
Troubleshooting is an intellectual process that involves isolating the cause of a malfunction and rectifying it. It is the heart and lifeblood of resolving technical issues and ensures efficiency and productivity across numerous sectors from information technology, to automotives, to household appliances. The capacity to troubleshoot fundamentally crafts an individual into a problem-solver, able to navigate and resolve any nuisances with relative ease. It is, almost indisputably, a versatile and invaluable skill to possess in this fast-evolving technologically driven society.
The prosperity of any enterprise is inevitably underpinned by their prowess to troubleshoot deftly, thereby ensuring minimal downtime and maintaining a high standard of service. Hence, it is of paramount importance for individuals working in technical sectors to possess proficient troubleshooting skills. This article aims to immerse the reader in the universe of troubleshooting, imparting an understanding of its nuances, its history, and the role it plays in various domains, all while outlining some helpful strategies to develop this critical skill.
By systematically understanding the techniques involved in troubleshooting, individuals can tailor their problem-solving course free of errors which results in an efficient resolution of the issue at hand. This article also intends to help workers and students enhance their troubleshooting skills for versatile application in their professional and academic lives, leading to adept problem solving and effective issue resolution.
Origin and Evolution of Troubleshooting
The birth of troubleshooting can be traced back to the times when humankind first began using tools and developing machines, nurturing the necessity to identify and rectify issues that inhibited productivity. In early times, troubleshooting was primarily employed in the field of mechanical engineering, assisting in identifying and rectifying manufacturing defects and malfunctions.
With the advent of systems like electricity grids and telecommunication networks during the industrial revolution, troubleshooting emerged as an essential practice to ensure the reliability and efficiency of these complex systems. As technology advanced further towards computers and electronics, troubleshooting methods evolved parallelly, bolstering the development and sophistication of our modern world.
Evolution of Troubleshooting Techniques
Over the centuries, troubleshooting techniques and problem-solving mechanisms have vastly matured. The invention of predictive and preventive maintenance technologies, ranging from AI-driven analytics to thermal imaging, has extensively transformed the process of troubleshooting. The ever-growing reliance on digital systems and smart machines has given gravity to the development of robust troubleshooting strategies. Machine learning and artificial intelligence have played a crucial role in determining this paradigm shift in troubleshooting procedures, offering swift and proactive issue identification and resolution.
Fundamentals of Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is, at its core, a systematic process leveraging logic, technical knowledge, and analytics. The raw ingredients of any troubleshooting process are essentially the identification of the issue, its isolation, and the subsequent resolution. This requires a comprehensive understanding of the system or technology involved and a structured approach to narrowing down and eliminating potential causes.
Understanding the problem
Having first-rate communication skills is fundamental in troubleshooting as it allows for effectual information gathering, leading to an accurate definition of the problem. This enables the troubleshooter to form a pointed hypothesis regarding the cause of the issue, thereby enabling them to target their subsequent actions more efficiently.
Tools and Techniques
Given the various technological domains where troubleshooting may be required, a broad range of tools are utilized. For instance, in computer systems, software diagnostic tools are used to pinpoint issues within the system. On the other hand, mechanical troubleshooting might require the use of physical instruments like multimeters or oscilloscopes. Regardless of the tools, the fundamental techniques stay the same: identifying, isolating, and resolving issues using informed hypotheses and targeted testing.
Troubleshooting in the Modern World
Today, troubleshooting permeates every aspect of our lives, from minor hiccups in our smartphones to critical system failures in the industry. Fundamentally, an efficient troubleshooting process can be the difference between operational success and failure. Across disciplines like information technology, automotives, and even everyday household appliances, the need for effective troubleshooting is undeniable.
Troubleshooting in IT
In the big and small organizations alike, IT troubleshooting skills are a prerequisite given the heavy reliance on digital systems. Consider a scenario where an online certificate course platform fails. IT troubleshooters would swiftly employ their skills, working their way from potential server issues to platform-specific bugs, ensuring minimal downtime and disruption to users.
The Future of Troubleshooting
With the advent of AI and smart technologies, the ways of troubleshooting are changing rapidly. Automated systems and self-diagnostic tools are gaining momentum, promising swift and proactive issue resolution. This could mean less human intervention in the troubleshooting process, with people assuming supervisory roles.
Developing Troubleshooting Skills
Problem-solving skills are vital in almost all careers, making the development of troubleshooting skills a critical charge. Proficient troubleshooters are known to have a sound knowledge base, sharp analytical thinking, and excellent communication skills. To foster these skills, it's crucial to get hands-on experience with the systems and technology you're interested in.
Importance of Continuous Learning
Keeping up with the pace of technological evolution requires continuous learning and updating of skills. Online courses, webinars, and technical literature can help you to learn more about the technologies in your field and improve your troubleshooting abilities.
