sense of belonging for all workers.
Mentorship and Sponsorship Programs
Establishing mentorship and sponsorship programs can also play a significant role in fostering an inclusive workplace culture. These programs help create connections between employees while providing guidance and support for career growth and development. By matching mentors and mentees with different gender identities, organizations can promote gender diversity and encourage the exchange of unique perspectives, thus nurturing an inclusive environment.
Accountability and Transparency
Lastly, organizations should strive for transparency and hold themselves accountable for achieving more inclusive workplace culture goals. Sharing workforce demographic statistics and setting targets for diversity and inclusion initiatives helps demonstrate a company's commitment to fostering gender inclusivity. Additionally, celebrating successes and learning from challenges encourages employees to collectively contribute to a more inclusive and welcoming workplace for all.
In conclusion, several strategies can be employed to create an inclusive workplace culture, including active engagement in diversity and inclusion programs, promoting open communication, adopting flexible work arrangements, establishing mentorship programs, and ensuring accountability and transparency. Such efforts can contribute significantly to fostering a sense of belonging for employees of all genders, ensuring a positive and inclusive working environment for all.

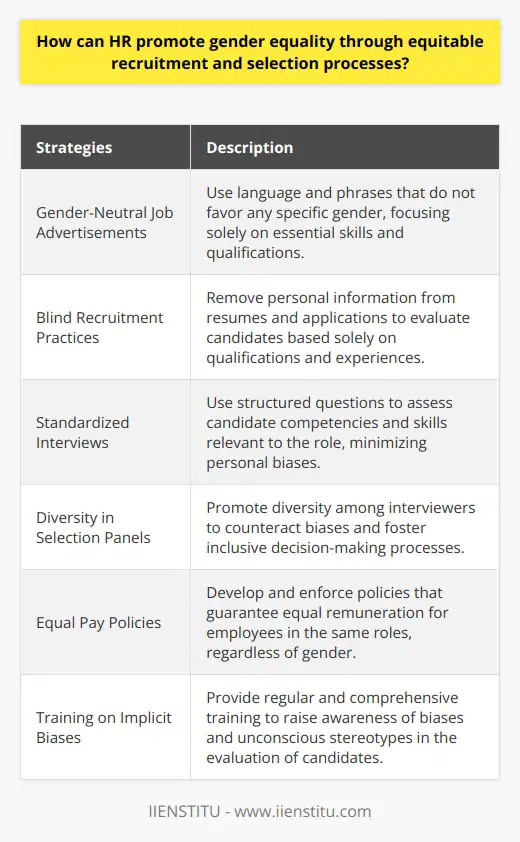
How can organizations design and implement professional development programs that promote gender equality and support individuals in reaching their full potential?
Understanding the Issue of Gender Inequality
To design and implement professional development programs that promote gender equality and support individuals in reaching their full potential, organizations must first comprehend the extent and nature of gender inequality in their specific context. This understanding can be achieved through research, data analysis, and consultation with employees.
Establishing Goals and Objectives
Based on the analyses of gender inequality, organizations should set clear goals and objectives for their professional development programs. These targets should focus on addressing gender gaps, enhancing representation of underrepresented groups, and fostering a more inclusive work environment.
Developing a Comprehensive Program
A comprehensive professional development program should encompass various aspects, including training, mentoring, networking, and leadership development. Training sessions should focus on raising awareness of unconscious bias and fostering a culture of equity and inclusion. Furthermore, mentees must have access to mentors from different gender and identity backgrounds to enhance diversity of perspectives.
Creating Opportunities for Leadership Development
Organizations must actively identify existing gender biases in leadership opportunities and work to dismantle them. Providing opportunities for women and gender minorities to participate in leadership programs will help these individuals build the necessary skills to advance in their careers and create a more inclusive organizational culture.
Encourage Networking and Collaboration
Forming networking groups and encouraging collaboration among employees can create an environment where individuals feel encouraged to share their experiences, perspectives, and expertise. This will enable organizations to learn from each other and to challenge biases and stereotypes that may exist.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting as Needed
Continual evaluation is essential in the development and implementation of professional programs. Organizations must monitor the progress of their initiatives and adapt their strategies as needed. This continuous improvement and accountability will ensure that organizations remain committed to achieving their objectives.
In conclusion, organizations can design and implement professional development programs that promote gender equality and support individual potential by understanding the extent of gender inequality within the organization, establishing goals and objectives, developing comprehensive training and mentoring initiatives, creating opportunities for leadership development, fostering networking and collaboration, and continually monitoring and adjusting the program. Effective execution of such programs requires commitment, resources, and a constant willingness to adapt and improve.
