In the ever-evolving world of business, the role of managers retains a critical position in steering organizations toward achieving their goals. As the fulcrum upon which business strategies turn, managers enact a series of functions that are paramount to corporate success. Their decisions, both strategic and operational, reverberate through the organization's structure, affecting every stakeholder from entry-level employees to the board of directors. This blog aims to dissect the intricate position held by managers, analyzing their quintessential duties, the competencies required for their roles, and the increasing complexities they face in contemporary organizations. By delving into key managerial responsibilities in modern businesses and highlighting the *importance of managerial functions in organizations*, we illuminate the essence of effective stewardship. We will also discuss the advantages of attaining an MBA or enhancing one's capabilities through specialized courses in the realm of management expertise.
The Multifaceted Role of Managers
Understanding Managerial Functions in Organizations
Often described as the backbone of an organization, managerial functions entail a series of predefined roles that are designed to ensure the smooth running of a business entity. Starting from the forethought of planning to the intricacies of controlling, the scope of a manager's job is vast and multi-dimensional. Initially conceived back in the industrial era, the nature of a manager's role has undergone a transformation, reflecting changes in the business environment and organizational needs.
The Four Pillars of Managerial Functions
Managerial functions are widely recognized as planning, organizing, leading, and controlling – collectively known as the management process.
Planning: The blueprint for future action
A critical task for managers is developing a roadmap for future activities through strategic planning. This foresight enables companies to define their direction and establish priorities. Managers are instrumental in setting goals and deciphering the methods by which such objectives will be achieved.
This element of managerial functions in organizations dictates the approach and establishes a framework for attainment, demanding specialized knowledge and foresight which can be enriched by an MBA degree.
Organizing: Structuring for efficiency and effectiveness
Once planning sets the stage, organizing invigorates the blueprint with tangible structures. Managers design an organizational architecture that delineates departments, work groups, and individuals' roles, focusing on efficient resource allocation. This structural composition facilitates the coordination of various segments of the organization and ensures that operational workflows are in sync with established strategic goals.
Leading: Steering the organization towards its goals
Leadership—the act of influencing and motivating staff to fulfill their roles—forms the very crux of a manager's daily activities. The role of managers in curbing attrition, promoting workforce morale, and fostering a robust organizational culture becomes indispensable. Managers, through their leadership styles, either inspire or derail the collective energy of their workforce, making it clear that a leader's guidance greatly impacts a business’s personality and output.
Controlling: Ensuring everything goes according to plan
The final aspect of managerial functions is 'controlling,' which involves the establishment of performance standards and the assessment of the actual performance against said standards. Through monitoring and evaluating, managers can intercede with corrective measures to address deviations, safeguarding the attainment of the organization's goals. It is a cyclical process that confirms the relevance of strategies over time and keeps the organization on course.
Growing up, I had the privilege of observing my father, a seasoned manager, navigate the complexities of his role. His ability to juggle multiple responsibilities while maintaining a sense of composure and direction left an indelible mark on my understanding of the importance of managerial functions in organizations. As I embarked on my own career, I began to appreciate the nuances of managerial roles and the profound impact they have on organizational success.
Driving Organizational Success
The potency of managerial decisions cannot be overstated. A manager wields the power to shape, direct, and revitalize the mechanisms of an organization. It is through adept management that a company can climb the hierarchical ladder of success, achieving stellar financial performance while sustaining high levels of employee engagement and customer satisfaction.
Fostering Innovation and Change
Managers are often regarded as agents of change, harnessing their positions to foster an environment conducive to innovation. An advanced managerial skillset, often honed by pursuing an MBA degree or specialized online courses with certificates, equips leaders to navigate through the turbulence of market dynamics, encouraging team members to step outside the paradigm of conventional thinking and embark on inventive ventures.
