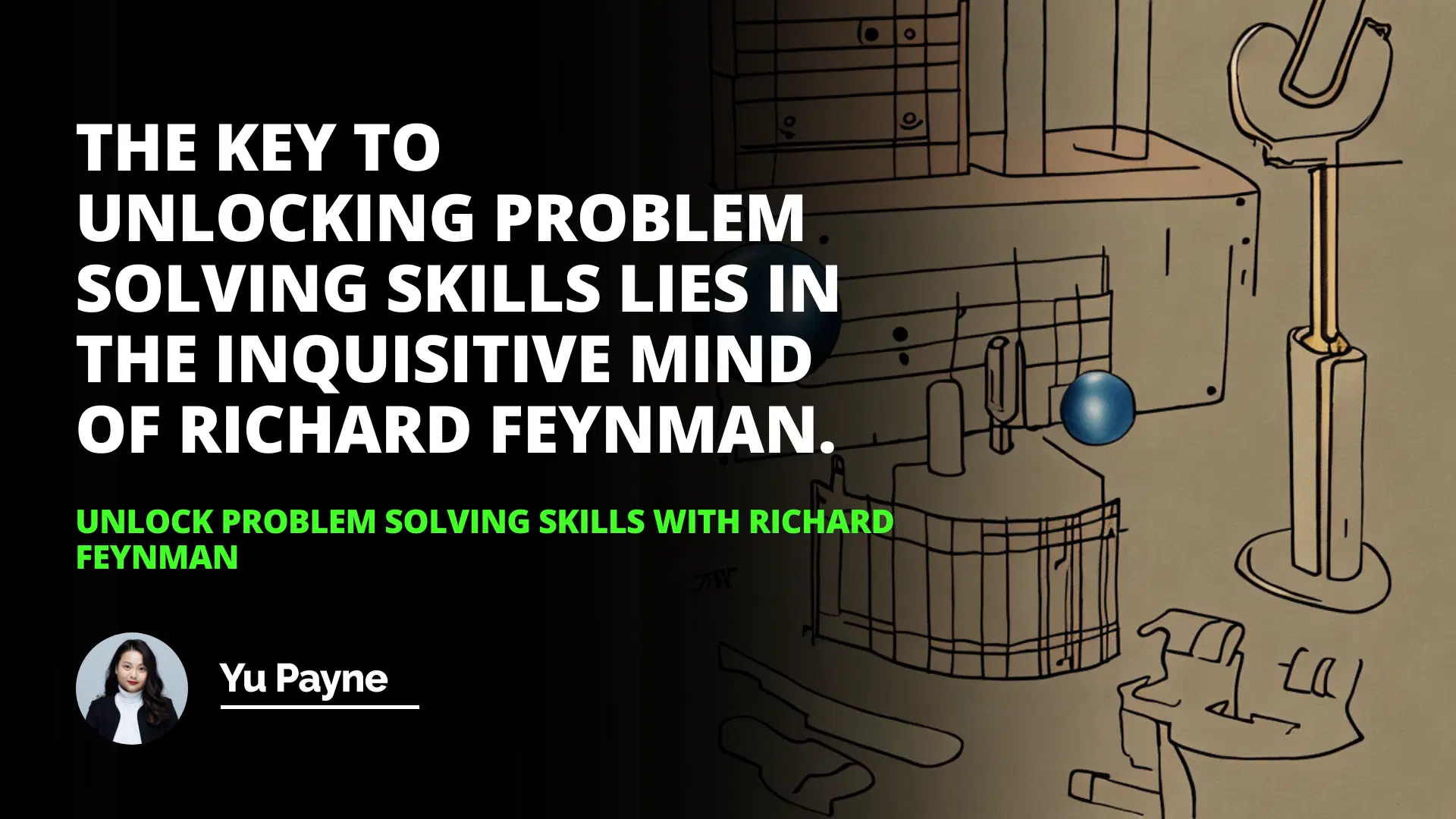
Richard Feynman was a Nobel Prize-winning physicist whose expansive personality and interests in many fields made him a unique thinker. He was known for challenging himself and his students to take new looks at the world around us, and his “by analogy” method of thinking is one of the dozen “new” ways of thinking.
This involves looking at a problem or concept and making connections between it and something more familiar, providing a new perspective on the problem or concept. In addition to using analogies, Feynman also believed that all theories should be questioned and open to alternative interpretations in order to gain a better understanding of our world and the problems we face. His thinking approach can be a valuable asset in any field of study.
Introduction
Who was Richard Feynman?
What was his “thinking” method?
Feynman’s Analogy Method
What is “by analogy”?
Introduction
Richard Feynman was a Nobel Prize-winning physicist whose expansive personality and interests in many fields made him a unique thinker. He was known for challenging himself and his students to take new looks at the world around us. In this article, we will explore Feynman’s “thinking” method, which he called “by analogy”, and how it can be used to benefit our own thinking processes.
Feynman’s Analogy Method
Feynman’s “by analogy” method of thinking is one of the dozen “new” ways of thinking, as defined in this book. It involves looking at a problem or concept and making connections between it and something else that is more familiar. This helps to provide a new perspective on the problem or concept, often leading to a better understanding. For example, Feynman was known for using analogies to explain complex scientific concepts. He would compare the behavior of electrons to the behavior of a spinning top or the behavior of light to the behavior of a wave in a pond. By making these connections, he was able to make difficult concepts easier to understand.
Alternative Theories
In addition to using analogies, Feynman also believed that all theories should be questioned and open to alternative interpretations. He argued that by questioning existing theories and exploring alternative interpretations, we could better understand our world and the problems we face. This approach allows us to think more critically and creatively, and it can help us to develop more accurate theories and solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Richard Feynman’s “by analogy” method of thinking can be a powerful tool for understanding complex problems and concepts. By making connections between the unfamiliar and the familiar, we can gain a better understanding of the world around us. Furthermore, by questioning existing theories and exploring alternative interpretations, we can think more critically and creatively and develop more accurate theories and solutions. Feynman’s approach to thinking can be a valuable asset in any field of study.
The key to unlocking problem-solving skills lies in the curious mind of Richard Feynman.
Frequently Asked Questions
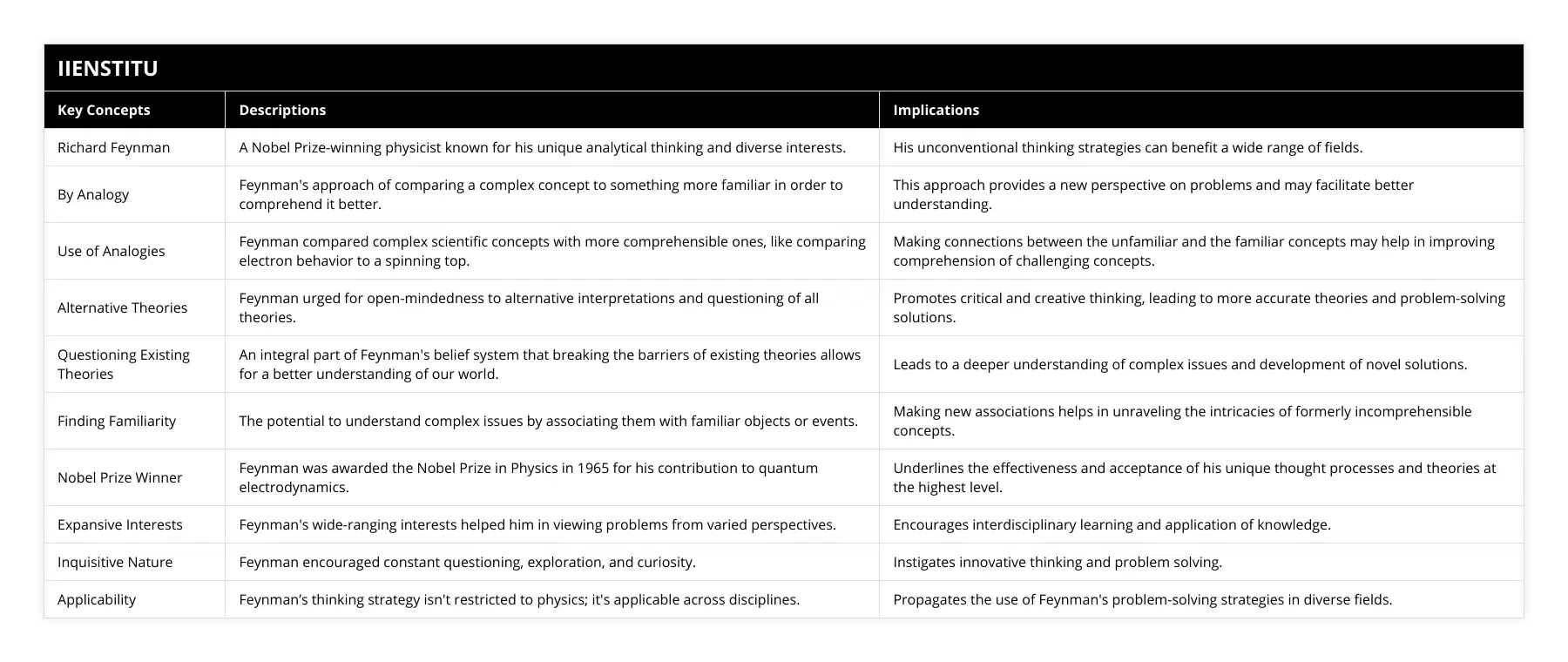
What is the main idea behind Richard Feynman's thinking method?
