System Approach to Inventory Control
Assessing Inventory Control Through System Approach
Challenges of Inventory Control Through System Approach
Logistics is anticipating, organizing, and controlling the movement and storage of materials within a company's supply chain. Logistics encompasses all the activities related to shipping, such as loading, storage, delivery, and inventory tracking. A sound logistics practice is essential to efficient inventory management and control. As such, companies need to have a thorough understanding of their supply chain and the dynamics of their supply chain. Properly organizing, monitoring, and controlling supply chain activities and inventory is crucial in remaining competitive and delivering quality products to customers.
System Approach to Inventory Control
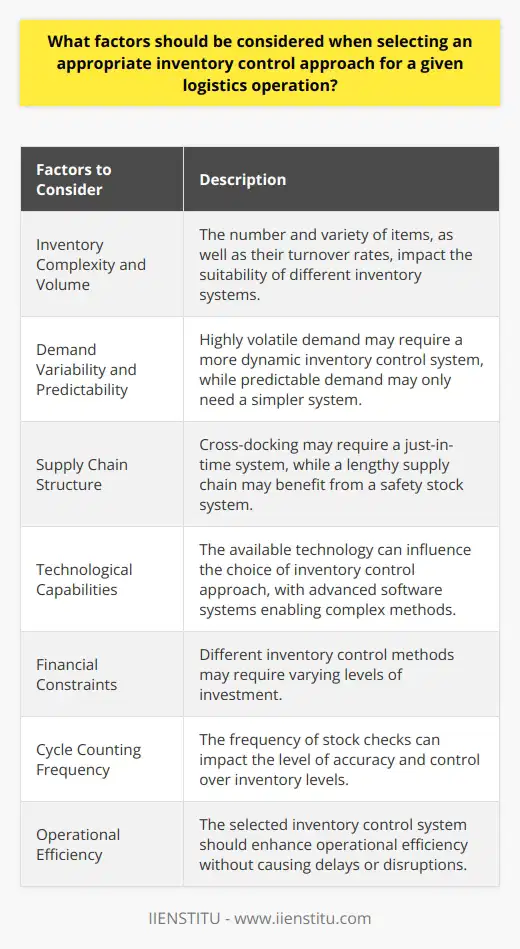
A system approach to inventory control focuses on optimizing the use of inventory to produce a competitive advantage. This approach involves analyzing inventory levels, ensuring the quantity and quality of materials are sufficient, and implementing an appropriate inventory-management system. In addition, the system approach to inventory control should consider improving customer service, enhancing profitability, and reducing costs.
With a system approach to inventory control, businesses can benefit from increased efficiency and improved customer service levels due to more accurate and reliable information about inventory levels. A well-designed system can also reduce the time required to accurately assess stock levels and help prevent inventory shortages and overstock. This approach can also assist businesses in making timely and accurate decisions related to their inventory.
Assessing Inventory Control Through System Approach
In assessing inventory control through the system approach, it is essential to consider the stocking level, the cost per unit of the inventory, the purchasing volume, and the inventories' age. Therefore, all these factors should be considered when implementing inventory management technologies. In addition, it is also necessary to consider the supply chain's stability and ability to interact with other business systems and processes.
Challenges of Inventory Control Through System Approach
There are some challenges associated with using a system approach to inventory control. One of the most significant challenges is the high cost of monitoring and maintaining the system. This high cost can include the cost of installation, training, upgrades, and support, which can add up quickly. In addition, supply chain delays, errors, and miscalculations can lead to stockout or overstock situations, all of which can be difficult to process and significantly impact the profitability of a business.
In conclusion, the system approach to inventory control is a cost-effective and efficient way of ensuring your inventory's accuracy and reliability, allowing you to meet customer demand and remain competitive in the marketplace. Utilizing the system approach can help you better see inventory levels, reduce the time required to assess stock levels, and maintain accurate inventory data correctly. However, it is essential to be aware of the associated costs and risks involved in the system approach to inventory control before making any changes.
Organizing and controlling inventory with a system-based approach will help maintain an efficient supply chain process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a system approach to inventory control, and how does it differ from other inventory management techniques?
