This article discusses Order Postponement, a process of delaying or breaking up an order for a customer for various reasons. It explains the benefits and challenges of this process and how it can be used to improve customer service. Benefits include providing customers with a more flexible ordering process and reducing inventory costs for the seller.
Challenges have difficulty managing the customer’s order, additional fees, and tracking the customer’s order. Sellers must weigh the benefits and challenges of Order Postponement before deciding whether or not to use it.
Introduction
What is Order Postponement?
Benefits of Order Postponement
Challenges of Order Postponement
Conclusion
Introduction: Customer service is a vital component of the logistics supply chain and involves a range of tasks that must be coordinated to ensure quality service delivery to customers.
Depending on the customer’s needs, orders may need to be postponed or executed in parts, known as Order Postponement. This article will discuss the benefits and challenges of Order Postponement and how it can be used to improve customer service.
What is Order Postponement?
Order Postponement is the process of delaying or breaking up an order for a customer for various reasons. For example, it could be because the customer needs to reschedule their requirements or because the seller has a product that is not currently available but will be available in the future. In either case, the customer’s order is postponed until the product is available or the customer’s requirements change.
This process is often used when the customer needs a product that is difficult to source or when the current stock cannot meet the customer’s needs.
Benefits of Order Postponement
Order Postponement can be beneficial for both the customer and the seller. For the customer, it can provide a more flexible ordering process, allowing them to receive the product when they need it rather than when it is available. This can help them to manage their inventory better and reduce the need for large orders.
Order Postponement can help minimize inventory costs for the seller, as they can order products in smaller batches and only when needed. It can also help to reduce the risk of overstocking and ensure that products are available when the customer needs them.
Challenges of Order Postponement
Although Order Postponement can be beneficial, it can also present some challenges. For one, managing the customer’s order can be difficult, as it may need to be broken up into smaller batches and shipped at different times. This can be time-consuming and can require additional resources to manage the orders.
Additionally, Order Postponement can be costly, as the seller may pay extra shipping and handling fees. Lastly, tracking the customer’s order can be challenging, as it may be split up into multiple shipments.
Conclusion: Order Postponement can be a valuable tool for improving customer service, as it allows customers to receive the products they need when they need them. However, it can also present challenges, such as difficulty tracking the customer’s order and additional costs. Therefore, sellers need to weigh the benefits and challenges of Order Postponement before deciding whether or not to use it.
Delaying orders can be the key to successful logistics management, but only when done with purpose and precision.
Related Course: Logistics Training Courses
Frequently Asked Questions
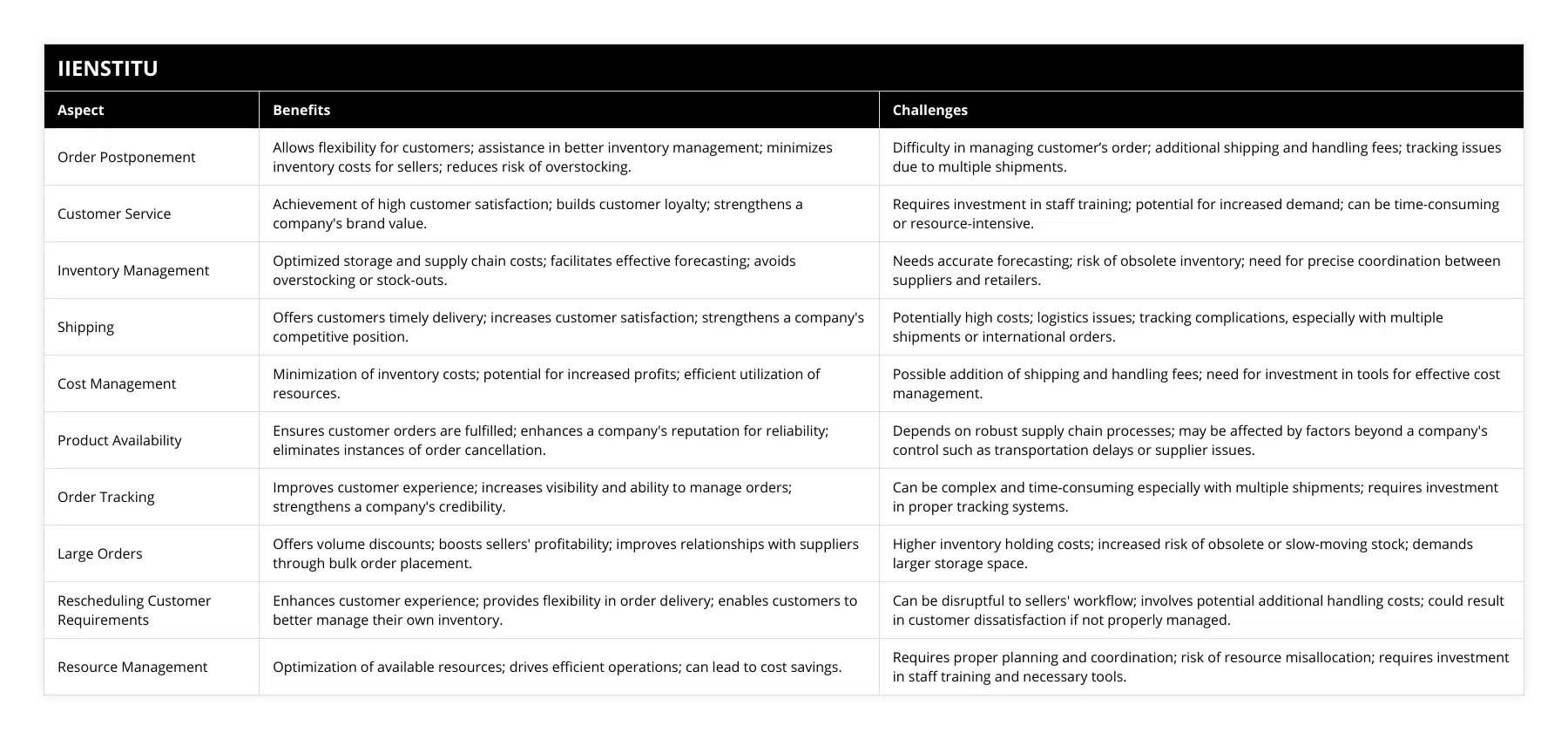
What are the key advantages of using order postponement to optimize logistics management?
Logistics management plays a vital role in the success of any business. As such, it is important to consider strategies that can help optimize the process and maximize efficiency. One such strategy is order postponement, which can provide numerous advantages for businesses.
Order postponement is a strategy that involves delaying the fulfillment of a customer’s order until the last possible moment. This means that instead of fulfilling orders as soon as they are received, the charges are stored in an inventory and only fulfilled when a customer places an order. This strategy can help businesses reduce inventory levels, improve customer service and reduce costs.
The primary advantage of using order postponement is that it allows businesses to reduce their inventory levels. This is because orders are stored in an inventory and only fulfilled when a customer places an order. This means companies can reduce inventory costs, as they do not need to keep as many items. Additionally, it can also help reduce the risk of overstocking, as businesses can delay the fulfillment of orders until demand is known with greater accuracy.
Order postponement can also help improve customer service. This is because it allows businesses to be more responsive to customer needs, as they can fulfill orders quickly and accurately. This can help improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, which can benefit businesses in the long run.
Finally, order postponement can help reduce costs. This is because businesses can avoid the costs associated with storing and shipping large quantities of items. Additionally, they can also avoid the costs associated with overstocking. This can help businesses save money and increase profitability.
In conclusion, order postponement can provide numerous advantages for businesses that use it. It can help reduce inventory levels, improve customer service, and reduce costs. Therefore, this strategy should be considered for companies looking to optimize their logistics management.
