Introduction
Carrying Cost of Inventory
Approaches to Inventory Management
Zero-Inventory Level
Conclusion
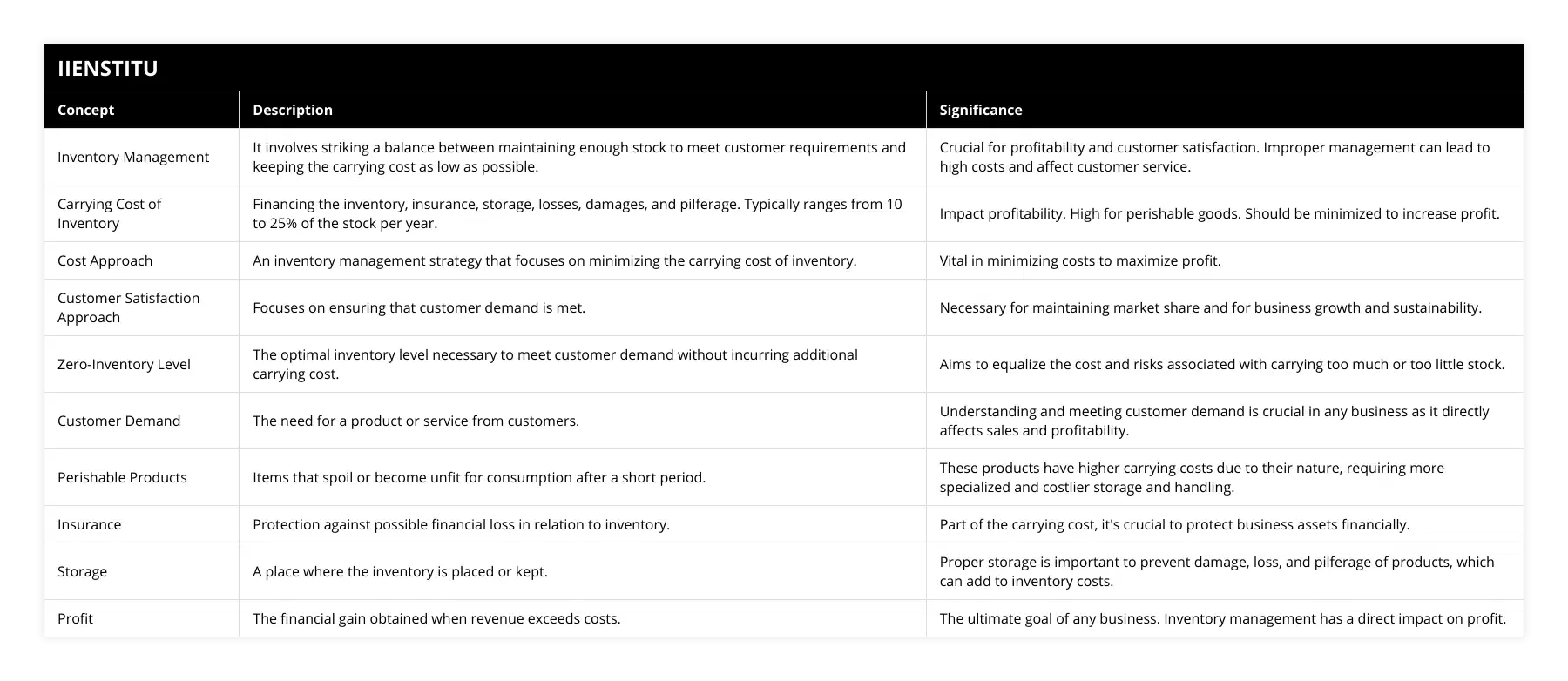
Introduction: Inventory management is a critical component of any successful business. It involves striking a balance between keeping enough inventory on hand to meet customer requirements and keeping the carrying cost of that inventory as low as possible. Unfortunately, the cost of carrying inventory can be high, eating away at profits if it is not managed correctly.
Carrying cost typically consists of financing the inventory, insurance, storage, losses, damages, and pilferages and can range from 10 to 25 percent of the total stock per year, depending on the product. It is exceptionally high for perishable products. However, even with the high carrying cost of inventory, it is still necessary to meet customer demand and maintain market share.
Carrying Cost of Inventory
The carrying cost of inventory is associated with keeping stock on hand. This cost can include financing, insurance, storage, losses, damages, and pilferage. The average carrying cost of stock can range from 10 to 25 percent of the total stock per year, depending on the product. For perishable products, the carrying cost can be even higher. These costs can add up quickly and can have a significant impact on profits if not managed properly.
Approaches to Inventory Management
There are two approaches to inventory management: cost and customer satisfaction. The cost approach focuses on minimizing the carrying cost of inventory, while the customer satisfaction approach focuses on ensuring that customer demand is met. Both methods are essential, as they both have an impact on profitability. The cost approach is vital to minimizing the carrying cost of inventory, while the customer satisfaction approach is essential for ensuring that customer demand is met.
Zero-Inventory Level
The goal of inventory management is to maintain an optimal inventory level. This level is known as the zero-inventory level. The zero-inventory level is the inventory level necessary to meet customer demand without incurring additional carrying costs. This level is determined by analyzing customer demand and inventory cost. It is important to note that the zero-inventory level is not a static number, as customer demand and carrying costs can fluctuate over time.
Conclusion: Inventory management is a critical component of any successful business. It involves striking a balance between keeping enough inventory on hand to meet customer requirements and keeping the carrying cost of that inventory as low as possible. Unfortunately, the cost of carrying inventory can be high, eating away at profits if it is not managed correctly.
There are two approaches to inventory management: cost and customer satisfaction. The goal of inventory management is to maintain an optimal inventory level, known as the zero-inventory level. This level is determined by analyzing customer demand and inventory cost. By adequately managing inventory, businesses can ensure that customer demand is met while minimizing the carrying cost of the merchandise.
Planning your logistics and inventory management can save you time, money, and resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of maximizing logistics with inventory management?