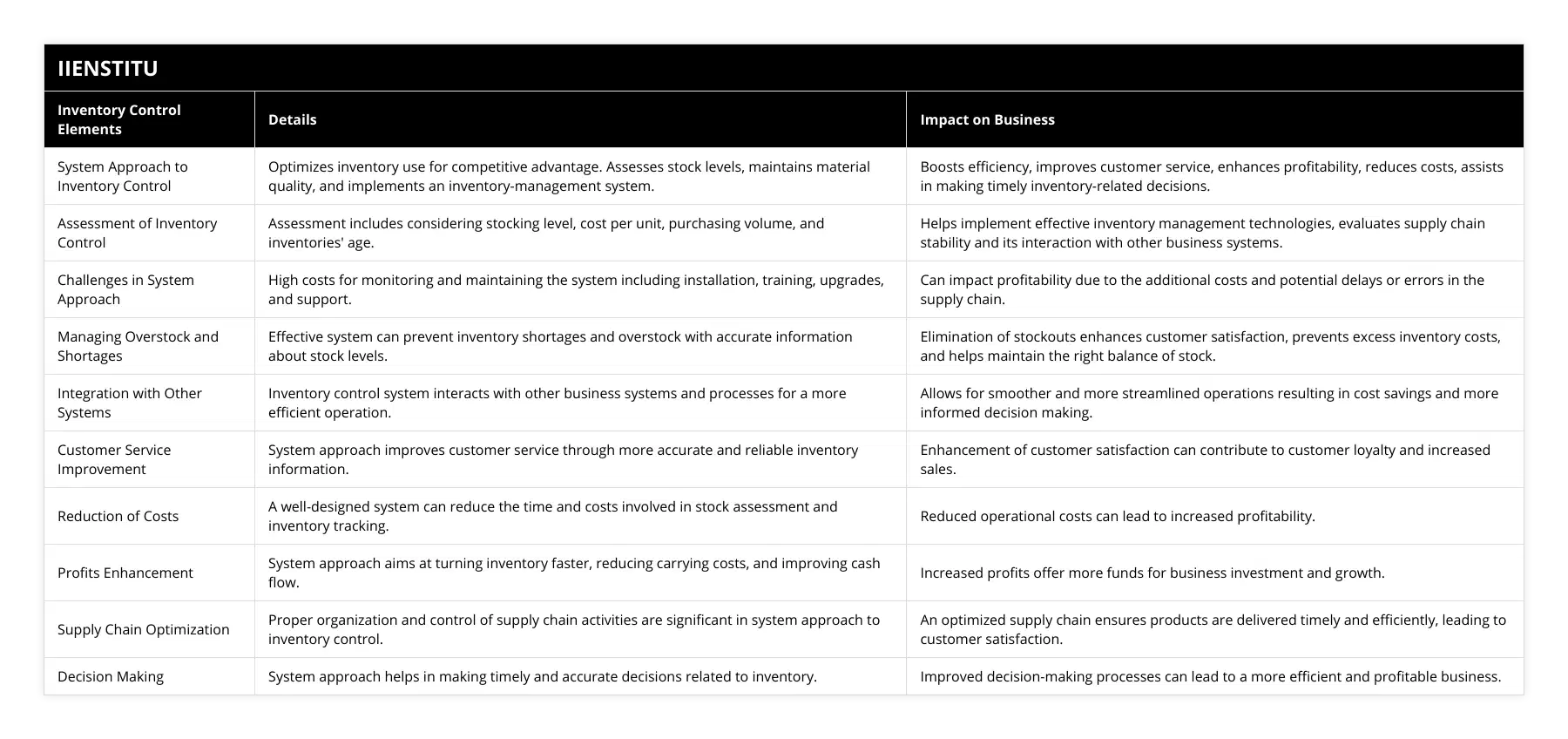
A system approach to inventory control is a method of inventory management that focuses on optimizing the use of inventory to produce a competitive advantage. This approach involves analyzing inventory levels, ensuring the quantity and quality of materials are sufficient, and implementing an appropriate inventory-management system. In addition, the system approach to inventory control should consider improving customer service, enhancing profitability, and reducing costs.
Unlike traditional inventory management techniques focusing on minimizing inventory costs, the system approach takes a more holistic view of the supply chain. This approach considers the entire supply chain's dynamics and seeks to optimize inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing costs. It also considers the interdependence of various supply chain activities, such as transportation, warehousing, and distribution, and how they impact inventory management. By focusing on the entire supply chain, the system approach can help businesses reduce waste, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
One of the main benefits of the system approach to inventory control is that it provides businesses with more accurate and reliable information about inventory levels. This helps companies to make more informed decisions about inventory management, such as when to order new inventory, how much to order, and when to sell or dispose of the old list. In addition, the system approach can help businesses reduce the time required to accurately assess stock levels and help prevent inventory shortages and overstock.
However, some challenges are associated with using a system approach to inventory control. One of the most significant challenges is the high cost of monitoring and maintaining the system. This high cost can include the cost of installation, training, upgrades, and support, which can add up quickly. In addition, supply chain delays, errors, and miscalculations can lead to stockout or overstock situations, all of which can be difficult to process and significantly impact the profitability of a business.
Overall, the system approach to inventory control is a cost-effective and efficient way of ensuring inventory accuracy and reliability, allowing businesses to meet customer demand and remain competitive in the marketplace. Utilizing the system approach can help enterprises to see inventory levels better, reduce the time required to assess stock levels, and maintain accurate inventory data correctly. However, it is essential to be aware of the associated costs and risks involved in the system approach to inventory control before making any changes.
What are the benefits of using a system approach to inventory control, and how can it improve customer service and profitability?
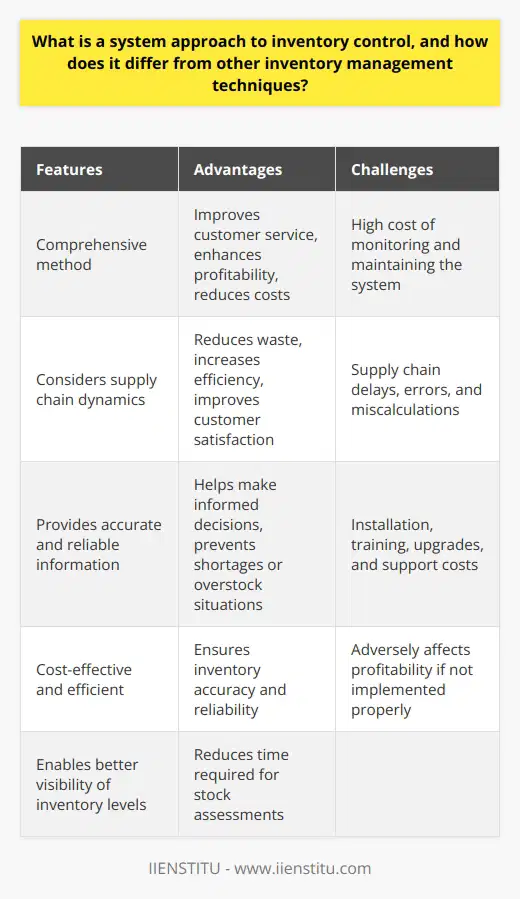
A system approach to inventory control can offer several benefits to a company. By utilizing this approach, a business can increase its efficiency and reduce its costs by maintaining an optimal inventory level. With accurate and timely information about inventory levels, a company can better meet customer demand, avoid stockouts and overstock, and reduce the time required to assess stock levels. A well-designed inventory management system can also help prevent errors, miscalculations, and delays, significantly impacting a company's profitability.