Richard Feynman was an American physicist who was known for his unorthodox approach to problem-solving and his ability to think outside the box. His unique way of thinking, which he referred to as the Feynman Method, is based on breaking a problem down into simpler parts and looking at them from different perspectives. The Feynman Method encourages people to take a step back and view the problem from a different angle rather than approaching it from a linear, logical perspective.
The main idea behind the Feynman Method is that it is more important to understand the concepts behind a problem rather than simply memorize the solutions. Feynman believed that breaking a problem down into its fundamental parts makes it easier to understand the underlying principles and develop a deeper understanding of the problem and its solutions. This approach encourages people to take a more creative approach to problem-solving, rather than simply relying on rote memorization or trial and error.
Another critical aspect of the Feynman Method is that it encourages people to think critically and ask questions about a problem. By looking at a problem from multiple angles, it is possible to identify potential solutions and explore different options. This is especially important when dealing with complex problems that require creativity and innovative solutions.
Finally, the Feynman Method encourages people to think differently and be open to new ideas. By approaching problems from different angles and considering different solutions, it is possible to develop innovative solutions that may not have been considered before. This approach can be constructive when dealing with complex, abstract problems.
In conclusion, the main idea behind Richard Feynman's thinking method is that it encourages people to think critically and explore different solutions. By breaking a problem down into its fundamental parts and looking at it from different perspectives, it is possible to develop a deeper understanding of the problem and develop creative solutions. This approach can be especially useful when dealing with complex, abstract problems.
How does Feynman's Analogy Method work and what are some examples of it?
Richard Feynman's Analogy Method is a strategy used by scientists to draw connections between concepts that appear to be unrelated. This approach is based on the idea that the same behavior between two different physical systems can be used to explain a phenomenon. Feynman's method allows scientists to find connections between the behavior of different systems and to use these connections to explain difficult concepts.
The Analogy Method is based on four main steps. First, the scientist must identify two different physical systems that display the same behavior. The scientist then collects data about the behavior of each system and compares the data. Next, the scientist identifies the similarities between the data from each system which allows them to draw an analogy between the two systems. Finally, the scientist uses analogy to explain the phenomenon.
The Analogy Method is an effective tool for scientists to better understand difficult concepts or processes. Feynman’s Analogy Method can be used to explain phenomena in a variety of fields, such as astronomy, physics, and chemistry. For example, astronomers can use the Analogy Method to explain the behavior of stars and planets. Physicists can use it to explain the behavior of particles, while chemists can use it to explain the behavior of molecules.
The Analogy Method is also useful for teaching difficult concepts to students. For example, a teacher can use the Analogy Method to explain how electricity works by comparing it to the flow of water in a river. By identifying similarities between the behavior of electricity and the flow of water, the teacher can explain the concept of electricity in an easier, more intuitive way.
In conclusion, Richard Feynman’s Analogy Method is a powerful tool that can be used to explain difficult concepts in a variety of fields. The method is based on four main steps: identifying two systems that display the same behavior, collecting data, identifying similarities between the data, and using the analogy to explain the phenomenon. The Analogy Method can be used to explain phenomena in astronomy, physics, and chemistry and can also be used to teach difficult concepts to students.
What are the benefits of using Feynman's approach to problem solving?
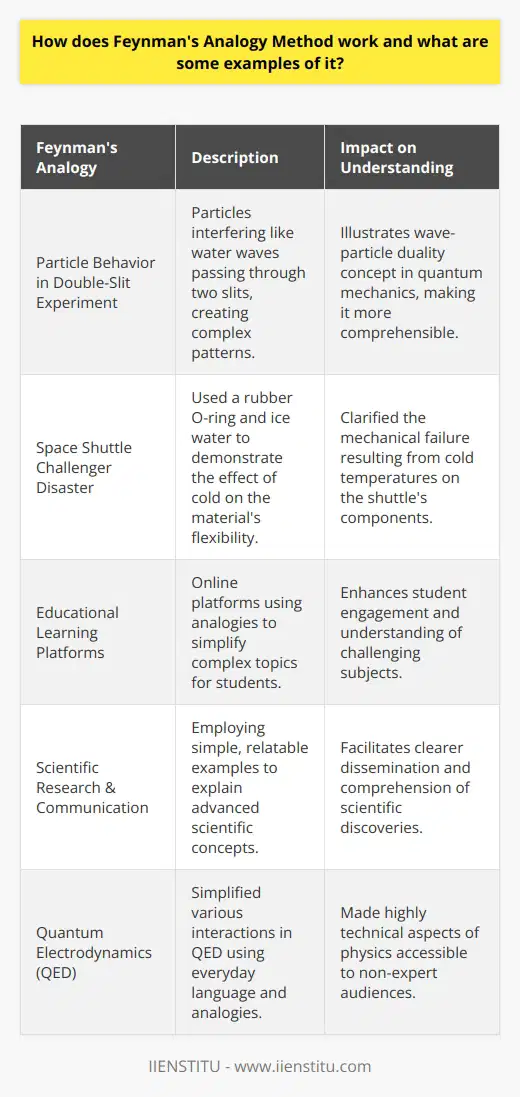
Feynman's approach to problem-solving is a popular method used by scientists, engineers, and students alike to identify, analyze and solve problems effectively. It is based on the teachings of physicist Richard Feynman and involves breaking down complex problems into their component parts to find solutions. This approach effectively tackles difficult problems and can have numerous benefits for those who use it.
The first benefit of using Feynman's approach is that it allows for a more thorough and comprehensive problem analysis. By breaking down the problem into its component parts, it is easier to identify and analyze each individual part and understand how they interact with each other. This allows for a deeper understanding of the problem and can lead to more accurate solutions.
The second benefit of Feynman's approach is that it encourages creative thinking. Breaking down the problem into smaller parts makes it easier to come up with innovative ideas and solutions. Furthermore, this approach encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which can benefit a wide range of situations.
The third benefit of Feynman's approach is that it can help to reduce the amount of time needed to solve a problem. Breaking down the problem into smaller parts makes it easier to identify the main issue and focus on finding a solution. This can help to speed up the process of problem-solving, making it more efficient and effective.
Finally, Feynman's approach to problem-solving is a great way to learn and develop problem-solving skills. Breaking down problems into smaller parts makes it easier to learn the problem-solving process and develop better problem-solving skills. This can be beneficial in a wide range of areas, including academic studies and professional careers.
In conclusion, Feynman's approach to problem-solving effectively tackles difficult problems and can have numerous benefits for those who use it. By breaking down complex problems into their component parts, it is easier to identify and analyze each part and understand how they interact. It also encourages creative and critical thinking, leading to more accurate solutions. Finally, it can help to reduce the amount of time needed to solve a problem and is a great way to learn and develop problem-solving skills.