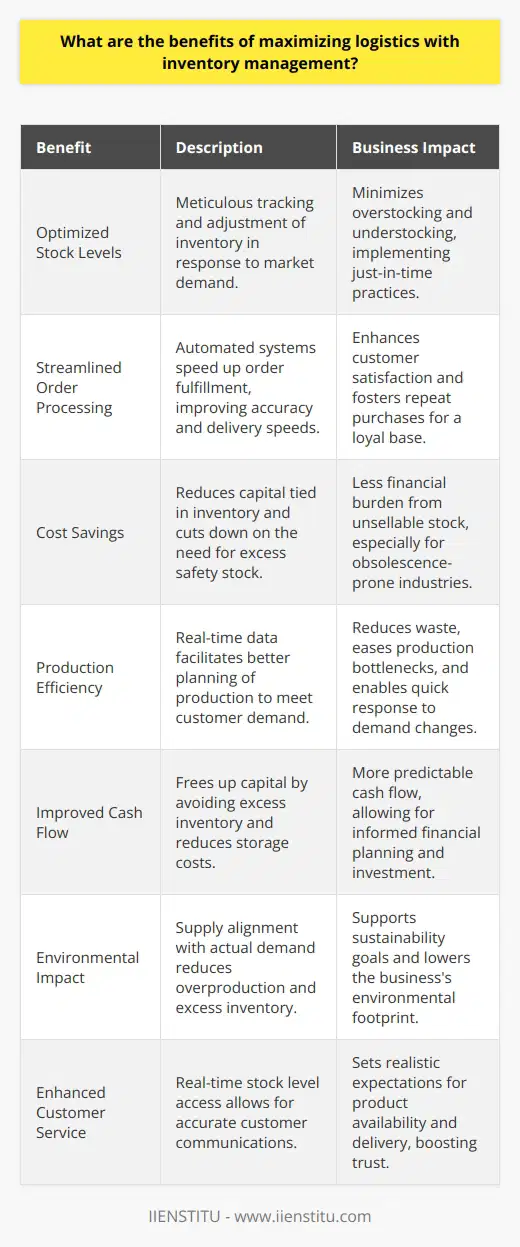
Maximizing logistics with inventory management is a crucial component of a successful business. Companies can improve their logistics by effectively managing inventory, leading to increased productivity, cost savings, and improved customer service.
Inventory management involves tracking and controlling stock, including monitoring stock levels, order patterns, and the supply chain. With an effective inventory management system, businesses can reduce the costs associated with inventory management, such as order processing, holding costs, and obsolescence. By having an accurate and up-to-date view of inventory levels, businesses can reduce the risk of stock outages and overstock.
Maximizing logistics with inventory management also makes businesses more efficient in their operations. By tracking stock levels, companies can anticipate customer demand and plan accordingly. This leads to increased efficiency in the supply chain and improved customer service. Additionally, businesses can use inventory management to manage their production processes better. As a result, companies can optimize production schedules and reduce waste by accurately tracking stock levels.
The use of inventory management also helps businesses improve their cash flow. Companies can forecast demand and plan their cash flow accordingly by having accurate information on stock levels. Additionally, companies can use inventory management to reduce their inventory costs by minimizing overstock, decreasing the cost of storage, and eliminating the need for safety stock.
Inventory management also enables businesses to manage their customer service better. With accurate information on stock levels, companies can quickly respond to customer orders and meet customer demands. This helps companies to create a positive customer experience, increasing customer loyalty and improving customer satisfaction.
Maximizing logistics with inventory management is a critical component of a successful business. By effectively managing inventory, companies can improve their logistics management, leading to increased productivity, cost savings, and improved customer service.
What are the different approaches to inventory management?
Inventory management is a crucial part of any business, as it helps to ensure that products are available when needed. There are several different approaches to inventory management, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
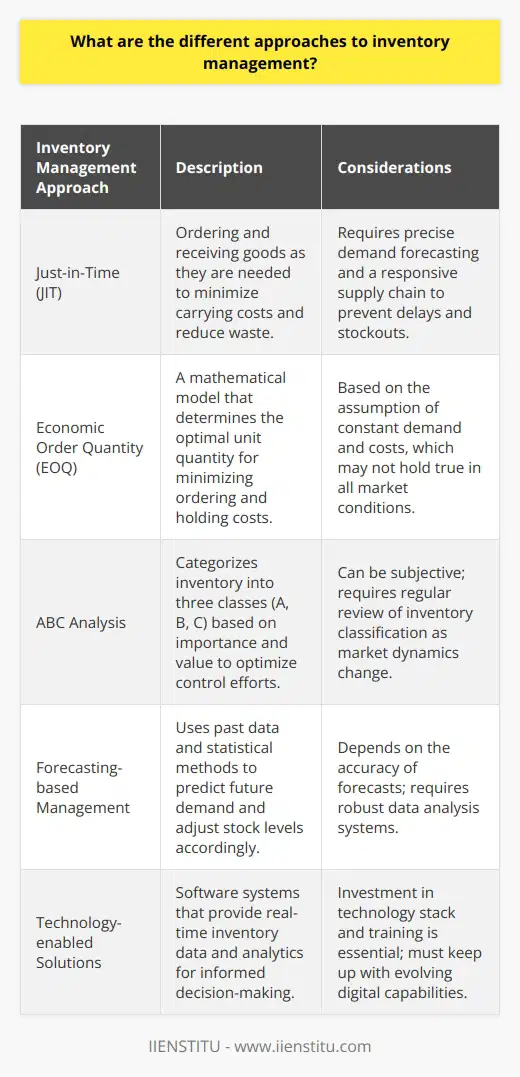
One approach to inventory management is the Just-in-Time (JIT) system. This approach emphasizes the timely delivery of inventory and strives to minimize the amount of stock on hand. The goal of JIT is to reduce costs associated with storage and inventory handling and reduce inventory losses due to obsolescence or expiration. The downside of this approach is that it may lead to product shortages if an unexpected surge in demand occurs.
Another approach to inventory management is the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) system. This approach is based on the idea that there is an optimal order quantity that minimizes the total cost of inventory. This approach aims to determine the optimal order quantity and then order the list in that quantity. This approach has the advantage of reducing costs associated with collecting and handling inventory, but it may lead to product shortages if demand exceeds the order quantity.
A third approach to inventory management is the ABC analysis. This approach divides inventory into three categories based on the importance of each item. This approach aims to prioritize inventory management efforts and ensure the essential things are in stock. The disadvantage of this approach is that it can be challenging to determine the importance of each item.
Finally, an inventory management system can also be based on forecasting. This approach uses historical data to predict future demand and orders inventory accordingly. This approach aims to ensure that the right amount of stock is available at the right time. The downside of this approach is that it can be difficult to estimate future demand accurately.
In conclusion, there are several different approaches to inventory management, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, selecting the method that best suits the business's needs is essential and is most likely to achieve the desired results.
How can a zero-inventory level be achieved?
Achieving a zero-inventory level is desirable for many businesses, as it reduces costs, streamlines processes, and increases efficiency. However, it can be a challenging process to implement. Here, we discuss the steps needed to reach a zero-inventory level and the potential benefits this can bring to a business.
The first step is to identify the inventory requirements for the business. This includes analyzing current inventory levels, determining future needs, and estimating the lead times for replenishing the inventory. Once these requirements have been established, the business can identify the minimum inventory levels needed to meet the demand.
The second step is to implement inventory control measures. This includes setting up inventory control systems, such as just-in-time inventory management and inventory tracking systems, to ensure that inventory levels are monitored and managed effectively. Additionally, it is essential to ensure that the inventory is accurately counted and that any discrepancies are addressed quickly.
The third step is to create an inventory optimization plan. This plan will provide a roadmap for reducing inventory levels while ensuring that customer service levels are maintained. This can be achieved by combining inventory reduction techniques, such as reducing the amount of stock kept in-house, reducing the number of suppliers, and implementing demand forecasting models.