Another significant benefit of the system approach to inventory control is that it can improve customer service levels. A company can increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention by ensuring that products are available when customers need them. In addition, accurate and reliable information about inventory levels can enable a business to fulfill customer orders more quickly and accurately, enhancing the customer experience.
The system approach to inventory control can also assist a business in enhancing its profitability. By optimizing inventory levels, a company can reduce the cost of carrying excess inventory, reduce inventory shortages, and decrease the need for emergency orders. This can lead to cost savings regarding storage costs, capital tied up in stock, and labor costs. A well-designed inventory management system can also enable a business to identify the most profitable products and prioritize their production and sales.
Overall, the system approach to inventory control can significantly benefit a business by reducing costs, improving customer service levels, and enhancing profitability. By utilizing this approach, companies can optimize their inventory levels, reduce the time required to assess stock levels, prevent stockouts and overstock, and improve their ability to fulfill customer orders accurately and quickly.
What are the challenges associated with implementing a system approach to inventory control, and how can businesses mitigate these challenges?
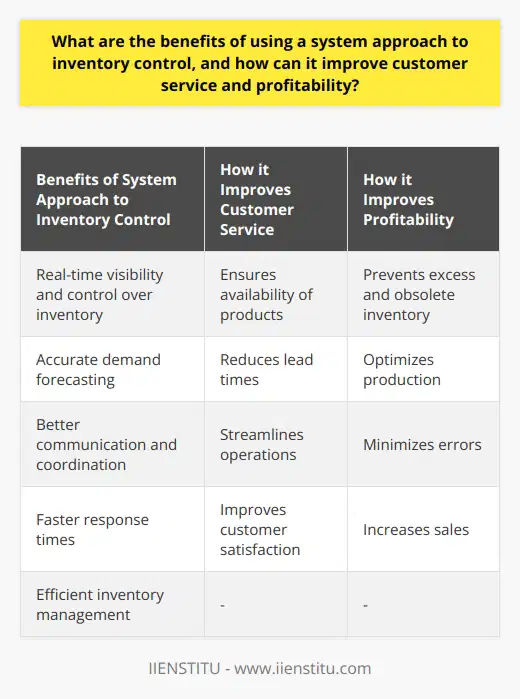
While a system approach to inventory control offers various benefits, several challenges are associated with implementing this approach. One of the most significant challenges is the high cost of monitoring and maintaining the system. The price includes installation, training, upgrades, and support, which can add up quickly. As a result, small and medium-sized businesses may find it challenging to allocate the necessary resources to implement and maintain a systematic approach to inventory control.
Another challenge is the system's complexity, requiring specialized knowledge and skills. Staff training and education on the system's technical aspects are essential, but these can take time and resources. The system's stability and compatibility with other business systems and processes also need to be considered, as the lack of integration can hinder the system's smooth operation and increase costs.
Furthermore, the accuracy and reliability of data in the inventory management system are critical. However, supply chain delays, errors, and miscalculations can lead to stockout or overstock situations, all of which can be difficult to process and significantly impact the profitability of a business. Therefore, the inventory management system must be continually monitored and updated to ensure data accuracy, and the supply chain must be monitored to ensure that inventory is delivered on time.
To mitigate these challenges, businesses can consider outsourcing their inventory management to third-party logistics providers who specialize in the system approach to inventory control. These providers have the resources, expertise, and technology to effectively implement and maintain the inventory management system. This can be more cost-effective for businesses as they can avoid investing in their inventory management infrastructure.
Another way to mitigate the challenges associated with implementing a systematic approach to inventory control is to start small and gradually expand the system's scope. For example, businesses can begin with a pilot project to test the system's feasibility and progressively integrate it into their operations. In addition, proper staff training and education can increase their competency and confidence in managing the system.
Implementing a systematic approach to inventory control can be challenging, but the benefits of increased efficiency, accuracy, and customer service levels can outweigh the costs. By carefully managing the implementation process, businesses can successfully leverage the advantages of the system approach to inventory control and improve their profitability.
What is inventory control in logistics management and why is it crucial for efficient supply chain operations?
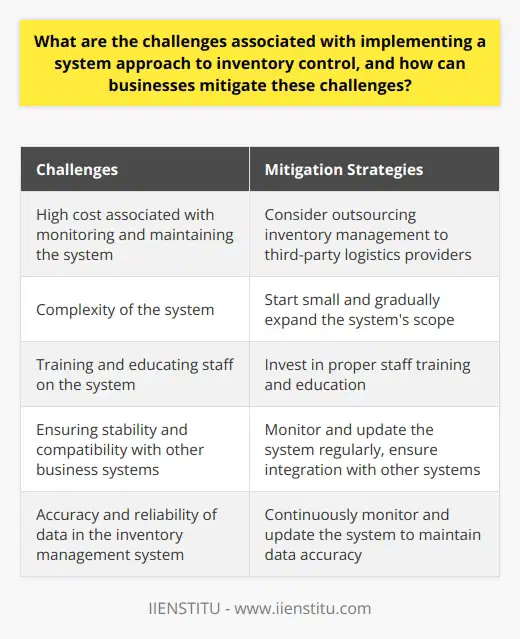
Defining Inventory Control in Logistics Management
Inventory control in logistics management refers to the oversight and optimization of the products and materials held by a business. It is a fundamental component of supply chain operations that aims to maintain an appropriate balance between minimizing costs and meeting customer demand.
