
This article examines the various costs associated with inventory and how they can affect a business’s bottom line. Inventory costs include the products, borrowing money to pay for them, and other costs such as storage and shrinkage. Additionally, businesses may be charged an interest rate on inventory loans.
There may also be other costs, such as paying for a building to store the inventory and paying people to move the inventory around. Shrinkage and outdated products can also be costly for businesses, and all of these costs should be considered when calculating the inventory's overall cost.
Introduction
Inventory Costs
Borrowing Money and Interest Rates
Other Costs
Shrinkage and Outdated Products
Introduction: Inventory costs are an essential consideration for any business. Keeping products in inventory is a necessary part of running a business, but it comes with a cost. This cost includes the products, borrowing money to pay for them, and other costs such as storage and shrinkage. This article will examine the various costs associated with inventory and how they can affect a business’s bottom line.
Inventory Costs
The most obvious cost associated with inventory is the product's cost. The supplier usually determines this cost based on the quantity of the product ordered and other factors such as shipping and taxes. If a business borrows money to pay for the inventory, the cost of the inventory will also include the interest rate the business pays on loan.
Borrowing Money and Interest Rates
When a business borrows money to pay for inventory, it will be charged an interest rate on loan. This rate will vary depending on the lender and the loan terms, but it is usually higher than the rate charged on other types of loans. This is because inventory loans are usually short-term, so the lender is taking on more risk. The interest rate on loan will add to the inventory cost and should be considered when calculating the inventory's overall cost.
Other Costs
Connecting Supply Chain Communities: How Culture Impacts Supply Chain Management
Optimizing Commodity Supply Chains: Finding Low Prices & High Quality
In addition to the inventory cost and the interest rate on loan, other costs are associated with keeping inventory. These costs include paying for a building to store the inventory and paying people to move the inventory around inside the building. These costs can add up quickly and should be considered when calculating the inventory's overall cost.
Shrinkage and Outdated Products
When products are kept in inventory, there is always the risk of them being lost, damaged, or stolen. This problem, often referred to as shrinkage can be costly for businesses. In addition, if products stay in a warehouse for too long, they can expire or become outdated, which can also be costly for businesses. It is essential for businesses to keep track of their inventory and to rotate their stock to avoid these types of losses regularly.
Conclusion: Inventory costs are an essential consideration for any business. Keeping products in inventory is a necessary part of running a business, but it comes with a cost. The inventory cost itself, borrowing money to pay for it, and other costs, such as storage and shrinkage, can all add up quickly. It is essential for businesses to be aware of these costs and to consider them when calculating the overall cost of their inventory.
Proper inventory management is essential for efficient supply chain management and cost optimization.
Frequently Asked Questions
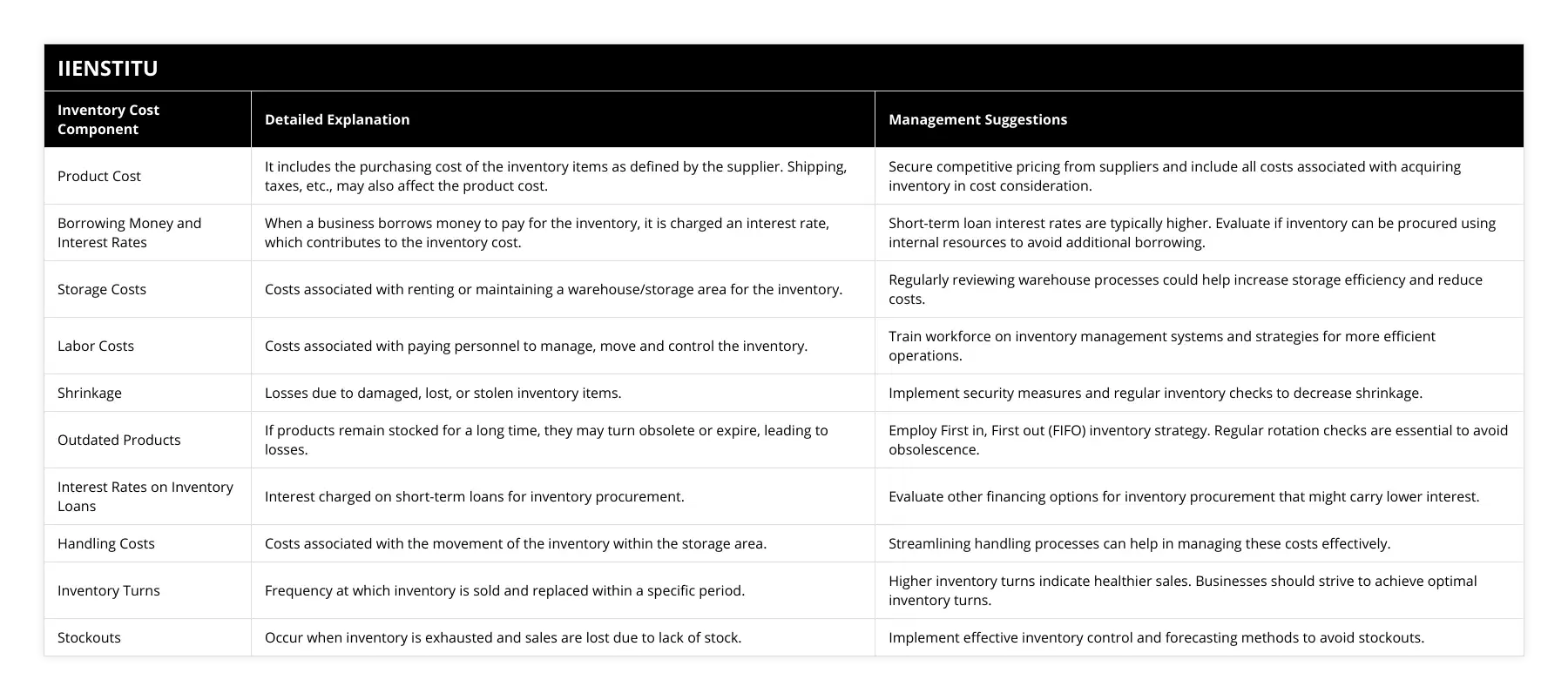
What strategies can businesses use to minimize inventory costs?
Businesses can minimize inventory costs through careful inventory management, taking advantage of discounts when available, reducing shrinkage and losses, implementing just-in-time inventory systems, and using stock control software.
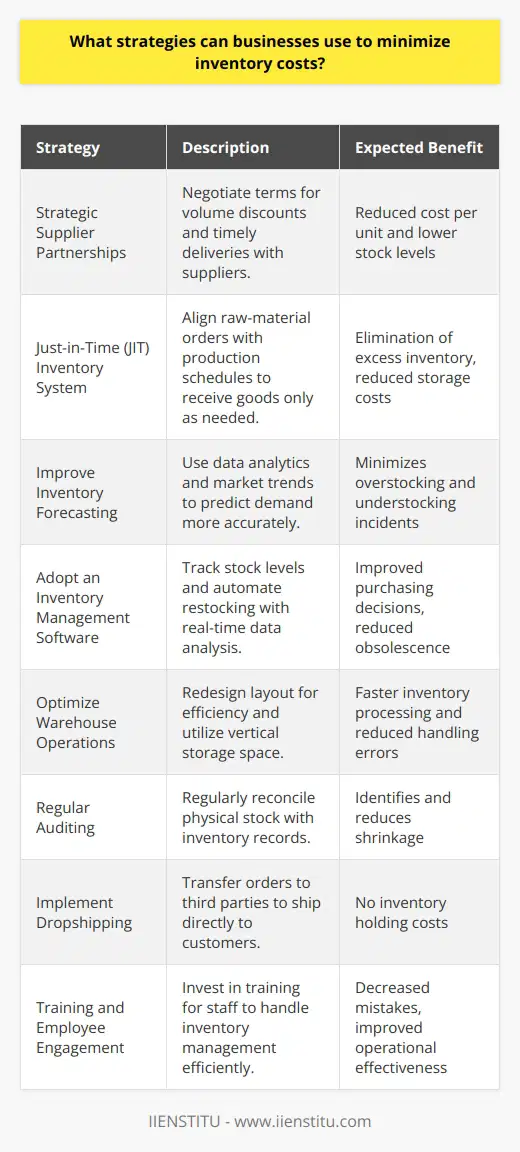
What strategies can be used to reduce inventory costs in supply chain management?
In the current business environment, the ability to reduce inventory costs is an important factor for supply chain management. Reducing inventory costs can increase profit margins and improve inventory performance. In this blog post, we will discuss some strategies that can be used to reduce inventory costs in supply chain management.
One strategy is to reduce the number of SKUs (stock-keeping units) in a inventory system. By reducing the number of SKUs, less inventory is needed to cover the same amount of demand. This can lead to lower inventory costs, as fewer stockouts and fewer items need to be replaced. Additionally, a reduction in the number of SKUs can lead to lower inventory tracking and management costs.
Another strategy is to use inventory optimization techniques. Inventory optimization techniques allow businesses to identify the optimal number of items to keep in inventory. This can help to reduce overstocking and stockouts, as well as improve inventory performance. Additionally, inventory optimization techniques can be used to identify the most cost-effective inventory locations, which can further reduce inventory costs.
Another strategy is to implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory management. JIT inventory management is a system of ordering and delivering inventory only when it is needed. By reducing the amount of inventory needed, businesses can significantly reduce inventory carrying costs. Additionally, JIT inventory management can improve customer service, as orders can be filled more quickly.
Finally, businesses can use technology to reduce inventory costs. Technology can be used to automate inventory tracking, monitoring, and forecasting. Automation can reduce labor costs associated with manual inventory management, as well as reduce the potential for human error. Additionally, technology can be used to reduce lead times, which can further reduce inventory costs.
In conclusion, there are several strategies that can be used to reduce inventory costs in supply chain management. These strategies include reducing the number of SKUs, using inventory optimization techniques, implementing JIT inventory management, and utilizing technology. By implementing these strategies, businesses can reduce inventory costs, improve inventory performance, and increase profit margins.
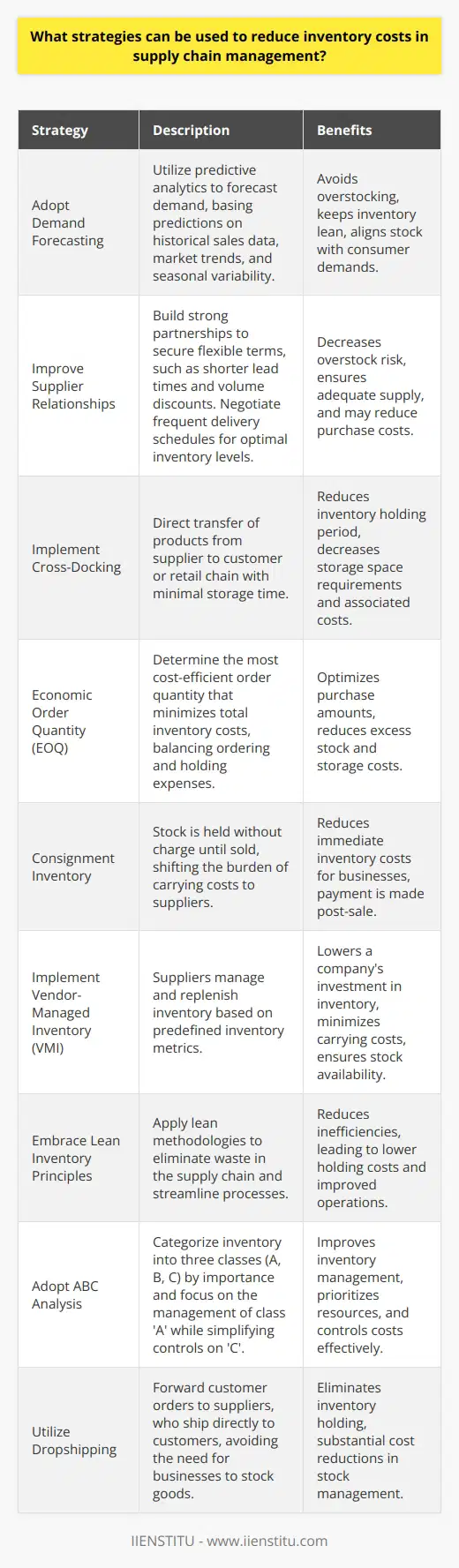
How can borrowing money and interest rates be used to maximize inventory costs?