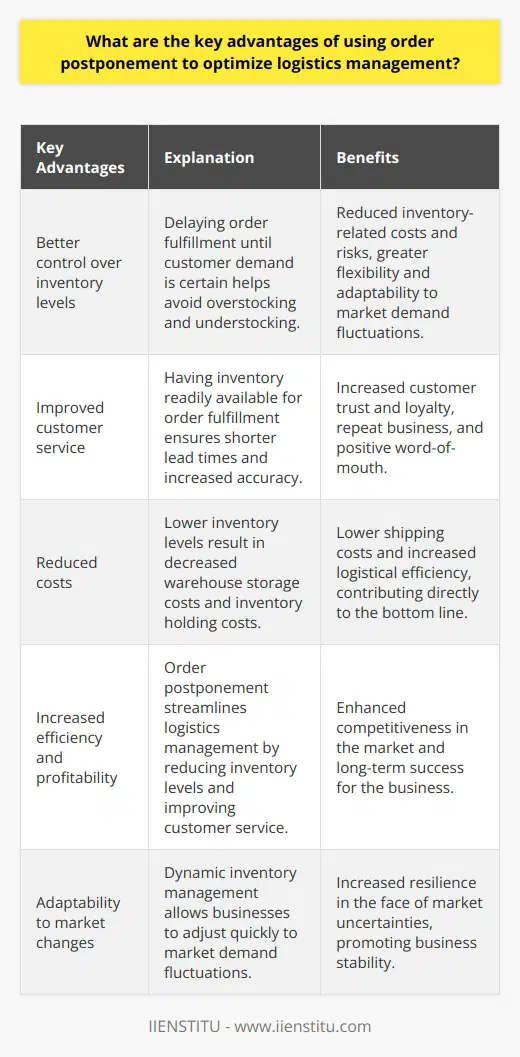
How can order postponement help reduce inventory costs?
As businesses strive to optimize their supply chain operations, inventory management has become an increasingly important consideration. Order postponement is one of the most effective techniques for reducing inventory costs. Order postponement is a strategy manufacturer, retailers, and distributors use to delay an order's delivery until it is most needed. This approach allows businesses to reduce inventory costs by reducing the amount of stock they need to maintain to fulfill customer demand.
Order postponement can be implemented in various ways, depending on the type of business and the nature of the product. For example, in the case of a manufacturing facility, a company can use postponement by delaying the release of a product until the last possible moment. This might involve waiting to manufacture specific components until the customer has placed an order or assembling and packaging a product until the order has been placed. By delaying the start of production, the company can reduce the amount of stock it needs to keep on hand to fulfill customer orders.
Retailers and distributors can also use order postponement to reduce inventory costs. For example, retailers may choose to delay the shipment of an item until the customer has placed an order, or a distributor may delay the shipment of an item until a certain number of orders have been set. By postponing a load of an item until the customer has placed an order, the company can reduce the amount of stock it needs to keep on hand to fulfill customer orders.
In addition to reducing inventory costs, order postponement can also help businesses to reduce their overall lead time. By postponing the delivery of an order until the moment when it is most needed, the company can reduce the amount of time it takes to fulfill customer orders. This can help to reduce operational costs and improve customer service, as orders can be fulfilled more quickly.
Order postponement is a powerful tool for reducing inventory costs and is an effective strategy for businesses of all sizes. By delaying the delivery of an item until the moment when it is most needed, companies can reduce the amount of stock they need to maintain and their overall lead time. In doing so, companies can reduce inventory costs and improve their profitability.
What strategies can be employed to overcome the challenges associated with order postponement?
Postponement of orders is an increasingly common phenomenon in the modern business environment due to various factors, including supply chain disruptions, market volatility, and changing customer demand. As a result, many organizations have had to develop strategies to manage the challenges associated with order postponement effectively.
One approach to overcoming the challenges of order postponement is the implementation of an inventory buffer. An inventory buffer is designed to store stock in anticipation of future demand or to act as a ‘safety net’ against delays in order fulfillment. An inventory buffer can also provide a cushion against unexpected directions by allowing organizations to fulfill orders they may not have anticipated quickly.
In addition to an inventory buffer, organizations can also manage order postponement challenges with proper forecasting and planning. First, organizations should create and monitor forecasts that provide insight into future customer demand and inventory levels. This helps businesses understand trends in customer demand and anticipate the need for a buffer of additional inventory. Additionally, organizations should use this forecasting data to plan for supply chain disruptions and other potential issues that could lead to order postponements.
Organizations can also mitigate the challenges of order postponement by increasing their collaboration with suppliers and vendors. Organizations can better understand the supply chain by working closely with suppliers and identifying potential issues that could lead to order postponements. Additionally, organizations should develop and implement contingency plans to respond quickly to supply chain disruptions or other problems that could cause order postponements.
Finally, organizations should also consider using technology to manage order postponement challenges. For example, organizations can use predictive analytics to provide better insight into future customer demand and anticipate potential order postponements. Additionally, organizations can use enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to manage their inventory, production, and supply chain processes. ERP systems allow organizations to respond better to changes in customer demand and quickly adapt their operations to meet market fluctuations.
In conclusion, order postponements can present a variety of challenges to organizations. However, organizations can effectively manage these challenges by implementing an inventory buffer, proper forecasting and planning, increased collaboration with suppliers, and using technology such as predictive analytics and ERP systems. By taking these steps, organizations can better manage the challenges associated with order postponement and ensure their operations remain efficient and effective.
What is the theoretical basis for the postponement principle in logistics?
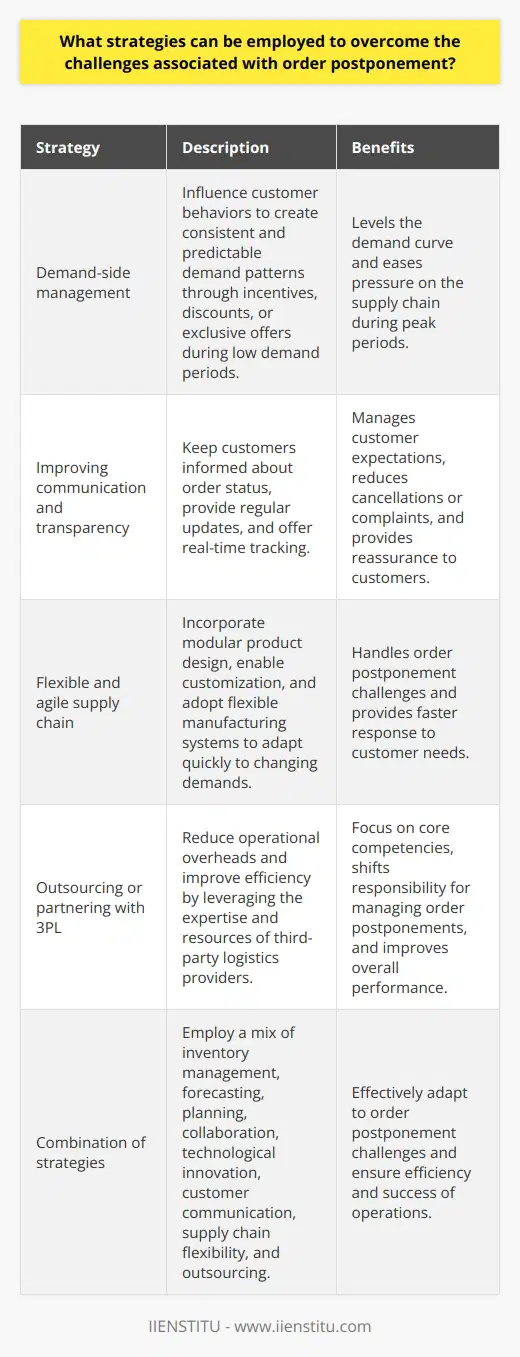
Theoretical Foundation of Postponement Principle
The postponement principle in logistics is grounded in two key theories: the inventory theory and the production-distribution theory. The inventory theory deals with managing stock levels to minimize costs, whereas the production-distribution theory focuses on the optimal coordination of manufacturing and transportation activities in a supply chain.
Inventory Theory and Postponement
The inventory theory aims to balance holding costs, ordering costs, and shortage costs to achieve the most cost-effective inventory management. The postponement principle is a strategy that delays certain activities in the logistics process, such as final product assembly or packaging, until customer orders are received. By doing so, this strategy reduces the holding costs associated with keeping finished goods inventory, as well as the risks of stock obsolescence or demand fluctuations. Furthermore, the postponement principle allows businesses to better tailor products to specific customer needs, which can lead to enhanced customer satisfaction and increased sales.
Production-Distribution Theory Implications
The production-distribution theory suggests that coordinating the activities of manufacturing, warehousing, and transporting goods can result in a more efficient and cost-effective supply chain. The postponement principle aligns with this theory by shifting some activities, such as customization or labeling, closer to the point of consumption. This can lead to reduced lead times, increased responsiveness, and minimized shipping costs. Moreover, postponing certain processes allows companies to consolidate shipments, resulting in lower overall transportation costs.
