Unionization has long been a significant factor in workplaces around the world. Unionization is part of a single union or the collective bargaining unit formed between a group of workers or employees and employers or an employer.
The primary purpose of unionization is to provide numerous job and workplace protections, such as increased job security, better wages, better working conditions, vacation and sick days, and more. Unionization has a long history, starting in the 19th century, and is still relevant today. In this blog post, we explore the impact of unionization on organizations, looking into both the positive and negative effects of unionization, mitigation strategies, and examples of successful unionizations.
Research on Organizational Impact
There have been numerous studies and surveys conducted on the impacts of unionization on organizations. Some positive effects of unionizing include increased job satisfaction, improved workplace safety and welfare, increased wages and benefits, and improved access to health insurance and retirement plans. Additionally, unionized employees have more access to resources, such as legal and job protection, which can help to reduce workplace grievances.
Unfortunately, there are some potential adverse effects of unionization on organizations. For instance, unionization can lead to increased labor disputes, strikes, delays in production, and possible legal costs. Additionally, union rules and regulations can make it difficult for organizations to adapt to changes in the market, leading to fewer opportunities for innovation and reduced agility.
Potential Mitigation Strategies
Fortunately, organizations can use some potential strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of unionization. One of the most important strategies is ensuring effective union-employer relations management. This can be done through employee engagement and training, which can help to create a more collaborative and open relationship between management and union representatives.
Furthermore, improved hiring processes can ensure that workers suitable for union membership are hired for the organization. Finally, organizations should also focus on providing enhanced wages and benefits for their employees to reduce the need for such workplace benefits to be negotiated through the union.
Examples of Successful Unionizations
There are numerous examples of successful unionization efforts in organizations. For instance, the American Federation of State, County, and Municipal Employees (AFSCME) is the largest union in the United States and has leveraged its collective bargaining power to negotiate improved wages and benefits for its members. Additionally, Air Canada is one of the many airline unions in the country, and its unionized members have successfully negotiated various uses, including pension and vacation days.
Conclusion: Unionization can have both positive and negative impacts on organizations. The positive effects of unionization include increased job satisfaction and improved workplace safety and welfare. The adverse effects can include increased labor disputes, delays in production, and potentially higher legal costs.
There are specific strategies that organizations can consider to mitigate the potential negative impacts, such as improved hiring processes and improved wages and benefits. However, further research is necessary to understand unionization's implications better and explore possible mitigation strategies.
When organizations prioritize, the interests of their employee's collective progress lead the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What impact does unionization have on the overall functioning of an organization?
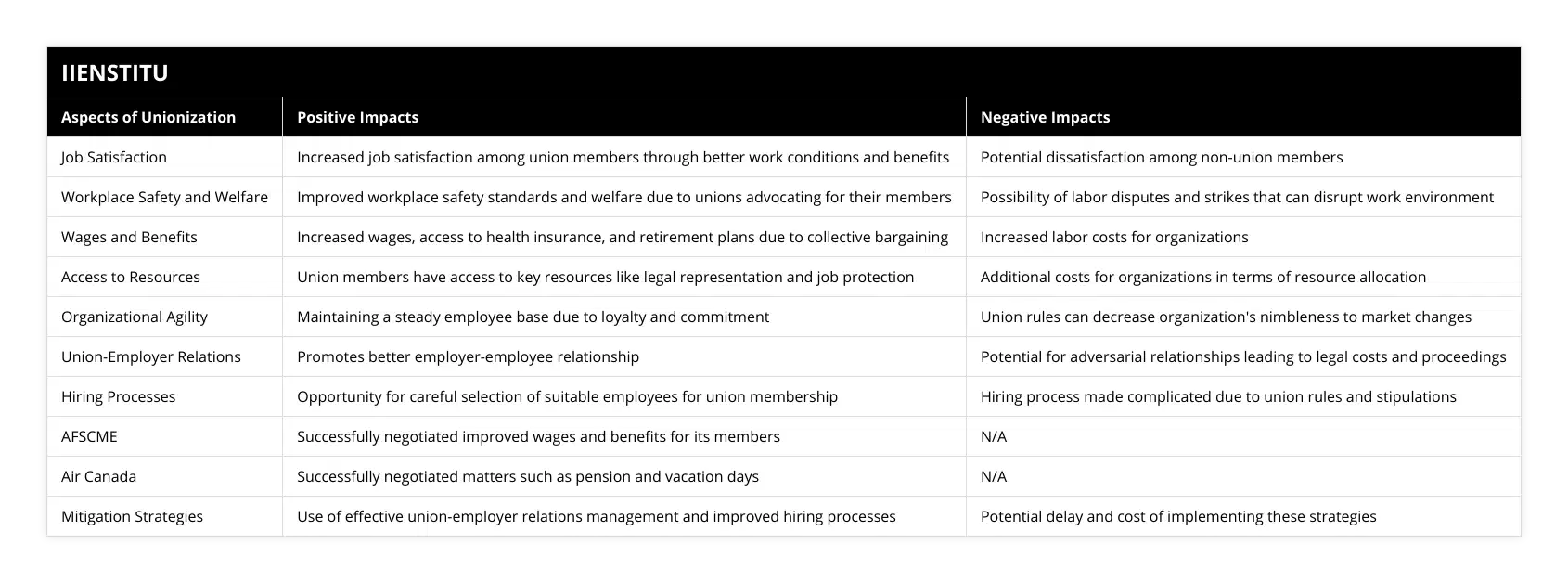
The ability of workers to form a labor union and collectively bargain with their employers has a significant impact on the overall functioning of an organization. Whether the block accepts or rejects the employer’s contract offer, each side wants a fair and equitable agreement to benefit the workforce. Unions can increase wages, provide better benefits, improve job security, and protect from unjustified dismissal and other abuses.
The unionization of workers can increase employee motivation, improve job satisfaction and create a better workplace atmosphere. As the union increases wages, benefits, and job security, employees may feel more secure in their jobs and work harder, produce higher quality work, and increase productivity and customer satisfaction. In addition, the additional wages and benefits of unionization lead to improved morale among employees who sense greater recognition for their efforts.
Unions can also effectively bargain with the employer for more worker-friendly policies on health care, vacation, and overtime pay. Union membership often results in a better work-life balance for employees, resulting in improved job performance.
On the other hand, organizations may experience higher labor costs due to unionization. This is because employers must pay union dues and give union members higher wages and benefits. Additionally, union-mandated rules can present operational and budgetary challenges.
Unionized organizations also have to deal with labor-management tension. This can lead to increased employee turnover and a less cooperative work environment. Additionally, unions may oppose restructuring and automation, hampering the organization’s ability to stay current and competitive.
In conclusion, unionization can have a significant impact on the overall functioning of an organization. Unions can improve wages, benefits, and job security, leading to higher employee motivation, job satisfaction, and a better workplace environment. However, they can also lead to higher labor costs, labor-management tension, and opposition to changes. Therefore, organizations must weigh the pros and cons before deciding whether to unionize their workforce.
What are some of the benefits of unionization for employees?
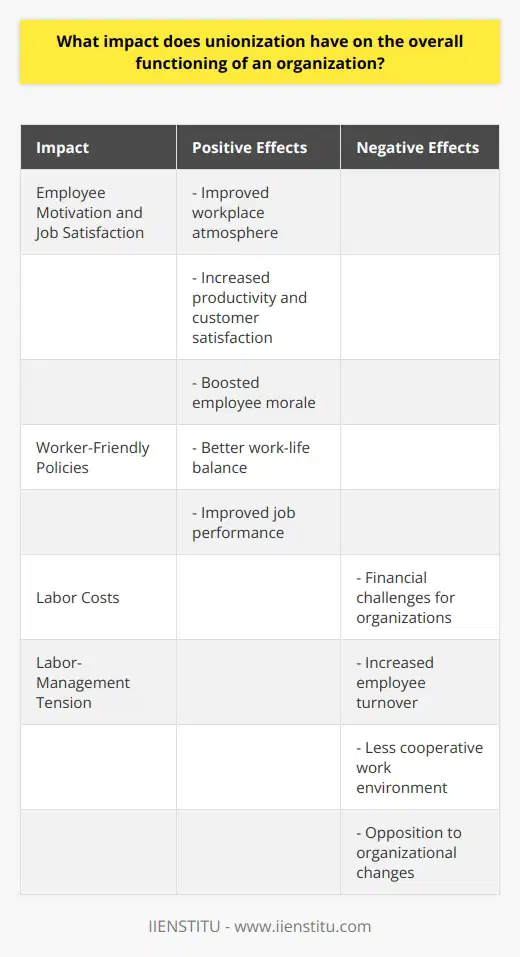
Unionization is a benefit for employees in many ways. Workers joining together and forming a union can have a collective voice and gain improved job security, wages, and working conditions.
First, unions can provide enhanced job security to employees. The association organizes bargaining units, which are groups of employees in the same job who have joined together to bargain with the employer. These bargaining units may negotiate better terms in the case of layoffs or downsizing and can fight to eliminate any unjust firings. This gives employees more job protection and assurance that their job is secure.
Second, unionization can offer increased wages and benefits. Union bargaining units can negotiate wages and benefits packages with employers, providing employees with more money and improved benefits. Unions can also arrange additional vacation or sick pay, retirement, holiday pay, and other job-related benefits. These increases in wages and benefits can make a significant difference in employees' lives.
