In today's ever-evolving business landscape, the principles that guide managerial decisions are under constant scrutiny. With rapid shifts in market dynamics, technology, and workforce expectations, the endurance of dated ideologies is tested. "Management Myths Debunked: Principles & Misconceptions" endeavors to elucidate common misapprehensions and bring empirical guidance to the forefront of business practice. This dissection of managerial folklore is not just an academic exercise, but a pragmatic guide intended to disentangle the rooted management myths that handicap organizational progress. The aim of this blog is to foster an environment where clarity in management practices is not the exception but the norm.
Management Myths and Why They Persist
Overview of common management myths
Management myths persist in boardrooms and coffee corners of corporations because they offer the comforting illusion of simplicity in the complex world of leadership. These persistent fictions, such as the belief that managers must exhibit unwavering strength or that high levels of stress yield productivity, can be alluring. However, they often eclipse the nuanced reality of effectively steering a team or an organization.
The role of pop culture and outdated practices in perpetuating myths
Pop culture, along with legacy practices cemented into corporate culture, plays a substantial role in maintaining these myths. The portrayal of leaders in media, the romanticizing of tireless work ethics in biographies, and the perpetuation of hierarchical dominance in traditional business literature all contribute to a skewed understanding of effective management principles.
Consequences of adhering to misconceptions in management
Adherence to these misconceptions can stifle innovation, encourage burnout, and ultimately erode the foundation of trust and adaptability that a dynamic workplace requires. When leaders uncritically accept these fallacies, they risk not only personal inefficacy but may also precipitate the company’s decline through outdated methodologies.
Overview of Common Management Misconceptions
The Myth of the Infallible Leader
Deconstructing the idea that managers must always be right
The myth of the infallible leader suggests that managers should maintain an aura of unassailability. This myth discourages the admission of mistakes, depriving the organization of valuable learning opportunities. In reality, the most effective leaders acknowledge their fallibility, which humanizes them and earns respect.
The value of vulnerability and admitting mistakes
Vulnerability is not antithetical to leadership but is an attribute that begets loyalty and fosters an open culture where ideas can be challenged constructively. By admitting to errors, leaders can set a precedent that mistakes are a natural part of the learning curve, not reasons for reprimand.
The Fallacy of the Complete Control
Challenging the notion that managers can control all aspects
The belief in total control within managerial roles is another prevalent misconception. In actuality, numerous factors influencing outcomes in a business setting are beyond direct managerial control such as market fluctuations, technological disruptions, or individual employee challenges.
Embracing uncertainty and fostering a flexible work environment
Leaders can benefit from embracing uncertainty and encouraging a culture that accommodates change. By acknowledging the limits of their control, managers can empower teams to become more agile, fostering innovation and emphasizing the importance of adaptability in the modern workplace.
The "One-Size-Fits-All" Management Approach
Exploring why tailored approaches are necessary
The concept of a "one-size-fits-all" approach to management negates the diverse range of individuals, projects, and contexts that the modern leader encounters. Management techniques must be tailored to the complexities of different environments, acknowledging that strategies effective in one scenario may falter in another.
Examples of successful adaptive management styles
Successful organizations often feature managers who adapt their style to the specific needs of their team and context. Adaptive management might involve different communication strategies, varied levels of autonomy, and the recognition that flexibility may often trump rigid adherence to standard procedures.
The Myth of the Non-Stop Work Ethic
Examining the detrimental effects of overworking
The glorification of relentless work is a pervasive management myth. The belief that longer hours translate into better results overlooks the detrimental effects on health, well-being, and ultimately productivity. Instead, a focus on results, rather than hours worked, is more congruent with modern understanding of efficiency.
Promoting work-life balance and improved productivity
Balancing work expectations with personal life is critical in sustaining long-term productivity and fostering an environment conducive to creativity and satisfaction. Organizations with empathetic approaches to work-life balance tend to enjoy better employee engagement and retention rates.