In summary, the theoretical basis for the postponement principle in logistics lies in the intersection of inventory theory and production-distribution theory. By delaying specific activities in the supply chain until customer orders arrive, the postponement principle enables businesses to optimize inventory management, reduce costs, and improve responsiveness to customer demands. This strategy can ultimately lead to increased efficiency and competitiveness in the constantly-evolving global marketplace.
How can data analytics be utilized to improve the effectiveness of postponement strategies in logistics operations?
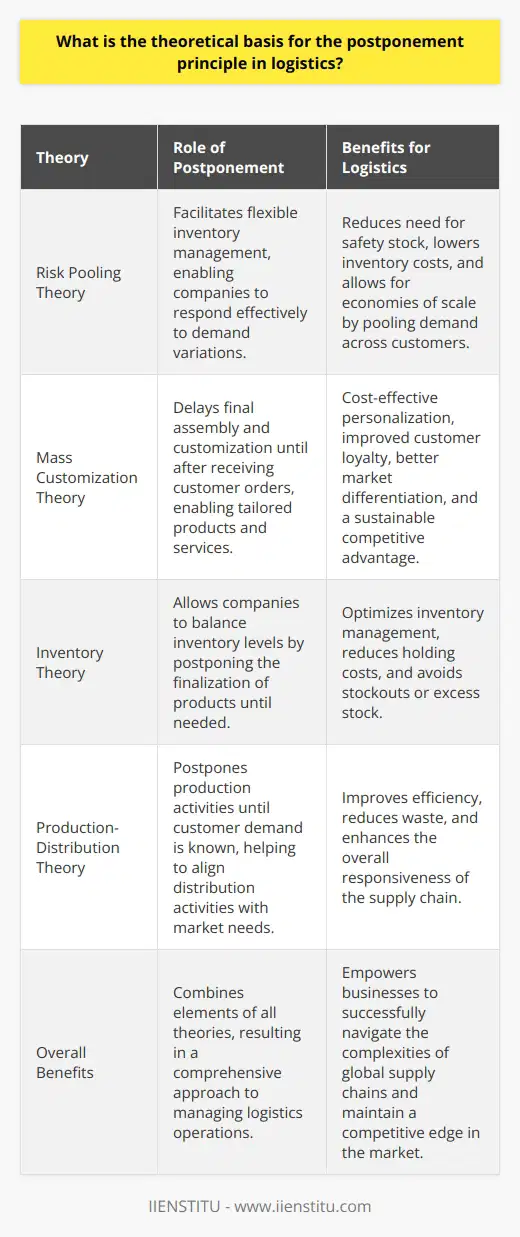
**Utilizing Data Analytics in Postponement Strategies**
Data analytics can enhance the effectiveness of postponement strategies in logistics operations by optimizing decision-making processes, reducing lead times, and increasing flexibility. To achieve this, businesses must identify key performance indicators (KPIs) and mine historical data for insights that inform postponement decisions.
**Optimizing Decision-Making Processes**
One of the main advantages of data analytics is the improvement of decision-making processes. By analyzing past data, companies can identify patterns and trends that allow them to predict future demands, thereby reducing uncertainties. This enables better-aligned postponement strategies, ensuring inventory availability for fluctuating customer demands and minimizing stockouts or overstocking scenarios.
**Reducing Lead Times**
By integrating data analytics into logistic operations, companies can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in their supply chain, allowing them to develop targeted, data-driven solutions. As a result, organizations can reduce lead times, which enables them to react faster to changes in demand, enhancing the effectiveness of postponement strategies.
**Increasing Flexibility**
Data analytics help increase supply chain flexibility, as businesses can assess the impact of various postponement strategies under different scenarios. Simulations and forecasting models powered by data analytics provide insights into how different postponements impact the supply chain, enabling organizations to design strategies that effectively balance cost, risk, and customer satisfaction.
**Leveraging Technological Advancements**
The adoption of machine learning and artificial intelligence in data analytics allows for more accurate predictions and quicker data processing. Utilizing these technologies in improving postponement strategies would result in increased effectiveness, as they would provide better demand forecasts and more detailed insights into supply chain performance.
**Conclusion**
Incorporating data analytics into logistics operations can lead to more effective postponement strategies, contributing to optimized decision-making processes, reduced lead times, and increased flexibility in addressing customer demands. By leveraging technological advancements, companies can further enhance their ability to create data-driven postponement strategies that improve overall supply chain performance.
In what industries and market contexts is the strategy of postponement most beneficial for optimizing logistics and customer satisfaction?
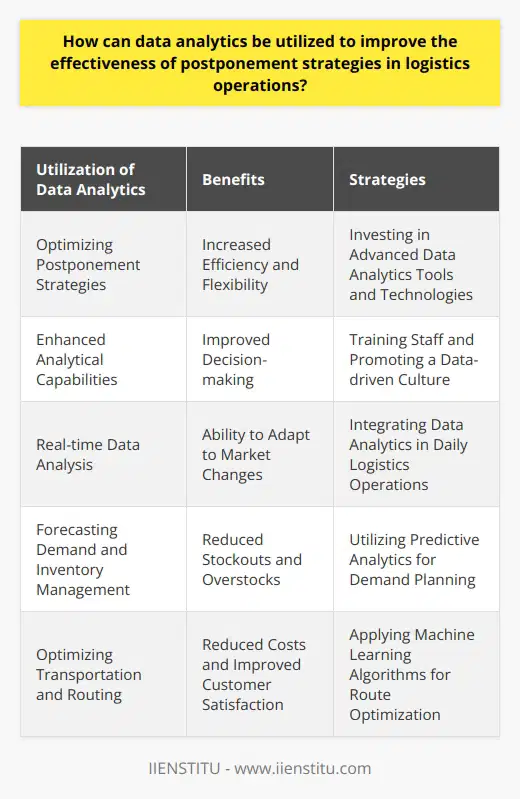
Benefits of Postponement in Various Industries
The strategy of postponement proves to be most beneficial for industries and market contexts where product customization or responsiveness to fluctuating demand plays a critical role in optimizing logistics and customer satisfaction. In such industries, implementing postponement tactics can significantly increase efficiency, reduce inventory costs, and enhance customer service levels.
Personalized Products and Services
In the realm of personalized products and services, such as customized apparel or accessories, the postponement strategy is particularly advantageous. By delaying the finalization of products until customer orders are received, companies can effectively tailor offerings to individual preferences while minimizing the risk of holding excessive or undesirable inventory. This agility in production and distribution creates a competitive advantage and increases customer satisfaction.
Technology and Electronics Industry
The fast-paced technology and electronics industry are characterized by rapidly evolving consumer demands and frequent product upgrades. Utilizing a postponement strategy, manufacturers can delay the assembly or introduction of specific components until market demands are better understood. This not only helps reduce inventory costs and obsolescence but also enables companies to respond more quickly to changes in demand, ensuring a higher degree of customer satisfaction.
Seasonal and Perishable Goods
In industries dealing with seasonal or perishable goods, such as the fashion, food, or beverage sectors, a postponement strategy allows companies to better align their production and distribution activities with the timing of customers' needs. By delaying the production or transportation of products until demand is clearer, these industries can avoid overstocking and subsequent markdowns, waste, or obsolescence. This ultimately leads to improved logistics efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Global Supply Chain Management
For companies operating in global markets or with complex supply chains, postponement tactics offer several potential benefits by allowing for the delay of product finalization, localization, or transportation until a more accurate market picture emerges. As a result, international firms can enjoy reduced lead times, decreased inventory costs, and faster response rates, ultimately enhancing both logistics performance and overall customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, the strategy of postponement is most advantageous in industries and market contexts where rapid responsiveness, product customization, or fluctuating demand are essential for optimizing logistics and customer satisfaction. The ability to delay production or distribution processes based on customer needs allows companies to save costs, improve efficiency, and ultimately provide better experiences for their customers.
What is the principle of postponement in logistics?
Understanding the Principle of Postponement
The principle of postponement in logistics refers to a supply chain management strategy that aims to minimize inventory costs, reduce the risk of stock obsolescence, and improve customer service levels by delaying the finalization of products until customer orders are received. Through this approach, companies producing and distributing goods can enhance their supply chain efficiency and responsiveness to market demands.