The Ethical and Social Dimensions
As the embodiment of an organization's ethics and principles, managers play a critical role in setting moral conduct standards. Reflecting societal values, managers are custodians of ethical practices, ensuring the organization strikes a balance between profitability and social responsibility. This broadens managerial responsibilities to encompass a more humanistic and sustainable approach to corporate governance.
Navigating the Complexities of Modern Workplaces
No longer confined to traditional management theories, today's managers navigate an increasingly complex and diverse global workplace. This entails harnessing cultural diversity, embracing technological advancements, and adopting cutting-edge digital tools to enhance organizational competitiveness and efficiency.
Understanding Managerial Functions in Organizations
Often described as the backbone of an organization, managerial functions entail a series of predefined roles that are designed to ensure the smooth running of a business entity. Starting from the forethought of planning to the intricacies of controlling, the scope of a manager's job is vast and multi-dimensional. Initially conceived back in the industrial era, the nature of a manager's role has undergone a transformation, reflecting changes in the business environment and organizational needs.
As Peter Drucker, the renowned management consultant, once stated, "Management is doing things right; leadership is doing the right things" (Drucker, 1999, p. 65). This quote encapsulates the essence of a manager's role, emphasizing the importance of both efficiency and effectiveness in their approach.
The Four Pillars of Managerial Functions
Managerial functions are widely recognized as planning, organizing, leading, and controlling - collectively known as the management process.
1- Planning: The Blueprint for Future Action
A critical task for managers is developing a roadmap for future activities through strategic planning. This foresight enables companies to define their direction and establish priorities. Managers are instrumental in setting goals and deciphering the methods by which such objectives will be achieved. This element of *managerial functions in organizations* dictates the approach and establishes a framework for attainment, demanding specialized knowledge and foresight which can be enriched by an MBA degree.
2- Organizing: Structuring for Efficiency and Effectiveness
Once planning sets the stage, organizing invigorates the blueprint with tangible structures. Managers design an organizational architecture that delineates departments, work groups, and individuals' roles, focusing on efficient resource allocation. This structural composition facilitates the coordination of various segments of the organization and ensures that operational workflows are in sync with established strategic goals.
3- Leading: Steering the Organization Towards Its Goals
Leadership--the act of influencing and motivating staff to fulfill their roles--forms the very crux of a manager's daily activities. The *role of leadership in effective management* cannot be overstated. Managers, through their leadership styles, either inspire or derail the collective energy of their workforce, making it clear that a leader's guidance greatly impacts a business's personality and output.
4- Controlling: Ensuring Everything Goes According to Plan
The final aspect of managerial functions is controlling, which involves the establishment of performance standards and the assessment of the actual performance against said standards. Through monitoring and evaluating, managers can intercede with corrective measures to address deviations, safeguarding the attainment of the organization's goals. It is a cyclical process that confirms the relevance of strategies over time and keeps the organization on course.
As Henry Mintzberg, a prominent management researcher, noted in his book "The Nature of Managerial Work," these four functions are not separate, sequential stages but rather interrelated and simultaneous activities that managers engage in (Mintzberg, 1973).
The Overarching Importance of Managers in an Organization
The *importance of managers in an organization* cannot be overstated. They are the linchpins that hold the various components of the business together, ensuring seamless operation and driving the organization towards its goals.
Driving Organizational Success
The potency of managerial decisions cannot be overstated. A manager wields the power to shape, direct, and revitalize the mechanisms of an organization. It is through adept management that a company can climb the hierarchical ladder of success, achieving stellar financial performance while sustaining high levels of employee engagement and customer satisfaction.
In their seminal work "In Search of Excellence," Peters and Waterman (1982) studied successful American companies and identified several key factors that contributed to their success, many of which were directly tied to effective management practices. They found that companies with strong, visionary leaders who fostered a culture of innovation and excellence tended to outperform their competitors.
Fostering Innovation and Change
Managers are often regarded as agents of change, harnessing their positions to foster an environment conducive to innovation. An advanced managerial skillset, often honed by pursuing an MBA degree or specialized online courses with certificates, equips leaders to navigate through the turbulence of market dynamics, encouraging team members to step outside the paradigm of conventional thinking and embark on inventive ventures.