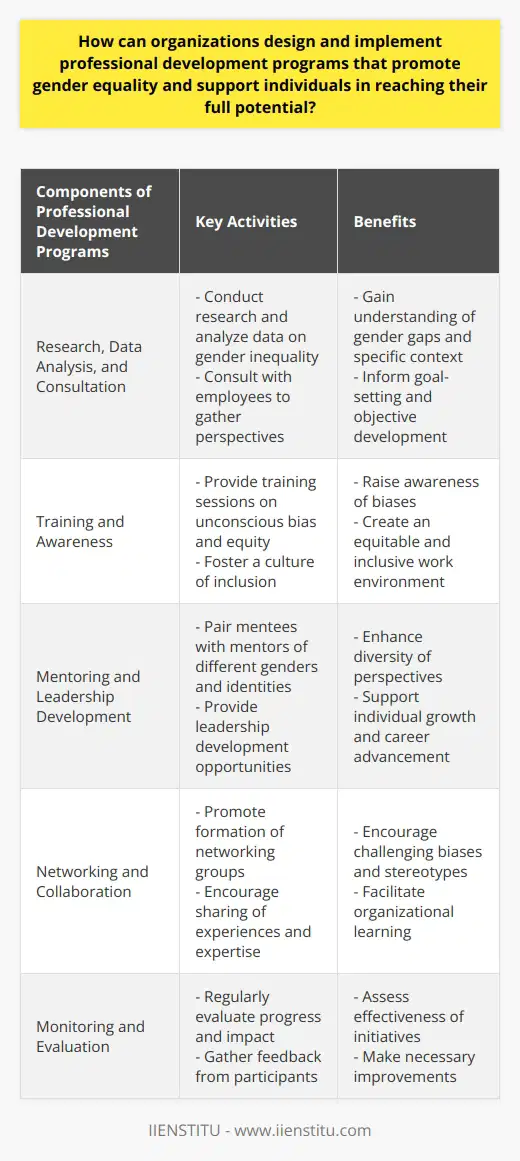
How can HR departments ensure equal pay and compensation across genders?
Examination of Pay Structure
To ensure equal pay and compensation across genders, HR departments must thoroughly examine their organization's pay structure. This involves conducting regular pay audits to identify any disparities in salaries, benefits, and bonuses based on gender. By analyzing data on employee performance, experience, and qualifications, HR professionals can assess whether pay gaps are justified or indicate gender-based discrimination.
Implementation of Transparent Policies
Another effective strategy is the implementation of transparent policies related to pay and compensation for all employees. HR departments should develop clear guidelines on salary determination, taking into account factors such as job responsibilities, education, and experience. These policies must be consistently applied to all employees, regardless of gender. Establishing transparency will not only minimize the potential for pay discrimination but also promote a culture of fairness.
Training and Awareness
HR departments should also focus on training and awareness initiatives to address unconscious bias and promote gender equality in the workplace. This may include mandatory training for recruitment and management personnel to ensure objective evaluation of candidates for hiring and promotion. Furthermore, HR professionals should actively promote diversity and inclusion by highlighting case studies and best practices that showcase the benefits of gender pay equality.
Accountability and Compliance
Building a framework for accountability and compliance is crucial in addressing gender pay disparity. HR departments should establish a system for monitoring and reviewing the implementation of equal pay policies. This may involve periodic reporting, audits, and analysis of compensation-related data to assess progress towards achieving gender pay parity. Additionally, HR professionals must develop grievance mechanisms for employees to report pay-related concerns and ensure adequate investigation and resolution of complaints.
In conclusion, HR departments play a critical role in ensuring equal pay and compensation across genders. By thoroughly examining pay structures, implementing transparent policies, promoting training and awareness, and establishing robust accountability and compliance frameworks, organizations can foster an environment of equality and fairness while minimizing the prevalence of gender pay discrimination.
What initiatives can be implemented to promote gender inclusivity in leadership roles and decision-making?
Creating Awareness and Advocacy
To begin with, raising awareness and advocating for gender inclusivity should be a top priority in promoting gender diversity in leadership. By organizing workshops, seminars, and panel discussions on gender inclusivity at various levels in organizations, stakeholders can understand the importance of balanced representation in decision-making roles.
Mentoring and Sponsorship Programs
Another effective initiative in fostering gender inclusivity is implementing mentorship and sponsorship programs within organizations. These programs would encourage experienced leaders to support and guide aspiring female leaders, helping them navigate their career paths, thereby increasing the number of women in leadership roles.
