In the striving for ever-greater efficiency and quality, the concept of Standard Work has become a cornerstone of operational excellence within business entities around the globe. Standard Work is defined as the most efficient method to produce a product or perform a service at a balanced flow, to meet customer demand. It specifies the sequence of tasks, the time taken for each phase, and the required inventory. The mandate of Standard Work in business cannot be overstated, as it strives to minify waste, ensure consistency, and foster a culture that prioritizes efficiency.
The evaluation and implementation of Standard Work principles are integral to maintain competitiveness in the corporate sphere. This approach enables organizations to establish benchmarks that are vital for the measurement and improvement of performance. Thus, engaging with the mechanisms of this methodology is immanent for any business desiring to optimize its operations.
This article examines the components and significance of Standard Work in enhancing performance efficiency. It offers an expert perspective, enriched with practical examples, vitality significant for leaders who aim to instill an ethos of continuous transformation within their organizations.
Understanding the Components of Standard Work
Takt Time
When discussing Standard Work, one cannot bypass the elemental concept of takt time. This is essentially the rate at which a finished product needs to be completed to satisfy customer demand. In other words, it is the heartbeat of any lean manufacturing system, synchronizing the pace of production with the sales rate.
For example, if customers demand 240 units per day and the factory operates for 480 minutes daily, the takt time would be two minutes per unit. This simple calculation helps to align production schedules with actual sales data, ensuring that production is neither over nor under the market requirement.
Examples within automotive manufacturing are testament to the efficacy of takt time. Here, precise calculations of takt time dictate assembly line speeds, drastically reducing idle times and overproduction. The effectiveness of aligning production pace with takt time is a testament to the method's significance and efficacy.
Work Sequence
The sequence in which work is carried out, or work sequence, is a pivotal component of Standard Work. It delineates the order of operations for tasks and establishes the most effective motion patterns to maximize efficiency and reduce fatigue.
To be practical, consider the work sequence of a barista making a latte. From grinding the coffee beans to pouring the milk, each step follows a set sequence to optimize the barista's movements and shorten the service time. The successful application demonstrates how even the simplest jobs can benefit markedly from an ordered sequence of actions.
Real-world examples further elucidate this concept. In a factory setting, the work sequence might dictate the specific order in which a machine operator completes the task, such as assembling parts before quality inspection. Adhering to a dictated work sequence is shown to reduce process variations and enable accurate projection of completion time.
Standard Inventory
The concept of Standard Inventory pertains to the amount of in-process inventory required to maintain a consistent workflow. It is a calculated buffer that accounts for the variability in production and supply chain uncertainties.
Understanding the optimal standard inventory level is essential for businesses to avoid either excess stock, which ties up capital, or too little, which risks halting the production line. For example, in a restaurant, the standard inventory of ingredients is calculated to ensure dishes are available throughout service without wastage of perishables.
In manufacturing, standard inventory is clearly demonstrated in the form of work-in-progress (WIP) units on the factory floor. A pre-determined number of WIP units between processes can accommodate machine downtime or other disruptions without affecting the overall workflow. This calculated approach informs a responsive production system, capable of adapting to unforeseen challenges while maintaining efficiency.
The Role of Standard Work in the Manufacturing Industry
Importance in Production Efficiency
The manufacturing industry's reliance on Standard Work cannot be understated when discussing production efficiency. The control it affords over each aspect of the manufacturing process translates directly into less variability and a more predictable output.
Consistency in production methods leads to predictability in product quality and delivery schedules– two critical elements customers count on. Standard Work fosters a disciplined approach to manufacturing, confining the range of action to reduce the probability of defects and delays.
Case Studies Demonstrating the Value of Standard Work
Case studies from leading manufacturing companies across the globe often reveal the transformative impact of Standard Work. One emblematic example comes from the automotive industry, where the systematic application of Standard Work led to a dramatic decrease in assembly errors, substantially improving the final product's reliability.
Another instance worth noting hails from electronics manufacturing, where the implementation of Standard Work methodologies resulted in a significant enhancement of production flow, culminating in improved lead times and reduced inventory costs. These cases stand as cogent evidence of the decisive role that Standard Work plays in achieving production dexterity and efficiency.