The fourth step is to review and adjust the inventory optimization plan regularly. This will ensure that the inventory levels remain at the desired level while ensuring that the demand is met. Additionally, regular reviews will help identify any potential problems and allow the business to take corrective action if necessary.
Finally, it is essential to evaluate the performance of the inventory optimization plan. This includes assessing the cost savings achieved, the impact on customer service, and the overall efficiency of the process. Additionally, it is essential to identify areas for improvement and address any issues that may arise.
Reaching a zero-inventory level can bring significant benefits to a business, including increased efficiency, streamlined processes, and reduced costs. Following the steps outlined above, companies can develop an effective inventory optimization plan and achieve a zero-inventory level.
How does inventory management contribute to overall logistics efficiency in supply chain operations?
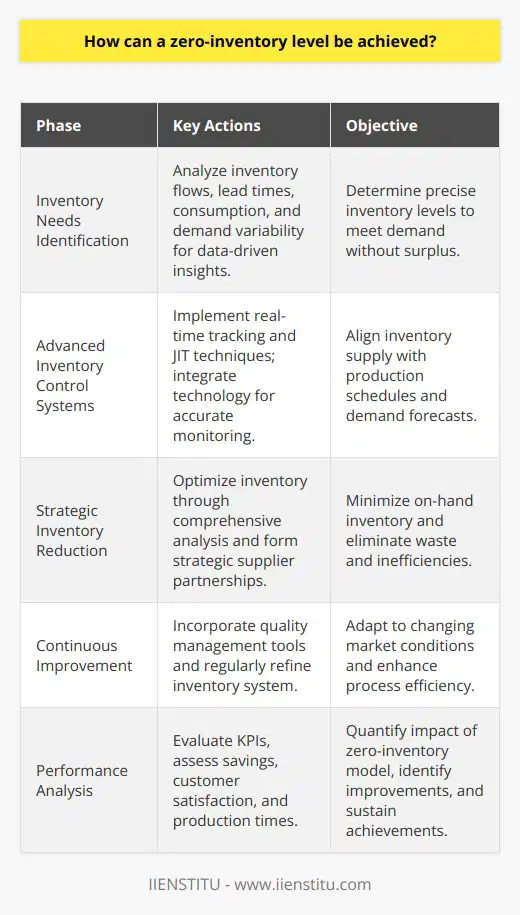
Role of Inventory Management in Logistics Efficiency
Inventory management is a crucial component in optimizing the overall efficiency of supply chain operations. Effective inventory management ensures that adequate stocks are maintained at all times to meet customer demand, without incurring excessive costs. An optimized inventory enables organizations to reduce lead times, improve material flow, and minimize stockouts, ultimately resulting in reduced operational costs and increased customer satisfaction.
Reducing Lead Times
A well-managed inventory facilitates swift product movement through the supply chain. By maintaining appropriate levels of stock and minimizing delays in the restocking process, supply chain operations can significantly reduce lead times. Consequently, customers receive their orders faster, enhancing the organization's reliability and reputation in the market.
Optimizing Material Flow
Effective inventory management contributes to a seamless flow of materials within the supply chain. By monitoring stock levels, identifying slow-moving items, and managing demand fluctuations, organizations can eliminate bottlenecks and ensure that products are readily available when needed. This continuous flow of materials accelerates the production process, helping organizations achieve a competitive edge.
Minimizing Stockouts
Inventory management plays a vital role in preventing stockouts, which can negatively impact customer satisfaction, brand loyalty and future sales. By accurately forecasting demand, monitoring stock levels, and adopting efficient replenishment strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of stockouts, ensuring that products are available to customers when needed.
Cost Reduction
Effective inventory management contributes to the minimization of costs associated with holding, moving, and replenishing stocks. By optimizing inventory levels and adopting efficient storage practices, organizations can avoid unnecessary expenses such as warehouse rent, handling charges, and disposal costs of obsolete or damaged products.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction
Optimized inventory management directly translates to improved customer satisfaction. With reduced lead times, consistent product availability, and timely order replenishment, customers are more likely to have a positive experience with the organization. Satisfied customers are likely to make repeat purchases, resulting in increased revenue and long-term business sustainability.
In conclusion, inventory management plays a pivotal role in enhancing logistics efficiency in supply chain operations. By reducing lead times, optimizing material flow, minimizing stockouts, lowering costs, and boosting customer satisfaction, effective inventory management can significantly contribute to the success of an organization.
In what ways are inventory management and logistics management interconnected in ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services?
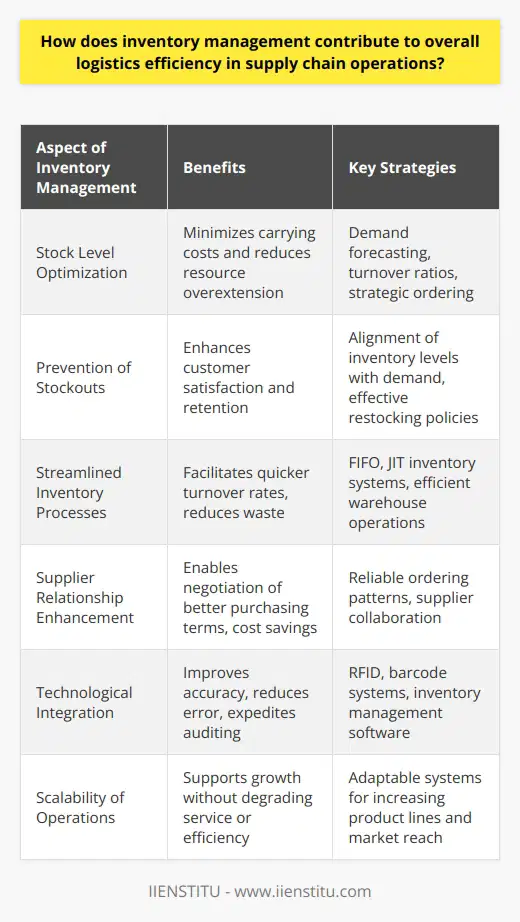
Interdependence of Inventory and Logistics Management
Inventory management and logistics management are two crucial components of supply chain management that ensure the uninterrupted flow of goods and services. This interconnectivity allows businesses to respond to customer needs effectively and operate at optimal efficiency.
Role of Inventory Management
Inventory management is responsible for striking a balance between holding sufficient stock to meet customer demand and maintaining cost efficiency. It involves determining the optimal inventory levels that should be consistent with customer demand patterns, thus helping companies maintain a high level of customer satisfaction. Additionally, inventory management involves monitoring the availability of raw materials, work-in-process items, and finished goods, and ensuring that the complete range of products is readily available for shipment when required.