What is the primary goal of the Feynman method of problem solving in relation to enhancing one's understanding of complex concepts?
The Feynman Method in Enhancing Conceptual Understanding
Principle and Purpose
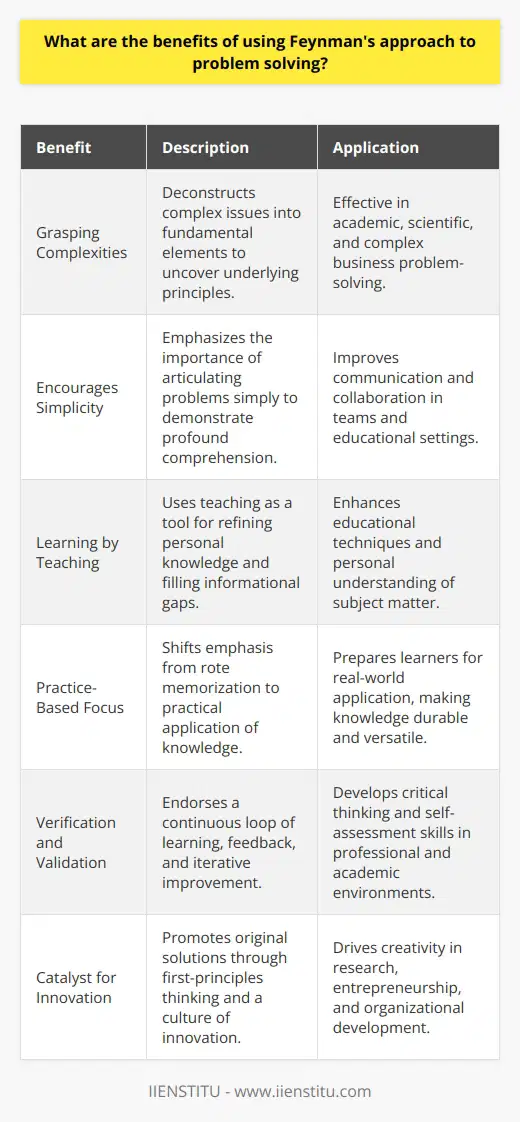
The primary goal of the Feynman method, named after its creator, physicist Richard Feynman, is to simplify and clarify complex concepts for enhanced understanding. This problem-solving approach aims to develop a deeper comprehension of intricate ideas by breaking them down into simpler components and effectively explaining them in accessible terms.
The Four-Step Process
The method consists of four key steps: identification, learning, explanation, and revision. First, one identifies the topic or concept they aim to understand. Next, they learn and acquaint themselves with the relevant information through study and research. Then, in the explanation stage, the learner attempts to articulate the topic in their own words, preferably as if teaching it to a novice audience. If gaps in understanding are revealed in this process, the individual revises and returns to the earlier steps to solidify their knowledge.
Visible Thinking and Feedback
This pedagogical strategy encourages visible thinking by requiring learners to externalize their understanding. The technique requires a clear articulation of ideas and concepts, which enables the identification of any gaps or misconceptions in the learner's knowledge. Seeking feedback from others also aids in refining understanding and clarifying ambiguities. Consequently, the individual becomes more adept at processing complex ideas and cognitively flexible in their problem-solving.
Boosting Retention and Application
The Feynman method fosters long-term retention of information and its application in practice. By actively engaging with the concept and explaining it in one's own words, the learner reinforces their understanding and ingrains the material in their cognitive framework. This approach leads to an increased ability to transfer and adapt their knowledge to new, unfamiliar contexts, thereby promoting critical thinking and innovation.
In conclusion, the primary goal of the Feynman method of problem-solving is to enhance understanding of complex concepts by deconstructing them into more accessible elements and developing a coherent, succinct explanation in one's own words. This process promotes deeper learning, higher-order thinking, and versatile knowledge application – an invaluable tool for mastering the intricacies of any subject matter.
How does the Feynman technique incorporate the notion of simplification in the process of learning and problem-solving?
The Role of Simplification in the Feynman Technique
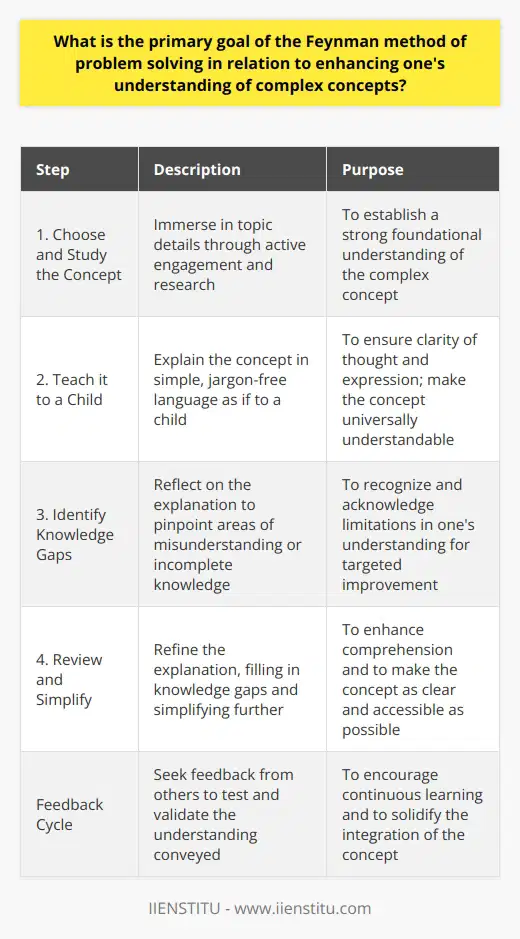
The Feynman technique, developed by renowned physicist Richard Feynman, embraces the idea of simplification as a cornerstone of effective learning and problem-solving. This method involves four key steps, aimed at condensing complex concepts into simplified, easily digestible information.
Step One: Identifying Knowledge Gaps
The first step entails identifying one's knowledge gaps by attempting to explain a concept or problem in simple terms. If unable to do so, learning deficiencies are highlighted, revealing areas that require further study and understanding.
Step Two: Breaking Down Concepts
Simplification becomes more evident in step two, where the learner breaks down the concept into its most basic components. This process facilitates the comprehension of complex ideas by presenting them in a structured, sequential manner.
Step Three: Conveying Information with Simplicity
The third step revolves around conveying the simplified concept to an imagined audience or a real one with limited knowledge of the subject. This exercise necessitates mastering the ability to express ideas clearly and coherently, using simple language and analogies.
Step Four: Review and Refine
Finally, the Feynman technique culminates with the continual review and refinement of the simplified explanations. This process ensures that the learner's understanding is accurate and well-grounded, thus simplifying complicated information while maintaining its essence.
In summary, the Feynman technique melds the notion of simplification with learning and problem-solving by breaking down complex ideas, presenting them in an accessible manner, and refining explanations for greater comprehension. This approach emphasizes the importance of understanding concepts at their core while effectively communicating them with simplicity and clarity.
Which learning strategies and cognitive approaches are most complementary to the Feynman technique, and how might they be applied together to maximize learning efficacy?