In the current business climate, inventory costs can quickly become a significant financial burden for many companies. The challenge of managing inventory costs is complex and requires a comprehensive strategy. One effective strategy to manage inventory costs is to borrow money at appropriate interest rates and use it to fund inventory purchases.
Interest rates are an important consideration when borrowing money to finance inventory purchases. When interest rates are low, it is generally more cost-effective to borrow money to purchase inventory. Low-interest rates reduce the total cost of the loan and can be used to purchase larger amounts of inventory. On the other hand, when interest rates are high, it may be more cost-effective to purchase inventory with existing funds as the cost of the loan may be too high.
In addition to borrowing money at an appropriate interest rate, it is also important to use the borrowed funds efficiently. Borrowed money should only be used to purchase inventory that is in demand and has the potential to generate profits. Furthermore, the inventory should be purchased in the most cost-efficient manner. This includes researching suppliers, negotiating lower prices, and monitoring inventory levels to ensure that inventory is not overstocked.
In summary, borrowing money at appropriate interest rates and using the funds to purchase inventory can be an effective way to manage inventory costs. When interest rates are low, borrowed funds can be used to purchase larger amounts of inventory. It is also important to use the borrowed funds efficiently, by only purchasing inventory that is in demand and has the potential to generate profits. By using this strategy, businesses can maximize their inventory costs and ensure they are making the most cost-effective purchases.
How can a supply chain optimize inventory cost?
Optimizing Inventory Costs: Multifaceted Approach
Inventory Cost Reduction Strategies
An optimized inventory cost can significantly improve a supply chain's overall performance. To achieve this, supply chain managers must utilize various strategies, including demand forecasting, inventory control systems, and supplier selection. Accurate demand forecasting enables informed decision-making regarding inventory levels, minimizing excess or insufficient inventory risks. Implementing inventory control systems, like automated replenishment programs, facilitates the efficient management of stock levels, reducing carrying and stockout costs.
Utilization of Technology
Another approach involves leveraging technology to streamline inventory management processes, such as adopting warehouse management systems and using Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. Warehouse management systems provide real-time visibility of inventory levels, enabling better coordination between supply chain partners, thereby reducing safety stock requirements. RFID technology enables improved tracking and tracing of products, ensuring minimal delays in product deliveries, and providing accurate data to refine demand forecasting models.
Supplier Selection Criteria
Choosing the right supplier also contributes to inventory cost optimization. Criteria such as pricing, lead times, and reliability should be thoroughly evaluated while selecting a supplier, as these factors directly impact inventory holding costs, missed sales opportunities, and overall supply chain effectiveness. Strong supplier relationships can enable businesses to negotiate lower prices, shorter lead times, and better delivery terms, thus reducing inventory costs.
Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory Management
Another effective technique in reducing inventory costs involves adopting just-in-time (JIT) inventory management. With JIT, inventory is ordered and received only as needed, minimizing holding costs and risks associated with obsolescence or damage. By synchronizing production and delivery schedules, businesses can significantly reduce their inventory holding costs, thus enabling streamlined operations and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the key to optimizing inventory costs lies in adopting a multifaceted approach that combines data-driven decision-making, technology utilization, strategic supplier selection, and JIT inventory management. By aligning these strategies across the supply chain, businesses can significantly reduce inventory costs, improve operational efficiency, and ultimately enhance overall performance.
What are the key factors to consider when implementing inventory management techniques in supply chain management?
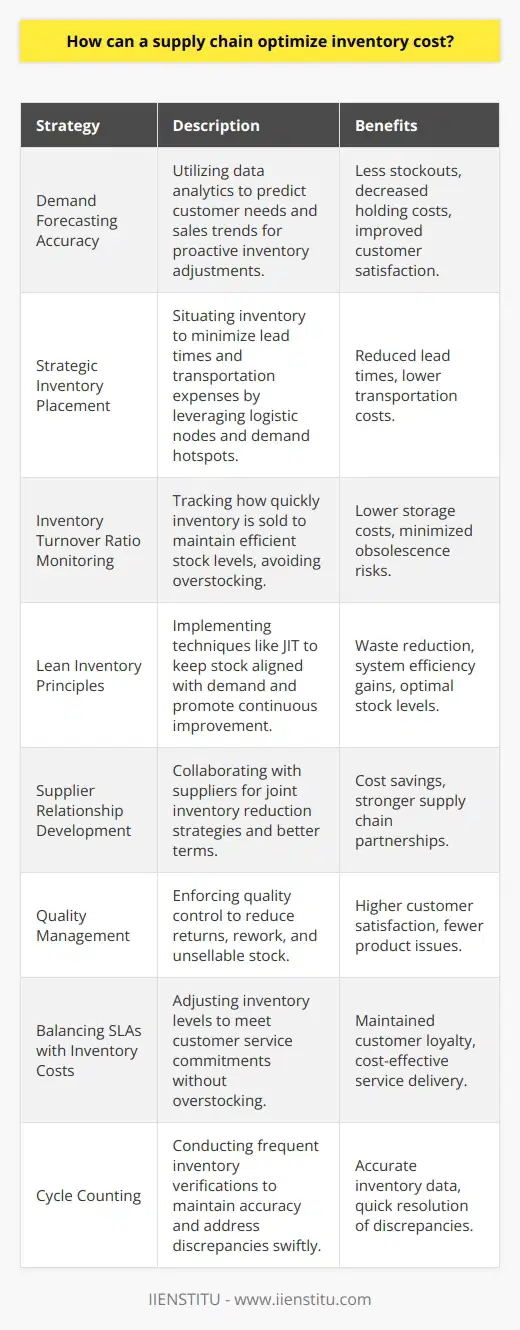
Key Factors in Inventory Management Implementation
Efficient Demand Forecasting
One of the critical factors in implementing inventory management techniques is the ability to predict customer demand accurately. Successful forecasting methodologies involve the collection and analysis of historical sales data, understanding market trends, and taking into account seasonal variations. These practices enable businesses to make informed decisions about inventory levels, avoiding overstocking or stockouts that could negatively impact customer satisfaction and profitability.
Supplier Relationship Management
Establishing strong relationships with suppliers is essential for effective inventory management. Close collaboration between supply chain partners fosters transparent communication, enabling companies to share information, track product quality, and ensure timely deliveries. By maintaining trust with suppliers, businesses can streamline procurement processes and reduce the occurrence of supply chain disruptions, promoting a more resilient and responsive inventory.
Effective Warehouse Management
Optimizing warehouse operations can significantly impact the efficiency of your inventory management system. This includes implementing best practices such as proper space utilization, layout design, and incorporating advanced technologies (e.g., RFID, barcode scanning) to facilitate quicker and more accurate inventory tracking. These measures help minimize human error, reduce inventory carrying costs, and enhance overall operational performance.
Adopting Advanced Technologies
Integrating advanced technology into the inventory management process can yield substantial benefits, including real-time visibility into inventory levels, enhanced tracking capabilities, and better data analytics. Implementing software that supports inventory optimization, such as ERP systems, boosts the accuracy of demand forecasts and aids in determining appropriate safety stock levels. Moreover, adopting technology solutions can minimize manual inventory tasks, freeing up valuable resources to focus on other aspects of the supply chain.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Lastly, successful inventory management is grounded in continuous monitoring and improvement. By consistently assessing inventory metrics, such as inventory turnover, stockout rates, and holding costs, businesses can identify areas requiring enhancement and devise strategies to address them. Regular performance evaluation enables organizations to remain agile and adaptable in the face of changing market conditions and maintain a competitive advantage in a dynamic business environment.
In conclusion, critical factors to consider when implementing inventory management techniques include efficient demand forecasting, supplier relationship management, effective warehouse management, the adoption of advanced technologies, and continuous monitoring and improvement. These components work together to create a resilient, responsive, and cost-effective inventory management strategy that maximizes customer satisfaction and organizational profitability.
What are the benefits of adopting a demand-driven inventory management approach in reducing costs?
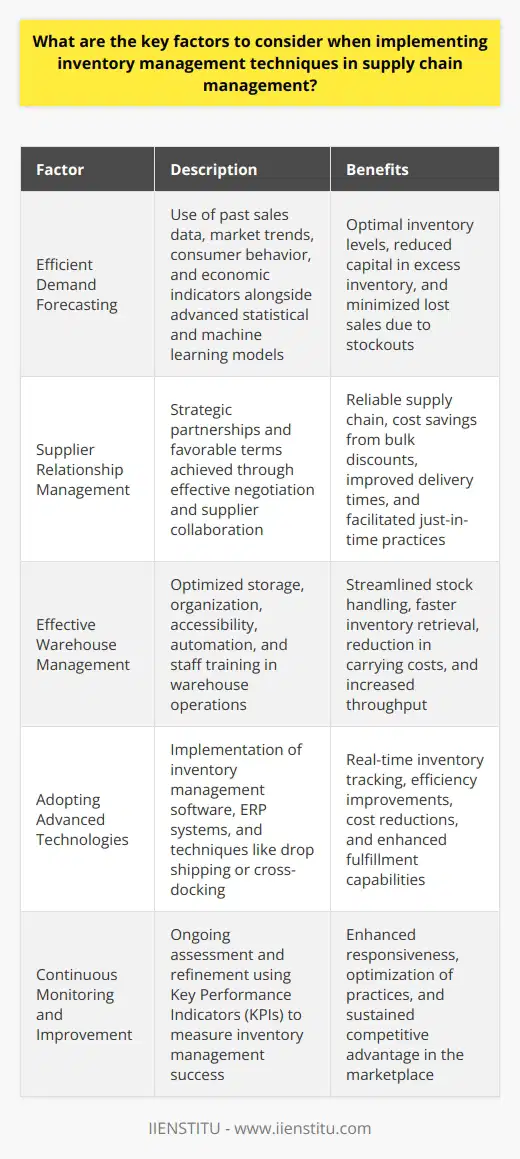
Subheadings: Effective Cost Reduction, Efficient Stock Management, Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Effective Cost Reduction
Adopting a demand-driven inventory management approach allows companies to accurately forecast customer demands, leading to significant cost reductions. By directly aligning inventory levels with actual demand, businesses can minimize the risk of overstocking or understocking, resulting in decreased holding and storage costs. Moreover, demand-driven strategies enable companies to improve their cash flow and boost financial performance as they only invest in products that are likely to sell quickly.