Conclusion
As we've explored throughout this article, troubleshooting is an indispensable skill in modern society. From its origin in manufacturing to its projected future interspersed with AI, the art and science of troubleshooting have shown its critical role in ensuring efficiency and productivity across various sectors. With a structured approach, good understanding of the problem, and the right tools, troubleshooting can indeed be a game-changer.
Final Tips and Suggestions
To sum up, empowerment in troubleshooting requires continuous learning, hands-on experience, a keen focus on understanding the problem accurately, and adept use of relevant tools. Always remember, effective troubleshooters are not those who never fail, but those who never quit in the face of failure. Keep learning, keep experimenting, and most importantly, keep troubleshooting. The horizon of efficient issue resolution is just a problem-solving course away.
Ace the art of troubleshooting and problem-solving to enhance your future endeavors. No issue is too big to resolve, and no problem is too small to ignore when you're armed with powerful troubleshooting skills. So stay curious, stay ambitious, and remember – the world's most complex issues are solved one troubleshooting step at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key steps involved in the systematic troubleshooting process for efficient issue resolution?
Systematic Troubleshooting Steps
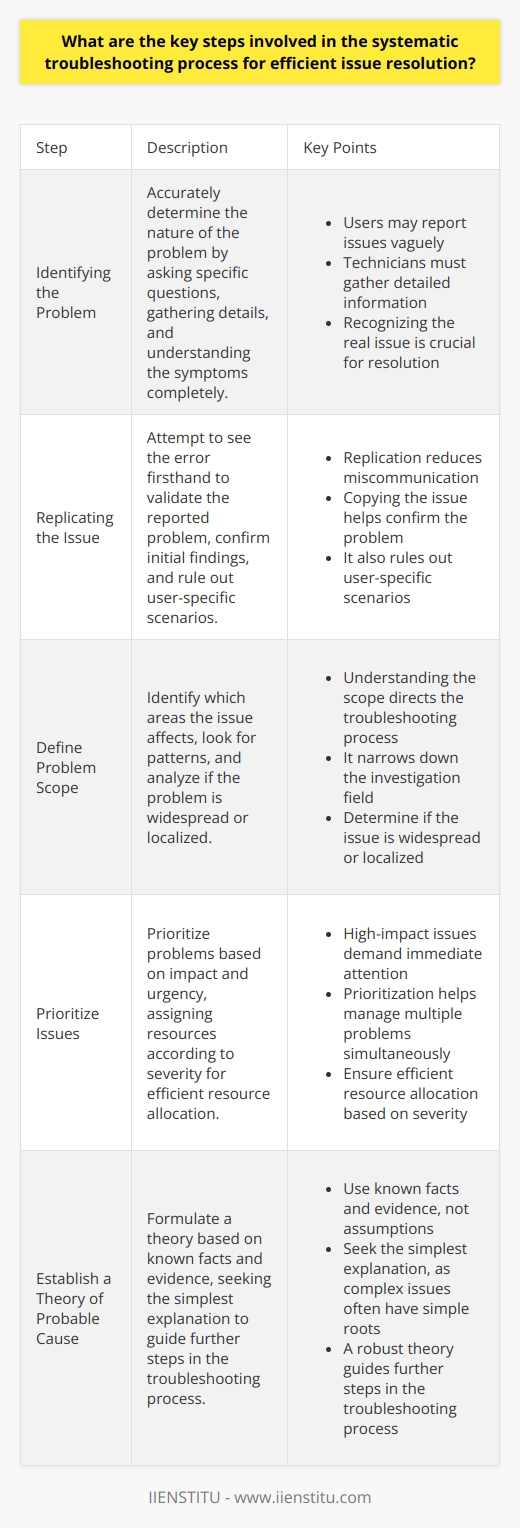
Identifying the Problem
Troubleshooting begins with problem identification. Users report issues, sometimes vaguely. Technicians must determine the problem's nature accurately. Ask specific questions. Gather details meticulously. Understand the symptoms completely. Recognizing the real issue is crucial for resolution.
Replicating the Issue
Next, replicate the user's problem. Attempt to see the error firsthand. Replication validates the reported problem. This step confirms the initial findings. Copying the issue reduces miscommunication. It also rules out user-specific scenarios.
Define Problem Scope
Determining the problem's scope follows. Identify which areas the issue affects. Look for patterns. Is the problem widespread? Analyze if it's localized. Understanding the scope directs the troubleshooting process. It narrows down the investigation field.
Prioritize Issues
Prioritize problems based on impact and urgency. High-impact issues demand immediate attention. Assign resources based on severity. This ensures efficient resource allocation. Prioritization helps in managing multiple problems simultaneously.
Establish a Theory of Probable Cause
Formulate a theory next. Use known facts. Base your theory on evidence, not assumptions. Seek the simplest explanation. Complex issues often have simple roots. A robust theory guides further steps.
Test the Theory
Testing your theory is critical. Implement a controlled environment. Replicate the problem. Apply a potential fix. Observe the results carefully. Record the outcomes. A failed test requires a new theory.