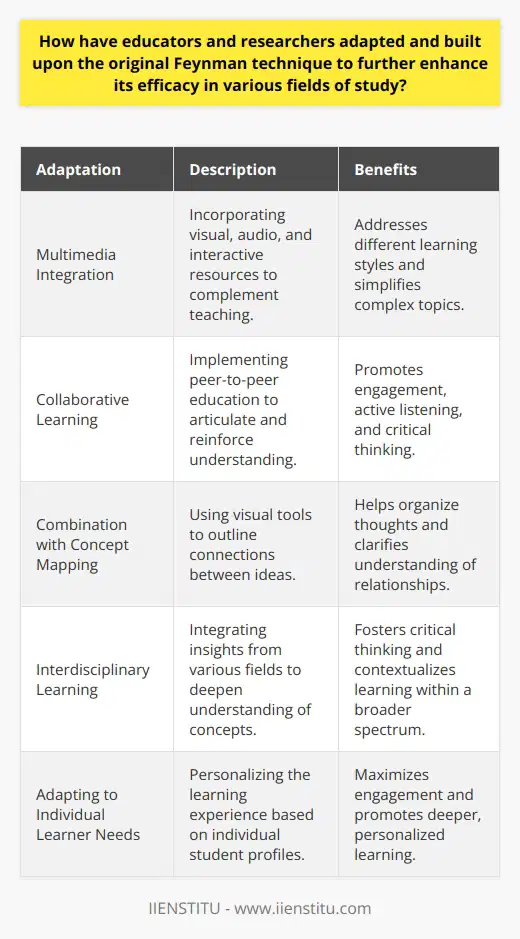
Incorporating Metacognitive Skills
The Feynman technique is a powerful learning tool that simplifies complex concepts through active summary and explanation. To maximize its effectiveness, it is useful to incorporate complementary learning strategies and cognitive approaches such as metacognitive skills, elaborative interrogation, and distributed practice. With these in place, a learner can better understand, retain, and apply the topic at hand.
Developing Self-Reflection
Metacognitive skills refer to the learner's awareness of their thought processes and the ability to adapt their learning strategies accordingly. Integrating metacognitive skills into the Feynman technique involves consistently evaluating one's understanding and identifying areas that require further study or clarification. This self-reflective approach allows learners to actively monitor, regulate, and optimize their learning process and ensures the efficacy of their endeavor.
Applying Elaborative Interrogation
Elaborative interrogation is a cognitive strategy that enhances understanding and retention by inquiring why a concept is true or probable. By integrating elaborative interrogation with the Feynman technique, learners can engage in a deep-level encoding process, thereby strengthening connections between new information and existing knowledge structures. This pairing allows individuals to identify gaps and inconsistencies in their understanding, while reinforcing their newly-acquired comprehension.
Incorporating Distributed Practice
Distributed practice, also known as spaced repetition or distributed learning, is a technique where new information is reviewed over an extended period with intervals between the reviews. Combining distributed practice with the Feynman technique helps reinforce long-term memory by reducing the cognitive load and providing ample opportunity for consolidation. By revisiting complex concepts and applying the Feynman technique consistently over time, learners can strengthen their neural connections and improve retention and retrieval of information.
In summary, the complementary learning strategies of metacognitive skills, elaborative interrogation, and distributed practice significantly enhance the efficacy of the Feynman technique. Through the incorporation of these techniques, learners can maximize their understanding, retention, and application of complex concepts.
What is the fastest way to learn the Feynman technique and how can it be effectively incorporated into one's study habits?
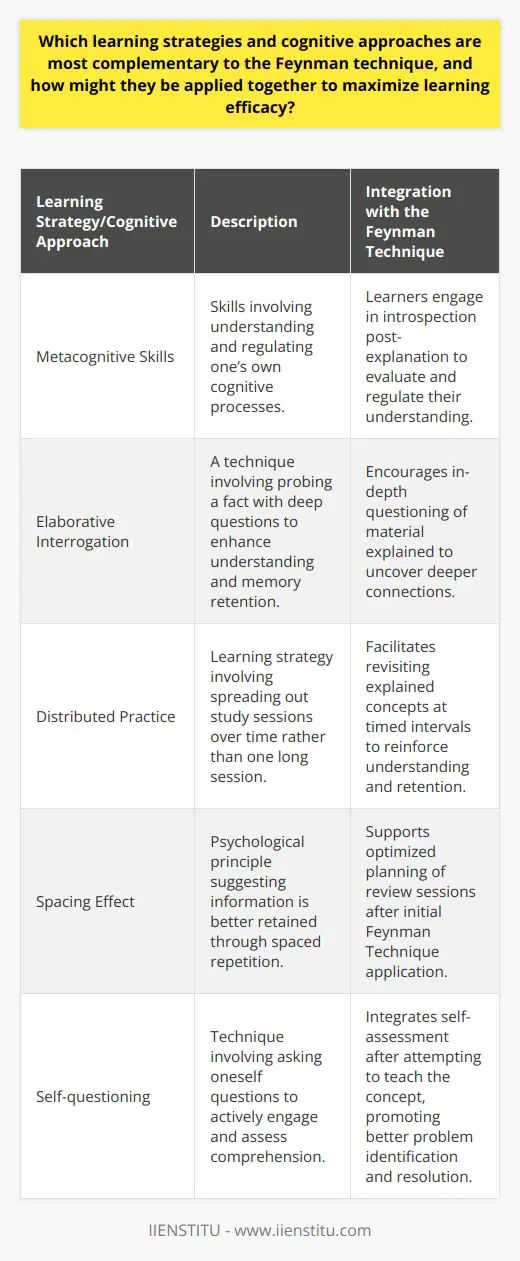
Fastest Way to Learn the Feynman Technique
To rapidly acquire the Feynman Technique, one must initially comprehend its fundamental principles which revolve around the simplification of complex concepts. The technique entails four essential steps: selecting a concept to learn, explaining it to an imaginary audience or in writing, identifying any gaps in understanding, and lastly, revisiting and refining the explanation. One can quickly gain proficiency in the Feynman Technique by practicing regularly and by embracing a growth mindset that considers gaps in understanding as opportunities for improvement.
Effective Incorporation into Study Habits
Consistent Practice
Consistency in utilizing the Feynman Technique is crucial for its effective application in one's studies. Regularly incorporating it into the learning process can help enhance the retention of information and facilitate better comprehension of challenging subjects.
Integration with Other Study Techniques
For optimal results, one should integrate the Feynman Technique into their existing study methods. For instance, combining this technique with active reading, note-taking, or spaced repetition can significantly enhance one's understanding and retention of material.
Setting Attainable Goals
Setting realistic goals for learning new concepts using the Feynman Technique can increase motivation and commitment to mastering it. One should prioritize breaking down complex ideas into manageable chunks and simplifying them for enhanced comprehension.
Peer Collaboration
Peer interaction can significantly aid in the effective application of the Feynman Technique. Working with classmates or study groups helps facilitate the exchange of diverse perspectives and explanations, thus promoting deeper understanding and robust learning experiences.
Timely Feedback and Refinement
Receiving timely feedback from educators or peers and making necessary refinements to the explanations ensures constant improvements in understanding. This practice aligns with the core principles of the Feynman Technique, enhancing its effectiveness in one's study habits.
In conclusion, the fastest way to master the Feynman Technique is through consistent practice and understanding its fundamental principles. Effectively incorporating it into one's study habits involves integrating it with other study strategies, setting attainable goals, engaging in peer collaboration, and seeking timely feedback for refinement.
What are the potential limitations or challenges one might encounter when employing the Feynman technique in problem-solving, and how can these be overcome?
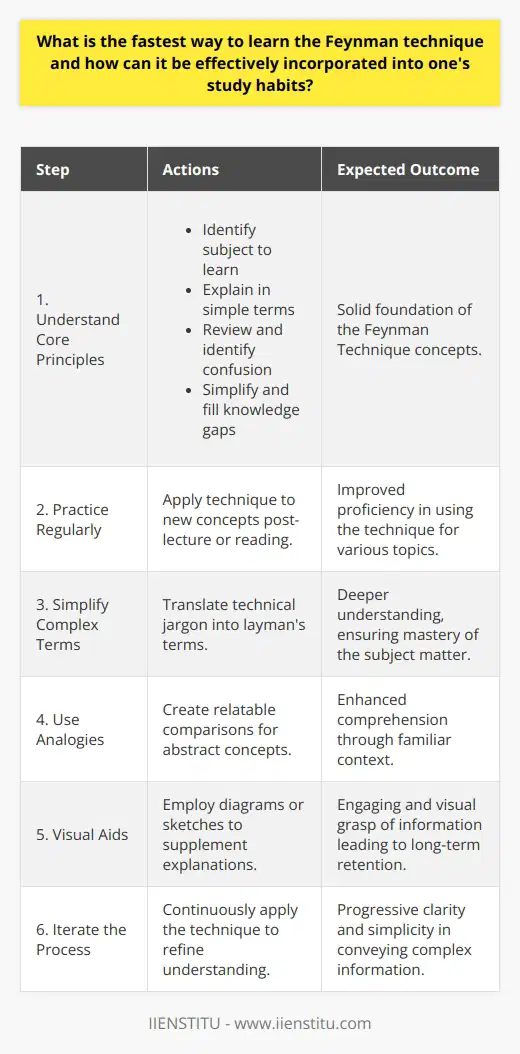
Limited Scope of Application
One potential limitation of the Feynman technique is its dependence on one's ability to grasp complex concepts and articulate them in simplified terms. For some individuals, this may prove difficult, especially when tackling highly technical subjects that require a profound understanding of specialized jargon or unique problem-solving techniques. To overcome this challenge, individuals can seek guidance from knowledgeable peers or utilize various informational resources, effectively collaborating and expanding their understanding of the subject matter.
