Private indexes are becoming increasingly important for businesses looking to improve their search capabilities and provide a better user experience for their employees or customers. By creating a private index, companies can ensure that their internal data is easily accessible and searchable while maintaining the security and privacy of sensitive information. In this article, we will explore the benefits of private indexes for businesses, discuss SEO strategies for private search engines, and provide tips on how to optimize a private index.
Introduction
What is a Private Index?
Benefits of Private Indexes
SEO for Private Indexes
Conclusion
What is a Private Index?
A private index is a search engine that is restricted to a specific group of users, typically within an organization. Unlike public search engines like Google or Bing, which index and provide search results from the entire internet, a private index only includes content from a company's internal network, databases, and resources. This allows businesses to create a customized search experience tailored to their specific needs and requirements.
Benefits of Private Indexes for Businesses
There are several key benefits to implementing a private index for your business:
1- Improved Search Relevance: By indexing only internal content, private indexes can provide more relevant search results for users. This is because the search engine can be optimized for the specific terminology, jargon, and content structure used within the organization.
2- Enhanced Security: Private indexes ensure that sensitive company information remains secure and accessible only to authorized users. This is particularly important for businesses dealing with confidential data, such as financial records or client information.
3- Increased Efficiency: With a private index, employees can quickly find the information they need without having to sift through irrelevant search results. This can lead to significant time savings and improved productivity across the organization.
4- Customization Options: Private indexes can be customized to meet the unique needs of a business. This includes defining specific search criteria, creating custom content classifications, and integrating with existing enterprise systems.
SEO Strategies for Private Search Engines
While private indexes are not crawled by public search engines like Google, it is still important to optimize your internal content for search. By implementing effective SEO strategies, you can improve the discoverability of important information within your organization and provide a better user experience for your employees.
Here are some key SEO strategies to consider when optimizing for private search engines:
1- Keyword Research: Just like with public search engines, keyword research is essential for optimizing your private index. Identify the common terms and phrases used within your organization and ensure that your content includes these keywords in a natural and relevant way.
2- Content Optimization: Ensure that your internal content is well-structured and includes relevant keywords in the page title, headings, and body text. Use descriptive and meaningful file names for documents and other resources to improve their searchability.
3- Metadata Optimization: Include relevant metadata, such as descriptions and tags, for your internal content. This will help the search engine understand the context and relevance of each piece of content, leading to better search results.
4- Internal Linking: Implement a clear and logical internal linking structure to help users navigate between related content. This will also help the search engine understand the relationships between different pieces of content and improve the overall search experience.
Understanding your unique content and audience is key to successful SEO for private indexes.
How to Optimize a Private Index
In addition to implementing SEO strategies, there are several technical considerations to keep in mind when optimizing a private index:
1- Choose the Right Search Engine: There are various options available for creating a private index, including open-source solutions like Apache Solr or Elasticsearch and commercial products like Google Search Appliance. Choose a search engine that meets your organization's specific needs and requirements.
2- Secure Your Index: Ensure that your private index is properly secured and accessible only to authorized users. Implement user authentication and access controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
3- Monitor and Analyze Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your private index and analyze user search behavior. This will help you identify areas for improvement and optimize the search experience over time.
4- Provide User Training: Ensure that your employees are properly trained on how to use the private index effectively. Provide guidance on search best practices and encourage users to provide feedback on their search experience.
Secure Search Solutions for Organizations
In addition to private indexes, there are other secure search solutions available for organizations looking to enhance their search capabilities while maintaining the security of sensitive data. These solutions often incorporate advanced security features, such as encryption and user authentication, to ensure that only authorized users can access the search results.
One example of a secure search solution is the use of a federated search approach. Federated search allows organizations to search across multiple internal and external data sources from a single search interface while maintaining the security and access controls of each individual source. This can be particularly useful for organizations with complex data architectures or those that need to integrate search capabilities across multiple systems.
Another approach is the use of enterprise search platforms, which provide a comprehensive search solution for large organizations. These platforms often include features such as document-level security, user authentication, and advanced content processing capabilities. They can also be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization and integrate with existing enterprise systems.
Internal Search Engine Optimization Tips
When optimizing an internal search engine, there are several best practices to keep in mind:
1- Understand Your Users: Take the time to understand the search needs and behaviors of your users. Conduct user research and analyze search data to identify common search queries, pain points, and areas for improvement.
2- Optimize Your Content: Ensure that your internal content is well-structured and includes relevant keywords. Use descriptive titles and headings, and provide clear and concise summaries of each piece of content.
3- Implement Faceted Search: Faceted search allows users to filter search results based on specific criteria, such as date, author, or content type. This can help users quickly find the information they need and improve the overall search experience.
4- Use Synonyms and Aliases: Implement synonym and alias management to ensure that users can find relevant content even if they use different terminology than what is used in the content itself. This can be particularly important for organizations with specialized or technical terminology.
Private Indexing Tools Comparison
There are various tools available for creating and managing private indexes, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. When choosing a private indexing tool, it is important to consider factors such as scalability, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
Some popular private indexing tools include:
Apache Solr: An open-source search platform that provides advanced full-text search capabilities and supports a wide range of data formats.
Elasticsearch: Another open-source search and analytics platform that offers real-time search capabilities and supports structured and unstructured data.
Google Search Appliance: A commercial search appliance that provides secure search capabilities for enterprise environments.
Microsoft SharePoint: A collaboration and document management platform that includes search capabilities for internal content.
When comparing private indexing tools, it is important to consider the specific needs and requirements of your organization. Factors to consider include the volume and complexity of your internal content, the number of users and their search behaviors, and the level of customization and integration required.
Improving User Experience with Private Indexes
One of the key benefits of implementing a private index is the ability to provide a better search experience for users. By tailoring the search results to the specific needs and behaviors of your users, you can help them find the information they need more quickly and easily.
To improve the user experience with your private index, consider the following tips:
1- Provide Relevant Search Results: Ensure that your search results are relevant to the user's query and provide the information they are looking for. Use techniques such as keyword optimization and relevance tuning to improve the accuracy of your search results.
2- Use Clear and Concise Titles and Summaries: Ensure that the titles and summaries of your search results are clear and concise, providing users with a quick overview of the content and its relevance to their query.
