Decision-making in business and everyday life is filled with uncertainty and potential risks. The stakes for making the right choice can be high, and the complexities involved require methodical and informed approaches. This is where risk analysis becomes an indispensable tool in an individual's problem-solving arsenal. By identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing potential risks, one can formulate strategies that not only mitigate potential downsides but also optimize overall decision-making efficacy.
This blog delves into the world of risk analysis techniques, outlining how they can lead to smarter, more informed decision-making. The aim is to furnish readers with a foundational understanding bolstered by practical methods for assessing and handling risk within various contexts.
🔊 Ready for an auditory reading experience? Just click the "Play" button right below this text and immerse yourself in our captivating audio version. Ideal for those who prefer listening to stories, or for times when you're multitasking. Engage with our content effortlessly - one simple click is all it takes to transform your reading into listening!
Understanding the Fundamentals of Risk Management
Risk management is a multifaceted discipline that plays a critical role in ensuring the stability and success of projects, businesses, and strategic initiatives. At its core, risk management involves identifying potential problems that could threaten the essential objectives of a project or enterprise and putting measures in place to avoid, minimize, or mitigate the impacts of those risks.
The role of risk analysis within the spectrum of risk management is crucial, serving as the detective work that unveils potential threats before they can manifest. This analytical phase lays the groundwork for the more proactive elements of risk management, allowing for preemptive action rather than reactive scrambling. Without risk analysis, risk management would akin to navigating a minefield without a map – perilous and imprudent.
The comprehensive process of risk management encompasses several other closely related fields, most notably decision analysis and risk assessment. These interconnected disciplines collectively contribute to an organization's ability to handle uncertainties effectively. Decision analysis provides the structural and logical framework for making complex decisions in the face of uncertainty, while risk assessment deals with the systematic approach to identifying and evaluating risks associated with particular decisions or operations. When interwoven effectively, these practices empower organizations to make decisions that are not only informed but strategic and resilient.
Comprehensive Techniques for Effective Risk Analysis
Qualitative Risk Analysis Methods
Qualitative risk analysis is an essential aspect of risk management that relies on the judgment and experience of experts to assess potential threats. This method often serves as the initial stage in the risk analysis process, particularly when quantitative data is scarce or when dealing with intangible risks like reputational harm or employee satisfaction. Techniques like SWOT Analysis, which scrutinizes an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, are staple qualitative tools.
Expert judgment and brainstorming sessions, in conjunction with systematic approaches like the Delphi method, serve to aggregate diverse insights and foster consensus among stakeholders. This level of analysis is especially useful in the early stages of project planning or when venturing into new and unstudied territories where precise numerical data may not yet be available.
The qualitative approach, nevertheless, does not come without limitations. The subjective nature of such analysis and its reliance on human perception mean that it is vulnerable to biases and inconsistencies. Thus, while qualitative methods can provide a valuable overview of the risks present, they are often bolstered by more objective, quantitative techniques to ensure a well-rounded risk assessment.
Quantitative Risk Analysis Methods
Quantitative risk analysis puts numbers to the risks, providing a more objective and measurable approach to understanding potential threats. This branch of analysis is vital in dealing with complex systems or when the consequences of risks carry significant financial implications. Techniques like decision tree analysis help dissect the pathways of decision-making, mapping out potential outcomes and associated probabilities in a structured manner.
Monte Carlo simulations are another cornerstone of quantitative analysis. By running a vast number of simulations, taking random samples from input probabilities and impacts, these simulations provide a statistical distribution of possible outcomes, allowing decision-makers to understand variability and the likelihood of different scenarios. Similarly, sensitivity analysis probes the impact of variations in inputs on the final outcome, highlighting which factors have the most sway on the decision or project at hand.
Quantitative techniques can furnish a stark picture of the potential consequences of risks, but they require robust data. Their deployment, therefore, must be founded on accurate and reliable information. Furthermore, numerical precision does not negate the need for managerial judgment — it merely informs it with empirical evidence, allowing for smarter and more strategic decision-making.
Hybrid Approaches to Risk Analysis
In the dynamic field of risk management, hybrid approaches have emerged that mesh both qualitative insights and quantitative rigor. These methodologies seek to capitalize on the strengths of each type of analysis while mitigating their respective limitations. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), for example, employs qualitative assessments to prioritize risks quantitatively through risk prioritization numbers, blending subjective expertise with an objective prioritization system.
The use of a risk matrix, which classifies risks according to their likelihood and impact, represents another hybrid technique. While the definitions of "likelihood" and "impact" may initially be qualitative, they can be supported by quantitative data and analysis, resulting in a more informed risk prioritization tool.