Impact of Logistics Management
Logistics management focuses on reducing lead times, transportation costs, and servicing customers by ensuring the timely and efficient movement of goods and materials through the supply chain. This involves coordinating and managing multiple activities such as transportation, warehousing, and distribution services. It also encompasses optimizing the choice of transportation mode, routing decisions, and negotiating favorable shipping rates, which significantly impact the cost of goods and services.
Synchronization for Smooth Flow
The interconnectivity between inventory and logistics management becomes apparent when businesses coordinate their efforts to fulfill customer orders. Efficiently managing inventory levels requires accurate demand forecasting and precise order tracking, both of which depend on effective logistics management. By facilitating information exchange between these two components, businesses can prioritize shipments, negotiate better shipping contracts, and optimize warehouse space utilization.
Unified System for Efficiency
A unified and integrated approach within inventory and logistics management enhances the flexibility of a company's supply chain to adapt to changing market demands. By continuously monitoring and sharing information across these departments, businesses can optimize their manufacturing processes, anticipate potential disruptions in the supply chain, and swiftly react to changes in demand patterns. This increased reliability and responsiveness can ultimately lead to higher customer satisfaction and competitive advantage in the market.
In conclusion, the interconnectivity between inventory and logistics management plays a vital role in facilitating the smooth flow of goods and services. Both components must function in tandem to strike a balance between cost efficiency and meeting customer demand, allowing a robust and resilient supply chain that adapts to fluctuating market conditions.
How can inventory optimization logistics lead to improved operational performance and cost reduction in the supply chain?
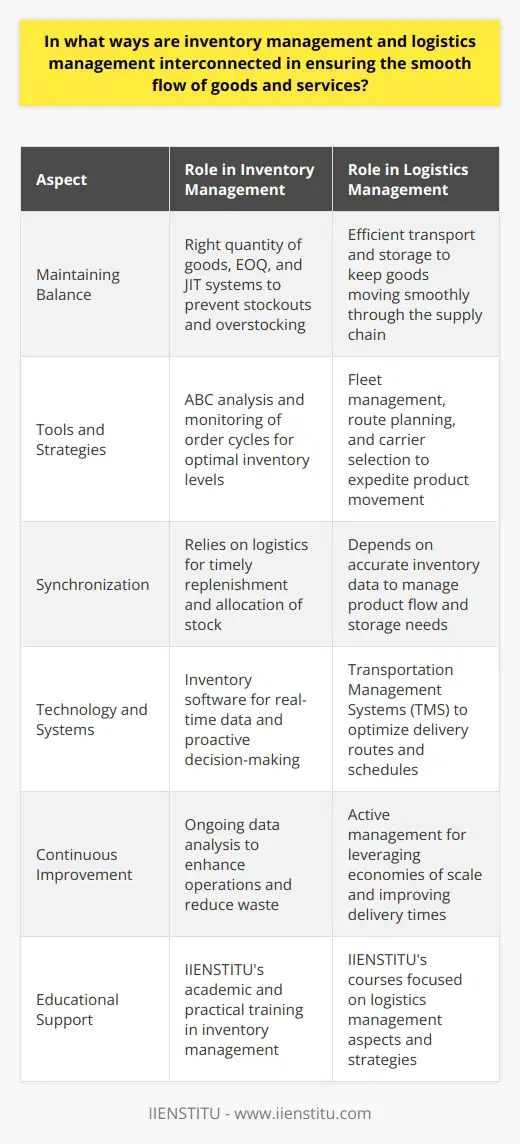
**Inventory Optimization Strategies**
Inventory optimization logistics address the challenge of maintaining the right amount of stock at the right time to meet customer demands. By utilizing advanced analytics, forecasting techniques, and inventory management tools, supply chain managers can effectively manage their inventory levels and achieve substantial cost reductions.
**Demand Forecasting and Planning**
Implementing accurate demand forecasting and planning methodologies are essential to optimizing inventory management. This process enables companies to predict the customer's future demands, allowing them to make data-driven decisions on how much inventory to hold. As a result, companies can avoid stockouts and minimize excess inventory, leading to improved operational performance and reduced warehousing costs.
**Continuous Replenishment Strategy**
The continuous replenishment strategy ensures the ongoing availability of products by frequently replenishing stock levels. This approach reduces lead times, lowers stock holding costs and enhances customer satisfaction. Additionally, it promotes collaboration between suppliers and manufacturers, leading to better visibility and coordination within the supply chain.
**Real-Time Inventory Tracking**
Effective inventory optimization logistics rely on real-time inventory tracking. Modern inventory management systems provide companies with real-time data on their inventory levels, enabling them to make informed decisions on replenishments and stock transfers. Accurate inventory tracking prevents stock obsolescence and helps companies maintain optimal inventory levels, resulting in significant cost savings.
**Lean Inventory Management**
Lean inventory management focuses on eliminating waste and inefficiencies in the supply chain. By identifying and addressing the root causes of excess inventory, companies can streamline their operations, reduce lead times and lower overall costs. Lean principles promote a just-in-time (JIT) approach to inventory management, ensuring that materials arrive when they are needed, thereby reducing inventory holding costs and waste.
**Supplier Management and Collaboration**
Supplier management and collaboration play a critical role in inventory optimization logistics. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers fosters open communication and better demand visibility, leading to improved responsiveness and flexibility within the supply chain. In turn, this results in better inventory planning and management, ultimately reducing lead times and lowering costs.
In summary, companies that leverage inventory optimization logistics can significantly improve their operational performance and reduce costs in the supply chain. By accurately predicting customer demands, implementing continuous replenishment strategies, tracking inventory in real-time, adopting lean inventory principles and collaborating with suppliers, supply chain managers can optimize their inventory levels and eliminate unnecessary waste and expenses.
How does inventory management contribute to logistics?
Impact of Inventory Management on Logistics
Effective inventory management plays a crucial role in the efficient functioning of logistics by ensuring that organizations maintain an appropriate level of stock to meet customer demands. Accurate inventory management techniques, such as just-in-time (JIT) and material requirements planning (MRP), assist in streamlining the logistical process by minimizing operational costs and maximizing customer satisfaction.
Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
One primary contribution of inventory management to logistics is the reduction in costs associated with holding inventory. By accurately forecasting demand and maintaining optimal stock levels, organizations can minimize warehousing expenses and decrease the risk of obsolescence. Additionally, efficient inventory management practices enable organizations to allocate resources more effectively, reducing buffer stock and preventing stockouts, which can lead to lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
Improved Supply Chain Visibility and Collaboration
Inventory management enhances supply chain visibility by providing real-time information regarding stock levels and movement. This transparency allows for better collaboration between stakeholders, as well as improved decision-making in managing the flow of goods. It also contributes to efficient demand planning, ensuring that businesses can effectively balance supply and demand, preventing overstocking or understocking.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Effective inventory management directly impacts customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability when needed. By having the right products in stock and readily available, organizations can fulfill customer orders in a timely manner, increasing the likelihood of repeat business and improving customer loyalty. Moreover, improved inventory management practices help businesses react more quickly to changes in customer preferences and market trends, allowing them to remain competitive in their respective industries.