Clayton Christensen, in his influential book "The Innovator's Dilemma," argues that managers play a crucial role in driving disruptive innovation within organizations. By allocating resources to new, potentially risky ventures and creating a culture that tolerates failure, managers can help their companies stay ahead of the curve and avoid being disrupted by newcomers (Christensen, 1997).
Managerial Responsibilities Beyond the Four Functions
While the four functions of management provide a solid foundation for understanding the *role of managers in an organization*, the reality is that a manager's responsibilities extend far beyond these core duties.
The Ethical and Social Dimensions
As the embodiment of an organization's ethics and principles, managers play a critical role in setting moral conduct standards. Reflecting societal values, managers are custodians of ethical practices, ensuring the organization strikes a balance between profitability and social responsibility. This broadens managerial responsibilities to encompass a more humanistic and sustainable approach to corporate governance.
In his book "Business Ethics: Ethical Decision Making and Cases," Ferrell et al. (2019) emphasize the importance of managers in fostering an ethical organizational culture. They argue that managers must lead by example, setting the tone for ethical behavior and making decisions that prioritize integrity and social responsibility.
Navigating the Complexities of Modern Workplaces
No longer confined to traditional management theories, today's managers navigate an increasingly complex and diverse global workplace. This entails harnessing cultural diversity, embracing technological advancements, and adopting cutting-edge digital tools to enhance organizational competitiveness and efficiency.
Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory, as outlined in his book "Culture's Consequences," provides a framework for understanding how managers can navigate cultural diversity in management (Hofstede, 2001). By recognizing and adapting to differences in power distance, individualism vs. collectivism, masculinity vs. femininity, uncertainty avoidance, and long-term vs. short-term orientation, managers can effectively lead teams across cultural boundaries.
Developing Managerial Skills and Competencies
Given the multifaceted nature of managerial roles and the challenges faced by managers in contemporary organizations, it is crucial for aspiring and current managers to continuously develop their skills and competencies.
The Benefits of an MBA for Aspiring Managers
Pursuing an MBA degree has become an increasingly popular path for those seeking to enhance their managerial capabilities. An MBA program provides a comprehensive education in various aspects of business management, including finance, marketing, operations, and strategy. It equips students with the skills required for successful managers, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, decision-making, and leadership.
Research has shown that MBA graduates tend to have higher earning potential and faster career progression compared to their non-MBA counterparts. A study by the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC) found that the median starting salary for MBA graduates in 2021 was $115,000, significantly higher than the median for bachelor's degree holders (GMAC, 2021).
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
In addition to formal education, managers must engage in continuous learning and skill development to stay relevant and effective in their roles. This can involve attending workshops, conferences, and seminars, as well as pursuing online courses and certifications.
The rise of massive open online courses (MOOCs) and other e-learning platforms has made it easier than ever for managers to access high-quality educational content from top universities and industry experts. By investing in their own development, managers can enhance their competencies, broaden their perspectives, and stay ahead of the curve in an ever-changing business landscape.
Conclusion: Emphasizing the Manager's Integral Role
Reflecting on the discussion, it becomes evident that managers are not merely functionaries but the driving force of an organization. This blog articulates the indispensability of adept management and underscores the continuous evolution required in managerial roles to meet the fluctuating demands of the business environment.
From the core functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling to the broader responsibilities of ethical leadership and navigating modern complexities, the role of managers in an organization is multifaceted and critical to success. By pursuing advanced education, such as an MBA, and engaging in continuous learning and skill development, managers can equip themselves with the competencies needed to excel in their roles and drive their organizations forward.
As organizations continue to evolve and face new challenges, the importance of effective management will only continue to grow. It is up to current and aspiring managers to rise to the occasion, embrace their integral role, and lead their organizations to new heights of success.