Common management misconceptions persist in boardrooms and coffee corners of corporations because they offer the comforting illusion of simplicity in the complex world of leadership. These persistent fictions, such as the belief that managers must exhibit unwavering strength or that high levels of stress yield productivity, can be alluring. However, they often eclipse the nuanced reality of effectively steering a team or an organization.
The Intuition versus Data-Driven Decision Making Dilemma
Correcting misunderstandings about the role of intuition
The dichotomy between intuition and data in decision-making creates a false dilemma in managerial thought. The misconception that intuition is inherently unreliable often undervalues the experience-based 'gut feelings' that can complement data analysis. Instead, effective managers balance instinct with rigorous data-driven insight.
The importance of evidence-based management decisions
Nonetheless, the significance of evidence-based management cannot be overstated. Making decisions rooted in data grants a certain level of predictability and removes biases, enabling more consistent and transparent outcomes. In modern management, being informed by data while also honoring experience-based intuition is the mark of nuanced leadership.
The Over-Emphasis on Hierarchical Structures
Importance of lateral thinking and a collaborative approach
An overt focus on hierarchical structures can stifle the potential of lateral thinking and cross-functional collaboration. MBA free course and online courses offer insights into contemporary organizational frameworks that prize flat hierarchies and collaborative decision-making over traditional power dynamics.
Benefits of flat management structures in certain contexts
Flat management structures empower personnel at all levels to contribute ideas, challenge the status quo, and take initiative. In dynamic sectors where innovation is paramount, such structures can prove particularly effective in harnessing the collective intellect of a diverse workforce.
Case Studies on Successful Management without Micromanagement
Introducing examples of companies thriving with autonomous teams
Real-life case studies of companies like Google, which has thrived through creating autonomous teams, illustrate the potential of decentralized decision-making. Such models foster a sense of ownership and responsibility at the individual and team levels, which can spur on productivity and innovation.
Lessons learned from these case studies
These case studies denote a pivotal lesson: that micromanagement and overt control can dampen motivation and creativity. Leaders who provide clear goals but also allow autonomy find that teams can self-organize effectively, often delivering beyond expectations.
Analysis of Failures Due to Management Myths
Discussing well-known business failures and the myths behind them
Some spectacular business failures can be traced back to misguided adherence to management myths. An obsession with control, a refusal to adapt, or a dismissal of work-life balance concerns can lead even titans to falter. A sober analysis of these failures offers salient warnings and lessons for contemporary managers.
Key takeaways for managers and leaders
These takeaways are paramount: that inflexibility, an autocratic approach, and neglect of employee well-being are more detrimental than beneficial to the organization. Correcting these misunderstandings is vital in steering a company away from potential pitfalls.
I remember a conversation I had with a senior executive at a Fortune 500 company a few years ago. He confided in me that he felt immense pressure to maintain an image of infallibility, even when he knew he had made a mistake. This belief, he admitted, often led him to double down on poor decisions rather than acknowledge and rectify them. It was a poignant example of how misinterpreted management principles can lead even the most experienced leaders astray.
The Role of Pop Culture and Outdated Practices in Perpetuating Myths
Pop culture, along with legacy practices cemented into corporate culture, plays a substantial role in maintaining these myths. The portrayal of leaders in media, the romanticizing of tireless work ethics in biographies, and the perpetuation of hierarchical dominance in traditional business literature all contribute to a skewed understanding of effective management principles.
As Kanter (2020) points out in her book "Think Outside the Building: How Advanced Leaders Can Change the World One Smart Innovation at a Time," the glorification of the lone, heroic leader in popular culture often obscures the reality that successful leadership is a collaborative effort (p. 67). This misrepresentation can lead managers to adopt a fallacy of complete control in their approach, neglecting the importance of delegation and trust in their teams.