Selecting the right mix of qualitative and quantitative elements often depends on the specific context of the decision or project and the information available. The incorporation of a varied toolkit of hybrid methods can enable a comprehensive and nuanced view of the risk landscape, enabling decision-makers to balance intuition and empirical analysis in their risk management strategies.
Implementing Risk Mitigation Strategies
After the diligent process of identifying and analyzing risks, the next crucial step is to implement risk mitigation strategies. These strategies are designed to reduce the likelihood of a risk occurring or to lessen its impact should it occur. They are essential components of a proactive risk management plan, ensuring that potential problems are addressed before they can have adverse effects.
Strategies take various forms, such as risk avoidance, transfer, acceptance, or reduction, and their application is typically informed by the findings of the preceding risk analysis. For instance, an organization may decide to purchase insurance to transfer financial risks or to establish redundant systems as part of a risk reduction strategy. These interventions must be carefully considered and tailored to the specific nature and scale of the risks involved.
Highlighting real-world applications of these strategies can underscore their value. For example, considering how a company navigated a potential supply chain disruption by diversifying its supplier base can provide a concrete illustration of risk mitigation in action. By linking theoretical concepts with actual cases, the abstract principles of risk mitigation become tangible and relatable, validating their relevance in smart decision-making processes.
Throughout this discourse, we have navigated the complex terrain of risk analysis and its critical role in smart decision-making. A clear appreciation has been developed for both qualitative and quantitative techniques, along with the innovative hybrid approaches that enhance the efficacy of risk management practices. We have underscored the indelible link between robust risk analysis and the development of sound risk mitigation strategies, affirming their collective value in forearming organizations and individuals against potential adversities.
The importance of rigorous risk analysis and well-planned mitigation strategies in decision-making cannot be overemphasized. They are the bedrock upon which resilient, responsive, and ultimately successful outcomes are built. As such, we call upon readers to embed these principles and techniques into their decision-making frameworks, for it is through such prudence that truly smart decisions are made.
Further Considerations:
As the field of risk analysis continues to evolve, so too must our approaches and tools. Advancements in technology, changes in regulatory landscapes, and the emergence of new risks necessitate ongoing education and adaptation. It is advisable for practitioners and stakeholders to incorporate new findings and methodologies as they become available, ensuring that their risk management capabilities remain at the cutting edge.
Continuous professional development, such as a problem solving skills course or an online mba course, can be invaluable resources in staying current with the latest risk management trends and practices. Our collective task is to nurture a culture of lifelong learning within the domain of risk analysis, fostering an environment where smart decision-making and effective risk management are not just aspirational goals but realized standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
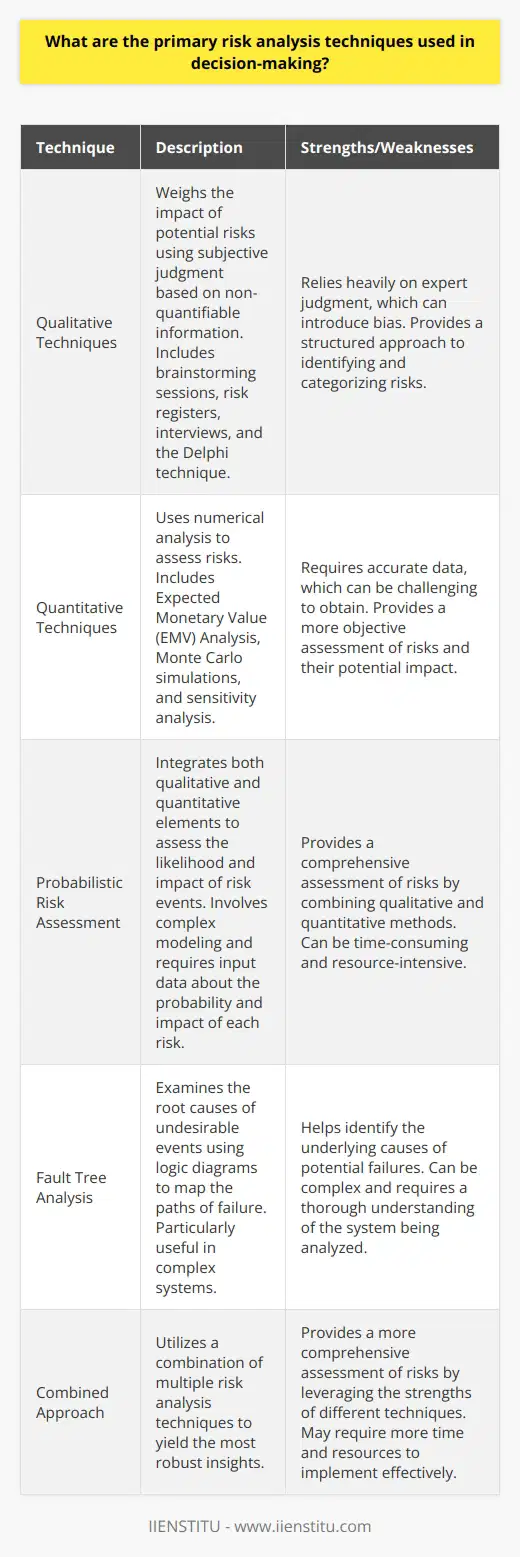
What are the primary risk analysis techniques used in decision-making?