Real-World Managerial Insights
In the world where theory intersects with practice, glimpses into successful managerial strategies offer invaluable insights. From the utility of an MBA degree in solving complex business problems to leveraging online courses with certificates for skill enhancement, managers' real-world experiences provide testamentary lessons on navigating the multifarious challenges that characterize the modern organizational landscape.
One such example is the story of Mary Barra, the CEO of General Motors. Barra, who holds an MBA from Stanford University, has been credited with leading GM through a period of significant transformation, including navigating the company through the COVID-19 pandemic and accelerating its transition to electric vehicles. Her leadership style, which emphasizes transparency, accountability, and a focus on the customer, has been widely praised and studied as a model for effective management in the 21st century (Colby, 2021).
Another example is the case of Satya Nadella, the CEO of Microsoft. Nadella, who pursued an MBA while working at Microsoft, has been credited with transforming the company's culture and business model, leading to a resurgence in its market value and competitiveness. He has emphasized the importance of continuous learning and has actively encouraged Microsoft employees to pursue online courses and certifications to enhance their skills and stay ahead of industry trends (Nadella, 2017).
These real-world examples underscore the value of advanced education and continuous learning in the practice of management. They also highlight the importance of managerial functions in organizations, as effective leaders like Barra and Nadella have demonstrated the impact that strategic planning, organizational design, leadership, and control can have on a company's success.
As aspiring and current managers seek to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape, they can draw inspiration and guidance from these real-world examples. By embracing the multifaceted nature of their roles, investing in their own development, and leading with purpose and vision, managers can make a profound difference in their organizations and leave a lasting legacy of success.
References
Christensen, C. M. (1997). The innovator's dilemma: When new technologies cause great firms to fail. Harvard Business School Press.
Colby, L. (2021). Road to power: How GM's Mary Barra shattered the glass ceiling. Portfolio.
Drucker, P. F. (1999). Management challenges for the 21st century. HarperBusiness.
Ferrell, O. C., Fraedrich, J., & Ferrell, L. (2019). Business ethics: Ethical decision making and cases (12th ed.). Cengage Learning.
Graduate Management Admission Council. (2021). Corporate recruiters survey report 2021. https://www.gmac.com/market-intelligence-and-research/research-library/employment-outlook/2021-corporate-recruiters-survey-report
Hofstede, G. (2001). Culture's consequences: Comparing values, behaviors, institutions, and organizations across nations (2nd ed.). SAGE Publications.
Mintzberg, H. (1973). The nature of managerial work. Harper & Row.
Nadella, S. (2017). Hit refresh: The quest to rediscover Microsoft's soul and imagine a better future for everyone. HarperBusiness.
Peters, T. J., & Waterman, R. H., Jr. (1982). In search of excellence: Lessons from America's best-run companies. Harper & Row.
Frequently Asked Questions
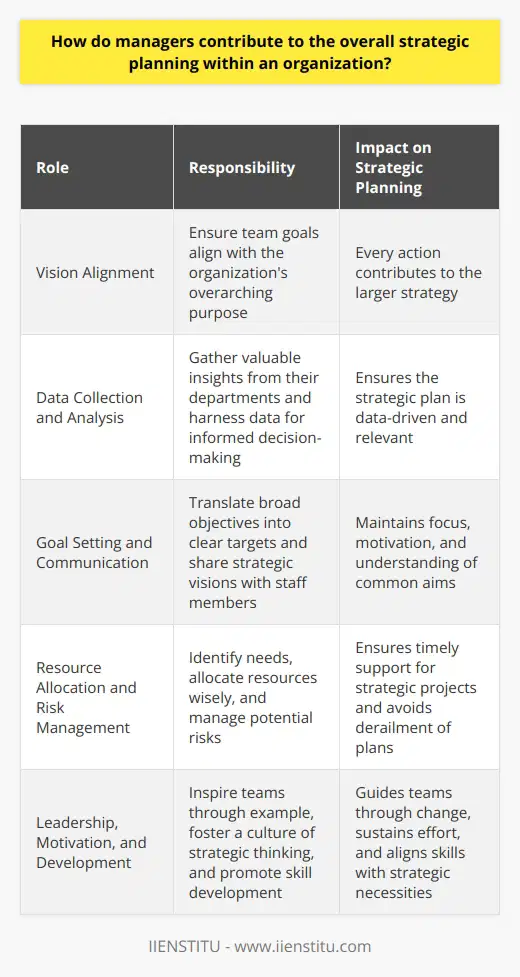
What are the key functions of managers in an organizational context?