Consequences of Adhering to Misconceptions in Management
Adherence to these misconceptions can stifle innovation, encourage burnout, and ultimately erode the foundation of trust and adaptability that a dynamic workplace requires. When leaders uncritically accept these fallacies, they risk not only personal inefficacy but may also precipitate the company's decline through outdated methodologies.
A striking example of this can be found in the case of Blockbuster, once a dominant force in the video rental industry. As streaming services began to gain traction, Blockbuster's leadership clung to the belief that their brick-and-mortar model was irreplaceable. This adherence to a dated business paradigm, rooted in the myth of the infallibility of traditional methods, ultimately led to the company's demise (Satell, 2014, p. 92).
Misinterpreted Management Principles
The Myth of the Infallible Leader
Deconstructing the Idea that Managers Must Always Be Right
The myth of the infallible leader suggests that managers should maintain an aura of unassailability. This myth discourages the admission of mistakes, depriving the organization of valuable learning opportunities. In reality, the most effective leaders acknowledge their fallibility, which humanizes them and earns respect.
As Brown (2018) argues in her book "Dare to Lead," vulnerability is not a weakness but a strength in leadership. By admitting to their own imperfections and mistakes, leaders create a culture where it is safe for others to do the same, fostering an environment of continuous learning and growth (p. 34).
The Value of Vulnerability and Admitting Mistakes
Vulnerability is not antithetical to leadership but is an attribute that begets loyalty and fosters an open culture where ideas can be challenged constructively. By admitting to errors, leaders can set a precedent that mistakes are a natural part of the learning curve, not reasons for reprimand.
I once worked with a CEO who made a point of sharing his own failures and learnings at every company-wide meeting. This practice not only made him more relatable to his employees but also encouraged a culture of transparency and continuous improvement. It was a powerful demonstration of how importance of vulnerability in leadership can transform an organization.
The Fallacy of Complete Control
Challenging the Notion that Managers Can Control All Aspects
The belief in total control within managerial roles is another prevalent misconception. In actuality, numerous factors influencing outcomes in a business setting are beyond direct managerial control, such as market fluctuations, technological disruptions, or individual employee challenges.
As Taleb (2012) notes in his book "Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder," the attempt to exert complete control over a complex system often makes it more fragile and susceptible to catastrophic failure (p. 58). Managers who understand the limits of their control are better equipped to build resilient, adaptable organizations.
Embracing Uncertainty and Fostering a Flexible Work Environment
Leaders can benefit from embracing uncertainty and encouraging a culture that accommodates change. By acknowledging the limits of their control, managers can empower teams to become more agile, fostering innovation and emphasizing the importance of adaptability in the modern workplace.
This principle is exemplified in the adaptive management styles examples of companies like Spotify and Netflix, which have thrived by embracing decentralized decision-making and fostering a culture of autonomy and accountability (Mankins & Garton, 2017, p. 112).
Debunking Management Beliefs
The One-Size-Fits-All Management Approach
Exploring Why Tailored Approaches Are Necessary
The concept of a one-size-fits-all approach to management negates the diverse range of individuals, projects, and contexts that the modern leader encounters. Management techniques must be tailored to the complexities of different environments, acknowledging that strategies effective in one scenario may falter in another.
As Goleman (2000) argues in his article "Leadership That Gets Results," the most effective leaders are those who can adapt their style to the needs of the situation and the individuals they are leading (p. 82). A blanket approach to management, no matter how well-intentioned, is likely to fall short in the face of complex, dynamic challenges.
Examples of Successful Adaptive Management Styles
Successful organizations often feature managers who adapt their style to the specific needs of their team and context. Adaptive management might involve different communication strategies, varied levels of autonomy, and the recognition that flexibility may often trump rigid adherence to standard procedures.
For example, at Google, managers are encouraged to adopt a coaching style of leadership, focusing on the growth and development of their team members rather than micromanaging their work (Harrell & Barbato, 2018, p. 45). This approach has been credited with fostering a culture of innovation and employee engagement that has driven the company's success.