Benefits of Postponement
In warehouses and distribution centers, postponement involves holding inventory in a semi-finished or generic state and only completing the final product assembly, packaging, or labeling once a specific customer demand is identified. This flexibility enables organizations to better match the production and delivery of goods with actual customer requirements, leading to reduced inventory levels, faster response to market changes, and decreased supply chain complexity.
Postponement Strategies
There are several postponement strategies that can be implemented, depending on the nature of the product and the specific requirements of the supply chain. The most common types include:
Manufacturing Postponement: This strategy refers to delaying the final assembly or manufacturing process until customer orders are received, thus reducing the risk of overproduction and obsolescence.
Packaging Postponement: By postponing the final packaging or labeling of products until the point of shipment, companies can better accommodate last-minute customer preferences or regulatory changes.
Logistics Postponement: This strategy involves centralizing distribution operations and maintaining inventory in regional hubs, which allows for quicker response times when customer orders are received and reduces the need for large amounts of finished goods inventory.
Time Postponement: Time postponement refers to delaying the launch of new products, promotions, or marketing campaigns to better align with customer preferences or seasonal demand fluctuations.
Implementing Postponement Techniques
Successful implementation of postponement strategies requires careful analysis of product characteristics, market demand patterns, and supply chain capabilities. Companies must evaluate the trade-offs between customization and standardization, as well as the costs and benefits of increasing supply chain flexibility. In addition, technological advancements, such as advanced analytics and flexible manufacturing systems, can facilitate the adoption and management of postponement processes.
In conclusion, the principle of postponement in logistics enables organizations to optimize their inventory management, increase supply chain responsiveness, and improve customer service levels by aligning production and distribution processes more closely with actual customer demands. By adopting and implementing postponement strategies, companies can achieve significant cost savings, reduce risk, and enhance their overall competitive advantage.
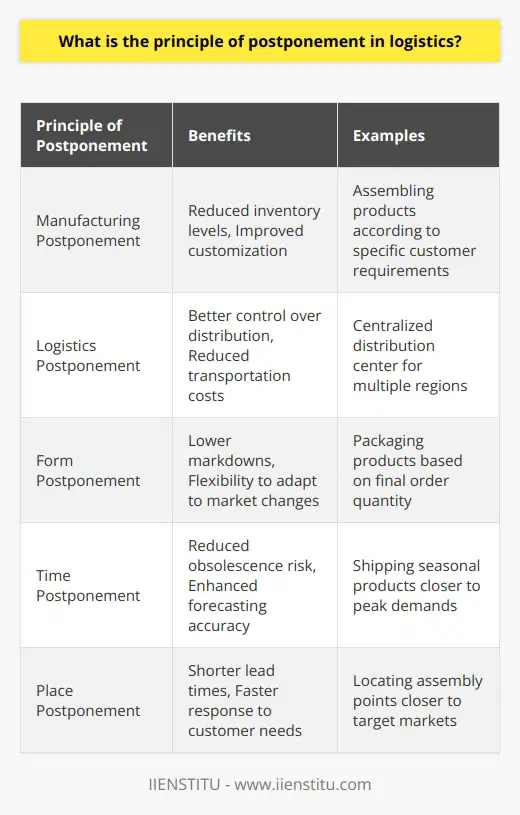
How does postponement work as a strategy in order to improve delivery efficiency?
Postponement as a Strategy for Efficiency
Underlying Concept
Postponement as a strategy involves delaying specific activities in the supply chain until actual customer orders are received. This approach enables companies to be more responsive to customer demands and reduce the risks associated with forecasting and inventory holding.
Inventory Reduction
One of the significant benefits of postponement is the reduction of inventory levels throughout the supply chain. Companies can avoid having excessive stock of finished goods while still meeting customer demands. This leads to lower storage costs and improved working capital.
Reduced Forecasting Errors
By postponing certain activities, companies can reduce the errors associated with predicting future customer demands. This is because the actual orders provide a more accurate picture of demand, which results in a better match between supply and demand. Such alignment ultimately contributes to enhanced delivery efficiency.
Enhanced Customization
Postponement strategies also enable companies to offer greater customization options to customers. By delaying specific operations, such as assembly or packaging, companies can tailor products to individual customer requirements, increasing customer satisfaction and overall efficiency in the delivery process.
Streamlined Operations
Implementing postponement strategies requires companies to streamline their operations to be more agile and responsive. As a result, companies can react more quickly to changes in demand or other external factors, such as market disruptions or competitor actions, to maintain efficient delivery.
Conclusion
In summary, postponement works as a strategy to improve delivery efficiency by reducing inventory levels, minimizing forecasting errors, enabling greater customization, and promoting streamlined operations. These benefits help companies better align their supply chain activities with customer demands, leading to higher levels of efficiency and customer satisfaction.
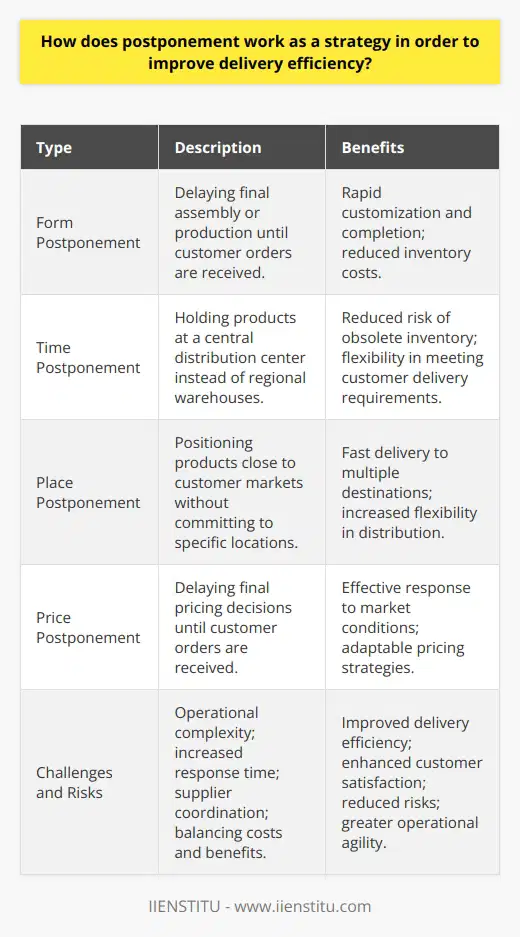
What is an example of postponement strategy in supply chain management?
Postponement Strategy Example
A prominent example of postponement strategy in supply chain management is the utilization of Dell's made-to-order approach. This approach, utilized by the American multinational computer technology company, allows customers to configure their computers according to their preferences and needs. Once the customer places an order, Dell initiates the manufacturing and assembly process, reducing lead times and improving overall customer satisfaction.
Made-to-Order Approach Benefits
The made-to-order approach incorporates the postponement strategy by delaying the final customization and assembly of products until a customer order is received. This mitigates the risk of holding excessive inventory, as well as reduces costs associated with obsolescence and warehousing. Additionally, this strategy allows Dell to offer a wide variety of customization options to its customers without significantly increasing production costs.
Customer Centricity and Competitive Advantage
By employing the postponement strategy, Dell successfully positions itself as a customer-centric organization, catering to the unique requirements of each individual customer. This tailored approach not only enhances brand loyalty but also creates a competitive advantage for the company in a saturated market. Moreover, Dell's made-to-order approach enables the company to rapidly respond to fluctuating market demands and changing consumer preferences, ensuring its products consistently meet customers' expectations.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the numerous benefits associated with the postponement strategy, there are certain challenges and limitations that must be considered. Implementing this approach requires a robust and efficient supply chain, capable of quickly responding to customer orders and delivering the end product with minimal delays. Additionally, there is a risk of customers becoming dissatisfied due to longer waiting times for customized products, as compared to readily available alternatives in the market.
Optimizing the Postponement Strategy
To overcome these challenges and effectively implement a postponement strategy, organizations must focus on refining their supply chain processes and prioritize customer satisfaction. This entails investing in advanced technology solutions for streamlining manufacturing and logistics, as well as developing strong partnerships with suppliers to ensure consistent and high-quality components. Moreover, effective communication and transparency with customers regarding lead times and delivery expectations are pivotal to maintaining a positive customer experience.