Finally, unionization can improve working conditions for employees. Unions can advocate for safer workplaces with better working conditions. They can negotiate for better hours, more breaks, improved health and safety measures, and better resource access. By joining together, workers can work to improve their work environment and make it more conducive to a better working experience.
In conclusion, unionization can provide many employee benefits, including increased job security, better wages, and improved working conditions. In addition, employees can gain collective power and ensure their interests are considered remade by joining together and forming a union. This can result in employees' better quality of life and contribute to a healthier and more productive workplace.
How does unionization influence labor relations in an organization?
In today's world, labor relations between employers and employees have become increasingly important, and the role of unionization in this context has taken on central importance. This article seeks to explain how unionization affects labor relations in an organization.
At its most basic, unionization is collective bargaining between workers and employers. This unionized labor aims to secure better wages, better working conditions, job security, benefits, and fair treatment for all union members. Unionized labor does this through collective negotiations with employers, representing the collective interests of its members.
When unionization enters a labor relationship, positive and negative factors affect the relationship between employers and employees. On the positive side, unionization may increase workers' collective bargaining power, allowing them to negotiate more effectively and strengthen their voices. Additionally, it provides enhanced protection for workers against exploitation and unfair treatment. The union can pursue legal remedies on behalf of its members if they experience discrimination or any other form of mistreatment.
At the same time, unionization may lead to increased labor costs for the organization since unionized workers generally demand higher wages than non-union workers. Furthermore, unions may use their collective bargaining power to delay or even completely prevent any attempts at automation, which can limit the organization's ability to remain competitive.
The level of unionization within a given organization may also influence its labor relations. When unionization is high, the union can usually block or significantly delay any management-initiated changes, making labor relations more adversarial. On the other hand, low levels of unionization can leave workers in a more vulnerable position, as they lack the collective bargaining power that the union can provide.
In conclusion, unionization can significantly influence labor relations in an organization. It can provide workers with substantial collective bargaining power and enhanced protection against exploitation. Still, it may also lead to increased labor costs and limit the organization's ability to remain competitive. Therefore, employers need to be aware of these potential effects when assessing the benefits and costs of unionization.

What impact did labor unions have on workplaces?
Impact on Working Conditions
Labor unions have significantly shaped and improved working conditions in numerous workplaces globally. By representing their members' interests, they bargain for better wages, fair work hours, and enhanced job security. Labor unions advocate for their members' rights, ensuring a substantial improvement in employee well-being and satisfaction.
Role in Workplace Safety
Furthermore, labor unions have played a pivotal role in enhancing workplace safety standards. They challenge employers to ensure adherence to safety regulations, thus compelling companies to offer safe working environments. Improved safety standards have led to the reduction in workplace accidents and injuries, as well as fostering a health-conscious organizational culture.
Influence on Employment Equality
Another notable impact of labor unions on workplaces is their promotion of employment equality. Labor unions actively address discriminatory practices, such as gender wage gaps and limited access to job opportunities for underrepresented groups. Consequently, they contribute to fostering more diverse and inclusive workplaces that guarantee equal treatment for all employees.
Effect on Worker Empowerment
Labor unions have also played an essential role in worker empowerment by providing a platform for them to express their grievances and negotiate for better working conditions. This collective voice allows employees to shape company policies and practices, resulting in a more democratic work environment that values worker input.
Conclusion
In summary, the impact of labor unions on workplaces has been profound and wide-ranging. Through advocating for improved working conditions, enhanced safety standards, employment equality, and worker empowerment, labor unions have contributed substantially to more equitable and safe employment environments.
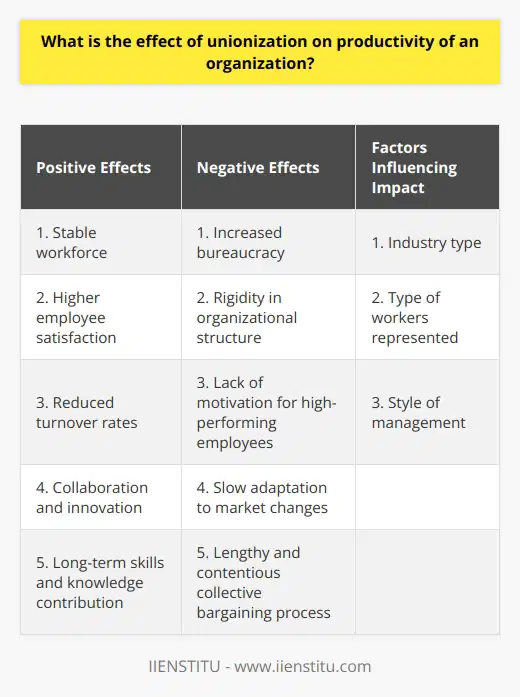
What is the effect of unionization on productivity of an organization?
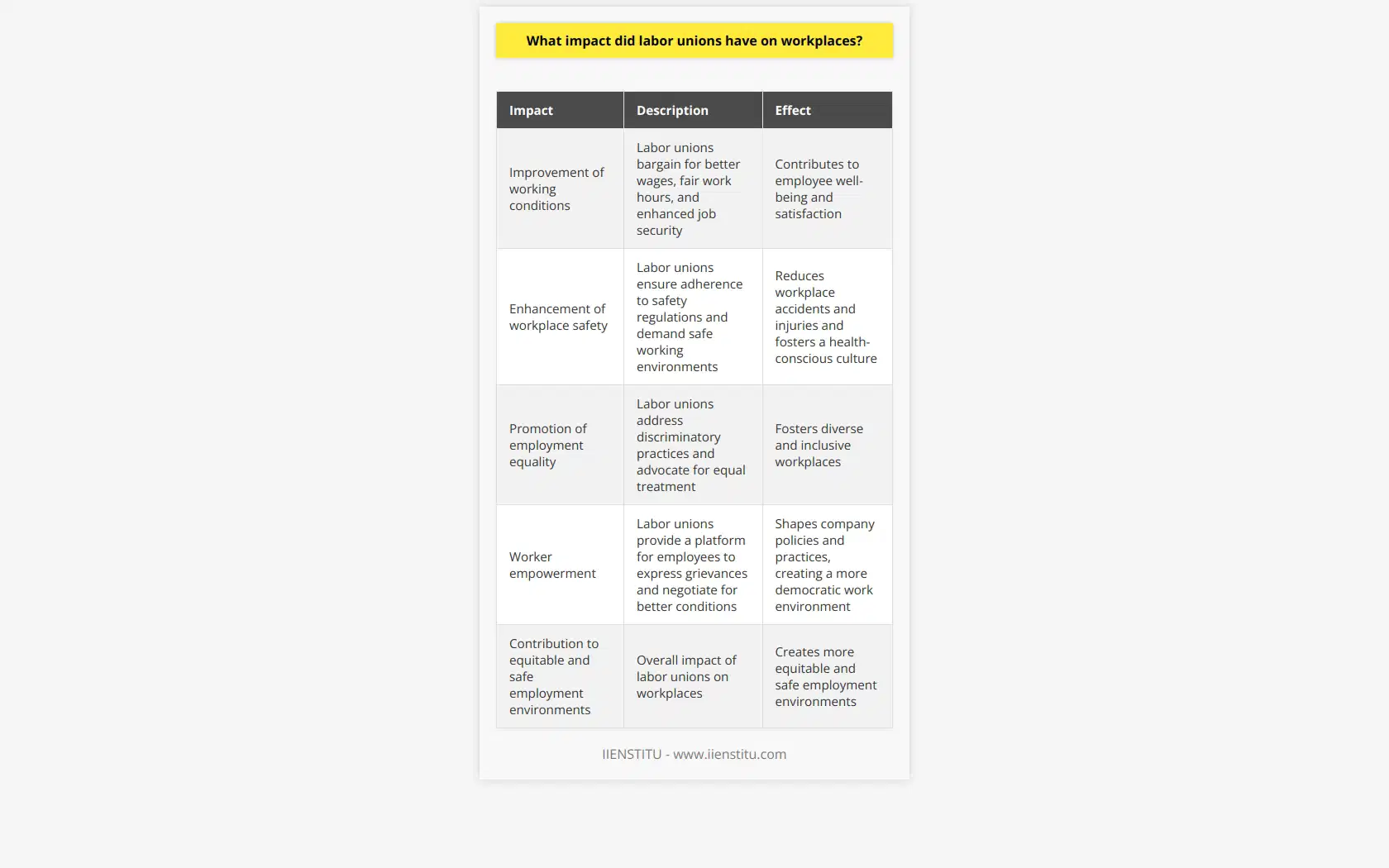
**Union-Productivity Relationship**
The effect of unionization on the productivity of an organization has been a topic of significant debate. Some argue that unions lead to higher productivity, while others claim that they cause a decline in efficiency. Nevertheless, examining the evidence reveals a complex relationship between unionization and productivity.
**Positive Impacts on Productivity**
One argument for the positive effect of unions on productivity is that they ensure a more stable workforce. Unions can provide employees with better wages and working conditions, making them more satisfied with their jobs and reducing turnover rates. Additionally, unions can foster a more collaborative work environment, where employees feel empowered to communicate and contribute their ideas. This involvement in decision-making can lead to innovation and increased organizational efficiency.