Key Benefits of Implementing Standard Work
Consistency in Output
A primary benefit of Standard Work is the consistency it brings to operational output. The systematic approach ensures that every output meets predetermined quality standards, significantly reducing the likelihood of variances and faults.
Enhanced Productivity
Standard Work also leads to enhanced productivity. By creating an optimal workflow, tasks are completed faster and with greater precision, maximizing the effective utilization of resources and personnel.
Improved Safety
Moreover, Standard Work inherently improves safety. Precise guidelines and sequences in operational processes minimize the risks associated with human error and ensure safer working environments for personnel. This focus on safety can contribute to a more satisfied and motivated workforce, indirectly contributing to productivity and efficiency.
Continuous Improvement Framework
Lastly, the principles of Standard Work offer a scaffold for continuous improvement. Through iterative analysis and adjustment of standards, businesses can remain agile and responsive to changing market demands and technological advancements. This perpetual cycle of enhancement cements the foundation for long-term competitiveness and success.
The Process of Implementing Standard Work
Identifying the Process
The road to implementing Standard Work begins with a detailed identification of the process that requires standardization. This involves a meticulous study of all tasks, movements, and outcomes associated with the process.
Breaking Down the Activity
Subsequently, the process is broken down into its constituent activities. Each step is scrutinized for efficiency and necessity, ensuring that only the most effective actions are incorporated into the standardized procedure.
Creating Standardized Work Charts
Once the optimum method is determined, creating standardized work charts and documentation is the next step. These visual and textual guides provide clear, succinct instructions for executing the work, serving as the touchstone for all operational efforts.
Continuous Improvement and Review
And finally, the essence of Standard Work lies not just in its implementation but also in its ongoing improvement and review. Regular audits and assessments ensure that the standard work remains relevant and adapts to new improvements or insights, maintaining the relentless pursuit of efficiency.
Challenges in Implementing Standard Work
Resistance to Change
One of the palpable challenges in implementing Standard Work is the innate resistance to change frequently exhibited by personnel. Altering established routines can invoke discomfort and insecurity, hampering the adoption of novel standards.
Ineffective Communication
A further impediment is ineffective communication. Without lucid explanation and rationale, employees might not grasp the significance or the mechanics of the changes being applied, leading to tepid cooperation or outright non-compliance.
Inadequate Training and Preparation
A lack of adequate training and preparation can also stifle the successful deployment of Standard Work. Ensuring that employees are comprehensively instructed and equipped to perform according to the newly established parameters is imperative for the realization of Standard Work’s fullest potential.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Adequate Worker Training
To surmount these challenges, robust and adequate worker training is indispensable. By offering comprehensive education on the principles and benefits of Standard Work, employees are more likely to appreciate the value and proactively participate in its implementation.
Effective Communication Strategies
Furthermore, effective communication strategies act as a catalyst for building consensus and alignment within the organization. Articulating the 'why' behind the 'what' can bridge understanding and foster a collective drive towards embracing standardization.
Leadership Engagement and Involvement
Lastly, leadership engagement and involvement are crucial. When leaders exemplify the adherence to Standard Work, it can significantly influence the organizational culture, setting a precedent for the workforce to emulate.
Standard Work in the Context of Lean Production
Definition and Principles of Lean Production
Lean Production is the comprehensive approach to operational management that seeks to eliminate waste while optimizing value to the customer. It relies substantially on principles that maximise efficiency, enhance flow, and ensure quality across the production pipeline.
Role of Standard Work in Lean Methodology
Within the realm of Lean methodology, Standard Work serves as a pivotal fulcrum. It is the tactical application that transforms the theoretical underpinnings of Lean into palpable, methodical action, ensuring that every process is repeatable, reliable, and resilient to variability.
Link between Lean Production and Standard Work
The inherent link between Lean Production and Standard Work is indisputable. Standard Work provides the stable groundwork upon which the edifice of Lean thinking is constructed. By solidifying best practices and establishing a baseline for improvement, Standard Work perpetuates the core aim of Lean—to deliver supreme value with minimal waste.