The Myth of the Non-Stop Work Ethic
Examining the Detrimental Effects of Overworking
The glorification of relentless work is a pervasive management myth. The belief that longer hours translate into better results overlooks the detrimental effects on health, well-being, and ultimately productivity. Instead, a focus on results, rather than hours worked, is more congruent with modern understanding of efficiency.
Research has consistently shown that overworking can lead to decreased productivity, increased stress, and higher rates of burnout (Pencavel, 2014, p. 2). Managers who perpetuate the myth of the non-stop work ethic may be inadvertently undermining the very results they seek to achieve.
Promoting Work-Life Balance and Improved Productivity
Balancing work expectations with personal life is critical in sustaining long-term productivity and fostering an environment conducive to creativity and satisfaction. Organizations with empathetic approaches to work-life balance tend to enjoy better employee engagement and retention rates.
Companies like Patagonia have built their success on prioritizing employee well-being, offering generous parental leave policies, flexible work arrangements, and encouraging employees to pursue their passions outside of work (Casey, 2019, p. 167). This approach has not only earned the company a loyal and dedicated workforce but has also been credited with fueling its innovative spirit.
Misconceptions in Management Corrected
The Intuition versus Data-Driven Decision Making Dilemma
Correcting Misunderstandings About the Role of Intuition
The dichotomy between intuition and data in decision-making creates a false dilemma in managerial thought. The misconception that intuition is inherently unreliable often undervalues the experience-based gut feelings that can complement data analysis. Instead, effective managers balance instinct with rigorous data-driven insight.
As Kahneman (2011) argues in his book "Thinking, Fast and Slow," intuition can be a powerful tool in decision-making, particularly when it is based on years of experience and expertise (p. 237). The key is to know when to trust intuition and when to defer to data.
The Importance of Evidence-Based Management Decisions
Nonetheless, the significance of data-driven decision making in leadership cannot be overstated. Making decisions rooted in data grants a certain level of predictability and removes biases, enabling more consistent and transparent outcomes. In modern management, being informed by data while also honoring experience-based intuition is the mark of nuanced leadership.
Companies like Amazon have made data-driven decision-making a core part of their culture, using metrics and analytics to guide everything from product development to customer service (Bryar & Carr, 2021, p. 92). This approach has enabled the company to make rapid, informed decisions that have fueled its growth and success.
The Over-Emphasis on Hierarchical Structures
Importance of Lateral Thinking and a Collaborative Approach
An overt focus on hierarchical structures can stifle the potential of lateral thinking and cross-functional collaboration. As Hamel (2012) argues in his book "What Matters Now: How to Win in a World of Relentless Change, Ferocious Competition, and Unstoppable Innovation," the most successful organizations of the future will be those that can harness the collective intelligence of their employees, regardless of their position in the hierarchy (p. 74). Online courses and other educational resources offer insights into contemporary organizational frameworks that prize flat hierarchies and collaborative decision-making over traditional power dynamics.
Benefits of Flat Management Structures in Certain Contexts
Flat management structures empower personnel at all levels to contribute ideas, challenge the status quo, and take initiative. In dynamic sectors where innovation is paramount, such structures can prove particularly effective in harnessing the collective intellect of a diverse workforce.
One notable example is Gore, the maker of Gore-Tex and other innovative materials. The company has a flat organizational structure, with no traditional hierarchy or job titles. Employees, known as "associates," are encouraged to take initiative and collaborate with each other based on their skills and interests, rather than their position in the company (Shipper & Manz, 2016, p. 150). This structure has been credited with fostering a culture of innovation that has kept the company at the forefront of its industry for decades.
Correcting Management Misunderstandings with Real-Life Examples
Case Studies on Successful Management without Micromanagement
Introducing Examples of Companies Thriving with Autonomous Teams
Real-life case studies of companies like Google, which has thrived through creating autonomous teams, illustrate the potential of decentralized decision-making. Such models foster a sense of ownership and responsibility at the individual and team levels, which can spur on productivity and innovation.