Developing Specific Inclusivity Policies
Developing and implementing gender inclusivity policies is also vital in ensuring fair representation in leadership roles. These policies may include targets for ensuring gender parity, flexible working arrangements, and providing gender-neutral parental leave. By enacting and enforcing such policies, organizations can create an environment where women thrive in leadership positions.
Training and Skills Development
Organizations should also invest in training and skills development to empower women with the necessary competencies to excel in decision-making roles. This can include leadership training, communication and negotiation skills enhancement, and offering specialized development programs catering to women's unique needs.
Recognizing and Challenging Stereotypes
Addressing gender stereotypes that hinder women's career progression is essential in promoting gender inclusivity. Organizations need to challenge these stereotypes and create a culture that values individual skills and abilities, breaking away from the harmful biases that perpetuate gender inequality in leadership roles.
Monitoring and Accountability
Lastly, organizations should regularly monitor their progress towards achieving gender inclusivity in leadership roles, highlighting areas for improvement. To guarantee accountability, companies can hire diversity officers, create committees, or engage external consultancies to evaluate their efforts and outcomes.
In conclusion, by implementing these various initiatives, organizations can foster gender inclusivity in leadership roles and decision-making processes. Implementing such measures ultimately contributes to organizational growth, innovation, and reinforces the importance of diversity and inclusion.

How can the impact of gender-focused training and policies be measured and assessed to ensure progress toward workplace gender equality?
Assessing Gender-Focused Training Outcomes
Measuring and assessing the impact of gender-focused training and policies is crucial to ensuring progress toward workplace gender equality. By employing objective evaluation methods, organizations can effectively oversee the outcomes of these programs.
Defining Evaluation Metrics
To begin, organizations should establish clear and quantifiable evaluation metrics. These may include the proportion of female employees in leadership positions, changes in gender pay gaps, or improvements in employee satisfaction and engagement.
Collection of Baseline Data
By gathering baseline data, organizations can observe changes in gender equality indicators over time. This data may include demographic information, employee surveys, and performance evaluations, allowing a comprehensive analysis of the workplace environment.
Monitoring Training Progress
Monitoring the progress of gender-focused training and policies is essential for ensuring their effectiveness. Regular evaluations can help organizations identify areas for improvement and adapt strategies as needed.
Employee Surveys and Feedback
Employee surveys are valuable tools for gauging the effectiveness of gender-focused training, as they provide critical insights into employee perceptions of the workplace environment. By measuring changes in employee attitudes over time, organizations can determine the overall impact of their training and policies.
Tracking Long-Term Impact
It is essential to monitor and assess long-term outcomes, as these changes may have significant implications on the organization's commitment to workplace gender equality. Long-term assessment may include employee retention rates, promotions, and professional development opportunities for all genders.
Involvement of External Partners
By collaborating with external partners, such as academics and gender experts, organizations can ensure that their evaluation processes are robust and comprehensive. These partners can provide objective feedback and recommendations to further improve the effectiveness of gender-focused training and policies.
In conclusion, measuring and assessing the impact of gender-focused training and policies is a crucial aspect of achieving workplace gender equality. Establishing clear evaluation metrics, collecting meaningful data, and consistently monitoring progress can all contribute to creating a more equitable and inclusive workplace for all employees.
How can HR promote gender equality through targeted professional development and upskilling initiatives?
Addressing Gender Disparities in the Workplace
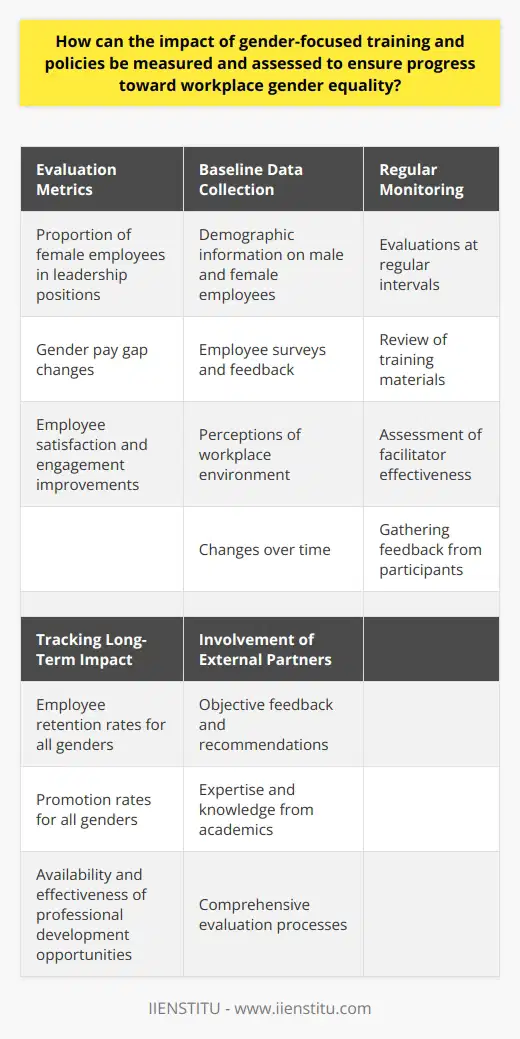
Human Resources (HR) plays an essential role in promoting gender equality by implementing targeted professional development and upskilling initiatives. By addressing the gender gap throughout the employee lifecycle, HR professionals can create a more equitable work environment where all employees can thrive.