Reduced Lead Times and Increased Responsiveness
Efficient inventory management enables logistics teams to monitor and control inventory levels closely, contributing to reduced lead times and increased responsiveness in addressing fluctuations in demand. It also allows for quicker response to market changes, maintaining optimal inventory levels, and ensuring that organizations can react promptly to any disruptions in the supply chain.
In conclusion, inventory management is a critical component in the overarching logistics framework, contributing to cost reduction, improved supply chain visibility, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased responsiveness in addressing market fluctuations. As organizations continue to seek ways to optimize their logistical processes, investment in effective inventory management techniques must remain a top priority.
Why is inventory management important to logistics management?
Significance of Inventory Management in Logistics Management
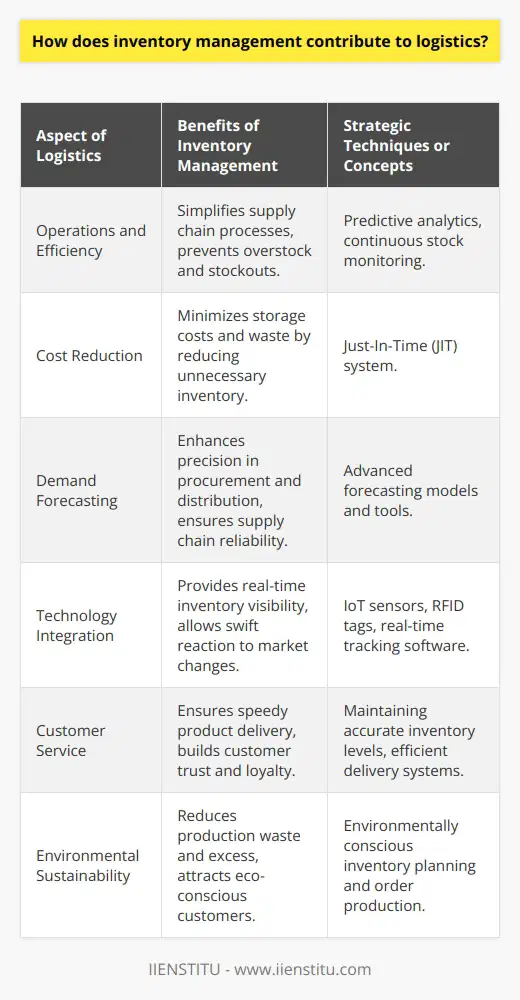
Effective Control Over Stock Levels
Inventory management holds paramount importance in logistics management as it enables businesses to maintain optimal stock levels. It provides an appropriate balance between holding too much inventory and risk of stockouts, thereby ensuring a smooth supply chain operation. By keeping track of stock levels, businesses can reduce associated storage costs, minimize wastage and obsolete inventory, and deploy a proactive approach in replenishing their stock as per demand fluctuations.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Efficient inventory management optimizes the order fulfillment process, resulting in satisfied customers. Through inventory control, companies can reduce the order processing time, ensuring timely delivery of products and services. In turn, this contributes to positive customer relationships, retaining existing customers while attracting new ones. Moreover, organizations can easily adapt their supply chain strategies with an effective inventory management system, tailoring their services as per customer needs and preferences.
Improved Financial Performance and Profitability
Efficient inventory management directly impacts a company's bottom line. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, businesses can reduce inventory carrying costs, including warehouse management expenses such as storage space, staffing, and insurance. Additionally, adequate inventory management allows companies to invest in more profitable opportunities by freeing up working capital tied up in excess stock. It also safeguards businesses from potential stockouts and subsequent loss of sales and customer goodwill.
Informed Decision-making
Inventory management fosters informed decision-making in logistics management by providing critical data and insights needed for supply chain planning. This data includes information on stock levels, lead times, supplier reliability, and demand patterns. Armed with this data, enterprises can accurately forecast future demand, adjust their sourcing strategies, and identify potential issues before they escalate. Furthermore, inventory visibility enables businesses to implement Just-In-Time (JIT) and lean management practices, reducing inventory holding costs and enhancing logistics efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inventory management plays a crucial role in effective logistics management. It substantially impacts businesses' financial performance, customer satisfaction, and overall supply chain efficiency. By practicing effective inventory management, companies can lower costs, enhance customer service, and make more informed decisions about their supply chain operations, contributing to long-term business success.
What is inventory control in logistics management?
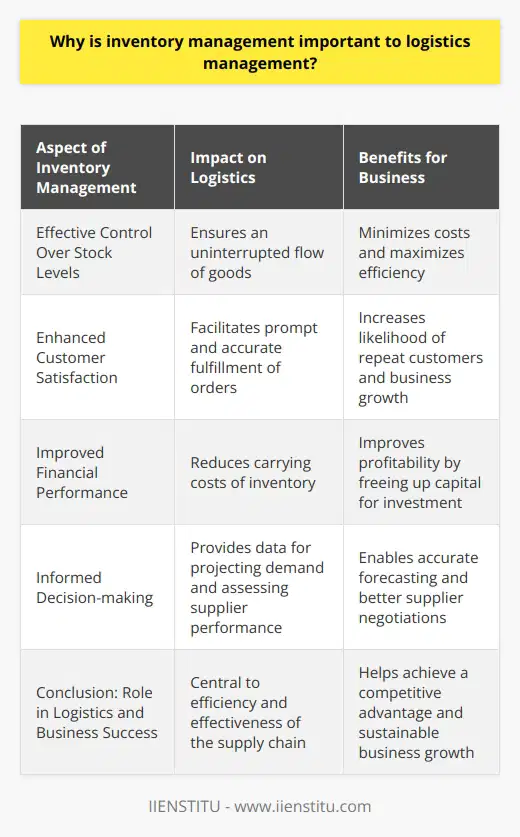
Understanding Inventory Control
Inventory control, a crucial aspect of logistics management, refers to the management and optimization of inventory levels across supply chains. This process involves monitoring, regulating, and organizing inventory to ensure adequate stock levels, minimize costs, and maintain customer satisfaction.
Importance of Inventory Control
Effective inventory control provides several benefits, including improved cash flow, increased efficiency, and reduced risk of stockouts or overstocking. Proper inventory control ensures that companies can meet customer demands promptly while avoiding the costs associated with holding excessive inventory.
Methods of Inventory Control
Various inventory control methods help businesses maintain optimal stock levels. These methods include:
Just-In-Time (JIT): This approach aims to minimize inventory levels by ordering and receiving goods only when needed, thus reducing storage costs and waste.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): EOQ is a mathematical formula that determines the optimal order quantity to minimize costs related to ordering, holding, and stockouts.
ABC Analysis: This method classifies inventory items into three categories (A, B, and C) based on their importance, with A items being the most valuable, to prioritize management efforts.