Conclusion
Reflecting on the discourse presented, the significance of Standard Work in the milieu of operational and production efficiency is clearly manifest. Its application engenders not only a more predictable and reliable output but also cultivates an environment where continuous improvement is not just a conceptual ideal but a tangible, systemic endeavor.
For organizations vested in their future economy and growth, further exploration and implementation of Standard Work principles emerge as an intelligent and necessary pathway. It is the practical expression of an operational conviction—that through disciplined standardization, the twin peaks of quality and efficiency can, indeed, be routinely ascended.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the core aspects of standard work principles that enhance organizational performance efficiency?
Core Aspects of Standard Work Principles
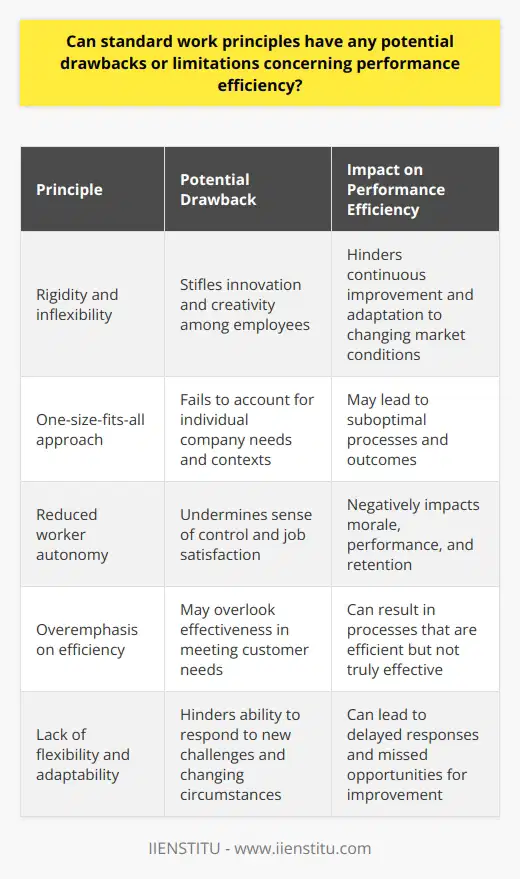
Organizational performance hinges on efficiency. Within this realm, standard work principles stand paramount. They ensure consistency, quality, and productivity. Here are key facets contributing to elevated performance.
Standardized Processes
Clarity guides action. Organizations must establish clear processes. They define steps in every task. Workers understand expectations. This leads to fewer errors.
Continuous Improvement
Performance thrives on refinement. Kaizen, or continuous improvement, exemplifies this. Companies should encourage ongoing feedback. Workers suggest enhancements. Processes evolve for efficiency.
Process Documentation
Records hold facts. Every process needs documentation. These documents guide training. They help benchmarking. Process audits rely on them.
Visual Management
Sight simplifies communication. Visual tools convey status instantly. Think diagrams, charts, and boards. They reveal process health at a glance. Workers spot problems faster.
Balanced Workload
Efficiency means balanced workloads. Overburdening leads to errors. Underutilization wastes resources. Smart work distribution maximizes throughput. It maintains quality.
Employee Training
Knowledge empowers employees. Training equips them with skills. It bridges knowledge gaps. Standard work becomes achievable. Proficiency grows across the board.
Timely Updates
Change is inevitable. Standard work must adapt. Timely updates to processes matter. They incorporate new best practices. They reflect current conditions.
Impact on Organizational Efficiency
Error Reduction
Standard work minimizes mistakes. Fewer errors save time. They conserve resources.
Time Savings
Process consistency accelerates workflows. Employees know their tasks well. Operations become seamless.
Resource Optimization
Resource use becomes more effective. Standard work identifies the necessary resources. Waste diminishes.
Increased Productivity
When workers follow set procedures, output rises. Processes flow without interruption.
Improved Morale
Understanding roles clarifies duties. Workers feel more competent. Satisfaction grows.
Enhanced Quality
Consistent steps produce uniform quality. Customers receive reliable products.
Better Scalability
Standardized operations adapt more easily. Expansion becomes manageable.
In sum, standard work principles create strong efficiency foundations. Better processes yield better performance. Organizations embracing these concepts stand to excel.