Evaluation of Recruitment Processes
One way that HR can promote gender equality is by examining recruitment processes and ensuring that these are free of gender bias. This includes the use of gender-neutral language in job descriptions and promoting diversity through advertising job opportunities in various platforms that appeal to different demographics. Furthermore, HR should consider implementing blind recruitment processes, where personal details are removed from the application to reduce the impact of unconscious bias in the selection process.
Mentoring and Networking Opportunities
Mentoring and networking programs tailored to female employees can help create pathways for career advancement. HR should work towards developing these programs to specifically target underrepresented employees, ensuring they receive personalized mentorship and networking with key stakeholders, ultimately leading to promotional opportunities and long-term career growth.
Skill Development and Training Programs
Another essential strategy for promoting gender equality is the implementation of targeted skill development and training programs. HR professionals should identify key skills that are crucial to career development and make these trainings accessible and inclusive for employees of all genders. Additionally, offering flexible working arrangements can create a more inclusive learning environment for everyone, particularly working parents, and those with caregiving responsibilities.
Supportive Work Culture
The work culture is vital in achieving gender equality. HR can take the lead in fostering an inclusive and supportive environment by encouraging open dialogue, addressing discrimination and work-life balance, and advocating for policies that support gender equality, such as equal parental leave and flexible work arrangements. This, in turn, creates a more inclusive and supportive work environment for employees, regardless of their gender.
Performance and Progress Tracking
Lastly, HR should establish a performance tracking system to analyze gender-related trends and identify areas where disparities exist. This information can be useful in developing targeted interventions, assessing their effectiveness, and continuously improving inclusive practices.
In conclusion, HR plays a crucial role in promoting gender equality in the workplace through targeted professional development and upskilling initiatives. By addressing gender disparities at each stage of the employee lifecycle, HR professionals can create more equitable work environments, fostering true inclusion and diversity.