Significance of Inventory Control
Efficient inventory control plays a vital role in supply chain operations. It is crucial to avoid stock shortages, excess storage costs, and dissatisfied customers. By strategically managing inventory levels, businesses can ensure a smooth production process and effective order fulfillment.
Types of Inventory Control Techniques
To achieve optimal inventory levels, several techniques can be employed. Common methods include just-in-time (JIT) ordering, safety stock calculation, economic order quantity (EOQ) analysis, and materials requirement planning (MRP). Through these techniques, businesses can better ascertain the optimal inventory level that minimizes costs while maintaining customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Control
Effective inventory control offers numerous advantages. Firstly, it helps maintain appropriate stock levels, which reduces the likelihood of surplus inventory and prevents stockouts. This subsequently translates to lower storage costs and increased customer satisfaction. Additionally, accurate inventory data aids in better forecasting of future demand, allowing businesses to proactively manage their supply chains.
Role of Technology in Inventory Control
Modern inventory control systems leverage technology to streamline and automate the inventory management process. By implementing software tools and analytics, businesses gain real-time access to inventory data, which enables more accurate decision-making and better collaboration among supply chain partners. This increased level of visibility and efficiency is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in today's rapidly evolving marketplace.
In conclusion, inventory control in logistics management is an essential aspect of efficient supply chain operations. It ensures that businesses effectively balance storage costs with customer demand, resulting in improved financial performance and enhanced customer satisfaction. Implementing proper inventory control techniques and leveraging technology can further drive success in today's competitive landscape.
What are the 4 types of inventory control systems, and how do they differ in their scope and functionality?
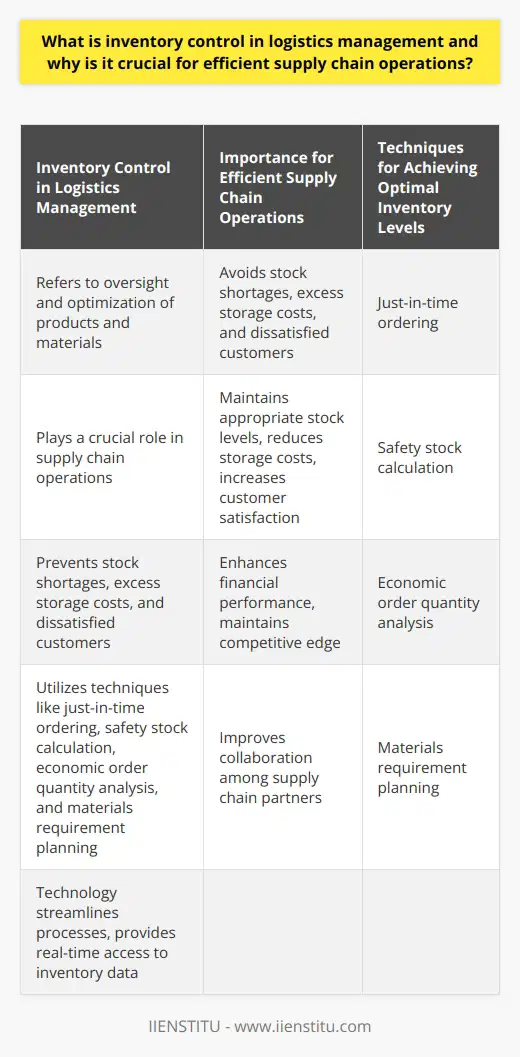
**Types of Inventory Control Systems**
Inventory control systems are essential tools for managing and monitoring the quantity, location, and status of goods within a company's supply chain. There are four main types of inventory control systems: manual, perpetual, periodic, and just-in-time (JIT). These systems differ in their scope and functionality, as discussed below.
**Manual Inventory Control**
The manual inventory control system relies on the physical counting and recording of stock by employees. This method involves manually updating inventory records, which can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to human error. While manual systems may be cost-effective for small businesses, they lack the real-time tracking and analytics capabilities provided by more advanced systems.
**Perpetual Inventory Control**
The perpetual inventory control system is a real-time, computerized method of tracking inventory levels. As items are received, sold, or moved within a warehouse, the system continuously updates the quantity and value of inventory. Perpetual systems are highly accurate and enable companies to maintain optimal stock levels, minimize stockouts and overstocks, and address discrepancies in a timely manner.
**Periodic Inventory Control**
The periodic inventory control system involves counting and updating inventory records at fixed intervals, such as weekly, monthly, or annually. This system requires less labor than manual systems but is less accurate than perpetual systems, as stock levels may change significantly between counts. The periodic system is best suited for businesses with lower inventory turnover and fewer stockkeeping units (SKUs).
**Just-in-Time Inventory Control**
The just-in-time (JIT) system is a highly efficient approach to inventory management that aims to minimize carrying costs by maintaining only the necessary stock levels for immediate production or sales needs. This system requires close cooperation with suppliers and a deep understanding of the supply chain to ensure timely delivery of inventory. JIT inventory control can reduce waste, storage costs, and the risk of obsolescence but requires accurate forecasting and relies heavily on supplier reliability.
In summary, the four types of inventory control systems - manual, perpetual, periodic, and just-in-time - are differentiated by their methods of stock tracking, management, and optimization. Companies should consider their specific inventory needs, resources, and supply chain dynamics when selecting the most suitable inventory control system for their operations.
What are the logistics activities in inventory management and how do they impact the overall success of a business?