Safety Stock: Maintaining safety stock involves setting aside extra inventory to buffer against unexpected supply delays or demand spikes, ensuring continuous product availability.
Reorder Point: This method calculates the inventory level at which new orders should be placed, considering lead times and average daily usage rates, to prevent stockouts.
Implementing Inventory Control Systems
Technology plays a significant role in inventory control, with modern software solutions offering real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making capabilities. These systems help streamline operations, reduce human error, and optimize inventory management processes. Some common inventory control systems include barcode scanning, radio-frequency identification (RFID), and automated inventory management software.
Incorporating Metrics and KPIs
To gauge the effectiveness of inventory control strategies, businesses can employ key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics. Some common KPIs include inventory turnover, carrying costs, stockout rates, and order lead time. Monitoring these metrics allows companies to identify areas for improvement and ensure efficient inventory management.
In conclusion, inventory control is a critical component of logistics management that helps businesses minimize costs, prevent stockouts, and maintain customer satisfaction. By employing various inventory control methods, utilizing modern technology, and leveraging measurable KPIs, businesses can optimize their inventory management processes and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
How does inventory management affect logistics in terms of cost control and resource allocation?
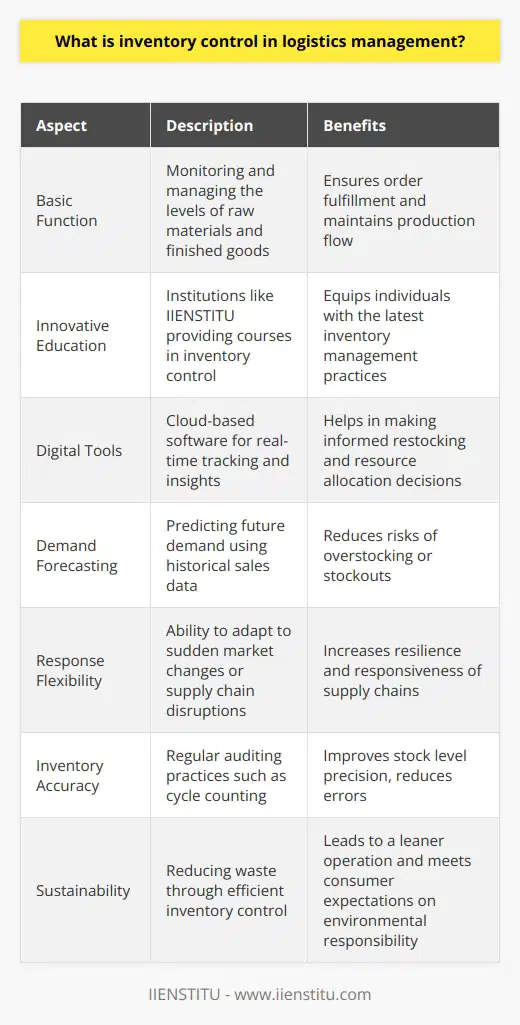
Impact on Cost Control
Effective inventory management directly influences logistics in terms of cost control by minimizing the carrying costs of stock, reducing the risk of stock obsolescence, and streamlining the order fulfillment process. Carrying costs include warehousing, handling, insurance, and taxes, which can constitute a significant proportion of the total logistics expenses. By optimizing inventory levels and turnover rates, organizations can minimize these costs and improve their overall profitability.
Reducing Stock Obsolescence
Another way inventory management affects logistics is through reducing the risk and costs associated with stock obsolescence. Efficient inventory tracking and forecasting systems allow companies to anticipate changes in demand and adjust their stock levels accordingly. This, in turn, helps prevent the accumulation of excess inventory and the associated carrying costs, as well as reducing the need for markdowns or write-offs of obsolete products.
Resource Allocation Efficiency
Effective inventory management also has significant implications for resource allocation within the logistics function. By maintaining appropriate stock levels and reducing the need for emergency replenishment orders, organizations can better plan their transportation and warehousing capacities. This improved utilization of resources, such as vehicles, labor, and storage space, contributes to the overall efficiency of the logistics operation and helps minimize costs.
Order Fulfillment Optimization
Furthermore, efficient inventory management directly impacts the order fulfillment process, an essential component of any logistics operation. By maintaining accurate records of stock on hand and employing demand forecasting methods, companies can ensure that products are readily available when customers place orders. This, in turn, leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty while also minimizing the costs associated with expedited shipping, overstocking, or stockouts.
In conclusion, effective inventory management plays a crucial role in optimizing logistics operations in terms of cost control and resource allocation. By minimizing carrying costs, reducing the risk of stock obsolescence, improving resource utilization, and streamlining order fulfillment processes, organizations can achieve significant cost savings and enhance their competitive position in the marketplace.
What are the key challenges and complexities when integrating inventory management with logistics processes?
Challenges in Integrating Inventory Management and Logistics Processes
Inadequate Information Visibility
One key challenge in integrating inventory management and logistics processes is the inadequate visibility of information between the different parties involved. This may result in inefficient communication channels, leading to poor management of inventory and inaccuracies in the logistical process.
Fluctuating Demand
Another issue that arises due to the integration is the fluctuating demand patterns of consumers. The demand for products in the market can constantly change, making it difficult for inventory management and logistics teams to predict and respond effectively to these shifts.
Mismatched Data Systems
The differences in data systems and software used by inventory management and logistics teams can also pose significant challenges in integration. These discrepancies can lead to unreliable data exchange and inconsistencies in performance metrics, ultimately hindering the decision-making process.
Inventory Control Dilemmas
The complexity of inventory control is another challenge in integrating logistics processes. An effective integration solution must balance the need to optimize inventory levels while maintaining customer service and avoiding stockouts or excessive surpluses that can impact profitability.
Lack of Process Standardization
The lack of standardized processes between inventory management and logistics departments can result in inefficient practices, increased errors, and decreased overall effectiveness. The standardization and clear definition of roles and responsibilities are critical factors in successful integration.
Global Supply Chain Management
Global supply chains present additional complexities for integration since inventory and logistics processes must coordinate across multiple international borders and adhere to different regulations, trade agreements, and fluctuating exchange rates.
Strategic Alignment
Lastly, companies face challenges in aligning their strategic goals with the inventory management and logistics processes. There must be a focus on implementing effective strategies and incorporating them into the overall business objectives for successful integration to take place.
In conclusion, the integration of inventory management with logistics processes is a complex feat, often hindered by inadequate information visibility, fluctuating demand patterns, and incompatible systems. Additionally, inventory control, process standardization, global supply chain management, and strategic alignment challenges must be addressed. To overcome these challenges, organizations must foster effective communication, adopt flexible and standardized processes, and align their strategic goals with their integration efforts.
How do advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence and automation, impact inventory management in the context of logistics optimization?