Understanding Managerial Functions
Managers serve as the pillars of any organizational structure. They are critical for ensuring that the organization runs efficiently and effectively. The key functions of managers, often aligned with Henri Fayol's classical theory of management, include planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Let’s delve into each of these functions.
Planning: The Blueprint of Success
Planning is foundational in management. Managers determine goals and the best course of action to achieve them. This requires foresight and strategic thinking. They assess current states, predict future conditions, and decide on objectives. Most importantly, they develop a plan to attain these objectives.
Organizing: Structuring for Efficiency
Organizing is about arranging resources and tasks. Managers set up the team structure, allocate resources, and assign responsibilities. This creates an organized system where employees know their roles. Managers work to lay out the relationships between jobs, departments, and employees. They ensure that everyone has the resources to complete their tasks.
Leading: Steering Towards Success
Leading refers to directing and motivating staff. Managers influence team behavior to achieve organizational goals. They communicate the vision, establish a shared sense of purpose, and inspire their team. Leading includes coaching, mentoring, and resolving conflicts.
Controlling: Keeping on Track
Controlling involves monitoring performance. Managers set standards to achieve goals. They measure ongoing activities to identify deviations from these standards. This function also includes corrective actions to address any issues. It guarantees that the organization stays on its planned course.
Managers wear many hats. They adapt their roles to the organization's needs. The functions mentioned guide their actions. They work to create a balance between these functions to drive success. Managers are not just leaders; they are planners, organizers, and controllers too. This multi-faceted approach is what allows businesses to thrive in competitive environments.
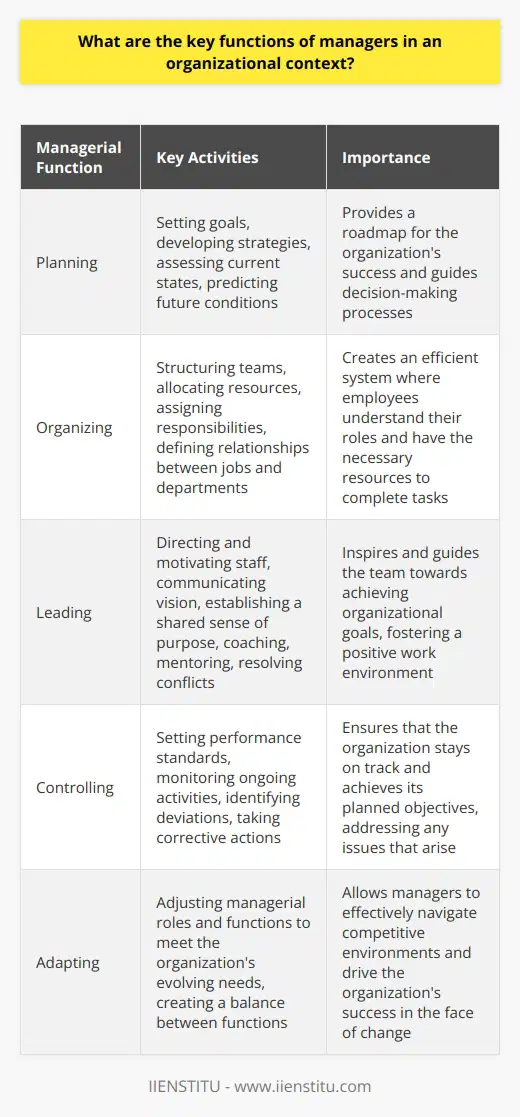
How does the role of a manager differ in various types of organizations?