As Bock (2015) details in his book "Work Rules!: Insights from Inside Google That Will Transform How You Live and Lead," Google's success has been built on a foundation of employee autonomy and trust. Managers at the company are encouraged to give their teams the freedom to make decisions and pursue innovative ideas, with the understanding that occasional failures are an acceptable part of the learning process (p. 184).
Lessons Learned from These Case Studies
These case studies denote a pivotal lesson: that micromanagement and overt control can dampen motivation and creativity. Leaders who provide clear goals but also allow autonomy find that teams can self-organize effectively, often delivering beyond expectations.
Other companies that have successfully adopted this approach include Netflix, which has a culture of "freedom and responsibility" that gives employees wide latitude in decision-making (Hastings & Meyer, 2020, p. 211), and Zappos, which has eliminated traditional managers in favor of self-organizing teams (Frei & Morris, 2012, p. 136).
Analysis of Failures Due to Management Myths
Discussing Well-Known Business Failures and the Myths Behind Them
Some spectacular business failures can be traced back to misguided adherence to management myths. An obsession with control, a refusal to adapt, or a dismissal of work-life balance concerns can lead even titans to falter. A sober analysis of these failures offers salient warnings and lessons for contemporary managers.
One prominent example is the collapse of Enron in 2001. As detailed in McLean and Elkind's (2013) book "The Smartest Guys in the Room: The Amazing Rise and Scandalous Fall of Enron," the company's downfall was largely due to a culture that valued short-term profits over sustainable growth, and that discouraged questioning of leadership decisions (p. 114). This adherence to the myth of the infallible leader and the glorification of a ruthless work ethic ultimately led to the company's implosion.
Key Takeaways for Managers and Leaders
These takeaways are paramount: that inflexibility, an autocratic approach, and neglect of employee well-being are more detrimental than beneficial to the organization. Correcting these misunderstandings is vital in steering a company away from potential pitfalls.
Other key lessons from business failures due to management myths include the importance of transparency and accountability (as in the case of WorldCom, where a culture of secrecy and fear enabled massive accounting fraud; Jeter, 2003, p. 156), and the need for continuous learning in management practices (as demonstrated by Kodak's failure to adapt to the digital revolution in photography; Lucas & Goh, 2009, p. 46).
Conclusion
Summary of Key Insights into Debunking Management Myths
Debunking management myths is an essential step toward enlightened leadership. By critically examining beliefs long held as truths, managers can unshackle themselves and their teams from counterproductive practices, paving the way for innovative, empathetic, and responsive leadership.
As we have seen, challenging misconceptions such as the infallibility of leaders, the need for complete control, the one-size-fits-all approach, and the glorification of overwork can open up new avenues for organizational success. By embracing vulnerability, adaptability, autonomy, and data-driven decision making, managers can create environments where creativity, collaboration, and continuous learning thrive.
Reinforcing the Need for Continuous Learning in Management
The need for continuous learning in management is underscored by the constantly changing business environment. Resources such as online courses, seminars, and even free MBA course offerings enable managers to remain agile in their professional development, ensuring that they stay abreast of evolving best practices.
As Drucker (2011) famously said, "We now accept the fact that learning is a lifelong process of keeping abreast of change. And the most pressing task is to teach people how to learn" (p. 32). This is particularly true for managers, who must not only continuously update their own skills and knowledge but also foster a culture of learning within their organizations.
Encouraging Reader Engagement and Sharing of Personal Experiences
The journey toward debunking management myths is a collective endeavor, enriched by shared knowledge and experiences. Readers are encouraged to engage with this material, reflect on their own practices, and share insights that might further assist in dispelling misinterpreted principles in the fascinating quest to redefine management.