**Negative Impacts on Productivity**
Conversely, critics argue that unions can reduce productivity due to the potential for increased bureaucracy and rigidity in organizational structure. Unions may prioritize seniority over performance, resulting in a workforce that is not always optimally utilized. Furthermore, unionized organizations may be slower to adapt to changes in market conditions or technological advancements due to the collective bargaining process, which can be lengthy and contentious.
**Moderating Factors**
The specific impact of unions on productivity may depend on several factors. These may include the industry in which the organization operates, the type of workers being represented, and the style of management. An organization that is heavily reliant on skilled labor may experience a stronger positive effect from unionization, as unions can help ensure the retention of these valuable employees. On the other hand, industries with a low-skilled workforce may be more susceptible to the negative effects of unions.
In conclusion, the effect of unionization on the productivity of an organization is multifaceted and depends on several factors. While unions can provide benefits in terms of worker stability and involvement, they may also introduce inefficiencies due to increased bureaucracy and reduced adaptability. Understanding this complex relationship can be useful for organizations considering unionization, as well as policymakers and researchers studying labor issues.
How are unions beneficial to companies?
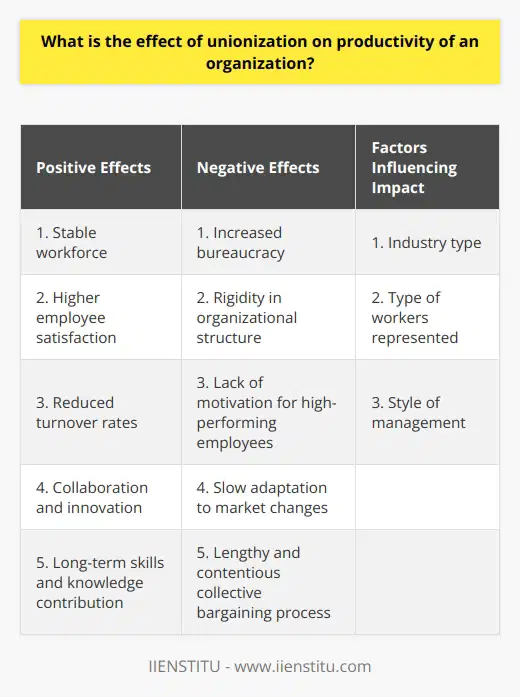
Advantages of Unions for Companies
Employee Satisfaction
Unions significantly contribute to companies by improving employee satisfaction. By negotiating fair wages, benefits, and working conditions, unions help reduce employee turnover and foster an engaged workforce. Furthermore, employees who feel valued are more productive and contribute positively to the company's growth.
Conflict Resolution
Unions provide a structured means for addressing employee grievances and resolving conflicts. By establishing a collective bargaining process, companies can alleviate interpersonal disputes and avoid costly litigation. In this regard, unions create an environment that promotes harmonious labor relations and supports the longevity of the company.
Health and Safety Standards
Unions work to ensure that companies uphold health and safety standards in the workplace. By doing so, they reduce the risk of accidents and injuries, minimizing workers' compensation claims and improving employee well-being in the process. Adherence to these standards also showcases the company's commitment to employee welfare and enhances its reputation.
Training and Skill Development
Many unions offer training and skill development programs for their members. By investing in employee education, unions help increase productivity and improve the quality of work that companies can expect from their workforce. In turn, this investment contributes to the competitiveness and success of the company in the market.
Promoting Equality and Fairness
Unions engage in collective bargaining in pursuit of equity and fairness for all employees. This encourages companies to adopt policies and practices that minimize discrimination, promote equal opportunity, and foster diversity. Ultimately, companies that promote an inclusive work environment experience increased morale and employee cohesion.
In summary, unions offer manifold benefits to companies. By pursuing employee satisfaction, conflict resolution, health and safety standards, training and skill development, and the promotion of equality and fairness, unions contribute significantly to a company's success and enhance its position in the market.
What are three negative effects of labor unions?
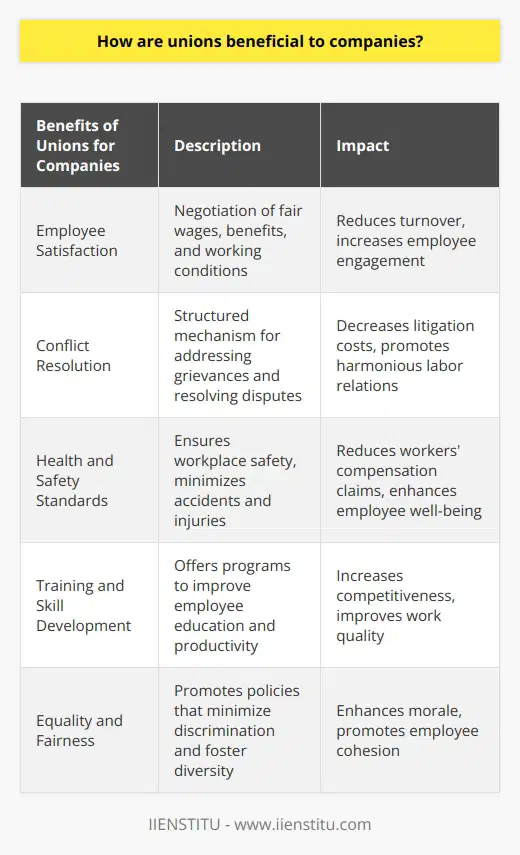
Negative Effect 1: Strikes and Disruptions
One of the most prominent negative effects of labor unions is the occurrence of strikes and work disruptions. When negotiations between union members and employers become stagnant, workers may choose to go on strike, leading to a halt in production and delivery of essential goods and services. Strikes not only create tension between employees and employers but also affect consumers who rely on the timely provision of such goods and services.
Negative Effect 2: Limiting Workplace Flexibility
Another unfavorable outcome of labor unions is the reduction of workplace flexibility. Strict union rules and regulations often require employers to adhere to specific hiring processes and seniority-based promotions, limiting chances for talented and deserving individuals to excel. Further, the inflexible working conditions may also prevent a company from quickly adapting to market changes or technological advancements, thereby hindering its overall growth and development.
Negative Effect 3: Increased Costs
The third negative effect of labor unions is the burden of increased costs for businesses. Unionized workers often demand higher wages, better benefits, and improved working conditions. While some of these demands are reasonable and just, meeting them frequently comes at the expense of a company's profitability. Higher labor costs may lead to higher prices for products and services, negatively affecting consumers and making it difficult for businesses to remain competitive in the market.
In conclusion, labor unions, although established with the noble intention of protecting workers' rights, can negatively impact various stakeholders, including employers, employees, and consumers. Strikes and disruptions cause significant delays and economic loss, while the rigidity of workplace rules hampers progress and innovation. Lastly, the increased costs of accommodating union demands can erode profits and hinder businesses from maintaining a competitive edge in the market. Considering these negative consequences, it is crucial for labor unions and employers to work collaboratively in finding mutually beneficial solutions that serve the interests of all parties involved.
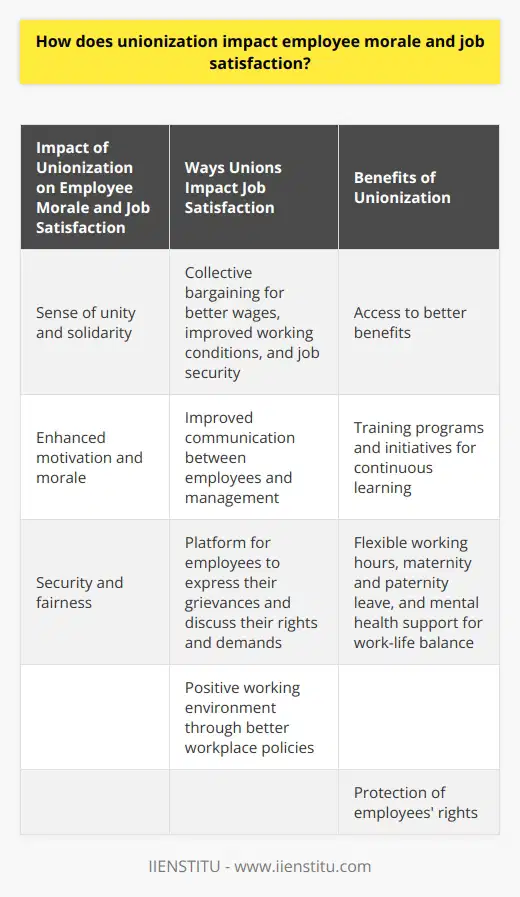
How does unionization impact employee morale and job satisfaction?
Impact on Employee Morale
Unionization can undoubtedly influence employee morale in various ways. First and foremost, it fosters a sense of unity among workers. When employees join forces under the same organization, they feel that their concerns are adequately represented, enhancing their motivation in the workplace.
Influence on Job Satisfaction
Furthermore, unions often engage in collective bargaining to negotiate employee benefits, such as better wages, improved working conditions, and job security. Consequently, these negotiated agreements enhance job satisfaction among unionized employees. Knowing that they have protection against arbitrary dismissal and the assurance of fair compensation enhances worker satisfaction in their jobs.
Improved Communication
Effective communication between employees and management is a critical determinant of employee morale and job satisfaction. Unionization helps bridge this communication gap by providing an organized platform for employees to express their grievances and discuss their rights and demands with the management. This improved communication can lead to better workplace policies, creating a positive working environment.