Difficulty in Simplification
Another challenge in employing the Feynman technique is distilling intricate ideas or lengthy processes into concise, layman's terms. This difficulty may arise due to ingrained expectations surrounding academic language, the breadth of the topic, or other factors. To overcome this obstacle, practice is crucial. By regularly applying the Feynman technique to a range of topics, learners can improve their ability to simplify and explain complex concepts without relying on convoluted language or lengthy explanations.
Inadequate Initial Understanding
A third limitation that may arise when using the Feynman technique is an insufficient grasp of the problem at hand. If a learner cannot accurately comprehend the fundamental concepts involved in their problem, they will struggle to articulate it in a simplified manner. In this case, the individual must return to studying the topic in greater depth, utilizing available resources such as textbooks, articles, videos, or expert advice. By strengthening their foundational knowledge, learners can more effectively implement the Feynman technique in their problem-solving efforts.
Risk of Oversimplification
The risk of oversimplification is another potential challenge inherent in the Feynman technique. While breaking down complex ideas, some may inadvertently omit crucial details or nuances, resulting in an inaccurate or incomplete representation of the concept. To combat this issue, learners should continuously revisit and revise their explanations, remaining mindful of the balance between simplification and accuracy. Input from knowledgeable peers or mentors can also be valuable in detecting and correcting oversimplifications.
In conclusion, the Feynman technique's limitations and challenges include the difficulty of simplification, inadequate initial understanding, and the risk of oversimplification. However, these hurdles can be overcome through diligent practice, collaboration with peers, and continuously revisiting and refining explanations to strike the ideal balance of simplicity and accuracy. By doing so, learners can harness the full potential of the Feynman technique, enhancing their problem-solving capabilities and overall understanding of complex concepts.
How have educators and researchers adapted and built upon the original Feynman technique to further enhance its efficacy in various fields of study?
**Adaptations to the Feynman Technique**
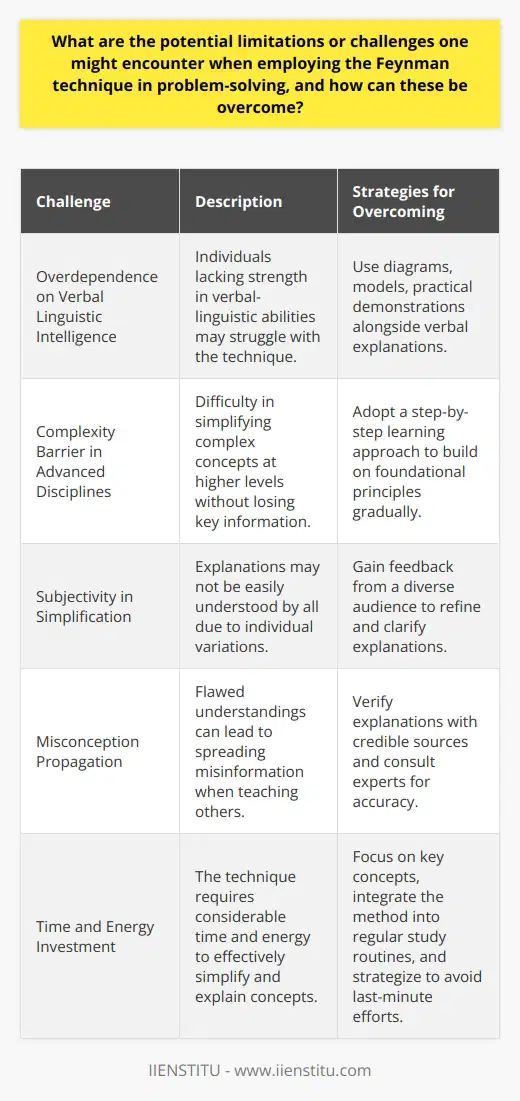
Educators and researchers have built upon the original Feynman Technique, which involves explaining complex concepts in simple terms, to further enhance its efficacy in various fields of study. One adaptation has been the incorporation of multimedia resources, such as videos and podcasts, which facilitate visual and auditory learners in their understanding of complex concepts. This modification promotes a more engaging learning experience and caters to diverse learning styles.
**Peer-to-peer Learning**
Another innovative development is the integration of peer-to-peer learning, in which students explain the material to each other using the Feynman Technique. This approach not only helps to solidify the understanding of the person explaining the concept but also encourages active listening and constructive feedback from the peer. Moreover, it fosters a cooperative learning environment and enhances critical thinking skills among learners.
**Concept Mapping**
Concept mapping has also been introduced to the Feynman Technique as a way to visually represent relationships between ideas. It allows students to identify gaps in their understanding and promotes better organization of their knowledge. This practice further assists in the identification of connections between different topics and facilitates the development of a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
**Interdisciplinary Approaches**
The Feynman Technique has been adapted to incorporate interdisciplinary approaches, bridging the gaps between various fields of study. By incorporating ideas and theories from multiple disciplines, learners gain a broader and more contextualized understanding of the concept at hand. This interdisciplinary approach fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills, promoting more well-rounded and versatile learners.
**Personalized Learning**
Lastly, the Feynman Technique has been tailored to accommodate personalized learning pathways. By taking into account individual learning styles, interests, and goals, educators and researchers have developed customized learning plans that optimize engagement and retention. This personalization ensures that learners can develop a deep understanding of the material, consider diverse perspectives, and identify potential areas for future exploration.
In conclusion, adaptations to the original Feynman Technique have led to enhanced efficacy in various fields of study through the incorporation of multimedia resources, peer-to-peer learning, concept mapping, interdisciplinary approaches, and personalized learning pathways. These modifications have not only made learning more engaging but also fostered critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deeper understanding among students.
What is the Feynman Technique for solving problems?
Understanding the Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique is a problem-solving strategy named after the renowned physicist Richard Feynman. It involves simplifying complex concepts and ideas to enhance one's understanding and develop effective solutions.
Four-step Process
To implement the Feynman Technique, individuals follow a four-step process as outlined below:
Identify the Problem
The first step involves pinpointing the precise issue that needs to be addressed. This means breaking down the topic into smaller, more manageable subtopics or questions.
Explain the Problem in Simple Terms
In this phase, the goal is to explain the problem in the simplest way possible, using everyday language accessible to a non-expert. By doing so, the individual gains a deeper insight into the problem and identifies any gaps in their understanding.
Identify Knowledge Gaps
During the process of simplifying the problem, the individual may encounter concepts they don't fully grasp. In this step, they need to identify these gaps and seek further information to improve their comprehension.
Review and Simplify
After filling in the knowledge gaps, the individual should go back and review their explanation. They can refine it further to provide a concise, easily digestible summary of the central issue and solution.
Benefits of the Feynman Technique
Employing the Feynman Technique offers various advantages, including enhanced learning and problem-solving capabilities. By forcing individuals to break down concepts into simple terms, they are likely to develop a more profound understanding of the subject matter.
Moreover, the technique encourages critical thinking and enables individuals to share their knowledge more effectively, as they learn to clearly articulate complex ideas. This is particularly beneficial for educators and professionals who need to communicate complex concepts to diverse audiences.
In conclusion, the Feynman Technique is an effective problem-solving and learning tool that promotes deep comprehension and efficient communication. By adopting this approach, individuals can expand their expertise in various subjects and increase their capacity to tackle complex challenges.