As we navigate the complexities of modern business, it is through open dialogue, continuous learning, and a willingness to challenge long-held assumptions that we can create more adaptive, resilient, and successful organizations. By shedding the myths of the past and embracing the realities of the present, we can pave the way for a brighter, more innovative future.
References
Bock, L. (2015). Work Rules!: Insights from Inside Google That Will Transform How You Live and Lead. Twelve.
Brown, B. (2018). Dare to Lead: Brave Work. Tough Conversations. Whole Hearts. Random House.
Bryar, C., & Carr, B. (2021). Working Backwards: Insights, Stories, and Secrets from Inside Amazon. St. Martin's Press.
Casey, S. (2019). Let My People Go Surfing: The Education of a Reluctant Businessman--Including 10 More Years of Business Unusual. Penguin Books.
Drucker, P. F. (2011). The Age of Discontinuity: Guidelines to Our Changing Society. Transaction Publishers.
Frei, F., & Morris, A. (2012). Uncommon Service: How to Win by Putting Customers at the Core of Your Business. Harvard Business Review Press.
Goleman, D. (2000). Leadership That Gets Results. Harvard Business Review, 78(2), 78-90.
Hamel, G. (2012). What Matters Now: How to Win
Frequently Asked Questions
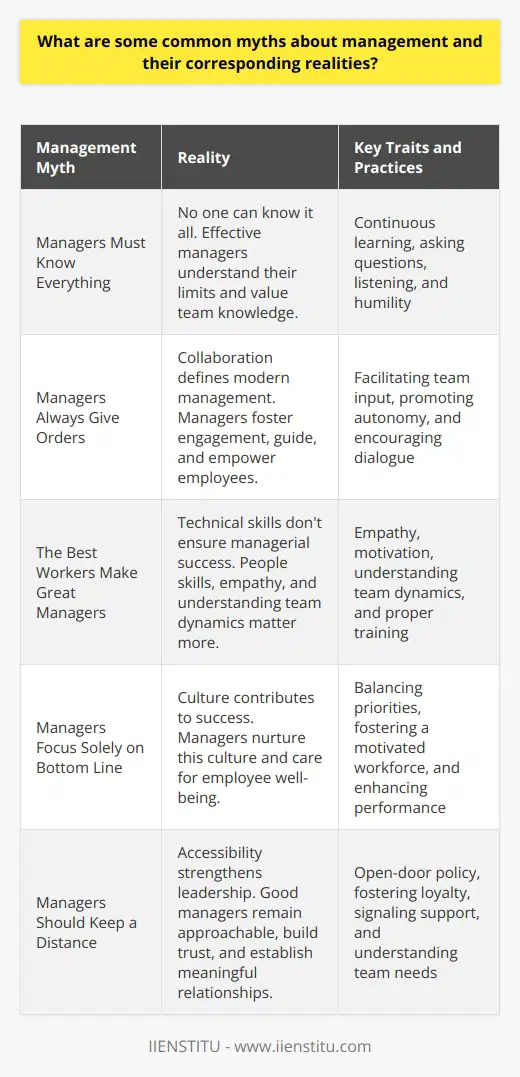
What are some common myths about management and their corresponding realities?
Debunking Common Management Myths
Myth 1: Managers Must Know Everything
Reality: No one can know it all. Effective managers understand their limits. They value team knowledge. They learn continuously. They ask questions. They listen. Humility paves the way for growth.
Myth 2: Managers Always Give Orders
Reality: Collaboration defines modern management. Managers foster engagement. They guide, not dictate. They empower employees. They promote autonomy. As facilitators, they encourage team input. Dialogue trumps monologue.
Myth 3: The Best Workers Make Great Managers
Reality: Technical skills don't ensure managerial success. People skills matter more. Managers need empathy. They must motivate. They understand team dynamics. Management is a different game. It requires training.