Training and Skill Development
Unions often provide access to training programs and skill development initiatives that enable employees to enhance their competencies, grow in their careers and stay relevant in the job market. This continuous learning culture significantly boosts employee morale, as well as their satisfaction with their job roles.
Addressing Work-Life Balance
Lastly, unions recognize the importance of work-life balance in maintaining employee morale and job satisfaction. They frequently negotiate for policies such as flexible working hours, maternity and paternity leave, and mental health support. These initiatives can significantly improve employees' quality of life and consequently contribute to increased satisfaction levels in their jobs.
In conclusion, unionization can have positive effects on employee morale and job satisfaction by offering protection, improving communication, and addressing work-life balance concerns. Access to better benefits, skill development opportunities and a positive work environment can heighten employees' motivation and satisfaction within their job roles.
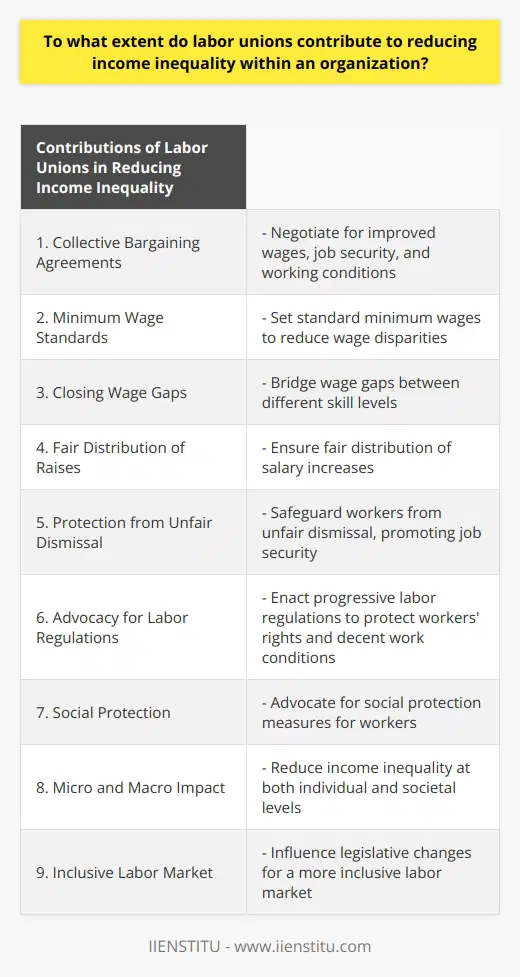
To what extent do labor unions contribute to reducing income inequality within an organization?
Role of Labor Unions in Reducing Income Inequality
Labor unions serve a significant function in addressing income inequality within an organization. By representing workers in collective bargaining agreements, unions actively contribute to the negotiation of better wages, job security, and working conditions. As a result, income inequality is substantially reduced amongst their members.
Wage Negotiations and Re-distribution
Through their collective bargaining efforts, labor unions secure equitable wage increases for their members. They establish a standard minimum wage, close the wage gap between skilled and unskilled workers, and ensure that raises are fairly distributed amongst employees. This equalizing effect holds significant importance in reducing income disparities on a micro level.
Job Security and Membership Benefits
Another vital component of labor unions' impact on income inequality is their role in promoting job security. By negotiating on behalf of their members, unions protect employees from unfair or arbitrary dismissal. Consequently, they ensure a stable flow of income and a higher degree of predictability for workers who might otherwise face instability and vulnerability in the labor market.
Collective Bargaining and Legislation
Labor unions also have an indirect impact on income inequality across industries by advocating for inclusive labor market policies. These organizations engage with lawmakers to enact progressive labor regulations that safeguard workers' rights, promote decent work conditions, and secure adequate social protection. As a direct outcome of such collective endeavors, a more equal society emerges in terms of income distribution.
In conclusion, labor unions significantly contribute to reducing income inequality within an organization by effectively negotiating for fair wages, job security, and better working conditions. Moreover, they engage in advocacy at the legislative level, promoting inclusive labor market policies that lead to broader improvements in income distribution. Overall, labor unions remain a crucial force in mitigating income disparities and fostering more equitable and inclusive workplaces.
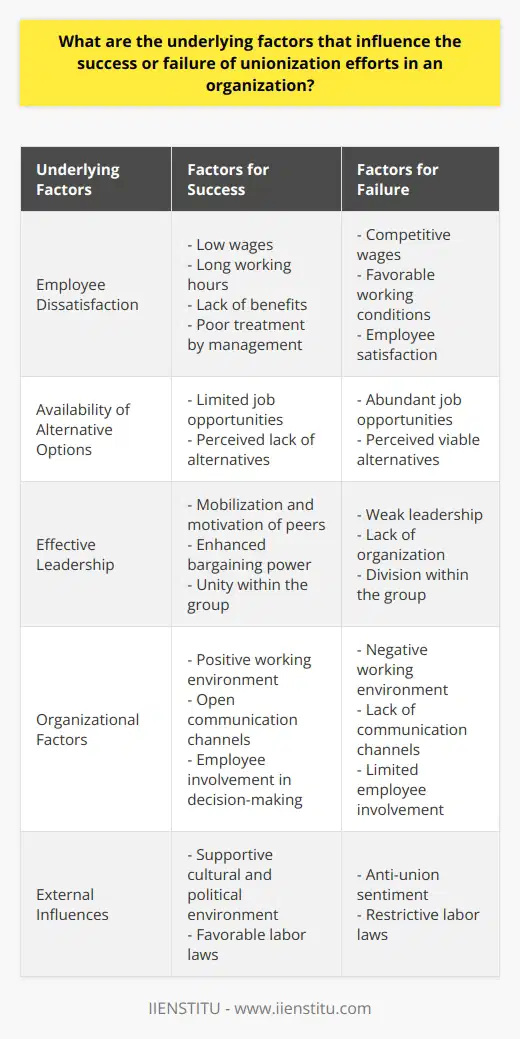
What are the underlying factors that influence the success or failure of unionization efforts in an organization?
Underlying Factors in Unionization Efforts
Success Factors
One crucial factor influencing the success of unionization efforts in an organization is employee dissatisfaction with their working conditions, wages, and benefits. Disgruntled employees are more likely to join or support a union to collectively bargain for improved conditions. Additionally, a lack of alternative options in the job market can encourage employees to unionize, as they may perceive collective bargaining as their most effective avenue for negotiation.
Effective Leadership
Another factor contributing to unionization success is effective leadership within employee groups keen on unionizing. Strong leaders have the ability to mobilize and motivate their peers, enhancing their group's bargaining power. Additionally, a well-organized and cohesive group of employees is more likely to attract the support of established unions and garner resources necessary for effective negotiation with the organization.
Organizational Factors
On the other hand, unionization efforts may face challenges in organizations that provide competitive wages and favorable working conditions. Employers who prioritize employee satisfaction and demonstrate a willingness to work collaboratively with their workforce may undercut the perceived need for unionization. Factors such as a positive working environment, open communication channels, and strong employee involvement in decision-making processes can also deter unionization efforts.
Challenges to Unionization
External factors, such as prevailing cultural, political, and legal environments, may hinder unionization efforts. In certain regions, anti-union sentiment may be prevalent, creating barriers to organizing and limiting potential support for employee groups. Furthermore, some jurisdictions have implemented labor laws designed to restrict union activities and protect employer rights. These restrictive legislative frameworks can discourage or outright impede unionization efforts in organizations.
In conclusion, the success or failure of unionization efforts in an organization is influenced by a combination of internal and external factors. Employees' dissatisfaction with their conditions and the presence of strong leadership within employee groups can promote successful unionization. Meanwhile, favorable working environments and external anti-union influences may pose challenges to these efforts.
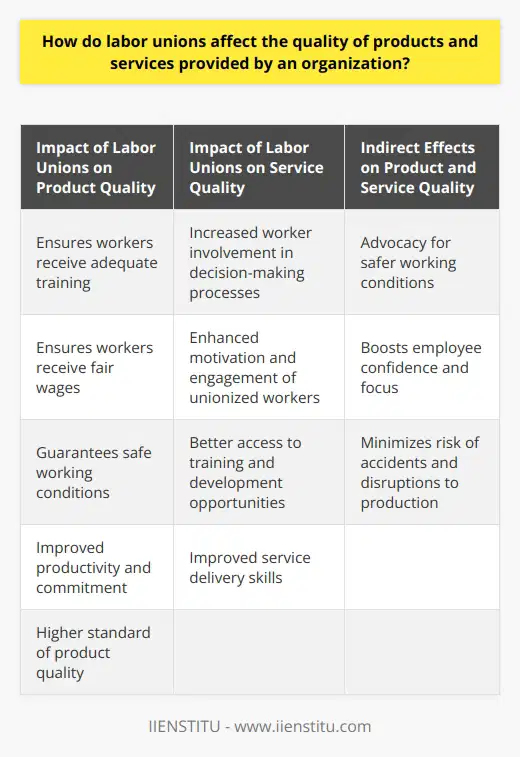
How do labor unions affect the quality of products and services provided by an organization?
Impact on Product Quality
Labor unions significantly influence the quality of products and services provided by an organization. They play a crucial role in ensuring workers receive adequate training, fair wages, and safe working conditions. These factors contribute to a higher standard of product quality, as employees who are well-trained, fairly compensated, and satisfied with their work environment tend to be more productive and committed to the company's success.