Risk Analysis in Decision-Making
Risk analysis plays a pivotal role in decision-making. It offers a structured approach to identifying and assessing potential risks. Such analysis allows decision-makers to anticipate what could go wrong. They can, thus, proactively devise strategies to mitigate those risks. Several primary techniques form the backbone of risk analysis in decision-making.
Qualitative Techniques
Qualitative risk analysis weighs the impact of potential risks. It uses subjective judgment based on non-quantifiable information. This method often starts with brainstorming sessions. Stakeholders and experts gather to identify possible risks.
Risk registers are another qualitative tool. These registers list identified risks and note their characteristics. They evaluate risks based on their probability and impact. The results may classify risks into categories such as ‘high’, ‘medium’, or ‘low’.
Interviews and Delphi technique are other qualitative methods. The Delphi technique involves a series of rounds of anonymous feedback from experts. Each round refines the assessment to reach a consensus.
Quantitative Techniques
Quantitative methods make use of numerical analysis. The Expected Monetary Value (EMV) Analysis is common. It calculates the probable cost of risk over time. This technique multiplies the cost of each risk by its probability.
Monte Carlo simulations provide another quantitative option. These simulations model the probability of different outcomes in complex systems. Analysts use them to see the range of potential results and their likelihood.
Sensitivity analysis explores how different values of an independent variable affect a particular dependent variable. It helps in identifying the risks that have the most impact on project outcomes.
Probabilistic Risk Assessment
This integrates both qualitative and quantitative elements. It assesses the likelihood of a risk event occurring. It also estimates the impact should the event occur. This multi-disciplinary method usually involves complex modeling. It requires input data about the probability and impact of each risk.
Fault Tree Analysis
Fault tree analysis examines the root causes of undesirable events. It uses logic diagrams to map the paths of failure. This technique is particularly useful in complex systems. It helps trace the chain of events leading to a failure.
These techniques provide a thorough examination of potential risks. Decision makers can use them to craft informed strategies. However, no single method stands as the infallible tool for risk analysis. Combining multiple techniques often yields the most robust insights.
Each method has its strengths and weaknesses. Qualitative methods rely heavily on expert judgment. This can introduce bias. Quantitative techniques require accurate data. This can be challenging to obtain. Despite these challenges, risk analysis remains an invaluable aspect of decision-making. It fosters proactive management and enhances the likelihood of achieving project goals.
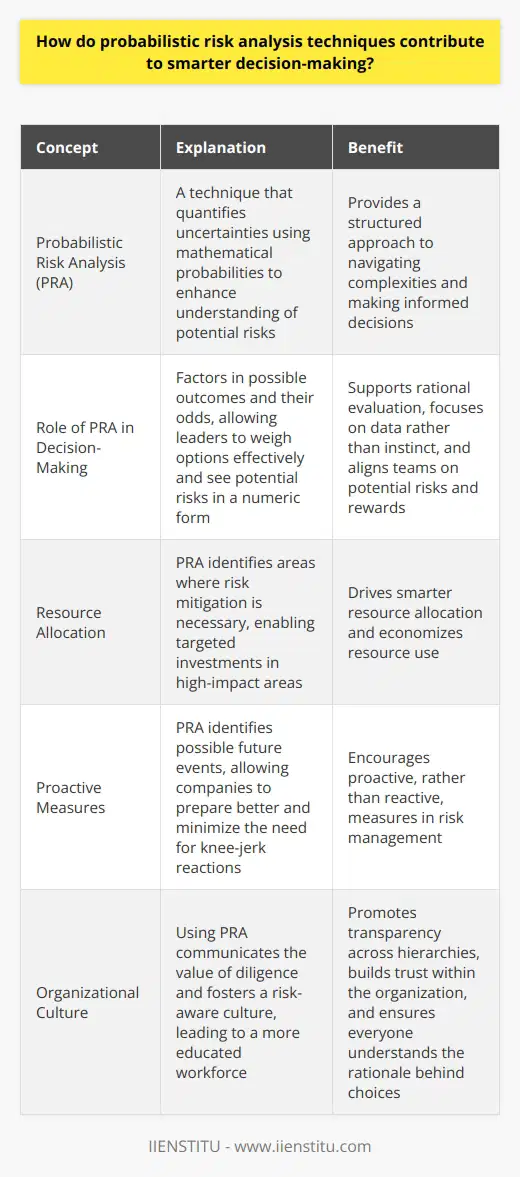
How do probabilistic risk analysis techniques contribute to smarter decision-making?