How can the implementation of standard work principles contribute to reducing process variances and improving productivity rates?
The Role of Standard Work in Process Optimization
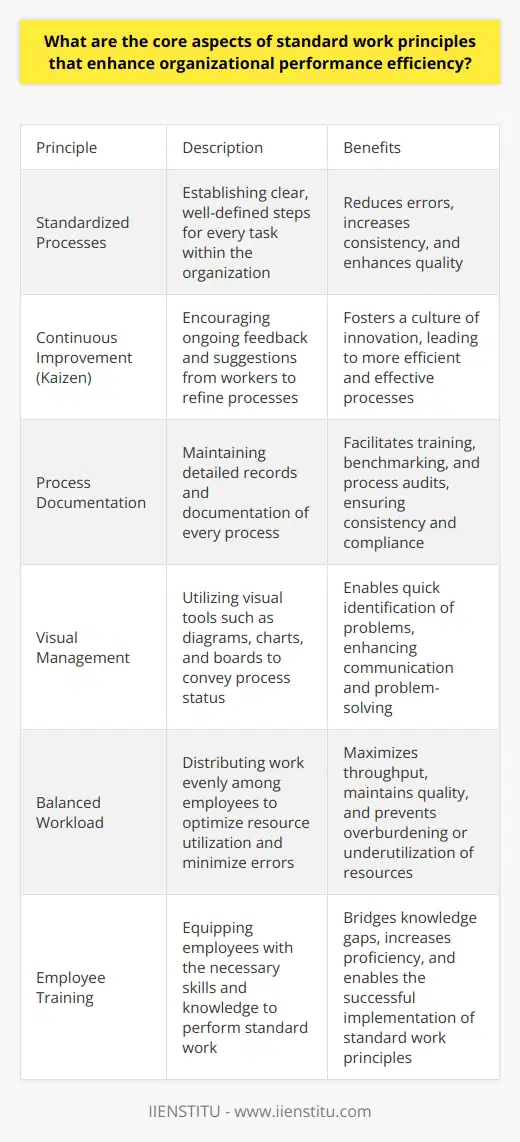
Understanding Standard Work
Standard work embodies a core principle. It drives lean methodologies. Organizations adopt it to stabilize operations. It forms the backbone of any high-functioning process. Standard work details the best way to perform a task. It outlines the most efficient sequence of activities. Timing, movement, and materials also find mention.
Reducing Process Variances
Variances threaten process consistency. They erode the foundations of productivity. When ignored, they grow pervasive. Standard work counteracts this. It establishes a blueprint. Each worker follows this blueprint. In doing so, variances decrease. How? Because uniformity replaces randomness. Alignment supersedes disparities.
Each process stage becomes predictable. Workflows undergo inspection and adaptation. Feedback helps refine standard work practices. Continuous improvement becomes tangible. Organizations witness fewer mistakes. Defect rates drop. Cost savings rise. The cumulative effect is notable.
Improving Productivity Rates
Productivity hinges on efficiency. Efficiency depends on reducing waste. Waste comes in many forms. Overproduction, waiting, and unnecessary motion are a few examples. Standard work confronts these head-on. It prescribes a workflow that minimizes waste.
A well-detailed standard work protocol includes:
- Exact work sequences
- Precise timing
- Specific workflow paths
In adhering to these, workers maximize their output. They need not guess their next step. Embedded instructions guide them. This saves time. It increases the rate of output.
Closing Thoughts
Implementing standard work is not a one-off exercise. It demands commitment. Regular reviews ensure relevance. Response to change is vital. When workers internalize standard protocols, consistency blossoms. Productivity flourishes. Profitability often follows.
In conclusion, standard work is more than a guideline. It is a strategic tool. It underpins organizational success. It holds the key to unlocking a more efficient, profitable future.
Can standard work principles have any potential drawbacks or limitations concerning performance efficiency?
Standard Work Principles and Performance Efficiency
Understanding Standard Work
Standard work forms the backbone of many industries. It offers a framework for consistency. Implementing its principles aims to optimize efficiency. However, even well-established systems exhibit shortcomings. Standard work is no exception.