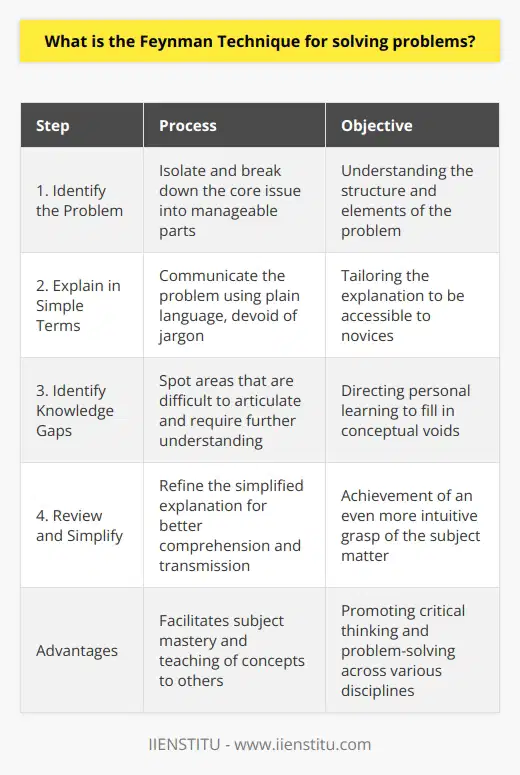
What are the 4 steps of Feynman Technique?
Understanding the Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique is a powerful learning and communication method developed by the renowned physicist, Richard Feynman. It focuses on simplifying complex concepts and breaking them down into digestible pieces of information. This technique involves four key steps: (1) choose a concept, (2) teach it to someone else, (3) identify the gaps in your understanding, and (4) review and simplify further.
Choose a Concept
Select a topic or idea that you want to understand deeply. It could be anything from a scientific principle to a philosophical argument. The primary goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the concept to effectively explain it to others.
Teach it to Someone Else
Imagine teaching the chosen concept to someone with no prior knowledge of the subject. This step forces you to simplify the idea and translate it into layman's terms. Explaining the concept in your own words helps solidify your understanding and reveals any areas where you may need to improve.
Identify Gaps in Understanding
As you attempt to teach the concept, you may come across gaps in your own understanding. Take note of these areas and the questions that arise. This process helps you actively engage with the material and challenges you to think critically, leading to deeper comprehension.
Review and Simplify Further
Once you have identified any gaps, return to the source material and study it with your newfound perspective. Fill in the gaps, then attempt to explain the concept again. This iterative process of learning, teaching, and refining ensures that your understanding continuously improves.
In conclusion, the Feynman Technique is an effective method for mastering complex concepts by simplifying them and identifying gaps in understanding through teaching to others. Through this iterative cycle of learning, teaching, and refining, one can achieve a deep understanding of various subject matters and effectively communicate complex ideas to others.
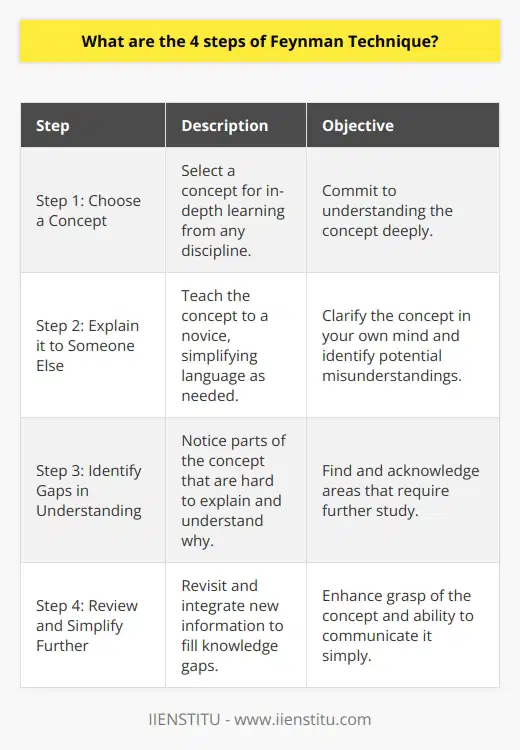
What can we learn from Richard Feynman?
Learning from Feynman's Approach to Problem Solving
Richard Feynman, a renowned physicist, serves as an exemplary figure for those seeking to enhance their problem-solving abilities. Feynman's approach to problem solving, often referred to as the 'Feynman Technique,' demonstrates several key aspects that we can adopt to improve our understanding and learning.
Developing Curiosity and Asking Questions
One critical takeaway from Feynman's approach is the importance of nurturing curiosity and consistently asking questions. Feynman believed that asking questions led to a deeper understanding of complex concepts. By questioning our assumptions and seeking clarification, we can widen our perspective and embrace the learning process more effectively.
Breaking Down Concepts into Simple Terms
Another vital skill we can learn from Feynman is the ability to break down complex concepts into simple and easy-to-understand terms. This process not only helps us comprehend the subject matter but also reinforces our understanding. By explaining intricate ideas in simpler language, we engage our underlying cognitive processes, which ultimately contribute to our overall learning experience.
Visualization and Thought Experiments
Feynman also encouraged the use of visualization and thought experiments as powerful learning tools. By actively imagining scenarios, we can mentally play out different possibilities and outcomes. This method helps us understand the implications of various concepts and ideas, thereby fostering a more profound comprehension of the subject matter.
Emphasizing the Importance of Persistent Effort
Feynman's success in solving complex scientific problems was not solely due to his intellectual prowess; his persistence and hard work played equally significant roles. His problem-solving approach offers a valuable lesson on the importance of consistent effort and deliberate practice to overcome challenges and achieve mastery in any field.
Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Learning
Finally, Feynman's work underscores the value of collaboration and interdisciplinary learning. By actively engaging with experts from diverse backgrounds, we can transcend restrictive boundaries and foster innovative thinking. Additionally, integrating different perspectives allows us to approach problems with a well-rounded understanding and refine our problem-solving skills.
In conclusion, there are several valuable lessons we can learn from Richard Feynman to enhance our problem-solving abilities and overall understanding. By fostering curiosity, simplifying complex concepts, visualizing scenarios, putting in consistent effort, and collaborating with others, we can improve our learning experience and unlock our full potential.
How do you learn anything with the Feynman Technique?
The Feynman Technique Implementation
Understanding the Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique is an innovative learning approach developed by Nobel Prize-winning physicist Richard Feynman, which emphasizes simplifying complex concepts and enhancing comprehension. This method requires individuals to teach a topic, identify knowledge gaps, and review information to achieve effective results.
Step 1: Choose a Topic and Study
Firstly, individuals must choose a specific topic or concept they wish to learn. By using textbooks or other reliable sources, they can gather comprehensive information about the subject, ensuring that they comprehend the content accordingly.
Step 2: Teach the Concept
Secondly, the learner should attempt to teach the concept to someone else, ideally without looking at any notes or references. It is crucial to use simple language and break down the topic into manageable segments. The teaching process reinforces the individual's understanding of the material while identifying any gaps in their knowledge.
Step 3: Identify and Fill Knowledge Gaps
During the teaching phase, learners may encounter difficulties when explaining specific aspects of the topic. This step encourages them to identify those areas where their understanding is weak and revisit the source material. By reviewing the information, they can fill the gaps in their knowledge and enhance their overall comprehension of the subject.
Step 4: Simplify and Use Analogies
Lastly, the Feynman Technique encourages learners to simplify the concept further and create analogies. This strategy helps make even the most complex subjects more accessible and understandable. Analogies allow individuals to relate abstract ideas to real-world scenarios or familiar concepts, thereby improving their retention of the material.
In conclusion, the Feynman Technique provides a systematic and effective approach to learning complex concepts by simplifying the content, identifying knowledge gaps, and using analogies. By following these steps, individuals can enhance their comprehension and retention of any subject matter, ultimately becoming more proficient learners.