What practices can be adopted to encourage meaningful dialogue about gender equality among employees and leadership?
Creating a Safe Space
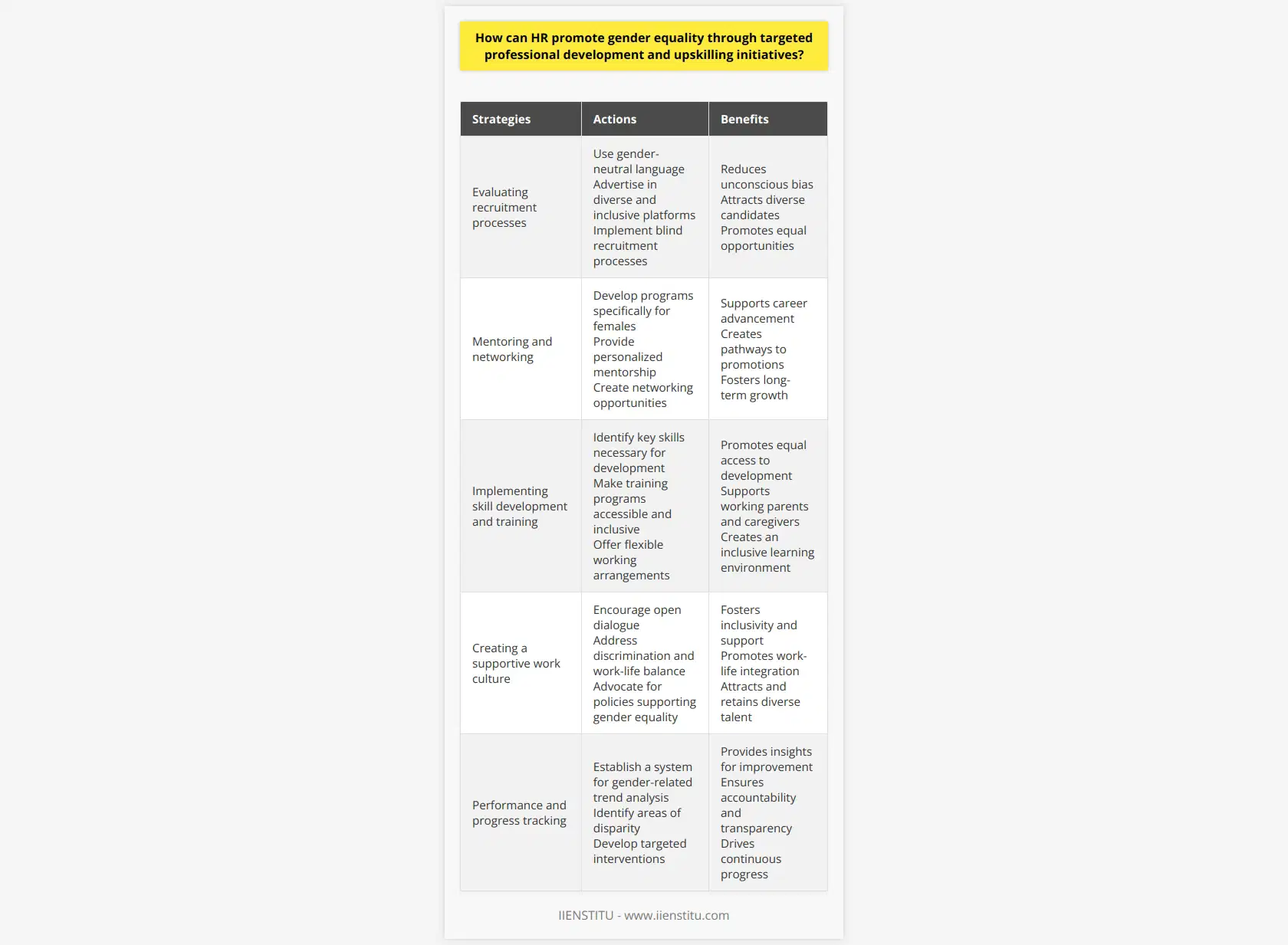
To encourage meaningful dialogue about gender equality among employees and leadership, it is essential to create a safe and inclusive environment that allows open and honest discussion. Implementing training and workshops focused on diversity, equity, and inclusion, as well as addressing unconscious biases, can help raise awareness and educate employees.
Promoting Active Listening
Active listening techniques should be promoted, which include giving full attention to the speaker, not interrupting, and asking questions for clarification. This practice not only ensures everyone's opinions are heard, but it also fosters respect and understanding among employees and leadership.
Facilitating Dialogue Initiatives
Companies can initiate gender equality-focused events, such as panel discussions, webinars, or town halls, where employees can share their experiences and voice concerns related to equality in the workplace. This way, employees can engage directly with leadership, allowing for clearer communication and addressing issues more effectively.
Implementing Employee Resource Groups
Creating Employee Resource Groups for women and gender minorities can contribute significantly to supporting and empowering employees. Such groups provide a platform for members to voice concerns, raise awareness, share resources, and develop strategies to address gender equality, ultimately fostering a more inclusive work environment.
Encouraging Allyship and Advocacy
Finally, advocating for gender equality should not solely rest on the employees directly affected by it. Encouraging allyship among employees and leadership means promoting active support and advocacy for gender equality initiatives, ensuring that they are genuinely inclusive and effective.
How can organizations establish and support employee resource groups to foster gender inclusion and equality in the workplace?
Creating Employee Resource Groups
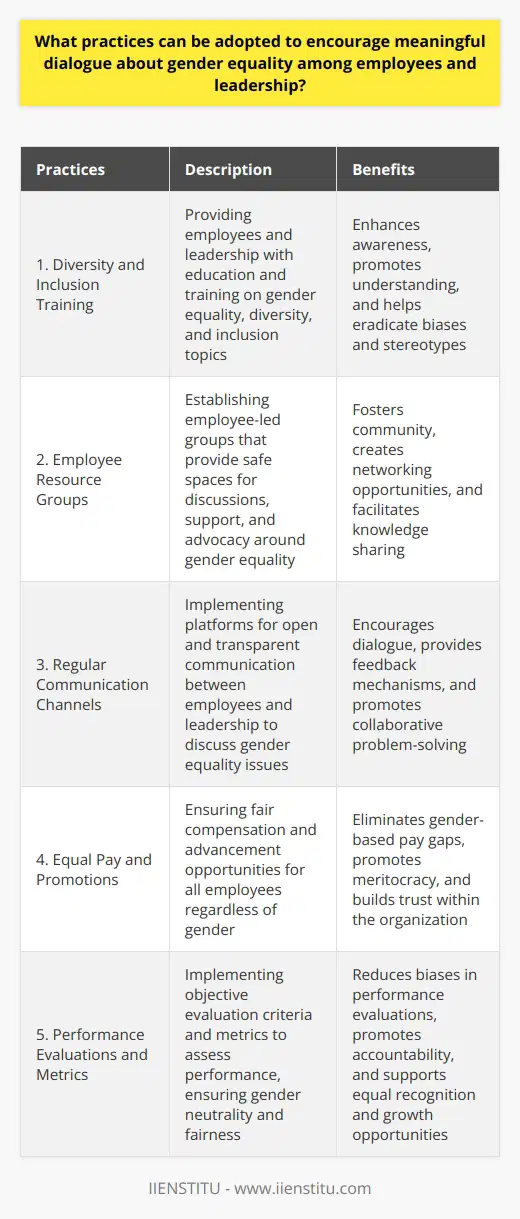
Organizations can establish and support employee resource groups (ERGs) to foster gender inclusion and equality in the workplace through a top-down approach. First, management must communicate the organization's commitment to supporting and promoting diversity initiatives. By creating a supportive environment, organizations enable the formation and growth of ERGs.