3- Provide Filtering and Sorting Options: Allow users to filter and sort search results based on various criteria, such as date, author, or content type. This can help users quickly find the most relevant information for their needs.
4- Offer Query Suggestions and Autocomplete: Provide query suggestions and autocomplete functionality to help users refine their search queries and find the information they need more quickly.
5- Gather User Feedback: Regularly gather feedback from users on their search experience and use this feedback to continuously improve the relevance and usability of your private index.
By focusing on improving the user experience, you can help ensure that your private index is a valuable and effective tool for your organization.
Creating Tailored Content for Private Search
Another key aspect of optimizing for private search is creating content that is tailored to the specific needs and requirements of your organization. By creating content that is relevant, informative, and easy to find, you can help improve the overall effectiveness of your private index.
Here are some tips for creating tailored content for private search:
1- Understand Your Audience: Take the time to understand the needs, preferences, and behaviors of your target audience. Use this information to create content that is relevant and valuable to them.
2- Use Clear and Descriptive Titles: Use clear and descriptive titles for your content that accurately reflect the topic and purpose of the content. This will help users quickly understand the relevance of the content to their search query.
3- Optimize for Keywords: Use relevant keywords throughout your content, including in the title, headings, and body text. This will help improve the search relevance of your content and make it easier for users to find.
4- Provide Comprehensive and Accurate Information: Ensure that your content provides comprehensive and accurate information on the topic at hand. Use reliable sources and fact-check your information to ensure accuracy.
5- Use Formatting and Multimedia: Use formatting techniques such as headings, bullet points, and images to break up your content and make it easier to read and navigate. Incorporate multimedia elements such as videos or infographics to provide additional context and engage users.
By creating tailored content for your private search, you can help ensure that your users have access to the information they need to do their jobs effectively.
Best Practices for Private Index SEO
Finally, let's discuss some best practices for optimizing your private index for search:
1- Conduct Regular Content Audits: Regularly review and audit your internal content to ensure that it is accurate, up-to-date, and relevant to your users. Remove or archive outdated content to improve the overall quality of your search results.
2- Implement Consistent Metadata: Use consistent metadata across your internal content, including titles, descriptions, and keywords. This will help improve the searchability of your content and make it easier for users to find what they need.
3- Monitor Search Analytics: Regularly monitor your search analytics to identify common search queries, click-through rates, and other key metrics. Use this information to optimize your content and improve the relevance of your search results.
4- Provide User Training: Provide training and guidance to your users on how to effectively use your private index. This can include tips on how to create effective search queries, how to use filtering and sorting options, and how to provide feedback on their search experience.
5- Continuously Improve and Iterate: Continuously monitor and analyze the performance of your private index and use this information to identify areas for improvement. Regularly update and optimize your content and search functionality based on user feedback and changing business needs.
By following these best practices, you can help ensure that your private index is a valuable and effective tool for your organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, private indexes are a powerful tool for businesses looking to improve their search capabilities and provide a better user experience for their employees or customers. By creating a customized search experience tailored to their specific needs and requirements, businesses can help ensure that their internal data is easily accessible and searchable while maintaining the security and privacy of sensitive information.
To optimize a private index for search, it is important to implement effective SEO strategies, including keyword research, content optimization, metadata optimization, and internal linking. It is also important to choose the right search engine for your needs, secure your index properly, monitor its performance regularly, and provide user training to ensure effective use.
By focusing on these key areas and continuously improving and iterating based on user feedback and changing business needs, you can help ensure that your private index is a valuable and effective tool for your organization. So if you're looking to improve your internal search capabilities and provide a better user experience for your users, consider implementing a private index today.
References
1- Arman, F., & Hattacharya, D. (2020). Enterprise Search and Discovery: Tools, Techniques, and Best Practices. CRC Press.
2- Croft, W. B., Metzler, D., & Strohman, T. (2015). Search Engines: Information Retrieval in Practice. Pearson Education.
3- Halvey, M., & Keane, M. T. (2007). An assessment of tag presentation techniques. In Proceedings of the 16th international conference on World Wide Web (pp. 1313-1314).
4- Hawking, D., Craswell, N., Bailey, P., & Griffihs, K. (2001). Measuring search engine quality. Information Retrieval, 4(1), 33-59.
5- Kumar, V., & Lang, K. R. (2007). Do search terms matter for online consumers? The interplay between search engine query specification and topical organization. Decision Support Systems, 44(1), 159-174.
6- Manning, C. D., Raghavan, P., & Schütze, H. (2008). Introduction to information retrieval. Cambridge University Press.
7- White, R. W., & Roth, R. A. (2009). Exploratory search: Beyond the query-response paradigm. In Synthesis lectures on information concepts, retrieval, and services (Vol. 1, No. 1).
Frequently Asked Questions
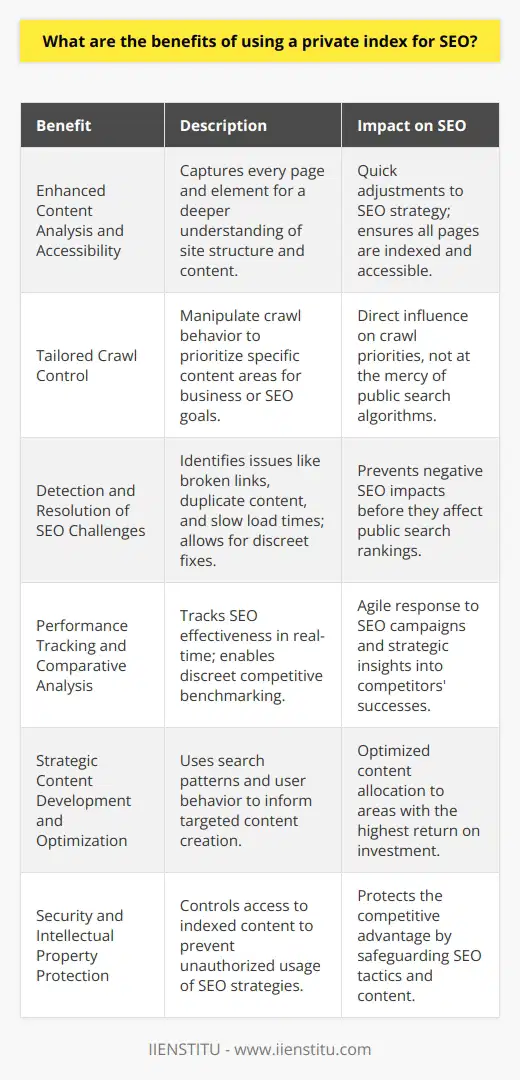
What are the benefits of using a private index for SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is an essential element of website design and optimization, and it is vital to ensure that search engines can easily find a website. Private indexes are a powerful tool to help optimize a website for SEO, and the benefits of using one are numerous.