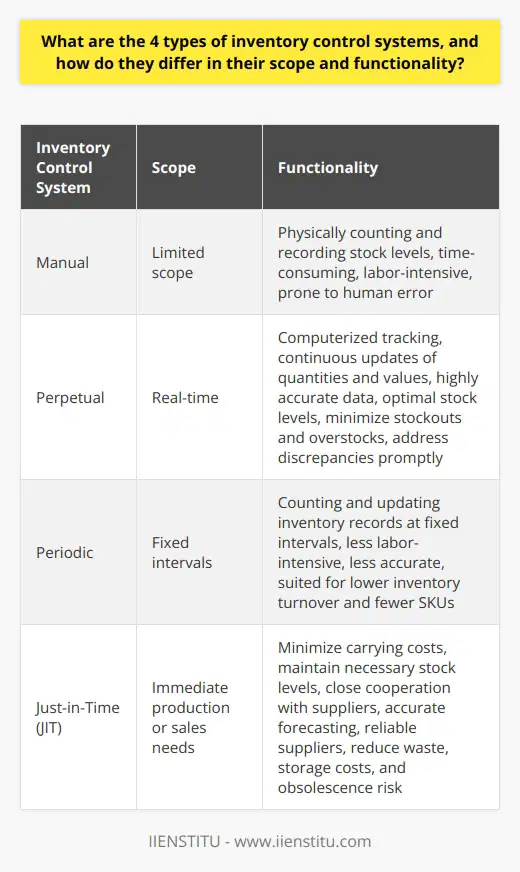
**Logistics Activities in Inventory Management**
The logistics activities in inventory management are crucial to ensure the smooth operation and success of a business. These activities include demand forecasting, inventory control, order processing, warehousing, transportation, and reverse logistics.
**Demand Forecasting**
Demand forecasting involves predicting future customer needs to determine the appropriate amount of inventory to maintain. Accurate demand forecasts enable businesses to minimize inventory costs and prevent stockouts or overstocks, ensuring product availability to meet customer needs.
**Inventory Control**
Inventory control involves managing the in-stock quantities and maintaining optimal inventory levels. It includes tracking, monitoring, and adjusting inventory levels to avoid excess stock or out-of-stock situations. Effective inventory control reduces storage costs, improves cash flow, and prevents obsolescence, thus contributing to the overall success of the business.
**Order Processing**
Order processing entails the efficient management of customer orders, from receipt to fulfillment. Timely and accurate order processing improves customer satisfaction by ensuring quick delivery times and reducing order errors. Efficient order processing directly impacts the company's reputation and customer retention rate, ultimately affecting its bottom line.
**Warehousing**
Warehousing involves the careful storage and management of inventory. Efficient warehousing processes allow businesses to optimize their storage space and stock preservation, reducing overall storage costs. Proper warehousing also ensures efficient order processing and faster product delivery, improving customer satisfaction levels and positively impacting the company's success.
**Transportation**
Transportation is a critical element in inventory management, as it moves products from the manufacturers or suppliers to warehouses and from warehouses to customers. A reliable and efficient transportation system ensures timely deliveries, reduced lead time, and lower transportation costs, all of which contribute to the overall success of the business.
**Reverse Logistics**
Reverse logistics deals with the return of products from customers to businesses for various reasons, such as defects or end-of-use. Effective management of reverse logistics processes helps businesses to reduce waste, recover value from returned items, and improve customer relations. Properly handling reverse logistics also enhances a company's brand image and promotes customer loyalty, thus impacting its overall success.
In conclusion, logistics activities in inventory management play a fundamental role in shaping a company's overall success. By efficiently managing demand forecasting, inventory control, order processing, warehousing, transportation, and reverse logistics, businesses can boost customer satisfaction, reduce costs, improve cash flow, and ultimately increase profitability.
What are the three approaches to inventory management, and how do they cater to different business needs?
Three Approaches to Inventory Management
Just-In-Time Method
The Just-In-Time (JIT) approach to inventory management aims to minimize stock levels by ordering supplies only when needed for production or sales. With this method, businesses can reduce carrying costs and free up working capital. JIT is particularly suitable for companies with predictable demand patterns, short lead times, and reliable suppliers. It requires strong coordination between suppliers and precise demand forecasting to avoid stockouts and ensure smooth operations.
Economic Order Quantity Model
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model calculates the optimal order quantity that minimizes the total cost of inventory, including ordering, holding, and stockout costs. This approach is based on a formula that balances the costs of placing orders and holding stocks while addressing service level requirements. The EOQ model is most effective for businesses with regular demand patterns and consistent supplier lead times. It helps firms avoid excess inventory accumulation and optimize cash flow.
ABC Analysis Technique
The ABC analysis technique classifies inventory items into three categories based on their value and importance. Category A items are high-value products with low sales volume, requiring close monitoring and tight control. Category B items have moderate value and sales frequency, while Category C items are low-value products with high sales volume. This method enables businesses to allocate resources effectively and focus on managing critical inventory items. It is particularly beneficial for companies with a large product assortment or diversified customer base, as it ensures efficient inventory management.
In conclusion, the three predominant approaches to inventory management, JIT, EOQ, and ABC analysis, cater to different business needs by addressing varying demand patterns, lead times, and product assortments. By selecting the appropriate method, firms can optimize their inventory management processes and achieve cost savings, enhanced cash flow, and higher customer satisfaction.
How does inventory control in logistics management contribute to cost reduction and efficiency in supply chain operations?