Constructing a Framework
Next, organizations should provide a framework to help foster the development of these groups. A clear set of guidelines, objectives, and goals for the ERGs can be essential for their success. Offering financial and logistical support, such as providing meeting spaces and funding for events, can further reinforce the organization's support for gender diversity initiatives.
Offering Leadership Opportunities
Beyond the creation and support of ERGs, organizations must also actively encourage the participation of employees, particularly in leadership positions within these groups. By offering opportunities for growth and development, organizations can empower employees to become champions of gender equality. Engaging male allies and encouraging them to participate in these groups can also contribute to breaking down gender barriers and promoting an inclusive environment.
Measuring Progress
Moreover, regular measurement and monitoring of progress on gender equality and inclusion initiatives can help maintain momentum and ensure that the ERGs are meeting their goals. By assessing the impact of these groups on representation, retention rates, and overall employee satisfaction, organizations can gauge their effectiveness in fostering a more inclusive work environment.
Providing Training and Education
Finally, organizations should provide training and education opportunities to all employees, including those involved in ERGs, that focus on gender sensitivity, unconscious bias, and inclusive leadership. This will equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to navigate challenges related to gender diversity and foster a more inclusive environment.
In conclusion, organizations that establish and support employee resource groups, along with providing frameworks, opportunities, and resources, will significantly contribute to fostering gender inclusion and equality in the workplace. By actively engaging employees in these efforts, organizations can create a more diverse, inclusive, and equal work environment for all.
How can HR promote gender equality by addressing biases within job descriptions and advertisements?
Mitigating Gender Bias in Job Descriptions
Promoting gender equality within an organization initiates from the recruitment process, where Human Resources (HR) plays a critical role. HR can help ensure fair and unbiased job descriptions and advertisements by comprehensively reviewing terminology, requirements, and benefits.
Unbiased Language
The use of gender-neutral language in job descriptions eliminates the unconscious bias that might deter potential applicants. HR should evade gender-loaded words, using instead gender-neutral words, like salesperson instead of salesman. Also, the pronouns should refer to both genders, thereby equally inviting all qualified individuals.
Removing Unnecessary Criteria
Many job descriptions include requirements or preferences that inadvertently discourage the participation of a particular gender. To address this, HR ought to delineate only essential qualifications, thereby triggering a greater influx of diverse candidates.
Inclusive Benefits
Often, benefits are inclined towards one gender, which can hamper equality. HR should outline inclusive benefits that encompass both the genders' needs. Parental leave rather than a term like maternity leave will ensure both genders feel valued and cared for by the organization.
Gender Equality Training
Promoting gender equality involves educating the recruitment team. HR should conduct workshops highlighting the importance of gender equality and providing tactics to isolate bias from the recruiting process.
In summary, HR plays a central role in championing gender equality in the workforce. Ensuring bias-free job descriptions and advertisements are an indispensable step in this process, ramping up the recruitment of both genders and fostering an inclusive work environment. All these measures would prove instrumental in stimulating the recruitment of diverse talents, which would eventually shape a more innovative, progressive, and balanced workplace.

What interventions can be implemented to mitigate the impact of gender stereotypes and norms on workplace dynamics and decision-making?
Proactive Measures Against Gender Stereotypes
Various interventions can reshape the workplace dynamics and decision-making, consequently diminishing the implications of gender stereotypes and norms. One such intervention entails enforcing strict anti-bias policies. Rigorous protocols can deter any gender-generated prejudices, ensuring a fair and inclusive environment for everyone.