Firstly, private indexes provide a more comprehensive view of a website’s content than is available through a public search engine. By indexing all content, private indexes can help optimize a website by providing an up-to-date overview of its content. This can be beneficial in terms of increasing the visibility of the website, as well as ensuring that the content is correctly indexed and accessible for search engines.
Secondly, private indexes can help identify and address any issues affecting a website’s SEO performance. Private indexes can be used to analyze a website’s content to identify potential areas of improvement. This can be particularly beneficial for websites that are not performing as well as they should be, as it can help identify and rectify any issues affecting their visibility in search engine results.
Thirdly, private indexes can be used to monitor the performance of a website’s SEO efforts. By tracking the performance of a website’s SEO campaigns over time, private indexes can provide valuable insights into how a website performs and what areas may need further optimization. This can be highly beneficial in helping to ensure that a website is always performing optimally in terms of search engine rankings.
Finally, private indexes can be used to compare a website's performance against its competitors. By analyzing the performance of a website’s competitors, private indexes can help to identify potential areas of improvement for a website and help to ensure that it is always performing better than its competitors.
In conclusion, private indexes can be a powerful tool to help optimize a website for SEO. By providing a comprehensive overview of a website’s content, identifying any issues affecting its performance, and monitoring its performance over time, private indexes can help to ensure that a website is always performing optimally in terms of search engine rankings.
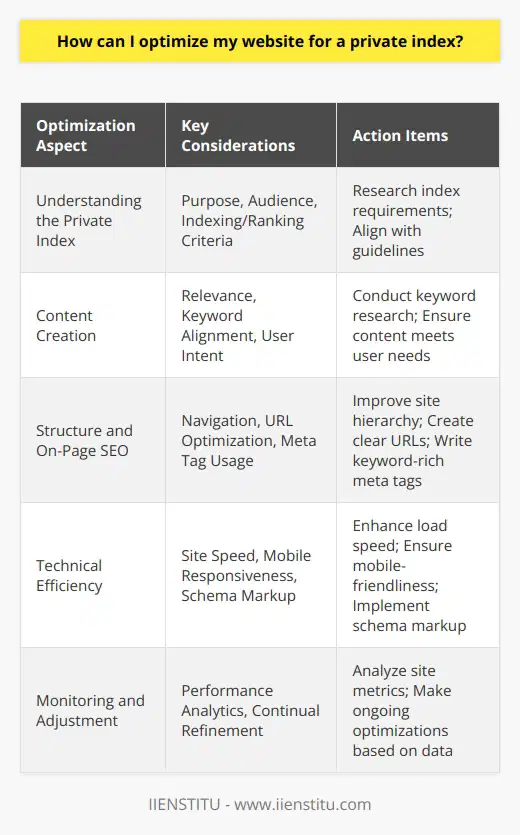
How can I optimize my website for a private index?
Optimizing a website for a private index can be daunting, as it involves understanding and navigating a complex set of technical components. However, with the right approach, achieving a high level of optimization for a private index is possible.
The first step in optimizing a website for a private index is understanding the technical components involved. This includes understanding the structure of the index, the types of webpages included, and the relationship between webpages and search engines. Once a basic understanding of the index has been achieved, the next step is identifying the critical areas of optimization.
The most critical areas of optimization are the website's content and the index's structure. Content optimization involves creating content targeted to the specific keywords used in the index. This can be done by creating content focused on the particular keywords and topics associated with the website. Content should also be optimized for the specific search engine used in the index. This can be done by using keyword research tools and analyzing the search results of the targeted search engine.
The structure of the index is also an essential factor in optimizing a website for a private index. The structure of the index should be optimized to ensure that webpages are easily found and indexed by the search engine. This can be done by creating a well-structured hierarchy of web pages and links within the website. Additionally, the website structure should be optimized to ensure that webpages are easily crawled and indexed by the search engine.
Finally, the last step in optimizing a website for a private index is to monitor the website’s performance in the index. This can be done by tracking the website’s ranking in the index and analyzing the search engine’s response to the website. Additionally, the website’s performance can be monitored by tracking the number of visitors and the amount of time spent.
By following these steps, website owners can optimize their website for a private index, resulting in higher rankings, improved visibility, and increased traffic. Ultimately, website owners should strive to optimize their website for the specific search engine used in the index to maximize the potential of the website.
What are the best practices for SEO when using a private index?
Search engine optimization (SEO) is an essential part of any website’s success, and using a private index can be a great way to maximize a website’s visibility in search results. However, it is essential to understand the best practices for SEO when using a private index to ensure that the website is optimized correctly and achieves the desired results.
The first step to SEO success is creating a website optimized for search engines. This means that the website should be structured correctly, and all the content should be accessible to index. This should include optimizing titles, meta descriptions, and other elements for SEO purposes. Additionally, it is essential to ensure that the content is keyword-rich and relevant to the website's topic.
Once the website is optimized correctly, it is essential to submit it to the private index. This is usually done via an XML sitemap, which allows the index to index the website’s contents easily. Additionally, the website should be regularly updated with fresh content to ensure it remains relevant to the private index.
Finally, monitoring the website’s performance in the private index is essential. This can be done using analytics software or other tools that track the website’s ranking in the index. This will help to identify any changes or optimizations that need to be made to ensure that the website is optimized correctly and achieves the desired results.
In conclusion, there are several best practices for SEO when using a private index. These include properly optimizing the website for search engines, submitting it to the private index, and regularly monitoring its performance. By following these best practices, websites can maximize their visibility in the personal index and achieve their desired results.