Create an Action Plan
Develop an action plan once you confirm a theory. Document the steps necessary for resolution. Plan thoroughly and methodically. Outline the tasks in sequence. Consider dependencies. Remember to have a rollback plan.
Implement the Solution
Carry out the solution next. Follow the action plan closely. Resolve the issue step by step. Monitor each stage. Precision is crucial for the implementation.
Verify System Functionality
After implementation, verify system functionality. Ensure the fix addresses the problem entirely. Confirm that no new issues have arisen. Perform a thorough system check. All systems must operate normally.
Document Findings
Lastly, document the findings. Write down the issue, the steps taken, and the resolution. Documentation helps in future troubleshooting. It provides a reference for similar issues. Create a knowledge base for efficient issue resolution.
Each step involves critical thinking and meticulous attention. Efficient troubleshooting depends on disciplined methodology. This systematic approach saves time and resources. It ensures effective problem resolution.
How can root cause analysis aid in understanding and resolving technical problems?
Understanding Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a systematic process. It identifies underlying issues in failure events. Technical problems often have complex causes. RCA seeks to uncover these rather than treating symptoms alone.
The Importance of RCA
RCA prevents future failures. It promotes a deeper understanding of problems. By identifying the root causes, we can prevent recurrences. This is crucial in complex systems.
Technical challenges are multifaceted. RCA breaks down complexity. It does so by examining the chain of causative factors. Teams can pinpoint where problems start.
The Process of RCA
A good RCA process follows clear steps. Define the problem clearly first. Gather data about the problem. Then, identify all contributory factors. Next, find the root cause. At last, generate solutions and implement them.
- Data Collection: Gather comprehensive data.
- Causal Factor Charting: Map out the sequence of events.
- Root Cause Identification: Use RCA tools like 5 Whys or Fishbone Diagrams.
- Solution Development: Create strategies for mitigation.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Put solutions in place and watch for changes.
Benefits of Utilizing RCA
RCA leads to more effective solutions. Problems do not recur if you address root causes.
RCA fosters a proactive culture. Team members learn to look beyond the obvious. They ask deeper questions and seek comprehensive answers.
Better resource utilization comes from RCA. Efforts focus where they will have the most impact. This makes practical and financial sense.
Challenges in RCA
RCA requires time and resources. These are often limited. However, the long-term benefits outweigh the costs.
RCA needs skilled personnel. They must know how to analyze complex data. Training and practice develop these skills.
Implementing RCA in Technical Fields
Teams must buy into the process. They must understand the value of RCA.
Documentation is key. Without good records, RCA becomes difficult. It relies on accurate data collection.
Regularly review RCA processes and outcomes. This ensures ongoing improvements.
RCA: Beyond Problem-Solving
RCA transforms how teams handle technical problems. They move from reactive to proactive. RCA equips them with the tools to find lasting solutions.
It not only solves existing issues. It prepares teams for future challenges. With RCA, technical teams build resilience and adaptability.

What is the role of documentation in troubleshooting strategies?
The Essence of Documentation in Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting remains an integral aspect of technical operations. It involves the systematic identification and resolution of problems within software, hardware, or systems. Effective troubleshooting requires methodical strategies and resourceful tools. Documentation stands as a pillar within these strategies, providing a framework for understanding, diagnosing, and resolving issues.
Documentation Offers Clarity
Documentation serves as the roadmap for systems and processes. It delineates the architecture and functionality of systems, enabling technicians to grasp complex interdependencies swiftly. With documentation, one has a point of reference. This clarity minimizes errors during diagnosis and fosters more accurate resolutions.
It Enhances Efficiency
Access to comprehensive documentation accelerates troubleshooting. Technicians can bypass the trial-and-error phase, proceeding directly to informed hypothesis testing. Documentation outlines standard operating procedures, making repetitive tasks faster and less prone to error.
- Guides offer speedy insight
- Flowcharts simplify complex processes
- Manuals provide detailed instructions
Documentation Aids in Knowledge Transfer
Documentation ensures knowledge persists beyond individual tenure. It captures expertise in a tangible format, enabling new team members to troubleshoot effectively. This transfer is vital for maintaining system integrity over time.
- Checklists ensure consistency
- FAQ sheets answer common queries
- Knowledge bases centralize information
It Enables Scalability
As organizations grow, the demand on support teams escalates. Documentation allows these teams to scale by providing a repository of solutions. Consistent documentation across the board ensures that all team members address issues uniformly.
Documentation Facilitates Continuous Improvement
The troubleshooting process benefits greatly from continuous improvement. Documentation that includes historical problems and their solutions becomes a precious learning tool. Teams can analyze past incidents to improve future responses.
- Logs can track recurring issues
- Reports highlight areas for development
- Reviews lead to process optimization
Conclusion
In conclusion, documentation is the backbone of effective troubleshooting. It empowers quick understanding, efficiency, knowledge transfer, scalability, and ongoing improvement. Its role is indispensable in crafting a strategic approach to problem-solving within technical environments.