In conclusion, the postponement strategy exemplified by Dell's made-to-order approach offers significant benefits in supply chain management, cost optimization, and customer satisfaction. Therefore, organizations seeking to gain a competitive edge in the market should consider its potential advantages and challenges when developing their supply chain strategies.
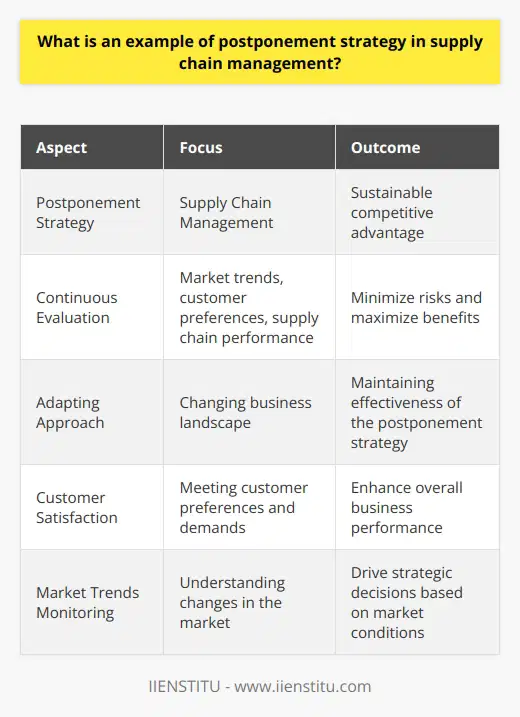
What is the role of data analytics in optimizing postponement strategies within the logistics industry?
Role of Data Analytics in Postponement Strategies
Data-Driven Decision Making
The role of data analytics in optimizing postponement strategies within the logistics industry is to enable data-driven decision making. By collecting and analyzing real-time data, companies can make well-informed decisions on how to manage supply chain risk, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Inventory Management
Data analytics helps companies to manage their inventories more effectively by providing insights into demand patterns and customer preferences. This information can be used to determine the optimal time to produce and ship goods, reducing excess inventory and minimizing stockouts.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is a crucial aspect of postponement strategies, allowing logistics companies to forecast demand and supply chain disruptions. By leveraging historical data and applying machine learning algorithms, organizations can create accurate predictions of future events, thus enabling them to create contingency plans and optimize resource allocation.
Demand Forecasting
Data analytics also plays a crucial role in demand forecasting, which is essential for determining when and where to delay production or shipment. By analyzing customer preferences, market trends, and seasonal fluctuations, companies can make strategic decisions on when to introduce new products, adjust pricing strategies, or vary inventory levels.
Supply Chain Visibility
Another benefit of data analytics in postponement strategies is the enhancement of supply chain visibility. By integrating data from various sources, such as suppliers, carriers, and customers, organizations can gain a clearer understanding of their supply chain processes, identify bottlenecks, and take proactive steps to mitigate potential issues.
Risk Mitigation
Through data analytics, companies can better identify, assess, and mitigate supply chain risks. This includes detecting potential disruptions, anticipating the impact of natural disasters, predicting changes in commodity prices, and anticipating fluctuations in currency exchange rates. By employing risk mitigation techniques, organizations can reduce the negative impacts of supply chain disruptions, thus optimizing their postponement strategies.
In conclusion, data analytics plays a vital role in optimizing postponement strategies by enabling data-driven decision making, improving inventory management, providing predictive analytics, enhancing demand forecasting, increasing supply chain visibility, and assisting in risk mitigation. By leveraging these capabilities, logistics companies can improve their operations, increase efficiency, and achieve competitive advantages in the market.
How can the implementation of postponement strategies contribute to overall sustainability within the supply chain?
Postponement Strategies for Sustainability
Postponement strategies refer to delaying specific supply chain processes until there is a clear demand signal. Implementing these strategies presents significant opportunities for enhancing overall sustainability within the supply chain.
Efficient Resource Utilization
Firstly, postponement strategies allow companies to utilize resources more efficiently by producing goods only when demand is confirmed. This leads to reduced overproduction, minimizing waste, and promoting better utilization of raw materials, energy, and labor.
Reduced Emissions
The implementation of postponement strategies also contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions. By streamlining production and distribution activities, companies can optimize transportation routes and reduce fuel consumption, thus minimizing their carbon footprint.
Inventory Management Improvements
Better inventory management is another positive outcome of implementing postponement strategies. By producing based on actual demand, companies can reduce excess inventory, freeing up valuable warehouse space and minimizing the potential for obsolete or expired products.
Optimized Product Lifecycle
In addition, postponement strategies can optimize the product lifecycle by enabling companies to respond quickly to changing customer needs and preferences. By adapting to market trends in real-time, companies can ensure that they are providing products that meet consumer demands, reducing instances of unsold or outdated products.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Finally, the implementation of postponement strategies encourages collaboration and communication among supply chain partners. By sharing information on demand forecasts and production schedules, companies can better coordinate their activities, leading to a more efficient, resilient, and sustainable supply chain.
In conclusion, the integration of postponement strategies within the supply chain can foster sustainability in various aspects - from efficient resource utilization to reduced emissions. By promoting better inventory management, optimizing the product lifecycle, and enhancing collaboration within supply chain partners, postponement strategies can significantly contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
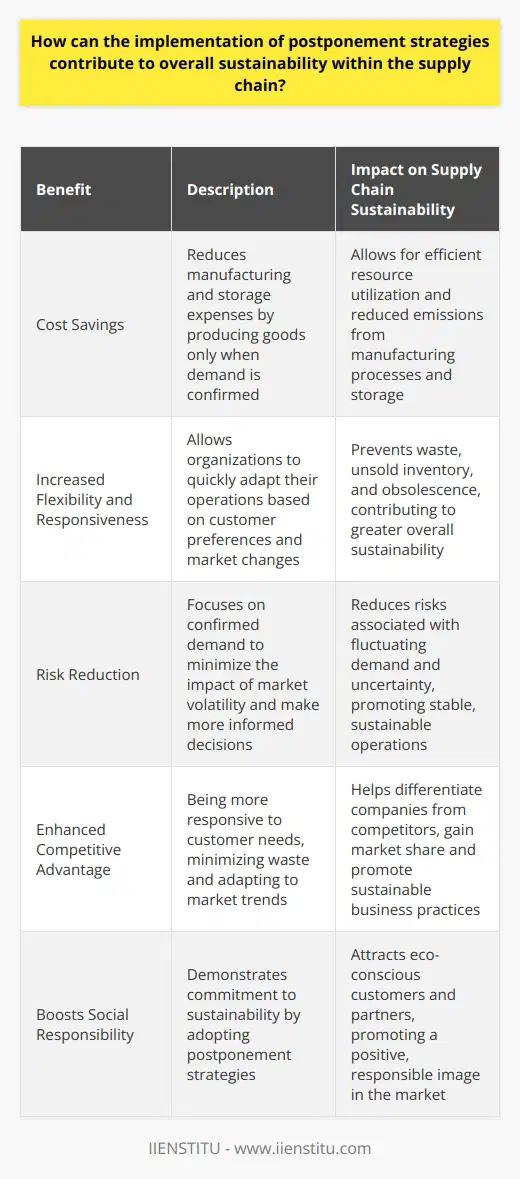
What factors should be considered when implementing a postponement strategy to ensure that it is most beneficial to both the company and its customers?
Adopting a Postponement Strategy
To maximize the benefits of a postponement strategy for both the company and its customers, several factors need to be considered. These include the type of postponement, supply chain dynamics, products involved, and company-customer communication.
Type of Postponement
There are various types of postponement strategies, such as manufacturing, geographic, and logistics postponements. Companies must evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of each type to choose the best fit for their business operations.
Supply Chain Dynamics
When implementing a postponement strategy, companies must understand the dynamics of their supply chain. Factors such as supplier and manufacturing lead times, inventory levels, and transportation costs are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of the postponement.
Product Characteristics
Successful postponement also requires considering the characteristics of the products involved. Highly customizable products with a wide variety of components are more suited for postponement strategies than standardized ones.
Customer Expectations
Managing customer expectations is fundamental for successful postponement strategies. Companies must balance the potential benefits of postponement with customers' demand for timely deliveries and consistent product quality.