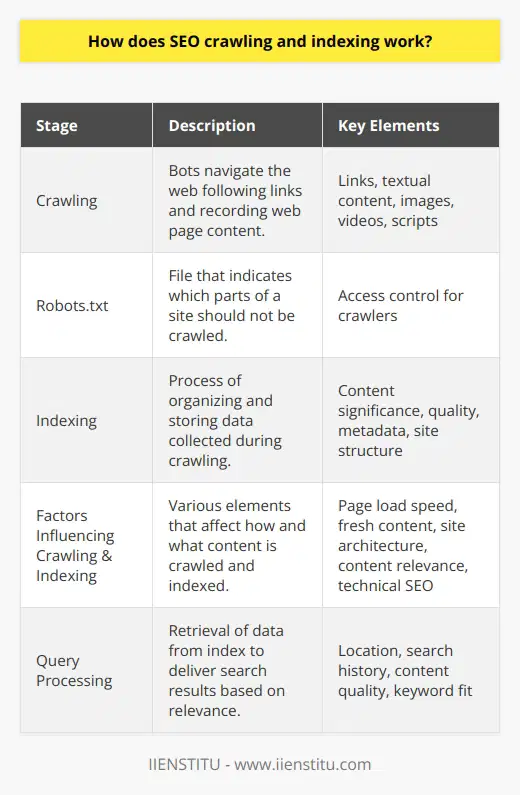
How does SEO crawling indexing work?
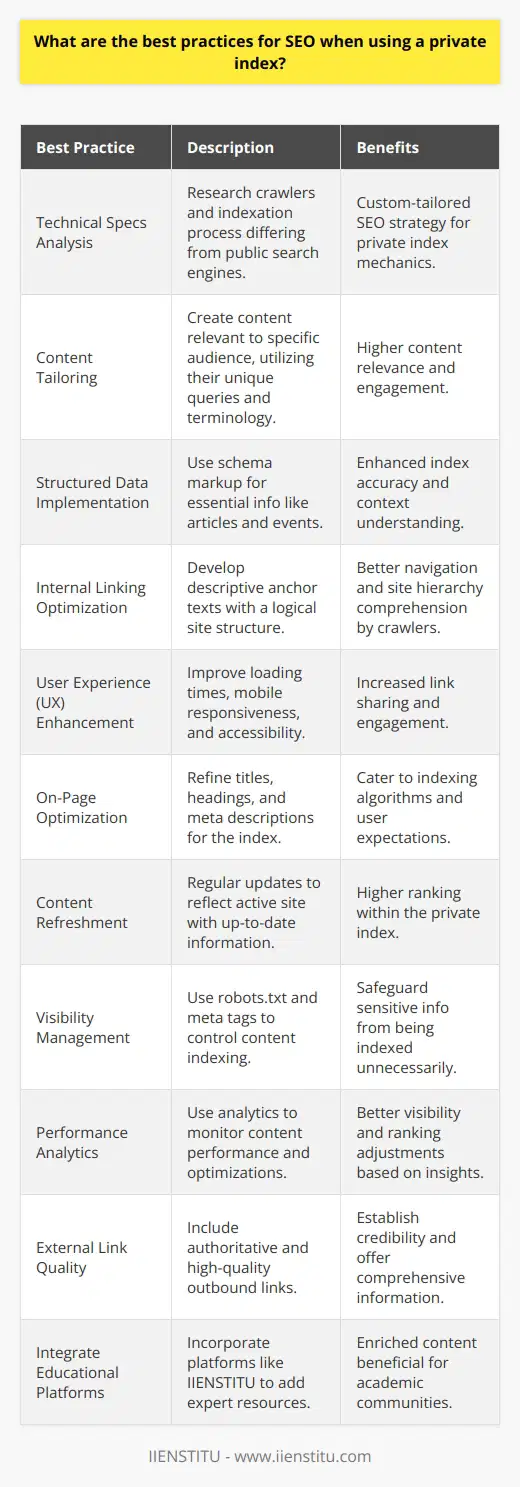
Understanding SEO Crawling Indexing
SEO crawling and indexing are critical components of search engine operations. Crawling is the first step and it refers to the process where search engines send out a team of robots, named crawlers or spiders, to find new and updated content.
Unraveling the Crawling Process
How does the crawling process work? Crawlers starts from a list of web addresses from past crawls and sitemaps provided by website owners. They follow links on these pages, in a systemic pattern. This way, they find fresh pages and updates to existing ones.
Comprehending Web Indexing
After the crawling phase, comes indexing. Here, the search engine processes the pages the crawlers found during the crawling process. It attempts to comprehend the content of a page to classify it appropriately in its colossal database – the search index. Websites that the search engine considers good and relevant are included in this index. Hence, indexing is the process of adding webpages into Google search.
SEO Significance of Indexing
The process of indexing is crucial for SEO because only 'indexed' pages will appear in the search results. As such, if your webpage is not indexed, it will remain invisible to the search engine and search users. A prime goal of SEO is to ensure that search engines can find, crawl, and properly index your web pages.
To conclude, SEO crawling and indexing are fundamental to enhancing the visibility of a webpage on search engines. Optimizing your website's indexation is one sure way to improve your website's ranking on search engine result pages. By understanding these processes, you can better align your SEO strategies and increase your website's visibility.
What are the two main ways to index content to make it searchable?