Myth 4: Managers Focus Solely on Bottom Line
Reality: Numbers matter, but they're not everything. Culture contributes to success. Managers nurture this culture. They care for employee well-being. They know a motivated workforce enhances performance. They balance priorities.
Myth 5: Managers Should Keep a Distance
Reality: Accessibility strengthens leadership. Good managers remain approachable. They build trust. They establish meaningful relationships. They understand their team's needs. An open-door policy fosters loyalty. It signals support.
Myth 6: Micromanagement Shows Strong Leadership
Reality: Micromanagement undermines trust. It stifles creativity. Managers should delegate. They trust their teams. They provide autonomy. They offer support from afar. This approach spurs innovation. It increases satisfaction.
Myth 7: Male Managers Exceed Female in Effectiveness
Reality: Leadership effectiveness knows no gender. Traits like empathy, decisiveness, and communication mark good leaders. Both men and women can exhibit them. Diverse perspectives enrich management. They defy stereotypes.
Managers navigate reality, not myth. Key traits include empathy, trust, and a learning mindset. They balance human and business needs. They are approachable and empowering. They champion team growth. They shun stereotypes. These truths guide successful management.
How have misconceptions about management principles misguided business strategies?
The Perils of Misunderstood Management
Misguided By Myths
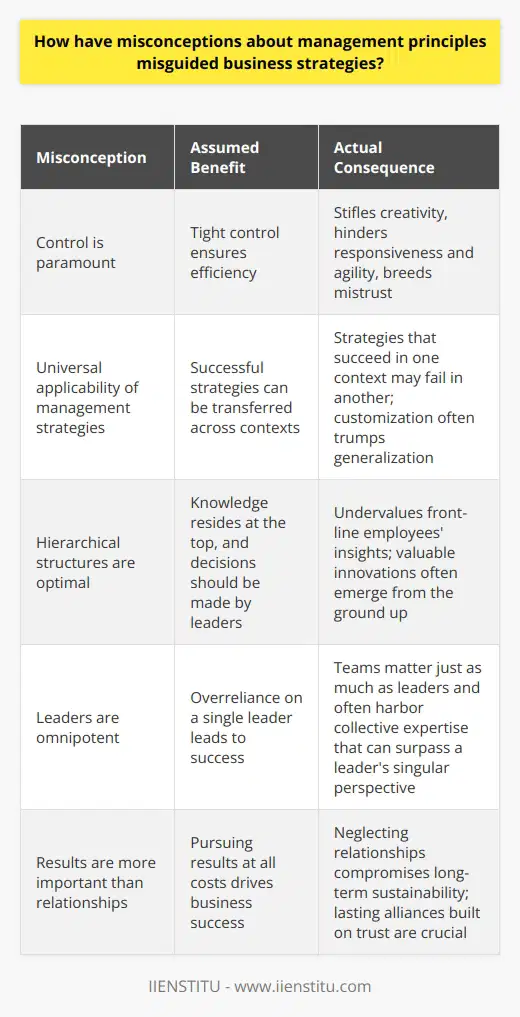
Management principles often fall prey to oversimplification. Leaders seek silver bullets. They desire simple solutions for complex problems. These desires spawn misconceptions. These misconceptions, in turn, misguide business strategies.
The Myth of Control
Consider the 'control is paramount' myth. Managers strive for total oversight. They assume tight control ensures efficiency. Yet, rigid structures stifle creativity. They also hinder responsiveness and agility. This oversight demands can breed mistrust. It suggests a lack of faith in staff abilities.
One-Size-Fits-All Fallacy
Another misconception is the universal applicability of management strategies. What succeeds in one context fails in another. Transferring strategies across different cultures and settings can backfire. Customization often trumps generalization. Adaptable strategies far exceed rigid ones.
Hierarchical Hang-ups
Hierarchies dominate traditional management thinking. Leaders at the top make decisions. Workers at the bottom carry them out. This setup assumes knowledge resides at the top. It undervalues front-line employees' insights. Yet, valuable innovations often emerge from the ground up.