Management in Different Organizational Contexts
Managers operate within diverse frameworks. Their roles shift accordingly. This change reflects organizational purpose, size, and culture. It also mirrors operational mechanisms and hierarchical structures.
For-Profit Corporations
In for-profit settings, managers focus on revenue. Profit maximization reigns supreme. Managers track performance metrics closely. They drive productivity and efficiency. Stakeholder value is paramount. Competition dictates strategic choices.
- Cost control is essential
- Innovation is frequently encouraged
- Accountability to shareholders is mandatory
Managers in these organizations seek market expansion. They harness new opportunities. Risk management forms a crucial part of their role.
Nonprofit Organizations
Managers in nonprofit entities pursue different objectives. Here, mission delivery takes center stage. They strive for social or environmental impact. Funds management still matters. But the focus shifts towards sustainability and outreach.
- Engagement with donors is critical
- Transparency gains heightened importance
- Community involvement is more pronounced
These managers balance financial health with organizational goals. They foster partnerships to amplify results. Influence and advocacy are key skills.
Government Agencies
Government agency managers uphold statutory mandates. They prioritize regulatory compliance and public service. Budget constraints often frame their decisions. They must navigate bureaucratic processes efficiently.
- Policy implementation is their core duty
- Fiscal responsibility underscores decision-making
- Political acumen is highly valuable
These managers engage with varied stakeholders. They must ensure equity in service delivery. Accountability to the public is non-negotiable.
Start-Ups
Start-up managers embody agility. They react to changing markets swiftly. Resourcefulness is a distinctive trait. Growth and scaling are ongoing pursuits.
- Adaptability is their watchword
- Vision casting directs the team
- Resource constraints mandate creativity
These leaders often undertake multiple roles. They mold company culture from scratch. They translate innovative ideas into viable business models.
Multinational Corporations
In multinationals, managers deal with complex dynamics. Cultural sensitivity becomes vital. They handle diverse regulatory environments. Global strategies supersede local tactics.
- Coordination across borders is essential
- Understanding of global markets is required
- Cross-cultural communication is indispensable
These managers foster global teamwork. They navigate international commerce laws adeptly. Balancing global and local needs is their challenge.
Conclusion
Managers adapt to organizational demands. Their responsibilities vary widely. Each type demands specific competencies. Success relies on managers’ flexibility. Aligning with organizational objectives is crucial. Managers enact strategies to achieve these goals. Their effectiveness is measured against organization-specific criteria. Managers across the spectrum leverage unique skills. They deliver results pertinent to their settings.