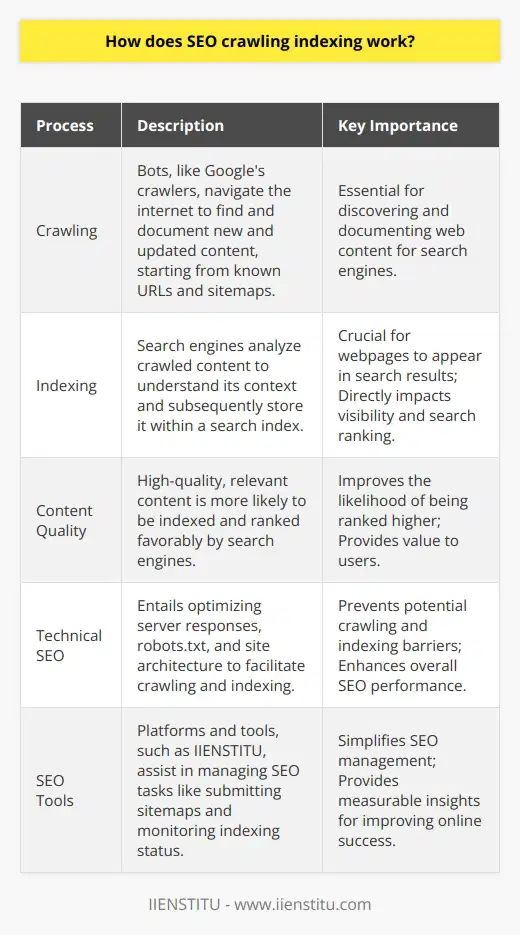
Indexing Methods
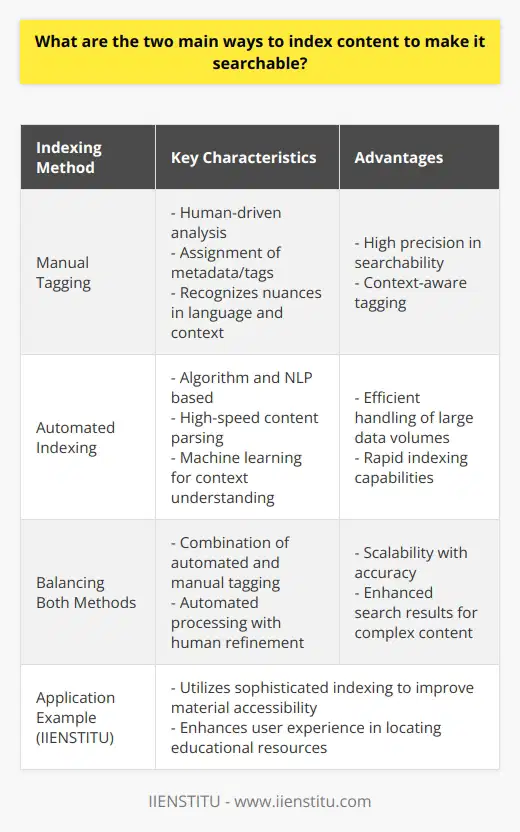
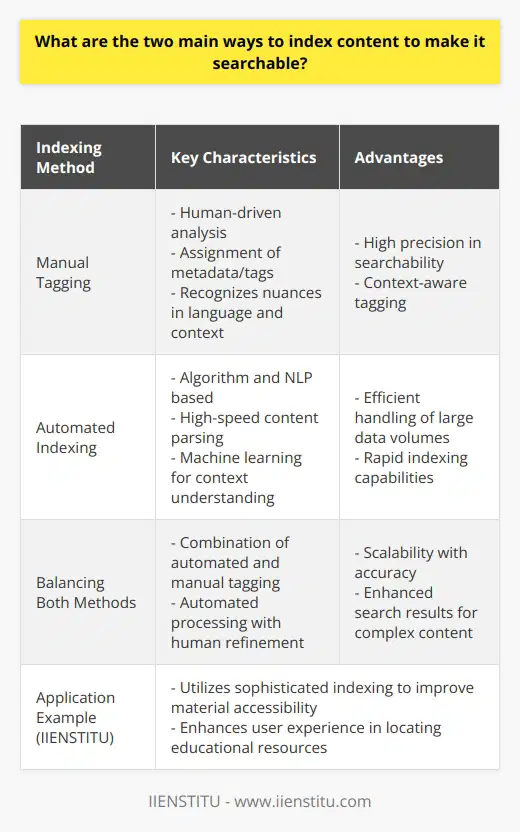
Indexing content for searchability primarily involves two methods; the 'manual tagging method' and the 'automated indexing method'.
Manual Tagging Method
The manual tagging method employs the use of human intuition and comprehension to organize data. Here, content creators or editors insert metadata or 'tags' into content. These tags highlight the main points, themes or subjects covered within the content. When a user inputs a search query matching these tags, the system retrieves and displays the relevant content. Manual tagging requires a robust understanding of the content since the quality and effectiveness of the index depend heavily on the appropriateness of the selected tags.
Automated Indexing Method
On the other hand, automated indexing is a computerized method that uses algorithms to scan and organize content. It involves programming a software or service to identify, understand, and categorize different elements within the content, without human intervention. This software extracts keywords from the content, interprets it, and catalogues it appropriately in the database. Hence, when a search query matches the extracted keywords, the content is retrieved and displayed.
Both methods have their advantages and limitations. Manual tagging offers a high level of accuracy but is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Conversely, automated indexing is comparatively easy and quick, yet it may not perform as accurately due to its inherent limitations in comprehending semantics and context. Therefore, to improve the searchability of content, it is often advantageous to implement a combination of both methods, where feasible. This allows an optimal balance between human accuracy and computer efficiency.
Do non-indexed pages affect SEO?
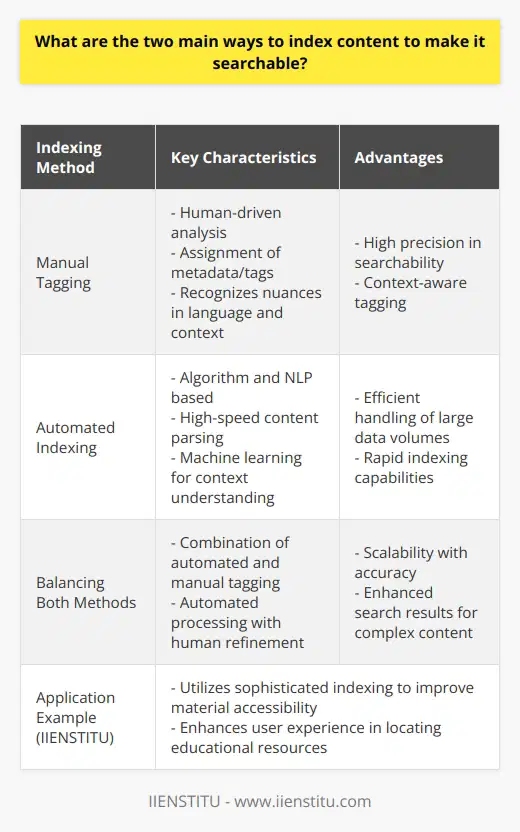
Impact of Non-indexed Pages on SEO
Yes, non-indexed pages do impact Search Engine Optimization (SEO). These pages, ignored by search engines, fail to contribute to a site's online visibility.
Significance of Indexed Pages
An indexed page is a webpage that search engines recognize. Engines like Google crawl these pages and consider them for search engine rankings. Consequently, an indexed page enhances your website's SEO potential. They elevate your chances of reach.