Efficient Stock Management
Integrating a demand-driven inventory system enables businesses to optimize stock replenishment processes effectively. By tracking sales patterns, seasonal trends, and other market factors, companies can ensure that they consistently maintain optimal inventory levels. This efficient stock management not only prevents losses incurred from expired or obsolete products, but also minimizes the likelihood of stockouts, leading to improved operational efficiency. Additionally, demand-driven inventory management allows companies to respond quickly to changes in demand, creating a more dynamic and adaptable supply chain.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Through demand-driven inventory management, companies gain valuable insights into customer preferences and buying patterns. This data-driven approach ensures that businesses consistently offer the right products in the right quantities, ultimately resulting in improved customer satisfaction. Moreover, by avoiding stockouts and reducing lead times, companies can ensure that customers receive their desired products promptly, further enhancing customer satisfaction levels. Overall, demand-driven inventory management fosters stronger customer relationships, leading to increased sales and brand loyalty.
How do you manage inventory in supply chain management?
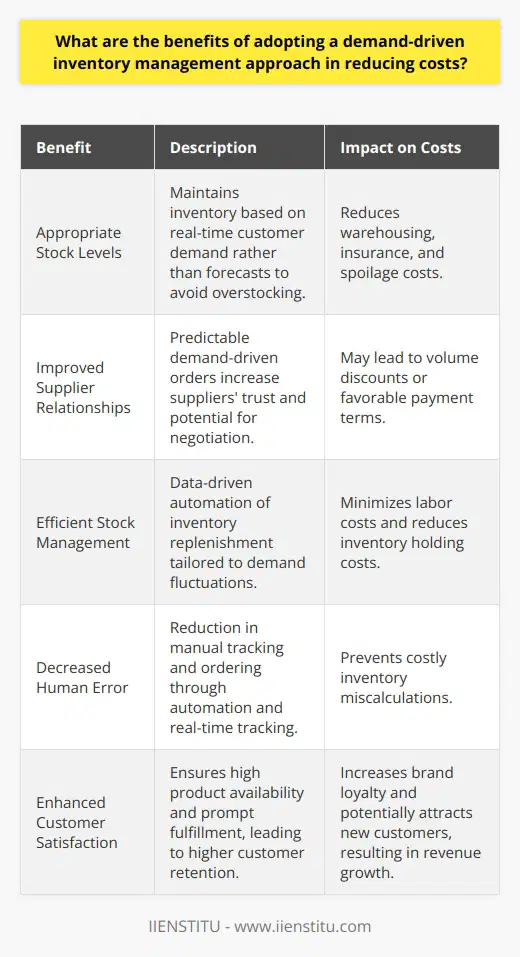
Effective Inventory Management Techniques
To manage inventory in supply chain management, several effective techniques can be employed to ensure a smooth flow of goods and minimize costs. First and foremost, accurate demand forecasting is essential in determining optimal stock levels. By analyzing historical sales data, seasonal fluctuations, and market trends, businesses can predict future demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
Utilization of Safety Stock
Another important aspect of inventory management is maintaining an appropriate level of safety stock. This serves as a buffer against unexpected surges in demand or disruptions in the supply chain, such as delays from suppliers or changes in market conditions. By establishing target service levels, companies can determine the appropriate amount of safety stock needed to ensure customer satisfaction without compromising financial performance.
Implementation of Inventory Control Systems
The implementation of inventory control systems, such as the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model, can assist in optimizing replenishment decisions. The EOQ model calculates the economically optimal order quantity that minimizes the total cost of inventory, including purchase, holding, and shortage costs. Moreover, employing a real-time inventory management system enables businesses to monitor stock levels, track inventory turnover, and identify slow-moving items.
Employing Just-in-Time (JIT) Approach
In addition, adopting a Just-in-Time (JIT) approach to inventory management can be beneficial in reducing excess stock and minimizing costs. The JIT strategy focuses on ordering and producing goods only when required, thereby reducing inventory holding costs and the risk of obsolescence. However, the success of the JIT approach relies on strong supplier relationships and accurate demand forecasting to prevent stockouts.
Collaboration with Suppliers and Customers
Lastly, fostering collaboration with suppliers and customers is paramount in inventory management. Through effective communication, data sharing, and collaboration, organizations can better anticipate demand changes and synchronize supply chain activities. Jointly developing forecasts, sharing sales information, and implementing vendor-managed inventory systems can result in improved inventory management and reduced costs.
In conclusion, effective inventory management in supply chain management entails a combination of accurate demand forecasting, adequate safety stock levels, optimized replenishment decisions, JIT strategies, and strong collaboration with suppliers and customers. By employing these techniques, businesses can achieve a well-balanced inventory that minimizes costs and maximizes customer satisfaction.
What is a great way to reduce inventory costs?
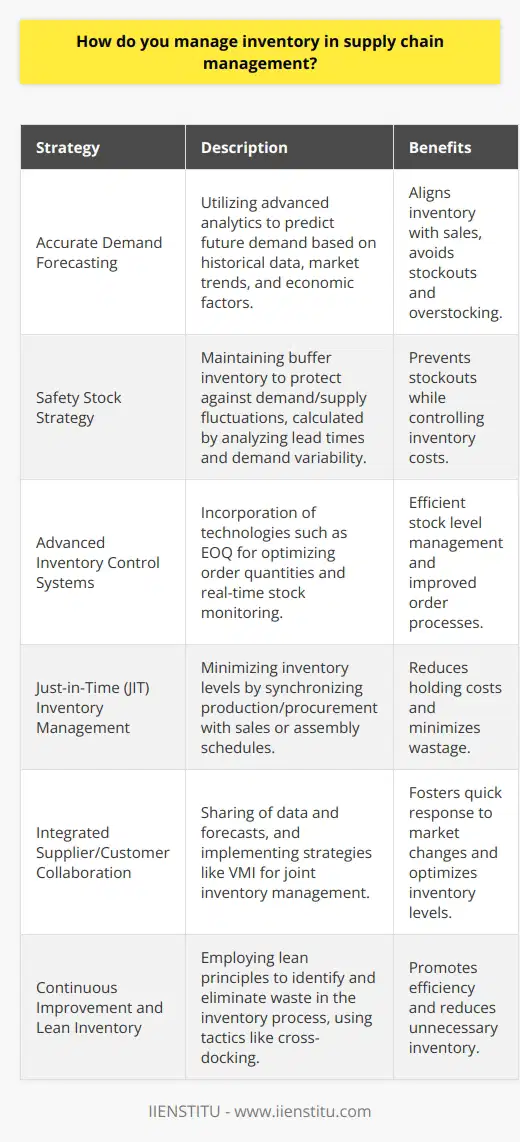
Effective Inventory Management
A great way to reduce inventory costs is through effective inventory management, which entails the accurate tracking of stock, efficient ordering processes, and the strategic placement of items to maximize sales. By ensuring that inventory is managed effectively, businesses can optimize their storage space, reduce holding costs, and minimize the risk of obsolescence or overstocking, ultimately leading to decreased overall inventory costs.
Utilizing Inventory Management Tools
To manage inventory effectively, it is crucial to have updated and accurate data on stock levels, order lead times, and sales patterns. This can be achieved by implementing inventory management tools that automatically synchronize inventory data and generate critical insights. By utilizing such tools, businesses can easily identify fast-moving items, pinpoint stock discrepancies, and prioritize items for re-ordering, ultimately promoting better decision-making and cost reduction.
Implementing Just-in-Time Inventory System
Adopting a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system can also significantly minimize inventory costs. JIT involves purchasing inventory only when there is an immediate demand so that the items arrive just in time to fulfill customer orders. This approach reduces the costs associated with holding surplus inventory, such as warehousing space and insurance expenses, while also minimizing the risk of stock obsolescence or spoilage. Additionally, JIT encourages businesses to improve their relationships with suppliers and streamline their order-processing systems, further contributing to cost savings.
Conducting Frequent Inventory Audits
Regularly conducting inventory audits can help businesses identify discrepancies, such as damaged items or stock shrinkage, thereby preventing costly financial losses. This process involves comparing the actual stock with the recorded inventory data to detect and resolve any discrepancies. Frequent inventory audits can also aid in optimizing inventory levels, improving sales forecasting accuracy, and reinforcing inventory management policies.
Emphasizing Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting plays a crucial role in reducing inventory costs. By predicting customer demand patterns, businesses can optimize their procurement process and maintain a balanced inventory to meet customer needs. Accurate demand forecasting reduces the risk of overstocking, which can lead to high holding costs, slow-moving items, and eventual markdowns or write-offs. Furthermore, it reduces the likelihood of stockouts that can lead to lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
In conclusion, reducing inventory costs requires the consistent implementation of effective inventory management strategies, such as utilizing inventory management tools, adopting a JIT inventory system, conducting frequent inventory audits, and emphasizing demand forecasting. These approaches can lead to significant cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and a more competitive business position.
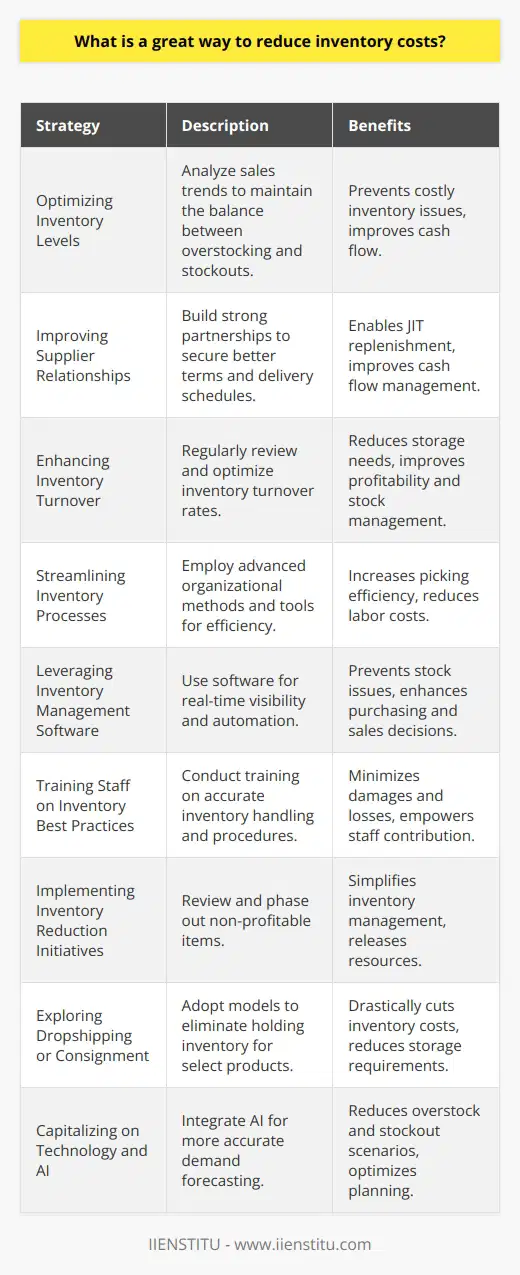
What are the 3 major inventory management techniques?
Major Inventory Management Techniques
Just-in-Time Inventory
The first major inventory management technique is the Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory method. JIT focuses on minimizing inventory levels in order to reduce carrying costs and storage expenses. By implementing JIT, a company only purchases and holds inventory that is required for immediate production, ultimately leading to lower inventory levels and reduced costs. This technique, however, may lead to increased reliance on suppliers, demanding flexibility, and responsiveness in supply chain management.
Economic Order Quantity Model
Secondly, the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model is widely utilized for determining the optimal order quantity that minimizes both the ordering and holding costs of inventory. The EOQ model is based on the principle that the ideal order quantity occurs at the point where ordering and holding costs are equal. By calculating the EOQ, companies can determine the most cost-effective inventory level that balances inventory-related expenses with the potential for stockouts, leading to improved efficiency in inventory management and control.