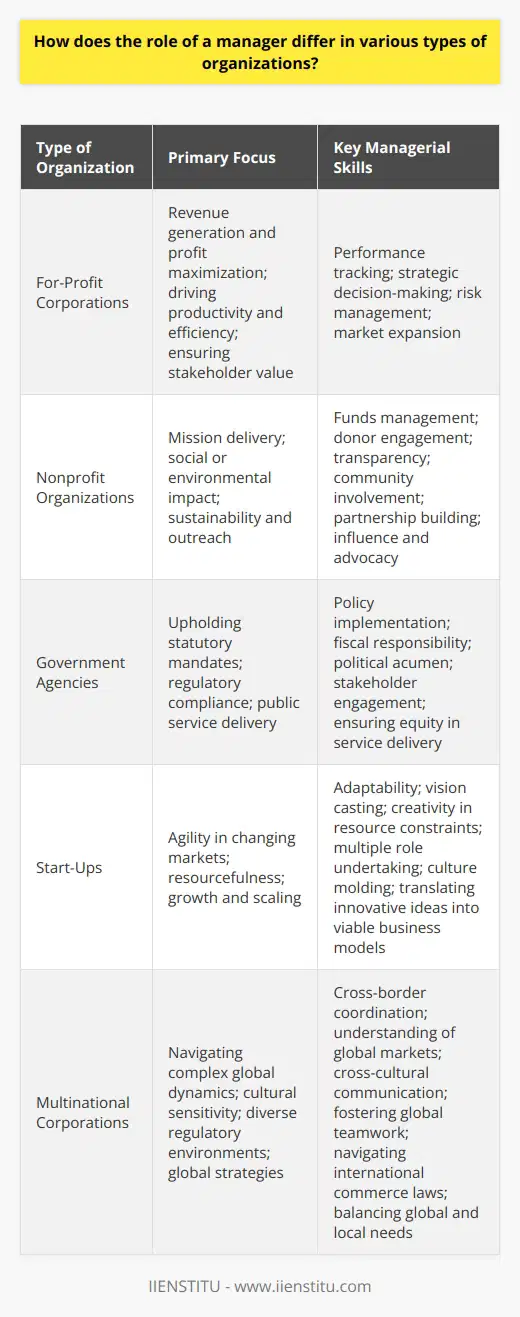
How do managers contribute to the overall strategic planning within an organization?
Managers and Strategic Planning
Managers play a crucial role in strategic planning. They serve as the bridge between top-level strategy and its execution. Their intimate knowledge of day-to-day operations positions them uniquely. They turn long-term visions into actionable tasks.
Understanding the Vision
Effective managers understand the organization's vision. They align team goals with this overarching purpose. This alignment ensures every action contributes to the larger strategy.
Insightful Data Gathering
Managers are data collectors. Their departments provide valuable insights. They harness this data for informed decision-making. This information feeds into the strategic plan, ensuring it is data-driven.
Goal Setting
Setting specific goals is a manager's forte. They translate broad objectives into clear targets. Teams then pursue these goals, moving the organization forward.
Communication Channels
Managers are communication hubs. They share strategic visions with staff members. Clear, consistent messaging maintains focus and motivation. Understanding strategy helps teams work towards common aims.
Resource Allocation
Effective resource management is key. Managers must identify needs and allocate resources wisely. They ensure their teams have what they need when they need it. Strategic projects depend on timely resource allocation.
Risk Management
Managers are on the front line of risk management. They identify potential hazards quickly. Their swift action avoids derailment of strategic plans. They balance risk with opportunity capably.
Adaptive Responses
The best-planned strategies encounter surprises. Managers must adapt. They adjust plans in response to challenges. This adaptability keeps the strategy relevant and keeps progress steady.
Continuous Feedback Loop
Feedback is essential for growth. Managers provide ongoing performance evaluations. They offer constructive criticism to team members. They celebrate successes that advance strategic objectives. This feedback refines the strategic plan continuously.
Leadership and Motivation
People follow strong leaders. Managers inspire teams through example. They foster a culture of strategic thinking. This leadership guides teams through periods of change. Motivation is a manager's tool to sustain effort over time.
Development and Training
Managers recognize skill gaps. They promote development opportunities for staff. Training aligns the team's skills with strategic necessities. A well-trained staff executes strategy more effectively.
Measurement and Analysis
Without measurement, there is no progress. Managers set key performance indicators (KPIs). They track progress diligently. Analysis of results drives future strategic adjustments.
Collaborative Efforts
Managers encourage collaboration. Teams unite to tackle strategic objectives. Cross-functional collaboration fosters innovation and synergy. This teamwork propels strategic projects.
Celebrating Milestones
Recognition boosts morale. Managers celebrate key milestones. These celebrations acknowledge the hard work done. They reinforce the importance of the strategic plan.
In summary, managers are strategic catalysts. They translate vision into reality. Their proactive involvement shapes the strategy at every level. Their multifaceted role underpins the organization's success. Managers make strategy work.