Managing Risks
Postponement strategies inherently involve an element of risk. Companies adopting the strategy must assess and mitigate potential risks such as supply disruptions, changes in demand, and unexpected events like natural disasters.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Balancing the costs and benefits of postponement is essential to ensure its success. Companies should consider operational factors such as manufacturing complexity, storage, and transportation costs when evaluating the economic feasibility of implementing a postponement strategy.
Continuous Improvement
Once a postponement strategy is implemented, companies must be open to continuous improvement. Analyzing customer feedback, regularly examining the supply chain, and optimizing the postponement process will ensure that the strategy remains relevant and beneficial for both the company and its customers.
In conclusion, when companies consider implementing a postponement strategy, careful evaluation of multiple factors, including the type of postponement, supply chain dynamics, and customer expectations, is required to ensure its success. By considering these factors, companies will be better equipped to optimize the benefits of postponement for their business and customer satisfaction.
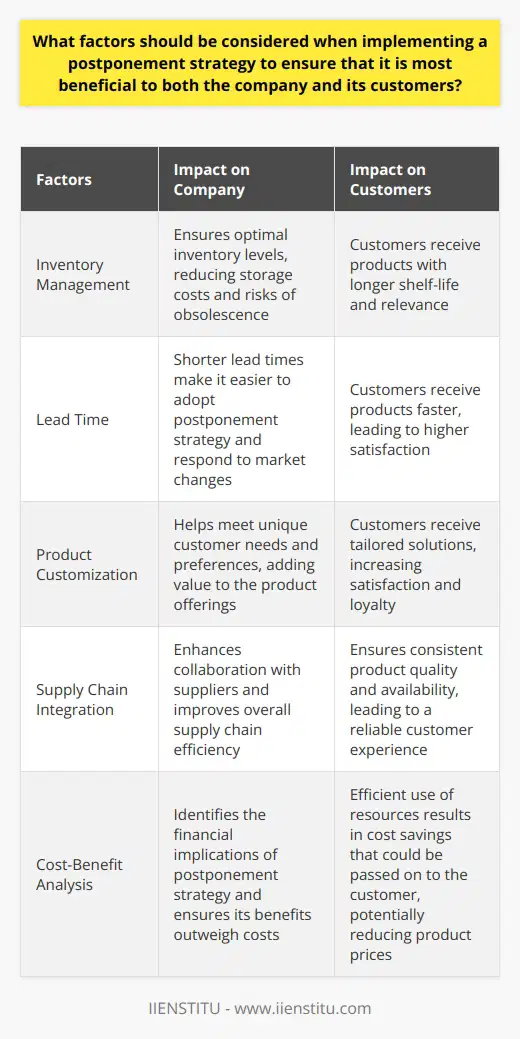
What are the critical factors that determine the success of a postponement strategy in supply chain management?
Factors Determining Success of Postponement Strategy
Effective Demand Forecasting
A crucial factor determining the success of a postponement strategy in supply chain management is effective demand forecasting. Accurate predictions of customer demand patterns enable companies to apply postponement techniques more efficiently, minimizing lead times, and reducing inventory costs.
Agile and Responsive Supply Chain
Another critical factor is the agility and responsiveness of the supply chain. Implementing postponement strategies requires flexible production processes and efficient logistics systems that can quickly react to changing demand. This adaptability enables companies to reduce the risk of stockouts and obsolete inventory while maintaining high customer service levels.
Supplier Collaboration
A strong collaboration with key suppliers is also essential for a successful postponement strategy. Close cooperation allows companies to share demand forecasts, mitigate supply chain disruptions, and optimize inventory management. In addition, establishing strategic partnerships with suppliers enables companies to leverage their expertise and jointly develop innovative postponement techniques.
Advanced Information Systems
Implementing postponement strategies requires advanced information systems that facilitate rapid communication between supply chain partners. These systems should be capable of handling large volumes of data, providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, orders, production plans, and distribution schedules. Moreover, advanced analytics can optimize decision-making by identifying opportunities to implement postponement strategies more effectively.
Customization and Standardization Balance
Lastly, finding the ideal balance between customization and standardization is a critical factor determining the success of a postponement strategy. Companies must assess the degree to which products or components can be standardized, allowing for a smoother integration of postponement techniques without compromising the uniqueness or quality of the final product.
In conclusion, the successful implementation of a postponement strategy in supply chain management hinges on effective demand forecasting, an agile and responsive supply chain, strong supplier collaboration, advanced information systems, and finding a suitable balance between customization and standardization. By addressing these critical factors, companies can optimize their supply chain performance, reduce costs, and better meet customer needs.
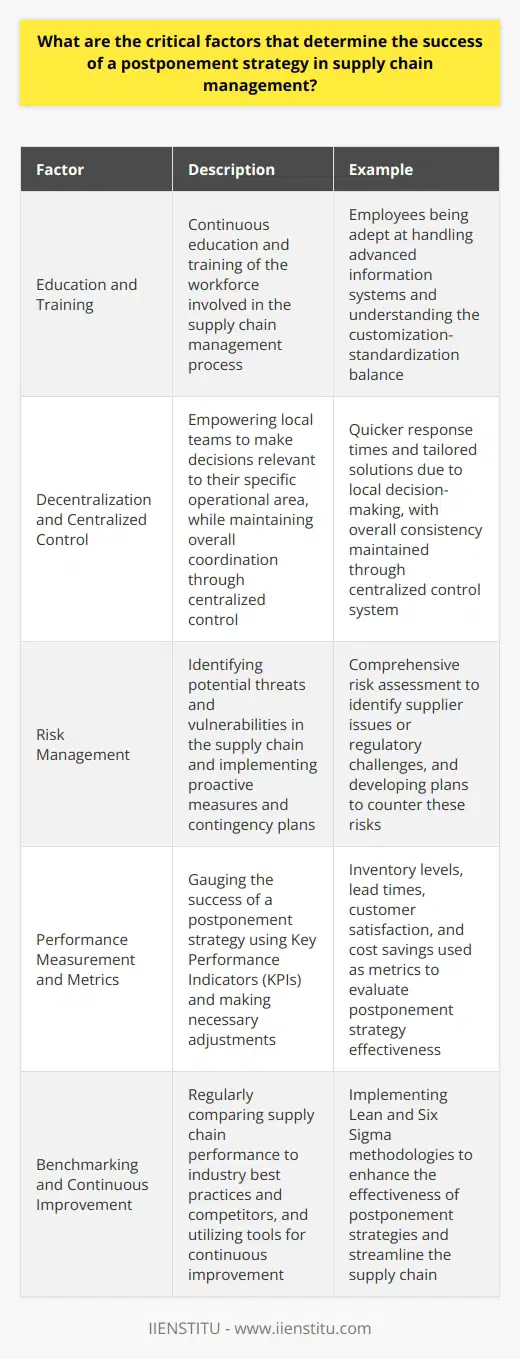
How do companies align their organizational structure and processes to effectively implement postponement strategies in logistics operations?
Defining Postponement Strategies in Logistics
Postponement strategies in logistics involve delaying certain activities or decisions until there is more information available, typically related to demand and supply chain conditions. Companies can use these strategies to optimize inventory management, reduce costs, and improve customer service. Aligning organizational structure and processes to effectively implement postponement strategies requires careful assessment and modification of existing systems.
Assessing Current Organizational Structure
First, companies must evaluate their current organizational structure, focusing on areas that may hinder or support postponement strategies. This involves identifying functional areas that influence decision-making related to demand and supply chain information, such as sales, planning, and logistics departments. Ideally, organizations should design cross-functional teams to facilitate better communication and enable collaborative decision-making.
Adapting Processes for Postponement
Next, companies should adapt their processes to accommodate postponement strategies. This includes the implementation of advanced planning systems that allow for real-time demand and supply chain data analysis, as well as adjustments to procurement, production, and distribution processes to ensure greater flexibility. Adjusting these processes enables companies to make informed decisions based on current conditions, reducing the likelihood of carrying excessive inventory or incurring additional costs.