Safety Stock Management
Lastly, Safety Stock Management is crucial for mitigating stockout risks and ensuring customer satisfaction by maintaining an appropriate buffer stock in the inventory. Safety stock is the additional inventory held to protect against fluctuations in demand and lead time, thereby preventing stockouts and minimizing the potential impact of lost sales or production delays. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the safety stock levels enables companies to proactively respond to market changes, ensuring optimal inventory levels are maintained, and customer demands are met.
Overall, employing these three major inventory management techniques - Just-in-Time Inventory, Economic Order Quantity Model, and Safety Stock Management - enables companies to optimize their inventory levels, minimize costs, and efficiently manage supply chain operations. Although each technique has its own unique benefits and challenges, a combination of these methods can lead to effective and sustainable inventory management practices that contribute to organizational success.
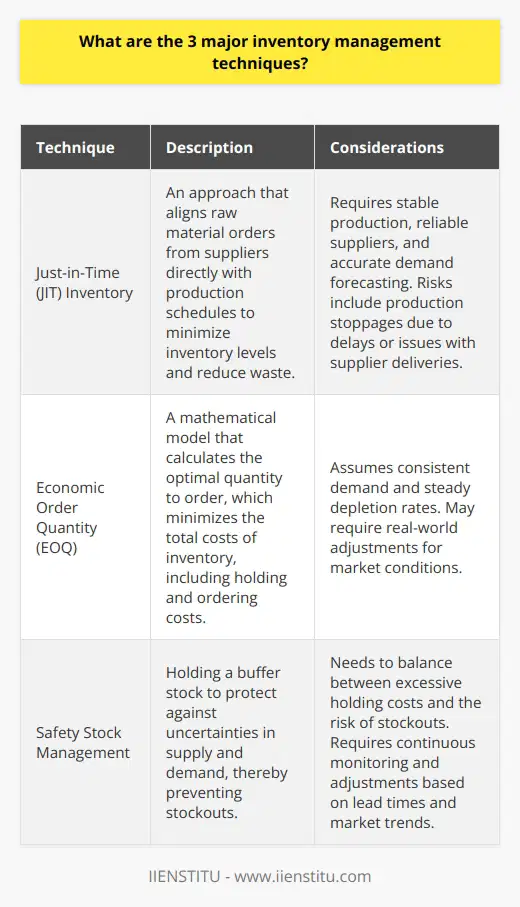
What is your best tip to improve the inventory management?
Effective Forecasting Techniques
A crucial tip for improving inventory management is to develop and implement effective forecasting techniques. This allows businesses to estimate the demand for a product accurately, informing their strategies for procurement, distribution, and storage. In turn, this leads to optimized inventory levels, reduced carrying costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Consistent Data Analysis
One essential aspect of successful inventory forecasting is consistent data analysis. By continually analyzing historical sales data, trends, and seasonality, businesses can better predict future demand fluctuations. Additionally, the use of advanced data analytics tools, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, can enhance the accuracy of inventory forecasts, leading to more effective inventory management strategies.
Regular Communication with Suppliers
Furthermore, maintaining open lines of communication with product suppliers and manufacturers is crucial for successful inventory management. Sharing sales and demand forecasts with suppliers allows them to plan for production and shipping accordingly, ensuring a steady flow of products into the warehouse. Regular communication also enables businesses to detect and resolve supply chain issues, mitigating potential stockouts or overstocks.
Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Implementing real-time inventory tracking systems, such as barcode or radiofrequency identification (RFID) technology, can significantly streamline the inventory management process. These technologies provide instant updates on stock levels, allowing businesses to react swiftly to changes in demand, fulfillment needs, or supply chain disruptions. Moreover, real-time tracking helps prevent human error in inventory counts, reducing inconsistencies, and improving overall efficiency.
Establishing Safety Stock Levels
An additional tip for improving inventory management is to establish safety stock levels for each product. Safety stock serves as a buffer to account for unexpected demand surges or supply chain delays, ensuring that customer orders can still be fulfilled. By implementing an effective safety stock strategy, businesses can improve their inventory turnover rate and reduce the risk of lost sales due to stockouts.
In conclusion, successful inventory management relies on effective forecasting techniques, consistent data analysis, clear communication with suppliers, real-time inventory tracking, and setting appropriate safety stock levels. These practices contribute to an efficient, cost-effective, and customer-centric inventory management system that is essential for businesses' growth and profitability.
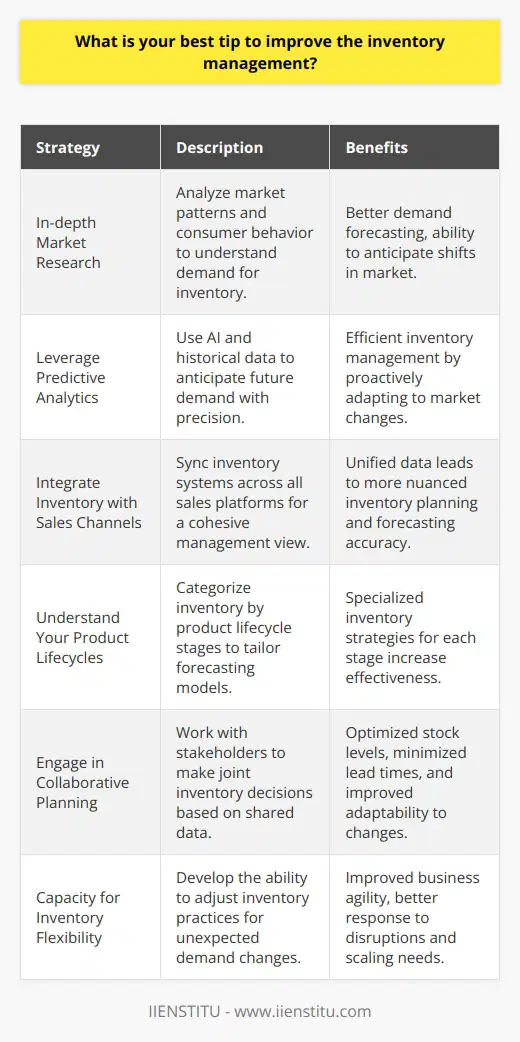
How can effective forecasting methods contribute to optimizing inventory costs in supply chain management?
Forecasting Accuracy and Inventory Costs
Effective forecasting methods play a crucial role in supply chain management by helping businesses predict future demand for their products. Accurate demand forecasts reduce uncertainty, leading to better inventory management and lower costs.
Demand Estimation Techniques
Using quantitative and qualitative techniques, businesses can estimate future demand more accurately. Quantitative methods, such as time series analysis and regression models, utilize historical sales data to identify trends and patterns. Qualitative methods, like Delphi technique and market research, rely on expert opinions and customer feedback to predict demand changes.
Reducing Safety Stock
Accurate demand forecasts allow businesses to maintain lower safety stock levels, reducing inventory carrying costs. Safety stock serves as a buffer against demand fluctuations, but overstocking leads to increased warehousing expenses and potential obsolescence. Businesses can reduce safety stock while still meeting customer service level expectations with effective forecasting techniques.
Improved Order Management
By optimizing order frequency and quantity, effective forecasting methods contribute to reducing inventory costs. Utilizing methods such as Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model, businesses can balance ordering and holding costs, minimizing their total inventory expenses. Accurate demand forecasts inform the EOQ input parameters, leading to lower expenditures on raw materials and finished goods.
Minimizing Stockouts and Excess Inventory
Effective forecasting reduces the risks of stockouts and excess inventory, both of which incur additional costs for businesses. Stockouts can result in lost sales, customer dissatisfaction, and increased operational costs due to expedited replenishment. Excess inventory contributes to obsolescence, spoilage, and high storage expenses. Reliable demand forecasts enable businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels, avoiding these negative consequences.
Enhanced Supplier Collaboration
Accurate demand forecasts also facilitate better collaboration between businesses and their suppliers, allowing them to work together in optimizing inventory levels. Through initiatives like Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI), suppliers can directly manage inventory at customers' warehouses, ensuring optimal stock levels by leveraging their demand forecast capabilities.
In conclusion, effective forecasting methods are essential for businesses aiming to optimize inventory costs in supply chain management. Accurate demand forecasts lead to reduced safety stock, improved order management, minimized stockouts and excess inventory, and enhanced supplier collaboration, ultimately resulting in a more efficient and cost-effective supply chain.
What role does technology play in streamlining inventory management and reducing costs?
Role of Technology in Inventory Management
Efficient Use of Data
Technology plays a crucial role in streamlining inventory management by facilitating efficient use of data. Advanced software solutions and analytics tools help businesses collect, organize, and analyze vast amounts of inventory data, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding stock levels, order frequency, and optimal storage solutions.
Automation and Integration
Another critical aspect of technology in inventory management is automation and integration. By automating routine tasks such as stock counting and order processing, businesses can save time, reduce manual errors, and improve overall operational efficiency. Additionally, integrating inventory management systems with other business processes, like sales and procurement, ensures seamless coordination and data exchange, resulting in a more efficient supply chain.
Real-time Monitoring and Control
Technology also enables real-time monitoring and control of inventory levels. Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as sensors and RFID tags, can provide continuous, real-time updates on inventory status, location, and conditions, reducing the need for manual checks and physical stocktakes. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of stockouts and overstocking, leading to lower overall inventory costs.
Demand Forecasting
By enabling more accurate demand forecasting, technology helps businesses optimize their inventory levels, preventing excess stock or stockouts. Machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics tools can analyze historical sales data and identify trends and patterns that inform future demand. This insight allows businesses to adjust their inventory strategies accordingly, reducing storage costs, wasted stock, and potential lost sales.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Finally, technology improves communication and collaboration among different stakeholders in the inventory management process. Cloud-based inventory management systems allow for real-time information sharing and collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. This increased level of transparency and communication allows for improved coordination, reducing lead times, stockouts, and excess inventory, ultimately lowering costs.
In conclusion, technology streamlines inventory management by enhancing data utilization, automating processes, enabling real-time monitoring, improving demand forecasting, and facilitating better communication among stakeholders. Consequently, businesses can significantly reduce costs and achieve greater efficiency in their inventory management processes.
How can a demand-driven approach enhance inventory management in a supply chain?
Demand-Driven Approach in Inventory Management
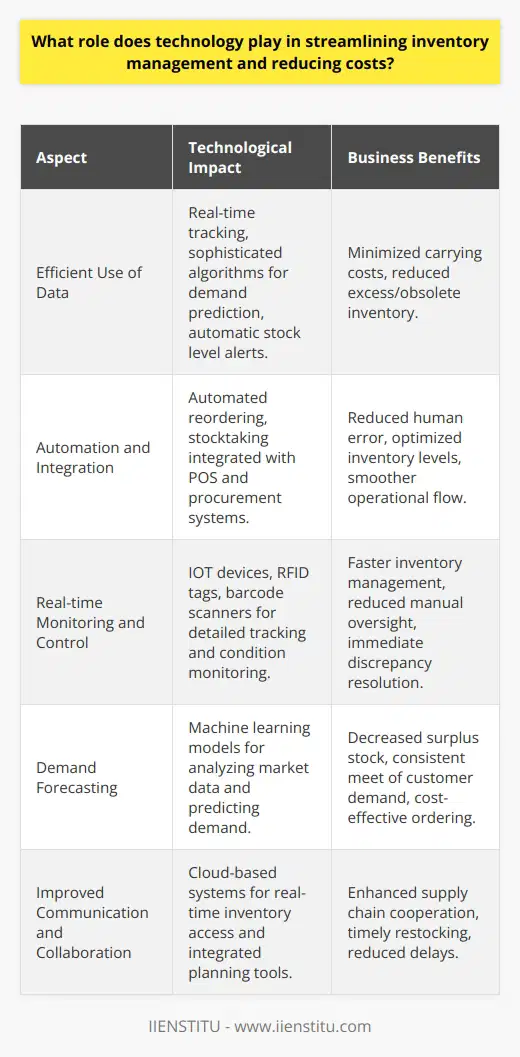
Effective inventory management is crucial for supply chain success, as it enables organizations to meet consumer demands while optimizing costs. A demand-driven approach can significantly enhance inventory management by allowing better alignment between supply and demand, leading to improved availability of goods and reduced lead times.