Drawbacks of Non-indexed Pages
Conversely, non-indexed pages do not appear in search engine results. They remain invisible to search engine algorithms. As such, they provide zero SEO value.
Effects on Link Equity
Additionally, non-indexed pages can control your site's link equity. They can hold back the flow of links to indexable pages on your website. It hampers the traffic and the overall SEO health of a site.
Role in Duplicate Content Issues
Non-indexed pages can help in addressing duplicate content issues as well. Ideally, pages with duplicate content should be non-indexed to prevent SEO penalties. However, this does not diminish the need for unique content on indexed pages.
To sum up, non-indexed pages do affect SEO. A meticulous balance between indexed and non-indexed pages is essential for ideal visibility and ranking. It ensures that your blog post garners the required attention and reach.
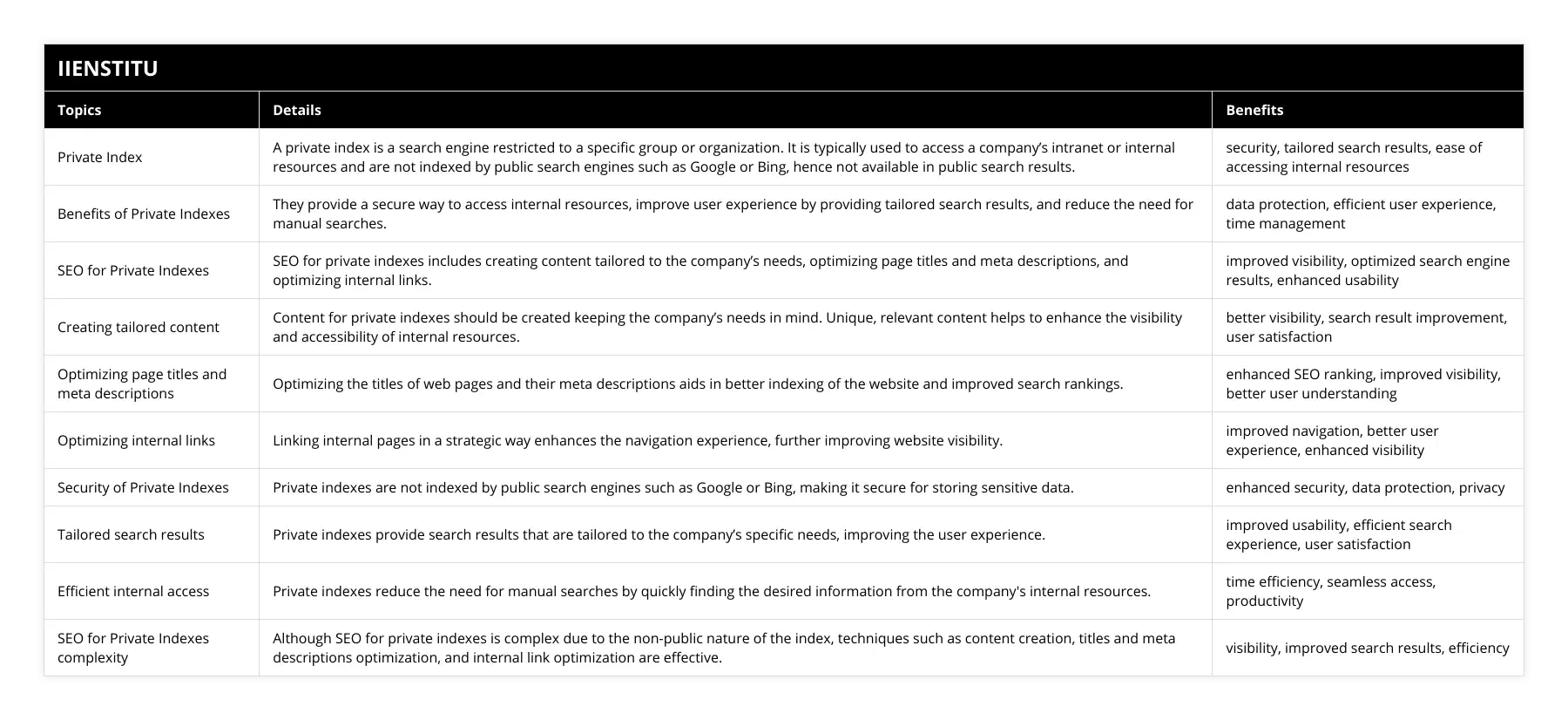
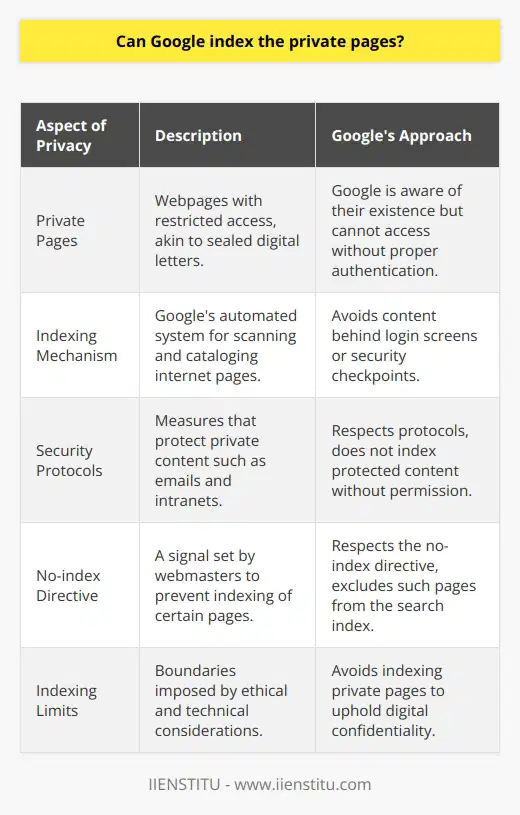
Can Google index the private pages?