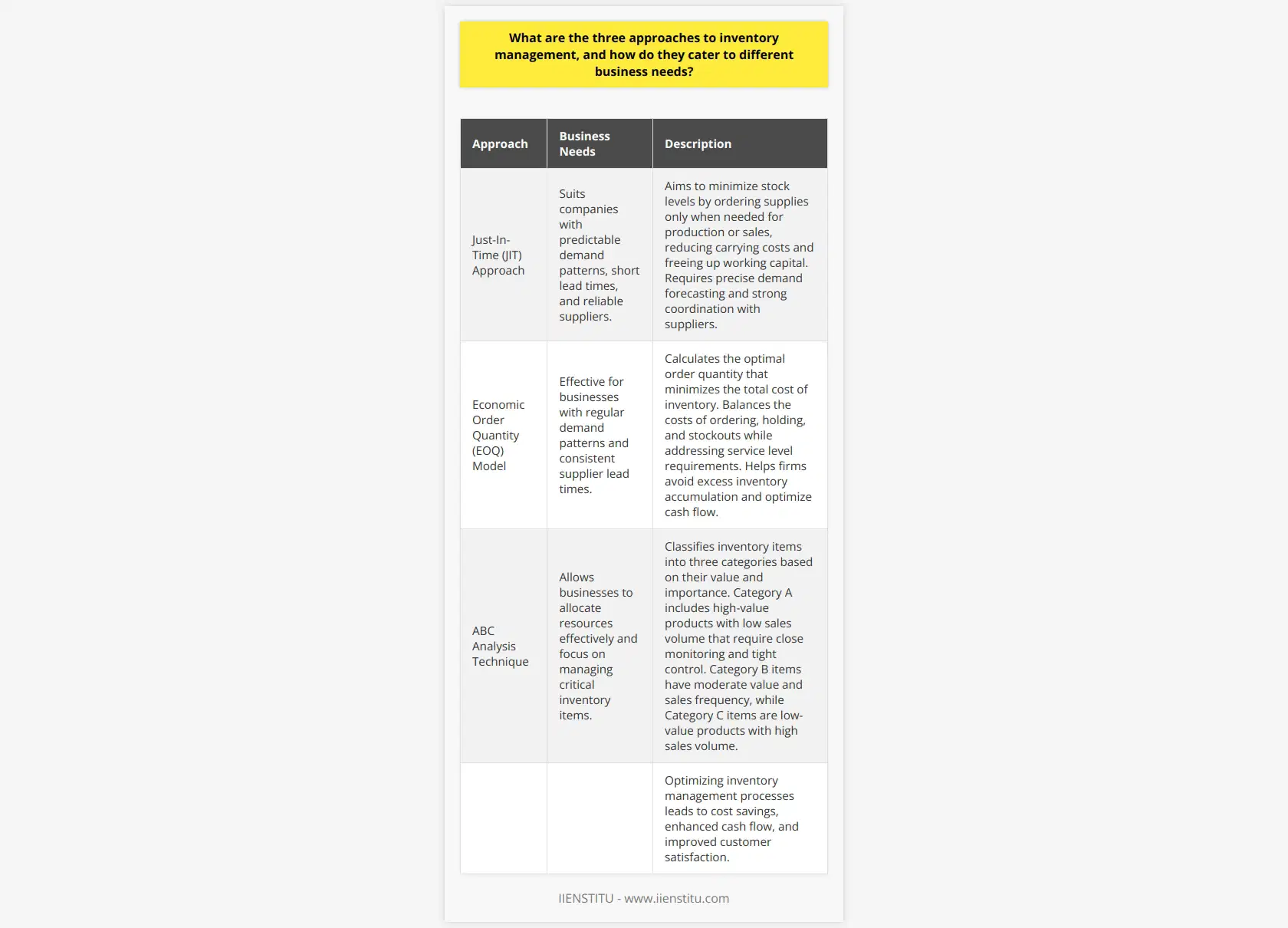
Role of Inventory Control in Cost Reduction
Inventory control is a critical aspect of logistics management that aims to maintain an optimal balance between stock availability and carrying costs. Efficient inventory control techniques help businesses reduce stock obsolescence, minimize stockouts, and prevent overstocking, thereby cutting costs and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
Improved Forecasting and Inventory Planning
Effective inventory control relies on accurate demand forecasting and inventory planning. Utilizing historical sales data, sales trends, and market analysis, businesses can optimize their inventory levels to meet customer demands. Accurate forecasting ensures the right products are available at the right time, minimizing stockouts and reducing the risk of holding obsolete inventory.
Minimizing Stockouts and Overstocking
Striking a balance between product availability and inventory holding costs is crucial to reducing costs and ensuring supply chain efficiency. Implementing inventory control techniques such as Just-In-Time (JIT) and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) can prevent stockouts and overstocking. JIT optimizes inventory management by ordering stock as needed, while EOQ calculates the most cost-efficient order quantity to minimize total inventory-related expenses.
Reducing Lead Time Variability
Lengthy and unpredictable lead times can increase the likelihood of stockouts and excessive inventory holding costs. By adopting inventory control measures, businesses can reduce lead time variability, allowing for more accurate demand forecasting, lower safety stock levels, and improved customer service.
Enhancing Supplier Collaboration
Inventory control efforts can enhance supplier collaboration, resulting in cost reduction and improved supply chain efficiency. By working closely with suppliers to share sales and inventory data, businesses can benefit from improved demand forecasting, and suppliers can plan production more effectively. This collaboration can result in lower lead times, higher fulfillment rates, and reduced stock obsolescence.
Boosting Automation and Technology Adoption
Embracing automation and technology in inventory management, such as barcode systems, RFID, and warehouse management software, can streamline the logistics process, reducing the risk of human error, increasing efficiency, and improving real-time inventory visibility. By integrating these solutions, businesses can optimize inventory levels, increase the accuracy of demand forecasts, and effectively manage stock movements.