The Capable Leader Misconception
Leaders are not omnipotent. Many believe otherwise. This belief leads to an overreliance on a single leader. Teams matter just as much as leaders do. They often harbor collective expertise. This expertise can surpass a leader's singular perspective.
Results Over Relationships
The pursuit of results often overshadows the importance of relationships. Good relationships drive business success. They foster trust, communication, and collaboration. Neglecting these relationships compromises long-term sustainability. Short-term gains pale in comparison to lasting alliances built on trust.
Incentive Illusions
Incentives are seen as motivation panaceas. We assume they always drive performance. This is not always true. Studies show excessive incentives can actually dampen motivation. They can even encourage unethical behavior. Motivation is more complex than mere incentives.
Innovation Obsession
Innovation is crucial. It cannot, however, be forced. The misconception of constant innovation puts unnecessary pressure on organizations. It often leads to innovation for its own sake. Not all innovation equates to improvement. Balance is key. So is recognizing when refinement trumps reinvention.
Technological Tunnel Vision
Many espouse technology as a cure-all. They push digital solutions indiscriminately. They overlook technology's potential disruptions. These disruptions affect both employees and customers. Thoughtful integration is necessary. It ensures technology enhances rather than hinders.
The Plight of Planning
Comprehensive planning appears infallible. Detailed plans promise control over the future. Yet, the future is inherently uncertain. Flexibility often triumphs over rigid planning. Adapting to changing circumstances often yields better outcomes.
In summary, misconceptions abound in management. They obscure the multifaceted nature of businesses. They promote one-size-fits-all solutions. Real-world business demands nuance. It requires an understanding of context. It calls for adaptability and balance. Successful management acknowledges these complexities. It shuns simplistic and misguided shortcuts for thoughtful, informed strategies.
In what ways do debunking management myths contribute towards organizational effectiveness?
Understanding Management Myths
Management myths pervade many organizations. They dictate how leaders interact with their teams and make decisions. Such myths often stem from outdated practices. They lack empirical support. Their perpetuation hinders growth. It affects morale. Ultimately, it impacts overall effectiveness.
The Role of Myth Debunking
Debunking management myths plays a crucial role. It brings about a necessary shift in perspective. Leaders become more open-minded. They consider evidence-based approaches. Employees feel heard and respected. This harmony fosters a better working environment.
Challenge Conventional Wisdom
Leadership requires a mix of courage and wisdom. Challenging the status quo is frightening but necessary. It promotes adaptability. Organizations become more agile. They respond better to change.
Promote Empirical Approaches
Evidence-driven management is essential. It replaces guesswork with data. Decisions become more informed. Risks get minimized. This reliability boosts confidence in leadership.
Benefits of Dispelling Management Myths
Improve Decision-Making
Myth debunking leads to better decisions. Assumptions give way to facts. Biases diminish. Clarity in decision-making emerges. Transparency increases. Trust grows.
Enhance Organizational Culture
An enlightened leadership approach also augments culture. Toxic myths can create hostile environments. Removing them allows positivity to flourish. Teams bond. Productivity climbs.
Foster Innovation
Innovation requires freedom from restrictive beliefs. Questioning myths opens new avenues. Creativity thrives. Novel solutions emerge. The organization stays competitive.
Attract and Retain Talent
Professionals seek dynamic workplaces. They shun rigid, myth-bound environments. An organization renowned for its modern practices draws talent. It keeps its best employees.
Increase Effectiveness
All these factors lead to greater organizational effectiveness. Goals become clearer. Strategies turn sharper. Execution improves. Results follow. The organization moves forward.
Debunking myths transforms a company's core. It demands bold leadership. It rests on a commitment to truth. The journey is complex. It requires persistence. The outcomes, however, are worth the effort. Organizations emerge stronger. They become more resilient, innovative, and effective. This evolution is vital for long-term success.