Accurate Demand Forecasting
A key feature of the demand-driven approach is accurate demand forecasting, which reduces uncertainties in inventory management. By leveraging data analytics and advanced algorithms, the demand-driven approach enables more precise predictions of future demand patterns, allowing companies to adjust inventory levels accordingly. This results in reduced stockouts and excess inventory, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Adaptive Inventory Replenishment
Demand-driven inventory management also focuses on adaptive inventory replenishment strategies, which continuously adjust to fluctuations in demand. Such adaptive strategies can prevent stockouts or surplus inventory by maintaining optimal stock levels, reducing holding costs and the risk of obsolescence. This streamlined approach to replenishment helps organizations stay competitive in dynamic market conditions, ensuring that the right products are available at the right time and quantities.
Improved Collaboration and Coordination
The demand-driven approach also relies on effective collaboration and coordination across supply chain partners. By sharing accurate demand information with suppliers, manufacturers can improve their production schedules and better manage raw material inventory levels. In turn, suppliers can ensure timely deliveries, avoiding delays and maximizing value for the supply chain as a whole. This collaborative approach also fosters stronger relationships among supply chain stakeholders, further enhancing supply chain efficiency.
Responsiveness to Consumer Needs
In an increasingly customer-centric marketplace, adopting a demand-driven approach enables organizations to swiftly respond to changing market demands. This responsiveness can boost an organization's ability to identify and capitalize on emerging opportunities, while also adapting to unforeseen challenges. By focusing on satisfying consumer needs, supply chain partners can bolster their market competitiveness and build long-lasting relationships with customers.
In summary, a demand-driven approach can dramatically enhance inventory management by enabling more accurate demand forecasting, adaptive inventory replenishment, improved collaboration across supply chain partners, and heightened responsiveness to consumer needs. By aligning supply and demand more effectively, organizations can optimize inventory levels, reduce costs, and achieve superior customer satisfaction.
What factors should be considered while selecting the appropriate inventory management technique for a specific industry?
Key Factors in Choosing Inventory Management Techniques
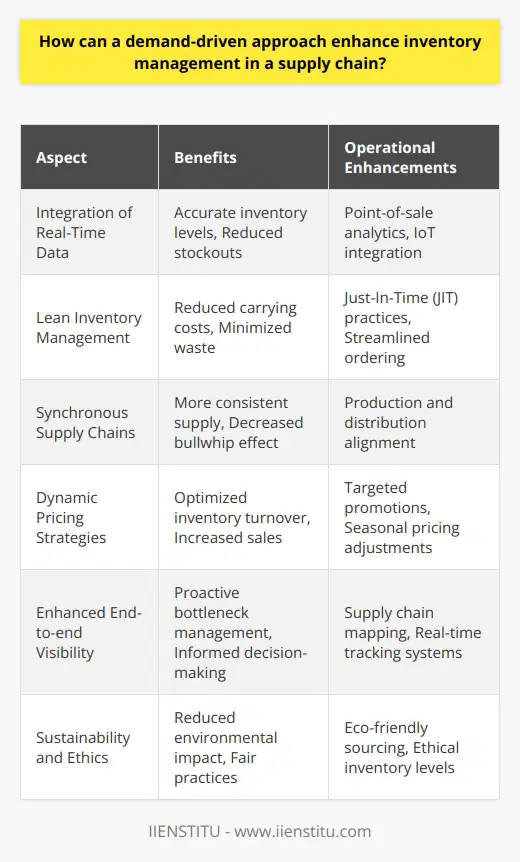
Industry Characteristics
Selecting the appropriate inventory management technique for a specific industry requires a comprehensive understanding of the industry's characteristics, such as product type, demand fluctuation, and operational constraints. An understanding of these factors will guide the choice of an inventory management method that best fits the industry.
Product Life Cycle and Demand
The product life cycle also plays a crucial role in determining the inventory management technique to adopt. For industries with short product life cycles, such as fashion or technology, a Just-in-Time (JIT) approach may be more suitable, as it minimizes inventory holding costs and the risk of obsolescence. On the other hand, industries with stable, predictable demand patterns, such as food and beverage or pharmaceuticals, may benefit from implementing the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model, ensuring a continuous flow of goods and reducing stockouts.
Supplier Reliability
In any industry, the relationship with suppliers has a direct impact on inventory management techniques. A reliable supplier enables a business to maintain an efficient supply chain, facilitating the choice of inventory management methods such as JIT or Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI). In contrast, businesses reliant on less consistent suppliers may need to maintain higher safety stock levels or utilize a more conservative inventory management method, like the EOQ model or periodic review system.
Warehousing and Storage
The existing warehousing and storage infrastructure is another factor to consider when selecting inventory management techniques. Industries with ample storage space may be more inclined to utilize an EOQ model, while those with limited space may opt for a JIT approach. Additionally, inventory management technologies, such as barcode systems and warehouse management systems, can significantly improve efficiency and reduce human error, which should also be factored into the decision-making process.
Cost Considerations
Finally, a crucial factor to consider when choosing inventory management techniques is cost. Each method has its own set of costs, including ordering, holding, and shortages. Businesses should select an inventory management technique that minimizes these costs while ensuring the efficient delivery of goods to customers. This may involve the use of sophisticated inventory management software capable of monitoring and analyzing various cost drivers to optimize the chosen technique.
In conclusion, multiple factors must be considered when selecting inventory management techniques for a specific industry. These factors include industry characteristics, product life cycle and demand, supplier reliability, warehousing and storage infrastructure, and cost considerations. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can select an inventory management technique that best suits their industry and ultimately enhances efficiency and profitability.
How do various inventory management techniques address the challenges of seasonality and fluctuating demand in different supply chains?
Understanding Seasonality and Fluctuating Demand
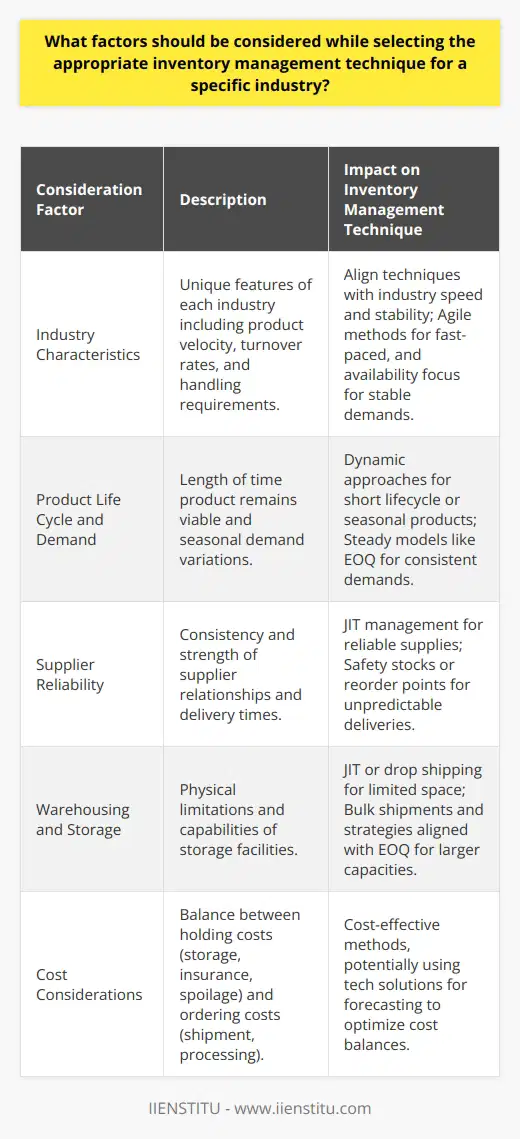
Seasonality and fluctuating demand significantly impact inventory management in supply chains. Understanding these patterns is crucial for implementing effective inventory management techniques. Demand forecasting plays an essential role in this process, enabling better anticipation of potential market changes, improved resource allocation, and optimized production schedules.
Demand Forecasting Techniques
One approach to addressing seasonality and fluctuating demand is employing time-series forecasting methods such as moving averages, exponential smoothing, and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) in demand planning. These techniques focus on analyzing historical data to predict future trends, adjusting for recurrent patterns in demand or any irregular fluctuations, and ultimately guiding inventory management decisions.
Safety Stock and Reorder Points
Another inventory management technique is setting appropriate safety stock levels and reorder points. This strategy helps ensure continuous product availability while minimizing excess inventory. Safety stock accounts for variability in demand and lead times, while reorder points trigger new orders when inventory reaches a predetermined level. Regularly reviewing and adjusting safety stock and reorder points helps maintain a balance between customer service levels and inventory costs.
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
Vendor-managed inventory (VMI) involves suppliers taking responsibility for maintaining optimal inventory levels. By using VMI, the supplier continuously monitors the customer's inventory and replenishes it based on predetermined triggers. This approach can be advantageous for both parties, reducing inventory holding costs and out-of-stock situations, provided the supplier has an accurate understanding of the demand.
Just-In-Time (JIT) Production
Just-in-Time (JIT) production aims to minimize inventory levels by synchronizing production activities with customer demand. This technique requires close collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to ensure timely delivery of products. JIT can help counteract the effects of seasonality and fluctuating demand by adapting production schedules in response to actual demand levels rather than relying on forecasts.
Collaborative Forecasting and Planning
Companies can also improve their inventory management by collaborating with suppliers and customers in forecasting and planning activities. Shared information and open communication among supply chain partners enable them to make better-informed decisions regarding production, inventory, and transportation. Including multiple partners in the decision-making process allows for a holistic approach to managing seasonality and fluctuating demand.
In conclusion, various inventory management techniques address challenges posed by seasonality and fluctuating demand. These approaches include demand forecasting, adjusting safety stocks and reorder points, VMI, JIT production, and collaborative forecasting and planning. Effective implementation of these techniques can help mitigate supply chain disruptions, optimize inventory levels, and enhance overall supply chain performance.
What are the 4 ways of achieving proper inventory control?
**Effective Demand Forecasting**
One critical method to achieve proper inventory control is effective demand forecasting. It involves predicting future product demand by analyzing historical sales data and market trends. Accurate forecasts enable better inventory planning, reducing stockouts, and minimizing excess stock.
**Inventory Management Techniques**
Implementing inventory management techniques, such as Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), Just-in-Time (JIT), and ABC analysis, is another essential approach to proper inventory control. EOQ calculates the optimal order quantity to minimize inventory costs, while JIT limits stock quantities by coordinating production with suppliers. ABC analysis classifies inventory items based on their value, ensuring that high-value items receive appropriate attention.
**Key Performance Indicators**
Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) offers a systematic way to gauge inventory performance. Essential inventory KPIs include stock turnover rate, order lead time, and stock accuracy. By tracking these KPIs, businesses can make data-driven decisions to optimize their inventory management and improve overall efficiency.