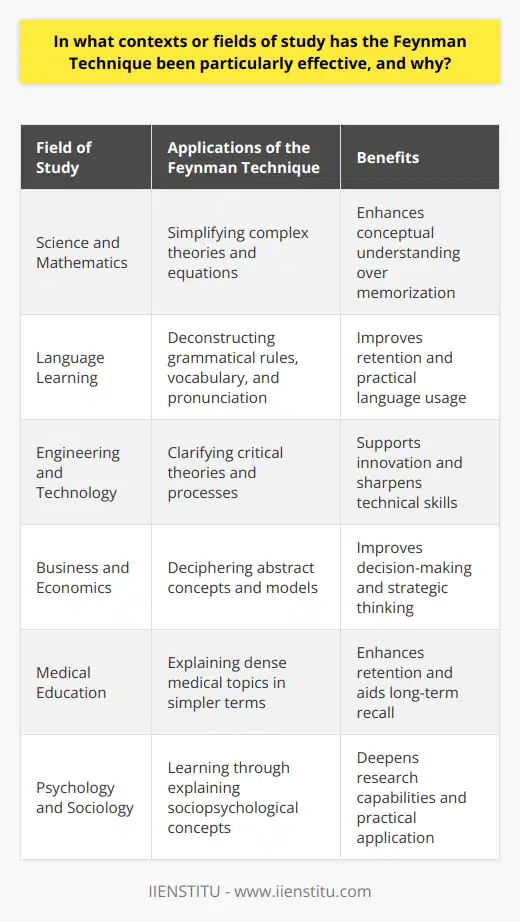
In what contexts or fields of study has the Feynman Technique been particularly effective, and why?
Effective Contexts for the Feynman Technique
Science and Mathematics
The Feynman Technique has been especially effective in engaging learners with complex subjects in science and mathematics due to its emphasis on clear and simple explanations. Through iterative and refined explanations, concepts from vast areas such as calculus, physics, and chemistry become more accessible.
Language Learning
Language acquisition also benefits from the Feynman Technique, as it encourages learners to explain words, phrases, and grammar rules to themselves or others in manageable terms. This approach ensures efficient retention and an improved understanding of complex linguistic constructs.
Engineering and Technology
The technique has proven particularly valuable in engineering and technological fields, where a deep and nuanced understanding of intricate systems and theories is essential. By explaining key concepts in simple terms, the Feynman Technique enables engineers and technicians to comfortably grasp complex ideas, improving problem-solving skills and enhancing expertise.
Business and Economics
In business and economics, studies suggest that the Feynman Technique can solidify understanding of foundational principles and aid practical applications. As students explain economic concepts clearly and concisely, they develop a more refined understanding and are better equipped for decision-making in real-life scenarios.
Medical Education
The complex nature of medical education makes it ripe for the application of the Feynman Technique, promoting better comprehension of dense material. By simplifying complex medical concepts and explanations, students can improve retention, reducing cognitive load while increasing long-term understanding.
Psychology and Sociology
The social sciences also benefit from the Feynman Technique, as it aids in comprehending multifaceted theories and social dynamics. Employing this strategy promotes clearer thinking and a more profound understanding of the field, facilitating more effective research design, analysis, and interpretation.
To conclude, the Feynman Technique has been demonstrably effective in various contexts and fields of study. Its potency arises from its emphasis on intelligent simplification and explanation, ensuring learners attain a more nuanced and grounded understanding of even the most challenging material.
Are there any specific prerequisites or foundational skills required in order to successfully apply the Feynman Technique?
Understanding the Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique aids in learning and retaining information by explaining complex concepts in a simplified manner. To effectively apply this technique, individuals must possess specific foundational skills and prerequisites.
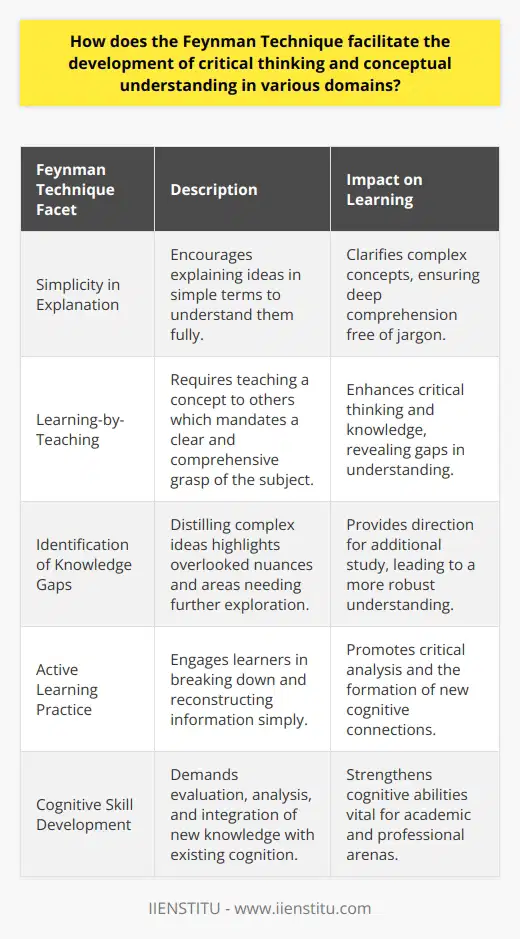
Grasping Basic Concepts
Firstly, a fundamental understanding of the subject matter is crucial. Individuals must be able to grasp the basic concepts, ideas, and terminologies associated with the topic in question. This initial comprehension enables them to address more complex ideas subsequently.
Effective Communication Skills
Secondly, sound communication skills are essential for the successful application of the Feynman Technique. The ability to articulate ideas succinctly yet comprehensively is vital in ensuring effective knowledge transfer. Consequently, individuals must be skilled in verbally expressing themselves and clarifying concepts.
Creative Problem-Solving
Thirdly, creative problem-solving skills are critical in utilizing the Feynman Technique. The process requires individuals to identify gaps in their understanding and subsequently simplify difficult concepts. As a result, they must be capable of recognizing and resolving ambiguities in their comprehension of the subject matter.
Employing Analogies and Examples
Lastly, the use of analogies and examples in illustration is a key aspect of the Feynman Technique. By relating complex ideas to simpler, familiar concepts, individuals can create a more accessible understanding of the subject. Developing the ability to identify and utilize appropriate examples is, therefore, an important prerequisite in effectively applying the technique.
In conclusion, the successful application of the Feynman Technique relies on a solid foundation of basic subject understanding, effective communication skills, creative problem-solving abilities, and the aptitude to employ analogies and examples. Developing these skills is crucial for individuals desiring to engage with complex information using this technique.
What is the fundamental principle underlying the Feynman Technique in the context of learning and problem-solving?
Fundamental Concept of the Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique provides a structure for understanding and simplifying complex ideas. Its foundational principle lies in conceptual clarity and coherent explanation.
Role in Learning
In the context of learning, it encourages translating complex subjects into a simple, everyday language. It tests a learner's understanding of a subject by challenging them to explain it without using jargon or complex terminology.
Significance in Problem Solving
The Feynman Technique also serves as a powerful problem-solving method. It promotes breaking down problems into simpler pieces. By visualizing and explaining each individual part, a broader understanding emerges. This aids in crafting targeted and effective solutions.
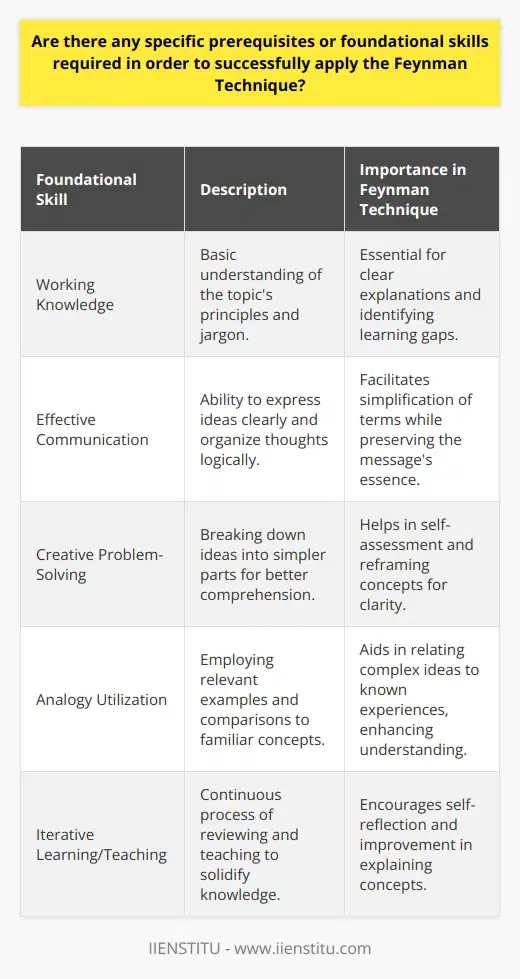
Process of the Feynman Technique
The process constitutes four steps. First, identify and write down the concept or problem. Second, practice explaining it in a simplified form. Third, revisit and identify gaps in knowledge, addressing them with further research. Finally, simplify and consolidate the explanation again. Brief explanations ensure successful comprehension.