Influence on Service Delivery
Furthermore, labor unions affect the quality of services provided through employee motivation and engagement. Unionized workers are more likely to be actively involved in decision-making processes, which gives them a sense of ownership and pride in the organization's performance. Union members also have better access to additional training and development opportunities, which directly benefits their service delivery skills.
Workplace Safety Improvements
By advocating for safer working conditions, labor unions can indirectly contribute to improved product and service quality. Employees who are confident that their safety concerns are being addressed are more likely to focus on their job responsibilities and provide exceptional service consistently. Additionally, a secure work environment minimizes the risk of accidents or injuries that could disrupt production and negatively impact an organization's offerings.
Strike Effects on Quality
However, labor unions can also adversely affect the quality of products and services provided in situations where strikes or other work stoppages occur. These events can lead to delays in production or delivery, which can diminish product quality and overall customer satisfaction. While strikes may be necessary in some cases to improve working conditions or negotiate fair wages, it is essential to consider the potential negative impact on the organization's output and reputation.
Balancing Interests for Quality Assurance
In summary, labor unions significantly impact the quality of products and services that organizations provide. While they can improve work conditions, employee satisfaction, and safety, they may also cause disruptions to business operations when disagreements arise. Therefore, it is crucial for companies and labor unions to work together, finding a balance between meeting worker demands and ensuring that their commitments to customers for high-quality products and services are maintained.
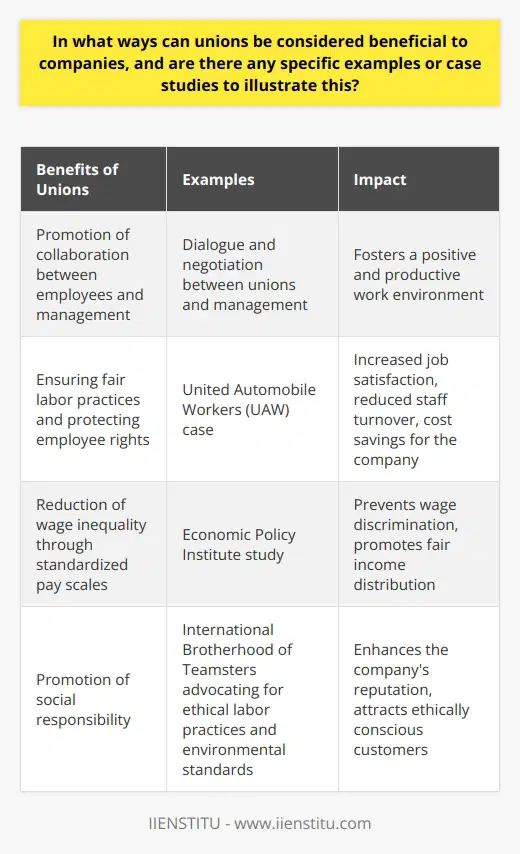
What role do labor unions play in shaping the employment and labor policies within an organization?
Labor Unions and Employment Policies
Labor unions play a vital role in shaping employment and labor policies within an organization through collective bargaining, advocating for workers' rights, and promoting fair labor practices.
Collective Bargaining
One of the primary functions of labor unions is negotiating employment terms and conditions, such as wages, working hours, and benefits, through a process called collective bargaining. Unions represent workers in negotiations with employers, ensuring that employees receive fair compensation and just working conditions. This collective bargaining power translates into influential input on labor policies, leading to better outcomes for workers within an organization.
Workers' Rights Advocacy
Labor unions advocate for the protection and enforcement of workers' rights as a crucial aspect of their mission. They work to ensure that organizations adhere to labor laws and regulations, along with promoting policies that support employee well-being. Through advocacy efforts, unions help shape workplace policies on issues such as health and safety, discrimination, and harassment. The role played by labor unions in advancing workers' rights directly influences the development and implementation of employment and labor policies within an organization.
Promotion of Fair Labor Practices
Promoting fair labor practices is another critical function of labor unions. They focus on creating equitable workplaces by addressing systemic issues, such as gender and racial inequalities. By actively pushing for fair labor practices, unions contribute to shaping equitable and inclusive labor policies. This commitment to fairness helps create work environments where all employees can thrive and succeed, regardless of their background or identity.
Conflict Resolution
Labor unions provide assistance in resolving workplace conflicts and disputes through established grievance procedures. These resolution processes ensure that employees can submit complaints and concerns without fear of retaliation. The union's involvement in resolving work-related disputes allows for a more just and equitable enforcement of labor policies within an organization.
In summary, labor unions actively contribute to shaping employment and labor policies within an organization by collectively bargaining for better working conditions, advocating for workers' rights, and promoting fair labor practices. Additionally, through conflict resolution processes, they help organizations enforce fair and equitable labor policies. This crucial role played by labor unions leads to improved working environments, benefiting employees and organizations alike.
What impact do unions have on company profits and can this effect be explained?
Unions' Influence on Company Profits
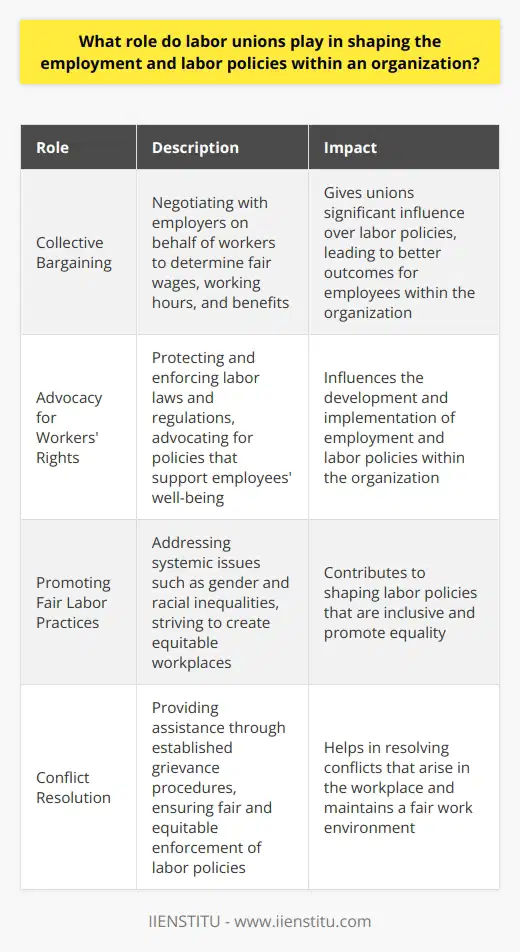
Unions significantly impact company profits by advocating for better wages, working conditions, and benefits for employees. This effect can be explained through various factors, such as negotiation power, influence on labor productivity, and union density.
Negotiation Power
One of the primary functions of a union is to represent employees in negotiating with employers on issues such as pay, working hours, and job security. When unions successfully negotiate better compensation packages for their members, the labor costs for companies increase, leading to reduced profits.
Labor Productivity Influence
Unions may have a positive effect on labor productivity by advocating for better working conditions, which can lead to increased employee motivation and commitment. Improved productivity can enhance the company's overall financial performance, potentially offsetting the costs associated with higher wages and benefits.
Union Density
The degree to which unions can impact company profits also depends on union density, which refers to the percentage of workers in a company or industry who are union members. High union density gives unions more bargaining power in negotiations, which can lead to greater effects on labor costs and company profits.
In conclusion, unions can have a substantial impact on company profits due to their role in advocating for improved wages, benefits, and working conditions for employees. The magnitude of this effect depends on various factors, such as the unions' negotiation power and influence on labor productivity, as well as the level of union density in the company or industry.
How do the pros and cons of unionizing a company influence organizational decision-making?
Influence of Unionization on Decision-Making
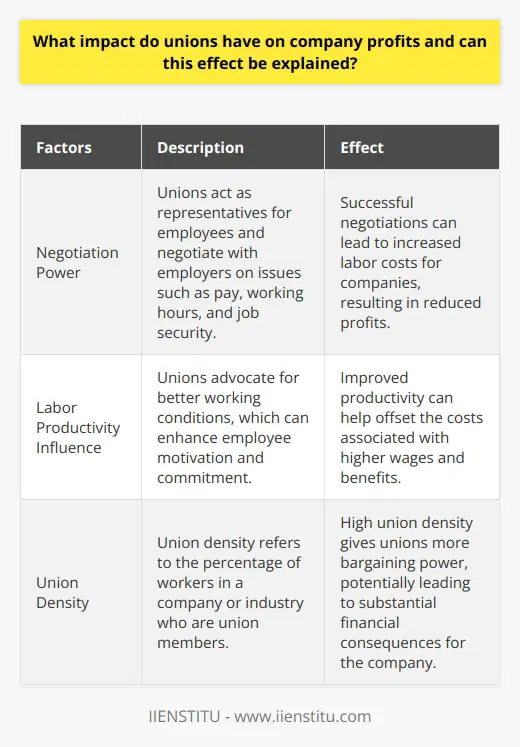
**Pros of Unionization**
Unionization significantly affects organizational decision-making in several ways. Firstly, by enhancing employee involvement during decision-making, it strengthens communication channels and nurtures a sense of responsibility among workers. When the workforce is actively engaged, management can access valuable insights resulting in better-informed decisions.