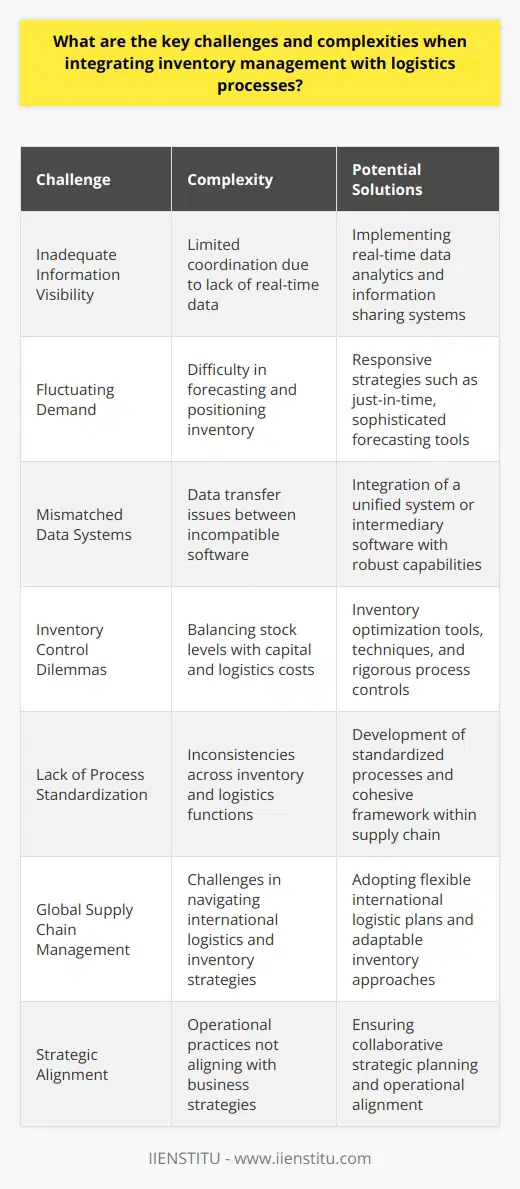
Optimizing Inventory Management with Technology Advancements
**AI-Enabled Forecasting**
Artificial intelligence (AI) significantly impacts inventory management by providing more accurate demand forecasting. With machine learning algorithms, AI systems can analyze historical data and detect patterns that contribute to demand variations. As a result, businesses can reduce stockouts, overstocking, and carrying costs, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and profitability.
**Automation in Warehouse Management**
Automation technologies, such as robotics and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) play a crucial role in enhancing warehouse operations. By automating routine tasks, such as transporting goods and packing orders, businesses can reduce labor costs, increase accuracy, and minimize errors in inventory management. Additionally, these solutions enhance operational efficiency, ultimately improving order fulfillment rates and customer satisfaction.
**Real-Time Inventory Tracking**
Advancements in technology, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID), enable real-time inventory tracking and management. These tools grant businesses constant visibility into stock levels and product movements, allowing for informed decision-making and proactive inventory management. Consequently, supply chain managers can maintain optimal inventory levels, streamline warehouse operations, and minimize the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
**Data-Driven Decision-Making**
Technological advancements in big data analytics and business intelligence tools have transformed the way businesses approach inventory management. By aggregating and analyzing data from various sources, companies can make data-driven decisions to optimize logistics processes, predict equipment maintenance needs, and identify potential bottlenecks. This insight translates into more efficient supply chain operations and improved inventory turnover rates, contributing to overall business success.
In conclusion, technology advancements, such as artificial intelligence, automation, and real-time inventory tracking, have significantly impacted inventory management in the context of logistics optimization. These solutions enable businesses to foresee demand, enhance warehouse operations, and make informed decisions based on data analysis, contributing to higher customer satisfaction, reduced costs, and increased profitability. As technology continues to evolve, businesses must adapt and integrate these solutions to remain competitive in today's dynamic market.
How does inventory management affect logistics in terms of customer satisfaction and order fulfillment?
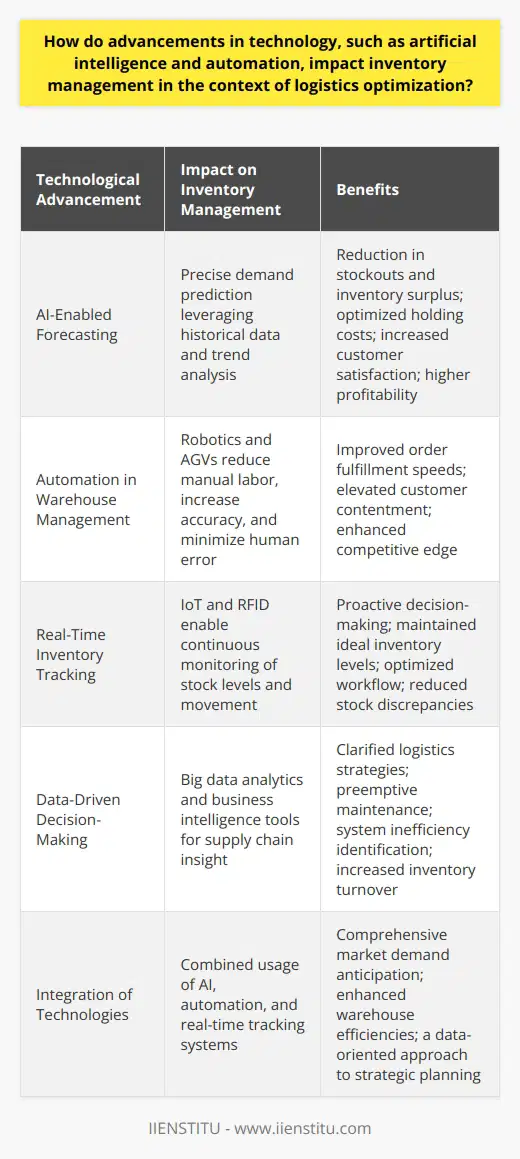
Impacts on Customer Satisfaction
Inventory management plays a crucial role in enhancing customer satisfaction levels. A proficient management system ensures that businesses can optimally fulfill customer orders. When customers receive expected items in a timely and accurate manner, their satisfaction increases. Furthermore, when a company can effectively manage its stock, it can quickly address customer needs, further boosting satisfaction levels.
Contribution to Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is another aspect significantly influenced by inventory management. The effective tracking of inventory levels allows companies to maintain enough stock for order fulfillment. Overstocking can lead to cash flow challenges, while understocking might lead to out-of-stock situations and delayed deliveries, causing customer dissatisfaction.
Stock Accuracy and Timely Delivery
For a company to meet its delivery times, reliable inventory management is essential. Good inventory control ensures that items are available for dispatch when orders are placed. With an accurate system, companies can avoid delays and maintain their delivery reputation, resulting in highly satisfied customers.
Reducing Overstocks and Understocks
Avoiding overstocks and understocks is also a crucial advantage of effective inventory management. Overstocks tie up capital and increase storage costs, while understocks can lead to missed sales opportunities. By accurately predicting demand, businesses can effectively manage stock levels, ensuring efficient and cost-effective operations.