Conclusion
Inventory control plays a pivotal role in logistics management by enabling businesses to minimize costs, improve customer service, and optimize supply chain operations. Effective inventory control techniques, supplier collaboration, and adoption of technology help organizations strike a balance between stock availability and carrying costs, ultimately contributing to cost reduction and increased supply chain efficiency.
What are the key components of a robust inventory control system in logistics, and how can organizations ensure its effective implementation?
Key Components of Inventory Control Systems
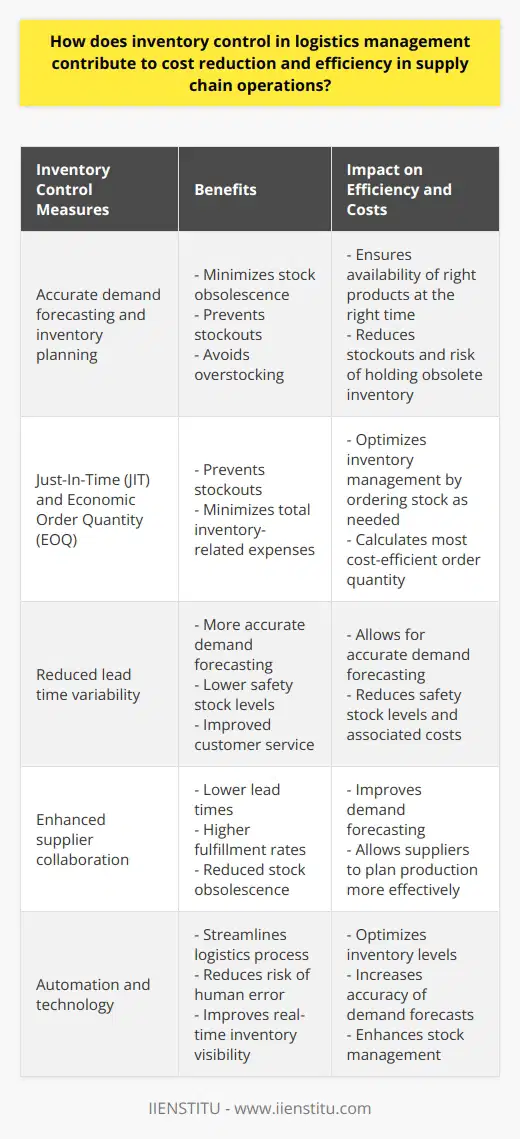
Effective inventory management is crucial in logistics as it ensures the accurate tracking and utilization of resources, minimizing costs, and increasing overall efficiency. A robust inventory control system comprises several key components that organizations should implement to achieve these goals.
Centralized Data Management
In today's digital age, a centralized data management system is essential to consolidate information from different functional areas across the supply chain. This enables real-time access and visibility of inventory levels, ensuring timely decision-making and streamlined operational processes.
Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting facilitates proactive inventory management by anticipating fluctuating customer needs, product life cycles, and seasonal trends. Organizations can employ historical sales data, market research, and advanced analytics techniques to develop precise forecasts and maintain optimal inventory levels.
Reorder Point Calculation
Determining reorder points is vital to maintain an adequate stock balance and avoid stockouts or overstocking situations. Organizations should consider factors such as lead time, order quantity, and safety stock in calculating reorder points, ensuring seamless supply chain operations.
Safety Stock Management
Safety stock serves as a buffer against uncertainties in demand and supply, protecting organizations from potential stockouts. By analyzing lead time variability and historical demand fluctuations, companies can determine the appropriate safety stock levels to minimize both stockouts and carrying costs.
Cycle Counting
Regular cycle counting of inventory, as opposed to annual physical counts, allows for more frequent monitoring of stock discrepancies and ensures data accuracy. This practice helps organizations quickly identify and resolve potential issues or inaccuracies in their inventory management system, improving overall efficiency and reducing losses.
Continuous Improvement and Training
Organizations should foster a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and updating inventory management processes and policies. Employee training and development should also be prioritized to equip the workforce with the necessary skills and knowledge to manage inventory effectively.
Using Technology
The implementation of technology, such as inventory management software, automated data collection tools, and warehouse management systems, can streamline operations and improve the overall accuracy and efficiency of the inventory control process.
In conclusion, organizations can ensure the effective implementation of a robust inventory control system by adopting a comprehensive approach that includes centralized data management, accurate demand forecasting, precise reorder point calculations, safety stock management, regular cycle counting, continuous improvement and training, and the integration of advanced technology. By focusing on these key components, companies can optimize their inventory management, increase efficiency, and ultimately, enhance their competitive edge in the market.
What is logistics inventory control and how does it contribute to effective supply chain management?
Understanding Logistics Inventory Control
Logistics inventory control is a critical aspect of supply chain management. It involves the careful monitoring and systematic regulation of items stocked within a warehouse or distribution center. These items could include raw materials, components, and finished products.
Impacts on Supply Chain Management
Effective logistics inventory control contributes in several ways to efficient supply chain management. Firstly, it ensures the availability of stock to meet customer demand, preventing stockouts and customer dissatisfaction.
Secondly, it helps control the cost associated with inventory holding, such as warehouse space, insurance, and loss through obsolescence. Accurate inventory management can reduce these costs and thereby increase profitability.
Role of Inventory Accuracy
Inventory accuracy is a key element of logistics inventory control. It prevents overstocking and understocking, helping to maintain an optimal balance. This balance is crucial. Too much inventory can result in increased holding costs; too little can lead to missed sales opportunities and customer dissatisfaction.
Employing Efficient Techniques
Techniques like Just-in-time (JIT) and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) are common in inventory control. JIT reduces warehousing costs by ordering goods to arrive as needed. EOQ determines the ideal order quantity to minimize total inventory costs.