Additionally, unionization ensures employee rights, which improves overall job satisfaction and retention rates. Happier employees perform better, leading to desirable outcomes and effective decision-making. Furthermore, unions facilitate a fair bargaining process, promoting transparency in deciding wages, benefits, and working conditions. This clarity of expectations minimizes misunderstandings and fosters trust between workers and management.
**Cons of Unionization**
Conversely, unionization also poses challenges to organizational decision-making processes. Unions may create rigidity by enforcing strict rules and procedures, limiting the flexibility of the management in formulating policies. These constraints can hinder efficiency and impede the company's ability to adjust to market demands.
Moreover, adversarial relationships might emerge between the management and the union, causing prolonged negotiations, conflicts, and delayed decisions. Companies may become less competitive due to the increased complexity in decision-making. Excessive demands by unions may lead to higher costs, reducing the organization's ability to invest in growth and innovation.
**Balancing Pros and Cons**
In order to make optimal decisions, organizations need to find a balance between the advantages and challenges of unionization. Management should adopt a collaborative approach, recognizing the value of an empowered workforce while ensuring that union demands do not obstruct progress. Communication, willingness to compromise, and a proactive attitude can help companies to strike the right balance between employee rights, organizational mobility, and sustainable growth.
In conclusion, the pros and cons of unionizing a company influence organizational decision-making by affecting communication, employee involvement, and management flexibility. Striving for a healthy balance between these factors is essential for the organization's overall success.
In what ways can unions be considered beneficial to companies, and are there any specific examples or case studies to illustrate this?
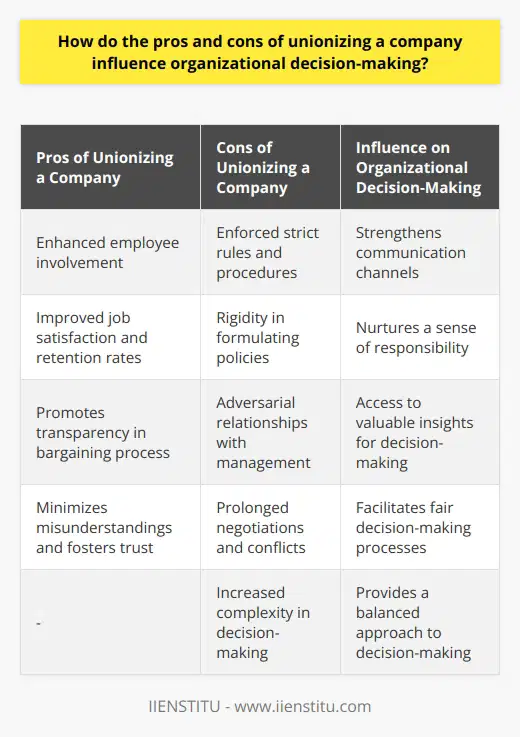
Promoting Collaboration between Employees and Management
Unions can be considered beneficial to companies in various ways such as promoting collaboration, ensuring fair labor practices, and increasing employee satisfaction. One of the primary benefits is the facilitation of communication between employees and management. By representing the collective interests of workers, unions help create a platform for dialogue and negotiation, encouraging a cooperative environment. This collaboration can lead to the development of better workplace policies and improved working conditions.
Enhancing Employee Satisfaction and Retention
Moreover, unions play an essential role in ensuring that employees are treated fairly and their rights are protected. When workers feel that their concerns are being addressed and their rights upheld, their satisfaction and morale are significantly increased. Higher employee satisfaction often leads to reduced staff turnover, ultimately benefiting the company in the form of reduced recruitment and training costs. The well-known case of the United Automobile Workers (UAW) demonstrates this benefit. As a result of the UAW's efforts, workers in unionized automobile plants in the United States experienced improved wages, benefits, and working conditions, which led to higher job satisfaction and loyalty.
Reducing Wage Inequality
Unions also contribute to reducing wage inequality by advocating for standardized pay scales and collective bargaining power. By negotiating on behalf of employees, unions can ensure that wages reflect the value of work and promote equality among workers. This standardized approach can prevent wage discrimination and contribute to a fairer distribution of income within the company. A study conducted by the Economic Policy Institute showed that unions helped reduce the wage gap between workers in various industries, such as manufacturing and service sectors.
Fostering Social Responsibility
Furthermore, unions can contribute to a company's corporate social responsibility by promoting ethical labor practices and environmental standards. For example, the International Brotherhood of Teamsters has played a crucial role in advocating for environmentally friendly transportation policies and promoting social responsibility within the transportation sector. By adhering to these practices, companies can enhance their reputation and attract customers who prioritize ethical consumption.
In conclusion, unions offer several benefits to companies, including promoting collaboration, ensuring fair labor practices, and fostering social responsibility. These benefits can lead to increased employee satisfaction, reduced turnover, and a positive reputation, ultimately contributing to the company's long-term success.
What are the benefits of unionization to the organization?
**Collective Bargaining Advantages**
Unionization brings several benefits to an organization, one of which is collective bargaining. Collective bargaining grants employees the power to negotiate contracts, wages, working conditions, and hours directly with the organization. As a result, a fairer agreement can be reached, leading to labor stability, increased morale, productivity, and reduced employee turnover rates.
**Employer-Employee Relationship Enhancement**
Union representation contributes to improved employer-employee relationships, as it encourages a more professional and respectful work environment. Unions provide a platform for employees to voice their concerns and grievances, which can lead to the resolution of workplace disputes more efficiently and effectively. In turn, this fosters a more open and transparent work culture that promotes trust, job satisfaction, and optimal performance among workers.
**Employee Rights Protection**
Unionization safeguards employees' rights, ensuring that they receive wages commensurate with their skills and experience. Unions work diligently to promote and enforce labor laws, inclusive of fair labor practices, minimum wage legislation, and safe working conditions. Consequently, organizations can decrease the potential for workplace conflicts and violations that might otherwise culminate in costly legal battles and negative publicity.
**Standardization of Workplace Policies**
Through unionization, organizations can develop clearly defined workplace policies that promote consistency, fairness, and equal treatment for all employees. Union-negotiated agreements address critical issues, such as job classifications, promotions, demotions, and grievance handling processes. These standardized policies not only foster a sense of job security but also contribute to eradicating workplace disparities and discrimination.
**Professional Development Opportunities**
Unions often provide professional development opportunities for employees in the form of training, workshops, and access to resources. Such initiatives enable employees to upgrade their skills and knowledge, promoting career advancement and improving job performance. In response, the organization benefits from having a skilled and well-trained workforce that adapts quickly to industry changes, increasing its competitive edge in the market.
In conclusion, unionization offers organizations numerous advantages, including fairer and more productive labor-management relations, improved transparency, protected employee rights, and a culture of continuous learning and development. Embracing union representation ultimately contributes to building a more harmonious, stable, and successful work environment for all stakeholders.

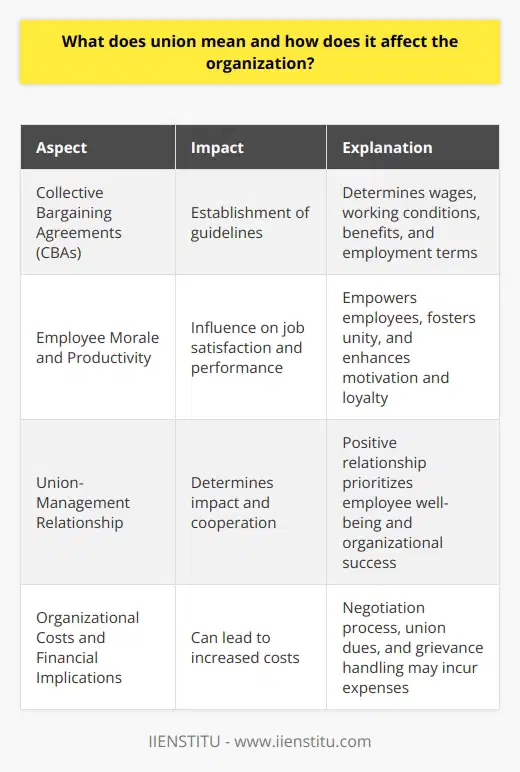
What does union mean and how does it affect the organization?
Union Definition
A union refers to an organization or association formed by a collective of workers to promote and protect their rights, interests, and welfare in the workplace. This group collaborates to negotiate with employers, primarily on aspects like wages, working conditions, benefits, and other employment terms. The ultimate goal of a union is to secure fair and equitable treatment for its members.
Impact on Organizational Operations
One significant effect of unions on organizations is the establishment of collective bargaining agreements (CBAs). These agreements create standardized rules governing working conditions, wages, benefits, and other employment terms for all union members. In effect, CBAs ensure consistency and predictability for both employees and employers.
Influence on Employee Morale and Productivity
Unions can also have a direct impact on employee morale and productivity. By voicing their concerns through a union, employees feel heard and valued. This sense of unity and empowerment can lead to increased job satisfaction and, in turn, improved productivity and performance. As a result, organizations with strong unions can leverage this advantage to foster a more positive work environment and bolster overall success.
Union-Management Relationship
The relationship between a union and an organization's management is vital in determining the union's influence on the organization. A healthy, collaborative relationship often fosters a work environment where both parties are genuinely invested in promoting employee well-being and organizational success. On the other hand, adversarial relationships between unions and management can result in conflict, negatively impacting the organization's overall performance.