In conclusion, inventory management plays a pivotal role in logistics, influencing customer satisfaction and order fulfillment. Efficient inventory management ensures customer demands are attended promptly and accurately. Moreover, it aids in maintaining a balance in stock levels, contributing to operational efficiency. By implementing effective inventory management systems, businesses can significantly improve their logistics and enhance customer satisfaction.
What are the best practices for integrating inventory management and logistics to ensure efficient and effective supply chain performance?
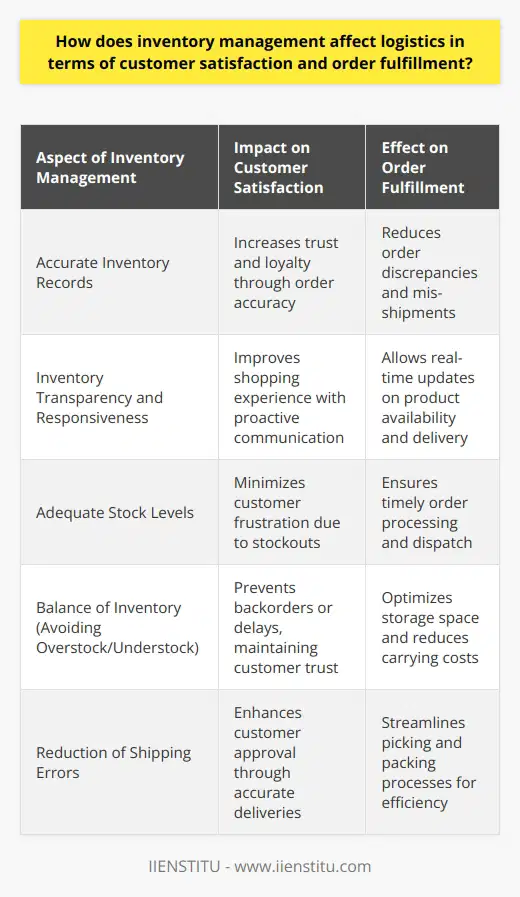
Inventory Integration Practices
Effective supply chain performance banks heavily on integrating inventory management and logistics. Such integration primarily involves consolidating product information, tracking and regulating stock levels, and managing transportation.
IT Systems and Strategies
Modern IT systems and strategies streamline these processes. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems unite all organizational operations, including inventory management and logistics. ERP supports real-time visibility of data, practical decision-making, and optimal resource utilization.
Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting marks another critical integration practice. It assists in maintaining adequate inventory levels, preventing stockouts or overstocks. The ultimate outcome is reduced costs and improved customer service.
Lean Management
Lean management embodies another important integration practice. It aids in eliminating waste, optimizing resources and improving operational efficiency. Lean management ensures the goods reach the destination on time without discrepancies.
Cross-Functional Teams
The establishment of cross-functional teams enhances coordination. These teams ensure smoother communication, reducing chances of misalignment between inventory and logistics. Consequently, this leads to a more efficient supply chain.
Vendor-Managed Inventory
Vendor-managed inventory (VMI) is a hallmark of successful integration. In VMI, suppliers maintain the retailer's inventory. The benefits encompass reduced stock holding, increased stock turns, and reduced lead time.
Just-in-Time Delivery
Just-in-Time delivery helps maintain low inventory levels, reducing the associated costs. This practice aligns closely with Lean management, and firms regularly combine these techniques for the most efficient outcomes.
Conclusively, effective integration of inventory management and logistics involves implementing modern technologies, accurate demand forecasting, Lean management, cross-functional teams, VMI, and Just-in-Time techniques. When adequately applied, these practices can dramatically improve supply chain performance.
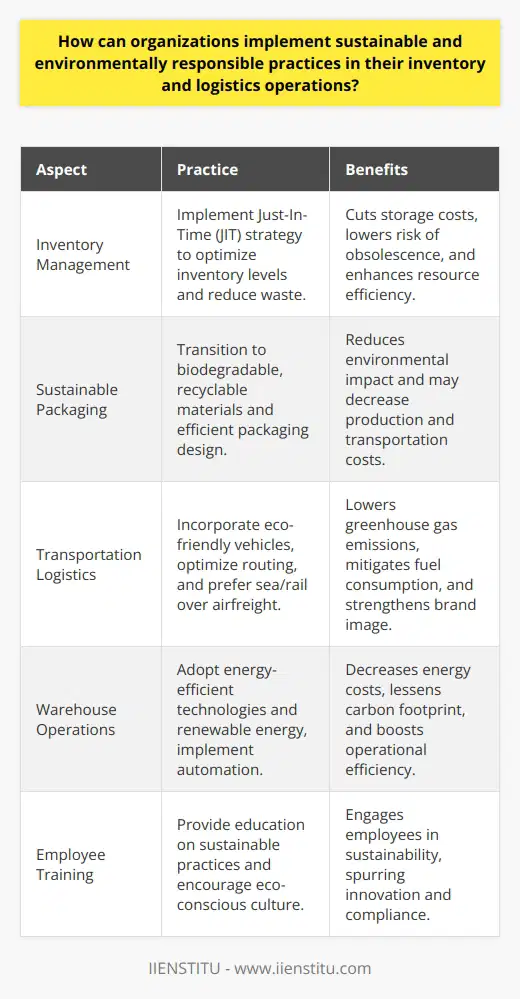
How can organizations implement sustainable and environmentally responsible practices in their inventory and logistics operations?
Sustainable Design of Inventory and Logistics
To embed sustainable operations into inventory and logistics, organizations can first focus on effective inventory management. This involves reducing overstocks to minimize waste and implementing a just-in-time inventory system. This technique prevents stockpiling, maintaining just enough inventory to fulfill orders and reducing waste.
Adopting Sustainable Packaging Practices
In addition, implementing environmentally responsible packaging can make a significant impact. Switching to reusable or biodegradable packaging materials limits the environmental footprint. Organizations can also choose suppliers who prioritize sustainability in their operations.
Transition to Green Transport Methods
Transportation logistics represent another area for environmental improvement. Shifting towards greener transport methods like electric vehicles or hybrid fleets lessens carbon emissions. Prioritizing transport routes with less environmental impact also contributes to sustainable logistics.
Optimizing Warehouse Operations
Inside the warehouse, operations can benefit from green technology. Energy-efficient lighting and heating systems reduce energy consumption. Also, digitalizing operations minimize paper usage and waste production.
Employee Education and Training
Finally, organizations should educate and train employees on sustainable practices. The efficacy of any implemented strategy depends heavily upon staff commitment and understanding.
An organization's commitment to environmentally responsible practice in its inventory and logistics management can lead to significant ecological and financial benefits. This commitment also enhances brand reputation, inviting greater customer support and loyalty. With the right approach and continuous commitment, businesses can both thrive and contribute positively to the environment.