Significance of Technology
Technological tools, such as inventory management software, also contribute. These systems provide real-time monitoring of inventory levels and movements. In essence, they aid in streamlining the process of logistics inventory control.
In conclusion, logistics inventory control is an indispensable part of supply chain management. Proper implementation can lead to efficient utilization of resources, cost reduction, customer satisfaction, and overall business profitability.

How can organizations strike a balance between maintaining adequate inventory levels and minimizing costs when implementing inventory control systems in logistics?
Implementing Optimized Inventory Control
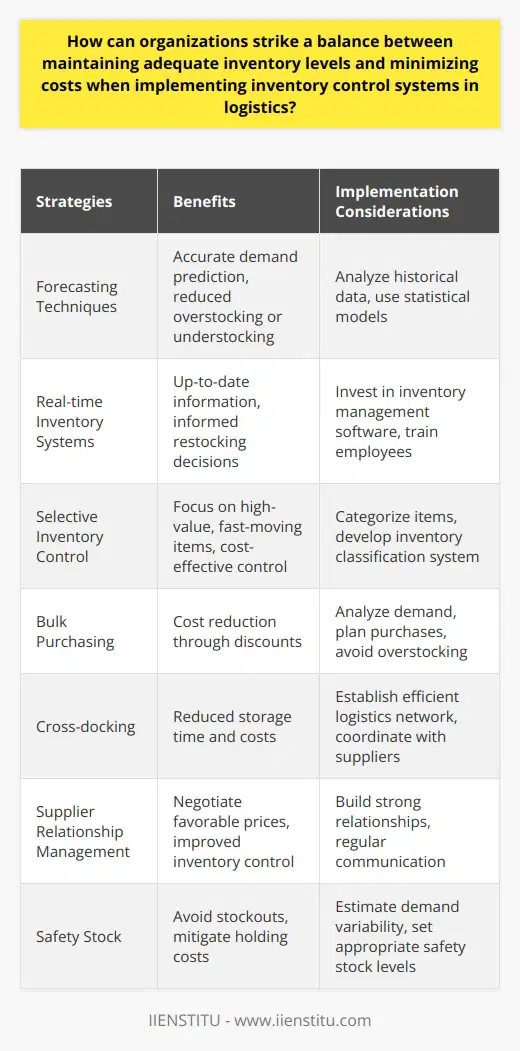
To achieve a balance between maintaining inventory levels and cost minimization, organizations can adhere to several strategies. Effective stock management is central to this optimization.
Use of Forecasting Techniques
Initially, companies should leverage historical data to predict future demand accurately. Effective forecasting significantly reduces overstocking or understocking, subsequently minimizing costs.
Investment in Real-Time Inventory Systems
Investing in real-time inventory systems can ensure optimal stock levels. These systems provide accurate and up-to-date information, helping make informed decisions about restocking.
Selective Inventory Control
Applying selective inventory control can be beneficial. Here, the organization categorizes its items based on value and turnover rate. High-value, fast-moving items receive prime attention, leading to cost-effective control.
Bulk Purchasing
Bulk purchasing is another strategy, albeit risky. While it may lead to cost reduction through discounts, companies must tread carefully to avoid overstocking.
Cross-Docking Downstream Suppliers
Cross-docking is an effective technique. It involves transferring incoming goods with outgoing shipments destined for similar locations. This process reduces storage time and costs.
Supplier Relationship Management
Furthermore, fostering good relationships with suppliers aids in obtaining the most favorable price and delivery conditions. It can contribute to cost reduction.
Use of Safety Stock
Lastly, holding safety stock - the minimum level of inventory acts as a buffer against unexpected demand. This protects against stockouts while mitigating excessive holding costs.
In conclusion, striking a balance between maintaining adequate inventory levels and minimizing costs calls for a blend of scientific forecasting, real-time inventory systems, selective inventory control, strategic purchasing, supplier management, and optimal safety stock levels. With these measures, organizations can achieve efficient inventory control in logistics.
What factors should be considered when selecting an appropriate inventory control approach for a given logistics operation?
Inventory Complexity and Volume
Inventory complexity and volume should be a primary concern when selecting an inventory control approach for a logistics operation. The amount and variety of items, and their turnover rates affect the suitability of different inventory systems.
Demand Variability and Predictability
The predictability and variability of demand also influence the choice of inventory control. Highly fluctuating demand requires a more dynamic inventory control system, while predictable demand may benefit from a simpler, static system.
Supply Chain Structure
The structure of the supply chain can also dictate inventory control methods. Cross-docking operations may necessitate a just-in-time inventory system, while operations in a lengthy supply chain may prefer a more robust safety stock system.
Technological Capabilities
The available technology within an organization can influence the choice of inventory control. Advanced software systems can handle complex inventory control methods, whereas manual methods may limit you to simpler systems.
Financial Constraints
Financial limitations also impact the choice of inventory system. Some methods require heavy investments in technology and staff training, while others offer cost-efficient alternatives. Remember, the objective is to minimize inventory costs while maintaining customer service levels.
Cycle Counting Frequency
Cycle counting, or the frequency of stock checks, can influence the choice of inventory control. A system with frequent cycle counts can support a high level of inventory accuracy and control.
Operational Efficiency
Lastly, the overall operational efficiency must be considered when choosing an inventory control system. The selected system should enhance operational efficiency and not cause delays or disruptions for the logistics operations. After all, the ultimate goal of logistics operations is to deliver goods in an efficient, prompt, and accurate manner.
To summarize, multiple factors should be considered when selecting an appropriate inventory control approach for a given logistic operation. Striking a balance across these dimensions helps companies optimally manage their inventory and meet customer demands efficiently and effectively.