Organizational Costs and Financial Implications
Unions may also have financial implications for organizations. The negotiation process for wages, benefits, and working conditions can often lead to increased costs for organizations. Additionally, union-associated expenses, such as union dues and fees associated with handling grievances, can impact an organization's financial performance. However, these costs might be offset by the benefits of having a motivated, loyal, and productive workforce.
In conclusion, unions have a multifaceted impact on organizations, affecting various aspects of operations, employee morale, management relationships, and financial performance. The degree and nature of this impact largely depend on the specific organizational context and the quality of the union-management relationship. When approached collaboratively and positively, unions can greatly contribute to an organization's overall success, encouraging employee satisfaction and loyalty.
What is the effect of unionization on productivity of an organization?
Unionization and Organizational Productivity
Understanding the Effects
The impact of unionization on an organization's productivity largely depends on the nature and objectives of both the union and the organization, as well as the strategies used to achieve their respective aims. Generally, a positive relationship exists between unionization and productivity, primarily driven by the union's influence on worker compensation, job security, and work conditions. This, in turn, leads to higher job satisfaction and motivation, directly contributing to improved organizational productivity.
Encouraging Skill Development
One significant effect of unionization is its promotion of skill development among employees. Unionized workers often have access to better training and skills development opportunities than their non-unionized counterparts. This increased investment in human capital results in a more skilled and knowledgeable workforce, which positively influences productivity levels within the organization.
Enhancing Job Satisfaction
Employees who work in a unionized environment usually have better job security, fringe benefits, and wages, as unions negotiate favorable terms and conditions for their members. This improvement in working conditions fosters higher job satisfaction among employees, which in turn reduces staff turnover rates and absenteeism, further enhancing organizational productivity.
Promoting Fairness
Unions play a crucial role in promoting fairness and equity within the workplace by advocating for collective bargaining agreements and standardized pay scales. As a result, employees experience a stronger sense of fairness and equality in their work environment, leading to improved morale and motivation. This positive work atmosphere contributes to an increase in overall organizational productivity.
Creating a Safe Work Environment
Through collective bargaining, unions work collaboratively with organizations to ensure adequate health and safety measures are in place. These measures not only help to reduce instances of workplace accidents and injuries but can also encourage employees to be more diligent and efficient in executing their tasks. By fostering a safer work environment, unionization helps to bolster employee motivation and productivity.
Balancing Benefits and Costs
However, while unionization can positively influence organizational productivity through the mechanisms outlined above, it is essential to acknowledge the potential costs associated with union activities. Negatively perceived strikes and work stoppages may offset the productivity gains. Therefore, a careful balance must be considered in evaluating the overall impact of unionization on organizational productivity.
In conclusion, unionization can lead to significant productivity gains within an organization by promoting skill development, enhancing job satisfaction, ensuring fairness, and creating a safe work environment. However, it is important to consider the potential costs and challenges related to union activities to accurately assess the overall impact on organizational productivity.
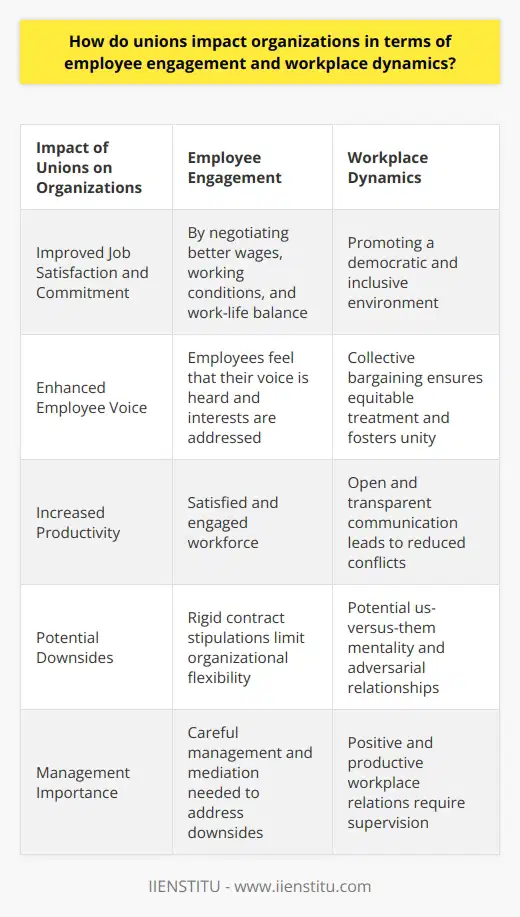
How do unions impact organizations in terms of employee engagement and workplace dynamics?
Impact on Employee Engagement
Unions majorly impact employee engagement in organizations. They provide a platform for dialogue between employees and management. This interaction facilitates a better understanding of employee rights and interests. Unions negotiate better wages, working conditions and work-life balance, leading to improved job satisfaction. Employees tend to be more committed and productive when they feel their voice is heard and their interests are addressed.
Influence on Workplace Dynamics
Unions also influence workplace dynamics. Their presence can promote a democratic and inclusive environment. They encourage collective bargaining which leads to equitable treatment of all employees. This collective approach creates a sense of unity among employees, thus strengthening peer relationships. Unionized environments also encourage open and transparent communication. This can lead to reduced workplace conflicts and disputes.
Balancing Negotiation and Satisfaction
A pivotal aspect of union influence is their role in the negotiation of contracts. They ensure that employees are compensated fairly, which can enhance job satisfaction. Simultaneously, they mediate between management and employees, balancing employer-employee relations. This approach fosters an atmosphere of respect and fairness, which is instrumental in fostering positive workplace dynamics.
Potential Downsides
However, unions also have potential downsides. They can impede organizational flexibility and adaptability due to rigid contract stipulations. There can also be a risk of fostering an us-versus-them mentality in organizations. If not managed correctly, this can lead to adversarial relationships between management and employees. These dynamics can restrict operational efficiency and could negatively impact employee engagement.
Conclusion
Overall, unions significantly influence employee engagement and workplace dynamics. They offer the potential to facilitate an engaged, satisfied workforce and a fair, respectful work environment. However, the potential downsides mandate careful management and mediation to ensure positive and productive workplace relations.
What are the benefits of unionization to the organization in terms of employee retention and overall stability?
Employee Retention Benefits
Unionization significantly aids in maintaining a stable workforce in an organization. Employees involved in unions are less likely to quit, primarily due to the appealing benefits and job security these unions provide. Stability is a key factor that unions bring into the mix, acting as a buffer between management and the staff, preventing hastily made decisions which could lead to unnecessary personnel changes.
Role in Dispute Resolution
Moreover, unions provide an established means of dispute resolution. They mediate issues between employees and management to cost-effective, mutually beneficial solutions. A fair process reduces employee turnover, ultimately contributing to a stable, satisfied workforce.
Promotion of Workplace Equality
Furthermore, unions advocate for equal treatment in the workplace. Unions prohibit discriminatory actions, veering organizations towards a diverse and inclusive environment. Nurtured in such an environment, employees are likely to stay, improving staff retention.
Impact on Employee Benefits
A compelling factor that aids in retaining employees is the ability of unions to negotiate better benefits. These entities bargain for competitive wages, reasonable working hours, and comprehensive healthcare policies. Employees not only feel accounted for but also secured.
Enhanced Communication Framework
Unions also foster transparent communication. They facilitate dialogues between the workforce and management, ensuring employee grievances don't go unheard or unresolved. This participative form of communication breeds satisfaction and trust, decreasing employee churn.
In conclusion, unionization plays a compelling role in employee retention and overall organizational stability. From guaranteeing fair working conditions to diving into dialogue-driven dispute resolutions, unions improve workforce satisfaction and longevity. Therefore, organizations with unions tend to enjoy lower staff turnover and a more stable workforce.

What does union mean in the context of power dynamics and decision-making processes within an organization?
Union in Power Dynamics
In the context of power dynamics within an organization, a 'union' refers to an organized group of workers. This group aims to balance the power equilibrium by advocating for collective rights and interests.
Collective Decision-Making
In decision-making processes, the union acts as a channel for negotiation between the employees and management. This collective approach ensures that each stakeholder's interests receive due consideration, promoting inclusivity in organizational decision making.
Advocate for Collective Rights
Unions ensure that power is not concentrated solely in the hands of the organization's management. They advocate for collective rights and influence decision-making processes, thereby decentralizing power within the organization.
Balancing Power Dynamics
The influence of unions in an organization ensures a fair distribution of power. This balance mitigates the risk of exploitation and injustice within the workplace. Consequently, unions foster a more democratic and equitable organizational culture.
Strengthening Employee Voice
Unions serve to strengthen the voice of the employees. They provide a unified platform for workers to express their concerns and aspirations. This collective influence counteracts the inherent power asymmetry between individual employees and management.
In conclusion, in the context of power dynamics and decision-making processes within an organization, union denotes a collective platform that promotes a more balanced, equitable, and democratic work environment. Through advocacy for workers' rights and collective decision-making, unions ensure an equitable distribution of power, mitigating the risk of exploitation while fostering organizational growth and sustainability.