Understanding Probabilistic Risk Analysis
Risk is inherent in every decision. Decision-makers often face uncertainties. Uncertainties can relate to various factors. For instance, market trends, environmental changes, or technological advancements. Probabilistic risk analysis (PRA) offers a solution. It quantifies uncertainties using mathematical probabilities. This enhances understanding.
Role of PRA in Decision-Making
PRA shapes informed decisions. It factors in possible outcomes and their odds. This allows leaders to weigh options effectively. They can see potential risks in a numeric form. It supports a rational evaluation.
PRA focuses on data, not instinct. This reliance on quantitative assessment excludes personal biases. Numbers provide a common language. This aligns teams on potential risks and rewards.
Smarter Decisions with PRA
PRA drives smarter resource allocation. It shows where risk mitigation is necessary. Investments can thus target high-impact areas. This economizes resource use.
Cost-benefit analysis is clearer with PRA.
It shows probable outcomes for each path.
Decision-makers craft strategies with foresight.
They can also prepare contingency plans.
PRA encourages proactive, not reactive, measures. It identifies possible future events. Companies can then prepare better. This minimizes the need for knee-jerk reactions.
Benefits Beyond Prediction
PRA promotes a risk-aware culture. By using PRA, organizations communicate they value diligence. Teams learn to consider risk in every project. This leads to a more educated workforce.
It showcases potential domino effects.
Personnel acknowledge interdependent risks.
They grasp the bigger picture in planning.
PRA fosters transparency across hierarchies. Everyone understands the rationale behind choices. There's a clear link between risks and strategies. This builds trust within the organization.
In summary, probabilistic risk analysis enhances decisions. It brings a structured approach to uncertainty. It quantifies the unpredictable. It thus aids in navigating complexities. Through PRA, smarter, more informed decisions guide the future.
How does sensitivity analysis aid in making informed decisions in risk-prone situations?
Understanding Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis stands as a critical tool. It enables robust decision-making. This happens especially under uncertain conditions. Through sensitivity analysis, decision-makers analyze model changes. These changes stem from different input variables. The technique helps identify which inputs affect outputs the most. With this knowledge, better decisions arise. Often, these relate to financial, engineering, and policy scenarios.
Sensitivity Analysis in Action
Consider a project with various inputs. Costs, timelines, and market conditions often vary. Sensitivity analysis tests these variables. It examines their impact on project outcomes. Stakeholders see potential variations in results. Thus, they can weigh risks against benefits. Different scenarios reveal the most critical variables. Businesses can prioritize these during planning.
Risk Management Strengthened
Sensitivity analysis shines in risk management. It dissects each variable. The analysis seeks to understand its influence on the final outcome. Thus, it helps forecast the effects of uncertainty. Managers can pinpoint high-risk areas. They can make data-driven defensive strategies. This approach minimizes negative impacts.
Informed Strategic Decisions
Sensitivity analysis informs strategic decisions. It offers a detailed view of potential changes. Leaders use this information. They craft strategies that can endure uncertain conditions. Adaptability becomes a strategic advantage. This approach helps companies remain resilient.
Benefits of Sensitivity Analysis
Improves understanding: It clarifies how variables interact.
Focuses efforts: It highlights which inputs matter most.
Supports transparency: It allows for open discussion on risks.
Encourages preparedness: Businesses can plan for different scenarios.
Facilitates communication: Teams can discuss findings effectively.
Challenges in Sensitivity Analysis
Despite its strengths, it has limitations. Assumptions are necessary for model building. These assumptions can be incorrect. They can mislead the analysis. Additionally, sensitivity analysis can be complex. It requires significant expertise. Moreover, the analysis does not provide definitive answers. Instead, it illuminates the range of possibilities.
Sensitivity analysis remains a powerful tool. It aids decision makers in navigating complex risks. It promotes informed and adaptive strategies. Organizations appreciate its value in risk-prone situations. By embracing sensitivity analysis, leaders enhance their foresight. They build resilience against unforeseen developments. As a result, they stand better equipped to face the uncertainties of the business world.