Gender Sensitization Training
Offering gender sensitization training is another effective method. These training sessions enlighten employees about the diverse gender spectrum and cultivates respect for differences, encouraging a bias-free workplace environment.
Promoting Diversity in Leadership
Moreover, promoting diversity in leadership roles can effectively counter the impact of gender norms. Varied leadership styles, stemming from a variety of gender identities, can help disrupt conventional norms promoting diversity in decision-making.
Implicit bias workshops
Participating in implicit bias workshops can help employees recognize and reduce their subconscious biases. These workshops furnish participants with strategies to combat inherent predispositions that can affect judgment and decision making.
Facilitating Open Discussions
Facilitating open discussions about gender-norms and stereotypes among employees can also prove beneficial. It can stimulate increased understanding and empathy among employees.
Inclusive Performance Appraisals
In panel meetings and performance appraisals, organizations should ensure an inclusive representation of different genders. This reduces the chance of gender-based bias influencing critical decisions.
Flexible working options
Finally, implementing flexible working options can counteract traditional gender roles that often pose challenges for women in terms of work-life balance.
In conclusion, interventions focusing on education, policy changes, and flexible work options can mitigate the influence of gender stereotypes and norms on workplace dynamics and decision-making. It is noteworthy that the primary objective of these interventions remains the creation of an inclusive and bias-free working environment.

How can HR departments utilize employee feedback to identify and address areas of gender inequality and foster greater inclusivity in the workplace?
Understanding Employee Feedback
HR departments can analyze employee feedback to identify existing gender inequalities. In most companies, feedback is often given through surveys, performance reviews, or suggestion boxes. To understand employees' perspective on gender issues, HR must ask relevant questions during these feedback sessions.
Analyzing Feedback for Gender Inequalities
When relevant feedback is collected, HR departments need to categorize and thoroughly analyze it. By looking at recurring patterns, imbalances in roles and responsibilities, or disparities in performance evaluations, areas of gender inequality would become visible.
Addressing Gender Inequalities
Once the HR department identifies gender disparities, it should design strategic actions to address them. For example, the promotion process could be adjusted if feedback reveals gender biases in career advancement opportunities.
Fostering Inclusivity
Following the action plan, HR can facilitate inclusivity workshops to educate employees about gender equality. They can also collaborate with senior management to revise policies and improve practices that perpetuate gender stereotypes.
Feedback as Measure of Success
Finally, HR can measure the success of these interventions by continuously collecting feedback. Any improvements in employees' perception of gender inclusivity or a decrease in incidences of gender inequality will indicate that the strategies were effective.
In conclusion, employee feedback serves as a valuable resource for HR departments to detect and address gender inequality issues, fostering greater inclusivity in workplaces. This dynamic approach not only promotes diversity but also enhances overall organizational performance.

How can HR promote gender equality by incorporating intersectionality into workplace policies and practices?
Understanding Intersectionality
To promote gender equality in the workplace, HR must first understand the concept of intersectionality. This refers to the interconnected nature of social categories such as race, class, and gender which indirectly form overlapping systems of discrimination or disadvantage.
Inclusion of Diverse Identities
HR can incorporate intersectionality into workplace policies by recognizing and valuing various identities. This approach means not only acknowledging all identities but also creating opportunities for every member, irrespective of their unique attributes.
Gender-Neutral Policies
Developing policies without gender bias is another method to promote gender equality. These policies should accommodate the needs of all genders without creating unequal conditions. For example, parental leave policies should cover both men and women.
Awareness and Training
HR should organize regular awareness and training programs that enlighten staff about intersectionality. The aim is to generate increased empathy and understanding amongst employees, and promote a culture of respect and inclusivity.
Monitoring and Feedback
Lastly, HR should constantly monitor this intervention by obtaining feedback from employees. By evaluating the effectiveness of these strategies and accepting constructive criticism, HR can continually refine and improve policies and practices.
Through these methods, HR can effectively infuse intersectionality into workplace policies and practices. Ultimately, this will foster an environment that promotes and supports gender equality.

What role can organizational leadership play in setting expectations and modeling behavior for promoting gender equality and inclusivity in the workplace?
Role of Leadership in Establishing Expectations
Organizational leadership holds a pivotal role in developing and setting expectations for gender equality. High-ranking officers are influential in designing policies, implementing changes, and creating a supportive environment. They shape the culture, set standards, and establish the guidelines of behavior in any given organization.
Leadership in Policy Making
Leaders have direct involvement in creating inclusive policies. They can mandate equal pay, equal opportunities for promotion, parental leaves, flexible work options, or gender sensitivity training. A policy designed and implemented effectively is a stepping stone towards gender equality.