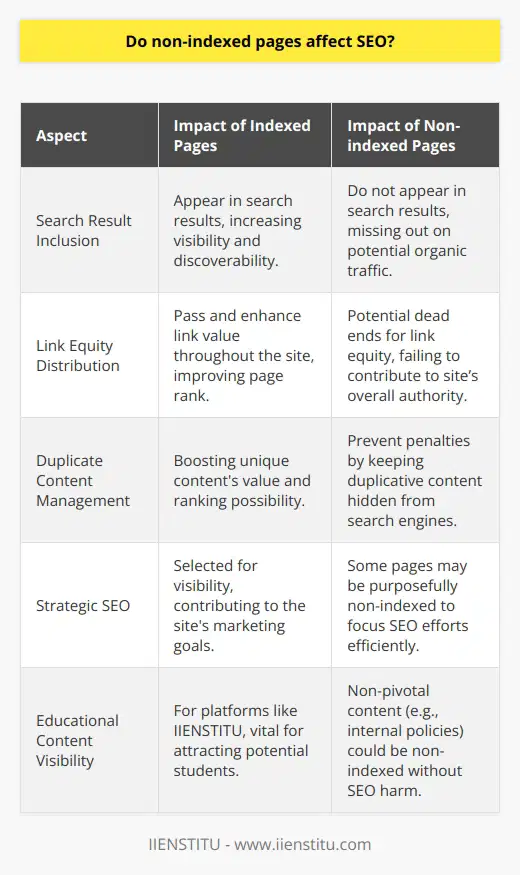
Understanding Google Indexing
Google's indexing system cannot typically index private pages or content. Private pages typically refer to pages that require a password or other forms of authentication for access.
Contextualizing Web Privacy
This stipulation extends to a range of web content including private blog posts, personal emails, and isolated intranet pages. Private data that is not publicly accessible is not within the domain of Google's indexing.
Google Bots and Access Limitation
Google uses crawlers, or bots, which explore the internet by following links across web pages to create an index. These bots are therefore limited by the access provided by those URLs.
Security Protocols and Indexing
Secure or private URLs, guarded by security protocols, restrict the access of these bots. Therefore, any content that is under a layer of authentication is not typically processed for Google's index.
Google's Crawling Limitation
In essence, if Google's bot cannot access specific content due to a lack of permission, such as a required login, that content most likely will not appear in the search engine's results.
Understanding No-Index Directives
Webmasters also have the ability to instruct Google's bots not to index specific pages, despite them being publicly accessible. They can do this through a method called a 'no-index directive.'
Conclusion on Private Page Indexing
In conclusion, while Google's indexing system is vast and comprehensive, it does not include private pages. The combination of access limitations and webmaster controls provides a level of privacy and discretion in Google's indexing process.
How to do indexing in SEO?
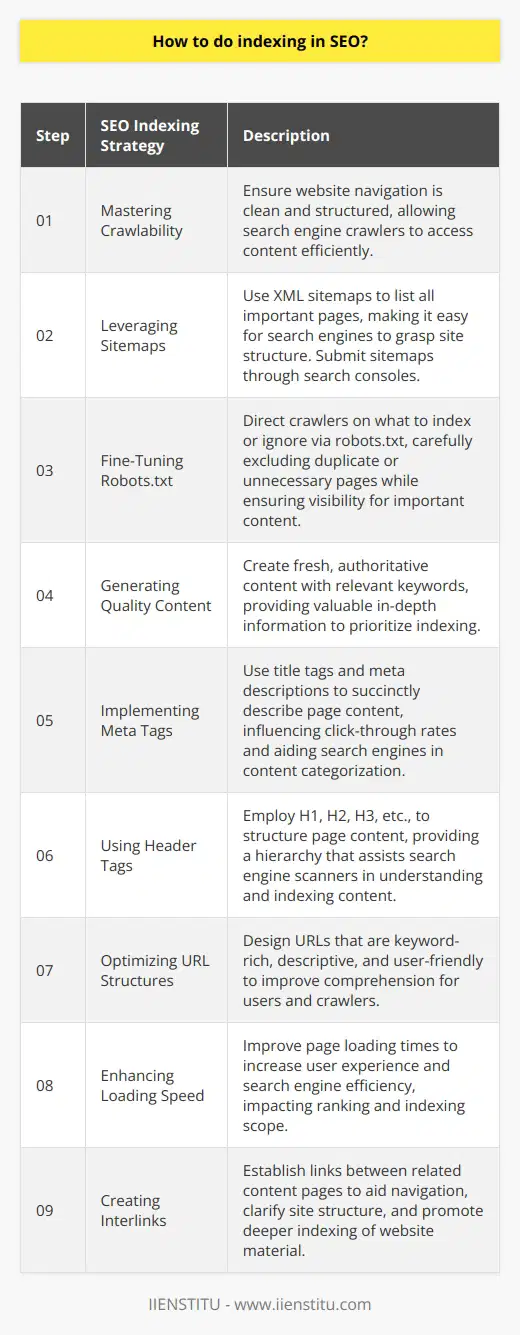
Understanding Crawlability
Optimizing your website for indexing begins with understanding crawlability. Search engines use programs called 'crawlers' or 'spiders' to scan the content of your website. Ensure these crawlers can easily navigate your site's pages and content.
Use of Sitemaps
Sitemaps act as guides for search engine crawlers, facilitating efficient site navigation. Publish a sitemap to ensure all your pages are discoverable. This can significantly boost the indexing of your website.
Optimizing Robots.txt Files
The Robots.txt file offers directives to search engine crawlers. Proper utilization can prompt crawlers to overlook certain pages. This can optimize indexing by ensuring crawlers focus on important, relevant content.
Creating Quality Content
High-quality, unique, and keyword-optimized content attracts search engine crawlers. Deliver consistent, valuable content that provides answers for user inquiries. This is essential for high ranking in search engine results.
Implementing Meta Tags
Meta Tags provide information about a webpage's content. Proper utilization of Meta Tags improves the interpretation of your webpage's content by crawlers, enhancing your site's indexing opportunities.
Using Header Tags
Using Header Tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) streamline page structure for better crawler navigation. Appropriately assigned tags direct crawlers to essential content parts, enhancing your pages' chance of indexing.
Optimizing URL Structures
Constructing clear, straightforward URL structures can benefit both users and search engine crawlers. URLs should be easily readable, containing relevant keywords that reflect the webpage's content.
Website's Loading Speed
Faster loading speeds improve the user experience and allow crawlers to index more pages during their visit. Hence, optimize page load times to ensure better indexing.