Conclusion
The Feynman Technique, in essence, validates mastery over a subject by the capacity to simplify its narrative. It further aids in problem-solving through comprehensive understanding. Hence, it aligns with Feynman's famous quote, 'If you can't explain it simply, you don't understand it well enough.'
How does the Feynman Technique facilitate the development of critical thinking and conceptual understanding in various domains?
Understanding Through Simplicity
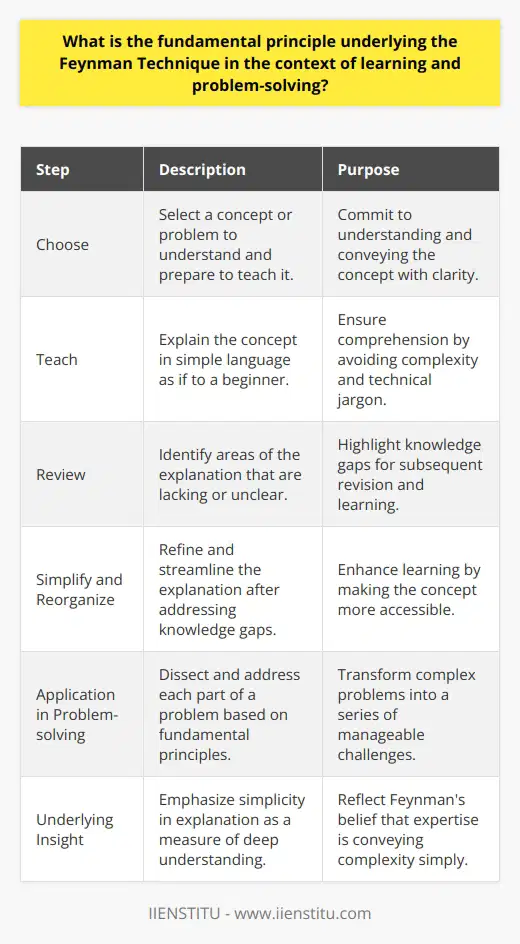
The Feynman Technique facilitates the development of critical thinking and conceptual understanding by breaking down complex ideas into their simplest forms. It encourages learners to distill a concept to its basic elements, thus deepening their understanding.
Principle of Learning-by-Teaching
The technique is a remarkably effective learning method due to its concept of learning by teaching. Paraphrasing and explaining information to others triggers metacognition (thinking about one's own thinking), which boosts critical thinking skills.
Revealing Knowledge Gaps
Attempting to explain concepts in straightforward terms exposes gaps in understanding. Through the Feynman technique, these gaps become opportunities for deeper exploration and learning, thereby promoting more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Promoting Active Learning
The Feynman Technique promotes active learning, where learners engage with the information. This hands-on approach cultivates the ability to critically analyze and synthesize concepts in various domains.
Stimulating Cognitive Abilities
By employing the Feynman Technique, learners stimulate different cognitive abilities including evaluation, analysis, and synthesis. This enhances the integration of new information with existing knowledge, facilitating a robust and well-rounded grasp of the subject area.
In conclusion, the Feynman Technique is an invaluable tool in promoting critical thinking and conceptual understanding across various domains. Its simplicity, focus on active learning, and ability to reveal knowledge gaps, stimulates cognitive processes encouraging in-depth learning.
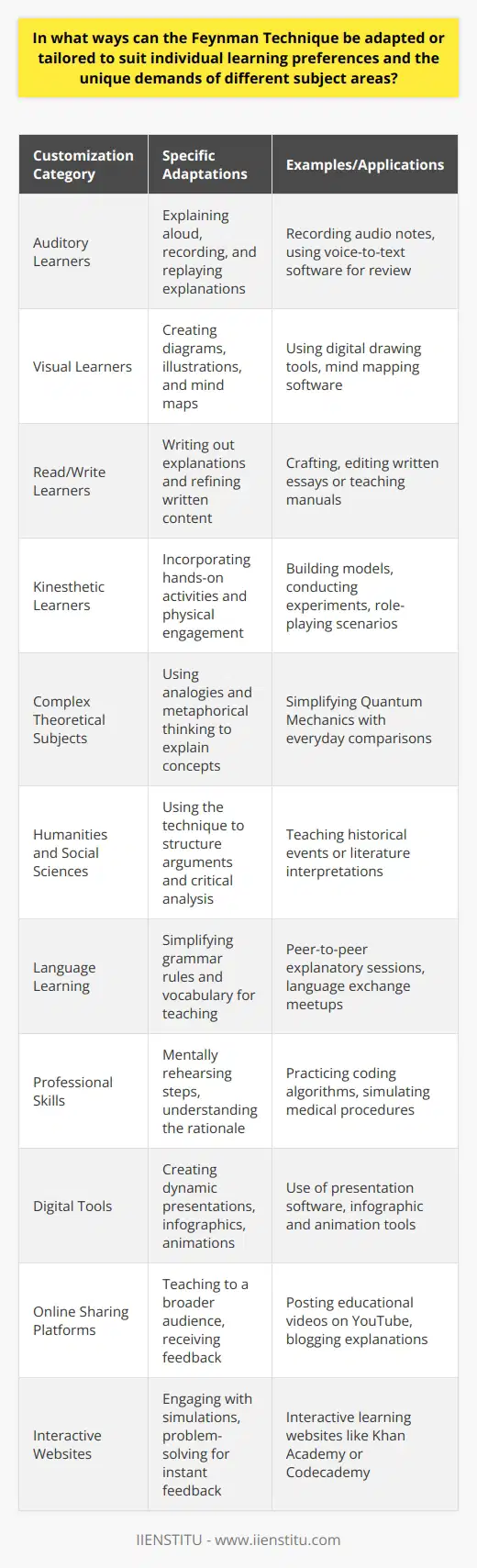
In what ways can the Feynman Technique be adapted or tailored to suit individual learning preferences and the unique demands of different subject areas?
Adapting the Feynman Technique to Individual Learning Preferences
The Feynman Technique in its simplest form, involves learning by teaching. However, we can tweak it to suit an individual’s learning style. For auditory learners, they might record and listen to their explanation to deepen understanding. Meanwhile, visual learners can include diagrams or mind maps in their notes.
Tailoring the Feynman Technique per Subject Areas
For subjects that require a deeper level of conceptual understanding, like Physics or Philosophy, the technique may need extended application or combination with other learning methods. Another subject area that could benefit from this technique is Mathematics. However, procedural understanding would become more important. Here, learner might break down steps and explain each one in the simplest terms.
Feynman Technique and Kinesthetic Learners
Kinesthetic learners, who learn by doing, can adapt the Feynman Technique to include physical activities. This could involve creating flashcards, physically sorting the concepts, or even teaching through physical demonstrations.
Combining the Technique with Technology Tools
The Feynman technique can be adapted to today's technology-powered learning environment as well. For example, learners could create digital mind maps or use online platforms such as YouTube to explain concepts, taking advantage of multimedia tools to simplify complicated subjects.
In Summary,
The Feynman Technique offers valuable opportunities for customisation. It can adapt to cater to personal learning preferences and subject needs. With a little imagination and creativity, one can tailor this technique to highly effective use.