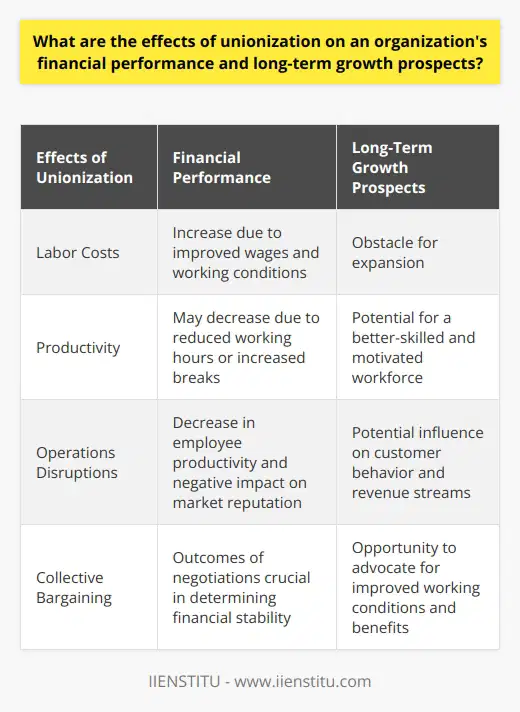
What are the effects of unionization on an organization's financial performance and long-term growth prospects?
Financial Performance Impact
Unionization significantly influences an organization's financial performance. Usually, unionized firms experience higher labor costs as unions compete to improve wages and working conditions for their members. These increased costs reduce overall profitability, impacting the organization's financial performance.
Union Influence on Employee Productivity
Moreover, unions can influence employee productivity. They negotiate to reduce working hours or increase breaks, reducing overall productivity. Decreased productivity may result in increased costs and decreased output, which hampers the company's competitive advantage.
Impact on Industrial Relations
Union activities also affect industrial relations. Strikes or work stoppages, common union tactics, disrupt operations. This disruption not only decreases employee productivity but also negatively affects the company's market reputation, which influences customer behavior and revenue streams.
Long-term Growth Prospects
Looking at long-term growth, unionization brings both challenges and opportunities. The increase in labor costs and potential disruptions may create hurdles for expansion. However, unionization can also lead to a better-skilled and motivated workforce through collective bargaining for improved working conditions and benefits.
The Role of Negotiations
The effect of unionization on an organization's financial performance and long-term growth prospects also significantly depends on successful negotiations between management and unions. Constructive dialogue can lead to solutions beneficial for both parties, contributing to financial stability and long-term growth.
In conclusion, unionization impacts an organization's finances and growth through multiple dimensions such as increased labor costs, altered productivity, industrial relations, and negotiation outcomes. These factors can either negatively or positively influence the financial performance and long-term growth of an organization. These effects entail a strategic approach to labor relations management to utilize unionization as an asset rather than a liability.
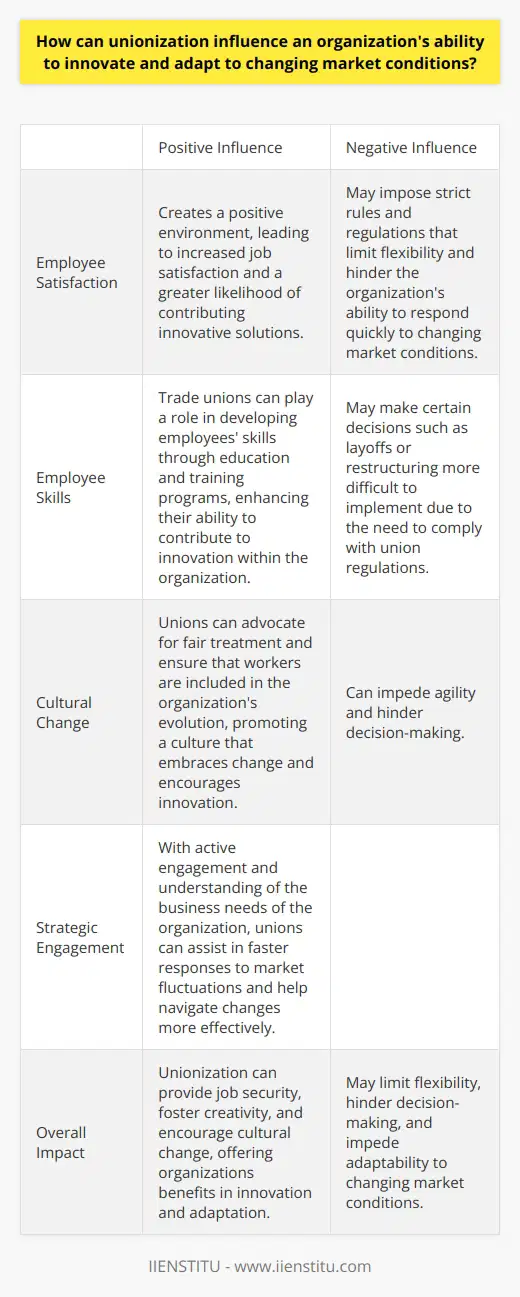
How can unionization influence an organization's ability to innovate and adapt to changing market conditions?
Union Influence on Organizational Innovation
Trade Union influence significantly affects corporate creativity and adaptability. Unions typically establish structures to ensure the interests of workers are met. They ensure job security and negotiate workplace conditions, indirectly influencing the overall organizational environment. This could either boost or hinder innovation, depending imperative organizational responses to the rapidly changing market.
Unleashing Creativity in Unionized Settings
Unions can foster creativity in organizations. With unions mediating and ensuring equitable treatment, employee satisfaction often increases. Employees who feel safe, respected, and recognized are more likely to contribute innovative solutions. Union-led worker education and training can also contribute to skill development, further driving innovation.
Unionization Effects on Flexibility
However, unions may limit organizational agility. Strict union rules might result in rigid operations, stifling flexibility in the rapidly evolving market scenario. Decisions such as layoffs or organizational restructuring might become bottle-necked due to stringent union regulations, potentially debilitating in fast-paced markets. Additionally, due to a possible focus on equitability and maintenance of existing conditions, unions may underprioritize innovative investments.
Promotion of Cultural Change
Balancing this, unions can promote a culture receptive to change. For example, they might champion fair treatment during periods of restructuring or technological change, ensuring workers are included in the organization's evolution. Unions can thus cushion social cost while steering organizations towards acceptance of change, sowing seeds for innovation.
Responding to Market Changes
While the union role is typically protective, a proactive approach could yield more substantial benefits. Unions that actively engage with strategic discussions, understanding and supporting business needs, can aid faster responses to market fluctuations.
In conclusion, unionization's influence on an organization's ability to innovate and adapt is complex and multifaceted. While it can cement security and promote cultural change conducive to innovation, it can also hinder agility. Recognizing and levering these aspects could support organizations in navigating market changes more pragmatically.
What role does unionization play in fostering a culture of diversity, equity, and inclusion within an organization?
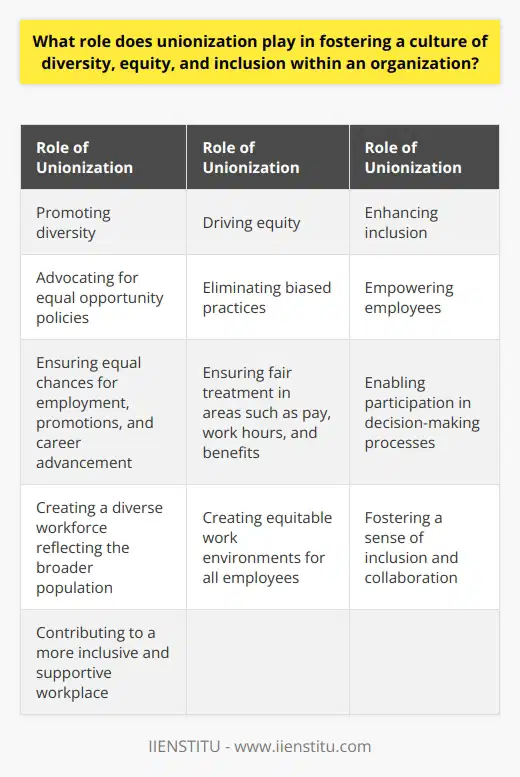
Promoting Diversity through Unionization
Unionization plays a pivotal role in fostering diversity within an organization. By serving as a platform for collective bargaining, unions advocate for the implementation of equal opportunity policies. These policies ensure that employees from diverse backgrounds get equal chances in employment, promotions, and career advancement.
Driving Equity via Unionization
Equity relates directly to unionization. Unions focus on fair treatment, pushing organizations to eliminate biased practices in pay, work hours, and benefits. Truly equitable organizations foster an environment where employees don't experience discrimination based on race, gender, age, or any other defining characteristic. Unions stand at the forefront of stimulating such organization-wide changes.
Inclusion Endorsed by Unionization
Inclusion forms the cornerstone of unionization. Unions encourage employees to have an active voice and engage in decision-making processes. This approach makes every member feel involved and acknowledged, regardless of their social identity or job role. Inclusion also boosts employees’ morale, cultivating a more collaborative and productive work environment.
In conclusion, unionization acts as a catalyst in manifesting a culture of diversity, equity, and inclusion within an organization. It introduces checks and balances that ensure equal treatment and opportunities for all, regardless of individual differences. Thus, a diverse, equitable, and inclusive culture not only results from unionization but also contributes to its strength and sustainability.