Modeling Behavior
Leaders also possess the power to model behavior. Through their conduct, leaders can demonstrate respect for inclusivity. They can refrain from using gender-biased language and enforce zero tolerance for any forms of bias or discrimination. When leaders take lead in modeling behavior, their actions are likely to permeate across the organization.
Creating a Supportive Environment
Leaders are responsible for fostering a supportive environment that empowers employees. By acknowledging individual differences, they can respect and celebrate diversity. The support provided by leaders is essential in enabling employees to feel safe, comfortable, and valued regardless of their gender.
Training and Educating Employees
Leadership also plays a critical role in training and educating employees about gender equality and inclusivity. Training programs can instill awareness, change perceptions, and encourage proactive behaviors. Education can stimulate a mindset shift which in turn propels a cultural shift towards gender equality.
In summary, leadership has a massive role in setting expectations and modeling behavior for promoting gender equality and inclusivity in the workplace. By establishing clear policies, modeling appropriate behavior, creating a supportive environment and providing training, leaders can pave the way to a more inclusive and equal working culture. Thus, it is imperative for leaders to step up and steer their organizations towards gender equality.
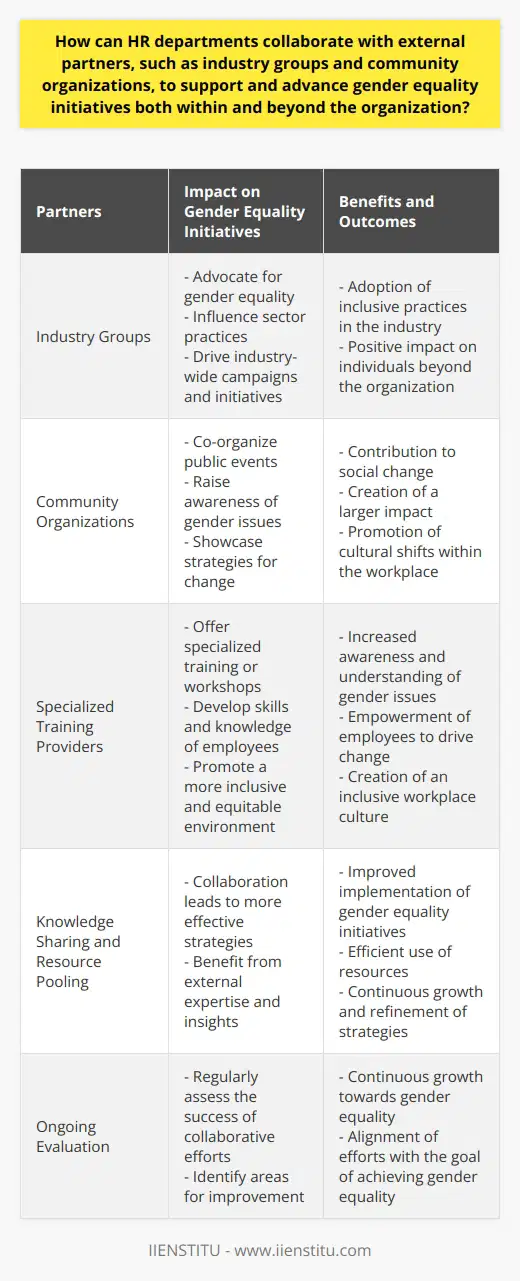
How can HR departments collaborate with external partners, such as industry groups and community organizations, to support and advance gender equality initiatives both within and beyond the organization?
Collaborative Partnerships
An effective strategy for HR departments is to form partnerships with external entities. Industry groups and community organizations present valuable allies in promoting gender equality. These alliances enable knowledge sharing, resource pooling, and the creation of more effective strategies.
Integrative Efforts for Gender Equality
These partnerships can have a direct impact on gender equality initiatives within the organization. For instance, external partners could offer specialized training or workshops. These aim at raising awareness, developing skills, and promoting cultural shifts within the workplace.
Extending Impact to Broader Communities
Additionally, collaborations can enhance gender equality efforts beyond the organization. HR departments could co-organize public events with community organizations. These programs can spotlight current gender issues and potential strategies for change. Similarly, industry-wide campaigns or initiatives can influence sector practices and mindset.
Measure for Continuous Improvement
It is essential to evaluate collaborative efforts towards gender equality regularly. By assessing the success of initiatives, HR departments can identify areas of improvement and actively refine and enhance their strategies.
In summary, HR departments can use partnerships with external organizations to amplify their impact on gender equality. This approach not only fosters a fairer internal environment, but it also contributes to broader social change.