**Regular Stock Audits**
Conducting regular stock audits helps maintain accurate inventory records, identify discrepancies, and prevent potential losses. Stock audits involve physically counting items, comparing them to inventory records, and resolving any discrepancies. This process ensures that the actual inventory levels align with the recorded information, allowing businesses to make well-informed decisions about purchasing and stock adjustments.
How can organizations leverage data analytics and real-time visibility for effective inventory management in supply chain operations?
Real-time Data Analytics
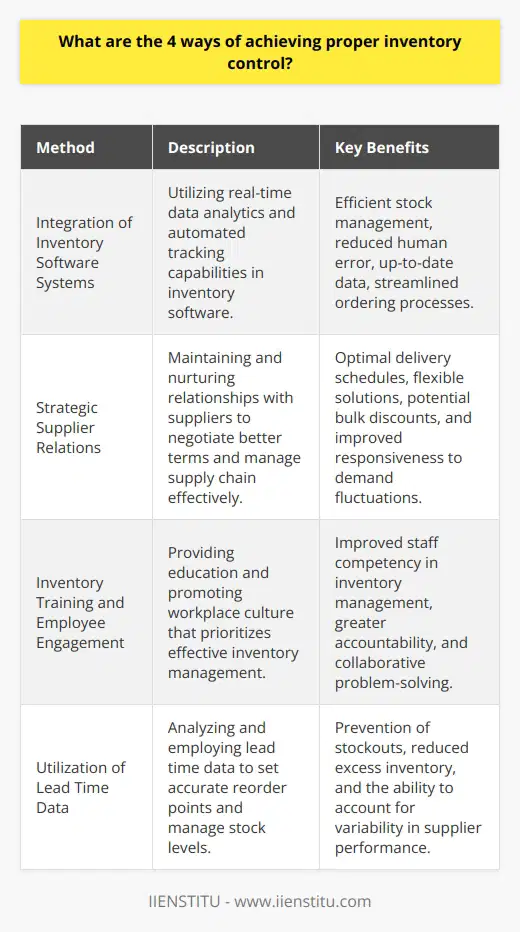
Organizations can leverage data analytics and real-time visibility by implementing tools and techniques that provide instant insights into inventory levels and supply chain performance. These tools enable organizations to make informed decisions on stock replenishment, demand forecasting, and warehouse optimization.
Demand Forecasting
One of the main ways to optimize inventory management is through accurate demand forecasting. By analyzing historical sales data, customer behavior, and market trends, organizations can predict future demand patterns more accurately. This allows them to maintain optimal inventory levels and prevent stockouts or excess inventory.
Inventory Positioning
Real-time data analytics also help organizations establish effective inventory positioning. By analyzing the movement of goods within the supply chain, organizations can identify optimal locations for storing inventory. This reduces lead times, minimizes transportation costs, and ultimately streamlines the supply chain process.
Warehouse Optimization
The use of data analytics in warehouse management can lead to significant efficiency improvements. By analyzing factors such as stock turnover, storage utilization, and order picking accuracy, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement changes to increase efficiency. This can result in faster order fulfillment, lower operating costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Automated Replenishment
Automating the replenishment process can help organizations maintain optimal inventory levels without the need for manual intervention. By leveraging real-time data analytics, organizations can set up automated triggers for stock replenishment, ensuring that inventory levels remain consistent with demand. This reduces labor costs and minimizes the risk of human error.
Proactive Issue Resolution
Real-time data analytics can also enable organizations to proactively identify and resolve issues within the supply chain. By monitoring indicators such as order lead times, supplier performance, and transportation delays, organizations can quickly detect potential disruptions and take corrective action before they impact inventory levels.
In conclusion, leveraging data analytics and real-time visibility enables organizations to optimize their inventory management and streamline supply chain operations. By harnessing these powerful tools, organizations can improve demand forecasting, enhance warehouse efficiency, reduce lead times, and maintain optimal inventory levels. As a result, they can improve overall supply chain performance and achieve a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
To what extent does cross-functional collaboration contribute to cost optimization in inventory management for supply chain efficiency?
Cross-functional Collaboration and Cost Optimization
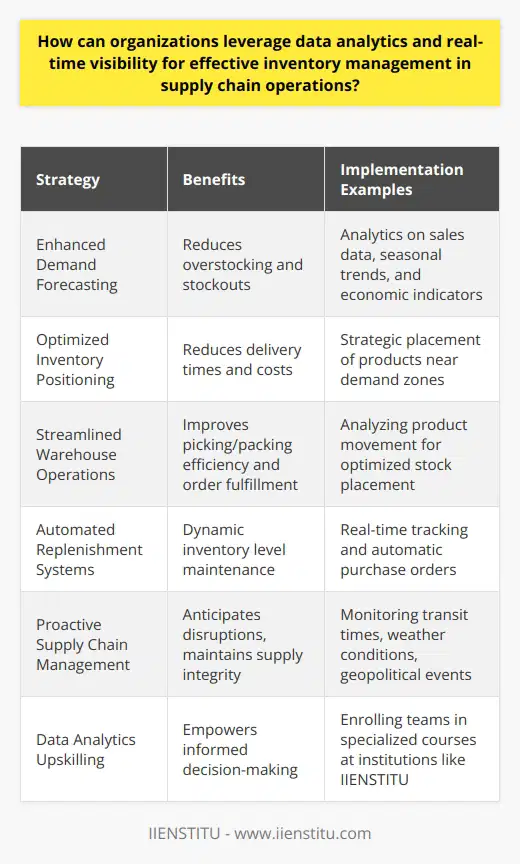
A crucial aspect for achieving supply chain efficiency is cross-functional collaboration among different departments involved in inventory management. By sharing knowledge and resources, as well as aligning objectives, these units work cohesively to optimize costs and improve performance.
Information Sharing and Forecasting Accuracy
One significant advantage of cross-functional collaboration is enhanced information sharing, which leads to better forecasting accuracy. Accurate demand and supply forecasts enable organizations to maintain the right inventory levels, reducing excess stock and stockouts, and consequently lowering holding and stockout costs.
Reduced Lead Times and Total Cost Reduction
Another dimension of supply chain efficiency impacted by cross-functional collaboration is the reduction in lead times. By improving coordination among departments, such as procurement, production, and distribution, organizations can streamline processes and enable faster decision-making. Shortened lead times lessen the need to hold high levels of inventory, translating into lower inventory carrying costs.
Improved Supplier Relationships and Collaboration
In addition to enhancing internal collaboration, cross-functional teams foster better relationships with suppliers. By engaging suppliers in the inventory management process and leveraging their expertise, organizations can make informed decisions that lead to more efficient supply chain operations. This collaborative approach can result in better pricing, product quality, and delivery performance, ultimately contributing to cost optimization.
Risk Management and Resilience
Lastly, cross-functional collaboration aids in building a resilient supply chain by facilitating risk management. By pooling the collective expertise of various departments, organizations can identify potential risks, develop mitigation strategies, and adapt to unforeseen disruptions in the supply chain. This proactive approach not only minimizes the probability of inventory shortages or excess but also enhances the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
In conclusion, cross-functional collaboration significantly contributes to cost optimization in inventory management for supply chain efficiency. By improving forecasting accuracy, reducing lead times, strengthening supplier relationships, and fostering risk management, organizations that actively engage in cross-functional practices can achieve substantial cost savings and service level improvements.
How can proper segmentation of inventory items lead to cost optimization in supply chain management?
Mitigating Costs through Segmentation
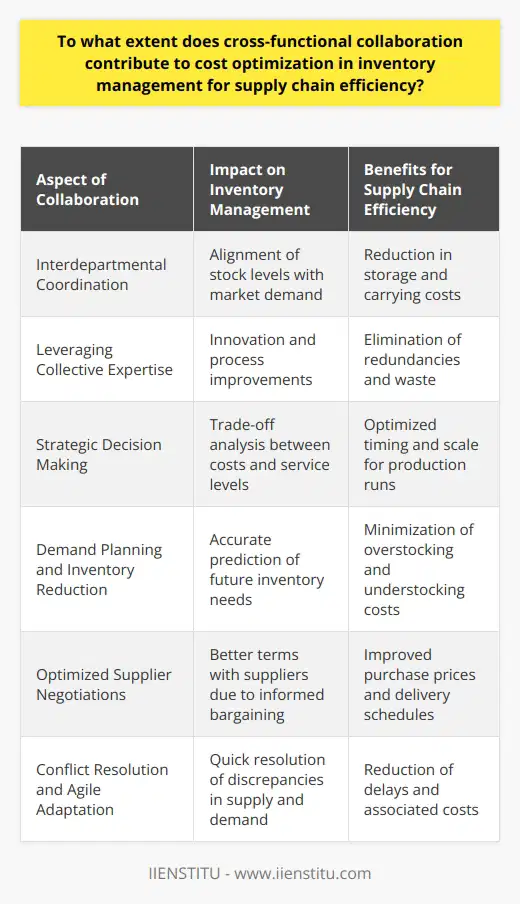
Effective inventory management is a crucial aspect of supply chain management, which involves the proper segmentation of inventory items. Adopting a strategic methodology for inventory classification leads to cost optimization through streamlined operations and efficiency improvements. This can be achieved through varied segmentation techniques, such as the ABC analysis, inventory turnover ratio, and demand variability.
ABC Analysis for Inventory Classification
A popular inventory segmentation approach is the ABC analysis, which categorizes items based on their economic importance. Class A items contribute most significantly to overall revenue, followed by class B items, while class C items are relatively less important. By focusing resources on high-revenue-generating items, businesses identify cost-saving opportunities and maximize profitability.
Inventory Turnover for Time-Sensitive Optimization
Cost optimization is also achieved by considering inventory turnover ratios. This metric measures how frequently an item is sold and replaced within a given period, signifying its demand. Higher turnover ratios suggest faster movement of inventory, while lower ratios indicate overstocking, leading to holding cost implications. Strategic prioritization of items with higher turnover ratios within the supply chain ensures reduced holding costs and obsolescence risks.
Demand Variability to Manage Supply Uncertainties
Additionally, segmenting inventory according to demand variability enables supply chain managers to better forecast product demand and anticipate supply uncertainties. High variability items require increased safety stock, whereas low variability items might need less buffer stock. Balancing safety stock levels ensures that organizations avoid stockouts and excess inventory holding costs. This balance, in turn, contributes to overall cost optimization within the supply chain.
In conclusion, proper segmentation of inventory items is crucial for effective supply chain management. Through incorporating techniques such as ABC analysis, inventory turnover, and demand variability, businesses can optimize costs by identifying revenue-generating items, avoiding excess inventory holding costs, and managing uncertainties in product demand.
In what ways can centralized inventory management contribute to overall cost savings and efficiency within a supply chain?
Centralized Inventory Management and Cost Savings
One key benefit of centralized inventory management is through reducing the volume of safety stock. By aggregating demand from various distribution points, firms can maintain lower inventory levels without incurring the risk of stockouts. This ultimately reduces holding costs and frees up working capital.
Improved Forecast Accuracy
With centralized inventory management, organizations can consolidate their demand data, leading to improved forecast accuracy. Accurate demand forecasts enable better production and inventory plans, optimizing the usage of resources, and minimizing excess stock. Consequently, this reduces costs associated with excess inventory and stock obsolescence.