Establishing Effective Communication Channels
Furthermore, companies must establish effective communication channels to enable efficient information sharing between different departments and functions. This can be achieved through integrating information systems and using collaborative tools that facilitate real-time information exchange. Effective communication is crucial, as postponement strategies hinge on accurate and timely data, allowing organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
Developing a Culture of Agility and Adaptability
Finally, implementing postponement strategies in logistics operations requires adopting a culture of agility and adaptability. Organizations should invest in employee training and development programs that emphasize these qualities, as well as encourage continuous improvement and innovation. This mindset allows companies to embrace postponement strategies effectively, adapting their operations as needed to optimize performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, aligning organizational structure and processes to effectively implement postponement strategies in logistics requires an integrated approach that involves assessing and adjusting existing structures, adapting processes, establishing effective communication channels, and fostering a culture that values agility and adaptability. By taking these steps, companies can optimize their logistics operations and better respond to changing market conditions.
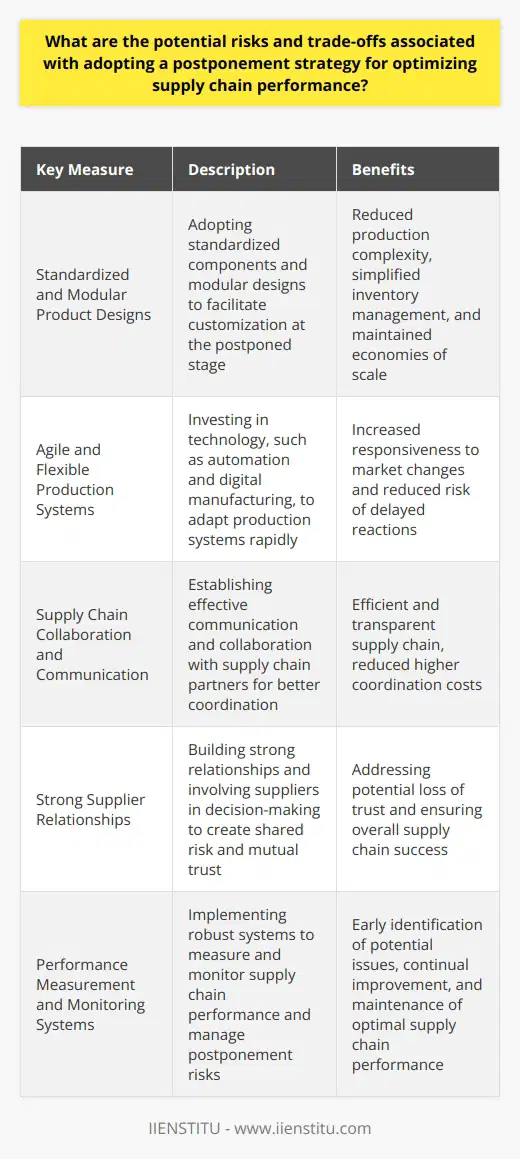
What are the potential risks and trade-offs associated with adopting a postponement strategy for optimizing supply chain performance?
Trade-offs in Postponement Strategy
The adoption of a postponement strategy offers the potential to optimize supply chain performance by enabling companies to reduce inventory costs, enhance product customization, and respond more effectively to market fluctuations. However, there are several risks and trade-offs that organizations must consider when implementing such an approach.
Increased Production Complexity
One possible trade-off of postponement is an increase in production complexity. As companies delay the final assembly or customization of their products, they need to manage a higher level of product variety, component interchangeability, and production processes. This can create challenges in resource allocation, production planning, and capacity utilization.
Reduced Economies of Scale
Implementing a postponement strategy may also result in reduced economies of scale due to lower production volumes of standardized components. The need to produce a broader range of customized products typically reduces the opportunities for cost reduction through high-volume production, which can adversely impact overall supply chain efficiency.
Higher Coordination Costs
With postponement, there may be higher coordination costs between supply chain partners to ensure that the right components and information are available when needed. This increase in communication, information sharing, and joint decision-making can introduce additional complexities and expenses into the supply chain management process.
Risk of Reacting Too Late
A key risk associated with implementing a postponement strategy is the possibility of reacting too late to market changes. Companies that rely on a delay in the production process must always ensure that they maintain an adequate level of responsiveness to rapidly changing customer demands or risk losing their competitive advantage.
Potential Loss of Supplier Trust
Lastly, the postponement strategy might lead to a potential loss of trust between the organization and its suppliers. As companies delay their production schedules, suppliers may perceive these actions as a lack of commitment or an attempt to transfer risks to them. This mistrust can negatively impact supplier relationships and weaken the overall effectiveness of the supply chain.
In conclusion, adopting a postponement strategy can offer significant benefits for optimizing supply chain performance. However, companies must carefully consider the associated risks and trade-offs, and implement appropriate measures to minimize these challenges, in order to successfully capitalize on the advantages of postponement.
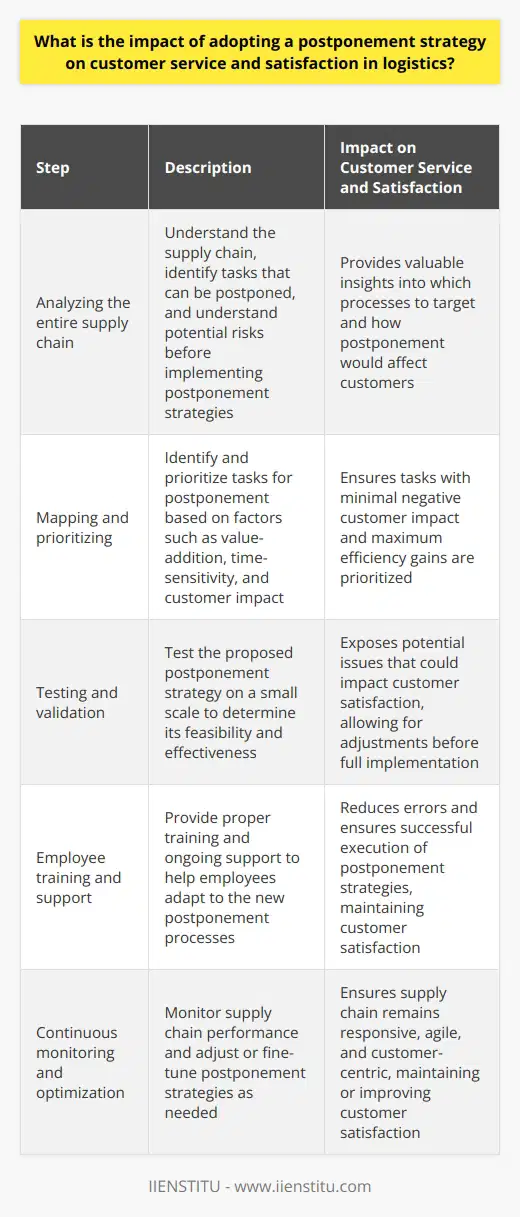
What is the impact of adopting a postponement strategy on customer service and satisfaction in logistics?
Impact on Customer Service
Adopting a postponement strategy in logistics involves delaying some supply chain activities until customer demand becomes more certain, leading to increased efficiency in inventory management. However, companies must weigh the benefits of such strategies against potential impacts on customer service and satisfaction.
Postponement and Response Time
One significant aspect to consider is the response time. By holding off on specific tasks such as product customization or packaging until actual order details are confirmed, companies can experience decreased lead times and faster order fulfillment. Customers generally appreciate speedy delivery, contributing to their overall satisfaction and loyalty.
Flexibility and Customization
Additionally, a postponement strategy can result in increased flexibility, allowing companies to better respond to customer preferences and expectations. By delaying certain activities, businesses have the opportunity to modify products to suit specific customer needs. This tailored approach can make the difference between winning or losing a sale, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Inventory Management Efficiency
Improved efficiency in inventory management can also lead to enhanced customer satisfaction. Adopting a postponement strategy often results in fewer instances of stockouts, overstocks, and obsolete inventory; thus, customers are more likely to find the products they need when they need them.
Potential Risks
However, there are potential drawbacks of implementing postponement strategies that could negatively affect customer service and satisfaction. Delaying certain supply chain activities may add complexity to operations, leading to potential errors, miscommunication, and increased costs. If not carefully managed, these risks can result in missed delivery deadlines, inferior product quality, or unanticipated stock shortages – all of which could damage customer relationships.
Balancing Factors
In conclusion, the impact of adopting a postponement strategy on customer service and satisfaction in logistics depends on a delicate balance between efficiency gains and possible risks. While postponement can improve response time, offer increased flexibility and customization, and ensure better inventory management, companies must carefully weigh these benefits against the potential drawbacks that can negatively impact customer satisfaction. By managing risks effectively, businesses can successfully implement postponement strategies while maintaining or enhancing customer service.