Interlinking Webpages
Interlinking webpages enables easy navigation for users and helps crawlers discover your content. Interlinking also transfers link juice across pages, boosting the ranking potential of linked pages.
In conclusion, diligent work on your website’s crawlability, content quality, and on-page SEO techniques can significantly improve indexing in SEO. These strategies increase the likelihood that your site's pages will appear in relevant search results, thereby driving more organic traffic to your site.
What are the two main ways to index content to make it searchable?
Keyword Based Indexing
One fundamental way to index content involves keyword analysis and optimization. This method entails identifying relevant search terms that readers may use when seeking your content. This strategy aims to boost visibility by increasing the likelihood of your blog post appearing in search results. It requires strategic selection and placement of keywords throughout your post.
Metadata Indexing
In addition to keyword indexing, metadata indexing serves as a crucial way to make content searchable. Metadata provides background information about a blog post, such as the author, date of publication, and a brief description. Search engines use this information to understand and categorize the content. Ensuring that your metadata accurately and concisely represents your blog post increases the probability of reaching the ideal readers.
Both keyword-based indexing and metadata indexing require conscious effort to effectively implement. Precisely selected, wisely positioned keywords increase the visibility of a blog post. Meanwhile, accurate metadata enhances a post’s relevance to potential readers. These combined methods ensure thorough indexing, improving the discoverability of blog posts among millions available online.
What are the two main ways to index content to make it searchable?
Keyword Optimization
The first principal method to index content for searchability involves keyword optimization. This process entails identifying and incorporating relevant keywords into the blog content. These keywords should mirror terms that potential blog readers would likely use during a web search. By aligning the blog’s verbiage with these search terms, search engines can more easily link the content to relevant inquiries.
Meta Tags Utilization
The second predominant method to index content is through the utilization of meta tags. Meta tags are snippets of text that describe a page's content and don't appear on the page itself but only in the page's source code. Meta tags function as a “behind the scenes” method of indexing, communicating directly with search engines as opposed to individual users. Proper implementation of meta titles and descriptions can significantly enhance a blog post's discoverability and visibility in search engine results. Implementing meta tags accurately can lead to an increase in the click-through rate and a better SEO ranking.
In conclusion, both keyword optimization and meta tag utilization are invaluable tools for increasing blog post searchability. These indexing methods work best when used in tandem, creating a comprehensive and thorough approach to SEO. Therefore, blog creators must understand and effectively employ both techniques to maximize their content's accessibility and visibility.
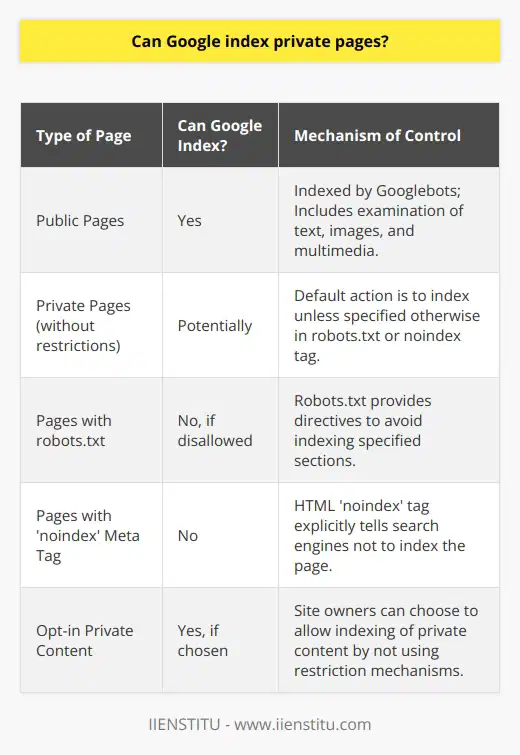
Can Google index private pages?
Understanding Google Indexing
Google Indexing involves the extraction of data to build a searchable index. It encompasses both public and private pages. However, it is not a simple process.
Indexing Public Pages
Google indexes public pages as a routine practice. Web crawlers, known as Googlebots, examine these pages to update Google's searchable index. This process includes analyzing the content, images, and videos on a page.
Private Pages and Google Indexing
Private pages, though, need special consideration. Theoretically, Google can index private pages. However, there are mechanisms in place to prevent unauthorized indexing of private content. Website owners can use a file known as the robots.txt to instruct Google not to index certain pages.
More about Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a public file that guides web crawlers. It tells them which pages to access, and which ones to avoid. With the help of this file, private pages remain unscanned by Googlebots.
User-Defined Control Over Indexing
Website owners also have control over their site's data. They can decide what content to make searchable. Using a 'noindex' meta tag, they can keep private pages from Google's index. This ensures private content does not appear in Google's search results.
In conclusion, while Google has the potential to index private pages, controls are in place to prevent this. Private pages will remain invisible to Google unless site owners decide otherwise.
Respect for Privacy
Ultimately, Google respects privacy considerations. Therefore, indexing only occurs at the discretion of site owners. This fosters a balance between maintaining an extensive, useful index and respecting the privacy of individuals and organizations.
How does SEO crawling and indexing work?
Understanding SEO Crawling
SEO crawling is primarily the process where search engine bots scan web content. Search engines send out crawlers, also known as spiders or bots, to discover publicly available webpages. The crawlers start with a list of URLs known as seeds, crawling the pages and then tracing the links on those pages to discover new URLs.
Role of Robots.txt
A critical aspect in the crawling process is Robots.txt. It is a file that website owners use to give instructions about their site to web robots. This file can include directives for the bots on which paths they can or cannot fetch from a certain site.
Indexing Web Pages
Once the crawling process is finished, the search engine proceeds to indexing. This is where it copies web pages, stores it in a database, to be retrieved later when needed for a search query. During indexing, the search engine analyzes the quality and relevance of content, location and other factors.
Content Quality and Relevance
The quality and relevance of content are crucial for a webpage’s visibility in search results. Google, for instance, uses a particular algorithm to determine the relevance of a page to a specific search query. This algorithm considers hundreds of factors, including keywords, site usability, and page load speed.
Processing Search Requests
Finally, when a user types in a search request, the search engine recalls the indexed information. It then provides the most appropriate and relevant websites according to the search query. Thus, effective SEO crawling and indexing can significantly improve a webpage's visibility and ranking on search engine results.