Enhanced Vendor Management
A centralized inventory system facilitates better vendor management by providing a comprehensive view of supplier performance. It allows organizations to negotiate better terms and discounts, derive economies of scale, and streamline procurement processes. By consolidating orders across multiple locations, organizations can leverage their buying power to negotiate lower prices and better payment terms.
Streamlined Transportation and Logistics
Centralizing inventory management also contributes to increased efficiency in transportation and logistics. Consolidating shipments from suppliers to a centralized location can reduce shipping costs, as larger shipments often have lower unit transportation costs. Additionally, a centralized inventory system can streamline the overall logistics process, leading to faster delivery times and better customer service.
Reduced Facility and Operational Expenses
Operating a central inventory facility can result in reduced overhead expenses compared to managing multiple warehouses. By consolidating inventory into a single location, organizations can benefit from economies of scale in terms of facility and labor costs. Furthermore, firms can optimize warehouse space by utilizing advanced storage solutions, thereby minimizing their facility overheads.
Enhanced Inventory Visibility and Control
Centralized inventory management provides increased visibility and control over the entire supply chain. It allows for real-time monitoring of inventory levels, leading to informed decision-making and proactive responses to potential stock shortages or surpluses. Moreover, having an integrated overview of inventory data can contribute to better planning and execution of sales, promotional campaigns, and new product launches.
In conclusion, centralized inventory management contributes to cost savings and efficiency in various ways, including reduced safety stock, improved forecast accuracy, enhanced vendor management, streamlined transportation and logistics, reduced facility and operational expenses, and enhanced inventory visibility and control. Adopting a centralized approach ensures a more efficient supply chain, ultimately improving profitability and competitiveness.
What are the potential risks and benefits associated with implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory management in a supply chain?
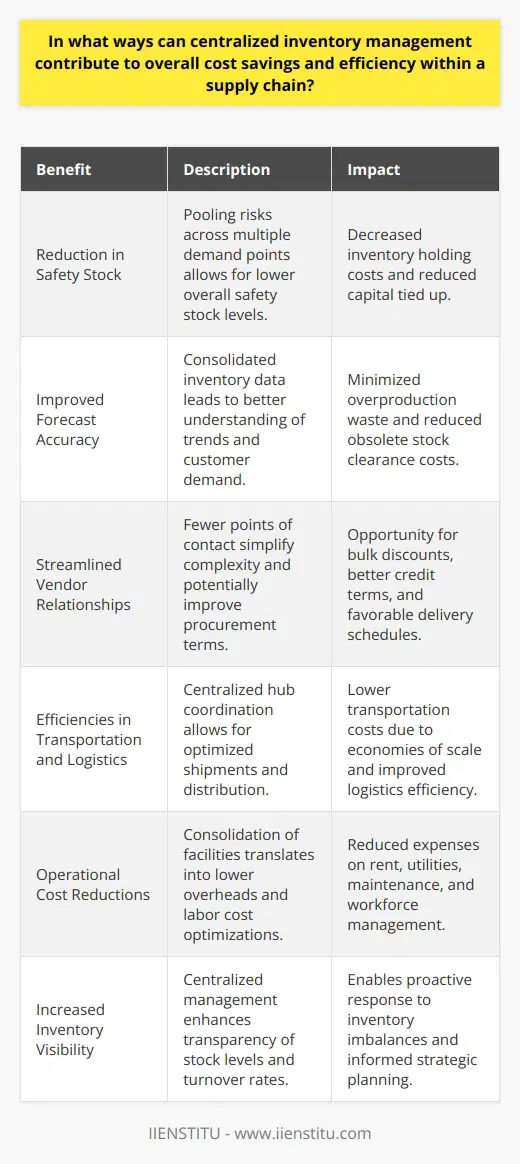
Potential Risks of JIT Inventory Management
Implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory management in a supply chain can undoubtedly offer numerous benefits. However, it also comes with potential risks that must be considered. One significant risk involves supply chain disruptions. If a supplier fails to deliver goods on time or if there are transportation delays, an organization relying on JIT may face material shortages. Consequently, this can halt production and lead to customer dissatisfaction.
Another risk factor is the constant need for effective coordination and communication between suppliers, manufacturers, and other key stakeholders. A lack of proper communication can destabilize the entire JIT system, causing delays and inefficiencies. Furthermore, companies using JIT must also contend with the risk of increased lead times. Since products are only produced when customer demand arises, ensuring that products are delivered on time may be more challenging than with traditional inventory systems.
Benefits of JIT Inventory Management
Despite the potential risks, JIT inventory management offers a host of benefits to supply chain operations. One of the most compelling advantages is its capacity to reduce inventory holding costs. With JIT, organizations can minimize the amount of inventory required, significantly lowering warehouse storage and management costs.
Another notable benefit is enhanced cash flow. By reducing inventory levels, businesses can free up cash that would otherwise be tied up in inventory. This increased liquidity can then be utilized for various purposes, such as expanding operations or investing in new opportunities.
JIT inventory management also tends to result in higher product quality. As the production process is more streamlined, companies can focus on ensuring that every batch of goods produced is of top quality, meeting customer expectations. Waste reduction is another crucial advantage, as JIT encourages businesses only to order and produce what is required. Consequently, this minimizes the risk of obsolescence and reduces the chances that resources will be wasted on excess inventory.
In conclusion, the adoption of JIT inventory management in a supply chain can lead to both risks and benefits. While the system may leave businesses more vulnerable to disruptions and increases the stakes for effective coordination, it can also lead to reduced inventory costs, improved cash flow, enhanced product quality, and waste reduction. Organizations must weigh these factors before embarking on a JIT inventory management strategy.
How do you maximize supply chain management to achieve cost optimization and efficiency?
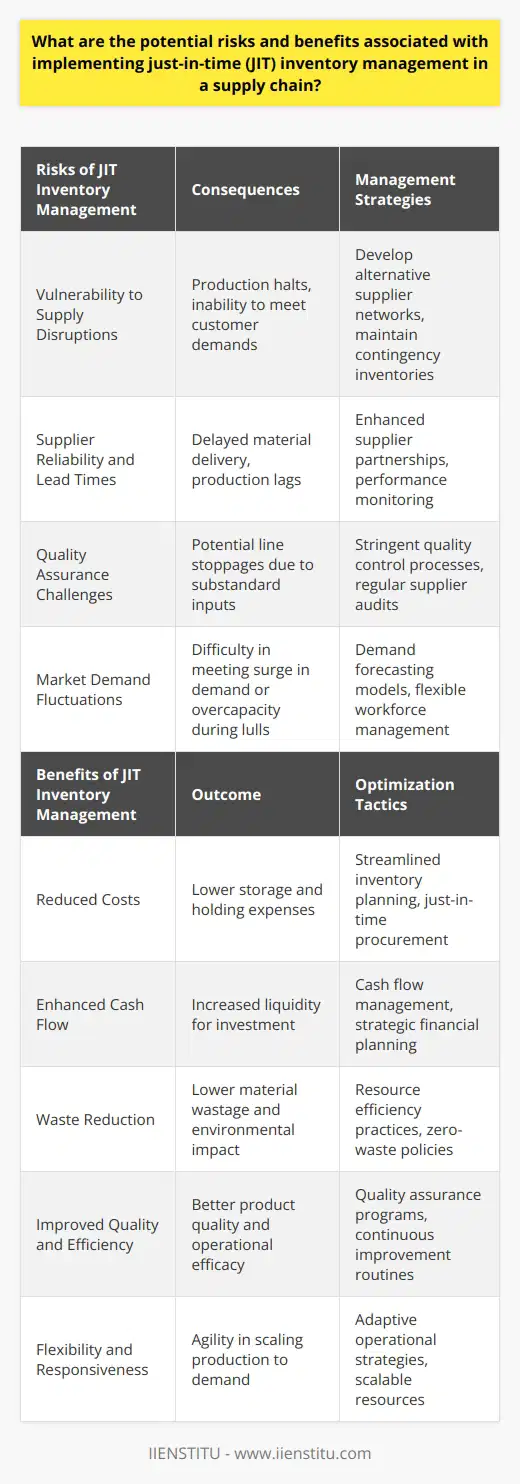
Strategic Planning for Maximum Efficiency
To maximize supply chain management for cost optimization, strategic planning is essential. Start by developing an integrated approach that aligns with your business objectives.
Performance Analysis
Analyzing performance metrics within your supply chain can expose inefficiencies. Utilizing this data may reveal opportunities for reducing costs and optimizing operations.
Procurement Strategy
A strategic procurement strategy is crucial. Engaging suppliers that provide high quality at low costs enhances profitability. Building lasting relationships with these suppliers can lead to beneficial partnerships.
Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization can significantly reduce costs. Better inventory management prevents overstocking, understocking, and other common mismanagements that drain profits. Adopting just-in-time inventory principles are beneficial.
Technology Integration
Technological advancement contributes to supply chain efficiency. The implementation of technology, such as predictive analytics, can provide invaluable insights. Optimization software can streamline processes and reduce manual efforts.
Employee Engagement
Promoting employee engagement plays a crucial role. Enabling employees with necessary skills improves operational efficiency. Training programs and continuous learning initiatives will keep the workforce competent and motivated.
Lean Process Applications
Adopting lean practices also enhances efficiency. It minimizes waste and maximizes productivity. Recognizing value-adding activities within your workflow and eliminating non-value-adding activities results in an efficient supply chain.
Continuous Improvement
Finally, the supply chain should undergo continuous improvements. Constant monitoring and adjusting processes will ensure sustained efficiency. Feedback mechanisms and regular audits help identify areas for enhancements.
In conclusion, maximizing supply chain management for cost optimization requires a multifaceted approach. Combining these aspects helps improve the overall efficiency of your supply chain operations. Adjusting to the ever-changing business environment guarantees competitiveness and sustainability.
What role does demand forecasting play in optimizing inventory levels and managing carrying costs within supply chain management?
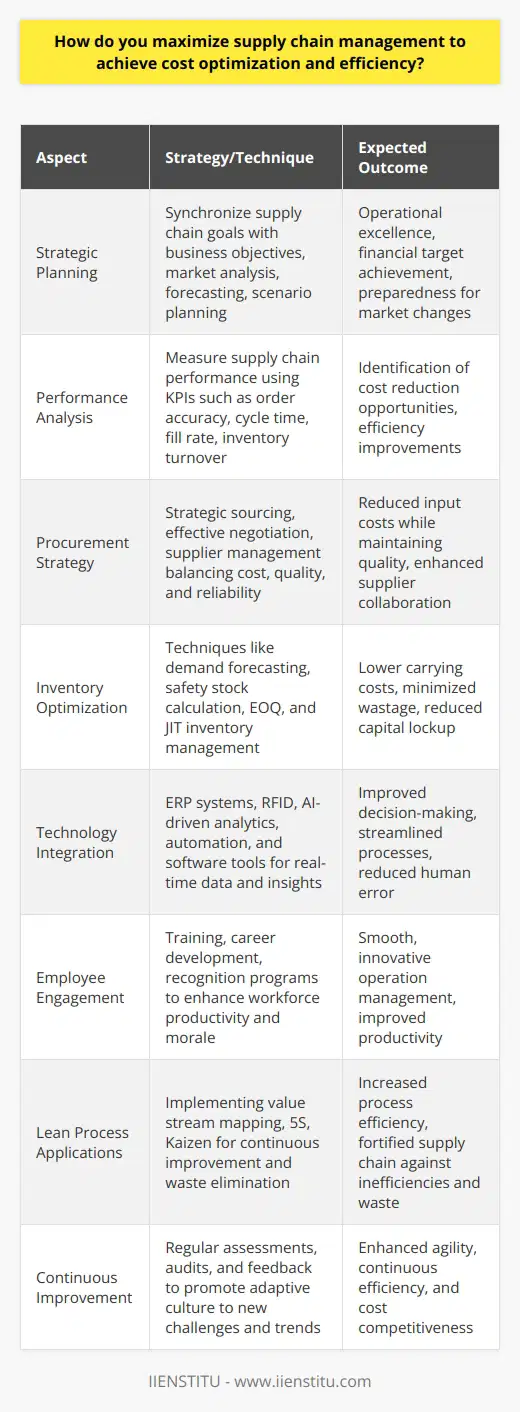
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
Demand forecasting plays a pivotal role in optimizing inventory levels within supply chain management. It enables firms to predict customer demand accurately over a specified period. Businesses use these predictions to manage their inventory, ensuring they have enough stock to meet customer needs, and not overspending on excess inventory that eats into profits.