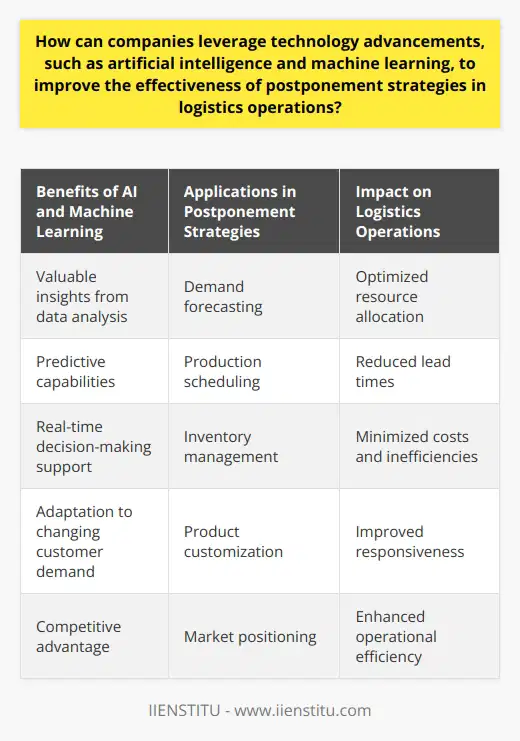
How can companies leverage technology advancements, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to improve the effectiveness of postponement strategies in logistics operations?
**Integrating AI and Machine Learning**
Companies can leverage advancements in technology, like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, to bolster the effectiveness of postponement strategies in logistics operations. Postponement strategies allow organizations to delay final product assembly or customization until there is actual customer demand. AI and machine learning can improve these strategies in several ways.
**Enhancing Demand Forecasting**
Firstly, AI-driven analytical tools can enhance demand forecasting by processing large amounts of data from various sources. Harnessing this information allows companies to make better-informed decisions on product assembly or customization timing. By predicting demand patterns more accurately, businesses can optimize inventory levels and minimize storage costs.
**Optimizing Resource Allocation**
Secondly, machine learning algorithms can assist in optimizing resource allocation. By continuously analyzing data on order patterns, stock levels, and lead times, these systems can identify inefficiencies and recommend adjustments in real-time. Such insights lead to improved operational efficiency and enable companies to make better use of available resources, boosting the overall effectiveness of postponement strategies.
**Facilitating Real-Time Decision Making**
AI and machine learning systems can also aid in real-time decision making. As these technologies can process massive amounts of data quickly, they provide current insights that support informed decisions. Access to prompt, reliable intelligence enables companies to respond more swiftly to shifts in customer demand and adjust their postponement strategies accordingly.
**Reducing Lead Times**
Finally, these technologies can help to reduce lead times by automating aspects of the supply chain. AI-powered robots, for example, can enhance warehouse operations by accurately picking, packing, and transferring goods while minimizing human error. In addition, machine learning algorithms can optimize transportation routes, leading to faster deliveries and overall shorter lead times. This can further improve the efficiency of postponement strategies, as companies can be more responsive to customer demand changes.
To conclude, integrating AI and machine learning technology can significantly improve the effectiveness of postponement strategies in logistics operations. From enhancing demand forecasting to optimizing resource allocation, these technologies can provide crucial insights, facilitate decision making, and streamline processes, resulting in increased operational efficiency and better responsiveness to customer demand.
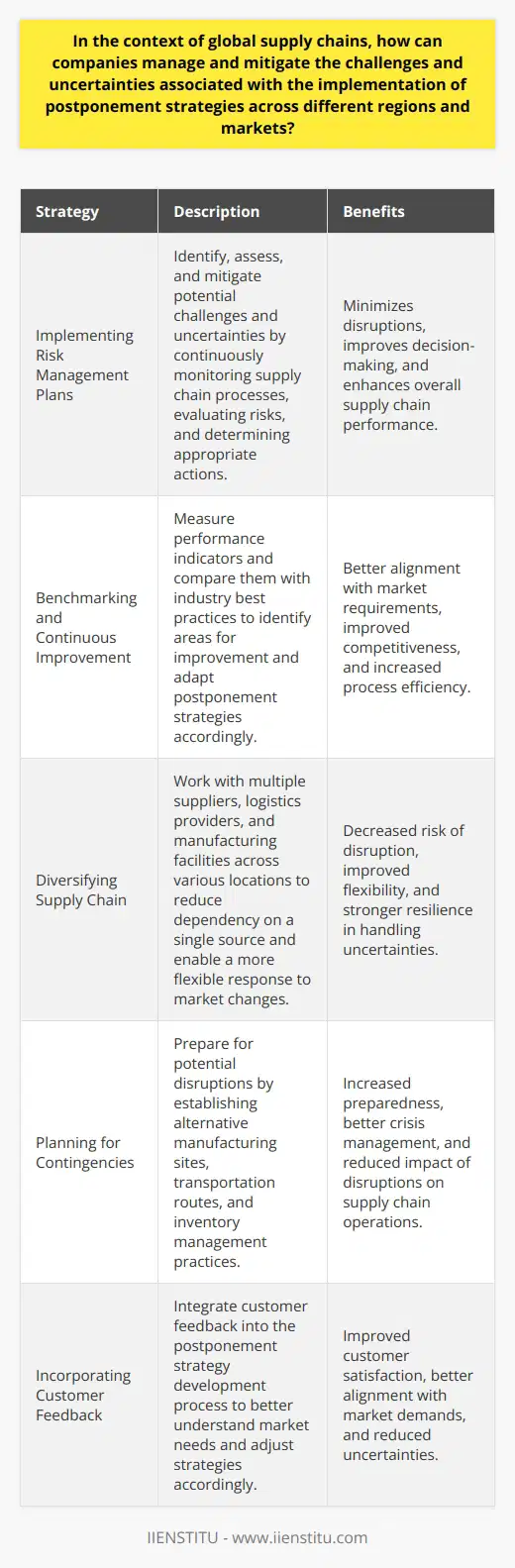
In the context of global supply chains, how can companies manage and mitigate the challenges and uncertainties associated with the implementation of postponement strategies across different regions and markets?
Challenges and Uncertainties in Postponement Strategies
In global supply chains, companies face challenges and uncertainties associated with implementing postponement strategies across differing regions and markets. To address these concerns, organizations can take specific actions.
Aligning Supply Chain Decisions with Market Dynamics
Companies should be deeply aware of regional variability in market dynamics. They must align their supply chain decisions with local customer preferences, demand fluctuations, and the presence of competition. By tailoring postponement strategies to individual markets, businesses can optimize responsiveness and reduce excess inventory risk.
Adapting to Regulatory Environment
Firms should stay updated on potential changes in trade regulations, export-import policies, and taxes across various regions. Companies must be prepared to adapt their postponement strategies based on such alterations, ensuring smooth operations and minimal impacts on the timely delivery of products.
Leveraging Technology for Visibility
Deploying advanced technology, such as big data analytics and artificial intelligence, can help organizations gain real-time visibility into their supply chains. These tools enable companies to gain insights into demand patterns, inventory levels, and lead times, allowing for better decision-making in implementing postponement strategies.
Building Collaborative Partnerships
Establishing strong relationships with suppliers, logistics providers, and other external stakeholders is crucial for managing uncertainties. Collaborative partnerships contribute to improved information sharing, risk identification, and the development of joint strategies to mitigate challenges arising from postponement.
Enhancing Flexibility in Production Processes
Companies must establish flexible production facilities, capable of handling varying product configurations and volumes at short notice. This enables firms to respond effectively to changing customer demands, allowing smooth implementation of postponement strategies and reduced inventory costs.
Investing in Workforce Training
Ensuring employees are efficiently trained and skilled in adopting postponement strategies is essential for mitigating challenges. Regular training programs can help teams stay up-to-date with best practices and improve the overall effectiveness of these strategies.
In conclusion, managing and mitigating challenges associated with postponement strategies across different regions and markets requires a multifaceted approach. By aligning with market dynamics, adapting to regulations, leveraging technology, building partnerships, enhancing flexibility, and investing in training, companies can successfully overcome uncertainties in global supply chains.