The Essence of Standard Work
Standard work hinges on predictability and uniformity. Repetition of proven practices leads to efficiency. These practices empower workers with clear expectations. They outline the tasks, sequence, and time for each activity. Thus, they ensure consistent results.
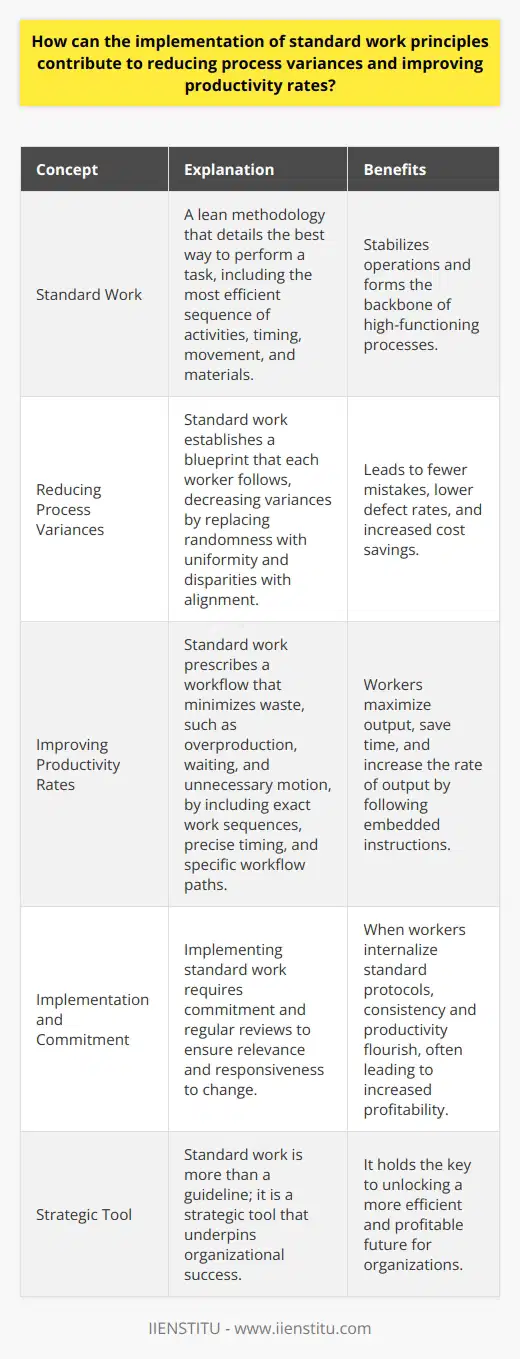
Potential Downsides of Inflexibility
Rigidity stifles innovation. Standard work emphasizes following the script. Deviations are seldom welcome. This can dampen the drive to innovate. Employees might feel their creativity is unwelcome. Therein lies a barrier to improvement.
Circumstances dictate applicability. No system fits all scenarios. Changes in market conditions often call for agility. Rigid adherence to standard work overlooks this need. It may delay the company's response to new challenges.
One-Size-Fits-All Approach Limitations
Companies differ. So do their needs. What works for one may fail for another. Standard work takes little account of this individuality. Thus, it may not always align perfectly with specific company contexts.
Impact on Worker Autonomy and Morale
Workers need a sense of control. Strict procedures can undermine this need. They might feel micromanaged. Reduced autonomy can lower morale and job satisfaction. These factors can negatively influence performance and retention.
Efficiency vs. Effectiveness
Efficiency does not guarantee effectiveness. Standard work often prioritizes efficiency. Yet, this does not always lead to effective outcomes. Meeting the real needs of customers takes more than just efficiency.
The Balance Between Standardization and Flexibility
The goal should not be to forsake standard work. Rather, it is to balance it with flexibility. Companies need both stable processes and the ability to innovate. This balance can drive sustainable performance.
- A focus on continuous improvement is key.
- Workers should have a voice in their work processes.
- Regular reviews of procedures can identify needed adaptations.
In Conclusion
Standard work principles have limitations. Not every principle suits every situation. Adaptation and flexibility are crucial. They can help overcome the inherent constraints of standard work. Thus, they ensure that performance efficiency remains dynamic, not just static.