Reduction of Carrying Costs
Additionally, demand forecasting helps manage carrying costs. These costs include storage, insurance, and potential depreciation costs, which can accrue over time when a business maintains high levels of stock. By accurately predicting demand, firms can minimize the amount of inventory they need to carry, thus decreasing these costs.
Increased Efficiency and Profitability
Moreover, proper demand forecasting also boosts efficiency and profitability. Firms can avoid stock depletion, leading to customer dissatisfaction and lost sales. They can also evade overstocking, which leads to wastage, especially for perishable goods. Both scenarios can disrupt operations and hurt the bottom line.
Overall, effective demand forecasting plays an essential role in supply chain management, affecting both inventory levels and carrying costs. By enhancing predictions of customer demand, businesses can optimize their inventory, minimize costs, increase efficiency, and maximize profitability.
How can implementing a centralized inventory management system help in decreasing lead times and improving overall supply chain performance?
Centralized Inventory Management: A Solution for Lead Time Reduction
A centralized inventory management system can significantly decrease lead time while enhancing supply chain performance. This approach works by consolidating inventory data in a single hub. The immediate access to real-time inventory data fosters informed decision making, promoting efficiency.
Improving Accuracy and Forecasting
In this system, the accuracy of inventory records improves, reducing errors. Correct data helps in demand forecasting, allowing companies to anticipate and satisfy customer needs. Accurate forecasts mean less overstock, understock, and dead stock. This decreases storage cost, wastage, and enhances customer satisfaction.
Optimizing Stock Levels
With centralized inventory management, companies can easily optimize their stock levels. Effective stock control is essential for reducing lead times. Companies can replenish stocks efficiently, avoiding stockouts and excess stock. This results in quick order fulfillment, reducing the waiting time for customers.
Enhancing Supplier Relationships
This system also paves the way for improving supplier relationships. When firms share inventory data with suppliers, they can better plan their production schedules. This collaborative approach reduces lead time and enhances the overall supply chain performance.
In conclusion, implementing a centralized inventory management system plays a crucial role in decreasing lead times and improving supply chain performance. By fostering informed decision-making, optimizing stock levels, and enhancing supplier relationships, it streamlines operations while boosting efficiency.
How do you establish an effective inventory management system that incorporates demand forecasting and inventory control within supply chain operations?
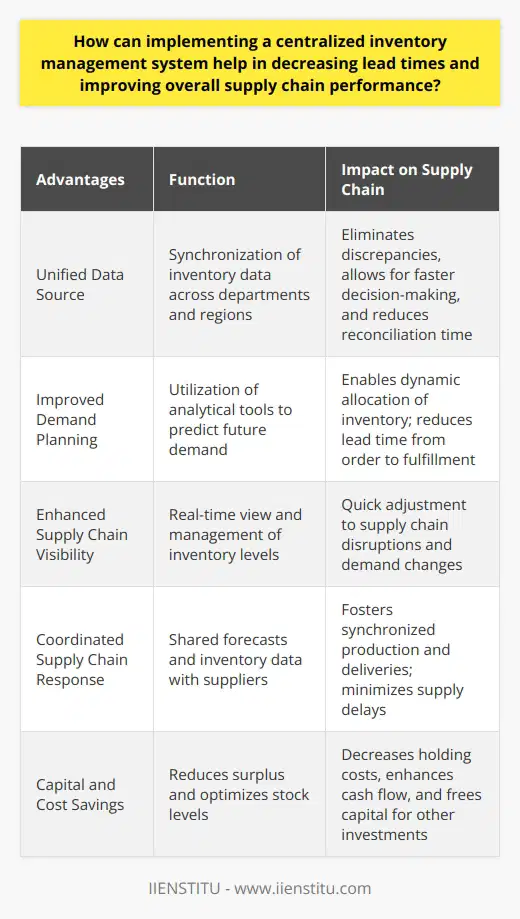
Understanding Customer Needs
An effective inventory management system begins with a deep understanding of customer needs and requirements. Customer satisfaction depends mainly on the availability of products and timely delivery.
Demand Forecasting
Assessing customer demand assists in predicting future requirements. Techniques such as time series analysis, causal models or professional judgment help to estimate demand more accurately. Reliable forecast data reduces both potential stock-outs and excess inventory.
Inventory Replenishment Strategies
An inventory control strategy ensures a balanced stock level to meet customer demand. Two commonly used strategies are Just-in-Time (JIT) and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ). JIT minimizes inventory by ordering goods only when required, while EOQ determines optimal order size minimizing total inventory costs.
Vendor Management
Developing a strong relationship with suppliers ensures efficient procurement and delivery processes. Regular communication with suppliers can provide insights into market fluctuations and potential supply chain disruptions.
Implementing Technology
Efficiency in inventory management can be achieved by implementing technology such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. These systems integrate all business processes including supply chain, inventory management, purchasing and sales. Real-time tracking of inventory status can also be enhanced with barcoding and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID).
Performance Measurement
Finally, to ensure a fully optimized inventory management system, you must track performance using inventory turnover ratios, stock-out frequency and carrying costs. This monitoring will help to reveal areas for improvement in operations and the overall supply chain.
By combining these strategies, a business can establish a more effective inventory management system incorporating both demand forecasting and inventory control, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and profitability.
What are the 5 steps to effective inventory systems and how can they help in achieving cost optimization and supply chain efficiency?
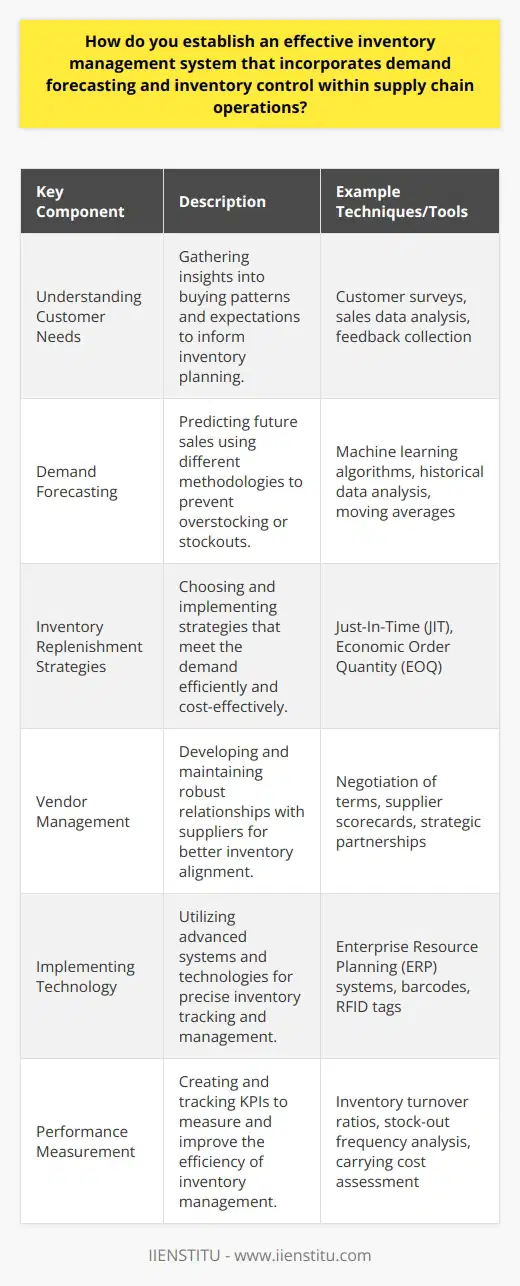
Identifying Inventory Needs
The first step towards effective inventory systems involves identifying inventory needs. This involves determining what you require to meet your customers' needs while minimizing holding costs.
Establishing Reorder Points
Next, you have to establish reorder points. Calculating this requires understanding the lead time demand for your inventory. It helps to prevent stockouts that lead to missed sales and unsatisfied customers.
Maintaining Safety Stock
Keeping a safety stock functions as a buffer for unforeseen fluctuations in demand. This saves on costs associated with rush orders or overstocking which can disrupt the supply chain integrity.
Performing Regular Audit
Implementing systematic audits forms the fourth part of managing inventory effectively. This approach compares physical inventory to recorded inventory. It identifies discrepancies, prevents theft, and ensures accurate records for planning and financial reporting.
Implementing Inventory Turnover Ratio
Finally, the fifth step requires calculating and managing the inventory turnover ratio. It measures how often businesses sell or use their inventory over a given time period. Businesses focus on increasing this ratio to reduce costs associated with holding inventory.
In conclusion, the five steps- identifying inventory needs, establishing reorder points, maintaining safety stock, performing regular audits, and implementing inventory turnover ratio- ensure cost optimization and supply chain efficiency. Adopting these steps leads to fewer overstock and stockout instances, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced carrying and ordering costs. Hence, they play a crucial part in the organization's overall competitiveness and profitability.
How can a supply chain maximize collaboration among cross-functional teams to streamline inventory management and reduce carrying costs?
Implementing Collaborative Strategies
Efficient supply chain collaboration can enhance inventory management and mitigate carrying costs. Cross-functional teams should maximize collaboration by formulating common goals. A shared vision can create a sense of purpose, encouraging team members to work together to achieve these goals.
Using Collaborative Tools
Digital collaboration tools can improve communication among team members, enabling seamless sharing of information. These tools can enhance synergies, encouraging collaborative problem-solving efforts. In essence, they may play a pivotal role in coordination, improving inventory management processes.
Adopting Agile Practices
Adopting agile practices makes processes flexible and responsive to changes. Clearly defined roles for each team member, with well-established deliverables and measurable outcomes, increase the team's productivity. Moreover, regular meetings and feedback sessions can keep everyone on the same page, fostering collaboration.
Promoting a Collaborative Culture
Promoting a culture of collaboration, grounded in trust and open communication, can be key in fostering an environment conducive to cooperation. This encourages team members to share their insights and ideas freely, allowing problems to be identified and addressed promptly.
Leveraging Technology
Advanced technologies, like artificial intelligence(AI) and the Internet of Things(IoT), can generate real-time data to improve decision-making processes. Integration of these technologies can help teams understand inventory needs better, making inventory management more efficient, and reducing associated costs.
Continuous Learning and Development
Learning and development opportunities cultivate individual team members' skills, enhancing their contribution to team efforts. Regular training sessions and workshops can improve their understanding of inventory management, ultimately reducing carrying costs.
Effective supply chain collaboration, built on shared goals, technological integration, and a collaborative culture, can streamline inventory management and reduce carrying costs. Consistent learning and development opportunities for team members will further bolster these efforts. The result is a more streamlined, cost-effective inventory management process.



